Features
ABOLISHING THE EXECUTIVE PRESIDENCY

by Dr Nihal Jayawickrama
The message of the 2022 “Aragalaya”, which drove a President and a Prime Minister and other members of that political family out of office, expressed in clear and explicit terms, was a complete rejection of the authoritarian, patronage-based, corrupt system of governance introduced into this country by the 1978 Constitution and its 21 Amendments. A total of 45 years of autocratic presidential rule marked by massive loss of human life and unprecedented levels of corruption, have demonstrated the need to restore the system of government that this country enjoyed for 25, if not 30, years since 1947.
The Parliamentary Executive System
I am old enough to have lived through all three post-Independence Constitutions of this country, and especially the first. In my view, the 1946 Constitution served the country and its peoples best. If the purpose of a national constitution is to establish the essential framework of government by creating the principal institutions and defining their powers, that was precisely what it did. Drafted by one trained legal draftsman, based on the report of the Soulbury Commission and related documents, and endorsed by the four major communities represented in the State Council, that Constitution served us for 25 years without any significant amendments. Expressed in only 92 sections, it was, in my opinion, the model constitution. If it failed in some respects, it was due to the absence of a Bill of Rights.
Under that parliamentary executive system of government, the Head of State, who was also Head of the Executive, and Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces, acted on the advice of the Prime Minister, while the Cabinet of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister and drawn from Parliament was charged with the direction and control of the Government and was collectively responsible to Parliament. That system facilitated regular democratic elections and periodic changes of government which enabled both right-wing and centrist or left-of-centre political parties to implement their respective economic and social policies without any hindrance.
The parliamentary executive system of governance it provided was flexible enough to deal effectively and expeditiously with the sudden death of the Prime Minister in 1951, an island-wide Hartal in 1953, the assassination of the Prime Minister in 1959, the attempted military Coup d’état in 1962, and the bloody JVP Insurgency in 1971. The independence of the Judiciary was protected, and so was that of the Public Service. As a Permanent Secretary under that Constitution during the first two years of my seven-year term, I had the freedom to supervise the departments assigned to the Ministry, subject only to policy directions from my Minister. On one occasion when I refused to comply with a specific non-policy direction, I was reported to the Prime Minister who, fortunately, had a clearer understanding of constitutional principles.
The Constitutional Head of State
For 30 years, the constitutional Head of State was the principal unifying figure in the country; the non-partisan, independent, symbol of the State. Opposition parties could approach the President in the knowledge that he was a neutral figure. When, in 1972, a conflict developed between the Constitutional Court and the National State Assembly, and the Judges refused to speak to the Speaker or the Ministers, it was at President’s House that each party sat on either side of the conference table, with the President at the head, to commence a dialogue to try to resolve their differences.
That exercise, however, failed. When, in 1976, following a long period of “cold war” between the Supreme Court and the Ministry of Justice, the Minister decided it was time to break the ice, and invited the Chief Justice and other Judges of the Supreme Court to the Ministry to tea, it was to President’s House that they proceeded instead, to complain of the invitation, which they perceived to be an interference with the judiciary. Mr William Gopallawa was not a mere ceremonial president; he was not a mere cipher. I was summoned by him on several occasions when he disagreed or felt uncomfortable with advice tendered to him, either by a Minister or the Prime Minister. He did not hesitate to invite the Prime Minister, or the Minister concerned, to reconsider the advice.
The Presidential Executive System
That parliamentary executive system of government was replaced in 1978 by a presidential executive system of government, not because the former, which prevails to this day in democratic countries from Canada and the United Kingdom, through India, Singapore, and Malaysia, to Australia and New Zealand, had somehow failed the people of Sri Lanka. It was replaced not because the people of Sri Lanka cried out aloud nostalgically for a return to some form of monarchical rule.
It was replaced because that was the wish and desire of one senior political leader who probably sincerely believed that that was the best form of government for our country. However, from 1966, during the next seven years, Mr. J.R. Jayewardene failed to convince his party leader, Mr. Dudley Senanayake, of his strong belief that an Executive President chosen directly by the people, seated in power for a fixed number of years, and not subject to the whims and fancies of an elected legislature, was what the country required.
He also proposed an electoral system where there were no electorates; where each political party presented a list of candidates; where the voter voted for the party; and the legislators were chosen from that list, the number depending on the votes cast for each party. He predicted that that system would enable the best equipped men and women in the country to take part in our political life. Little did he know that 50 years later the “best equipped men and women” would include 90 parliamentarians who had not even attempted to sit the GCE “O” Levels. Prime Minister Dudley Senanayake did not support this proposal; nor did the UNP Working Committee.
At the general election of July 1977, when he led his party to an unprecedented five-sixth majority in the National State Assembly (NSA), Prime Minister Jayewardena was able to fulfil his dream project. In October of that year, a Bill to amend the Constitution, certified by his Cabinet as being “urgent in the national interest”, which sought to transfer all the executive powers of the Prime Minister to the President, and for the incumbent Prime Minister to be deemed the first nationally elected President, was passed by the NSA. On February 4, 1978, that constitutional amendment was brought into force, and Mr. Jayewardene was sworn-in on Galle Face Green as the first Executive President of Sri Lanka.
Meanwhile, a Select Committee of the NSA was established to consider the revision of the 1972 Constitution. At the concluding stages of that Committee, the Government tabled a wholly new draft constitution, the author of which was not disclosed. On August 31, 1978, with the TULF and the SLFP walking out, and with none voting against, the NSA enacted the Constitution of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka. On September 8, 1978, the new Constitution was brought into operation, and the 168 members of the NSA were deemed to have been elected as Members of the new Parliament that was established.
Parliamentary Majority Essential
The 1978 Constitution, under which the President was the source of all power and patronage and was beyond the reach of the law and the judiciary, was a Constitution of Mr Jayewardene, by Mr. Jayewardene, for Mr Jayewardene. Dr Colvin R. de Silva’s prescient plea that he should not bequeath it to his successors, was ignored. The success of his project, however, was entirely dependent on one essential factor – that the President elected by the people was supported by a clear majority in the Parliament elected by the people.
I attended a few meetings of the select committee as an adviser to Mrs Bandaranaike and Mr Maithripala Senanayake, since neither of them was a lawyer. At one of the meetings, I had occasion to ask Mr Jayewardene what the position would be if a political party opposed to the President secured a majority in Parliament. He thought that would be unlikely during his term of office, but if that were to happen, he said he would take a step back and be a constitutional Head of State. He, of course, ensured that that did not happen during his presidency by securing an extension of the life of Parliament for a further six-year term through an amendment of the Constitution, a rigged referendum, and through many other devices such as obtaining undated letters of resignation, maintaining secret files on the financial and other activities of his Ministers, and by imposing civic disabilities on his political opponents.
His successors, however, were either not so fortunate, or did not possess his political acumen. In August 1994, UNP President Wijetunge, faced with a Parliament in which the United Front had a majority, chose to take a step back to spend the last three months of his term as a constitutional Head of State. In 2001, President Kumaratunge, faced with a Parliament controlled by the UNP, chose “cohabitation” for a while, and then used her presidential powers to dissolve Parliament prematurely, having previously assured the Speaker that she would never do that while a political party other than her own commanded a working majority. In the next 10 years, both she and President Rajapaksa regularly lured Members of the Opposition to secure the majority which they required, using methods that should have alerted any self-respecting Bribery Commissioner and kept him awake at night.
One does not need to be reminded of the shambolic relationship that prevailed between the President and the Prime Minister in the “Yahapalana” government; nor of the inconceivable situation today where the President is compelled to function with a Cabinet of Ministers and a parliamentary majority politically opposed to him.
A Political Consensus Exists
For over 30 years, every major political party has pledged to restore the parliamentary executive form of government. For that purpose, every major political party has supported the election of the President by Parliament (or other representative body).
In 2000, President Chandrika Kumaratunge, as head of the SLFP government presented a draft Constitution which provided for the President and two Vice-Presidents (the latter drawn from ethnic communities different to that of the President) to be elected by Parliament.
In 2013, the Ranil Wickremesinghe-led UNP published the text of the principles upon which a new Constitution would be formulated after it forms a government. Among them was that the Executive Presidency would be abolished.
In 2015, President Sirisena stood before the casket bearing the remains of the late Rev. Maduluwawe Sobitha and, with his head bowed, swore an oath that he would ensure that all remnants of executive power would be removed from the office of the President of the Republic.
In 2018, a panel of experts appointed by the UNP/SLFP Yahapalana Government led by President Sirisena and Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe prepared and published a draft Constitution which required the President to be elected by Parliament and to exercise many of his/her powers on advice.
In 2018, the JVP headed by Anura Kumara Dissanayake, presented a Bill to amend the Constitution to enable the non-executive President to be elected by Parliament.
In 2021, the SJB led by Sajith Premadasa proposed an amendment to the Constitution to enable a non-executive President to be elected by Parliament.
A Referendum Is Not Required
The 1978 constitution introduced for the first time into the Sri Lankan constitutional process the concept of a referendum. In the tradition of the Greek city states, actual decision-making was being restored to the people. The articles of the constitution which Parliament may not amend without approval at a referendum are regarded as the fundamental elements of the State and are explicitly set out in Article 83. They are: its name (art. 1), its unitary character (art.2), the inalienability of the people’s sovereignty (art.3), its national flag (art.6), its national anthem (art.7), its national day (art.8), the foremost place accorded to Buddhism (art.9), the freedom of thought, conscience and religion (art.10), the prohibition of torture (art.11), any extension of the term of office of the President (art.30), and any extension of the life of Parliament (art.62).
The introduction of a referendum appears to have been intended as a means of ensuring that these fundamental elements would ordinarily remain unaltered. In that regard, the Constitution has distinguished the principle from its implementation. For example, while the life of Parliament or the term of office of the President cannot be extended without approval at a referendum, any reduction of the life or term can be achieved by an amendment passed in Parliament. Similarly, while the concept of the people’s sovereignty is unalterable (thus preventing its alienation to a monarch, a military officer or to a particular community), the manner of its exercise is left to be determined by Parliament. Thus, a requirement that the executive power of the people be exercised by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister is an amendment capable of being made by Parliament by a two-thirds majority without reference to a referendum, as was held by the Supreme Court in 2015.
Unfortunately, the decision of the Bench of three Judges of the Supreme Court (Chief Justice Sripavan and Justices Ekanayake and Dep) on the 19th Amendment which enabled Parliament to amend the Constitution to require the President to act on the advice of the Prime Minister in respect of several matters, has not been followed in subsequent determinations. For example, the proposal made in 2019 by the JVP that the impending election to the office of the then non-executive Presidency be by a majority vote in Parliament was rejected by the Supreme Court. Justice De Abrew held that that would violate Article 4, and that any amendment of Article 4 requires approval by the people at a referendum. Article 4 is not an entrenched provision specified in Article 83. He also ignored the fact that Article 40 of the Constitution already provided for Parliament to elect the President in certain circumstances.
Replacement of List-System with Constituencies
The election of members of parliament from 25 District lists, based on proportional representation, was introduced by Mr. J.R. Jayewardene as an integral element in the presidential executive system of governance. Since each District encompassed several former constituencies, the expenditure involved in campaigning in such a large extent of territory, and the need to raise money for that purpose from various sources, inevitably on a quid pro quo basis, has been identified as one of the principal factors leading to corruption. The return to the single-member/multi-member constituencies, combined with a system of proportional representation to ensure that unrepresented interests are adequately represented, ought to be an essential adjunct to a parliamentary executive system of governance.
Features
The State of the Union and the Spectacle of Trump
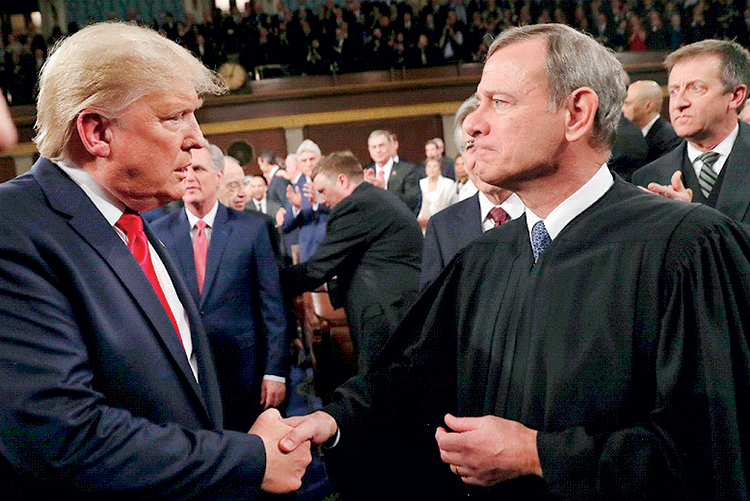
President Donald J. Trump, as the American President often calls himself, is a global spectacle. And so are his tariffs. On Friday, February 20, the US Supreme Court led by Chief Justice John Roberts and a 6-3 majority, struck down the most ballyhooed tariff scheme of all times. Upholding the earlier decisions of the lower federal courts, the Supreme Court held that Trump’s use of ‘emergency powers’ to impose the so called Liberation Day tariffs on 2 April 2025, is not legal. The Liberation Day tariffs, which were comically announced on a poster board at the White House Rose Garden, is a system of reciprocal tariffs applied to every country that exported goods and services to America. The court ruling has pulled off the legal fig leaf with which Trump had justified his universal tariff scheme.
Trump was livid after the ruling on Friday and invectively insulted the six judges who ruled against Trump’s tariffs. There was nothing personal about it, but for Trump, the ever petulant man-boy, there isn’t anything that is not personal. On Tuesday night in Washington, Trump delivered his first State of the Union address of his second presidency. The Chief Justice, who once called the State of the Union, “a political pep rally,” attended the pomp and exchanged a grim handshake with the President.
Tuesday’s State of the Union was the longest speech ever in what is a long standing American tradition that is also a constitutional requirement. The Trump showmanship was in full display for the millions of Americans who watched him and millions of others in the rest of world, especially mandarins of foreign governments, who were waiting to parse his words to detect any sign for his next move on tariffs or his next move in Iran. There was nothing much to parse, however, only theatre for Trump’s Republican followers and taunts for opposing Democrats. He was in his usual elements as the Divider in Chief. There was truly little on offer for overseas viewers.
On tariffs, he is bulldozing ahead, he boasted, notwithstanding the Supreme Court ruling last Friday. But the short lived days of unchecked executive tariff powers are over even though Trump wouldn’t let go of his obsessive illusions. On the Middle East, Trump praised himself for getting the release of Israeli hostages, dead or alive, out of Gaza, but had no word for the Palestinians who are still being battered on that wretched strip of land. On Ukraine, he bemoaned the continuing killings in their thousands every month but had no concept or plan for ending the war while insisting that it would not have started if he were president four years ago.
He gave no indication of what he might do in Iran. He prefers diplomacy, he said, but it would be the most costly diplomatic solution given the scale of deployment of America’s fighting assets in the region under his orders. In Trump’s mind, this could be one way of paying for a Nobel Prize for peace. More seriously, Trump is also caught in the horns of a dilemma of his own making. He wanted an external diversion from his growing domestic distractions. If he were thinking using Iran as a diversion, he also cannot not ignore the warnings from his own military professionals that going into Iran would not be a walk in the park like taking over Venezuela. His state of mind may explain his reticence on Iran in the State of the Union speech.
Even on the domestic front, there was hardly anything of substance or any new idea. One lone new idea Trump touted is about asking AI businesses to develop their own energy sources for their data centres without tapping into existing grids, raising demand and causing high prices and supply shortages. That was a political announcement to quell the rising consumer alarms, especially in states such as Michigan where energy guzzling data centres are becoming hot button issue for the midterm Congress and Senate elections in November. Trump can see the writing on the wall and used much of his speech to enthuse his base and use patriotism to persuade the others.
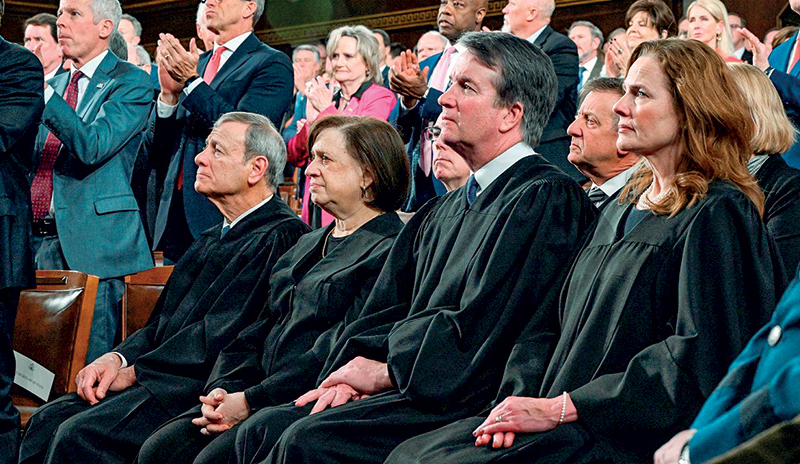

Political Pep Rally: Chief Justice John G. Roberts sits stoically with Justices Elena Kagan, Bret Kavanaugh, and Amy Coney Barrett, as Republicans are on their feet applauding.
Although a new idea, asking AI forces to produce their own energy comes against a background of a year-long assault on established programs for expanding renewable energy sources. Fortunately, the courts have nullified Trump’s executive orders stopping renewable energy programs. But there is no indication if the AI sector will be asked to use renewable energy sources or revert to the polluting sources of coal or oil. Nor is it clear if AI will be asked to generate surplus energy to add to the community supply or limit itself to feeding its own needs. As with all of Trump’s initiatives the devil is in the details and is left to be figured out later.
The Supreme Court Ruling
The backdrop to Tuesday’s State of the Union had been rendered by Friday’s Supreme Court ruling. Chief Justice Roberts who wrote the majority ruling was both unassuming and assertive in his conclusion: “We claim no special competence in matters of economics or foreign affairs. We claim only, as we must, the limited role assigned to us by Article III of the Constitution. Fulfilling that role, we hold that IEEPA (International Emergency Economic Powers Act) does not authorize the President to impose tariffs.”
IEEPA is a 1977 federal legislation that was enacted during the Carter presidency, to both clarify and restrict presidential powers to act during national emergency situations. The immediate context for the restrictive element was the experience of the Nixon presidency. One of the implied restrictions in IEEPA is in regard to tariffs which are not specifically mentioned in the legislation. On the other hand, Article 1, Section 8 of the US Constitution establishes taxes and tariffs as an exclusively legislative function whether they are imposed within the country or implemented to regulate trade and commerce with other countries. In his first term, Trump tried to impose tariffs on imports through the Congress but was rebuffed even by Republicans. In the second term, he took the IEEA route, bypassing Congress and expecting the conservative majority in the Supreme Court to bail him out of legal challenges. The Court said, No. Thus far, but no farther.
The main thrust of the ruling is that it marks a victory for the separation of powers against a president’s executive overreach. Three of the Court’s conservative judges (CJ Roberts, Neil Gorsuch, and Amy Coney Barrett) joined the three liberal judges (all women – Sonia Sotomayor, Elana Kagan and Ketanji Brown Jackson) to chart a majority ruling against the president’s tariffs. The three dissenters were Brett Kavanugh, who wrote the dissenting opinion, Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito. Justices Gorsuch, Kavanaugh and Barrett were appointed by Trump. Trump took out Gorsuch and Barrett for special treatment after their majority ruling, while heaping praise on Kavanaugh who ruled in favour of the tariffs. Barrett and Kavanaugh attended the State of the Union along with Roberts and Kagan, while the other five stayed away from the pep rally (see picture).
The Economics of the Ruling
In what was a splintered ruling, different judges split legal hairs between themselves while claiming no special competence in economics and ruling on a matter that was all about trade and economics. Yale university’s Stephen Roach has provided an insightful commentary on the economics of the court ruling, while “claiming no special competence in legal matters.” Roach takes out every one of Trump’s pseudo-arguments supporting tariffs and provides an economist’s take on the matter.
First, he debunks Trump’s claim that trade deficits are an American emergency. The real emergency, Roach notes, is the low level of American savings, falling to 0.2% of the national income in 2025, even as trade deficit in goods reached a new record $1.2 trillion. America’s need for foreign capital to compensate for its low savings, and its thirst for cheap imported goods keep the balance of payments and trade deficits at high levels.
Second, by imposing tariffs Trump is not helping but burdening US consumers. The Americans are the ones who are paying tariffs contrary to Trump’s own false beliefs and claims that foreign countries are paying them. 90% of the tariffs have been paid by American consumers, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Small businesses have paid the rest. Foreign countries pay nothing but they have been making deals with Trump to keep their exports flowing.
According to published statistics, the average U.S. applied tariff rate increased from 1.6% before Trump’s tariff’s to 17%, the highest level since World War II. The removal of reciprocal tariffs after the ruling would have lowered it to 9.1%, but it will rise to 13% after Trump’s 15% tariffs. The registered tariff revenue is about $175 billion, 0.6% of U.S. gross domestic product. The tariff monies collected are legally refundable. The Supreme Court did not get into the modalities for repayment and there would be multiple lawsuits before the lower courts if the Administration does not set up a refunding mechanism.
Lastly, in railing against globalization and the loss of American industries, Trump is cutting off America’s traditional allies and trading partners in Europe, Canada and Mexico who account for 54% of all US trade flows in manufactured goods. Cutting them off has only led these countries to look for other alternatives, especially China and India. All of this is not helping the US or its trade deficit. The American manufacturers (except for sectoral beneficiaries in steel, aluminum and auto industries), workers and consumers are paying the price for Trump’s economic idiosyncrasies. As Roach notes, the Court stayed away from the economic considerations, but by declaring Trump’s IEEPA tariffs unconstitutional, the Court has sent an important message to the American people and the rest of the world that “US policies may not be personalized by the whims of a vindictive and uninformed wannabe autocrat.”
by Rajan Philips
Features
The Victor Melder odyssey: from engine driver CGR to Melbourne library founder

He celebrated his 90th birthday recently, never returned to his homeland because he’s a bad traveler
(Continued from last week)
THE GARRAT LOCOS, were monstrous machines that were able to haul trains on the incline, that normally two locos did. Whilst a normal loco hauled five carriages on its own, a Garrat loco could haul nine. When passenger traffic warranted it and trains had over nine carriages or had a large number of freight wagons, then a Garret loco hauled the train assisted by a loco from behind.
When a train was worked by two normal locos (one pulling, the other pushing) and they reached the summit level at Pattipola (in either direction), the loco pushing (piloting) would travel around to the front the train and be coupled in front of the loco already in front and the two locos took the train down the incline. With a Garraat loco this could not be done as the bridges could not take the combined weight. The pilot loco therefore ran down single, following THE TRAIN.
My father was stationed at Nawalapitiya as a senior driver at the time, and it wasn’t a picnic working with him. He believed in the practical side of things and always had the apprentices carrying out some extra duties or the other to acquaint themselves with the loco. I had more than my fair share.
After the four months upcountry, we were back at Dematagoda on the K. V. steam locos. From the sublime to the ridiculous, I would say after the Garret locos upcountry. Here the work was much easier and at a slower pace, as the trains did not run at speed like their mainline counterparts. The last two months of the third year saw us on the two types of diesel locos on the K.V. line, the Hunslett and Krupp diesels, which worked the passenger trains. For once this was a ‘cushy, sit-down’ job, doing nothing exciting, but keeping a sharp lookout and exchanging tablets on the run. The third year had come to an end and ‘the light at the end of tunnel was getting closer’.
The fourth year saw us all at the Diesel loco shed at Maradana, which was cheek by jowl with the Maradana railway station. The first three months we worked with the diesel mechanical fitters and the following three months with the electrical fitters. Heavy emphasis was placed on a working knowledge of the electrical circuits of the different diesel locos in service, to ensure the drivers were able to attend to electrical faults en-route and bring the train home. This was again a period of lectures and demonstrations
We also spent three months at the Ratmalana workshops, where the diesels were stripped down to the core and refitted after major repairs, to ensure we had a look at what went on inside the many closed and sealed working parts. This was again a 7.00am to 4.00pm day job. Back again at the Diesel shed, Maradana, saw us riding as assistants for the next three months on all the diesel locos in service – The Brush Bragnal (M1), General Electrical (M2), Hunslett locos (G2) and Diesel Rail Cars.
After the final written test on Diesel locos, we began our fifth and final year, which was that of shunting engine driver. The first six months were spent at Maligawatte Yard on steam shunting locos and the next three months shunting drivers on the diesel shunting locos at Colombo goods yard. The final three months were spent as assistants on the M1 and M2 locos working all the fast passenger and mail trains.
I was finally appointed Engine Driver Class III on July 6, 1962, as mentioned earlier I lost eight months of my apprenticeship due to being ill and had to make up the time. This appointment was on three years’ probation, on the initial salary of the scale Rs 1,680 – 72 – Rs 2,184, per annum.
Little did the general traveling public realize that they had well trained and qualified engine drivers working their trains to time Victor was stationed in Galle until December 1967, when he resigned from the railway to migrate to Melbourne, Australia to join the rest of his family. He was the last of 11 siblings to leave Ceylon. Their two elder children were born in Galle. Victor and Esther had three more children in Australia. The children, three boys and two girls) were brought up with love and devotion. They have seven grandchildren and two great grandchildren. They meet often as a family.
He worked for the Victorian State Public Service and retired in 1993 after 25 years’ service. At the time of retirement, he worked for the Ministry for Conservation & Environment. He held the position of Project Officer in charge of the Ministry’s Procedural Documents.
He worked part-time for the Victorian Electoral Office and the Australian Electoral Office, covering State and Federal Elections, from 1972 to 2010. From 1972 to 1982 and was a Clerical Officer and then in 1983 was appointed Officer-in-Charge, Lychfield Avenue Polling Booth, Jacana which is my (the writer’s) electorate.
As part of serving the community Victor participated in a number of ways, quite often unremunerated. He worked part-time for the Department of Census & Statistics, and worked as a Census Collector for the Census of 1972, 1976, 1980 and then Group Leader of 16 Collectors in his area for the 1984, 1988, 1992, 1996, 2000, 2004, 2008 and 2012.
In 1970, Victor began this library, now known as the ‘Victor Melder Sri Lanka Library’, for the purpose of making Sri Lanka better known in Australia. On looking back he has this to say: “Forty-five years later, I can say that it is serving its purpose. In 1993 President Ranasinghe Premadasa of Sri Lanka bestowed on me a national honor – ‘Sri Lanka Ranjana’ for my then 25 years’ service to Sri Lanka in Australia. I feel very privileged to be honored by my motherland, which I feel is the highest accolade one can ever get.”
There were many more accolades over the years:
15.10. 2004, Serendib News, 2004 Business and Community Award.
4.2.2008, Award for Services to the SL Community by The Consulate of Sri Lanka in Victoria (by R. Arambewela)
2024 – SL Consul General’s Award
In 2025 , Victor was one of the ten outstanding Sri Lankans in Australia at the Lankan Fest.
An annual Victor Melder Appreciation award was established to honour an outstanding member by the SriLankan Consulate.
The following appreciation by the late Gamini Dissanayake is very appropriate.
Comment by the late Minister Gamini Dissanayake, in the comment book of the VMSL library.
A man is attached to many things. Attachments though leading to sorrow in the end
are the living reality of life. Amongst these many attachments, the most noble are the attachments to one’s family and to one’s country. You have left Sri Lanka long ago but “she” is within you yet and every nerve and sinew of your body, mind and soul seem to belong there. In your love for the country of your birth you seem to have no racial or religious connotations – you simply love “HER” – the pure, clear, simple, abstract and glowing Sri Lanka of our imagination and vision. You are an example of what all Sri Lankan’s should be. May you live long with your vision and may Sri Lanka evolve to deserve sons like you.
With my best Wishes.
Gamini Dissanayake, Minister from Sri Lanka.
15 February 1987.
The Victor Melder Lecture
The Monash council established the Victor Melder Lecture which is presented every February. It is now an annual event looked forward to by Melbournians. A guest lecturer is carefully chosen each year for this special event.
Victor and his library has featured on many publications such as the Sunday Times in 2008 and LMD International in 2026.
“Although having been a railway man, I am a poor traveler and get travel sickness, hence I have not travelled much. I have never been back to Sri Lanka, never travelled in Australia, not even to Geelong. I am happiest doing what I like best, either at Church or in this library. My younger daughter has finally given up after months of trying to coax, cajole and coerce me into a trip to Sri Lanka to celebrate this (90th) birthday.
I am most fortunate that over the years I have made good friends, some from my school days. It is also a great privilege to grow old in the company of friends — like-minded individuals who have spent their childhood and youth in the same environment as oneself and shared similar life experiences.”
Victor’s love of books started from childhood. Since his young years he has been interested in reading. At St Mary’s College, Nawalapitiya, the library had over 300 books on Greek and Roman history and mythology and he read every one of them.
He read the newspapers daily, which his parents subscribed to, including the ‘Readers Digest’.His mother was an avid fan of Crossword Puzzles and encouraged all the children to follow her, a trait which he continues to this day.
At his workplace in Melbourne, Victor encountered many who asked questions about Ceylon. Often, he could not find an answer to these queries. This was long before the internet existed. He then started getting books on Ceylon/SriLanka and reading them. Very soon his collection expanded and he thought of the Vicor Melder SriLanka Library as source of reference. It is now a vast collection of over 7,000 books, magazines and periodicals.
Another driver of his service to fellow men is his deep Catholic faith in which he follows the footsteps of the Master.
Victor was baptized at St Anthony’s Cathedral, Kandy by Fr Galassi, OSB. Since the age of 10 he have been involved with Church activities both in Sri Lanka and Australia. He remains a devout Catholic and this underlies his spirit of service to fellowmen.
He began as an Altar Server at St Mary’s Church, Nawalapitiya, and continued even in his adult life. In Australia, Esther and Victor have been Parishioners at St Dominic’s Church, Broadmeadows, since 1970.He started as an Adult Server and have been an Altar Server Trainer, Reader and Special Minister He was a member of the ‘Counting Team’ for monies collected at Sunday Masses, for 35 years.
He has actively retired from this work since 2010, but is still ‘on call’, to help when required. To add in his own words
“My Catholic faith has always been important to me, and I can never imagine my having spent a day away from God. Faith is all that matters to Esther too. We attend daily Mass and busy ourselves with many activities in our Parish Church.
For nearly 25 years, we have also been members of a religious order ‘The Community of the Sons & Daughters of God’, it is contemplative and monastic in nature, we are veritable monks in the world. We do no good works, other than show Christ to the world, by our actions. Both Esther and I, after much prayer and discernment have become more deeply involved, taking vows of poverty, obedience and chastity, within the Community. Our spirituality gives us much peace, solace and comfort.”
“This is not my CV for beatification and canonization. My faith is in fact an antidote for overcoming evil, I too struggle like everyone else. I have to exorcise the demons within me by myself. I am a perfect candidate for “being a street angel and home devil” by my constant impatience, lack of tolerance and wanting instant perfection from everyone. “
The above exemplifies the humility of the man who admits to his foibles.
More than 25 years ago The Ceylon Society of Australia was formed in Sydney by a group of Ceylon lovers led by Hugh Karunanayake. Very soon the Melbourne chapter of the organization was formed, and Victor was a crucial part of this. At every Talk, Victor displayed books relevant to the topic. For many years he continued to do so carrying a big box of books and driving a fair distance to the meeting place. Eventually when he could no longer drive his car, he made certain that the books reached the venue through his close friend, Hemal Gurusinghe.
He also was the guest speaker at one of the meetings and he regaled the audience with railway stories.
Victor has dedicated his life on this mission, and we can be proud of his achievements. His vision is to find a permanent home for his library where future generations can use it and continue the service that he commenced. The plea is to get like-minded individuals in the quest to find a suitable and permanent home for the Victor Melder Srilankan Library.
by Dr. Srilal Fernando
Features
Sri Lanka to Host First-Ever World Congress on Snakes in Landmark Scientific Milestone

Sri Lanka is set to make scientific history by hosting the world’s first global conference dedicated entirely to snake research, conservation and public health, with the World Congress on Snakes (WCS) 2026 scheduled to take place from October 1–4 at The Grand Kandyan Hotel in Kandy World Congress on Snakes.
The congress marks a major milestone not only for Sri Lanka’s biodiversity research community but also for global collaboration in herpetology, conservation science and snakebite management.
Congress Chairperson Dr. Anslem de Silva described the event as “a long-overdue global scientific platform that recognises the ecological, medical and cultural importance of snakes.”
“This will be the first international congress fully devoted to snakes — from their evolution and taxonomy to venom research and snakebite epidemiology,” Dr. de Silva said. “Sri Lanka, with its exceptional biodiversity and deep ecological relationship with snakes, is a fitting host for such a historic gathering.”
Global Scientific Collaboration
The congress has been established through an international scientific partnership, bringing together leading experts from Sri Lanka, India and Australia. It is expected to attract herpetologists, wildlife conservationists, toxinologists, veterinarians, genomic researchers, policymakers and environmental organisations from around the world.
The International Scientific Committee includes globally respected experts such as Prof. Aaron Bauer, Prof. Rick Shine, Prof. Indraneil Das and several other authorities in reptile research and conservation biology.
Dr. de Silva emphasised that the congress is designed to bridge biodiversity science, medicine and society.
“Our aim is not merely to present academic findings. We want to translate science into practical conservation action, improved public health strategies and informed policy decisions,” he explained.
Addressing a Neglected Public Health Crisis
A key pillar of the congress will be snakebite envenoming — widely recognised as a neglected tropical health problem affecting rural communities across Asia, Africa and Latin America.
“Snakebite is not just a medical issue; it is a socio-economic issue that disproportionately impacts farming communities,” Dr. de Silva noted. “By bringing clinicians, toxinologists and conservation scientists together, we can strengthen prevention strategies, improve treatment protocols and promote community education.”
Scientific sessions will explore venom biochemistry, clinical toxinology, antivenom sustainability and advances in genomic research, alongside broader themes such as ecological behaviour, species classification, conservation biology and environmental governance.
Dr. de Silva stressed that fear-driven persecution of snakes, habitat destruction and illegal wildlife trade continue to threaten snake populations globally.
“Snakes play an essential ecological role, particularly in controlling rodent populations and maintaining agricultural balance,” he said. “Conservation and public safety are not opposing goals — they are interconnected. Scientific understanding is the foundation for coexistence.”
The congress will also examine cultural perceptions of snakes, veterinary care, captive management, digital monitoring technologies and integrated conservation approaches linking biodiversity protection with human wellbeing.
Strategic Importance for Sri Lanka
Hosting the global event in the historic city of Kandy — a UNESCO World Heritage site — is expected to significantly enhance Sri Lanka’s standing as a hub for scientific and environmental collaboration.
Dr. de Silva pointed out that the benefits extend beyond the four-day meeting.
“This congress will open doors for Sri Lankan researchers and students to access world-class expertise, training and international partnerships,” he said. “It will strengthen our national research capacity in biodiversity and environmental health.”
He added that the event would also generate economic activity and position Sri Lanka as a destination for high-level scientific conferences, expanding the country’s international image beyond traditional tourism promotion.
The congress has received support from major international conservation bodies including the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Save the Snakes, Cleveland Metroparks Zoo and the Amphibian and Reptile Research Organization of Sri Lanka (ARROS).
As preparations gather momentum, Dr. de Silva expressed optimism that the World Congress on Snakes 2026 would leave a lasting legacy.
“This is more than a conference,” he said. “It is the beginning of a global movement to promote science-based conservation, improve snakebite management and inspire the next generation of researchers. Sri Lanka is proud to lead that conversation.”
By Ifham Nizam
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoBathiya & Santhush make a strategic bet on Colombo
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoSeeing is believing – the silent scale behind SriLankan’s ground operation
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoProtection of Occupants Bill: Good, Bad and Ugly
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPrime Minister Attends the 40th Anniversary of the Sri Lanka Nippon Educational and Cultural Centre
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoCoal ash surge at N’cholai power plant raises fresh environmental concerns
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoHuawei unveils Top 10 Smart PV & ESS Trends for 2026