Business
WNPS Anawilundawa wetland regeneration project achieves key milestones with generous support of Hemas Plc
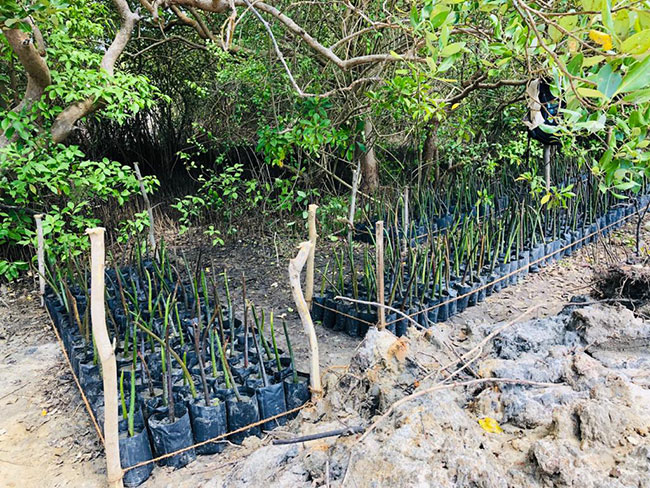

Sri Lanka’s current mangrove cover, estimated to be 15-000 19,000 Hectares, is a mere 0.3% of the total landmass and is critically low, putting the island at risk from the impact of climate change and natural disasters such as storm surges and Tsunamis. Mangroves are an integral part of our forests and constitute about 2% of Sri Lanka’s total forest cover – they are very much a part of the fast dwindling 17% of our primary forests.
WNPS’s Accelerated Natural Regeneration of Mangroves (ANRM) Project was launched with the goal of regenerating the damaged mangrove habitats in Anawilundawa Wetlands and building sustainable livelihoods in surrounding communities. The project aims to restore approx. 45 hectares (110 acres) of the mangrove ecosystem at Anawilundawa, which have been destroyed due to shrimp farming.
WNPS partnered the Department of Wildlife Conservation on this project in the first half of 2020 and despite the chaos caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, the project has successfully reached its initial milestones including recording of the faunal and floral species in a section of the surrounding habitats, creating a mangrove plant nursery using harvested seeds from the site and establishing baseline data for the project.
This important conservation project is to be conducted by Sri Lanka’s Department of Wildlife Conservation (DWC), Department of Forests (FD), Wayamba University (Science Partner), facilitated by the Wildlife & Nature Protection Society (WNPS).
Referred to as “Blue forests” coastal and marine ecosystems consisting of mangrove forests, seagrass meadows and tidal salt marshes are some of the most efficient carbon sequestration tools found in nature. They can store up to ten times more CO2 per unit area than tropical rainforest, making them a powerful weapon against global warming and climate. These natural ecosystems also play a key role in the country’s coastal protection and provides protection from storm surges and catastrophic events like floods & tsunamis. Not only this, mangrove ecosystems provide sustainable livelihoods for many rural communities.
In the late 1990’s over 50% of Sri Lanka’s Mangrove habitat was destroyed to establish Shrimp Aquaculture, severely affecting the functioning of coastal ecosystems. This destruction of ecosystems is compounded by the fact that it also cripples livelihoods that depended on Mangroves associated small industries like Artisanal Fishing, Firewood, Herbal Medicine and Tourism. Anawilundawa Wetlands was one such damaged habitat, which is a wetland ecosystem of global importance and one of six RAMSAR sites in Sri Lanka.
It is home to over 150 species of birds; both resident and migratory, 20 species of mammals and over 70 species of butterflies; whilst over 50% of the country’s freshwater fish species are found in these waters. Human intervention on restoration of mangrove habitats is needed to ensure that this destroyed habitat is brought back to its original glory, comprising all flora and fauna that were specific to the ecosystem.
This requires the careful systematic, scientific process of Accelerated Natural Mangrove Regeneration, with minimal external intervention. In addition, a critical dimension of this process is the engagement of local communities to ensure the regeneration of sustainable livelihoods in the communities that live around these mangrove habitats. The ANRM project takes into account all these elements and WNPS hopes to continue with upcoming project plans, now that the worst of the pandemic seems to be behind us.
WNPS is thankful to Hemas Consumer Brands who have come on board as a long-term financial partner on the ANRM project, to assist the regeneration of mangrove habitats as well as to enhance local livelihoods. Part of Sri Lanka’s Hemas Group, Hemas Consumer Brands, is a leading manufacturer in beauty and personal care sector. Their operations are focused on the three components of Sustainability; Environment, Social, and Economic and partner with conservation organisations on several environmental conservation projects to protect and restore Sri Lanka’s natural environment.
Founded in 1894, the Wildlife & Nature Protection Society (WNPS) focuses on the conservation of wildlife, forests, marine eco-systems as well as endangered species. Their mission is to protect Sri Lanka’s rich natural heritage by galvanizing policymakers, scientists, activists, nature lovers and the public; to preserve nature and wildlife through sustained conservation activities built on science, legislation, education and citizen mobilization. For the last 127 years WNPS has been working with many stakeholders including the government, scientists, policy makers, conservationists, educators, activists and the private sector, to protect Sri Lanka’s rich natural heritage of flora and fauna, for our future generations.
If you would like to find out more about the ANRM project, please visit www.wnpssl.org or email info@wnpssl.org
Business
Middle East escalation sends oil soaring; Sri Lanka faces price shock despite assurances on supply

Global oil prices surged sharply yesterday following coordinated US and Israel-backed strikes on Iran, and Tehran’s retaliatory attacks targeting US interests in the region, alongside escalating hostilities involving Hezbollah in Lebanon. The renewed instability in the Middle East – the artery of the world’s energy supply – has sent tremors through financial markets and triggered fresh anxiety in oil-importing nations such as Sri Lanka.
Brent crude climbed steeply in early Asian trading, with traders pricing in the risk of supply disruptions through critical maritime chokepoints, particularly the Strait of Hormuz, through which nearly a fifth of global oil passes. Market analysts say the spike reflects not only immediate supply fears but also the potential for prolonged geopolitical tension that could keep prices elevated for months.
Meanwhile, Asian equities reacted nervously to the unfolding crisis. Major indices across the region retreated as investors fled risk assets, concerned that higher energy costs could dampen growth and reignite inflationary pressures.
Asian oil and gas stocks – the only winner in Asian equity markets – rallied strongly, reflecting expectations of higher revenues amid rising crude prices. This divergence of falling broader markets alongside rising oil shares signals investor anticipation of higher inflation and weaker consumer demand in emerging markets like Sri Lanka.
Meanwhile, reports of increased Chinese crude purchases are further compounding market anxiety. If Beijing accelerates buying to secure strategic reserves in anticipation of supply constraints, global prices could climb even further because China’s procurement strategy has great influence on the world oil price.
“Should Chinese demand rise while Middle Eastern exports face disruption, the supply-demand imbalance could tighten considerably, amplifying volatility in global energy markets”, say global energy market analysts.
In Sri Lanka, long queues have begun forming at fuel stations amid fears of shortages and higher pump prices once new shipments arrive. The government has sought to calm public nerves, stating that sufficient stocks are available for approximately one month and that fresh supplies are being sourced from India and Singapore.
Deputy Minister of Tourism, Dr. Ruwan Ranasinghe said that as Sri Lanka imports refined products primarily from India and trading hubs such as Singapore, direct disruptions to Middle Eastern sea routes would not immediately interrupt supply chains. He maintained that there is no cause for panic buying.
In an unusual show of political maturity, Prasad Siriwardena, an Opposition MP from the Samagi Jana Balawegaya (SJB) urged the public to remain calm and refrain from hoarding, warning that artificial shortages could emerge if panic-driven stockpiling spreads.
However, former minister Wimal Weerawansa criticised the government for failing to build a strategic reserve of at least three months, arguing that Sri Lanka’s total dependence on imported fuel leaves it dangerously exposed to prolonged geopolitical shocks.
Weerawansa contended that the government failed to anticipate the likelihood of US-Iran tensions escalating into direct confrontation and should have proactively guided petroleum authorities to secure adequate reserves in advance.
Meanwhile, an independent analyst told this reporter on the condition of anonymity that the global economic spillover could have wide-ranging consequences on Sri Lanka, outlining five factors.
Energy costs that feed into transportation, manufacturing and food prices
Tighter monetary policy risks as the Central Bank may hesitate to cut rates if inflation resurges
Slower growth as consumers and businesses reduce spending when energy costs rise
A widening trade deficit as Sri Lanka would face increased import bills
Pressure on the Rupee as increased dollar outflows for fuel imports could strain foreign exchange reserves
In conclusion, he said, “One can only hope that diplomacy prevails before oil’s surge turns into a sustained economic storm for the global economy.”
by Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
How ‘distant wars can quickly arrive at the domestic pump’

The harsh economic realities behind soothing words
Sri Lanka’s fragile economic recovery faces a renewed external threat as escalating conflict involving Iran sends global oil prices sharply higher, raising concerns over inflation, foreign reserves and fiscal stability.
While authorities insist there is no immediate fuel shortage, economists warn that prolonged instability in the Middle East could trigger a familiar and painful chain reaction in an import-dependent economy still recovering from its worst financial crisis in decades.
The state-run Ceylon Petroleum Corporation (CPC) confirmed that the country currently holds sufficient petrol and diesel stocks for more than a month.
Energy Minister Eng. Kumara Jayakody assured that scheduled shipments remain unaffected and urged the public to refrain from panic buying, warning that artificial demand could disrupt smooth distribution.
But behind those reassurances lies a harsher economic reality: Sri Lanka does not need a physical fuel shortage to suffer — a sustained spike in global crude prices alone could be enough.
Market jitters intensified amid fears that any escalation could threaten shipping through the Strait of Hormuz, the narrow maritime corridor through which a significant share of the world’s oil supply passes daily. Even speculation of disruption has historically been sufficient to push prices sharply upward.
Sri Lanka sources refined fuel from multiple markets, including India and Southeast Asia. However, global benchmark prices ultimately determine import costs. If crude prices remain elevated, the country’s monthly fuel import bill could surge — placing fresh strain on dollar reserves.
Higher oil prices would ripple across the entire economy. Transport, electricity generation, manufacturing, agriculture and food distribution are all energy-sensitive sectors. A sustained price increase could reverse recent gains in inflation control.
The Central Bank of Sri Lanka has worked to stabilise inflation and the rupee through tight monetary discipline. Analysts caution that a renewed oil shock could complicate this effort, widening the trade deficit and pressuring the exchange rate.
“Sri Lanka is structurally vulnerable to energy price shocks. Even without direct supply disruption, higher global prices immediately translate into macroeconomic stress, a senior economic analyst said.
The government is currently operating under strict fiscal consolidation targets as part of its recovery programme. A rising fuel bill could expand subsidy pressures or force politically sensitive fuel price adjustments.
Any increase in administered fuel prices would inevitably feed into cost-of-living pressures, testing public tolerance amid ongoing austerity.
Beyond oil markets, instability in the Middle East carries another risk: remittances. The Gulf region remains a key source of foreign employment for Sri Lankans and a crucial inflow of foreign exchange.
Any economic slowdown or labour disruption in the region could dampen remittance flows, reducing one of the country’s most stable dollar lifelines.
An energy expert said for Sri Lanka, the Iran conflict is not merely a distant geopolitical event. It is a potential economic stress test at a moment when stability remains hard-won.
“Whether this turns into a temporary price spike or a prolonged oil shock will determine how severely it tests the country’s recovery trajectory. For now, policymakers are watching global markets closely — aware that in today’s interconnected economy, distant wars can quickly arrive at the domestic pump.”
By Ifham Nizam
Business
SLT Group reports strong FY 2025 performance driven by cost savings and efficiency

The SLT Group reported substantial cost savings for the full year ended 31 December 2025, fuelling significant profit growth and demonstrating consistent execution throughout all key metrics. The strong performance was driven through disciplined expense management, reduced finance costs, and strategic operational improvements.
Group Performance
The SLT Group ended FY 2025 as a strong year, with substantial improvement in profitability. Profit After Tax (PAT) surged 221% versus the previous year to Rs. 10 billion, compared to Rs. 3.1 billion in FY 2024, sustained through cost savings, reduced finance costs, and steady revenue growth for fixed and mobile segments.
Group revenue grew 3% to Rs. 114.2 billion, with SLT PLC contributing a 2% increase and Mobitel reporting a stronger 5% growth. Operating expenses (excluding depreciation and amortization) was Rs. 72 billion, resulting in a 5.5% improvement in EBITDA to Rs. 42.2 billion and a 26.9% increase in operating profit to Rs. 14.2 billion.
Finance costs continued to decline as the Group reduced debt and benefited from lower interest rates, contributing to an 88% increase in Profit Before Tax to Rs. 11.3 billion. Group interest costs decreased 21% to Rs. 7,054 million, primarily attributable to finance cost reduction at SLT PLC.
Dr. Mothilal de Silva, Chairman of the SLT Group, commented, “The SLT Group’s financial performance for FY 2025 underscores the effectiveness of our strategic direction and the robustness of our operations. Through stringent cost management and prudent financial stewardship, we delivered significant improvements in profitability while simultaneously advancing both our fixed and mobile businesses. This performance reinforces our commitment to leveraging the momentum of 2025 to drive sustainable long-term growth and strengthen stakeholder confidence. I extend my sincere gratitude to all our stakeholders, particularly our loyal customers, for their continued trust, and to our employees for their dedication and outstanding resilience.
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-
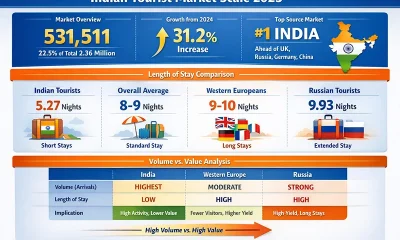
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans













