Features
‘UN fudged Lankan casualty figures’ – Lord Naseby

by Palitha Senanayake
The United Nations Human Rights Council at its 57th session adopted a resolution extending the mandate of the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) Project on Sri Lanka Accountability by one year. Babu Ram Pant, Deputy Regional Director for South Asia at Amnesty International, has commented extensively on this resolution.
International perversion
The source of these allegations of human rights violations against Sri Lanka is the controversial report called the ‘Dharusman (UNPOE pr United Nations Panel of Experts.) report,’ which the UN Secretary-General commissioned in 2010 after Sri Lankan forces defeated LTTE terrorism. The Secretary-General justified the commissioning of this report, stating that ‘the report is for his personal knowledge.’ This is a strange move to start with because in the UN, HR violation investigations are commissioned by resolutions of the UN Security Council and never by the UN Secretary-General ‘for his knowledge’ in his personal capacity. However, since the report was published, it received authenticity and UN and international blessings to make a case against Sri Lanka.
This ‘international perversion’, however, does not end there. In its mandate, the report further maintained that its task was to look into the ‘accountability to the International Humanitarian and Human Rights law, on the final stages of the Sri Lankan conflict’. This, again, is twisted advocacy to suit one’s agenda as what logically applies to the situation is only international humanitarian law and certainly not Human Rights law.
Expert Opinion
Confronted by these allegations of the UNSG and his ‘experts’, the Sri Lankan government in 2012 hired a team of independent experts, whose expertise in international conflicts and international law was beyond question. This team comprised
Professor DM Crane
Sir Desmond De Silva QC
Rodney Dixon QC
Professor Michael Newton -Professor of the Practice of law, Vanderbilt University School of Law.
Major General Sir John Holmes DSO OBE MC- UN Under-Secretary for Humanitarian Affairs 2007-2010
These eminent persons had served on various international investigation panels. After studying the issues in detail, they submitted their reports to the government of Sri Lanka. They were all in agreement that the Sri Lankan case should be viewed under International Humanitarian Law and not under International Human Rights law.
The applicability of IHRL and its relevance can be explained as follows. It is an accepted fact that the LTTE was the most organized terrorist unit in the world. This fact signifies that the conflict in Sri Lanka was an armed conflict between two sets of forces, namely the SL security forces and the LTTE.
In such a context, international law, as spelt out by the ICRC statute, is very clear in stating that the law that applies to an armed conflict is international humanitarian law, and not International Human Rights law.
Further, as the above experts on international law have pointed out, “International law provides civilian protection while simultaneously allowing for military objectives to be fulfilled, which is the central goal of International Humanitarian Law (IHL). The death of civilians during a conflict, no matter how grave or regrettable, does not in itself constitute a war crime. In particular, the three principals
1. Distinction
2. Military necessity and
3. Proportionality
should guide the legality of action under IHL.
Distinction means that no civilians should be targeted intentionally, Military necessity means that targeting of the particular object should be necessary for the advancement of the troops, and Proportionality is that, the collateral damage (civilian and property) should be justifiable to the military advantage anticipated to be achieved’ – Sir Desmond de Silva QC Page 23.
Therefore, if Sri Lankan forces are to be made guilty of war crimes, charges may have to be brought either on the grounds of intentionally targeting civilians, attacking with no military necessity or for disproportionate killings, over and above the military advantage.
Tendentious allegation
In addition to the above, the Darusman report, makes another tendentious allegation against the Sri Lankan forces. It says in paragraph 137:
137. In the limited surveys that have been carried out in the aftermath of the conflict, the percentage of people reporting dead relatives is high. The number of credible sources has estimated that there could have been as many as 40,000 civilian deaths. Two years after the end of the war, there is still no reliable figure for civilian deaths, but multiple sources of information indicate that a range of up to 40,000 civilian deaths cannot be ruled out at this stage. Only a proper investigation can lead to the identification of all of the victims and the formulation of an accurate figure for the total number of civilian deaths.
Now, this is the figure that is widely quoted to discredit Sri Lanka’s armed forces. Further a figure of 40,000 appears somewhat ‘disproportionate’ in a conflict of this nature and therefore it can be used to make the Sri Lankan forces out to be guilty under international law although the claims made by the UNPOE have not been substantiated.
The Darusman report contradicts the number of ‘dead persons during the conflict’ furnished by the UN country team stationed in the conflict zone for that specific purpose. The US State Department report says the number of deaths is 6,710 from January 2009 to April 2009. The UN’s Country team report prepared by Gordon Weise, the country team leader, states that the figure of casualties is 7,714 from January 2nd to 13th May 2009. The two reports have a basis on daily counts, and they were prepared on the current basis while the conflict was raging, whereas this Darusman report, having come after two years since the end of the battle, presents a figure of 40,000 casualties without a basis or naming a source for the same.
Here is how the Panel justifies its reasons for questioning the first COG (UN Country team) figure:
135.
The number calculated by the United Nations Country Team provides a starting point but is likely to be too low for several reasons. First, it only accounts for the casualties that were observed by the networks of observers who were operational in LTTE-controlled areas. Many victims may not have been observed at all. Second, after the United Nations stopped counting on May 13th, the number of civilian casualties likely proliferated. Due to the intensity of the shelling, many civilians were left where they died and were never registered, brought to a hospital, or even buried. This means that, in reality, the total number could easily be several times that of the United Nations figures.
The country team was stationed in the war zone to prevent and record violations of the international laws of conflict, and the most crucial part of that operation was recording the number of dead in the fighting. The members of this panel, before casting aspersions on the quality of the information found on the Country-Team report, should do well to re-examine the authenticity of their own information sources because their sources, such as the Tamil Diaspora and the ‘Peace’ NGOs, could be highly partisan since they have lost their relevance (and also contributions) since this conflict came to an end.
Lord Naseby
On 01 November 2017, Lord Naseby, a member of the British House of Lords, moved a resolution in the British Parliament to the effect that the number of civilians killed in the final stage of the Sri Lankan conflict was around 7,000 and not 40,000. Accordingly, he suggested to the Parliament that Britain should change its perspective towards the Sri Lankan issue at the UN Human Rights Commission.
Even though Lord Naseby’s assertion is based on the reports of the Defense Attaché of the British Embassy in Colombo at the time of the war, it needs loads of optimism to expect that the British Government will accept these statistics and change its official position towards Sri Lanka at international forums, especially at the UN Human Rights Council where they have co-sponsored the US resolution against Sri Lanka.
Lord Naseby, subsequently airing his views to Mandy Clerk of the British media, stated, “I went into the civilian factor of this war because the figures I had did not add up to the official figures. So, I applied under the freedom of information, requesting the reports of the Defense Attaché of our embassy in Colombo at the time of the war. I received 26 reports, but that did not include the final few days of the war situation. So, I made another appeal, and there I received a further 12 reports. These reports had enough evidence to prove that nobody in the Sri Lankan government ordered to kill people and that was not the intention. The reports said that the casualty figure is around 7,200 civilians and the report further mentioned that a quarter of those casualties could be the LTTE cadres because they did not wear a uniform towards the last stages of the conflict. Then I went to the University Teachers of Jaffna, which is a professional organization of Tamil University teachers, and they said, ‘ it is about 7000’.
Verified Official Statistics
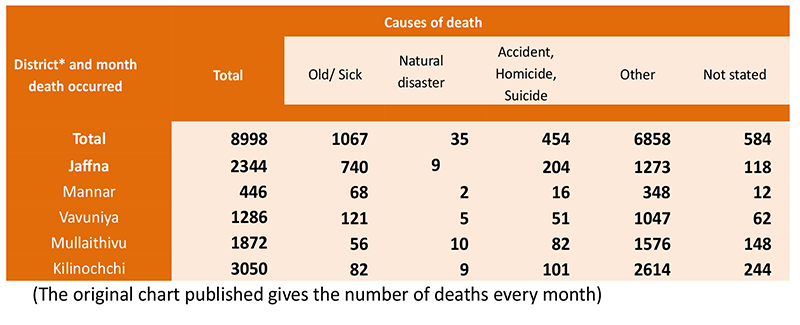
The Department of Census and Statistics performs its customary population survey for the whole of Sri Lanka every 10 years, but due to the LTTE activity, it has not been able to collect data in the North and East since the 1981 survey. Thus, during these years, the officers of respective kachcheries have been issuing population estimates when required for official purposes. However, since the conflict ended in 2009, and given the conflicting claims made by interested parties, including the Catholic Church, the Department commenced an exclusive survey for the northern province in June 2011. This survey was specially designed to ascertain, with verification, the number of people living as well as those who have died, especially during 2009 so that death certificates could be issued on account of them to their next of kin.
This survey was spearheaded by the following officers for each of the regions as follows,
Jaffna – S Udayakumaran (Head of the District Statistics office)
Mannar – M. Vithiyananthaneshan (Head of the District Statistics offic)
Kilinochchi – K.Velupillai (Head of the District Statistics office)
Vavuniya – M. Thyagalingam (Head of the District Statistics office)
Mullaitivu – N. Gangatharan (Head of the District Statistics office)
Following are the results of this survey
Thus, the above schedule gives the death toll as 8,998 during the period, including 1,067 who died due to old age/sickness, and the numbers are enumerated on the house-to-house survey regarding the cause of death. Death certificates were issued to all persons in this schedule and even those that did not explain their cause of death and stated as ‘not stated.’ People do not disclose the cause of death for various reasons, and most of such undisclosed deaths fall into the category ‘other’, meaning deaths due to terrorism. Therefore, it is possible that the number of deaths due to conflict situation was 7,442 (6,858+ 584).
Now, these death counts are reported of persons who were born and lived in the five districts where the conflict raged and also in the districts from where the LTTE used human shields. Therefore, when the Darusman report claims 40,000 deaths, such additional deaths have to be of people who were not born or did not live in these districts.
In modern times, dominant nations do not have to use weapons to subjugate others. They could just as well ‘Weaponize human rights’ to achieve the same end. That way, they could wear the cloak as the “Champions of Human rights,” hiding their authentic characters as killers, decimators and dominators.
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
Features
A Tribute to Professor H. L. Seneviratne – Part II

A Living Legend of the Peradeniya Tradition:
(First part of this article appeared yesterday)
H.L. Seneviratne’s tenure at the University of Virginia was marked not only by his ethnographic rigour but also by his profound dedication to the preservation and study of South Asian film culture. Recognising that cinema is often the most vital expression of a society’s aspirations and anxieties, he played a central role in curating what is now one of the most significant Indian film collections in the United States. His approach to curation was never merely archival; it was informed by his anthropological work, treating films as primary texts for understanding the ideological shifts within the subcontinent
The collection he helped build at the UVA Library, particularly within the Clemons Library holdings, serves as a comprehensive survey of the Indian ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement and the works of legendary auteurs. This includes the filmographies of directors such as Satyajit Ray, whose nuanced portrayals of the Indian middle class and rural poverty provided a cinematic counterpart to H.L. Seneviratne’s own academic interests in social change. By prioritising the works of figures such as Mrinal Sen and Ritwik Ghatak, H.L. Seneviratne ensured that students and scholars had access to films that wrestled with the complex legacies of colonialism, partition, and the struggle for national identity.
These films represent the ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement of West Bengal rather than the commercial Hindi industry of Mumbai. H.L. Seneviratne’s focus initially cantered on those world-renowned Bengali masters; it eventually broadened to encompass the distinct cinematic languages of the South. These films refer to the specific masterpieces from the Malayalam and Tamil regions—such as the meditative realism of Adoor Gopalakrishnan or the stylistic innovations of Mani Ratnam—which are culturally and linguistically distinct from the Bengali works. Essentially, H.L. Seneviratne is moving from the specific (Bengal) to the panoramic, ensuring that the curatorial work of H.L. Seneviratne was not just a ‘Greatest Hits of Kolkata’ but a truly national representation of Indian artistry. These films were selected for their ability to articulate internal critiques of Indian society, often focusing on issues of caste, gender, and the impact of modernisation on traditional life. Through this collection, H.L. Seneviratne positioned cinema as a tool for exposing the social dynamics that often remain hidden in traditional historical records, much like the hidden political rituals he uncovered in his early research.
Beyond the films themselves, H.L. Seneviratne integrated these visual resources into his curriculum, fostering a generation of scholars who understood the power of the image in South Asian politics. He frequently used these screenings to illustrate the conflation of past and present, showing how modern cinema often reworks ancient myths to serve contemporary political agendas. His legacy at the University of Virginia therefore encompasses both a rigorous body of writing that deconstructed the work of the kings and a vivid archive of films that continues to document the work of culture in a rapidly changing world.
In his lectures on Sri Lankan cinema, H.L. Seneviratne has frequently championed Lester James Peries as the ‘father of authentic Sinhala cinema.’ He views Peries’s 1956 film Rekava (Line of Destiny) as a watershed moment that liberated the local industry from the formulaic influence of South Indian commercial films. For H.L. Seneviratne, Peries was not just a filmmaker but an ethnographer of the screen. He often points to Peries’s ability to capture the subtle rhythms of rural life and the decline of the feudal elite, most notably in his masterpiece Gamperaliya, as a visual parallel to his own research into the transformation of traditional authority. H.L. Seneviratne argues that Peries provided a realistic way of seeing for the nation, one that eschewed nationalist caricature in favour of complex human emotion.
However, H.L. Seneviratne’s praise for Peries is often tempered by a critique of the broader visual nationalism that followed. He has expressed concern that later filmmakers sometimes misappropriated Peries’s indigenous style to promote a narrow, majoritarian view of history. In his view, while Peries opened the door to an authentic Sri Lankan identity, the state and subsequent commercial interests often used that same door to usher in a simplified, heroic past. This critique aligns with his broader academic stance against the rationalization of culture for political ends.
Constitutional Governance:
H.L. Seneviratne’s support for independent commissions is best described as a hopeful pragmatism; he views them as essential, albeit fragile, instruments for diffusing the hyper-concentration of executive power. Writing to Colombo Page and several news tabloids, H.L. Seneviratne addresses the democratic deficit by creating a structural buffer between partisan interests and public institutions, theoretically ensuring that the judiciary, police, and civil service operate on merit rather than political whim. However, he remains deeply aware that these commissions are not a panacea and are indeed inherently susceptible to the ‘politics of patronage.’
In cultures where power is traditionally exercised through personal loyalties, there is a constant risk that these bodies will be subverted through the appointment of hidden partisans or rendered toothless through administrative sabotage. Thus, while H.L. Seneviratne advocates for them as a means to transition a state from a patron-client culture to a rule-of-law framework, his anthropological lens suggests that the success of such commissions depends less on the law itself and more on the sustained pressure of civil society to keep them honest.
Whether discussing the nuances of a film’s narrative or the complexities of a constitutional clause, H.L. Seneviratne’s approach remains consistent in its focus on the spirit behind the institution. He maintains that a healthy democracy requires more than just the right laws or the right symbols; it requires a citizenry and a clergy capable of critical self-reflection. His career at the University of Virginia and his continued engagement with Sri Lankan public life stand as a testament to the idea that the intellectual’s work is never truly finished until the work of the people is fully realized.
In the context of H.L. Seneviratne’s philosophy, as discussed in his work of the kings ‘the work of the people’ is far more than a populist catchphrase; it represents the practical application of critical consciousness within a democracy. Rather than defining ‘work’ as labour or voting, H.L. Seneviratne views it as the transition of a population from passive subjects to an active, self-reflective citizenry. This means that a democracy is only truly ‘realized’ when the public possesses the intellectual autonomy to look beyond the ‘right laws’ or ‘right symbols’ and instead engage with the underlying spirit of their institutions. For H.L. Seneviratne, this work is specifically tied to the ability of the people—including influential groups like the clergy—to perform rigorous self-critique, ensuring that they are not merely following tradition or authority, but are actively sustaining the ethical health of the nation. It is a perpetual process of civic education and moral vigilance that moves a society from the ‘paper’ democracy of a constitution to a lived reality of accountability and insight.
This decline of the ‘intellectual monk’ had a catastrophic impact on the political landscape, particularly surrounding the watershed moment of 1956 and the ‘Sinhala Only’ movement. H.L. Seneviratne posits that when the Sangha exchanged their role as impartial moral advisors for that of political kingmakers, they became the primary obstacle to ethnic reconciliation. He suggests that politicians, fearing the immense grassroots influence of the monks, entered a state of monachophobia, where they felt unable to propose pluralistic or fair policies toward minority communities for fear of being branded as traitors to the faith. In H.L. Seneviratne’s framework, the monk’s transition from a social servant to a political vanguard effectively trapped the state in a cycle of majoritarian nationalism from which it has yet to escape.
H.L. Seneviratne’s work serves as a multifaceted critique of the modern Sri Lankan state and its cultural foundations. Whether he is dissecting what he sees as the betrayal of the monastic ideal or celebrating the humanistic vision of an Indian filmmaker, his goal remains the same: to champion a world where intellect and compassion are not sacrificed on the altar of political power. His legacy at the University of Virginia and his continued voice in Sri Lankan discourse remind us that the work of the intellectual is to provide a moral compass even, indeed especially, when the nation has lost its way.
(Concluded)
by Professor
M. W. Amarasiri de Silva
Features
Musical journey of Nilanka Anjalee …

 Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Well, our spotlight today is on ‘Nilanka – the Singer,’ and not ‘Nilanka – the Singing Doctor!’
Nilanka’s journey in music began at an early age, nurtured by an ear finely tuned to nuance and a heart that sought expression beyond words.
Under the tutelage of her singing teachers, she went on to achieve the A.T.C.L. Diploma in Piano and the L.T.C.L. Diploma in Vocals from Trinity College, London – qualifications recognised internationally for their rigor and artistry.
These achievements formally certified her as a teacher and performer in both opera singing and piano music, while her Performer’s Certificate for singing attested to her flair on stage.
Nilanka believes that music must move the listener, not merely impress them, emphasising that “technique is a language, but emotion is the message,” and that conviction shines through in her stage presence –serene yet powerful, intimate yet commanding.
Her YouTube channel, Facebook and Instagram pages, “Nilanka Anjalee,” have become a window into her evolving artistry.
Here, audiences find not only her elegant renditions of local and international pieces but also her original songs, which reveal a reflective and modern voice with a timeless sensibility.
Each performance – whether a haunting ballad or a jubilant interpretation of a traditional hymn – carries her signature blend of technical finesse and emotional depth.
Beyond the concert hall and digital stage, Nilanka’s music is driven by a deep commitment to meaning.
Her work often reflects her belief in empathy, inner balance, and the beauty of simplicity—values that give her performances their quiet strength.
She says she continues to collaborate with musicians across genres, composing and performing pieces that reflect both her classical discipline and her contemporary outlook.
Widely acclaimed for her ability to adapt to both formal and modern stages, with equal grace, and with her growing repertoire, Nilanka has become a sought-after soloist at concerts and special events,
For those who seek to experience her artistry, firsthand, Nilanka Anjalee says she can be contacted for live performances and collaborations through her official channels.
Her voice – refined, resonant, and resolutely her own – reminds us that music, at its core, is not about perfection, but truth.
Dr. Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe also indicated that her newest single, an original, titled ‘Koloba Ahasa Yata,’ with lyrics, melody and singing all done by her, is scheduled for release this month (March)
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoLibrary crisis hits Pera university
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days ago‘IRIS Dena was Indian Navy guest, hit without warning’, Iran warns US of bitter regret
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoSri Lanka evacuates crew of second Iranian vessel after US sunk IRIS Dena