Features
Sustainable economic development in Sri Lanka: Role of mass media in transforming public beliefs and attitudes
By Dr. A K M R Bandara
Head/Department of Agricultural Systems
Faculty of Agriculture
Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka has been facing an economic crisis like never before. This crisis emerged with the COVID-19 pandemic mainly due to a drop in external earnings from tourism and foreign employment which are common to almost all countries in the region, including Bangladesh and India. However, those countries were able to recover due to the maintenance of external earnings reserves (buffer of dollars). Sri Lanka never gave much thought to reserving foreign earnings to face disasters, like COVID. The situation becomes acute with the incidence of repayment of interest and shares of foreign borrowings. Sri Lanka drew foreign loans substantially, after 2010, to develop highways, Mattala airport, and Nelum Pokuna which did not generate dollars to repay the loans. In this context, successive governments continued to borrow foreign loans to repay existing loans. Since the information on dollar inflows and outflows is not available to the public and the exchange rate is artificially controlled by the government, the dollar problem was not visible to the public until it has become a crisis.
There are lots of articles explaining the reasons for the economic problems, but no adequate information is available to resolve the problems. Factors affecting economic development have been discussed for over two centuries in the development literature in economics. Adam Smith, the father of economics, pointed out that low taxes, peace, and justices are the main factors that determine the economic development in 1776. However, evidence shows that economic development cannot be achieved by ensuring these three factors anymore, and it is more complicated when countries are struggling to achieve economic development that comprises of both quantitative and qualitative development. Quantitative development means an increase in quantity and value of the products and services of a country known as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) while qualitative development is the improvement of the quality of life of the people. When examining the development of many countries, including developed countries, economic development has been achieved mainly by changing the behaviour of the people. During the last 74 years, after independence, Sri Lanka has not given due attention to human aspects of economic development. Hence, the game of conflict instead of the game of cooperation, has grown in the country over the years and continues until now. The game of cooperation is necessary for economic development in which all individuals, politicians, and members of the society alike are searching for cooperative solutions for issues related to economic development.
Social transformation
In the case of social transformation, mass media can play a bigger role by increasing awareness. With the development of information and communication technology (ICT), passing information through media is very fast and effective. The media has already made a big impact on controlling corruption and changing political ideology from time to time through increasing awareness. Similarly, media can play a bigger role in economic development in the country. Today extensive awareness is going on highlighting who is wrong but not what should be done. Past is the past and it is not good to linger in the past. This article focuses on the role of mass media in economic development.
Performance (P) of a person depends on three factors: 1) knowledge (K), 2) skills (S) and 3) attitudes (A) known as KSA. Knowledge is to know things. It links with the brain. Skills are the ability to apply knowledge to do things and are linked with parts of the body because skills develop through doing things using hands, observing things through eyes, and hearing things through the ears. Attitudes are feelings, ideas, and thoughts and they link with the heart. There are two models explaining the relationship between performance and its determinants of knowledge, skills, and attitudes. One is the additive model (P= K+S+A) and another is the multiplicative model (P=K x S x A). The additive model is an old one and it says the performance of the person depends on three factors separately. For example, if the person has no skills, they will perform to some extent due to the other two factors but not to a great extent. Alternatively, the multiplicative model says that performance depends on three factors collectively. For example, if the person has no skills the performance is zero. In other words, performance and determinants work together and they are equally impotent to determine the performance of a person. This model has further improved giving more weight to the attitudes. Accordingly, the new performance model has the square of the attitudes (P = K x S X A2) illustrating that attitudes play a significant role person’s performance. Since economic development depends on the summation of individual performance, the highest priority should be given to the attitudinal changes in society. Mass media is the most effective tool in this regard. The following attitudinal changes are required for economic development.
Negative mindset
Society, especially public sector employees, has a negative mindset about privatization. This is mainly due to fear of losing jobs and benefits. It is necessary to highlight success stories in Sri Lanka and other countries through printed and electronic media. The best example is the privatization of the Department of Telecommunication in Sri Lanka. Before privatization people had to wait more than six months to get a connection even after payments. Similarly, repairing a breakdown took days and weeks. Now, the situation has completely changed. Also, employees are better off. Another negative attitude is setting up private entities. This is due to fear of competition. The principle is competition creates efficiency and efficiency leads to development. The best example is the banking sector. At the time of government monopoly with the presence of only the Bank of Ceylon and People’s Bank, customers were in the queue for a long time to deposit and withdraw money.
The situation completely changed with the establishment of the private banks.The society also has a negative attitude toward foreign direct investment. The most popular argument against foreign direct investments is the sale of national assets. Most countries, such as India, Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore, have developed with foreign direct investments. Countries need foreign investments to develop their economies because domestic savings are inadequate for investments which generate returns, such as foreign earnings, employment, and technologies. Competition is now high for foreign investments as many countries are encouraging foreign direct investments by providing facilities such as low-rent land, and tax reliefs. India established free trade zones to attract foreign investments. The principal objective of foreign investment is obtaining foreign money. One of the reasons for the current foreign currency crisis is negative attitudes regarding foreign direct investments.
Need for attitudinal change
Changing the attitude of the employees in the government sector is urgently required for economic development. Both local and foreign investors complained about the long process of getting things done through government organizations. Studies found that Turkey needs 6 hours for start-ups; Thailand needs 7 days and Sri Lanka needs more than 6 months. Moreover, employee productivity is low in Sri Lanka. In the garment sector, three people require getting the work done by one person in Pakistan. It is required to inculcate among employees that taxpayers’ money is spent on their salaries. The situation is more crucial in Sri Lanka because over 80 percent of the tax comprises indirect tax paid by the public. Government sector employees are the servants of the public, not the masters or puppets of politicians. The public should respect those who provide better services, not the title of the position. In the recent past, the government introduced a luxury bus service to travel from the railway station to government offices to reduce traffic in Colombo city. It failed because of attitude problems. High-ranking officials wish to come to the office by vehicle and have somebody to take their bags to the office. The situation is the same or worst with politicians.
The expenditure pattern of the households also needs to be changed for economic development. In Sri Lanka, unnecessary expenditure is high compared to income whereby the domestic saving ratio is low. It is less than 25% of the DGP whereas in India the figure is 35%. Sri Lankans spend huge amounts of money on house construction and purchasing vehicles because they have social value. There is a slogan in India that is “be Indians, act Indians”. The life of the Indian people is simple. They mainly depend on things produced in India. Also, they do not spend money unnecessarily. University lecturers use motorcycles to travel short distances including travel to university. The use of bicycles is common in Japan though it produces vehicles in large quantities.
The government is planning to declare the year 2023 as the year of agriculture. The success of this programme hinges on a change in the attitudes of the participants of the agricultural value chain. At present, farmers do not plan production based on the market requirements while traders are reluctant to provide information to farmers on market requirements. Also, traders hide pricing information and they do not like to establish relationships with farmers. Hence, the agricultural value chain in Sri Lanka is fragmented and disorganised resulting in high transaction costs, severe price fluctuations, low farm income, high consumer price, poor quality, and high post-harvest losses. It is an accepted fact that a sustainable agricultural value chain is required for agricultural development. Donor-funded projects such as Agricultural Modernisation Project, Smallholder Agribusiness Partnership Project, and Climate Smart Agriculture are developing agricultural value chains, but success is in question due to the lack of business discipline. In business, the customer is the king. There is no business without customers. Customers need quality, convenient and safe food at an affordable price.
Price control
In Sri Lanka, the popular mechanism used to stabilise food prices is price control. It is now an outdated tool that creates artificial shortages in the market resulting from the inability to supply products. The government does not have buffer stocks and no adequate foreign currency to import any more to solve this issue. Hence, the measures should be made to increase production in the country rather than controlling the price. For instance, India introduced a three crops programme to control vegetable price hikes. Under this, the most popular short terms crops were selected. Another issue in the value chain is low prices at the harvest time causing hardship to the farmers who are mainly depending on farming income. The farmers think that the government should purchase the products at a reasonable price. This is also an old concept and is not given priority at present because of huge financial losses incurred by the Treasury. This issue can be solved by delayed selling from time to time rather than selling the entire stocks at harvest time. The government’s role is to provide financial and technical facilities to set up farm-level storage facilities. There is no country where guaranteed prices are stipulated for perishables and prices are determined by market-led production planning.
Attitudinal changes are required in the decision-making process. Evidenced-based decisions are lacking. A scientific decision-making process should be adopted. It includes five steps: 1) identification of the problem, 2) finding alternative solutions, 3) evaluation of each alternative 4) selection of the best alternative, and 5) implementation of the best alternative. Also, proactive decisions are required instead of reactive decisions which are taken after the problem happened and provide solutions to the effect of the problem rather than the root causes of the problem.
In Sri Lanka, it is necessary to raise awareness of four management functions: planning, organising, directing, and controlling. Planning includes the formulation of vision, mission, objectives, strategies, and activities. Organizing is the allocation of resources and staff to implement the plan. Directing means the provision of instructions necessary to undertake activities. Controlling includes monitoring the project activities in line with the plan. Most of the projects formulated, especially in agriculture, are limited to the planning function and monitoring is poor in many foreign funded projects. Many countries in the region have established, long-term continuous plans one after another that does not alter with the change of ruling party of the government. For example, India is implementing the 12th five-year plan after independence. Also, monitoring reports are submitted every year to the parliament. Educating all the stakeholders including the community is essential for the success of government projects such as home gardening. Past projects such as home gardening and tree planting fail due to poor management. The media should be alert in these areas.
Youth participation in agriculture
Youth participation in agriculture is poor and there is a need to motivate the youth to return to this vital sector. There are success stories here as well as abroad. The global trend now is the promotion of high-tech agriculture such as precision agriculture and digital agriculture. In these fields, youth entrepreneurs are urgently required.
All in all, the necessary condition for economic development is attitudinal changes in the society. The role of mass media is to raise the evidence-based awareness to facilitate the attitudinal changes. Priority should be given to making awareness of how developed countries such as Japan recovered from their crisis after the World War II by changing attitudes. Print media can provide opportunities to publish articles while electronic media can provide opportunities for discussions. At present, the media is engaged in such activities, but those efforts are not adequate to change the mindset of the Sri Lankan society.
Features
Ukraine crisis continuing to highlight worsening ‘Global Disorder’
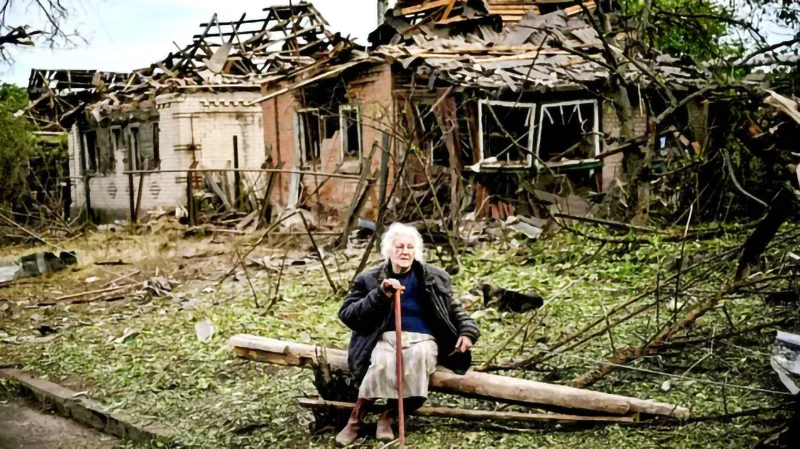

 The world has unhappily arrived at the 4th anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine and as could be seen a resolution to the long-bleeding war is nowhere in sight. In fact the crisis has taken a turn for the worse with the Russian political leadership refusing to see the uselessness of its suicidal invasion and the principal power groupings of the West even more tenaciously standing opposed to the invasion.
The world has unhappily arrived at the 4th anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine and as could be seen a resolution to the long-bleeding war is nowhere in sight. In fact the crisis has taken a turn for the worse with the Russian political leadership refusing to see the uselessness of its suicidal invasion and the principal power groupings of the West even more tenaciously standing opposed to the invasion.
One fatal consequence of the foregoing trends is relentlessly increasing ‘Global Disorder’ and the heightening possibility of a regional war of the kind that broke out in Europe in the late thirties at the height of Nazi dictator Adolph Hitler’s reckless territorial expansions. Needless to say, that regional war led to the Second World War. As a result, sections of world opinion could not be faulted for believing that another World War is very much at hand unless peace making comes to the fore.
Interestingly, the outbreak of the Second World War coincided with the collapsing of the League of Nations, which was seen as ineffective in the task of fostering and maintaining world law and order and peace. Needless to say, the ‘League’ was supplanted by the UN and the question on the lips of the informed is whether the fate of the ‘League’ would also befall the UN in view of its perceived inability to command any authority worldwide, particularly in the wake of the Ukraine blood-letting.
The latter poser ought to remind the world that its future is gravely at risk, provided there is a consensus among the powers that matter to end the Ukraine crisis by peaceful means. The question also ought to remind the world of the urgency of restoring to the UN system its authority and effectiveness. The spectre of another World War could not be completely warded off unless this challenge is faced and resolved by the world community consensually and peacefully.
It defies comprehension as to why the Russian political leadership insists on prolonging the invasion, particularly considering the prohibitive human costs it is incurring for Russia. There is no sign of Ukraine caving-in to Russian pressure on the battle field and allowing Russia to have its own way and one wonders whether Ukraine is going the way of Afghanistan for Russia. If so the invasion is an abject failure.
The Russian political leadership would do well to go for a negotiated settlement and thereby ensure peace for the Russian people, Ukraine and the rest of Europe. By drawing on the services of the UN for this purpose, Russian political leaders would be restoring to the UN its dignity and rightful position in the affairs of the world.
Russia, meanwhile, would also do well not to depend too much on the Trump administration to find a negotiated end to the crisis. This is in view of the proved unreliability of the Trump government and the noted tendency of President Trump to change his mind on questions of the first importance far too frequently. Against this backdrop the UN would prove the more reliable partner to work with.
While there is no sign of Russia backing down, there are clearly no indications that going forward Russia’s invasion would render its final aims easily attainable either. Both NATO and the EU, for example, are making it amply clear that they would be staunchly standing by Ukraine. That is, Ukraine would be consistently armed and provided for in every relevant respect by these Western formations. Given these organizations’ continuing power it is difficult to see Ukraine being abandoned in the foreseeable future.
Accordingly, the Ukraine war would continue to painfully grind on piling misery on the Ukraine and Russian people. There is clearly nothing in this war worth speaking of for the two peoples concerned and it will be an action of the profoundest humanity for the Russian political leadership to engage in peace talks with its adversaries.
It will be in order for all countries to back a peaceful solution to the Ukraine nightmare considering that a continued commitment to the UN Charter would be in their best interests. On the question of sovereignty alone Ukraine’s rights have been grossly violated by Russia and it is obligatory on the part of every state that cherishes its sovereignty to back Ukraine to the hilt.
Barring a few, most states of the West could be expected to be supportive of Ukraine but the global South presents some complexities which get in the way of it standing by the side of Ukraine without reservations. One factor is economic dependence on Russia and in these instances countries’ national interests could outweigh other considerations on the issue of deciding between Ukraine and Russia. Needless to say, there is no easy way out of such dilemmas.
However, democracies of the South would have no choice but to place principle above self interest and throw in their lot with Ukraine if they are not to escape the charge of duplicity, double talk and double think. The rest of the South, and we have numerous political identities among them, would do well to come together, consult closely and consider as to how they could collectively work towards a peaceful and fair solution in Ukraine.
More broadly, crises such as that in Ukraine, need to be seen by the international community as a challenge to its humanity, since the essential identity of the human being as a peacemaker is being put to the test in these prolonged and dehumanizing wars. Accordingly, what is at stake basically is humankind’s fundamental identity or the continuation of civilization. Put simply, the choice is between humanity and barbarity.
The ‘Swing States’ of the South, such as India, Indonesia, South Africa and to a lesser extent Brazil, are obliged to put their ‘ best foot forward’ in these undertakings of a potentially historic nature. While the humanistic character of their mission needs to be highlighted most, the economic and material costs of these wasting wars, which are felt far and wide, need to be constantly focused on as well.
It is a time to protect humanity and the essential principles of democracy. It is when confronted by the magnitude and scale of these tasks that the vital importance of the UN could come to be appreciated by human kind. This is primarily on account of the multi-dimensional operations of the UN. The latter would prove an ideal companion of the South if and when it plays the role of a true peace maker.
Features
JVP: From “Hammer and Sickle” to Social Democracy – Or not?

The National People’s Power (NPP), led by the Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP), came to power promising democratic renewal and long-awaited economic, educational, healthcare, and social transformation. It pledged to build a modern Sri Lanka rooted in democratic values while steering the country toward its vision of Democratic Socialism. For many supporters, the NPP’s rise to the pinnacle of political power represents a historic opportunity to reset the nation’s direction.
Yet recent developments have stirred unease. Statements by several senior ministers and certain policy signals have prompted critics to question whether the government’s path remains firmly democratic. Some warn that in the pursuit of rapid development and social justice, central pillars of the NPP’s election campaign, there may be a growing temptation to consolidate power in ways that edge toward policies of old “Hammer & Sickle.”
Is the NPP committed to pluralistic democratic socialism, or is Sri Lanka witnessing the early signs of a more centralised political model? To answer this question, it is necessary to revisit the JVP’s ideological history, examine the pressures that shape governing parties once in power, and weigh the potential consequences, both promising and perilous, of any shift in direction.
History of the JVP
The JVP emerged in the mid-1960s with a revolutionary agenda, mobilising youth through its Five Lecture Programme, which criticised capitalist policies, questioned the country’s “real independence,” opposed Indian influence, and called for armed struggle. This ideology culminated in the 1971-armed uprising against the elected government, leading to widespread violence, a harsh state crackdown, mass arrests, and the banning of the party.
Although suppressed, the JVP later re-entered democratic politics after its leaders were imprisoned and eventually pardoned. In the 1980s, after electoral defeat, the JVP shifted from strict Marxist-Leninist ideology toward a national, framework known as “Jathika Chinthanaya”, while maintaining strong opposition to Indian involvement.
However, it launched a second violent insurgency in 1988–1989, resulting in significant loss of life and severe repression, including the killing of its leader, Rohana Wijeweera. These events marked a decisive turning point, after which the party gradually moved away from armed struggle and embraced parliamentary politics.
By 1994, the JVP abandoned armed insurrection and embraced parliamentary democracy. While retaining its Marxist-Leninist identity, it adopted a more pragmatic socialist approach, seeking influence through elections rather than violence.
Embracing Parliamentary Democracy
The party served as Ministers and Deputy Ministers under President Chandrika Kumaratunga (2004–2005) and later supported Mahinda Rajapaksa in the 2005 presidential and subsequent parliamentary elections. Between 2005 and 2010, the JVP aligned with the Rajapaksa government in opposing federalism and supporting a unitary state.
Historically, the JVP opposed federalism. Under Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD), however, there appears to be a strategic shift toward decentralisation and inclusivity, without formally endorsing federalism. Since 2019, the NPP/JVP has criticised successive governments for failing to implement the 13th Amendment fully. This transformation is real and should be acknowledged.
Reports indicate the NPP/JVP is drafting a new constitution, but there is limited public clarity on its position regarding abolishing the Executive Presidency and devolving powers to Provincial Councils. Sri Lanka can chart a path toward a united, prosperous future where all citizens feel valued and represented. Therefore, I hope that NPP will consider the Provincial Councils in their current form might best serve as a relic of the past, making way for more cohesive and efficient systems of governance.
It is also a fact that many parties have historically criticised the Executive Presidency while in opposition, only to retain it in power. Whether the NPP/JVP will pursue genuine reform remains a subject of debate.
Democratic Concerns State Power
A recent statement by a senior Cabinet Minister that the party holds government power but has not yet “captured” broader state power raises fundamental questions. In a parliamentary democracy, winning government is the highest legitimate authority a party can obtain. Government power is temporary which is granted by voters, limited by the Constitution, and revocable at elections.
State power is permanent and it lies with state institutions i. e. the judiciary, administrative service, armed forces, law enforcement, and independent commissions. These bodies must remain politically neutral and serve the Constitution, to prevent any ruling party from dominating the permanent machinery of governance.
To frame democratic victory as incomplete without “capturing” state power, suggests a conception of power that goes beyond electoral legitimacy. It echoes a revolutionary mindset highlighting the real transformation requires ideological alignment of the state itself.
Past few decades, Sri Lanka has suffered from politicised institutions. Replacing one form of control with another is not reform, it is substitution.
Judiciary and Due Process
Public frustration over past corruption is understandable. However, allegations must be addressed through due legal process. In a democracy, individuals are innocent until proven guilty in a court of law. When parliamentarians publicly pass judgments on opposition figures before judicial proceedings conclude, it risks undermining the rule of law and raising concerns about political overreach.
Concerns are further heightened when there are perceptions that the rule of law is not applied equally, particularly if members of the governing party are treated differently in similar circumstances in the recent past. Unequal enforcement of legal standards can erode public trust in institutions. If such patterns persist, they may raise broader questions about the strength and impartiality of democratic governance.
Village-Level Courts

Democratic Concerns
State Power
In another recent statement, by a senior Minister reiterated one of his earlier proposals to establish judicial courts at the village level to adjudicate certain legal cases, depending on the nature and severity of the alleged offences. While improving local access to justice may enhance efficiency, such courts require strong institutional safeguards.
As this proposal raises serious concerns, it bears characteristics often associated with totalitarian systems, where village-level courts may be controlled by ruling party “cadres” who preside over legal matters and pass judgments against individuals. Without strong safeguards to ensure independence, transparency, and adherence to the rule of law, such courts could be misused to suppress dissent and curtail legitimate political opposition.
Any reform of the judicial system must uphold constitutional protections and preserve the separation of powers. Failing to do so could raise broader concerns about democratic accountability and institutional independence.
Civil / Administrative Service
Before 1978, Sri Lanka’s civil service was widely respected for its professionalism and independence. Over time, however, political appointments increasingly influenced senior administrative positions.
There are growing concerns that some recent appointments to high-level administrative service posts by the NPP may also be politically motivated. Many voters expected systemic reform and a decisive shift toward merit-based governance under the NPP/JVP. It is disappointing to observe indications that similar patterns of politicisation may be continuing.
The real test of reform lies not in rhetoric but in institutional safeguards. Transparent selection criteria, independent oversight mechanisms, and clear accountability structures are essential to ensuring that the administrative service remains professional and non-partisan.
History shows that democracy does not usually collapse overnight. It erodes gradually when ruling parties seek to align permanent institutions with their own ideological or political objectives.
Strengthening institutional independence is not optional, it is imperative. Sri Lanka’s democratic future depends not only on who holds power, but on how responsibly that power is exercised.
Media Freedom
“I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it”
(Evelyn Beatrice Hall, describing Voltaire’s belief in freedom of speech.)
Recent reports suggest the NPP/JVP government is dissatisfied with parts of the media, accusing some outlets of political bias and even proposing bans for allegedly spreading false information. Such actions would be undemocratic and would weaken constructive criticism.
Governments already possess legal remedies for defamation. If laws are inadequate, they may be reviewed. However, this must not undermine the media’s fundamental right to fair, independent, and legitimate criticism of those in power.
Every government dislikes criticism. But mature democracies tolerate it. Any attempt to restrict the media risks eroding democratic freedoms and should be adamantly opposed by all who value an independent media.
Religion and Public Conduct
In the past, opposition parties accused the JVP of being hostile to religion, particularly toward Buddhist monks aligned with political opponents. Confirming this accusation, recently a few NPP/JVP ministers, MPs, and party supporters have publicly criticised Buddhist monks who speak and organise meetings against the government.
At the same time, social media contains intolerable language about the conduct of certain Buddhist monks. While misconduct by members of the clergy is concerning, it does not justify hostile or disrespectful reactions from politicians or the public.
Responding with anger and division contradicts the very Dhamma many claim to defend. Using monks as political tools, or attacking them publicly, only deepens social divisions. If there are genuine concerns about the monastic order, they should be addressed respectfully through proper religious channels rather than through public humiliation.
Economic Democracy
Following Sri Lanka’s 2022 fiscal crisis, the NPP/JVP revised its economic policy and aligned itself with a framework closer to Social Democracy. This shift suggests that the JVP has accepted capitalism as the economic system necessary to revive the collapsed economy. At the same time, it has emphasised redistribution, welfare measures, and regulatory reforms aimed at reducing inequality.
The NPP/JVP’s economic policy now focuses on reforming capitalism rather than replacing it. The party initially sought to renegotiate the IMF agreement to ease the burden on the public. However, it was unable to secure significant changes. A key long-term objective remains reducing dependency on imports. The NPP aims to promote local industries and agriculture, while supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to reduce unemployment and expand export capacity.
Although the party pledged to strengthen state-owned enterprises through improved management rather than outright privatisation, recent developments indicate a shift toward public-private partnerships and selective privatisation.
Overall, economic progress is gradually aligning with these reformed Capitalist policies. This approach marks a significant departure from the original “Hammer and Sickle” ideology associated with classical Marxist theory as articulated by thinkers such as Karl Marx, Vladimir Lenin, and Friedrich Engels.
If judged solely on economic direction, the shift from revolutionary rhetoric to reformist governance appears substantial.
Bribery and Corruption
The nation is deeply grateful to the NPP government for taking bold steps to minimise bribery and corruption, which have long been a cancer eating away at our society. For decades, this practice has existed from top politicians to the lowest levels of the state sector, and even within society at large. Full credit must be given to the NPP government for prioritising the fight against this unethical and deeply rooted problem. It is hoped that the law will be applied equally to everyone, irrespective of status or party affiliation.
However, the public remains sceptical about the delay in pressing charges against the alleged culprits. During the election campaign, the JVP claimed that it possessed substantial evidence, over one hundred files, sufficient to prosecute members of previous governments accused of misusing public funds. Are they now discovering that the evidence is not as concrete as initially suggested?
Conclusion
Having analysed the current situation of the NPP/JVP, it is evident that there are conflicting statements from some senior figures in the JVP. Some favour the continuation of the traditional “Hammer and Sickle” policies. Others within the NPP emphasise and implement aspects of Social Democratic policies. Considering these differences, the nation is entitled to seek clarity regarding the government’s present direction.
It remains to be seen whether the JVP is merely marking time before reintroducing its former ideological policies, or whether it has genuinely chosen the path of Social Democracy.
By Gamini Jayaweera
Features
Valentine’s Day fundraiser … a huge success
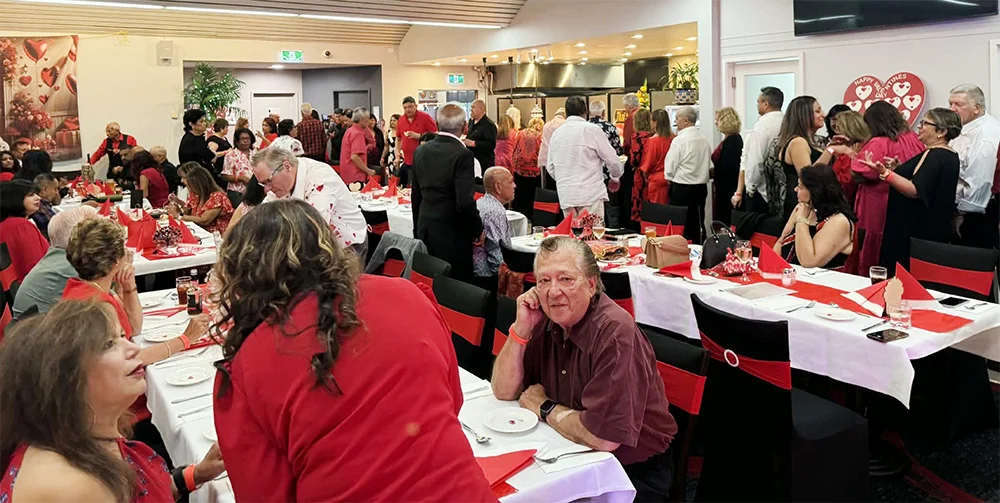

In Melbourne, Australia, catering veteran Chris Cannon hosted the annual Valentine’s Day fundraiser at the Springvale RSL, with all proceeds being donated to the Home of Compassion in Sri Lanka, run by the Mother Teresa Sisters.
The Valentine’s Day fundraiser was held on 14 February and the event featured music by Shey and George (of Redemption fame) and DJ Jeremy Ekanayake.

Shey and George providing the entertainment
The international buffet was a spread of Thai specialties and yummy Sri Lankan dishes and the large crowd present enjoyed the setup thoroughly, I’m told.
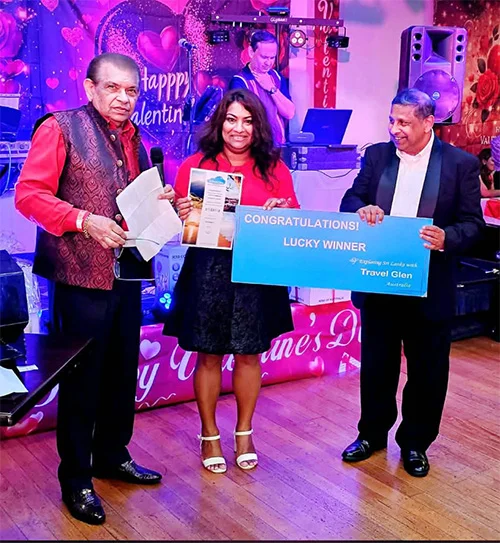

The lucky winner … trip to Sri Lanka
The Thai Street Food buffet was provided by Chris Cannon’s catering service, with his Thai wife, Annie, doing the needful.
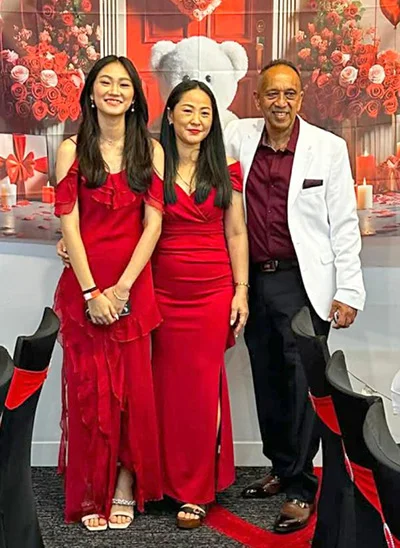

The Cannon Team: Alice, Annie and Chris
His daughter, Alice, also played an active part in this fundraiser.
Chris, a Sri Lankan-born Melbourne resident, who has been hosting this annual event for several years, with all proceeds going to charity, attributes the success of this Valentine’s Day fundraiser to the team that worked tirelessly to make it a happening event.

Rose and a teddy for the ladies
“I’m ever so grateful to the Team that was responsible for the success of this fundraiser. They all worked with enthusiasm and the smiles on their faces, at the end of the event, said it all.”
It was a sell-out, with every lady receiving a rose and a teddy but, unfortunately, said Chris “we had to disappoint several who wanted tickets as it was a limited space venue.”
What’s more, there were also attractive prizes on offer, including a seven nights stay in Sri Lanka.
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoWhy does the state threaten Its people with yet another anti-terror law?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoReconciliation, Mood of the Nation and the NPP Government
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoVictor Melder turns 90: Railwayman and bibliophile extraordinary
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoVictor, the Friend of the Foreign Press
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoNew Zealand meet familiar opponents Pakistan at spin-friendly Premadasa
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoTariffs ruling is major blow to Trump’s second-term agenda
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoECB push back at Pakistan ‘shadow-ban’ reports ahead of Hundred auction













