News
The Caspian Sea is set to fall by 9 metres or more this century – an ecocide is imminent
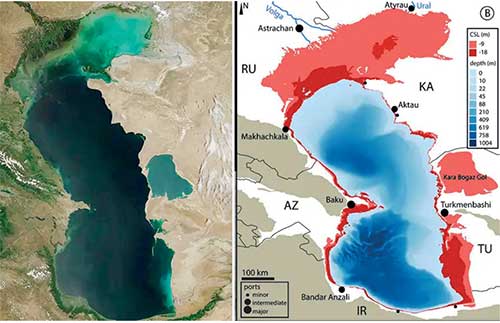
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image of the Caspian Sea, left, on June 4, 2010. The map on the right shows the impact of Caspian Sea level projections of -30 feet and -60 feet at the end of the 21st century. Red regions fall dry.(NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team / Map by Prange, M., Wilke, T. & Wesselingh, F.P. The other side of sea level change.)
Imagine you are on the coast, looking out to sea. In front of you lies 100 metres of barren sand that looks like a beach at low tide with gentle waves beyond. And yet there are no tides.
This is what we found when we visited the small harbour of Liman, on the Caspian Sea coast of Azerbaijan. The Caspian is actually a lake, the largest in the world and it is experiencing a devastating decline in its water level that is about to accelerate. By the end of the century the Caspian Sea will be nine metres to 18 metres lower. That’s a depth considerably taller than most houses.
It means the lake will lose at least 25 per cent of its former size, uncovering 93,000 sq km of dry land. If that new land were a country, it would be the size of Portugal.
As we found in our new research, the crisis may well result in an ecocide as devastating as the one in the Aral Sea, a few hundred kilometres to the east. The Caspian’s surface is already dropping by 7 cm every year, a trend likely to increase.
In five years, it might be about 40 cm lower than today and in ten years almost one metre lower. Maritime countries worldwide are coming to terms with one metre or so of sea level rise by the end of the century. The Caspian Sea faces a drop of that size — except it will happen within a decade.
Climate change is the culprit. The Caspian Sea waters are isolated, its surface is already around 28 metres below global oceans. Its level is the product of how much water is flowing in from rivers, mostly the mighty Volga to the north, how much it rains and how much evaporates away.
At the end of the century, the Volga and other northern rivers will still be there. However, a projected temperature rise of about 3? to 4? in the region will drive evaporation through the roof.
Future misery despite past crises
The Caspian Sea has a history of violent rises and falls. In Derbent, on the Caucasus coast of Russia, submerged ancient city walls testify to how low the sea was in medieval times. Around 10,000 years ago, the Caspian was about 100 metres lower. A few thousand years before that it was about 50 metres higher than today and even overspilled into the Black Sea.
Yet people who lived beside the sea were able to overcome the swings. No human infrastructure was around to be destroyed and many animal species simply moved up and down with the sea levels, as they had done over the past 2 million years or so. But this time is different. The fall will affect the Caspian’s unique and already stressed animal and plant life, along with human societies along the coasts.
In some areas, the coastline is about to retract hundreds of metres a year or more. Can you imagine building new piers and harbours that fast? By the time they are ready, the sea will have moved kilometres or tens of kilometres further away. Coastal promenades will soon be landlocked. The beaches of today will be the sand ridges stranded in barren plains of tomorrow.
The drop will also affect lowland rivers and deltas around the Caspian Sea. Once-fertile plains will become too dry for watermelon and rice farming to continue.
Unique Caspian life in peril
The town of Ramsar, on the Iranian coast, gave its name to a global wetland convention. But as the sea recedes, the town is becoming landlocked and the surrounding wetlands will be gone within decades.
The shallower “shelves” of the northern and eastern Caspian are major food supplies for fish and birds, yet the entire northern and eastern shelves will transform in dry barren lands. This will devastate fish species, the Caspian seal and a richness of molluscs and crustaceans species unique to the sea.
These Caspian inhabitants have already suffered badly in the past century from pollution, poaching and invasive species. About 99 per cent of Caspian seal pups are raised on the winter ice of the north Caspian. Yet both the winter ice and indeed the whole north Caspian will disappear.
Remaining biodiversity hotspots in depths between 50 metres and 150 metres will be affected as rivers dump nutrients into the deeper central basins combined with rising temperatures. This will decrease oxygen levels and developing ecological dead zones could affect the remaining refuges of Caspian species. A genuine ecocide is around the corner.
The situation cries for action, but possibilities are limited. Rising global CO2 levels, the main driver of climate conditions causing the Caspian crisis, can only be dealt with global agreements. In Soviet times, large scale water diversions from Siberian rivers were proposed to deal with the shrinking Aral Sea to the east. But such large works — in the case of the Caspian Sea, a canal from the Black Sea might be considered — come with huge ecological and geopolitical risks.
Yet action is necessary to safeguard the Caspian Sea’s unique plants and animals and the livelihood of the people who live around it. The stranded small harbour in Liman is further from the sea every year. If no action is taken, it will be left alone in more than one way.
(The Conversation)
News
Cabinet approves construction of new 300 bed Base Hospital in Deniyaya

The Cabinet of Ministers approved the resolution forwarded by the Minister of Health and Mass Media to relocate the Deniyaya Base Hospital after constructing a new hospital with a capacity of 300 beds at an estimated cost of Rupees 6,000 million.
The Southern Provincial Department of Health has acquired a plot of land in Handford estate which is approximately 03 kilometres away from the town for this purpose.
News
Cabinet nod to legally empower methodology for implementing the ‘Praja Shakthi’ poverty alleviation national movement

The Cabinet of Ministers granted approval for the resolution furnished by the Minister of Rural Development, Social Security and Community Empowerment to instruct the Legal Draftsman to draft a bill to legally empower the implementation of ‘Praja Shakthi’ (Strength of the Community) poverty alleviation national movement
News
NPP not under Indian pressure to hold PC polls – JVP

…preliminary work started on new Constitution
JVP General Secretary Tilvin Silva yesterday (17) maintained that the NPP government was not under Indian pressure to hold the long delayed Provincial Council elections.
The top JVP official said so appearing on Sirasa Pathikada, anchored by Asoka Dias. Tilvin Silva said that neither the devolution nor terrorism issues had been discussed during his meeting with External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar and Deputy National Security Advisor Pavan Kapoor, in New Delhi. This was Tilvin Silva’s first visit to India.
Declaring that politics hadn’t been on the agenda, the JVPer said that the Indian focus was entirely on economic development and technology.
The JVP General Secretary visited India under the Indian Council for Cultural Relations’ (ICCR) Distinguished Visitors Programme from 5-12 February 2026. General Secretary Silva was accompanied by Kitnan Selvaraj, MP, Ilankumaran Karunanathan, MP, JVP Central Committee Member Janaka Adhikari, JVP’s Media Unit Head Hemathilaka Gamage and Member of JVP’s International Relations Department Kalpana Madhubhashini. The delegation visited New Delhi, Ahmedabad and Thiruvananthapuram.
Responding to another query, Tilvin Silva said that Dr. S. Jaishankar had reiterated that India would always remain a true and trusted partner for Sri Lanka, in accordance with its ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’ and Vision ‘MAHASAGAR.’
Referring to the second JVP insurrection in the late 1980s, the JVPer claimed that they had not been against India but responded to the actions of the then Indian government.
Sri Lanka enacted the 13th Amendment to the Constitution in the wake of the Indo-Lanka peace accord of July 1987 to pave the way for Provincial Councils.
Tilvin Silva said that since they came to power, Indo-Sri Lanka relations had changed. “India has realised we could work together,” he said.
The JVP official said that preliminary work was underway, regarding the formulation of a new Constitution. The abolition of executive presidency and creation of an Office of President sans executive powers, too, would be addressed, he said, adding that the strengthening of the legislature was the other issue at hand.
Pointing out that the NPP had 2/3 majority in Parliament and could introduce a new Constitution on their own, Tilvin Silva said that they intended to obtain views of all and study the past processes in a bid to secure consensus. The JVP, as the party that campaigned against the introduction of executive presidency, way back in 1978, would lead the current effort to do away with the existing Constitution, he said.
Tilvin promised that they would implement what was in their manifesto.
The interviewer also raised the issue of abolishing the pensions for ex-Presidents. Tilvin Silva said that the Supreme Court, too, had approved the move to abolish pensions to ex-MPs. Therefore there was no issue with that, however, the ex-Presidents pensions couldn’t be done away with as they were made through the Constitution. That would be addressed when the government introduced a new Constitution in consultation with other stakeholders.
By Shamindra Ferdinando
-

 Life style3 days ago
Life style3 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoThailand to recruit 10,000 Lankans under new labour pact
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoMassive Sangha confab to address alleged injustices against monks













