Features
REFLECTIONS ON THE LIFE AND TIMES OF LAKSHMAN KADIRGAMAR

by Tissa Jayatillake
From the time I was old enough to cultivate an interest in politics, I have familiarized myself with the life and times of those political personalities I took a liking to. The late Dudley Senanayake (who incidentally died in 1973 a day after Lakshman Kadirgamar’s 41st birthday) was the first I took to and I consider it my loss that I did not have the opportunity to get to know him personally.
Of the several politicians that I have subsequently taken note of, there were two I got particularly close to and they were both, coincidentally enough, Oxonians who happened also to be presidents of the Oxford Union in their time. I refer to Lalith Athulathmudali and Lakshman Kadirgarmar. Athulathmudali did not attend a local university prior to going up to Oxford, as did Kadirgamar. The former’s cake, (to borrow a metaphor from Kadirgamar himself) was not baked at home, unlike that of the latter for whom Oxford was only the icing on his superlative, home-produced, academic confection.
Although Lakshman Kadirgamar and I belonged to two different generations, we shared certain commonalities. Though not of Kandy, we both had our early education in that city (he at Trinity, I at Kingswood) and we were both products of the University of Ceylon, Peradeniya. If memory serves, he was a resident of Arunachalam Hall, which was also where I spent my undergraduate years. He was a ‘citizen of the world’, a Sri Lankan and a Tamil. Likewise I, too, prefer to transcend narrow boundaries and take pride in being in that order, a human resident of this planet, a Sri Lankan, and then a Sinhalese.
I liked Kadirgamar’s academic bent of mind. If he and I were given to clichés, I would have called him ‘a voracious reader’. I should, instead, describe him as a man of books. And many were the times when we compared notes on literary texts we both had read and enjoyed. Not infrequently he telephoned me to double check on a quotation from a Shakespearean play that he wished to include in a lecture or a speech he was writing up. He publicly denounced bribery and corruption in public office, a particular aversion of mine, which is not a safe or fashionable public stance for a politician to take and I admired him for his courageous stand.
Furthermore he was unpretentious, charming, mellow-toned and possessed of a fine if often ironic sense of humour. And there was something else he was proud to be– an outstanding sportsman. The last attribute meant, by definition, that he was by instinct and training, fair-minded. Could one possibly ask for more? My one regret is that I did not get to know Lakshman Kadirgamar as intimately earlier than I actually did. I console myself with the thought that quality ever trumps quantity when it comes to most good things of life. As Ranil Wickremesinghe noted in the course of his tribute to Lakshman Kadirgamar in Parliament, a meal with the late minister offered food for the body as well as the mind. On most occasions a mere chat over a drink with him provided such nourishment for the soul.
Apart from our regular meetings to talk of issues of the day, there were two key projects dear to his heart that brought us together and helped cement our friendship. Given the rich heritage we Sri Lankans are heirs to, Lakshman Kadirgamar was of the view that we should give to the world, as he so aptly put it, ‘something more than just tea, tourism and terrorism’. He thus had a long-term plan to enable Sri Lanka to continue to contribute to the world of culture and the arts as also to the further refinement of international relations and diplomacy. It was his desire to have a book published on a Sri Lankan artist that would be ‘an ideal brand label for Sri Lanka, an image which may be projected all over the world as the face of Sri Lanka in all of its many forms’.
The result of his endeavours in this regard is the monumental and exquisite The World of Stanley Kirinde (2005) authored by Sinharajah Tammita-Delgoda. Having initiated the book project, he next set his sights on the production of an academic journal for the study of politics and diplomacy via the Bandaranaike Centre for International Studies (BCIS) of which he was now chairman. He invited me to serve as editor and together we put in many hours to get International Relations in a Globalizing World (IRGW) off the ground. Lakshman Kadirgamar’s last public act on the evening of that fateful twelfth of August, 2005, was to preside over the ceremony to mark the release of the inaugural issue of IRGW. It was Kadirgamar’s expectation, through the regular publication of IRGW, to raise the level of Sri Lanka’s contribution to diplomacy. All these best-laid plans and goals were shattered on that dreadful August night in 2005. Unfortunately Lakshman Kadirgamar did not live to see (though he saw the finished product and admiringly flipped through its pages) the release of The World of Stanley Kirinde scheduled for 18 August, 2005.
In this tenth year after his death, it is as good a time as any, to assess dispassionately the late foreign minister’s contribution to Sri Lanka and the world, and to imagine the kind of role he might have played had he lived beyond his 73rd year. I consider Lakshman Kadirgamar to be one of the finest twentieth century Sri Lankans and far and away the best foreign minister Sri Lanka has had to- date. He was widely read and intelligent and, at the same time, hard-working and disciplined. He had the courage of his convictions and the inner strength to hold fast to his ideals from his entry into the fickle world of politics in 1994 until his tragic end in 2005.
I tend to view Lakshman Kadirgamar’s performance on the domestic political front less enthusiastically than that of his on the international stage. It is entirely possible that my lukewarm view has less to do with any inadequacy of Kadirgamar’s and more to do with my aversion to realpolitik, especially to its Sri Lankan variety. As I have asserted in an earlier tribute to him (2005), Lakshman Kadirgamar was the quintessential Sri Lankan. Almost a year before his death, in September 2004, he made a profound statement on Japanese National Television (NHK) that encapsulated his credo:
I am first and foremost a citizen of Sri Lanka. I do not carry labels of race or religion or any other label. I would say quite simply that I have grown up with the philosophy that I am a citizen of the world. I do not subscribe to any particular philosophy; I have no fanaticism; I have no communalism. I believe there should be a united Sri Lanka. I believe that all our peoples can live together, they did live together. I think they must in the future learn to live together after this trauma is over. We have four major religions in the country: Buddhism, Islam, Hinduism and Christianity. All these religions exist very peacefully. They get on very well. I see no reason why the major races in the country, the Tamils and the Sinhalese, cannot again build a relationship of confidence and trust. That is my belief.
It is this fervent belief in the essential goodness of his country and fellow citizens that form the cornerstone of his diplomatic labours. It was also the driving force behind his brilliant and spellbinding performance as our foreign minister. I relished in particular the manner in which he finessed the challenge of LTTE terrorism. To say it was primarily Lakshman Kadirgamar’s powers of persuasion and skillful handling of domestic issues and their international ramifications that redeemed Sri Lanka’s sullied image is surely no exaggeration. Dedicated, experienced and effective Sri Lankan Foreign Service personnel played their part in this restoration process, but the helmsman was clearly Lakshman Kadirgamar.
In their measured tributes to a book published in honour of Lakshman Kadirgamar (Roberts: 2012), three seasoned American diplomats I know intimately, Karl (Rick) Inderfurth, Peter Burleigh and Shaun Donnelly who interacted closely with Kadirgamar have testified to the latter’s major successes on the international stage, during his lifetime and even posthumously. Chris Patten, the British politician, reinforces this fact when he notes in the same publication that:
Lakshman Kadirgamar spent much of his diplomatic energy and his formidable eloquence in attempting to persuade foreign governments to proscribe the LTTE in their own countries and stop the raising of funds for terrorism in Sri Lanka. He scorned the ‘Nelsonian’ attitude to terrorism of some countries. He was particularly active in supporting the drafting of the 1997 UN Convention for the Suppression of Terrorist Bombings. The respect he enjoyed internationally meant that his assassination nudged some foreign governments into taking a tougher line in prohibiting active support for the LTTE in their own countries.
Peter Burleigh in a recent personal communication reiterated this foremost aspect of Kadirgamar’s achievement when he noted:
I personally believe that his efforts to get important governments like Australia, the UK and the US to ban money transfers to the LTTE was a key contribution to the long-term effort to defeat the group. And his personal efforts, and effectiveness, in that regard were essential to that success.
Although I recognize that politics may well be the art of the possible, my limited experience of it as a practitioner and deeper awareness of it as student, make me conclude that politics is a murky and dismal business. I have often wondered why men of the sensitivity of Neelan Thiruchelvam and Lakshman Kadirgamar ever took to politics. In a statement over national television in 1994, Lakshman Kadirgamar spelt out his reasons for doing so. I quote below the operative paragraph of that statement:
I have had a privileged life by birth, by education, by access to opportunities, and I have always felt that a time must come when you must give something back to the society in which you have grown up and from which you have taken so much. So-called educated people must not shirk responsibilities in public life. I have reached that stage in life when, without being heroic about it, I feel I should participate more fully in public life.
Whilst not taking anything away from his invaluable and splendid contribution as foreign minister, I remain convinced that he could have given more back to the society from which, by his own admission, he had taken so much by opting for a different if less glamorous public role than that of a high visibility politician. As with similarly gifted men as S.W.R.D Bandaranaike, N.M Perera, Pieter Keuneman, Felix Dias Bandaranaike and Lalith Athulathmudali before him, I am left with the nagging feeling that his stint in politics somehow diminished Lakshman Kadirgamar in the end. Such diminution as occurred may well have been due to the corrosive nature of politics and not due to any inherent flaw in Kadirgamar’s character.
Perhaps he permitted his colleagues and his party to exploit his standing in society and his professional stature when he decided ‘without being heroic about it. . . [to] participate fully in public life’. Be this as it may, I remain disappointed by the narrow political role he played in the difficult and often acrimonious days of Sri Lanka’s French-style co-habitation government. This was the period between December 2001 and April 2004, when Kadirgamar’s party leader, Chandrika Kumaratunga, despite her party being out of power, was yet the constitutional head of government whilst Ranil Wickremesinghe as prime minister was in effective control of Parliament. Kadirgamar now was assigned the role of advisor to the president on international affairs, with Tyronne Fernando occupying the portfolio of foreign affairs.
On becoming prime minister in February 2002, Ranil Wickremesinghe entered into a Ceasefire Agreement (CFA) with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). The CFA was brokered by the Norwegians, who were at the time involved in Sri Lanka’s peace process, and Wickremesinghe presented his cabinet and his president with a fait accompli. Although initially Kadirgamar’s statement in Parliament in 2002 in response to that of the prime minister reflected a refreshing degree of constructive cooperation, a little over a year later in a speech in Parliament on 8 May, 2003, doubtless on the authority of President Kumaratunga and the Parliamentary Group of the People’s Alliance, Kadirgamar attacked the CFA arguing that it was ‘a structurally flawed document’. Clearly Kadirgamar was here being sucked into petty politics as borne out by a subsequent observation of General Satish Nambiar, the well-known Indian strategic expert engaged by the government of Sri Lanka at that time. In a communication in January 2010 dealing with that fraught situation of 2003, Nambiar refers to a one-on-one lengthy meeting he had with Kadirgamar during his last visit to Sri Lanka in 2003. In the course of that meeting Nambiar had told Kadirgamar that he was hurt by the suggestions made by some of Kadirgamar’s party members that he [Nambiar] was manipulating his report. Nambiar comments:
[Kadirgamar’s]disarming response was typical of him: that I should allow for the politics of the situation where the parties will use any means to put the ruling dispensation on the defensive. [Roberts: p. 204]
When one reads Kadirgamar’s 8 May, 2003 speech in hindsight, one clearly recognizes that his arguments against the CFA are not without merit. But the key point that needs emphasis here is that by being a willing party to political manipulation of something as highly sensitive as the CFA, Kadirgamar had begun to slip somewhat from the lofty pedestal of statesmanship he had been on hitherto. In the process, Kadirgamar and his political companions failed to give any credit whatsoever or even the benefit of the doubt to Wickremesinghe.
We now know though that through the CFA the LTTE were led into a corner and to peace negotiations, with some even referring to it as ‘a peace trap’. Wickremesinghe’s CFA, for all of its ‘structural flaws’, was as much a ploy as was the Kumaratunga government’s 1998 decision to use the Norwegians as ‘facilitators’ in the unofficial conversations between the then government and the LTTE. And, yet, Kumaratunga and her paarty were now opposing, seemingly for the sake of opposition, the Norwegians (their ‘facilitators’) and Wickremesinghe, for the signing of the CFA with Kadirgamar lending his forensic debating skills for the cause in Parliament. A similar but less nationally harmful political misjudgement was Kadirgamar’s decision, despite sincere and pragmatic advice against the move from close associates, to contest the incumbent Secretary- General of the Commonwealth in 2003. He was roundly defeated by 40 to 11.
On balance, Kadirgamar’s overall achievement as politician and foreign minister, despite blemishes referred to above, is marvellous. Unlike the average gifted person who tends to rest on his laurels, Kadirgamar was exceedingly hard-working from beginning to end. Like a good lawyer, he always studied his brief well and, like a good sportsman, he was ever thorough in his preparation. It is this careful preparation in combination with his ability and flair that made Kadirgamar who he was. He was consistent and relentless in his opposition to political violence which he saw as a threat ‘to the stability within and between states throughout the world’.
Well before the cataclysmic ‘9/11’, he warned western governments of the dangers of terrorism and called for joint action to deal with the scourge. Among his several notable speeches on the problems of terrorism, perhaps the most influential was that he made at Chatham House, London, on 15 April, 1998 at a meeting held under the auspices of the Royal Institute of International Affairs and the International Foundation of Sri Lankans. ‘[A] terrorist act’,Kadirgamar asserted at Chatham House, ‘is seen as an attack on society as a whole, on democratic institutions, on the democratic way of life. A terrorist attack is an act of war against society’.
In similar vein was his lecture delivered on 13 September, 2010 at The Potomac Institute of Policy Studies in Washington D.C., approximately a year before ‘9/11’. Kadirgamar was thus resolute in his principled opposition to the use of violence as a means of seeking political gain, both at home and abroad. At the same time, he recognized our need to address the underlying causes that lead communities to acts of violence. Hence much as he decried the political violence of the LTTE, he did recognize the need for social and political justice to those marginalized citizens in our midst. In this context, the following remarks he made during an interview he gave to Business Today (Colombo, March 1997, p.20) are most salutary:
[T]he ultimate, permanent, durable solution to this problem will not come from force of arms alone. It will not come from conquest or our vanquishing the LTTE. It has to come by acceptance of the people in their entirety, by the Sinhala and the Tamil people. That is a political settlement. And, a political settlement that is perceived by the communities, by the majority and the minorities, to be fair and just. It must be a settlement that is enshrined in law, and it must be enshrined in the hearts of the people.
Thus Kadirgamar’s opposition to violence was both principled and pragmatic. However, he did not allow his justifiable antipathy to violence to ensnare Sri Lanka’s collective future. Lakshman Kadirgamar was no narrow nationalist. In pursuing a solution to the crisis of nation-building in Sri Lanka, he did not take a partisan stance. He was Sri Lankan to the core.
A tragedy in Lakshman Kadirgamar’s life and career is that neither the zealots among the Sinhalese who mourned his untimely death and cheered him on in life nor their counterparts within the Tamil community who rejoiced in his death and vilified him in life understood or yet understand the man. The Sinhala zealots mistook his opposition to the separatist extremism of the LTTE as a sign of his ‘pro-Sinhalaness’. The moral inadequacy of the zealots amongst the Tamils made it impossible for them to understand Kadirgamar’s heartfelt aversion to ethnic labels. It also led them to their erroneous conclusion that Kadirgamar’s championing of an overarching Sri Lankan identity was an act of political expediency at best and a manifestation of ‘anti-Tamilness’ at worst. The continuing tragedy of Sri Lanka is that there are too many amongst us who think and feel like these zealots referred to above. So long as Sri Lanka holds within it men and women of such a tribal mindset, so long will it remain a blighted country.
It is true that Lakshman Kadirgamar had high political ambitions and that he was keen on becoming prime minister on being approached to don that mantle. He would have, deservedly in my view, been our first Tamil prime minister had plans worked out. In fairness to him, the fact that he did not jockey for the post of prime minister bears repetition. I was then, and am now more so of the view, that the conferment of the prime ministership on Lakshman Kadirgamar, however interim an appointment it might have been, would have been good for Kadirgamar and for Sri Lanka.
I am also confident that had he yet been amongst us after the military defeat of the Tamil Tigers in May 2009, Kadirgamar would have played a cardinal role in recreating a feeling of Sri Lankanness in our society that transcends religion and ethnicity without endangering the multi-faceted personality of our country. His quiet but effective contribution in assisting the government in the restoration of the Jaffna public library is illustrative of the kind of effort he would have put in on behalf of national resuscitation and regeneration.
Lakshman Kadirgamar was ‘a scholar-statesman who was both a realist and idealist’. Despite the deleterious impact of politics on him, his years in our national legislature served to raise the level of political discourse, both at home and abroad, several notches higher. He will be remembered by future generations of Sri Lankans for the values and principles he lived and died for.
Features
Challenges to addressing allegations during Sri Lanka’s armed conflict

A political commentator has attributed the UK sanctions against four individuals, three of whom were top ranking Army and Navy Officers associated with Sri Lanka’s armed conflict, to the failure of successive governments to address human rights allegations, which he describes as a self-inflicted crisis. The reason for such international action is the consistent failure of governments to conduct independent and credible inquiries into allegations of war crimes; no ‘effective investigative mechanism’ has been established to examine the conduct of either the Sri Lankan military or the LTTE.
He has not elaborated on what constitutes an “effective investigative mechanism. He has an obligation and responsibility to present the framework of such a mechanism. The hard reality however is that no country, not even South Africa, has crafted an effective investigative mechanism to address post conflict issues.
INVESTIGATIVE MECHANISMS
The hallmark of a credible investigative mechanism should be unravelling the TRUTH. No country has ventured to propose how such a Mechanism should be structured and what its mandate should be. Furthermore, despite the fact that no country has succeeded in setting up a credible truth-seeking mechanism, the incumbent government continues to be committed to explore “the contours of a strong truth and reconciliation framework” undaunted by the failed experiences of others, the most prominent being South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission.
South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission is often cited as the gold standard for post conflict Mechanisms. Consequently, most titles incorporate the word “Truth” notwithstanding the fact that establishing the “Truth” was a failure not only in South Africa but also in most countries that attempted such exercises.
Citing the South African experience, Prof. G. L. Peiris states: “pride of place was given to sincere truth-telling which would overcome hatred and the primordial instinct for revenge. The vehicle for this was amnesty…… Despite the personal intervention of Mandela, former State President P. W. Botha was adamant in his refusal to appear before the Commission, which he deemed as ‘a fierce unforgiving assault’ on Afrikaaners” (The Island, 01 April, 2025). In the case of Sri Lanka too, disclosures to find the “Truth” would be all about the other party to the conflict, thus making Truth seeking an accusatory process, instead of a commitment to finding the Truth. The reluctance to engage in frank disclosure is compounded by the fear of recrimination by those affected by the Truth.
Continuing Prof. Peiris cites experiences in other countries. “Argentina, the power to grant amnesty was withheld from the Commission. In Columbia, disclosure resulted not in total exoneration, but in mitigating sentences. In Chile, prosecutions were feasible only after a prolonged interval since the dismantling of Augusta Pinochet’s dictatorship ….” (Ibid).
The mechanisms adopted by the countries cited above reflect their own social and cultural values. Therefore, Sri Lanka too has to craft mechanisms in keeping with its own civilisational values of restorative and not retributive justice for true reconciliation, as declared by President J. R, Jayewardene in San Francisco as to what the global attitude should be towards Japan at the conclusion of World War II. Since the several Presidential Commissions appointed under governments already embody records of alleged violations committed, the information in these commission reports should be the foundation of the archival records on which the edifice of reconciliation should be built.
ESTABLISHING DUE CONTEXT
The suggestion that an independent and credible inquiry be conducted into allegations of war crimes reflects a skewed understanding of the actual context in which the armed conflict in Sri Lanka occurred. Even the UNHRC has acknowledged that the provisions of “Article 3 common to the four Geneva Conventions relating to conflicts not of an international character is applicable to the situation in Sri Lanka, as stated in para. 182 of the OISL Report by the UNHRC Office. Therefore, the correct context is International Humanitarian Law with appropriate derogations of Human Rights law during an officially declared Emergency as per the ICCPR.; a fact acknowledged in the OISL report.
Consequently, the armed conflict has to conform to provisions of Additional Protocol II of 1977, because “This Protocol, which develops and supplements Article 3 common to the Geneva Conventions is the due context. There is no provision for “alleged war crimes” in the Additional Protocol. Although Sri Lanka has not formally ratified Additional Protocol II, the Protocol is today accepted by the Community of Nations as Customary Law. On the other hand, “war crimes” are listed in the Rome Statute; a Statute that Sri Lanka has NOT ratified and not recognized as part of Customary Law.
Therefore, any “investigative mechanism” has to be conducted within the context cited above, which is Additional Protocol II of 1977.
SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE
On the other hand, why would there be a need for Sri Lanka to engage in an independent and credible inquiry into allegations, considering the following comment in Paragraph 9.4 and other Paragraphs of the Lessons Learnt and Reconciliation Commission (LLRC)?
“In evaluating the Sri Lankan experience in the context of allegations of violations of IHL (International Humanitarian Law), the Commission is satisfied that the military strategy that was adopted to secure the LTTE held areas was one that was carefully conceived in which the protection of the civilian population was given the highest priority”
9.7 “Having reached the above conclusion, it is also incumbent on the Commission to consider the question, while there is no deliberate targeting of civilians by the Security Forces, whether the action of the Security Forces of returning fire into the NFZs was excessive in the context of the Principle of Proportionality…” (Ibid)
The single most significant factor that contributed to violations was the taking of Civilians in the N Fire Zone hostage (NFZ) by the LTTE. This deliberate act where distinction between civilian and combatant was deliberately abandoned, exposed and compromised the security of the Civilians. The consequences of this single act prevent addressing whether military responses were proportionate or excessive, or whether the impact of firing at make-shift hospitals were deliberate or not, and whether limiting humanitarian aid was intentional or not. These issues are recorded and addressed in the Presidential Commission Reports such as LLRC and Paranagama. This material should be treated as archival material on which to build an effective framework to foster reconciliation.
UK SANCTIONS
Sanctions imposed by the UK government as part of an election pledge for Human Rights violations during the armed conflict is a direct act of intervention according to Article 3 of the Additional Protocol of 1977 that is the acknowledged context in which actions should be judged.
Article 3 Non-intervention states:
1 “Nothing in the Protocol shall be invoked for the purpose of affecting the sovereignty of a State or the responsibility of the government by all legislative means, to maintain or re-establish law and order in the State or to defend the national unity and territorial integrity of the State”.
2 “Nothing in the Protocol shall be invoked as a justification for intervening directly or indirectly, for any reason whatsoever, in the armed conflict or in the internal or external affairs of the High Contracting Party in the territory on which the conflict occurs”.
Targeting specific individuals associated with the armed conflict in Sri Lanka is a direct assault of intervention in the internal affairs of Sri Lanka. The UK government should be ashamed for resorting to violating International Law for the sake of fulfilling an election pledge. If Sri Lanka had issued strictures on the UK government for not taking action against any military officers responsible for the Bloody Sunday massacre where 26 unarmed civilians participating in a protest march were shot in broad daylight, Sri Lanka would, in fact be intervening in UK’s internal affairs.
CONCLUSION
The UK’s action reflects the common practice of making election pledges to garner targeted votes of ethnic diasporas. The influence of ethnic diasporas affecting the conduct of mainstream politics is becoming increasingly visible, the most recent being the Tamil Genocide Education Week Act of Ontario that was dismissed by the Supreme Court of Canada on grounds the Provincial Legislations have no jurisdiction over Federal and International Laws.
However, what should not be overlooked is that the armed conflict occurred under provisions of common Article 3 of the Geneva Conventions. This Article is developed and supplemented by Additional Protocol II of 1977. Therefore, since all Geneva Conventions are recognised as Customary Law, so should the Additional Protocol II be, because it is a development of common Article 3.
Imposing sanctions under provisions of Additional Protocol II amounts to Intervention in internal affairs of a State as stated in Article 3 of the Protocol; II cited above. Such interventions are prohibited under provisions of international law.
The need to revive independent and credible inquiries after the lapse of 16 years is unrealistic because those who were perpetrators and victims alike cannot be identified and/or located. Furthermore, the cost of disclosure because of the possibility of retribution would compromise their security. A realistic approach is to use the material recorded in the Presidential Commission Reports and treat them as archival records and use the lessons learnt from them to forge a workable framework that would foster unity and reconciliation with the survivors in all communities This is not to live in the past but to live in the here and now – the present, which incidentally, is the bedrock of Sri Lanka’s civilisational values.
by Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
The Silent Invasion: Unchecked spread of oil palm in Sri Lanka

Sri Lanka’s agricultural landscape is witnessing a silent yet profound transformation with the rapid expansion of oil palm plantations. Once introduced as a commercial crop, the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) is now at the center of a heated debate, with environmentalists and scientists warning of its devastating ecological consequences.
Speaking to The Island research scientist Rajika Gamage, said: “The spread of oil palm in Sri Lanka is not just a concern for biodiversity, but also for water resources, soil stability, and even local economies that rely on traditional crops.”
A Brief History of Oil Palm Cultivation
Oil palm, originally from West and Central Africa, was first cultivated for commercial purposes in Java in 1948 by Dutch colonists. It reached Malaysia and Indonesia by 1910, where its lucrative potential drove large-scale plantations.
According to Gamage, in Sri Lanka, the first significant oil palm plantation was established in 1968 at Nakiyadeniya Estate by European planters, initially covering a mere 0.5 hectares. Today, oil palm cultivation is predominantly concentrated in Galle, Matara, and Kalutara districts, with smaller plantations in Colombo, Rathnapura, and Kegalle.
Over the decades, he says the commercial viability of oil palm has prompted its expansion, often at the cost of native forests and traditional agricultural lands. Government incentives and private investments have further accelerated the spread of plantations, despite growing concerns over their environmental and social impacts.
Economic Boon or Environmental Curse?
Supporters of oil palm industry argue that it is the most efficient crop for vegetable oil production, yielding more oil per hectare than any other alternative. Sri Lanka currently imports a significant amount of palm oil, and expanding local production is seen as a way to reduce dependence on imports and boost local industries. However, Gamage highlights the hidden costs: “Oil palm plantations deplete water sources, contribute to soil erosion, and threaten native flora and fauna. These are long-term damages that far outweigh the short-term economic benefits.”
One of the primary environmental concerns is the aggressive water consumption of oil palm, which leads to the depletion of underground aquifers. This is particularly evident in areas such as Kalu River and Kelani River wetlands, where native ecosystems are being severely affected. Additionally, soil degradation caused by extensive monoculture farming results in loss of fertility and increased vulnerability to landslides in hilly regions.
Furthermore, studies show that oil palm plantations disrupt the natural habitats of endemic species. “Unlike rubber and coconut, oil palm does not support Sri Lanka’s rich biodiversity. It alters the soil composition and prevents the regeneration of native plant species,” Gamage explains. The loss of forest cover also exacerbates human-wildlife conflicts, as displaced animals venture into human settlements in search of food and shelter.
A Threat to Indigenous Agriculture and Culture
Beyond environmental concerns, oil palm is also threatening traditional crops like kitul (Caryota urens) and palmyrah (Borassus flabellifer), both of which hold economic and cultural significance. “These native palms have sustained rural livelihoods for centuries,” says Gamage. “Their gradual replacement by oil palm could lead to economic instability for small-scale farmers.”
Kitul tapping, an age-old tradition in Sri Lanka, provides a source of income for thousands of families, particularly in rural areas. The syrup extracted from kitul is used in local cuisine and traditional medicine. Similarly, palmyrah has deep roots in Sri Lankan culture, particularly in the Northern and Eastern provinces, where its products contribute to food security and local industries.
The rise of oil palm plantations has led to the clearing of lands that once supported the traditional crops. With large-scale commercial investments driving oil palm expansion, small-scale farmers are finding it increasingly difficult to sustain their livelihoods. Gamage warns, “If we allow oil palm to replace our native palms, we risk losing not just biodiversity, but also a vital part of our cultural heritage.”
The Global Perspective: Lessons from Other Nations
Sri Lanka is not the first country to grapple with the consequences of oil palm expansion. Malaysia and Indonesia, the world’s leading producers of palm oil, have faced severe deforestation, biodiversity loss, and socio-economic conflicts due to unchecked plantation growth.
In Indonesia, for example, vast tracts of rainforest have been cleared for palm oil production, leading to habitat destruction for endangered species such as orangutans and Sumatran tigers. Additionally, indigenous communities have been displaced, sparking legal battles over land rights.
Malaysia has attempted to address some of these issues by introducing sustainability certifications, such as the Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil (MSPO) standard. However, implementation challenges remain, and deforestation continues at an alarming rate.
Sri Lanka can learn valuable lessons from these experiences. Implementing strict land-use policies, promoting agroforestry practices, and ensuring transparency in plantation expansion are crucial steps in mitigating environmental damage while supporting economic development.
The Urgent Need for Action
Despite these concerns, Sri Lanka has yet to enforce strict regulations on oil palm expansion. Gamage urges authorities to intervene: “It is imperative that we implement policies to control its spread before it is too late. The unchecked expansion of oil palm will lead to irreversible environmental damage.”
To address this issue, experts suggest a multi-pronged approach:
Stronger Land-Use Policies
– The government must enforce restrictions on oil palm cultivation in ecologically sensitive areas, such as wetlands and forest reserves.
Reforestation and Rehabilitation
– Efforts should be made to restore degraded lands by reintroducing native tree species and promoting sustainable agroforestry.
Supporting Traditional Agriculture
– Incentives should be provided to farmers growing traditional crops like kitul and palmyrah, ensuring that these industries remain viable.
Public Awareness and Education
– Raising awareness among local communities about the environmental and social impacts of oil palm can empower them to make informed decisions about land use.
Sustainable Alternatives
– Encouraging research into alternative vegetable oil sources, such as coconut oil, which has long been a staple in Sri Lankan agriculture, could reduce reliance on palm oil.
As Sri Lanka stands at a crossroads, the decisions made today will determine the country’s ecological and agricultural future. While the economic benefits of oil palm are undeniable, its long-term environmental and social costs cannot be ignored. The challenge now is to strike a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability before the damage becomes irreversible.
In conclusion Gamage said, “We must act now. If we allow oil palm to spread unchecked, future generations will bear the cost of our inaction.”
Sri Lanka has the opportunity to take a different path—one that prioritises biodiversity conservation, sustainable agriculture, and the well-being of local communities. The time for decisive action is now.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
A plea for establishing a transboundary Blue-Green Biosphere Reserve in Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay
Blue-green land and waterscapes act as ecological corridors across land and water in creating an ecological continuity in order to protect and restore the habitats of native and naturalised species.
In addition, these ecological corridors also help to conserve and improve the habitats of migratory species, as well. One of the main objectives of establishing blue-green land-waterscapes is to reconcile increasing local/regional development and human livelihood challenges in a sustainable manner while, at the same time, safeguard biodiversity and their habitats/ecosystems, as far as possible.
While green landscapes are natural and semi-natural terrestrial vegetation types like natural forests and grasslands, blue waterscapes are aquatic or semi-aquatic vegetation types such as seagrass meadows, mangroves and coastal and other wetlands. These vegetated coastal ecosystems known as ‘blue carbon’ ecosystems are some of the most productive on Earth and located at the interfaces among terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments. They provide us with essential ecosystem services, such as serving as a buffer in coastal protection from storms and erosion, spawning grounds for fish, filtering pollutants and contaminants from coastal waters thus improving coastal water quality and contributing to all important food security.
In addition, they capture and store “blue” carbon from the atmosphere and oceans at significantly higher rates per unit area than tropical forests (Figure 1) and hence act as effective carbon sinks. By storing carbon, these ecosystems help to reduce the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, thus contributing significantly to mitigate the effects of climate change.

Figure 1: Carbon storage in different vegetation types (Source – What Is Blue Carbon and Why Does It Matter? – Sustainable Travel International)
.Blue-green Carbon Markets
The recognition of blue carbon (BC) ecosystems (primarily mangroves, seagrasses and tidal marshes) as an effective natural climate solution paved the way for their inclusion within carbon markets. Blue carbon is the marine analog of green carbon, which refers to carbon captured by terrestrial (i.e., land-based) plants. The blue-green carbon market involves buying and selling carbon credits from projects that protect and restore coastal and marine ecosystems (blue carbon) and terrestrial ecosystems (green carbon). Since Blue Carbon ecosystems have higher carbon sequestration (capture and store) potential compared to their terrestrial counterparts, blue Carbon credits are worth over two times more than green carbon credits. They offer opportunities for commercial enterprises to offset carbon emissions and in turn support climate action.
Blue Carbon projects are expected to grow twofold in the near future. With the recent surge in international partnerships and funding, there is immense growth potential for the blue carbon market. However, it is critically important to look beyond the value of the carbon sequestered to ensure the rights and needs of local communities that are central to any attempt to mitigate climate change using a blue and green carbon project.
Blue Carbon projects can serve as grassroot hubs for sustainable development by developing nature-based solutions in these ecosystems thus contributing to both climate change mitigation and adaptation. Globally, numerous policies, coastal management strategies, and tools designed for conserving and restoring coastal ecosystems have been developed and implemented. Policies and finance mechanisms being developed for climate change mitigation may offer an additional route for effective coastal management. The International Blue Carbon Initiative, for example, is a coordinated, global program focused on conserving and restoring coastal ecosystems for the climate, biodiversity and human wellbeing.
Until recently, most of these opportunities focus on carbon found in the above ground vegetative biomass and do not account for the carbon in the soil. On the other hand, blue carbon, in particular has the potential for immense growth in carbon capture economics in the near future and can provide significant socioeconomic and environmental benefits. Consequently, blue -green carbon habitats in the Gulf of Mannar – Palk Bay region represent invaluable assets in climate change mitigation and coastal ecosystem conservation and sustainable development.
Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay Trans-boundary Region
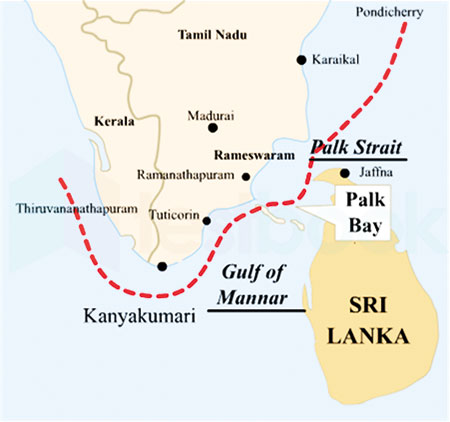
The Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay region form a transboundary area within the waters of southeastern India and northwestern Sri Lanka. This region supports dense seagrass meadows having a high level of marine biodiversity including marine mammals such as dugong. Sea turtles are frequent visitors to the gulf while sharks, dolphins, sperm and baleen whales too, have been reported from this area. The Mannar region is recognized as an Important Marine Mammal Area (IMMA) of the world by IUCN (Figure 2) and also an Important Bird Area by Birdlife International. This region as a whole is a store house of unique biological wealth of global significance and as such is considered as one of the world’s richest regions from a marine biodiversity perspective.
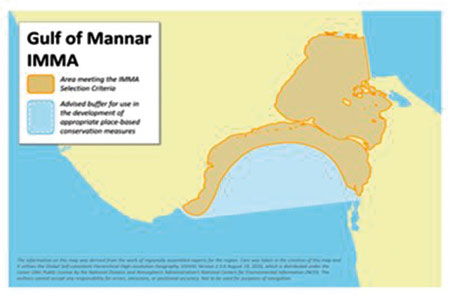
Figure 2. Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay IMMA (Source – IUCN Joint SSC/WCPA Marine Mammal Protected Areas Task Force, 2022 IUCN-MMPATF (2022)
Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve – India
India has already declared a part of this region as the UNESCO Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve covering an area of 10,500 km2 of ocean with 21 islands and the adjoining coastline. The islets and coastal buffer zone include beaches, estuaries, and tropical dry broadleaf forests, while the surrounding seascape of the Marine National Park (established in 1986) and a 10 km strip of the coastal landscape that include seaweed communities, seagrass communities, coral reefs, salt marshes and mangrove forests form the coastal and marine component of the biosphere reserve on the Indian side of the Gulf of Mannar.
Sri Lankan ‘Proposed’ Biosphere Reserve
On the Sri Lankan side of the Palk Bay there is a semi-enclosed shallow water body between the southeast coast of India and Sri Lanka, with a water depth maximum of 13 m. To the south, a chain of low islands and reefs known as Adam’s Bridge or Rama Setu (Rama’s Bridge), separates Palk Bay from the Gulf of Mannar. The Palk Bay leads to Palk Strait (Figure 3). Palk Bay is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar. Sediments discharged by rivers and transported by the surf currents as littoral drift settle in this sink.
On the Sri Lankan side of the Palk Bay, studies are being conducted by the Dugong and Seagrass Conservation Project to establish an additional 10,000 hectares of Marine Protected Area to support the conservation of dugongs and their seagrass habitat in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay. This project will involve the preparation of a multiple-community-based management plan in conjunction with government, fishing communities and the tourism industry.
With this valuable information emerging from projects of this nature, Sri Lanka has real opportunities to create a large marine protected area in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay region and eventually merging them together with the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve of India to form a trans-boundary biosphere Reserve.
Terrestrial cum Marine Spatial Plan for the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay Region
Therefore, an excellent opportunity awaits both the Governments of Sri Lanka and India to collaborate in preparing of a terrestrial and marine spatial plan for this region, a prerequisite before going further on designing and implementing large scale development plans in establishing wind energy farms, mineral sand extraction, fishing industry, oil exploration and tourism development.
Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning (CMSP) is an integrated, place-based approach for allocating coastal and marine resources and space, while protecting the ecosystems that provide these vital resources.
On the Indian side, the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere reserve is well established and functional. On the Sri Lankan side, already there are three DWLC managed protected areas i) Adam’s Bridge Marine National Park (# 29 in the map – 18,990 ha declared in 2015), ii) Vedithalathiv Nature Reserve (# 35 -29,180 ha declared in 2016) and iii) Vankalai Sanctuary ( # 97 -4839 ha declared in 2008) (Figure 4) which can serve as the core zone of the Sri Lankan counterpart of a trans-boundary biosphere reserve. Due to the integrated nature of shallow wetland and terrestrial coastal habitats, Vankalai Sanctuary, in particular is highly productive, supporting high ecosystem and species diversity.
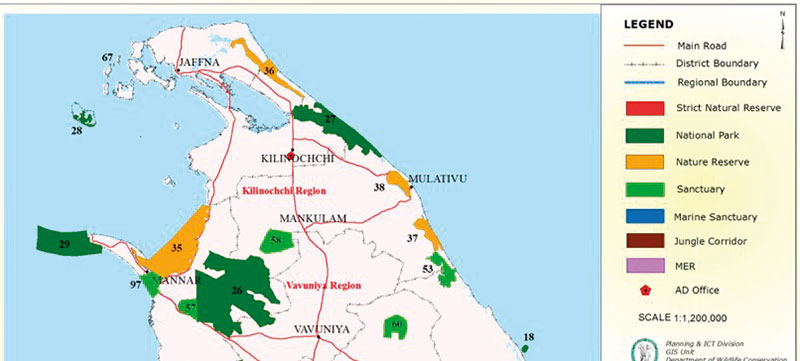
Figure 4: Protected Areas in Norther Sri Lanka Managed by the Department of Wildlife Conservation Source: DWLC
This site provides excellent feeding and living habitats for a large number of water bird species, including annual migrants, which also use this area on arrival and during their exit from Sri Lanka.
Having several coastal and marine protected areas already within the Sri Lankan territory provide an excellent opportunity to establish the Gulf of Mannar – Palk Bay blue-green Biosphere Reserve (Sri Lanka) initially and eventually to join up seamlessly with the already established Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve on the Indian side to create a trans-boundary blue-green biosphere reserve.
This makes perfect sense because unlike sedentary plant species, mobile animal and plant groups (phytoplankton, in particular) do not respect human demarcated territorial boundaries. The provision of a common and unhindered protected coastal and marine passage for their customary movement for food and raising young is therefore of crucial importance in conservation management. Scientific evidence-based selection of additional areas, if necessary and their respective boundaries are best be determined in consultation with expert groups on marine mammals and reptiles, birds, fish, coastal vegetation conservation, sociology and industrial development from both sides of the divide.
Proper spatial planning needs to be done before large-scale development plans are designed and implemented in order to avoid conflicts of interest leading to inordinate delays and teething problems in project initiation. As a priority, the protected blue-green core and buffer regions need to be demarcated for their conservation. This could best be done in this narrow passage of land and water between Sri Lanka and India
( Palk Strait & Gulf of Mannar) by preparing a marine and terrestrial spatial plan along the UNESCO Man and Biosphere conceptual guidelines differentiating core, buffer and transition zones. While the protected areas in the core and buffer zone provide all important ecosystem services that would also serve as breeding ground for fish, crustaceans, marine reptiles, birds and mammals thereby provisioning sustainable industries to be developed in the surrounding transition areas demarcated in the joint spatial plan.
In addition, the Satoyama Global Initiative established by the Japanese at UNESCO as a global effort in 2009 to realise ‘societies in harmony with nature’ in which – Satoumi – specifically referring to the management of socio-ecological production landscapes in marine and coastal regions, is also a good model to be considered for conservation of biodiversity and co-existence between humans and nature.
Final Plea
In order to take this proposal forward from the Sri Lankan side, a number of useful baseline reports are already available including, but not limited to, the following: i. Biodiversity Profile of the Mannar District (CEJ & USAID 2022), ii. The Gulf of Mannar and its surroundings (IUCN 2012), iii) Atlas of Mangroves, Salt Marshes and Sand Dunes of the Coastal Area from Malwathu Oya to Pooneryn in the Northwestern Coastal Region, Sri Lanka (Ecological Association of Sri Lanka, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2020). iv. Integrated Strategic Environment Assessment of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka (CEA 2014).
If this proposal to establish a Trans-boundary Blue-Green Biosphere Reserve in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay is acceptable in principle to the Governments of Sri Lanka and India, it would be ideal if the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program UNESCO which is an intergovernmental scientific program whose mission is to establish a scientific basis for enhancing the relationship between people and their environments to partner with the relevant Government and non-governmental agencies in both countries in making it a reality. This proposed concept has all the necessary elements for developing a unique sustainable conservation cum industrial development strategy via nature-based solutions while at the same time contributing to both climate change mitigation and adaptation.
by Emeritus Professor Nimal Gunatilleke,
University of Peradeniya
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoSri Lanka’s eternal search for the elusive all-rounder
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoBid to include genocide allegation against Sri Lanka in Canada’s school curriculum thwarted
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoGnanasara Thera urged to reveal masterminds behind Easter Sunday terror attacks
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoTo play or not to play is Richmond’s decision
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoComBank crowned Global Finance Best SME Bank in Sri Lanka for 3rd successive year
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoSanctions by The Unpunished
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMore parliamentary giants I was privileged to know
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoIPL 2025: Rookies Ashwani and Rickelton lead Mumbai Indians to first win