Features
Defence and Diplomacy are linked

Dr Sarala Fernando
Defence expenditure has not been a subject of public discussion in Sri Lanka, which was understandable during the difficult years of the armed conflict. Even after the armed conflict ended , there was no public opposition to the continued dedication of a major share of budgetary resources to the Defence Ministry to spearhead the reconstruction and rehabilitation of the conflict- affected areas in the North and East.
Since that time, the Army has provided leadership in a number of areas of interest to the UN. For example, the de-mining programe clearing thousands of acres for the safe return of civilians, has created positive publicity for Sri Lanka and enabled the signing of related international agreements, all contributing to building the image of a responsible military on international fora.
Since deploying its first contingent in 1958, official press releases remind that Sri Lanka has been contributing to UN Peacekeeping operations in some of its most hostile and demanding deployments, and has 557 including female officers currently in service toward ensuring international peace and security. Our authorities should also revive the initiative to collect illegal small arms and light weapons island-wide under the UN SALW (Small Arms and Light Weapons) programme. This will address concerns over rising gun crime and discourage new domestic gun manufacturing.
Since the end of the armed conflict, Sri Lankans have waited patiently over a decade now for the peace dividend in the hope that it would enable more robust social expenditure. Now that Sri Lanka has declared bankruptcy and opted to go to that “lender of last resort”, several articles are appearing commenting on down sizing of the military, re-balancing the three forces in view of current and emerging threats etc, based on some expectation that limits would be imposed on defence expenditure under the IMF programme.
In such a historical context and given the experience and assets within the security forces, it is to be expected that any strategic planning for “right sizing” the defence budget, would be undertaken in-house within the security forces. This article suggests that the Foreign Ministry with its research and training arms, the Lakshman Kadirgarmar Institute (LKI) and the Bandaranaike International Diplomatic Training Institute (BIDTI) should also be involved in these discussions. Any re-shaping of defence strategy would benefit from the perspectives of diplomacy especially in relation to developments in the wider world, some of which are mentioned in this article.
From the initial public statements by the Defence Ministry it seems the emphasis has been on troop reduction. The Deputy Minister of Defence announced recently that the Ministry planned to reduce the number of soldiers from the current strength of 200,783 to 135,000 by 2024. Is this to be achieved through creation of a reserve as some academics have suggested? The Air Force has just announced a strength reduction from 35,000 to 27,000 including a policy to increase its female share to 30%.
However, in this exercise, to avoid confusion, public diplomacy would call for the holding back of all media advertisements for new recruitment to the armed forces. There are lessons to be learned also from elsewhere: the recent initiative to reduce the public service through a scheme to grant five years no-pay leave abroad, has predictably led to the departure of the most talented and capable, leaving Ministries in a quandary to retrain those remaining behind who are demoralized, compounding human resources management problems. It is also worth noting that Sri Lanka is reducing its trained forces at a time when some developed countries are facing recruitment problems to their forces and offering many incentives even to foreign nationals.
Our Deputy Minister of Defence also referred to a “strategic blueprint” aiming to produce “a technically and tactically sound and well-balanced defense force by the year 2030 in order to meet upcoming security challenges”. Such a strategic plan would be a new and welcome development however the question remains how other Ministries, concerned institutions and a public consultation would be factored into the in-house deliberations.
Any such strategic planning should take into account that Sri Lanka is probably unique in that it is recognized internationally as particularly vulnerable for a country of our size and geography, being exposed to both man-made and natural disasters. This calls for any national security strategy to take a two prong approach. With regard to conflict prevention, having faced two youth insurrections which had to be put down by lethal force, one cannot over emphasize the importance of strengthening human intelligence gathering and early warning.
This task is never easy due to the difficulty of coordinating intelligence agencies with differing mandates, as even the United States learned after 9/11. Recent arrests in Tamil Nadu of persons charged with attempting to revive the LTTE insurgency confirmed the need for continued vigilance on the arms and drug smuggling networks which we had thought had been dismantled after the end of the armed conflict. As an island nation with a huge expanse of coastal territory to monitor, the armed forces need to integrate air, sea and land operations for maritime protection and seizure of arms, ammunition, explosives and detonators and a never ending flow of drugs.
Early warning is even more problematic with regard to natural disasters as major climate events like earthquakes seemingly defy prediction. Research is still emerging on the impact of a war like in Ukraine on the climate crisis. However, even to amateur eyes, the dropping of thousands of missiles, bombs and artillery shells on the ground and exploding in the air, virtually on a daily basis, must not only pollute but also impact the fragile surrounding geology. In neighbouring Turkey, two major earthquakes of 7.8 and 7.5 magnitude occurred on February 6 this year followed by a series of aftershocks.
All the way down the seismic line in Asia, even as far as Fiji region on June 10 (5.9 magnitude) significant earthquakes are occurring since the tragedy in Turkey. Indian scientists have been predicting a major earthquake in India and had also issued a warning to Sri Lanka before the current string of tremors began to be experienced here in May/ June along the southern coast and as far as Gampola in the central hills.
In this background, the recent visit to Sri Lanka by the Executive Secretary of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) assumes significance when Sri Lanka on June 6 announced the successful completion of its domestic ratification process for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) , with grant of Cabinet approval. The CTBT was signed by Sri Lanka on October 24, 1996 but ratification was stalled for many years due to political pressures. Under the Treaty´s global verification regime, a network of 321 monitoring stations were to be set up – spanning some 90 countries – able to record shock waves generated by possible nuclear explosions and other sources in the atmosphere, under water or underground. The network includes 50 primary and 120 auxiliary seismic stations whose data can be used to help distinguish between possible nuclear explosions and the many thousands of earth tremors registered annually.
Sri Lanka signed a Facility Agreement with the CTBTO in June 2000 which led the way for the establishment of an auxiliary seismological station in Pallekelle, Kandy, as part of the International Monitoring System (IMS) to verify compliance with the CTBT. Hardly any public information is available on the current status of this Kandy station and whether it is operational, although any data collected would be valuable both in the context of the earth tremors Sri Lanka is experiencing recently and in the wider context of a possible nuclear radiation threat arising out of the war in Ukraine. Interestingly the Sri Lanka Air Force has been training in the last months for handling a chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear explosives emergency under international technical assistance from the IAEA (International Atomis Energy Authority).
The significance of the CTBTO ratification is dwelt on here to meet public skepticism over Sri Lanka’s diplomatic forays into the worlds of disarmament and elimination of all forms of weapons of mass destruction. Engaging in multilateral diplomacy, foreign diplomats would often ask their Sri Lankan counterparts why Sri Lanka was so interested in the two extremes of the world, the sea bed and outer space. However, there was always a basis in national interest. The close involvement of Sri Lankan diplomats in the Law of the Sea negotiations under UN auspices eventually led to its taking into account of Sri Lanka’s position as a developing state, as also the peculiarities of her continental shelf in the southern part of the Bay of Bengal whereby under the special method of delimitation Sri Lanka will be able to claim parts of the seabed well beyond the 350 miles cut off point provided under the general provisions.
As for outer space, Arthur Clarke, the scientist-writer residing in Sri Lanka, was instrumental in drawing Sri Lanka’s attention many years ago to the advent of Artificial Intelligence as well as the many benefits of outer space and the need to keep space peaceful. Since those early days, Sri Lanka has been in the forefront of efforts to prevent an arms race in outer space, underlining the increasing importance of satellites for communications and many peaceful uses of remote sensing as well as addressing the global threat posed by space debris.
Today United Nations as agreed by member states has set a target of achieving by 2030, 17 goals for sustainable development and human security ,including poverty alleviation, quality education, good health, clean water, clean energy, decent work, industry innovation, reduced inequality, sustainable cities, responsible consumption and production, encompassing both life on land and under water, together with climate action. Taking into consideration the international classification of Sri Lanka as a country particularly vulnerable to both conflict and natural disasters, this article suggests that Sri Lanka in the present economic crisis, take a step back from “rapid economic growth” models which all too often deplete its natural resources including water, forests, stone, gravel and sand, and instead focus on careful management of its natural wealth, ecosystems and biodiversity.
Judging by press articles, the navy is already working in cooperation with the private sector and other organizations as well as with the general public, in several areas such as marine and coastal protection, installing reverse osmosis plants etc. The army is best known for its outreach work in agriculture and food production, hospital and university education, however these initiatives have not gained full recognition due to resentment of local farmers and market contradictions in the field and resistance from faculty and students in the formal education and health sectors.
A more feasible possibility lies in building upon the strengths in logistics and engineering Sri Lanka’s military had developed during the armed conflict. Are there innovations here which may be commercialized or taken up in public-private partnerships contributing to import substitution and domestic savings? The army engineers work on solving practical problems and have succeeded in tackling issues like the flooding of Nuwara Eliya town by tracing the flow of water, unblocking the obstacles and constructing the required drainage channels.
They should be given an opportunity to work on the perennial flooding affecting towns in Galle, Matara and Ratnapura in low cost projects at a time when the era of grand hydraulic construction led by the Irrigation Department seems to be coming to an end. Uma Oya with its delays and cost-overruns may probably be the last such project due to the scale of public protests since the tunneling apparently had caused all the wells in the neighbouring areas to run dry.
The strengths of the armed forces come into public view mainly in a time of emergency when the armed forces form the first line of rescue. Yet other countries have already placed critical infrastructure like reservoirs under military management and control, viz. the United States Army Corps of Engineers which operates and maintains the safety of dams across a huge expanse of territory. Elsewhere, foreign militaries have even been engaged in the management of local parks i.e. by training local rangers in African countries to control poaching and educate communities to protect their wild life treasure. Can our defence research and training institutes (Buttala for example is strategically located in the proximity of two major parks Udawalawe and Yala) partner with the wildlife authorities and contribute to mitigating the human-elephant conflict?
From Kavan to Muthuraja, Sri Lanka’s international image has been reeling on huge publicity over the abuse and neglect of domestic elephants. The latest incident made international news headlines when that majestic tusker Muthuraja once gifted to Sri Lanka was airlifted by the Thai government back to Thailand for medical treatment. In Thailand , elephants with special characteristics are considered as national treasure by the Thai Royal family and cared for in the palace grounds by the Thai armed forces. Instead of just conveying official apologies to the Thai government, should not our Prime Minister have asked the Thai government for assistance to train our mahouts and an exchange programme for our vets to learn from the elephant hospital and sanctuary in Thailand and help bring the care of all domestic elephants under some systematic care?
The Sri Lankan armed forces dispose of many research and training institutions scattered around the country. Some thought should be given to better coordination and managing of these resources in the national interest. For example the proposed national Climate Change University could be conceptualized not as an independent institute but positioned as a central lynchpin within the network of defence research and training institutes. Sri Lanka is in fact very good at setting up research and training institutes in every field, the problem come with implementing research findings and giving employment to trained students, which means this valuable human capital ends up going overseas to help other countries instead of contributing to the national good.
In time, many of these R&D institutions find it difficult to maintain large buildings and staff, which is a problem not unique to Sri Lanka. It is worth recalling that the UN at its inception was intended to have all its affiliates in one centre in New York in order to share administrative costs but subsequently various powerful individuals worked with their national authorities to take away the specialized agencies like FAO to Rome, ILO to Geneva etc
(Sarala Fernando, retired from the Foreign Ministry as Additional Secretary. Her last Ambassadorial appointment was as Permanent Representative to the UN and International Organizations in Geneva . Her Ph.D was on India-Sri Lanka relations and she writes now on foreign policy, public diplomacy and protection of heritage).
Features
Trump’s Delinquent War Game: No Early End in Sight

It is fruitless analyzing US President Trump’s reasons for going to war with Iran or the conflicting outcomes he says he is looking to have in the end. It is quite possible that he may have made the decision to attack Iran after being cajoled by Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. It is a good time to attack because Iran is at its weakest moment yet posing an imminent threat warranting a pre-emptive attack. Strange and circular reasoning is needed to justify unnecessary wars.
True to form, Trump did not consult any of his western allies the way his predecessors did in similar situations. He ignored NATO as much as he ignored the UN. Nor did Trump go through the internally established broad consultation and focused decision making processes that US presidents usually undertake before committing American forces abroad. The Congress, the institution under Article I of the American Constitution, was also habitually ignored .
It is likely that Trump secured tacit support from other Middle East governments, especially the Gulf states of Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, UAE and Oman that are Iran’s neighbours. The latter may seem to have been hoping to have it both ways – letting US and Israel take out Iran’s reprehensible regime while appearing to stay neutral in the fight. That calculation or miscalculation explosively backfired when Iran started firing drones and missiles not only into Israel but practically into every Arabian (Persian) Gulf country, hitting not only American bases but also civilian centres. The welcoming reputation of the Gulf countries as secure oases for foreign investment, tourism, sports and entertainment has been seriously shattered.
Escalating War
In addition to the six Gulf states, Iranian missiles have reached Iraq, Jordan and far away Cyprus. Even Turkey and Azerbaijan have been targeted. Israel has been hit and has suffered casualties far more in the few days of fighting than it has in all the past aerial skirmishes. The US outposts are under attack as well. The Embassy in Kuwait was hit on Monday. The next day two drones fell on the US Embassy in Riyad, Saudi Arbia, apparently the most fortified American outpost abroad. This was followed by drone attacks on the US Consulate in Dubai and on the American military base in Qatar, the largest in the region. Six American servicemen have been killed and 18 injured in the first four days of the war.
The Trump Administration that has been notorious for picking countries to deny US visas, is now asking Americans to return home from 14 Middle East countries for the sake of their own safety. Washington has closed its embassies in Riyadh and in Kuwait and has ordered non-emergency staff and families to depart from its other embassies in the region. But leaving the embattled region is not easy with flights cancelled and air space closed. Belatedly, the State Department is scrambling to make arrangements to help stranded Americans find their way out by air or by land to neighbouring countries. It is the same story with governments of other countries whose citizens are living and working in large numbers in the Middle East. The monarchs of Middle East depend on migrants of many hues to do their blue collar and white collar labour while keeping their citizens in cocoons of comfort. That equilibrium is now under threat.
Iran’s losses are of course significantly higher, already hit by over 2,000 Israeli and US missiles reaching multiple targets in 26 of Iran’s 31 provinces. Over a thousand people have been killed including 180 students in a girls’ school in the south. Buildings and infrastructure and installations are being devastated. Israel has opened a full second front in Lebanon using the thoughtless Hezbollah’s aerial provocation as excuse for once again badgering Beirut and its suburbs. A week into the war there is no early end in sight. Only escalation.
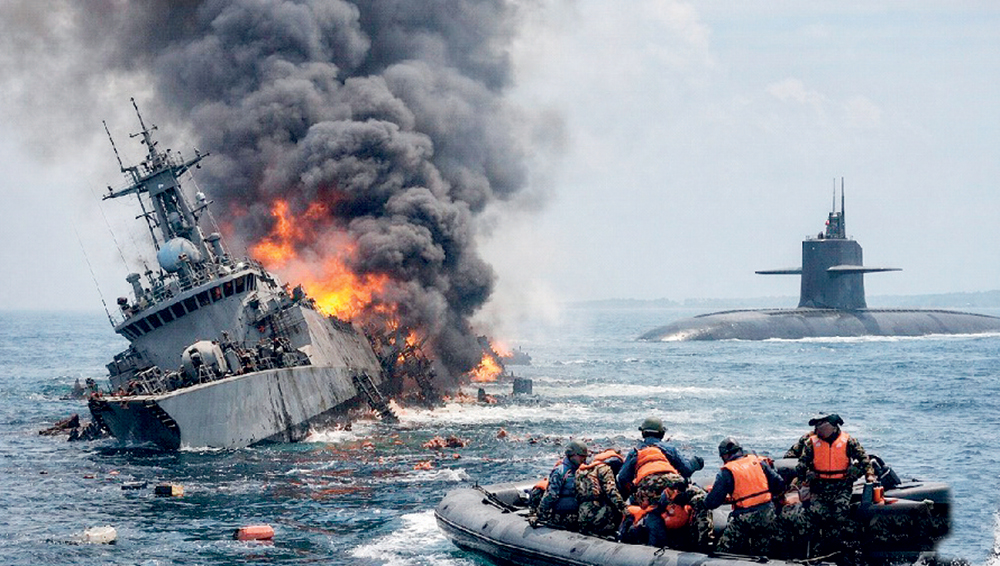
Not only Iran but even the US is extending the waves of war. A US submarine torpedoed without warning and sank the IRIS Dena, a Moudge-class Iranian frigate, in the Indian Ocean not far from Galle. The frigate had about 130 sailors on board and was sailing home after participating in the International Fleet Review (IFR) and multilateral exercise, MILAN-2026, organized by the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam. The frigate was reportedly not carrying weapons in keeping with the protocol for international naval exercises. Also, according to reports, Americans were in the know of the Fleet Review in India and its participants. Yet the US Secretary of War, Pete Hegseth, went on public television to say: “An American submarine sunk an Iranian warship that thought it was safe in international waters,. Instead, it was sunk by a torpedo. Quiet death.” How tragically surreal!
It fell to little Sri Lanka to respond to the distress call of the sinking sailors. Sri Lanka’s navy and emergency services have done an admirable job in fulfilling their humanitarian responsibilities. The Sri Lankan government has also handled a difficult situation, complicated by a second Iranian ship, with poise and purpose. On the other hand, unless I missed it, I have not seen any official reaction by the Indian government to the reckless sinking of one of its guest ships. An opposition parliamentarian of the Congress Party, Pawan Khera, has been cited as asking on X, “Does India have no influence left in its own neighbourhood? Or has that space also been quietly ceded to Washington and Tel Aviv?”
India is not the only one that has ceded space and time to the bullying whims of Donald Trump. With the exception of Spain, the entire West is literally genuflecting for fear of getting hit by tariffs. Notwithstanding the US Supreme Court ruling much of Trump’s tariffs to be illegal, and a Federal Court now ordering that the collected monies should be paid back to those who had paid them. The situation is a far cry from the European reaction and the public lampooning of Bush and Blair when they went to war in Iraq two decades ago.
The Missile Math
Two factors may objectively determine the course and the duration of Trump’s war: weapons stockpiles and the oil and natural gas markets. Higher prices of oil and natural gas will increase domestic pressure on Washington to find an offramp to the war sooner than later. Other countries may have to suffer not only higher prices but also shortages of fuel. The weapons are a different matter.
The ongoing aerial warfare involves the use of drones and missiles to attack as well using defensive missiles to detect and destroy incoming projectiles before they hit their targets. After the beating it took last year and this week, Iran has no missile defense system to speak of, but it has both a stockpile of drones and missiles and capacity for rapidly producing them. The military question is whether Iran’s stockpile of offensive drones and missiles can outlast the combined defensive missile stockpile of the US, Israel and the Middle Eastern countries. There is no clear answer, only speculations about Iran and US concerns over its own stockpile.
The “troubling missile math,” as it has been called is underscored by the concern expressed by US Secretary of State Marco Rubio, that Iran has the capacity for “producing, by some estimates, over 100 of these missiles a month. Compare that to the six or seven interceptors that can be built a month.” The worry is also about the depleting impact that the extended use of interceptors against Iran will have on American stockpiles elsewhere in the world, especially in areas involving China. That is part of the standard military calculation. What is bizarre now is that after starting the war on a whim last Saturday, Trump is convening a meeting within a week on Friday with weapon manufacturers to urge them to produce more.
Secretary Rubio also added that destroying Iran’s missile capacity is the goal of the US campaign. Iran’s missile capacity involves different missiles with different flight ranges. The shorter the range the larger the stock. Iran does not have the standard two-way intercontinental ballistic missile, and it is nowhere near developing them. The current Administration has recklessly claimed that Iran is capable of launching missiles to hit America and has unfairly named and blamed all previous presidents for not doing anything about it.
Trump’s predecessors were fully aware of America’s unmatched military superiority and Iran’s utter limitations. They were also aware that going to war with Iran to destroy its drones and limited range missiles will create more problems without solving any. The Obama Administration in consort with China, UK, France, Germany and Russia produced the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) committing Iran to have nuclear programs for peaceful uses only. Trump tore up the Obama plan and instead of using the opportunity this year to create a new and stronger program, chose to start a war instead.
As things are, unless the US-Israel axis succeeds in literally obliterating all drones and missile production resources in Iran, Iran will retain the capacity to produce drones and short-range missiles with which it could torment its neighbours for long after Trump and Netanyahu declare the war to be over. It may never be a long-range menace – in fact, it never was – but it could become an even greater short-range nuisance.
The US is no longer indicating a time limit for the war to end. For Netanyahu, it is not going to be an endless war. Of the two, Israel might be having some clear objectives to be achieved before ending the war. For Trump and his Administration, on the other hand, the objectives of the war are chaotically evolving on a daily basis, and the world will have to wait till the man of the deal finds some outcome or outcomes that can be shown as success and call it quits.
Regime Change: Insult after Injury
Iran’s Supreme Leader and forty or so other top Iranian leaders were taken out in the first minute of the fight by “pinpoint bombing”, as Trump boasted in his auto-poetic truth social post. But the Iranian regime has not collapsed. It has shown remarkable structure and durability despite the death of its Supreme Leader. It is America that is showing its inability to contain its Supreme Leader from going berserk on the world through tariff and bombing terror – in spite of all the checks and balances that Americans thought they have constitutionally practised and honed over 250 years. It is also poetic comeuppance for the Iranian regime that, after 47 years, it should now face its undoing by an unhinged American hegemon for theocratically subverting the 1979 revolution from realizing any of its secular possibilities.
Trump now wants to add insult to injury by forcing himself into the succession process for selecting a successor to Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran has a well-established succession process, almost akin to the conclave in the Vatican, in which a body of 88 elder clerics, the Assembly of Experts, are convened to elect through a secret vote the new Supreme Leader. Over the last few days, it has been widely reported that the late Khamenei’s 56 year old son Mojtaba Khamenei has emerged as the leading candidate to succeed his father as the next Supreme Leader. His political strength and leadership claim are reportedly based on his close connections to the powerful Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
Mojtaba is said to have been the shadow Supreme Leader in recent years making decisions in place of his ageing father. For that reason, he is reviled by Iranians who are opposed to the regime and who have been oppressed by the regime. There are also allegations and rumours about his amassing wealth and investing in properties and opening bank accounts in London and Geneva. At the same time, there could also be sympathy for him in the ruling circles because it was not only his father and his mother who were killed in the first minute bombing but also his wife and his son. While ideologically he has been a hawk, Mojtaba is also described as a “pragmatist.” Being pragmatic in the current context, according an unnamed Tehran academic, would imply that Mojtaba Khamenei will be seeking revenge for the US-Israeli attacks on his family and his country – not through victory in war but by ensuring “the survival of the Islamic Republic.”
President Trump is not bothered about the dynamics and nuances of Iranian leadership politics and has no hesitation in inserting himself into the succession process. In an interview with the American news website Axios, Trump has declared that he wants to be personally involved in the Iranian succession process, and that the selection of the younger Khamenei would be “unacceptable” to him, because “Khamenei’s son is a lightweight.” “I have to be involved in the appointment, like with Delcy [Rodríguez] in Venezuela,” Trump went on, because “we want someone that will bring harmony and peace to Iran.”
Comparing Venezuela and Iran is no less preposterous than the Bush Administration’s decision to invade Iraq in addition to Afghanistan in order to punish Al Quaeda for 9/11. Trump now appears to be seeking not a wholesale regime change but a retail leadership change in the old regime. This is only the latest addition to his lengthening wish list for the war with no method or plan to achieve any of them. Add to the growing list the news that the CIA is putting together a Kurdish insurgent force to foment “a popular uprising” within Iran.
That would be back to the future and the return of the CIA, but in a totally different situation from what it was 73 years ago when the CIA, in partnership with Britain’s MI6, staged the 1953 coup that ousted the government of then Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh and reinforced the monarchical rule of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, the Shah of Iran. The purported plan now is to arm and organize Kurdish forces in Iran and Iraq to engage the Iranian security forces and thereby to create internal spaces for Iranian civilians to come out to the streets and take over their country. Those who are entertaining this plan are also aware of its inherent dangers and cross-border and pan-ethnic implications for Iraq and even Turkey and Syria. Trump is reportedly aware of the plan but may not be bothered about its unintended consequences.
by Rajan Philips
Features
How Helmut Kohl braved the tsunami, P-TOMs and Kadirgamar assassination

This is the place to introduce the episode of ex-Chancellor Helmut Kohl of Germany. “This legendary unifier of post war Germany was at a small hotel in Hikkaduwa undergoing Ayurveda treatment when the Tsunami struck. A German Minister who owned a house in Hikkaduwa and visited Lanka regularly had recommended Ayurveda treatment to The Chancellor and head of her party- the Christian Democrats.
The German Embassy was at its wits end because Kohl had disappeared without a trace. They contacted us and we activated our Grama Sevaka network to find that Kohl had been taken to the safety of his home by a hotel employee. When we offered to send a helicopter to bring him to Colombo the Chancellor had replied that it was not necessary as he was well looked after by his host. He came by car the following day in order to thank CBK for her help.
I went to President’s House with Kohl who seemed quite relaxed in his coloured shirt, crumpled pants, a grey seersucker coat and rough boots. He was full of praise for the Sri Lankan people who had helped him and all the tourists in distress due to the Tsunami. Kohl said that he wanted to help in the rehabilitation of the south in his personal capacity. When he got back to Germany he set up a group of rich friends called “Friends of Helmut Kohl” who sent money to build a hospital in Mahamodera, Galle.
The money was lodged in the German Embassy. But the usually lethargic Health department dragged its feet on the construction work on the guise that the money was not sufficient for their grandiose hospital plans ignoring the value of the superb gesture by Kohl. Unfortunately he died before the completion of the project and therefore could not keep his pledge to come to Galle for its opening.
Later in time I was a member of a Parliamentary delegation led by Speaker Karu Jayasuriya which included Sampanthan, Rauf Hakeem, Anura Dissanayake and several others. I suggested to our group that we pay a belated tribute to Helmut Kohl who had died a few months previously. This was immediately welcomed by the parliamentarians and the organizers of the tour and we jointly paid our heartfelt tribute to a great friend of Sri Lanka who was an eye witness to the success of our rehabilitation effort.
Post Tsunami Operational Management Structure (P-TOMS)
The Tsunami was particularly harsh on the eastern and northern coastline because it was directly in the way of the giant waves created in Indonesia and deflected to our shores. It also created a transformation of the political scene and the nature of the war. The LTTE had invested considerable resources in building up its “Sea Tigers”. They wanted control of the northern seas in order to increase their supply of weapons and ammunition. The Sea Tigers established a presence in east Thailand so that arms could be purchased from Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand. The fighting in the Indo-China theatre was over and the cut rate weapons market was flourishing.
Our embassy in Bangkok had an army officer who was monitoring terrorist activities but he was helpless because Thai officials in the lower echelons were in the pay of the LTTE. In addition to that problem, the mediocre officials of our Foreign Ministry were no match for the determined LTTEers one of whom had married an influential Thai lady. With money coming in from expatriates they had even set up a shipping line which was so well run that they could finance weapons buying for the LTTE with its profits.
We had received intelligence that the LTTE was preparing for a major “Sea Tiger” operation from their base in Mullaitivu. This base area concept shows the advanced thinking of the LTTE which was attempting – then unsuccessfully – to even manufacture a low cost submarine. Fortunately for us the Tsunami wiped out the base of the “Sea Tigers” together with many of their assets such as boats, proto-type submarines and diving gear.
True to form they sent signals for talks which they had earlier broken. Their diaspora had mounted a campaign to collect funds for rehabilitation. At this stage the UN got into the act and with the World Bank and IMF persuaded the CBK government to consider a power sharing arrangement principally for the rehabilitation of the North and East. It was to be called P-TOMS. CBK appointed Jayantha Dhanapala as the head of SCOPP – a secretariat to coordinate the relief effort in the North and East. The World Bank appointed Peter Harrold, its representative in Colombo, to coordinate the P-TOMS effort with SCOPP.
Estimates were made by SCOPP regarding the amount necessary for the rehabilitation of the North and East. This budget became the talking point of several successive regimes who promised to allocate such funds in exchange for Tamil votes in the North. Mahinda Rajapaksa’s agents held this figure as a bait to promote a boycott of the Presidential poll in 2005 which threw the election which was in Ranil’s pocket to MR thereby changing the destiny of the LTTE as well of the country. [MR cleared the 50 percent hurdle by only 25,000 votes].
Perhaps to strengthen the push for P-TOMS, Kofi Annan the Secretary General of the UN arrived with a large contingent of staffers and I was asked to meet and greet him in Katunayake. We gave Annan a grand welcome but he seemed distracted and was only interested in getting his Swedish wife who was hanging back, into the spotlight. CBK had several discussions with him but we ran into a snag in that he wanted to visit the North and meet Prabhakaran.
Perhaps some of the big powers had got to him as he was in the midst of a scandal about his son from his first marriage who was facing charges of corruption. The scandal was rocking UN headquarters. Annan who was elevated from his earlier status as a UN functionary to satisfy African members, was according to several biographers, indebted to the west and could not end his tenure to the satisfaction of the majority of the UN membership.
CBK, already under pressure for mishandling the P-TOMS campaign, was adamant that Annan should not meet the LTTE which would have given the terrorists parity of status with the SL state. Since such an interpretation was circulated by virtually all political parties in the South she was pushed to a very difficult position. After much discussion Annan settled for a helicopter tour of the North. I found that he was a weak leader who was led by his nose by Mark Mallock Brown – his chief of staff, who had been in charge of UN operations even during its disastrous forays in the Congo.
Mallock Brown was later identified as a camp follower of the West who compromised the credibility of the UN. I have memories of Mallock Brown holding forth on their next step here while Annan and Dhanapala were mere passive listeners. This Western initiative of P-TOMS did not finally see the light of day. But it split the ruling coalition of the PA and JVP irrevocably and Mahinda Rajapaksa burnished his credentials as an opponent of the project. He became popular with the PA and its allied parties over and above CBK.
When the P-TOMS project was to be placed before Parliament Mahinda as Prime Minister refused to present it on the floor of the House. CBK was too weak to dismiss him partly because Lakshman Kadirgamar also was a strong opponent of P-TOMS. Instead she got Maithripala Sirisena to present the proposal. But the Opposition which was joined by the JVP including its functioning Ministers, took to the streets. The JVP members demonstrated and disturbed the proceedings from the well of the House and then resigned “en masse” from the government putting its majority in jeopardy. Mahinda’s anti-P-TOMS stand endeared him to the JVP, which had earlier preferred Kadirgamar to him, and helped him to garner votes which went a long way in ensuring his ultimate victory. He had become so powerful that CBK had no option but to accommodate him.
Assassination of Lakshman Kadirgamar
Another blow was struck at CBK and the government by the I TTE when they assassinated Lakshman Kadirgamar near the swimming pool of his house. He had a successful kidney transplant in India – with a Buddhist monk from Balangoda donating a kidney – and was asked to swim regularly as exercise by his doctors. I knew of this arrangement because when we travelled together he always asked the Foreign Office to put him tip in a hotel with a heated swimming pool.
He was about to enter the water in the swimming pool when a LTTE sniper shot him through a window in a neighbourhood flat. This dastardly crime wits condemned unanimously by the international community. India sent her Foreign Minister to attend the funeral. Ksdirgamar’s death brought CBK’s Government to the brink of collapse. The JVP though leaving the Government respected LK and paid a tribute to him by arranging for their leaders to follow his hearse on foot to Kanatte.
It must be mentioned here that LK nearly pipped Mahinda for the post of PM in 2004. He had the backing of the JVP who wanted CBK to appoint LK and in the alternative appoint Maithripala Sirisena as PM. He was also supported by India but CBK was afraid that Mahinda will break up the party if he was deprived of the Premiership. After LK’s demise she undertook a mini reshuffle and Anura Bandaranaike had his ambition of being Foreign Minister realized.
To succeed him as Minister of Industries and Foreign Investment she appointed me in addition to my portfolio of Minister of Finance. Arjuna Ranatunga was the Deputy Minister of Industries and I left most of the administrative work to him. When we had an investment promotion meeting in Delhi I invited Arjuna and Aravinda de Silva to be our delegates and they stole the show among the cricket mad Indian investors. All the tables at dinners hosted by us were taken and we had many friends appealing to us to get them reservations even at the last minute.
We had such good relations that I was invited to take part in popular TV talk shows. I remember that Shekhar Gupta invited me for a discussion on our health services with Kajol – the top Hindi film actress who was brand ambassador for Narendra Modis “clean Bharat” campaign. She was a charming young lady who recounted her enjoyable stay in Sri Lanka when she accompanied her mother Tanuja who was shooting a film in Colombo with Vijaya Kumaratunga as her co-star.
After LKs murder the fear of the LTTE was so strong that CBK could not even attend the funeral ceremony. PM Mahinda Rajapaksa represented her. This death was a bitter blow to me because as an old Trinitian friend he would always consult me on party matters. I still have a letter he wrote to me about a coffee t able book on the art of Stanley Kirinde which he sponsored in honour of our mutual college friend.
(This book is available at the Vijitha Yapa bookshops)
(Excerpted from vol. 3 of the Sarath Amunugama autobiography)
Features
The amazing biodiversity of Sri Lanka:

Nations Trust WNPS Monthly Lecture
An overview of the plants & animals on this magical island
Thursday 19 March 2026, 6.00 pm, Jasmine Hall, BMICH
In the first part of this talk, Author-Photographer Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne points out that Sri Lanka is disproportionately rich in species. He presents possible reasons for this and then makes the case that Sri Lanka is one of the best all-round wildlife destinations in the world. In the second part of the talk, he takes a whirlwind tour of several branches of the tree of life from bacteria to elephants. He uses this tour of life forms as a framework to showcase the richness of biodiversity in Sri Lanka.
He points out that very little has been done on the study of groups such as fungi and mosses and remarks how his proposal for a special visa for exchange programs, internships and volunteering could enable local academics to gain access to expertise and experienced volunteer hours from people overseas who have a passion for these areas of natural history.
With plants, he outlines the major groups of plants which are the bryophytes, lycopods, ferns and spermatophytes. The latter also knows as seed plants include the conifers (gymnosperms) and flowering plants (angiosperms). He makes reference to what is found in Sri Lanka to illustrate the importance of certain groups, such as the dipterocarp trees which are the giants of the rainforest. His photographs will illustrate examples such as carnivory, because plants employ a wide range of life strategies.
The talk will provide a very brief outline of the animal kingdom with its vast and sprawling evolutionary tree. Starting with animals that evolved early such as the sponges, he will draw attention to a few of the phyla which holds larger animals. Not surprisingly, more attention will be given to the vertebrates which command most of the popular attention. However, he will also reference invertebrate groups such as the butterflies and dragonflies, the two most popular groups of insects. Although Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne was the first to brand Sri Lanka for big game safaris, in this talk, he will bring in many of the other plant and animal groups which although lacking ‘safari appeal’ are nevertheless important in terms of biodiversity and being the subjects of research.
As Sri Lanka positions itself as a destination for high-value, experience-driven tourism, the conservation of its natural heritage becomes not just an environmental priority but an economic imperative. This lecture will be especially valuable for tourism professionals, hospitality leaders, policymakers, conservationists, students, photographers, and nature enthusiasts seeking to understand the true asset underpinning Sri Lanka’s future.
According to Rohan Pethiyagoda, ‘Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne is without question the most celebrated field naturalist the country has produced’. Bill Oddie (British TV Naturalist) has said no single individual has done so much to publicise a country for its wildlife. The speaker has authored and photographed more than 25 books and 400 articles and has played a pivotal role in branding Sri Lanka as a wildlife destination.
The WNPS Monthly Lecture Series, established in 2000, is one of Sri Lanka’s longest-running and most respected conservation knowledge platforms. Featuring leading local and international experts, the series addresses critical environmental issues through science-based insights and open public dialogue. Beyond the lecture hall, these sessions foster collaboration, inspire research, and often seed conservation projects and advocacy initiatives. The series remains a cornerstone of Sri Lanka’s conservation community—connecting knowledge with action
The Lecture is supported by Nations Trust Bank and is open all, entrance free
- Sloth Bear – Yala (pix by Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne)
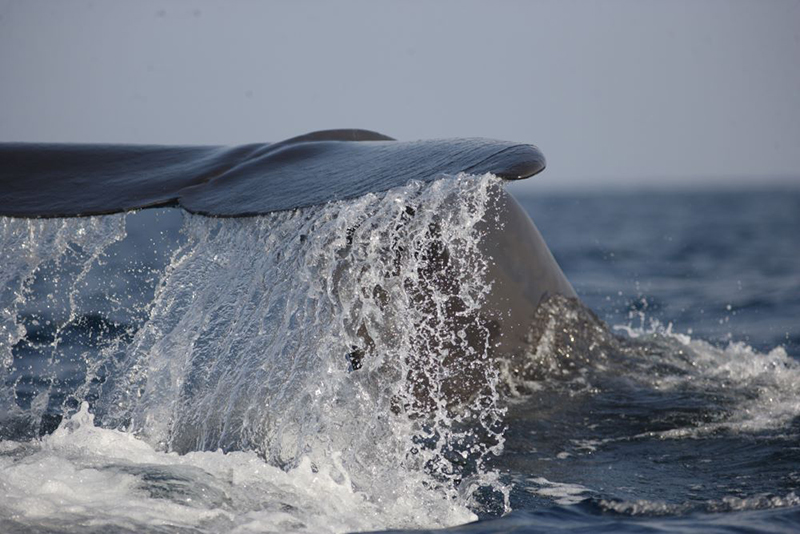
- Sperm Whale – Kalpitiya
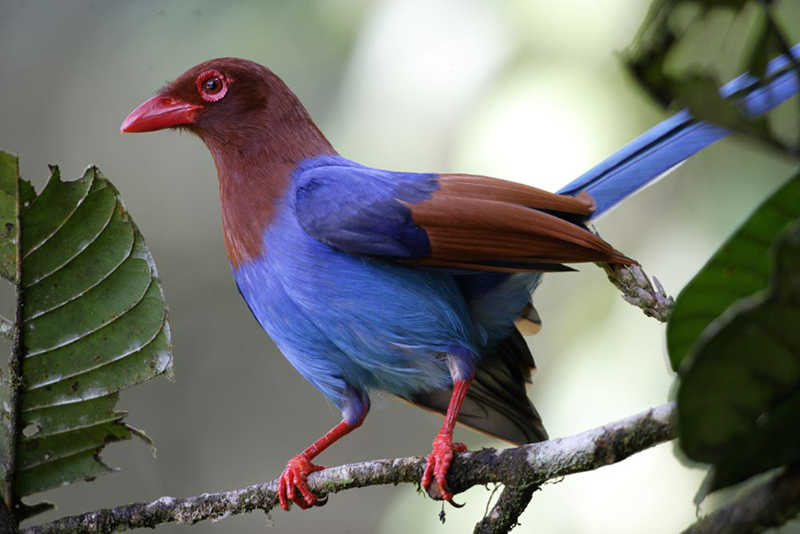
- Sri Lanka Blue Magpie – Sinharaja
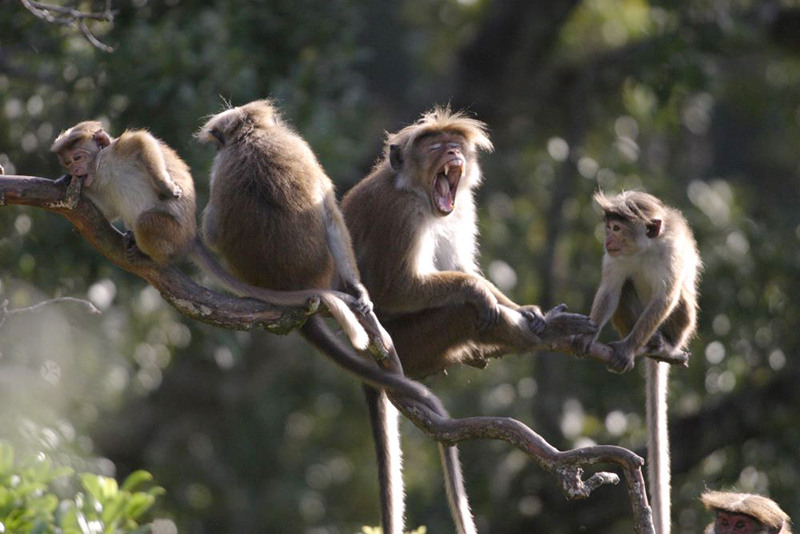
- Toque Monkey – Hakgala
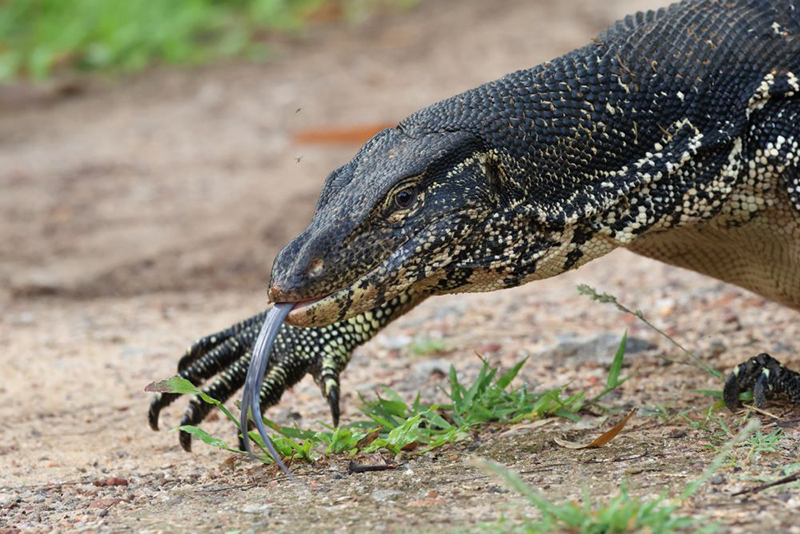
- Water Monitor – Diyasaru
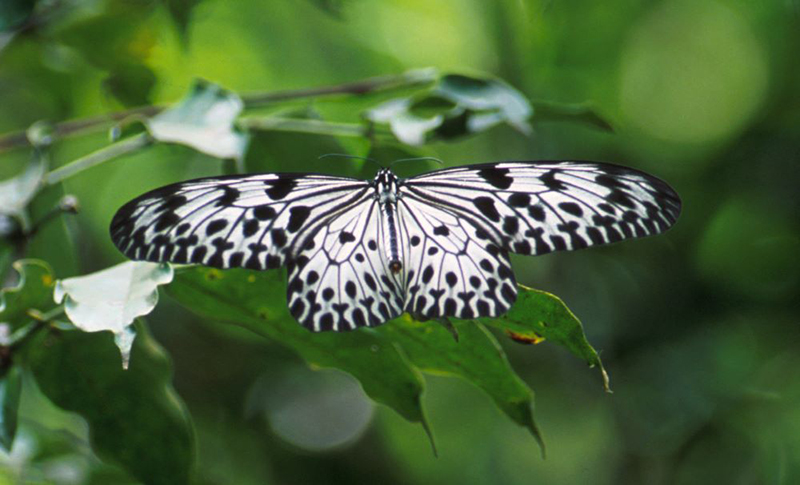
- Ceylon Tree Nymph
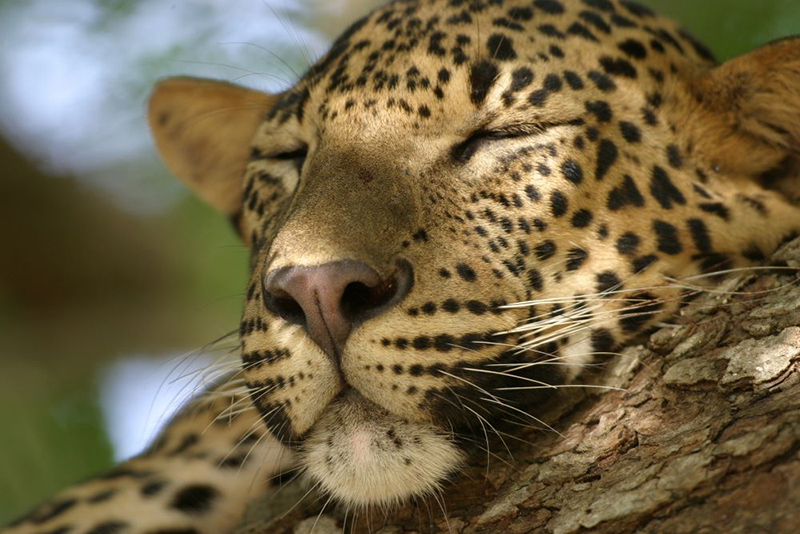
- Leopard
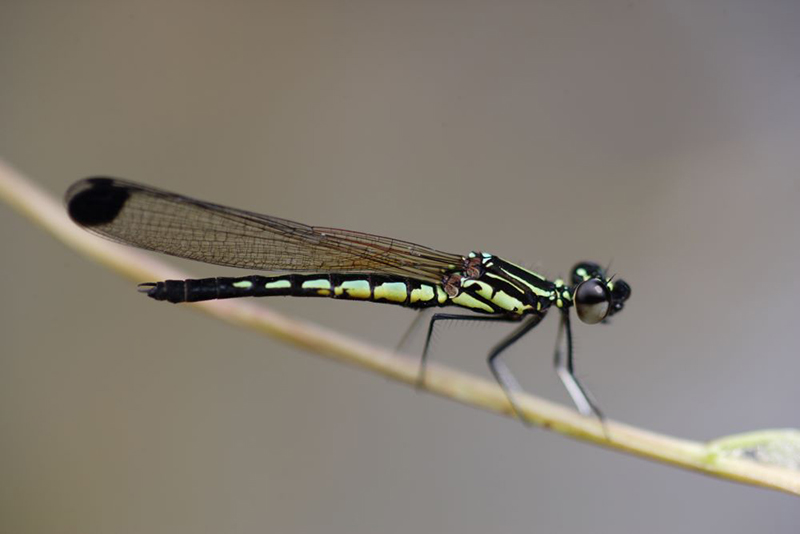
- Adam’s Gem (Libellago greeni) male – Talangama
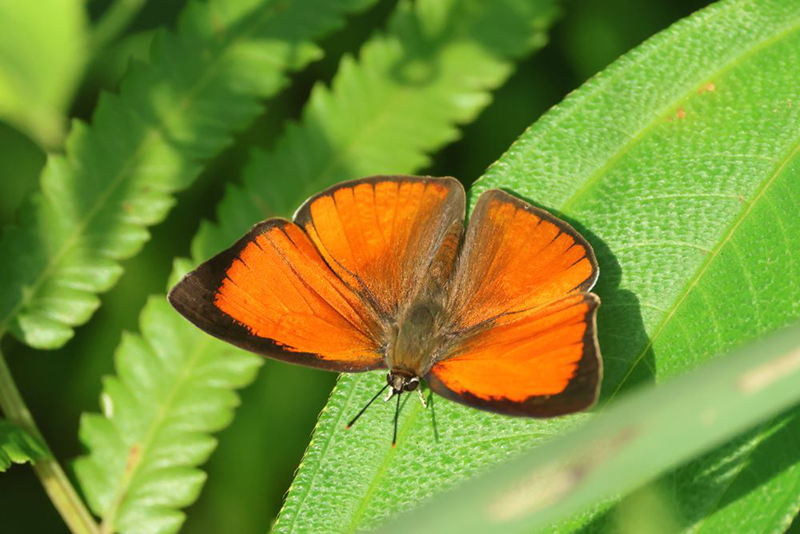
- Indian Sunbeam – Beddegana
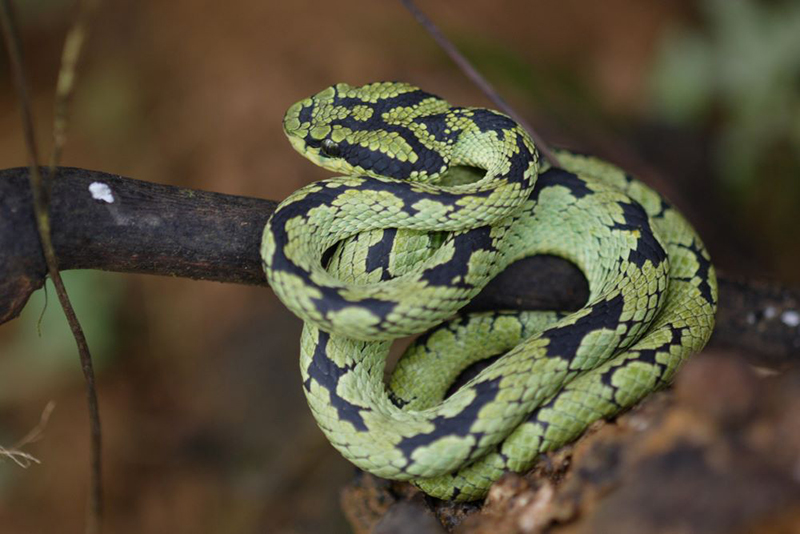
- Green Pit Viper – Sinharaja
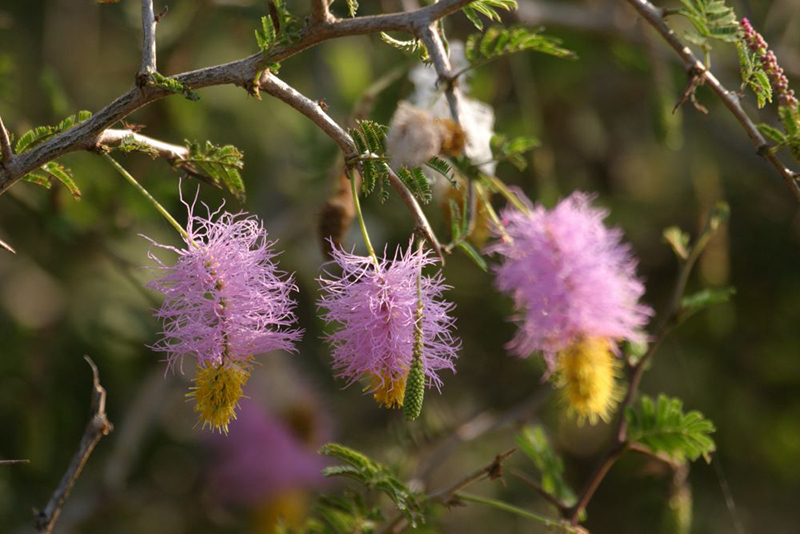
- Dichrostachys cinera – (Andara) Yala
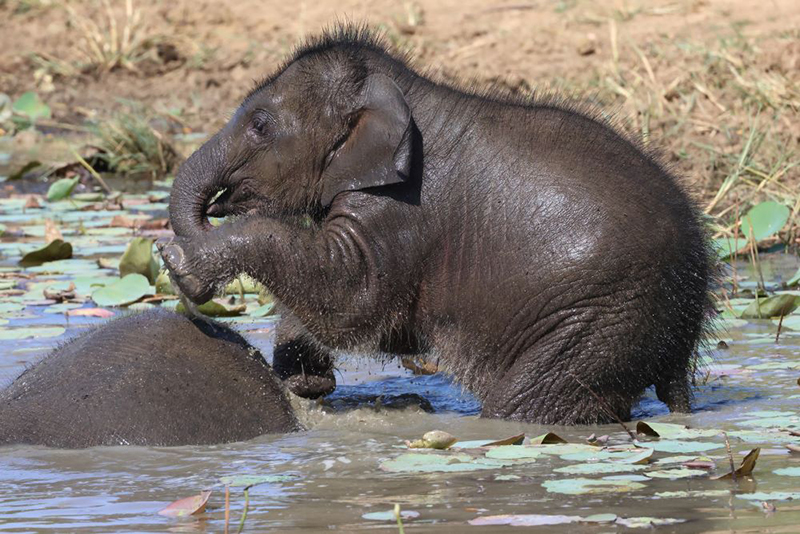
- Asian Elephant – Yala
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA