Features
Defence and Diplomacy are linked

Dr Sarala Fernando
Defence expenditure has not been a subject of public discussion in Sri Lanka, which was understandable during the difficult years of the armed conflict. Even after the armed conflict ended , there was no public opposition to the continued dedication of a major share of budgetary resources to the Defence Ministry to spearhead the reconstruction and rehabilitation of the conflict- affected areas in the North and East.
Since that time, the Army has provided leadership in a number of areas of interest to the UN. For example, the de-mining programe clearing thousands of acres for the safe return of civilians, has created positive publicity for Sri Lanka and enabled the signing of related international agreements, all contributing to building the image of a responsible military on international fora.
Since deploying its first contingent in 1958, official press releases remind that Sri Lanka has been contributing to UN Peacekeeping operations in some of its most hostile and demanding deployments, and has 557 including female officers currently in service toward ensuring international peace and security. Our authorities should also revive the initiative to collect illegal small arms and light weapons island-wide under the UN SALW (Small Arms and Light Weapons) programme. This will address concerns over rising gun crime and discourage new domestic gun manufacturing.
Since the end of the armed conflict, Sri Lankans have waited patiently over a decade now for the peace dividend in the hope that it would enable more robust social expenditure. Now that Sri Lanka has declared bankruptcy and opted to go to that “lender of last resort”, several articles are appearing commenting on down sizing of the military, re-balancing the three forces in view of current and emerging threats etc, based on some expectation that limits would be imposed on defence expenditure under the IMF programme.
In such a historical context and given the experience and assets within the security forces, it is to be expected that any strategic planning for “right sizing” the defence budget, would be undertaken in-house within the security forces. This article suggests that the Foreign Ministry with its research and training arms, the Lakshman Kadirgarmar Institute (LKI) and the Bandaranaike International Diplomatic Training Institute (BIDTI) should also be involved in these discussions. Any re-shaping of defence strategy would benefit from the perspectives of diplomacy especially in relation to developments in the wider world, some of which are mentioned in this article.
From the initial public statements by the Defence Ministry it seems the emphasis has been on troop reduction. The Deputy Minister of Defence announced recently that the Ministry planned to reduce the number of soldiers from the current strength of 200,783 to 135,000 by 2024. Is this to be achieved through creation of a reserve as some academics have suggested? The Air Force has just announced a strength reduction from 35,000 to 27,000 including a policy to increase its female share to 30%.
However, in this exercise, to avoid confusion, public diplomacy would call for the holding back of all media advertisements for new recruitment to the armed forces. There are lessons to be learned also from elsewhere: the recent initiative to reduce the public service through a scheme to grant five years no-pay leave abroad, has predictably led to the departure of the most talented and capable, leaving Ministries in a quandary to retrain those remaining behind who are demoralized, compounding human resources management problems. It is also worth noting that Sri Lanka is reducing its trained forces at a time when some developed countries are facing recruitment problems to their forces and offering many incentives even to foreign nationals.
Our Deputy Minister of Defence also referred to a “strategic blueprint” aiming to produce “a technically and tactically sound and well-balanced defense force by the year 2030 in order to meet upcoming security challenges”. Such a strategic plan would be a new and welcome development however the question remains how other Ministries, concerned institutions and a public consultation would be factored into the in-house deliberations.
Any such strategic planning should take into account that Sri Lanka is probably unique in that it is recognized internationally as particularly vulnerable for a country of our size and geography, being exposed to both man-made and natural disasters. This calls for any national security strategy to take a two prong approach. With regard to conflict prevention, having faced two youth insurrections which had to be put down by lethal force, one cannot over emphasize the importance of strengthening human intelligence gathering and early warning.
This task is never easy due to the difficulty of coordinating intelligence agencies with differing mandates, as even the United States learned after 9/11. Recent arrests in Tamil Nadu of persons charged with attempting to revive the LTTE insurgency confirmed the need for continued vigilance on the arms and drug smuggling networks which we had thought had been dismantled after the end of the armed conflict. As an island nation with a huge expanse of coastal territory to monitor, the armed forces need to integrate air, sea and land operations for maritime protection and seizure of arms, ammunition, explosives and detonators and a never ending flow of drugs.
Early warning is even more problematic with regard to natural disasters as major climate events like earthquakes seemingly defy prediction. Research is still emerging on the impact of a war like in Ukraine on the climate crisis. However, even to amateur eyes, the dropping of thousands of missiles, bombs and artillery shells on the ground and exploding in the air, virtually on a daily basis, must not only pollute but also impact the fragile surrounding geology. In neighbouring Turkey, two major earthquakes of 7.8 and 7.5 magnitude occurred on February 6 this year followed by a series of aftershocks.
All the way down the seismic line in Asia, even as far as Fiji region on June 10 (5.9 magnitude) significant earthquakes are occurring since the tragedy in Turkey. Indian scientists have been predicting a major earthquake in India and had also issued a warning to Sri Lanka before the current string of tremors began to be experienced here in May/ June along the southern coast and as far as Gampola in the central hills.
In this background, the recent visit to Sri Lanka by the Executive Secretary of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) assumes significance when Sri Lanka on June 6 announced the successful completion of its domestic ratification process for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) , with grant of Cabinet approval. The CTBT was signed by Sri Lanka on October 24, 1996 but ratification was stalled for many years due to political pressures. Under the Treaty´s global verification regime, a network of 321 monitoring stations were to be set up – spanning some 90 countries – able to record shock waves generated by possible nuclear explosions and other sources in the atmosphere, under water or underground. The network includes 50 primary and 120 auxiliary seismic stations whose data can be used to help distinguish between possible nuclear explosions and the many thousands of earth tremors registered annually.
Sri Lanka signed a Facility Agreement with the CTBTO in June 2000 which led the way for the establishment of an auxiliary seismological station in Pallekelle, Kandy, as part of the International Monitoring System (IMS) to verify compliance with the CTBT. Hardly any public information is available on the current status of this Kandy station and whether it is operational, although any data collected would be valuable both in the context of the earth tremors Sri Lanka is experiencing recently and in the wider context of a possible nuclear radiation threat arising out of the war in Ukraine. Interestingly the Sri Lanka Air Force has been training in the last months for handling a chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear explosives emergency under international technical assistance from the IAEA (International Atomis Energy Authority).
The significance of the CTBTO ratification is dwelt on here to meet public skepticism over Sri Lanka’s diplomatic forays into the worlds of disarmament and elimination of all forms of weapons of mass destruction. Engaging in multilateral diplomacy, foreign diplomats would often ask their Sri Lankan counterparts why Sri Lanka was so interested in the two extremes of the world, the sea bed and outer space. However, there was always a basis in national interest. The close involvement of Sri Lankan diplomats in the Law of the Sea negotiations under UN auspices eventually led to its taking into account of Sri Lanka’s position as a developing state, as also the peculiarities of her continental shelf in the southern part of the Bay of Bengal whereby under the special method of delimitation Sri Lanka will be able to claim parts of the seabed well beyond the 350 miles cut off point provided under the general provisions.
As for outer space, Arthur Clarke, the scientist-writer residing in Sri Lanka, was instrumental in drawing Sri Lanka’s attention many years ago to the advent of Artificial Intelligence as well as the many benefits of outer space and the need to keep space peaceful. Since those early days, Sri Lanka has been in the forefront of efforts to prevent an arms race in outer space, underlining the increasing importance of satellites for communications and many peaceful uses of remote sensing as well as addressing the global threat posed by space debris.
Today United Nations as agreed by member states has set a target of achieving by 2030, 17 goals for sustainable development and human security ,including poverty alleviation, quality education, good health, clean water, clean energy, decent work, industry innovation, reduced inequality, sustainable cities, responsible consumption and production, encompassing both life on land and under water, together with climate action. Taking into consideration the international classification of Sri Lanka as a country particularly vulnerable to both conflict and natural disasters, this article suggests that Sri Lanka in the present economic crisis, take a step back from “rapid economic growth” models which all too often deplete its natural resources including water, forests, stone, gravel and sand, and instead focus on careful management of its natural wealth, ecosystems and biodiversity.
Judging by press articles, the navy is already working in cooperation with the private sector and other organizations as well as with the general public, in several areas such as marine and coastal protection, installing reverse osmosis plants etc. The army is best known for its outreach work in agriculture and food production, hospital and university education, however these initiatives have not gained full recognition due to resentment of local farmers and market contradictions in the field and resistance from faculty and students in the formal education and health sectors.
A more feasible possibility lies in building upon the strengths in logistics and engineering Sri Lanka’s military had developed during the armed conflict. Are there innovations here which may be commercialized or taken up in public-private partnerships contributing to import substitution and domestic savings? The army engineers work on solving practical problems and have succeeded in tackling issues like the flooding of Nuwara Eliya town by tracing the flow of water, unblocking the obstacles and constructing the required drainage channels.
They should be given an opportunity to work on the perennial flooding affecting towns in Galle, Matara and Ratnapura in low cost projects at a time when the era of grand hydraulic construction led by the Irrigation Department seems to be coming to an end. Uma Oya with its delays and cost-overruns may probably be the last such project due to the scale of public protests since the tunneling apparently had caused all the wells in the neighbouring areas to run dry.
The strengths of the armed forces come into public view mainly in a time of emergency when the armed forces form the first line of rescue. Yet other countries have already placed critical infrastructure like reservoirs under military management and control, viz. the United States Army Corps of Engineers which operates and maintains the safety of dams across a huge expanse of territory. Elsewhere, foreign militaries have even been engaged in the management of local parks i.e. by training local rangers in African countries to control poaching and educate communities to protect their wild life treasure. Can our defence research and training institutes (Buttala for example is strategically located in the proximity of two major parks Udawalawe and Yala) partner with the wildlife authorities and contribute to mitigating the human-elephant conflict?
From Kavan to Muthuraja, Sri Lanka’s international image has been reeling on huge publicity over the abuse and neglect of domestic elephants. The latest incident made international news headlines when that majestic tusker Muthuraja once gifted to Sri Lanka was airlifted by the Thai government back to Thailand for medical treatment. In Thailand , elephants with special characteristics are considered as national treasure by the Thai Royal family and cared for in the palace grounds by the Thai armed forces. Instead of just conveying official apologies to the Thai government, should not our Prime Minister have asked the Thai government for assistance to train our mahouts and an exchange programme for our vets to learn from the elephant hospital and sanctuary in Thailand and help bring the care of all domestic elephants under some systematic care?
The Sri Lankan armed forces dispose of many research and training institutions scattered around the country. Some thought should be given to better coordination and managing of these resources in the national interest. For example the proposed national Climate Change University could be conceptualized not as an independent institute but positioned as a central lynchpin within the network of defence research and training institutes. Sri Lanka is in fact very good at setting up research and training institutes in every field, the problem come with implementing research findings and giving employment to trained students, which means this valuable human capital ends up going overseas to help other countries instead of contributing to the national good.
In time, many of these R&D institutions find it difficult to maintain large buildings and staff, which is a problem not unique to Sri Lanka. It is worth recalling that the UN at its inception was intended to have all its affiliates in one centre in New York in order to share administrative costs but subsequently various powerful individuals worked with their national authorities to take away the specialized agencies like FAO to Rome, ILO to Geneva etc
(Sarala Fernando, retired from the Foreign Ministry as Additional Secretary. Her last Ambassadorial appointment was as Permanent Representative to the UN and International Organizations in Geneva . Her Ph.D was on India-Sri Lanka relations and she writes now on foreign policy, public diplomacy and protection of heritage).
Features
The US-China rivalry and challenges facing the South

 The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
Thanks to the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies (RCSS), Colombo the above window of opportunity was opened on December 8th for those sections of the public zealously pursuing an understanding of current issues in global politics. The knowledge came via a forum that was conducted at the RCSS titled, ‘The US-China Rivalry and Implications for the Indo-Pacific’, where Professor Neil DeVotta of the Wake Forest University of North Carolina in the US, featured as the speaker.
A widely representative audience was present at the forum, including senior public servants, the diplomatic corps, academics, heads of civil society organizations, senior armed forces personnel and the media. The event was ably managed by the Executive Director of the RCSS, retired ambassador Ravinatha Aryasinha. Following the main presentation a lively Q&A session followed, where many a point of interest was aired and discussed.
While there is no doubt that China is fast catching up with the US with regard to particularly military, economic, scientific and technological capability, Prof. DeVotta helped to balance this standard projection of ‘China’s steady rise’ by pointing to some vital facts about China, the omission of which would amount to the observer having a somewhat uninformed perception of global political realities.
The following are some of the facts about contemporary China that were highlighted by Prof. DeVotta:
* Money is steadily moving out of China and the latter’ s economy is slowing down. In fact the country is in a ‘ Middle Income Trap’. That is, it has reached middle income status but has failed to move to upper income status since then.
* People in marked numbers are moving out of China. It is perhaps little known that some Chinese are seeking to enter the US with a view to living there. The fact is that China’s population too is on the decline.
* Although the private sector is operative in China, there has been an increase in Parastatals; that is, commercial organizations run by the state are also very much in the fore. In fact private enterprises have begun to have ruling Communist Party cells in them.
* China is at its ‘peak power’ but this fact may compel it to act ‘aggressively’ in the international sphere. For instance, it may be compelled to invade Taiwan.
* A Hard Authoritarianism could be said to characterize central power in China today, whereas the expectation in some quarters is that it would shift to a Soft Authoritarian system, as is the case in Singapore.
* China’s influence in the West is greater than it has ever been.
The speaker was equally revelatory about the US today. Just a few of these observations are:
* The US is in a ‘Unipolar Moment’. That is, it is the world’s prime power. Such positions are usually not longstanding but in the case of the US this position has been enjoyed by it for quite a while.
* China is seen by the US as a ‘Revisionist Power’ as opposed to being a ‘Status Quo Power.’ That is China is for changing the world system slowly.
* The US in its latest national security strategy is paying little attention to Soft Power as opposed to Hard Power.
* In terms of this strategy the US would not allow any single country to dominate the Asia-Pacific region.
* The overall tone of this strategy is that the US should step back and allow regional powers to play a greater role in international politics.
* The strategy also holds that the US must improve economic ties with India, but there is very little mention of China in the plan.
Given these observations on the current international situation, a matter of the foremost importance for the economically weakest countries of the South is to figure out how best they could survive materially within it. Today there is no cohesive and vibrant collective organization that could work towards the best interests of the developing world and Dr. DeVotta was more or less correct when he said that the Non-alignment Movement (NAM) has declined.
However, this columnist is of the view that rather being a spent force, NAM was allowed to die out by the South. NAM as an idea could never become extinct as long as economic and material inequalities between North and South exist. Needless to say, this situation is remaining unchanged since the eighties when NAM allowed itself to be a non-entity so to speak in world affairs.
The majority of Southern countries did not do themselves any good by uncritically embracing the ‘market economy’ as a panacea for their ills. As has been proved, this growth paradigm only aggravated the South’s development ills, except for a few states within its fold.
Considering that the US would be preferring regional powers to play a more prominent role in the international economy and given the US’ preference to be a close ally of India, the weakest of the South need to look into the possibility of tying up closely with India and giving the latter a substantive role in advocating the South’s best interests in the councils of the world.
To enable this to happen the South needs to ‘get organized’ once again. The main differences between the past and the present with regard to Southern affairs is that in the past the South had outstanding leaders, such as Jawaharlal Nehru of India, who could doughtily stand up for it. As far as this columnist could ascertain, it is the lack of exceptional leaders that in the main led to the decline of NAM and other South-centred organizations.
Accordingly, an urgent task for the South is to enable the coming into being of exceptional leaders who could work untiringly towards the realization of its just needs, such as economic equity. Meanwhile, Southern countries would do well to, indeed, follow the principles of NAM and relate cordially with all the major powers so as to realizing their best interests.
Features
Sri Lanka and Global Climate Emergency: Lessons of Cyclone Ditwah
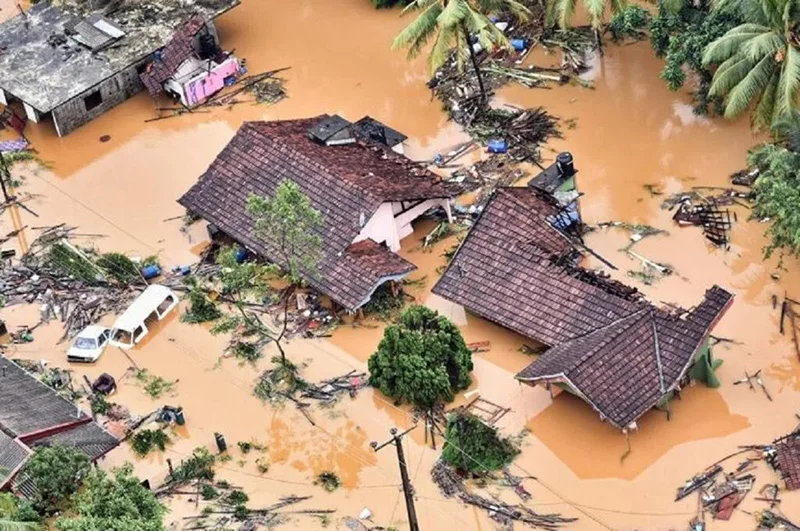

Tropical Cyclone Ditwah, which made landfall in Sri Lanka on 28 November 2025, is considered the country’s worst natural disaster since the deadly 2004 tsunami. It intensified the northeast monsoon, bringing torrential rainfall, massive flooding, and 215 severe landslides across seven districts. The cyclone left a trail of destruction, killing nearly 500 people, displacing over a million, destroying homes, roads, and railway lines, and disabling critical infrastructure including 4,000 transmission towers. Total economic losses are estimated at USD 6–7 billion—exceeding the country’s foreign reserves.
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have led the relief efforts, aided by international partners including India and Pakistan. A Sri Lanka Air Force helicopter crashed in Wennappuwa, killing the pilot and injuring four others, while five Sri Lanka Navy personnel died in Chundikkulam in the north while widening waterways to mitigate flooding. The bravery and sacrifice of the Sri Lankan Armed Forces during this disaster—as in past disasters—continue to be held in high esteem by grateful Sri Lankans.
The Sri Lankan government, however, is facing intense criticism for its handling of Cyclone Ditwah, including failure to heed early warnings available since November 12, a slow and poorly coordinated response, and inadequate communication with the public. Systemic issues—underinvestment in disaster management, failure to activate protocols, bureaucratic neglect, and a lack of coordination among state institutions—are also blamed for avoidable deaths and destruction.
The causes of climate disasters such as Cyclone Ditwah go far beyond disaster preparedness. Faulty policymaking, mismanagement, and decades of unregulated economic development have eroded the island’s natural defenses. As climate scientist Dr. Thasun Amarasinghe notes:
“Sri Lankan wetlands—the nation’s most effective natural flood-control mechanism—have been bulldosed, filled, encroached upon, and sold. Many of these developments were approved despite warnings from environmental scientists, hydrologists, and even state institutions.”
Sri Lanka’s current vulnerabilities also stem from historical deforestation and plantation agriculture associated with colonial-era export development. Forest cover declined from 82% in 1881 to 70% in 1900, and to 54–50% by 1948, when British rule ended. It fell further to 44% in 1954 and to 16.5% by 2019.
Deforestation contributes an estimated 10–12% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Beyond removing a vital carbon sink, it damages water resources, increases runoff and erosion, and heightens flood and landslide risk. Soil-depleting monocrop agriculture further undermines traditional multi-crop systems that regenerate soil fertility, organic matter, and biodiversity.
In Sri Lanka’s Central Highlands, which were battered by Cyclone Ditwah, deforestation and unregulated construction had destabilised mountain slopes. Although high-risk zones prone to floods and landslides had long been identified, residents were not relocated, and construction and urbanisation continued unchecked.
Sri Lanka was the first country in Asia to adopt neoliberal economic policies. With the “Open Economy” reforms of 1977, a capitalist ideology equating human well-being with quantitative growth and material consumption became widespread. Development efforts were rushed, poorly supervised, and frequently approved without proper environmental assessment.
Privatisation and corporate deregulation weakened state oversight. The recent economic crisis and shrinking budgets further eroded environmental and social protections, including the maintenance of drainage networks, reservoirs, and early-warning systems. These forces have converged to make Sri Lanka a victim of a dual climate threat: gradual environmental collapse and sudden-onset disasters.
Sri Lanka: A Climate Victim
Sri Lanka’s carbon emissions remain relatively small but are rising. The impact of climate change on the island, however, is immense. Annual mean air temperature has increased significantly in recent decades (by 0.016 °C annually between 1961 and 1990). Sea-level rise has caused severe coastal erosion—0.30–0.35 meters per year—affecting nearly 55% of the shoreline. The 2004 tsunami demonstrated the extreme vulnerability of low-lying coastal plains to rising seas.
The Cyclone Ditwah catastrophe was neither wholly new nor surprising. In 2015, the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) identified Sri Lanka as the South Asian country with the highest relative risk of disaster-related displacement: “For every million inhabitants, 15,000 are at risk of being displaced every year.”
IDMC also noted that in 2017 the country experienced seven disaster events—mainly floods and landslides—resulting in 135,000 new displacements and that Sri Lanka “is also at risk for slow-onset impacts such as soil degradation, saltwater intrusion, water scarcity, and crop failure”.
Sri Lanka ranked sixth among countries most affected by extreme weather events in 2018 (Germanwatch) and second in 2019 (Global Climate Risk Index). Given these warnings, Cyclone Ditwah should not have been a surprise. Scientists have repeatedly cautioned that warmer oceans fuel stronger cyclones and warmer air holds more moisture, leading to extreme rainfall. As the Ceylon Today editorial of December 1, 2025 also observed:
“…our monsoons are no longer predictable. Cyclones form faster, hit harder, and linger longer. Rainfall becomes erratic, intense, and destructive. This is not a coincidence; it is a pattern.”
Without urgent action, even more extreme weather events will threaten Sri Lanka’s habitability and physical survival.
A Global Crisis
Extreme weather events—droughts, wildfires, cyclones, and floods—are becoming the global norm. Up to 1.2 billion people could become “climate refugees” by 2050. Global warming is disrupting weather patterns, destabilising ecosystems, and posing severe risks to life on Earth. Indonesia and Thailand were struck by the rare and devastating Tropical Cyclone Senyar in late November 2025, occurring simultaneously with Cyclone Ditwah’s landfall in Sri Lanka.
More than 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions—and nearly 90% of carbon emissions—come from burning coal, oil, and gas, which supply about 80% of the world’s energy. Countries in the Global South, like Sri Lanka, which contribute least to greenhouse gas emissions, are among the most vulnerable to climate devastation. Yet wealthy nations and multilateral institutions, including the World Bank, continue to subsidise fossil fuel exploration and production. Global climate policymaking—including COP 30 in Belém, Brazil, in 2025—has been criticised as ineffectual and dominated by fossil fuel interests.
If the climate is not stabilised, long-term planetary forces beyond human control may be unleashed. Technology and markets are not inherently the problem; rather, the issue lies in the intentions guiding them. The techno-market worldview, which promotes the belief that well-being increases through limitless growth and consumption, has contributed to severe economic inequality and more frequent extreme weather events. The climate crisis, in turn, reflects a profound mismatch between the exponential expansion of a profit-driven global economy and the far slower evolution of human consciousness needed to uphold morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom.
Sri Lanka’s 2025–26 budget, adopted on November 14, 2025—just as Cyclone Ditwah loomed—promised subsidised land and electricity for companies establishing AI data centers in the country.
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake told Parliament: “Don’t come questioning us on why we are giving land this cheap; we have to make these sacrifices.”
Yet Sri Lanka is a highly water-stressed nation, and a growing body of international research shows that AI data centers consume massive amounts of water and electricity, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
The failure of the narrow, competitive techno-market approach underscores the need for an ecological and collective framework capable of addressing the deeper roots of this existential crisis—both for Sri Lanka and the world.
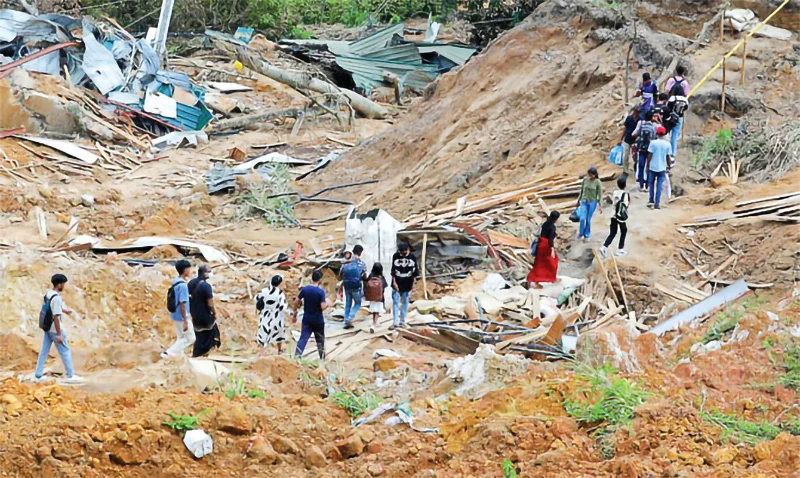

A landslide in Sri Lanka (AFP picture)
Ecological and Human Protection
Ecological consciousness demands
recognition that humanity is part of the Earth, not separate from it. Policies to address climate change must be grounded in this understanding, rather than in worldviews that prize infinite growth and technological dominance. Nature has primacy over human-created systems: the natural world does not depend on humanity, while humanity cannot survive without soil, water, air, sunlight, and the Earth’s essential life-support systems.
Although a climate victim today, Sri Lanka is also home to an ancient ecological civilization dating back to the arrival of the Buddhist monk Mahinda Thera in the 3rd century BCE. Upon meeting King Devanampiyatissa, who was out hunting in Mihintale, Mahinda Thera delivered one of the earliest recorded teachings on ecological interdependence and the duty of rulers to protect nature:
“O great King, the birds of the air and the beasts of the forest have as much right to live and move about in any part of this land as thou. The land belongs to the people and all living beings; thou art only its guardian.”
A stone inscription at Mihintale records that the king forbade the killing of animals and the destruction of trees. The Mihintale Wildlife Sanctuary is believed to be the world’s first.
Sri Lanka’s ancient dry-zone irrigation system—maintained over more than a millennium—stands as a marvel of sustainable development. Its network of interconnected reservoirs, canals, and sluices captured monsoon waters, irrigated fields, controlled floods, and even served as a defensive barrier. Floods occurred, but historical records show no disasters comparable in scale, severity, or frequency to those of today. Ancient rulers, including the legendary reservoir-builder King Parākramabāhu, and generations of rice farmers managed their environment with remarkable discipline and ecological wisdom.
The primacy of nature became especially evident when widespread power outages and the collapse of communication networks during Cyclone Ditwah forced people to rely on one another for survival. The disaster ignited spontaneous acts of compassion and solidarity across all communities—men and women, rich and poor, Buddhists, Christians, Muslims, and Hindus. Local and international efforts mobilized to rescue, shelter, feed, and emotionally support those affected. These actions demonstrated a profound human instinct for care and cooperation, often filling vacuums left by formal emergency systems.
Yet spontaneous solidarity alone is insufficient. Sri Lanka urgently needs policies on sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate resilience. These include strict, science-based regulation of construction; protection of forests and wetlands; proper maintenance of reservoirs; and climate-resilient infrastructure. Schools should teach environmental literacy that builds unity and solidarity, rather than controversial and divisive curriculum changes like the planned removal of history and introduction of contested modules on gender and sexuality.
If the IMF and international creditors—especially BlackRock, Sri Lanka’s largest sovereign bondholder, valued at USD 13 trillion—are genuinely concerned about the country’s suffering, could they not cancel at least some of Sri Lanka’s sovereign debt and support its rebuilding efforts? Addressing the climate emergency and the broader existential crisis facing Sri Lanka and the world ultimately requires an evolution in human consciousness guided by morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom. (Courtesy: IPS NEWS)
Dr Asoka Bandarage is the author of Colonialism in Sri Lanka: The Political Economy of the Kandyan Highlands, 1833-1886 (Mouton) Women, Population and Global Crisis: A Politico-Economic Analysis (Zed Books), The Separatist Conflict in Sri Lanka: Terrorism, Ethnicity, Political Economy, ( Routledge), Sustainability and Well-Being: The Middle Path to Environment, Society and the Economy (Palgrave MacMillan) Crisis in Sri Lanka and the World: Colonial and Neoliberal Origins, Ecological and Collective Alternatives (De Gruyter) and numerous other publications. She serves on the Advisory Boards of the Interfaith Moral Action on Climate and Critical Asian Studies.
Features
Cliff and Hank recreate golden era of ‘The Young Ones’

 Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
The duo, who first performed together in the 1950s as part of The Shadows, brought the house down with their classic hits and effortless chemistry.
The concert, part of Cliff’s ‘Can’t Stop Me Now’ tour, featured iconic songs like ‘Summer Holiday’, ‘The Young Ones’, ‘Bachelor Boy’, ‘Living Doll’ and a powerful rendition of ‘Mistletoe and Wine.’
Cliff, 85, and Hank, with his signature red Fender Stratocaster, proved that their music and friendship are timeless.
According to reports, the moment the lights dimmed and the first chords of ‘Move It’ rang out, the crowd knew they were in for something extraordinary.
Backed by a full band, and surrounded by dazzling visuals, Cliff strode onto the stage in immaculate form – energetic and confident – and when Hank Marvin joined him mid-set, guitar in hand, the audience erupted in applause that shook the hall.
Together they launched into ‘The Young Ones’, their timeless 1961 hit which brought the crowd to its feet, with many in attendance moved to tears.
The audience was treated to a journey through time, with vintage film clips and state-of-the-art visuals adding to the nostalgic atmosphere.
Highlights of the evening included Cliff’s powerful vocals, Hank’s distinctive guitar riffs, and their playful banter on stage.

Cliff posing for The Island photographer … February,
2007
Cliff paused between songs to reflect on their shared journey saying:
“It’s been a lifetime of songs, memories, and friendship. Hank and I started this adventure when we were just boys — and look at us now, still up here making noise!”
As the final chords of ‘Congratulations’ filled the theatre, the crowd rose for a thunderous standing ovation that lasted several minutes.
Cliff waved, Hank gave a humble bow, and, together, they left the stage, arm-in-arm, to the refrain of “We’re the young ones — and we always will be.”
Reviews of the show were glowing, with fans and critics alike praising the duo’s energy, camaraderie, and enduring talent.
Overall, the Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin reunion concert was a truly special experience, celebrating the music and friendship that has captivated audiences for decades.
When Cliff Richard visited Sri Lanka, in February, 2007, I was invited to meet him, in his suite, at a hotel, in Colombo, and I presented him with my music page, which carried his story, and he was impressed.
In return, he personally autographed a souvenir for me … that was Cliff Richard, a truly wonderful human being.
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoFinally, Mahinda Yapa sets the record straight
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka: