Features
Towards necessary exercise in discursive disentanglement?

(Prof. Sasanka Perera’s recent speech as guest speaker to the National Academy of Sciences)
In present times, there is an intriguing, but at times seemingly dangerous entanglement between science, belief and state policy or government action. This kind of phenomena range from the government’s sudden ban of Glyphosate in 2015; the state sponsorship of a conference on the air power of the mythical king Ravana to the layers of stories surrounding the advent of what is now popularly known as the Dammika Peniya. These are merely three well-known phenomena from a whole series of such phenomena in the country with varying impacts on social life, politics and commerce. As a collective of occurrences with their own structure of associated events, these phenomena have not been reckoned with seriously. We have not carefully reflected upon them and asked ourselves why they are more evident now, and what their broader consequences and reasons for manifestation might be. As a result, we do not have credible sociological explanations for these phenomena that goes beyond popular rhetoric. These phenomena are seemingly dangerous too, because many of them defy what we might think of as commonsense and leads in the direction of collective chaos and counter-productive action on the part of the state. And in this journey, ‘science’ is one of the most obvious casualties.
To me, all this points to a contradictory entanglement involving science, belief, and state policy when ideally such contradictory entanglements should not take place. By ‘science’ I do not merely mean the vast systems of knowledge that originated in the west, which now have global hegemony including in our country. Instead, science is any system of knowledge “concerned with the physical world” and phenomena emanating from this world along with formal “observations and systematic experimentation.”i In other words, a “science involves a pursuit of knowledge” that covers “general truths” as well as “the operations of fundamental laws.”ii In this sense, Ayurveda, Unnani, present day engineering, allopathic medicine or any other system of formal knowledge are mostly matters of science though the bases for their fundamentals would vary considerably from the more dominant post-enlightenment sciences to much older systems of knowledge.
Similarly, by ‘belief’, I mean not only matters of faith rooted in religion and tradition but also contemporary beliefs that are created by the repetitive circulation of ideas across media whether they are based on fact and science or not. Often, these ideas address contemporary issues and politics though they might be camouflaged in a rhetoric of the past, resort to specific conventions, and identity politics. And these associations are quite important today given the propensity for fake news and the enhanced ability of people to accept these ideas easily without being formally countered.
In the same sense, ‘state policy’ and actions linked to such policies are expected to be based on formal legal principles and empirical facts, and ideally should have nothing to do with matters of faith or untested assumptions and should benefit the polity.
Generally, I consider science, belief, and state policy to be independent discourses with their own epistemological routes and purposes though there will be close and necessary interactions among these such as between science and state policy. At other times, as we are seeing now, this association can be between belief and state policy where science might be eclipsed.
My intention today is to simply place in context three recent phenomena of this kind that are structurally very similar but contextually very different, which I think would explain to some extent how this amalgamation of discourses function, and the ways in which their politics manifest. As far as I am concerned, what I have to say today are simply preliminary thoughts about which I would like to think further and theorize.
Phenomenon 1: Glyphosate Ban
The use of the weedicide glyphosate was banned by presidential order in 2015. In a paper published in the same year, Jayasumana, Gunatilake and Siribaddana note that people in areas where kidney disease has become endemic have been exposed to multiple heavy metals and glyphosate.iii Their conclusion as far as I could see as a non-expert, was very vague, which amounted to the following observation: “Although we could not localize a single nephrotoxin as the culprit” “multiple heavy metals and glyphosates may play a role in the pathogenesis.”iv This is one of several public articulations related to this matter that has some semblance of what I may call scientific noise, but clearly inconclusive.
The ban was quite sudden and was implemented following on the heels of intense lobbying by Member of Parliament and Presidential Advisor, Reverend Athuraliye Rathana. He argued along with his supporters that this chemical caused chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in the North Central and Uva Provinces. But what is clear is no reliable and specific scientific evidence was offered by him or the President’s Office as the basis for the ban. In this overall process, it does not seem that the Registrar of Pesticides; Fertilizer Secretariat; Medical Research Institute and Tea Research Institute, all of whom could have presented valuable and more formal input into the decision were consulted. It almost seems that the ban found its genesis in the popular belief that chemicals are bad.
The fact that there is considerable prevalence of kidney disease in parts of the country is a fact, which needs to be more rigorously studied to work out its causes. Personally, I am not a supporter of excessive use of chemicals for anything including agriculture, and to the extent possible, I have made changes in my personal lifestyle to address this anxiety. But that kind of personal, emotional or popular anxieties cannot be the foundation for state level decision-making, particularly if the government and the people both subscribe to the idea of commercial agriculture and the eradication of hunger.
The consequences of the ban have been substantial in monetary terms. It caused production costs to increase substantially and the industry, particularly the tea sector, incurred losses up to 10-20 billion rupees annually while the ban lasted. Though the ban was eventually partially lifted, even at that time, no credible and conclusive data supporting the ban existed. So, it appears, that the ban was solely based on a popular and largely correct general belief of the negative impacts of chemicals, tempered by political rhetoric emanating from matters of faith and popular beliefs. I am sure we can all agree, while we can entertain popular beliefs or even conspiracy theories among people, if they are injected into broader politics and formation of state policy, that would have serious consequences as this event has shown. Part of the problem here is not only the undue credence given to freely circulating popular notions without situating them in the context of formal and reliable knowledge, information and science, but the ability of popular political leaders to convert untested ideas into practices of state policy and action without facing consequences.
Phenomenon 2: The State’s Embrace of Ravana
People of my generation will know that Ravana and his flying machine were merely elements in an interesting story in our youth while in some parts of the country specific local stories linked to this myth circulated. Unlike India and elsewhere in South Asia and in the east right up to Bali, there is no evidence of Ramayana performances which may have included a dramatization of the Ravana narrative in Sinhala cultural lore. But this situation has dramatically changed in recent times where Ravana’s popularity has rapidly increased among a cross section of the people, while his name and alleged historicity have also been openly embraced by the state.
By 2019, the story of Ravana had been directly appropriated by the Sri Lankan state and engrossed in a highly superficial but allegedly scientific discourse on aviation. In July 2019, Civil Aviation Authority of Sri Lankan organized a “conference of civil aviation experts, historians, archaeologists, scientists and geologists” in Katunayake.v The Authority’s Vice Chairman at the time, Shashi Danatunge told Indian media, “King Ravana was a genius. He was the first person to fly. He was an aviator. This is not mythology; it’s a fact. There needs to be a detailed research on this. In the next five years, we will prove this.”vi He further noted, “they had irrefutable facts to prove that Ravana was the pioneer and the first to fly using an aircraft.”vii The conference’s main conclusion was “that Ravana first flew from Sri Lanka to today’s India 5,000 years ago and came back.”viii Many conference participants in their own peculiar wisdom, dismissed the powerful stories narrating Ravana’s kidnapping of Lord Rama’s wife Sita, as a mere “Indian version.”ix For them, this was not possible because Ravana was a noble king.”x
Intriguingly, one part of the myth cluster became a fact while another became fiction based simply on nothing more concrete than emotional and nationalist appeal. The ideas expressed in public on this matter were not private articulations of individuals. Particularly the Vice Chairman of Civil Aviation was speaking as a representative of a state agency. Also, the general conclusions of the conference and the acceptance of the Ravana story as historical fact could simply not be entrained by formal historiography and archaeology.
By 2020, the same agency took its sense of scientificity of these claims even further by launching a research project looking for evidence of Ravana’s flying and his “aviation routes.”xi The theme of the project was, “King Ravana and the ancient domination of aerial routes now lost.”xii Towards this, the Civil Aviation Authority placed advertisements in national newspapers asking people to send in evidence they may have. The purported scientific objective and the reason for the Civil Aviation Authority’ central involvement in this state-sponsored effort was explained as follows: 1) Because the Civil Aviation Authority was “the main aviation regulatory authority in Sri Lanka,” it was the most logical entity to host such and effort, and 2) Because “there are multiple stories over the years about Ravana flying aircrafts and covering these routes” there was a necessity “to study this matter.”xiii
Though there are seemingly rational and seemingly scientific ‘noises’ in this episode, the entire exercise is enveloped in taking myth as fact, and that too, with the direct participation of the state.
Phenomenon 3: The Advent of the Dammika Peniya
Now we come to the advent of the Dammika Peniya which is formally known as ‘ශ්රී වීර භද්රධම්ම කොරෝනා නිවාරණ ප්රතිශක්ති ජීව පානය’ (Shri Vira Bhdradhamma Corona Nivaranana Prathishakthi Jiva Panaya). According to its inventor, Mr Dammika Bandara, the formula for the syrup was given to him by Goddess Kali in a dream. This is a crucial point in which the genesis of this syrup differs from the more formal discourses of knowledge in Ayurveda and Sinhala medicine, within which this claim is located.
It was a claim protected by rhetoric of local medical superiority, power of ancient knowledge and very loud articulations of cultural and political nationalism. But certain things need to be understood clearly. Even within the structure of faith and belief in Sinhala culture, goddess Kali, the alleged ultimate progenitor of the syrup is not known for healing. She is seen more as a powerful deity but with considerable destructive potential. More typically associated with healing is goddess Pattini. So, the claim seems to be out of place even in the context of conventional Sinhala myth and belief. Second, though Ayurveda and Sinhala medicine have associations with faith and ritual, the bulk of their formal discourses on medicine are based on experimentation, repetitive practice and fine-tuning and formally scripted knowledge or that which is handed over word of mouth across generations. My maternal grandfather wrote two books in the early 1970s after he had retired from his Ayurvedic practice and teaching. The first was called Rasayana saha Vajikarana (රසායන සහ වාජිකරණ) in which he presented a specific body of knowledge already known to his field, but with fine-tuning offered by his own practice and studies. The second, called Avinishchitha Aushada (අවිනිශ්චිත ඖෂධ) was very different. It dealt with a series of plants whose medical utility was unknown or unsure. In it, he dealt with the unknown, based on both generations of institutionalized uncertainty as well as conjecture on his part, but based on his long years of practice and observation. Both these point to the nature of the scientific discourse of contemporary Ayurveda.
Compared to this kind of background, Mr Bandara offers a set of contradictions. He is not a medical practitioner, but a mason by profession who runs a small Kali shrine in his neighborhood. However, his claim over having invented a treatment for Corona received massive publicity via media outlets supportive of the state and unreserved public support from numerous local and national political leaders including the Minister of Health and the Speaker of Parliament all of whom consumed the concoction in public along with some of their colleagues. This does not tantamount to formal state support as in the other two cases. But such open adulation and support by senior members of the government is a public performance of confidence for an untested medication with a dubious claim. These actions played a major role in ensuring large numbers of people flocking to Mr Bandara’s house in Kegalle in search of this ‘miracle’ drug – in the midst of a pandemic. This is not a general condemnation of traditional medicine. In the 1950s, the establishment of the Ayurvedic Research Institute was to offer traditional medicine a sound research and dissemination base and bring it on par with formal understanding of science. But Dammika Peniya has no such provenance; it simply came from a dream according to its inventor himself, and such provenance simply cannot be the basis for its public adulation by political leaders. Most criticisms of the concoction and its provenance were vociferously put down in public as acts of anti-nationalism and lack of respect for traditional culture. A dubious study involving several colleagues of the Wathupitiwala Hospital and a handful of test cases had taken place though it is not clear to me if this exercise even had ethical clearance. A committee consisting of medical professionals has now been appointed to undertake a clinical study of the concoction using acceptable clinical trial criteria and practices. Its results have not yet been published.
What does all this mean?
All these three incidents have several obvious things in common:
the core notions in all stories are based on popular assumptions and untested ideas;
they all have powerful political and state support directly or indirectly;
their main arguments are governed by belief whether tempered by faith or by the mere repetition of mass circulating non-facts; and
in all cases, science in the formal sense – from allopathic medicine, Ayurveda and natural sciences to archaeology and history – have been dispelled even though such input could have more sensibly impacted these discourses if they were formally made available.
Moreover, the public manifestation and power of these discourses became possible due to the very clear inability of the public services directly associated with these contexts to be guided by formally collected data and scientific conclusions and their inability to advise their political Masters, and withstand the pressures of political interference. Such political interference is obviously not based on advice from subject experts or from a clear political vision, but from short-term political agendas for popular mobilization. This main conditionality allowed these unstable claims to become part of national politics and in some cases become policy or in the very least lead to actions sanctioned by the state.
But how does one explain the massive public support especially for the last two incidents. I have noticed for many years that people in our country, and particularly the Sinhalas seem to have a desperate urge to be part of grand historical claims and narratives. But I have not yet been able to gather adequate data or theorize what might be going on. But one can tentatively make some observations. The rediscovery of Ravana and brining him from the pages of myth and epic narrative of the Ramayana to state-sponsored formal discourses of populist and non-empirical historicization, and therefore formal reiteration of myth itself shows the urge to control what might be thought of as a popular and powerful narrative of the past. The way in which Sinhalas have reinvented Ravana over the last decade or so is not only as an aviator, but also as an engineer, medical expert, inventor, scientist and scholar. And this is done within an idiom of nationalist discourse that insists a pre-Vijayan and wholly Sri Lankan civilization once existed in which Ravana is a central attraction. These claims also assert this civilization was somehow superior to the cultural landscape across the ocean in the rest of South Asia. This seems to me to be more like what anthropologists would call millenarian mythmaking where Ravana appears at least in part as a millenarian hero. Generally, millenarian stories, beliefs and heroes have to do with delivering a society from danger, introduction of new ideas and technologies to ensure the safety of a collective, and so on. Such stories generally manifest in times of crisis. In the case of the Ravana story, the preoccupation is to recreate an important place for Lanka in the broader political history of South Asia in the context of a politically unstable present.
Even the story of the Dammika Peniya has some of these millenarian features. After all, it was presented as a very local remedy for COVID 19 based on a lost Sri Lankan body of scientific knowledge delivered directly by a goddess in a dream. And that too at a time when people were desperate to be safe and keen to protect their livelihoods from the vagaries of Corona virus at a time the state’s effort at controlling it appeared to be faltering. The Peniya seemed to be a sign of miraculous deliverance from the island’s past glory emerging in the midst of its chaotic present.
To end this preliminary sketch let me refer to a final comment. It seems to me, these kinds of stories emerge in times of crises – be these emotional, social, or political crises. This is not unique to Sri Lanka, and can also be seen in many other parts of the world in structurally similar circumstances. These stories have their genesis in realms of conjecture. I am not objecting to the deployment of conjecture as such. Most good ideas in all our disciplines would often begin with conjecture. As we know, the philosophy of science has shown us the importance of “assumptions, foundations, methods” and “implications of science.”xiv Reflections in philosophy of science also indicate the efforts to distinguish between what is considered science and what is thought of as non-science.xv It is in the latter domain where untested conjecture would generally be located until they can be given a basis in science or dispelled.
In this general context, it seems to me, these stories allow people to be part of a more powerful and often a winning idea of history and hyper-real present even though that domain of belief might have very little or nothing to do with lived reality as such. Partly, these can also be seen as coping mechanisms in difficult and turbulent times. But these are clearly not remedies for very real socio-political or public health issues that can be utilized brazenly by the state as long as their core ideas remain in domains of belief and conjecture.
The collective failure that typifies our situation is the inability of many people to understand this commonsense and as a result, become dangerously entangled in the internal logic of these stories, which have no external empirical foundations except for the real-life calamities some of them might generate. It is also likely our political leaders consciously and deliberately promote these stories and phenomena to divert people’s attention from evolving crises.
In this situation, I find it unfortunate that Sri Lankan social sciences have not yet spent the time to collect these stories and study them more carefully in their border social and political contexts and offer a more coherent, empirically-based, and nuanced theoretical explanation.
(Sasanka Perera is a trained anthropologist and is a professor at South Asian University in New Delhi. This is the text of a guest lecture delivered at the Induction Ceremony of the National Academy of Sciences of Sri Lanka on 22 January 2021)
Features
The US-China rivalry and challenges facing the South

 The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
Thanks to the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies (RCSS), Colombo the above window of opportunity was opened on December 8th for those sections of the public zealously pursuing an understanding of current issues in global politics. The knowledge came via a forum that was conducted at the RCSS titled, ‘The US-China Rivalry and Implications for the Indo-Pacific’, where Professor Neil DeVotta of the Wake Forest University of North Carolina in the US, featured as the speaker.
A widely representative audience was present at the forum, including senior public servants, the diplomatic corps, academics, heads of civil society organizations, senior armed forces personnel and the media. The event was ably managed by the Executive Director of the RCSS, retired ambassador Ravinatha Aryasinha. Following the main presentation a lively Q&A session followed, where many a point of interest was aired and discussed.
While there is no doubt that China is fast catching up with the US with regard to particularly military, economic, scientific and technological capability, Prof. DeVotta helped to balance this standard projection of ‘China’s steady rise’ by pointing to some vital facts about China, the omission of which would amount to the observer having a somewhat uninformed perception of global political realities.
The following are some of the facts about contemporary China that were highlighted by Prof. DeVotta:
* Money is steadily moving out of China and the latter’ s economy is slowing down. In fact the country is in a ‘ Middle Income Trap’. That is, it has reached middle income status but has failed to move to upper income status since then.
* People in marked numbers are moving out of China. It is perhaps little known that some Chinese are seeking to enter the US with a view to living there. The fact is that China’s population too is on the decline.
* Although the private sector is operative in China, there has been an increase in Parastatals; that is, commercial organizations run by the state are also very much in the fore. In fact private enterprises have begun to have ruling Communist Party cells in them.
* China is at its ‘peak power’ but this fact may compel it to act ‘aggressively’ in the international sphere. For instance, it may be compelled to invade Taiwan.
* A Hard Authoritarianism could be said to characterize central power in China today, whereas the expectation in some quarters is that it would shift to a Soft Authoritarian system, as is the case in Singapore.
* China’s influence in the West is greater than it has ever been.
The speaker was equally revelatory about the US today. Just a few of these observations are:
* The US is in a ‘Unipolar Moment’. That is, it is the world’s prime power. Such positions are usually not longstanding but in the case of the US this position has been enjoyed by it for quite a while.
* China is seen by the US as a ‘Revisionist Power’ as opposed to being a ‘Status Quo Power.’ That is China is for changing the world system slowly.
* The US in its latest national security strategy is paying little attention to Soft Power as opposed to Hard Power.
* In terms of this strategy the US would not allow any single country to dominate the Asia-Pacific region.
* The overall tone of this strategy is that the US should step back and allow regional powers to play a greater role in international politics.
* The strategy also holds that the US must improve economic ties with India, but there is very little mention of China in the plan.
Given these observations on the current international situation, a matter of the foremost importance for the economically weakest countries of the South is to figure out how best they could survive materially within it. Today there is no cohesive and vibrant collective organization that could work towards the best interests of the developing world and Dr. DeVotta was more or less correct when he said that the Non-alignment Movement (NAM) has declined.
However, this columnist is of the view that rather being a spent force, NAM was allowed to die out by the South. NAM as an idea could never become extinct as long as economic and material inequalities between North and South exist. Needless to say, this situation is remaining unchanged since the eighties when NAM allowed itself to be a non-entity so to speak in world affairs.
The majority of Southern countries did not do themselves any good by uncritically embracing the ‘market economy’ as a panacea for their ills. As has been proved, this growth paradigm only aggravated the South’s development ills, except for a few states within its fold.
Considering that the US would be preferring regional powers to play a more prominent role in the international economy and given the US’ preference to be a close ally of India, the weakest of the South need to look into the possibility of tying up closely with India and giving the latter a substantive role in advocating the South’s best interests in the councils of the world.
To enable this to happen the South needs to ‘get organized’ once again. The main differences between the past and the present with regard to Southern affairs is that in the past the South had outstanding leaders, such as Jawaharlal Nehru of India, who could doughtily stand up for it. As far as this columnist could ascertain, it is the lack of exceptional leaders that in the main led to the decline of NAM and other South-centred organizations.
Accordingly, an urgent task for the South is to enable the coming into being of exceptional leaders who could work untiringly towards the realization of its just needs, such as economic equity. Meanwhile, Southern countries would do well to, indeed, follow the principles of NAM and relate cordially with all the major powers so as to realizing their best interests.
Features
Sri Lanka and Global Climate Emergency: Lessons of Cyclone Ditwah
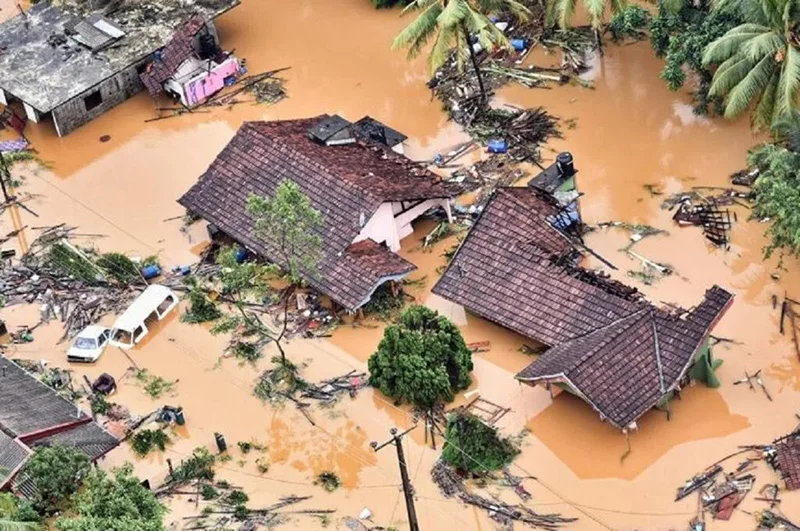

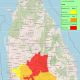
Tropical Cyclone Ditwah, which made landfall in Sri Lanka on 28 November 2025, is considered the country’s worst natural disaster since the deadly 2004 tsunami. It intensified the northeast monsoon, bringing torrential rainfall, massive flooding, and 215 severe landslides across seven districts. The cyclone left a trail of destruction, killing nearly 500 people, displacing over a million, destroying homes, roads, and railway lines, and disabling critical infrastructure including 4,000 transmission towers. Total economic losses are estimated at USD 6–7 billion—exceeding the country’s foreign reserves.
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have led the relief efforts, aided by international partners including India and Pakistan. A Sri Lanka Air Force helicopter crashed in Wennappuwa, killing the pilot and injuring four others, while five Sri Lanka Navy personnel died in Chundikkulam in the north while widening waterways to mitigate flooding. The bravery and sacrifice of the Sri Lankan Armed Forces during this disaster—as in past disasters—continue to be held in high esteem by grateful Sri Lankans.
The Sri Lankan government, however, is facing intense criticism for its handling of Cyclone Ditwah, including failure to heed early warnings available since November 12, a slow and poorly coordinated response, and inadequate communication with the public. Systemic issues—underinvestment in disaster management, failure to activate protocols, bureaucratic neglect, and a lack of coordination among state institutions—are also blamed for avoidable deaths and destruction.
The causes of climate disasters such as Cyclone Ditwah go far beyond disaster preparedness. Faulty policymaking, mismanagement, and decades of unregulated economic development have eroded the island’s natural defenses. As climate scientist Dr. Thasun Amarasinghe notes:
“Sri Lankan wetlands—the nation’s most effective natural flood-control mechanism—have been bulldosed, filled, encroached upon, and sold. Many of these developments were approved despite warnings from environmental scientists, hydrologists, and even state institutions.”
Sri Lanka’s current vulnerabilities also stem from historical deforestation and plantation agriculture associated with colonial-era export development. Forest cover declined from 82% in 1881 to 70% in 1900, and to 54–50% by 1948, when British rule ended. It fell further to 44% in 1954 and to 16.5% by 2019.
Deforestation contributes an estimated 10–12% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Beyond removing a vital carbon sink, it damages water resources, increases runoff and erosion, and heightens flood and landslide risk. Soil-depleting monocrop agriculture further undermines traditional multi-crop systems that regenerate soil fertility, organic matter, and biodiversity.
In Sri Lanka’s Central Highlands, which were battered by Cyclone Ditwah, deforestation and unregulated construction had destabilised mountain slopes. Although high-risk zones prone to floods and landslides had long been identified, residents were not relocated, and construction and urbanisation continued unchecked.
Sri Lanka was the first country in Asia to adopt neoliberal economic policies. With the “Open Economy” reforms of 1977, a capitalist ideology equating human well-being with quantitative growth and material consumption became widespread. Development efforts were rushed, poorly supervised, and frequently approved without proper environmental assessment.
Privatisation and corporate deregulation weakened state oversight. The recent economic crisis and shrinking budgets further eroded environmental and social protections, including the maintenance of drainage networks, reservoirs, and early-warning systems. These forces have converged to make Sri Lanka a victim of a dual climate threat: gradual environmental collapse and sudden-onset disasters.
Sri Lanka: A Climate Victim
Sri Lanka’s carbon emissions remain relatively small but are rising. The impact of climate change on the island, however, is immense. Annual mean air temperature has increased significantly in recent decades (by 0.016 °C annually between 1961 and 1990). Sea-level rise has caused severe coastal erosion—0.30–0.35 meters per year—affecting nearly 55% of the shoreline. The 2004 tsunami demonstrated the extreme vulnerability of low-lying coastal plains to rising seas.
The Cyclone Ditwah catastrophe was neither wholly new nor surprising. In 2015, the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) identified Sri Lanka as the South Asian country with the highest relative risk of disaster-related displacement: “For every million inhabitants, 15,000 are at risk of being displaced every year.”
IDMC also noted that in 2017 the country experienced seven disaster events—mainly floods and landslides—resulting in 135,000 new displacements and that Sri Lanka “is also at risk for slow-onset impacts such as soil degradation, saltwater intrusion, water scarcity, and crop failure”.
Sri Lanka ranked sixth among countries most affected by extreme weather events in 2018 (Germanwatch) and second in 2019 (Global Climate Risk Index). Given these warnings, Cyclone Ditwah should not have been a surprise. Scientists have repeatedly cautioned that warmer oceans fuel stronger cyclones and warmer air holds more moisture, leading to extreme rainfall. As the Ceylon Today editorial of December 1, 2025 also observed:
“…our monsoons are no longer predictable. Cyclones form faster, hit harder, and linger longer. Rainfall becomes erratic, intense, and destructive. This is not a coincidence; it is a pattern.”
Without urgent action, even more extreme weather events will threaten Sri Lanka’s habitability and physical survival.
A Global Crisis
Extreme weather events—droughts, wildfires, cyclones, and floods—are becoming the global norm. Up to 1.2 billion people could become “climate refugees” by 2050. Global warming is disrupting weather patterns, destabilising ecosystems, and posing severe risks to life on Earth. Indonesia and Thailand were struck by the rare and devastating Tropical Cyclone Senyar in late November 2025, occurring simultaneously with Cyclone Ditwah’s landfall in Sri Lanka.
More than 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions—and nearly 90% of carbon emissions—come from burning coal, oil, and gas, which supply about 80% of the world’s energy. Countries in the Global South, like Sri Lanka, which contribute least to greenhouse gas emissions, are among the most vulnerable to climate devastation. Yet wealthy nations and multilateral institutions, including the World Bank, continue to subsidise fossil fuel exploration and production. Global climate policymaking—including COP 30 in Belém, Brazil, in 2025—has been criticised as ineffectual and dominated by fossil fuel interests.
If the climate is not stabilised, long-term planetary forces beyond human control may be unleashed. Technology and markets are not inherently the problem; rather, the issue lies in the intentions guiding them. The techno-market worldview, which promotes the belief that well-being increases through limitless growth and consumption, has contributed to severe economic inequality and more frequent extreme weather events. The climate crisis, in turn, reflects a profound mismatch between the exponential expansion of a profit-driven global economy and the far slower evolution of human consciousness needed to uphold morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom.
Sri Lanka’s 2025–26 budget, adopted on November 14, 2025—just as Cyclone Ditwah loomed—promised subsidised land and electricity for companies establishing AI data centers in the country.
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake told Parliament: “Don’t come questioning us on why we are giving land this cheap; we have to make these sacrifices.”
Yet Sri Lanka is a highly water-stressed nation, and a growing body of international research shows that AI data centers consume massive amounts of water and electricity, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
The failure of the narrow, competitive techno-market approach underscores the need for an ecological and collective framework capable of addressing the deeper roots of this existential crisis—both for Sri Lanka and the world.
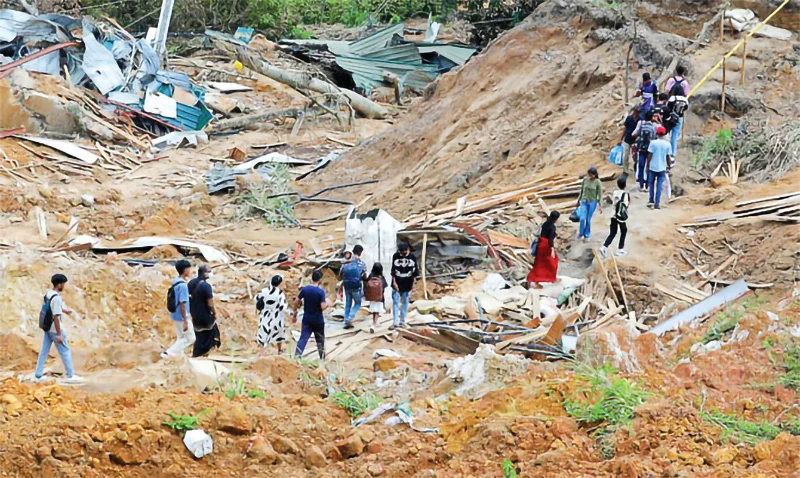

A landslide in Sri Lanka (AFP picture)
Ecological and Human Protection
Ecological consciousness demands
recognition that humanity is part of the Earth, not separate from it. Policies to address climate change must be grounded in this understanding, rather than in worldviews that prize infinite growth and technological dominance. Nature has primacy over human-created systems: the natural world does not depend on humanity, while humanity cannot survive without soil, water, air, sunlight, and the Earth’s essential life-support systems.
Although a climate victim today, Sri Lanka is also home to an ancient ecological civilization dating back to the arrival of the Buddhist monk Mahinda Thera in the 3rd century BCE. Upon meeting King Devanampiyatissa, who was out hunting in Mihintale, Mahinda Thera delivered one of the earliest recorded teachings on ecological interdependence and the duty of rulers to protect nature:
“O great King, the birds of the air and the beasts of the forest have as much right to live and move about in any part of this land as thou. The land belongs to the people and all living beings; thou art only its guardian.”
A stone inscription at Mihintale records that the king forbade the killing of animals and the destruction of trees. The Mihintale Wildlife Sanctuary is believed to be the world’s first.
Sri Lanka’s ancient dry-zone irrigation system—maintained over more than a millennium—stands as a marvel of sustainable development. Its network of interconnected reservoirs, canals, and sluices captured monsoon waters, irrigated fields, controlled floods, and even served as a defensive barrier. Floods occurred, but historical records show no disasters comparable in scale, severity, or frequency to those of today. Ancient rulers, including the legendary reservoir-builder King Parākramabāhu, and generations of rice farmers managed their environment with remarkable discipline and ecological wisdom.
The primacy of nature became especially evident when widespread power outages and the collapse of communication networks during Cyclone Ditwah forced people to rely on one another for survival. The disaster ignited spontaneous acts of compassion and solidarity across all communities—men and women, rich and poor, Buddhists, Christians, Muslims, and Hindus. Local and international efforts mobilized to rescue, shelter, feed, and emotionally support those affected. These actions demonstrated a profound human instinct for care and cooperation, often filling vacuums left by formal emergency systems.
Yet spontaneous solidarity alone is insufficient. Sri Lanka urgently needs policies on sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate resilience. These include strict, science-based regulation of construction; protection of forests and wetlands; proper maintenance of reservoirs; and climate-resilient infrastructure. Schools should teach environmental literacy that builds unity and solidarity, rather than controversial and divisive curriculum changes like the planned removal of history and introduction of contested modules on gender and sexuality.
If the IMF and international creditors—especially BlackRock, Sri Lanka’s largest sovereign bondholder, valued at USD 13 trillion—are genuinely concerned about the country’s suffering, could they not cancel at least some of Sri Lanka’s sovereign debt and support its rebuilding efforts? Addressing the climate emergency and the broader existential crisis facing Sri Lanka and the world ultimately requires an evolution in human consciousness guided by morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom. (Courtesy: IPS NEWS)
Dr Asoka Bandarage is the author of Colonialism in Sri Lanka: The Political Economy of the Kandyan Highlands, 1833-1886 (Mouton) Women, Population and Global Crisis: A Politico-Economic Analysis (Zed Books), The Separatist Conflict in Sri Lanka: Terrorism, Ethnicity, Political Economy, ( Routledge), Sustainability and Well-Being: The Middle Path to Environment, Society and the Economy (Palgrave MacMillan) Crisis in Sri Lanka and the World: Colonial and Neoliberal Origins, Ecological and Collective Alternatives (De Gruyter) and numerous other publications. She serves on the Advisory Boards of the Interfaith Moral Action on Climate and Critical Asian Studies.
Features
Cliff and Hank recreate golden era of ‘The Young Ones’

 Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
The duo, who first performed together in the 1950s as part of The Shadows, brought the house down with their classic hits and effortless chemistry.
The concert, part of Cliff’s ‘Can’t Stop Me Now’ tour, featured iconic songs like ‘Summer Holiday’, ‘The Young Ones’, ‘Bachelor Boy’, ‘Living Doll’ and a powerful rendition of ‘Mistletoe and Wine.’
Cliff, 85, and Hank, with his signature red Fender Stratocaster, proved that their music and friendship are timeless.
According to reports, the moment the lights dimmed and the first chords of ‘Move It’ rang out, the crowd knew they were in for something extraordinary.
Backed by a full band, and surrounded by dazzling visuals, Cliff strode onto the stage in immaculate form – energetic and confident – and when Hank Marvin joined him mid-set, guitar in hand, the audience erupted in applause that shook the hall.
Together they launched into ‘The Young Ones’, their timeless 1961 hit which brought the crowd to its feet, with many in attendance moved to tears.
The audience was treated to a journey through time, with vintage film clips and state-of-the-art visuals adding to the nostalgic atmosphere.
Highlights of the evening included Cliff’s powerful vocals, Hank’s distinctive guitar riffs, and their playful banter on stage.

Cliff posing for The Island photographer … February,
2007
Cliff paused between songs to reflect on their shared journey saying:
“It’s been a lifetime of songs, memories, and friendship. Hank and I started this adventure when we were just boys — and look at us now, still up here making noise!”
As the final chords of ‘Congratulations’ filled the theatre, the crowd rose for a thunderous standing ovation that lasted several minutes.
Cliff waved, Hank gave a humble bow, and, together, they left the stage, arm-in-arm, to the refrain of “We’re the young ones — and we always will be.”
Reviews of the show were glowing, with fans and critics alike praising the duo’s energy, camaraderie, and enduring talent.
Overall, the Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin reunion concert was a truly special experience, celebrating the music and friendship that has captivated audiences for decades.
When Cliff Richard visited Sri Lanka, in February, 2007, I was invited to meet him, in his suite, at a hotel, in Colombo, and I presented him with my music page, which carried his story, and he was impressed.
In return, he personally autographed a souvenir for me … that was Cliff Richard, a truly wonderful human being.
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoFinally, Mahinda Yapa sets the record straight
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka: