Opinion
Reducing Trade Deficit

By DR. C. S. WEERARATNA
A trade deficit typically occurs when a country does not produce enough goods for its citizens. When production cannot meet demand as in Sri Lanka, there is a need to import thereby widening the trade deficit. A persistent trade deficit is detrimental to a country’s economy because it is financed with debt. The trade deficit in Sri Lanka had been persistent over a long period of time (Table 1)
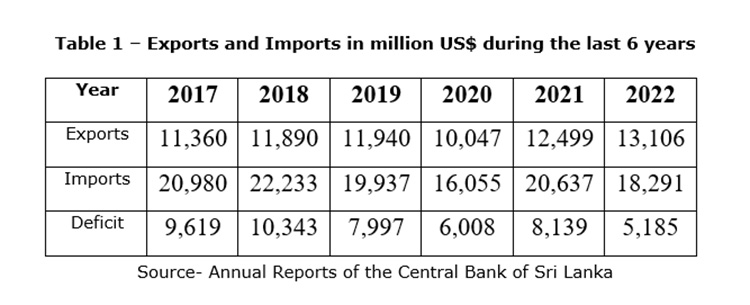 Persistent Trade Deficit tends to have a negative impact on employment, growth, and value of the currency. If we are to reduce the trade deficit it is essential that exports are increased and imports are reduced as much as possible.
Persistent Trade Deficit tends to have a negative impact on employment, growth, and value of the currency. If we are to reduce the trade deficit it is essential that exports are increased and imports are reduced as much as possible.
Increase export earnings
The dire need to increase our export earnings to meet the severe financial crisis we are facing today has been emphasised by many. As indicated in Table 1, exports during the last six years (this is the case even in earlier years) have not increased by any substantial amount in spite of an Export Development Board and numerous other related authorities. Increasing exports is of paramount importance to improve our economy. It is because of the importance of increasing exports that the government brought a National Export Strategy. But what are we going to export?
Plantation Sector
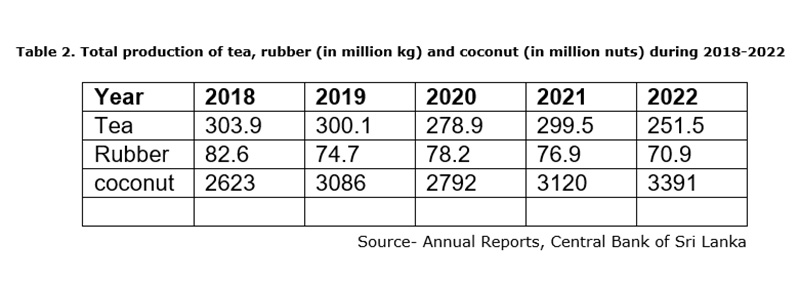
Our major exports are plantation crops, tea, rubber and coconut. Around 800,000 ha are cultivated with plantation crops. However, as indicated in Table 2, the production of these major export crops does not show any substantial increase during the last five years.
As shown in Table 2, tea production has been fluctuating around 275 million kg per year during the last few years. Annual rubber production shows a tendency to decrease. Coconut production has fluctuated around 300 million nuts per year. This appalling situation in the plantation sector can be attributed to many factors, but the Ministry of Plantation Industries and the relevant authorities appear to have not taken effective strategies to remedy this situation. If the productivity of this sector is raised, it would be possible to increase foreign exchange earnings thereby reducing the trade deficit. It is necessary that the relevant authorities take appropriate action to increase the production of the plantation crops.
A large number of crops other than tea, rubber and coconut cultivated in Sri Lanka have a high potential as export crops. There are 24 agro-ecological zones, each characterised by specific climate and soil. This makes it possible to cultivate different types of crops. Among these are spice crops such as cinnamon, pepper and nutmeg, tuberous crops, horticultural and floricultural crops, medicinal herbs etc. which have a considerable export potential. In 2020, spice crops earned around US $ 400 million. There are many organizations such as the Ministries of Agriculture, Industry and Commerce, Export Development Board, Industrial Development Board etc. but, there appears to be no proper plan to increase the production of these crops.
Out of the 6.5 million hectares of land, around 2.0 million hectares are in the Wet Zone. About 75% of it is cultivated and most of this land is of low-productivity mainly due to soil degradation. In the Dry Zone, out of the 4.5 million hectares only about 2 million hectares are in productive use. Thus, there is a large extent of potentially cultivable land in the Dry Zone. Most of the soils in the Dry Zone are relatively more fertile than those in the Wet Zone. Non-availability of adequate rainfall during the Yala season is one of the limiting factors of crop production in the Dry Zone. However, better water management practices would reduce this limitation. Also, various major irrigation projects such as Mahaveli, Kirindi Oya, Muthukandiya and Inginimitiya provide irrigation to about 200,000 hectares in the Dry Zone. The recently inaugurated Moraghakanda project is expected to provide irrigation water to nearly 80,000 ha. The numerous minor irrigation projects too would increase the irrigable area in the Dry Zone. Thus, there is a considerable potential to increase the level of crop production in Sri Lanka, export of which would enable to increase exports and reduce trade deficit.
Agro-Industries:
Promoting industries based on agriculture (agro-industries) will have a considerable positive impact on increasing export earnings thereby reducing trade deficit. There is an urgent need to develop agro-industries in Sri Lanka, which will have a tremendous positive impact on employment and rural poverty. A large number of crops cultivated in Sri Lanka, including rice, have a considerable potential in various agro-industries. However, only rubber, coconut and a few fruit crops are used in industries. Crops such as cassava, horticultural and floricultural crops, medicinal herbs, cane, bamboo, sunflower, castor, ayurvedic herbs such as katuwelbatu , etc. have a considerable potential as export crops, but are not cultivated to any appreciable extent for want of better and improved varieties, technological know-how, relevant market information etc. Development of agro-industries will also increase export income and will have a tremendous positive impact on the economy of the country, and also provide employment opportunities among rural people. Private sector can be involved in such projects for which appropriate technical assistance needs to be given by the relevant public organisations. However, there appears to be no proper long-term plan to develop agro-industries, except for some ad-hoc projects. The Ministries of Industries and Agriculture should implement an effective Agro-Industrial Development Programme, in collaboration with the private sector, which undoubtedly would improve export income, employment opportunities and incomes in the rural areas.
Small and Medium-Term Industries
Products of crop based Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), have a high export potential and play a very important role in economic development of Sri Lanka because they have the capacity to achieve rapid economic growth, while generating a considerable extent of employment opportunities. Promotion of SMEs would result in increasing industrial output of the country, leading to more exports. However, not much emphasis appears to have been placed on improving SMEs, except providing loans from banks. A main factor which limits the SME sector is inadequate raw materials.
Increasing cost of Imports
While some talk about strategies to increase exports, there appears to be not much emphasis on reducing crop-based imports, which will have an appreciable impact on reducing trade deficit. Our import costs are likely to increase due to escalation of freight costs as a result of Houthi attacks in the red sea. This will widen our trade deficit.
Most of the food imported such as sugar, milk food, lentils, onion, maize, etc., which involves around US$ 2,000 million annually, can be locally produced, thereby reducing expenditure on food imports. For example, nearly 16% of food imports is spent on importing sugar, most of which can be locally produced. Sugar production in the country has not increased by any appreciable amounts during the present decade in spite of three sugar companies, Pelwatta, Sevanagala and Hingurana and the Sugarcane Research Institute. Kantale sugar factory remains closed over a long period, while a plan to cultivate sugarcane in Bibile remains shelved. There are crops such as coconut, kitul and palmyrah which can be used to manufacture sugar-based substances such as jaggery and treacle, but there appears to be no effective strategy to promote the production of these crops.
With regard to milk production we have around 1 million cattle consisting of mostly indigenous breeds. Their productivity is low (1-3 litres/day) mainly due to the poor nature of the breeds and inadequate low-quality feed supply. As a result, annually we import nearly 300 million US dollars worth of milk and other dairy products. There appears to be no effective plan to increase local milk production by improving the local breeds and supply of cattle feed. The dairy industry has a potential to contribute considerably to Sri Lanka’s economic development. But, instead of implementing an effective viable plan to develop the dairy industry in the country, the government imported around 20,000 cattle from New Zealand and Australia involving USD 73 million. Importing cattle to improve the dairy industry in the country is a futile action, as importing cattle alone is not going to increase milk production in the long run, unless there is an effective programme to upgrade local cattle breeds, promote cultivation of improved pasture grasses which can be grown under coconut and provide better veterinary practices.
Nearly 300 million US dollars worth of rice (a carbohydrate) is imported annually when there are many tuberous crops such as innala, sweet potato, yams which can replace a part of the rice we import thereby reducing expenditure on imports.
Eppawala Apatite (EA), which was discovered a few decades ago still remains partly underutilized. EA can be used to manufacture phosphate fertilisers. But still we grind the rock and use the ground apatite as a P fertiliser, while spending millions to import Single Superphosphate and Triple Super Phosphate, which can be manufactured from EA.
The expenditure on subsidiary crops such as chillies, green gram, ground nut, potato etc, is millions of US dollars. The average per hectare yields and the extent of these crops have not increased by any appreciable amount during the last decade. In fact, chili production has decreased during the last few years. In the recent past, a former Minister of Agricultural Development Chamal Rajapaksa, appointed an Advisory Panel to make proposals to develop the agricultural sector in the country so that there is a quantitative and qualitative increase in crop production at a lower cost with no damage to the environment. During the last few years numerous programmes such as “AMA’, Waga Sangramaya and Govi Sevana” were implemented. All these activities/programmes, appear to have not made any appreciable positive impact on the agricultural sector of the country indicated by increasing expenditure on food.
Science and Technology.
Effective use of Science and Technology (S&T) would tend to reduce imports and increase exports. During the last two decades, effective use of Science and Technology (S&T) enabled most of the South and South East Asian countries to develop substantially. However, in Sri Lanka, in spite of a number of scientific organisations such as the National Science Foundation, National Institute of Fundamental Studies, National Research Council of Sri Lanka, National Science and Technology Commission, which use a considerable amount of scarce financial resources, S&T has been used to a relatively very little extent to decrease imports which will tend to reduce trade deficit thereby improving the economy of the country.
A primary objective of use of S&T in a developing country such as Sri Lanka must be to conduct appropriate studies on the critical issues and advise the authorities on relevant action to be taken. Science and Technology need to be used to utilise locally available resources. Conducting research alone will not lead to economic development, unless the technologies developed by research are commercialised. Organisations such as the Industrial Development Board, the Board of Investments etc. need to coordinate with the relevant scientific organisations to attract investments on commercialisation of proven technologies. Vidatha Centers have been established in many DS Divisions to commercialise S&T. Perhaps the Ministry of Technology and Research may indicate to what extent these Vidatha Centers have been effective in commercialising S&T.
In Sri Lanka, during the last two decades, perhaps a few hundreds of research studies, involving billions of rupees worth of scarce resources, have been conducted. Findings of these research projects were presented at numerous conferences, seminars etc. It is important that we utilise these research findings to find solutions to some of the pressing problems of the country. But there appears to be no effective system to achieve this. Instead, the authorities are concerned in conducting more and more seminars and symposia without any plan to effectively utilise the findings/conclusions.
The authorities concerned should discuss these issues and take appropriate action. There has been rhetoric on economic development during the last few years. It is meaningful and effective actions that are necessary.
Opinion
The unconscionable fuel blockade of Cuba
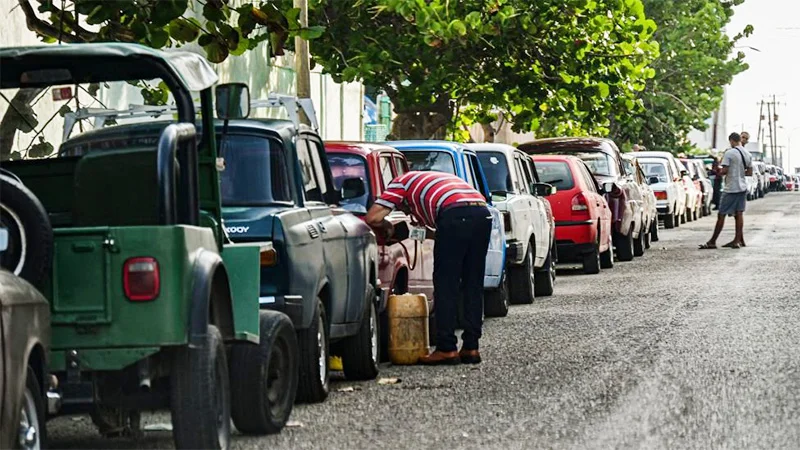

Cuba, a firm friend in need for Sri Lanka and the world, is undergoing an unprecedented crisis, not of natural causes, but one imposed by human design. It’s being starved of energy, which is almost as essential as water and air for human survival today. A complete and total embargo of oil in today’s world can only spell fatal, existential disaster, coming on top of the US economic blockade of decades.
The UN Secretary General’s spokesman has expressed the Secretary General’s concern at the “humanitarian situation in Cuba” and warned that it could “worsen, if not collapse, if its oil needs go unmet”.
Cubans are experiencing long hours without electricity, including in its hospitals and laboratories which provided much needed medicines and vaccines for the world when they were most needed. Cuba which relies heavily on tourism has had to warn airlines that they have run out of jet-fuel and will not be able to provide refueling.
Cuba is being denied oil, because it is being ridiculously designated as a “sponsor of terrorism” posing a threat to the United States, the richest, most powerful country with the most sophisticated military in the history of the world.
On the 29th of January 2026, the President of the United States issued an executive order declaring that the policies, practices and actions of the Cuban Government pose an “unusual and extraordinary threat… to the national security and foreign policy of the United States” and that there is “national emergency with respect to that threat”, and formally imposed what the Russian Foreign Ministry called an “energy blockade” on Cuba.
Responding within days to the US President’s executive order seeking to prevent the provision of oil to Cuba from any country, the Independent Experts of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) strongly condemned the act stating that “the fuel blockade on Cuba is a serious violation of international law and a grave threat to a democratic and equitable international order,” and that it is “an extreme form of unilateral economic coercion with extraterritorial effects, through which the United States seeks to exert coercion on the sovereign state of Cuba and compel other sovereign third States to alter their lawful commercial relations, under threat of punitive trade measures”.
They warn that the resulting shortages “may amount to the collective punishment of civilians, raising serious concerns under international human rights law”. They advocate against the “normalization of unilateral economic coercion” which undermines the international legal order and the multilateral institutions.
https://www.ohchr.org/en/press-releases/2026/02/un-experts-condemn-us-executive-order-imposing-fuel-blockade-cuba
Global Concern – Will Colombo add its voice?
The Group of G77 and China which has 134 countries issued a special communique in New York stating that “these measures are contrary to the purposes and principles of the Charter of the United Nations and international law, and undermine multilateralism, international economic cooperation and the rules-based, non-discriminatory, open, fair and equitable multilateral trading system with the World Trade Organization at its core.”
The Non-Aligned Movement also issued a communique expressing its “deep concern” at the “new extreme measures aimed at further tightening the economic, commercial and financial embargo imposed against the Republic of Cuba, including actions intended to obstruct the supply of oil to the country and to sanction third States that maintain legitimate commercial relations with Cuba.”
Sri Lanka is a member of both these groups. These two statements also speak for the Sri Lankan state, as well as all other members of these groups.
However, there has been no statement so far from Colombo expressing concern. One hopes that there will be one soon. One also hopes that this administration’s rightward turn in economics doesn’t also extend to abandoning all sense of decency towards those friends who stood by Sri Lanka when it needed them. This would not bode well for us, when we need help from our friends again.
The Sri Lankan parliament has a Cuba-Sri Lanka Friendship Association. Its President is Minister Sunil Kumara Gamage who was elected to this position for the Tenth Parliament. I hope the parliamentary friendship extends to at least expressing concern and solidarity with the Cuban people and an appeal for the immediate end to this extreme measure which has had such distressing impact on Cuba and its people.
Countries like Vietnam, Russia, China, Namibia and South Africa have already issued statements.
South Africa’s ruling African National Congress (ANC) has issued its own statement, strongly condemning this measure, calling it a “direct assault on the Cuban people” and a “deliberate economic sabotage and strangulation”. They call for “the immediate lifting of the fuel blockade and the trade embargo” calling on “the progressive forces and countries of the world, committed to progressive internationalism, peace, and prosperity, to join the ANC in solidarity against imperialist and colonialist aggression and to take further concrete actions in solidarity with Cuba.”
Before the JVP revealed itself in power to have metamorphosed into something other than its self-description before it was elected to government, with ubiquitous Che Guevara images and quotes at its rallies and party conventions, one would have expected something at least half-way as supportive from it. However, with new glimpses and insights into its trajectory in its current incarnation, one doesn’t really know the contours of its foreign policy aspirations, preferences and fears, which have caused an about-turn in all their previous pronouncements and predilections.
On a recent TV interview, a former Foreign Secretary and Ambassador/PR of Sri Lanka to the UN in New York praised the current President’s foreign policy speech, citing its lack of ideology, non-commitment to concepts such as “non-alignment” or “neutrality” and its rejection of ‘balancing’ as beneficial to Sri Lanka’s “national interest” which he went on to define open-endedly and vaguely as “what the Sri Lankan people expect”.
While this statement captures the unprecedented opacity and indeterminate nature of the President’s foreign policy stance, it is difficult to predict what this administration stands for, supports and thinks is best for our country, the world and our region.
Despite this extreme flexibility the administration has given itself, one still hopes that a statement of concern and an appeal for a reversal of the harsh measures imposed on a friendly country and long term ally at the receiving end of a foreign executive order that violates international law, could surely be accommodated within the new, indeterminate, non-template.
FSP, Socialist Alliance stay true
Issuing a statement on February 1st, the Frontline Socialist Party (FSP), the JVP breakaway, was the first to condemn and denounce the new escalation. It said in its statement that this “decision which seeks to criminalize and punish sovereign states for engaging in lawful trade with Cuba -particularly in relation to fuel supplies- represents an act of economic warfare and blatant imperialist coercion.” The FSP urged all progressive movements to “raise their voices against this criminal blockade and reject the normalization of economic aggression and collective punishment.”
The Executive Committee of the Socialist Alliance of Sri Lanka comprising the Communist Party of Sri Lanka, Lanka Sama Samaja Party, Democratic Left Front and Sri Lanka Mahajana Party, wasted no time in condemning what it called the “escalation of the decades-long criminal blockade” against Cuba by the United States. It said that the energy embargo has transformed “an inhuman blockade into a total siege” which it says seeks to “provoke economic collapse and forcible regime change”.
https://island.lk/socialist-alliance-calls-on-govt-to-take-immediate-and-principled-action-in-defence-of-cuba
In its strongly worded message issued by its General Secretary, Dr. G. Weerasinghe, the alliance calls on the government to demonstrate “principled courage” and to publicly condemn the “economic siege” at all international forums including the UN. It also asks the government to co-sponsor the UNGA resolution demanding an end to the US blockade, which seems unlikely at this stage of the administration’s rightward evolution.
The Socialist Alliance concludes by saying that “Silence in the face of such blatant coercion is complicity” and that this “imperialist strategy” threatens the sovereignty of all independent nations. However prescient these words may be, the government has yet to prove that terms such as “sovereignty” and “independence” are a relevant part of its present-day lexicon.
Cuba Flotilla
The plight of the people of Cuba under the energy blockade has moved those inspired by the Global Sumud Flotilla which sailed to Palestine with aid, to initiate a similar humanitarian project for Cuba. An alliance of progressive groups has announced their intention to sail to Cuba next month carrying aid for Cubans. It is called the “Nuestra América Flotilla” (https://nuestraamericaflotilla.org/).
While Mexico and China have already sent aid, the organisers recognise the need for more. David Adler, who helped organise the Sumud Flotilla is also helping the Cuba flotilla. This effort has been endorsed by the Brazilian activist who came into prominence and gained global popularity during the Sumud flotilla, Thiago Avila.
The organizers hope that this month’s successful Mexican and Chinese aid deliveries to Cuba may indicate that unlike in the case of the Sumud Flotilla to Occupied Palestine, the aid flotilla to Cuba will reach the people of Cuba without interception.
Shape of the emerging world order
At the on-going Munich Security Conference, the German Chancellor announced that the Rules-Based-Order has ended. With Europe dealing with the real threat of the forcible annexation of Greenland by the United State, their longtime ally, it is no wonder that he declared the end of the old order.
At the same venue, Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (AOC), Congresswoman representing New York, questioned whether the Rules-Based-Order ever existed, when the rules seem to apply only to some. Characteristically clear-sighted and forthright, the progressive US Democrat said exceptions to the rules were carved out in the world to suit the US and when that happens too often, those exceptions become the rule. She asked if we have actually been living in a “pre-Rules Based Order”, rather than one that had already been established.
Regarding the January oil blockade of Cuba, AOC issued a statement saying that the world is entering an “era of depravity”.
The UN has long advocated against Unilateral Coercive Action, which threatens countries with trade sanctions, financial restrictions, asset freezes and blockades without authorization by the United Nations system. These have also been referred to as “private justice”, which brings home the chilling nature of these measures.
Are these ruptures with even the bare minimum of predictable behaviour in international relations, the birth-pangs of a new era emerging in a world almost incomprehensible in its behaviour towards states and peoples, starting with the genocide in Occupied Palestine? The nightmares have not yet reached their peak, only signaled their downward spiral. With enormous US aircraft carriers circling Iran, what would the fate of that country and the region and perhaps the world be, in a few weeks?
Cuba is under siege right at this moment of danger. An exemplary country which helped the world when it faced grave danger such as the time of Covid 19, Cuba and the selfless Cuban people are now in dire need.
Cuba has never hesitated to help Sri Lanka, and could be relied on unconditionally for support and solidarity at multilateral forums. Sri Lankan medical students have had the benefit of training in Cuba and Cuban medicines and vaccines have served the world, as have their doctors. And now, as Cuban Ambassador Maria del Carmen Herrera Caseiro, who as a skillful young diplomat in Geneva in 2007-2009 was helpful to Sri Lanka’s successful fightback at the UNHRC, said at the UNESCO this month, the new blockade will “directly impact Cuban education, science and the communication sectors”.
Sri Lanka has consistently voted against the decades-long economic blockade of Cuba by the United States, whichever administration was in power. This recent escalation to a full embargo of fuel supplies to this small island struggling against an already severe economic blockade, requires a response from all those who have benefited from its generosity including Colombo, and every effort to prevent a humanitarian crisis on that island.
[Sanja de Silva Jayatilleka is author of ‘Mission Impossible Geneva: Sri Lanka’s Counter-Hegemonic Asymmetric Diplomacy at the UN Human Rights Council’, Vijitha Yapa, Colombo 2017.]
Sanja de Silva Jayatilleka
Opinion
Legislators’ pensions – Denying a legitimate expectation

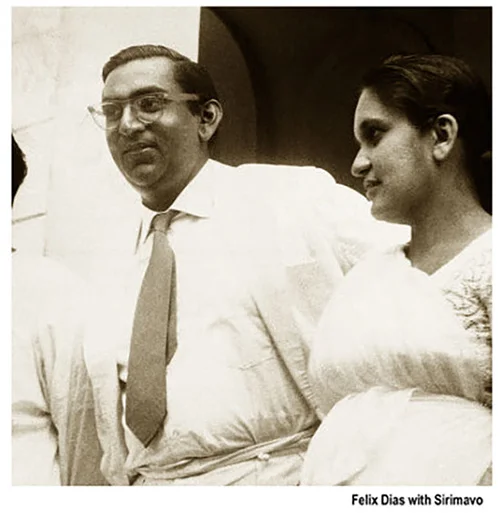
In 1976, the late Felix R. Dias Bandaranaike initiated the legislation that would provide a person who had retired after serving in the national Legislature for a minimum period of five years with a pension during his or her lifetime. The Parliamentary Pensions Act No.1 of 1977 is applicable to any Sri Lankan citizen who had served in the Legislature since July 7, 1931. A person who has served for the minimum period in the aggregate is entitled to a monthly payment of a pension amounting to one-third of the substantive monthly allowance currently payable to a Member of Parliament, and a maximum of two-thirds of such substantive monthly allowance if he has served for a period of fifteen years as such Member. The rationale for this legislation was to ensure that participation in the Legislature will not be the prerogative of the affluent.
The government now proposes to repeal this Act with retrospective effect. The Supreme Court has ruled that the Bill may be passed with a simple majority.
Unfortunately, the original 1977 Act was thereafter amended by successive governments in 1982 and 1990 to enable the payment of a pension, not only to a retired legislator, but also to a widowed spouse, and thereafter to any surviving children as well. Those amending Acts negated the purpose for which the original Act was enacted in 1977, and perhaps even contributed to the government’s decision to abolish the right to a pension altogether.
During the past fifty years, every person who was elected to the national legislature had a legitimate expectation that when he or she ceased to serve in that capacity, having done so for at least five years, that retiree will receive a monthly sum from the parliamentary non-contributory pension scheme. That is a statutory entitlement which retired legislators now enjoy in common with thousands of others who had similarly served the State in public or judicial capacities. In public law, a well-established concept is that of legitimate expectation. In their dealings with the public agencies, private persons are entitled to rely upon statements or decisions notified to them. That is the legitimate expectation of any citizen.
 It may be reasonable to deny a pension to a legislator who has subsequently been elected to the office of President and thereby become entitled to a presidential pension in terms of Article 36 of the Constitution. It may also be reasonable to deny (or perhaps suspend for a specified period) the payment of a pension to a legislator who has subsequently been disqualified from being elected to the legislature under Article 89 of the Constitution by reason of a conviction under the Bribery Act or for a corrupt practice under the law relating to elections, or upon being imposed a sentence of imprisonment for a period in excess of two years following a conviction for a criminal offence.
It may be reasonable to deny a pension to a legislator who has subsequently been elected to the office of President and thereby become entitled to a presidential pension in terms of Article 36 of the Constitution. It may also be reasonable to deny (or perhaps suspend for a specified period) the payment of a pension to a legislator who has subsequently been disqualified from being elected to the legislature under Article 89 of the Constitution by reason of a conviction under the Bribery Act or for a corrupt practice under the law relating to elections, or upon being imposed a sentence of imprisonment for a period in excess of two years following a conviction for a criminal offence.
The government, of course, has the right to decide to terminate the entitlement of a legislator to a pension. Parliament has the right to give effect to that decision. However, sound public policy requires that a law should be prospective, and not retrospective. The Parliament ought, therefore, to retain the Parliamentary Pensions Act No. 1 of 1977 (but not the 1982 and 1990 amendments) and provide that it shall not apply to any legislator who is elected to such office on or after the date on which the amending Act comes into force. It is significant that Article 36 of the Constitution, which declares the entitlement of the President to a pension, states quite explicitly that any amendment or repeal of that Article shall not have retrospective operation. Why, then, should legislators be subjected to a different standard?
by Dr Nihal Jayawickrama
Opinion
A paradox of history

There seems to be a striking similarity between ancient Greece and modern Britain. Both countries remain paradoxes of history. Greece was a small city state constantly at war with neighbouring countries. It did not have a big army, but it had considerable sea power. However, Greece was a leading state over the whole of the Mediterranean. In fact, Greece was once a super power in the Western world.
Britain was very powerful in the 19th century. British justice was administered in Africa, India and Ceylon. British factories flourished in many countries and schoolchildren started reading R.L. Stevenson’s ‘Treasure Island’ and the works of Rudyard Kipling. What Ralph Waldo Emerson said in the 1850s is still valid today. He said, “If there’s one test of national genius universally accepted, it is success; and if there be one successful country in the universe for the last millennium, that country is England. It is the best of actual nations.”
In World War I, Britain faced a crushing defeat. Eventually, the British Empire was reduced to a Commonwealth. World War II shattered the image of Britain further. Although Britain lost much of its power, it continued to be an influential country. Even after achieving independence, India retained English as an official language. The British parliament system is well established in many Commonwealth countries. Some people still wonder how England still exercises its influence over the minds of men and women.
Staying power
There are many powerful countries in the world today such as the United States, Russia and China. Although England is not a super power, she has staying power. According to Oliver Wendell Holmes, a good part of greatness is simply being there. For that matter, England has been there for many centuries. So far no other country has been able to defeat her. As a result, sometimes we wonder whether we can have a world without England.
England has had an unwritten Constitution for a very long time. Other countries have emulated her political institutions. The British people have an established church with complete religious freedom. Although there are social classes in Britain, there has been no major clash among them. Unlike in many other countries, there are only two leading political parties in England. When the Labour Party is in power, the government is not subservient to labour. Similarly, when the Conservative Party is in power, the government is not conservative.
Most British colonies in the East including India and Ceylon did not sever the cultural and emotional links with Britain and retain them even after achieving independence. India became independent in 1947, but she decided to retain English as an official language. By doing so, India produced a number of English writers such as R.K Narayan. However, Ceylon did not give English any official status and treated it as a link language. As a result, students paid less attention to learning English. They were made to understand that everything can be done by learning Sinhala and Tamil. We have failed to produce English writers in the calibre of J. Vijayatunga who wrote ‘Grass for my feet.’
Politically shrinking
The United Kingdom is politically shrinking. However, its influence vibrates throughout the world. English has brought many nations together. There is a common understanding among countries that share the English language and literature. William Shakespeare’s dramas are staged in countries such as China where English is not an official language. People have come to the conclusion that English has become a broker of ideas and institutions.
England is not an aggressive country. However, if provoked, it can deliver a mortal blow to its enemy. British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher showed her mettle as the iron lady. Britain held the fort against the might of Napoleon Bonaparte who ruled France. The country can still boast of a heavy moral credit. The British stick to their international agreements. The power of England draws mainly from its language. British people say ‘It’s right’ when it is right’. When it is not right, they say, ‘It’s not right.’ Meanwhile English occupies a pre-eminent place in world languages. All the research work in many parts of the world is available in English. You can learn any subject easily through English.
Apart from the language, people respect British standards which are technical specifications and quality benchmarks developed by the British Standards Institution. The United Kingdom’s independent national standards body was established in 1901. It maintains over 37,000 standards covering industries such as construction, manufacturing and technology ensuring safety and reliability.
British English
Standard British English is the variety of English that has undergone codification to the point of being socially perceived as the standard language associated with formal schooling, language assessment and official print publications. For historical reasons dating back to the rise of London in the ninth century, the form of language spoken in London and the East Midlands became the Standard English used in schools, universities, literature and law.
British English functions as one of the two major foundational and standard varieties of the English language alongside American English. It serves as a primary reference point for spelling and grammar. It acts as a global standard, and international institutions are often defined by specific pronunciation.
Most Sri Lankan doctors primarily move to England for postgraduate training, higher specialisation and better career prospects. They are driven by superior training infrastructure, world-class facilities and globally recognised qualifications.
To sum up, when you think of learning an international language, there is no alternative to English. If you wish to read literature, you cannot ignore eminent English dramatists and poets such as William Shakespeare and John Milton. Many leading Sri Lankans like S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike were Oxford University products. Therefore, English deserves to be made an official language in Sri Lanka.
By R.S. Karunaratne
-

 Life style2 days ago
Life style2 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:













