Opinion
Sri Lankan democracy enters new phase of forced retreat

Text of the speech delivered by
Prof. Jayadeva Uyangoda
at the launch of the book,
Democracy and Democratization in Sri Lanka: Paths, Trends and imaginations, September 09, 2023, at Kamatha Cultural Center Auditorium, BMICH. Prof. Uyangoda is the Editor of this two-volume publication.
I have no doubt at all that the Chairperson of the BCIS, the Board of Academic Affairs, the BCIS management, the chapter contributors, and the BCIS staff are delighted to see the two volumes of Democracy and Democratization in Sri Lanka: Paths, Trends and imaginations in print. This, as far as I know, is the first major academic publication undertaken by the BCIS. It is Madam Chandrika Kumaratunga’s vision, initiative, guidance and unwavering support that has made this notable achievement possible.
It is she who proposed this research project’s thematic focus. She trusted the Academic Board and the research team and gave them a free hand to develop and work on it. At the same time, I apologize to her on behalf of the team for giving her a few anxious moments.
There were some delays caused partly by the general crisis triggered by the Covid-19 pandemic. Besides, the missed deadlines set during normal times were unavoidable in a project of research and publication of this magnitude, carried out in a time of exceptional crises in our society, politics and the everyday life. For me as the lead researcher and the Editor, seeing these two volumes in print is a worthy reward for two and half years of hard labour.
Context
We at the BCIS began to conceptualize and plan this publication on the experience of democracy in our country, at a time when the Sri Lankan people were on the verge of losing their democratic heritage. When the year 2019 began, the threat of a hard authoritarian system replacing a weak and battered democratic order had indeed become alarmingly real.
We at the BCIS Board of Academic Affairs and its Chairperson felt that an analysis of why a promising democracy at the time of independence had failed so abysmally is a theme warranting critical scholarly inquiry and explanation.
Thus, we launched this research and publication project on democracy and democratization in Sri Lanka in mid -2020. As I have already mentioned, the Covid-19 Pandemic of 2021 came while we had just begun our work. It interfered with our project in a variety of ways, including halting most of the research.
More significantly, the Pandemic had led to a new political process in Sri Lanka. It can be termed as accelerated backsliding of democracy spearheaded by one faction of the ruling elites. It appeared almost like the last stage of Sri Lanka’s democracy.
But, Sri Lanka’s democracy, even in retreat, has shown that it has had some magical capacity for surprises. And that is exactly what we witnessed during the Spring and Summer of 2022. Sri Lankan citizens suddenly woke up demanding more democracy than what the political elites were willing to concede.
During the Aragalaya of 2022, the ordinary people, citizens without wealth or power, rose up demanding substantive democratic reforms. The ordinary citizens in their capacity as demos began to make claims to their ownership of democracy. They also highlighted that Sri Lanka’s democracy in general and representative democracy in particular, were in a deep crisis.
It was indeed an attempt by the people, demos, to re-generate as well as re-invent democracy in Sri Lanka. That is why the citizens’ protest in 2022 diserves to be acknowledged as a significant turning point in the somewhat twisted process of democratization in Sri Lanka.
In brief, the events of 2022 provided new perspectives and critical insights immensely useful to our own work on democracy and democratization in Sri Lanka. It showed us that the ordinary people play a powerful role as an agency for democratization. Their faith in democracy is far greater than that of the elites who exploit democracy for predatory ends. That is the spirit with which these two volumes evolved.
Organisation of the Book
The book has 22 chapters divided into two volumes. They are written by Sri Lankan scholars. The chapters are lined up under six themes which are as follows:
· Democracy in South Asia and Sri Lanka: Historical and Conceptual Contexts.
· Constitutional and Institutional Crises of Democracy in Sri Lanka.
· Democracy in the Social and Ethnic margins
· Alternative Forms of Democratic Thinking and Practice
· Democracy, Discontent and Resistance
· Protests as a Vector of Democratisation.
I want to share with you very briefly what I as the Editor see as unique about this book.
· This is the first book-length scholarly work exclusively devoted to the theme of democracy in Sri Lanka.
· All chapter contributors are Sri Lankan scholars who have been witnesses to the rise, decline and attempts at regeneration of democracy.
· The analysis developed in the chapters do not belong to a specific disciplinary area of the social sciences, such as political science or constitutional law. There is a plurality of approaches from the fields of social sciences and humanities.
· The book does not advocate or campaign for any particular version or variant of democracy. It argues for the plurality of democracy as a political concept and practice. Yet all chapter contributors stand for bringing the normative ethics of equality, freedom, justice and social emancipation back to the theory and practice of democracy.
Key Messages
What are the messages that these two volumes with chapters on diverse themes convey? Let me share with you a few of them that have a direct bearing on how we should view democracy and democratization anew.
· Democracy, as an organizing principle of political and social life, has strongly local social and popular roots in Sri Lanka as it has been the case elsewhere globally: It is a historical fact that modern democracy in Sri Lanka is an aspect of the European colonial legacy: However, people of Sri Lanka from various social classes have appropriated it and made use of it for their own social interests. In this process, there has been a double transformation. While the local society and its politics has been altered by liberal democracy, the local society has also changed the idea of democracy with a substantive, though subtle, critique of liberal democracy.
This has two theoretical implications. Firstly, the Sri Lankan people have not been passive recipients of a Western, European, or colonial, political idea. Secondly, they have played an active, agential role in appropriating and transforming that European idea. This book describes it as a creative process of ‘localizing democracy.’
· Ideas and practices of democracy have preceded the invention of the language of democracy
: Genealogies of the idea and practices of democracy predates its colonial origins in Sri Lanka and South Asia. The impulses and desires for democracy have always been there everywhere and whenever there were organized political power in the form of the state in pre-modern societies too. Historical and literary evidence in ancient and pre-colonial India and Sri Lanka show that the human desire for freedom from domination, independence, autonomy and justice have been integral to the social and political struggles within organized social formations.
It has been so in the processes of state formation in ancient Sri Lanka and South Asia, as elsewhere. This is the primary historical essence of ‘universalism’ of the idea of democracy. In other words, the idea and practices of democracy have been there in many forms in pre-colonial societies long before the language of modern democracy has been invented and the impulses for democracy rigidly formalized and frozen in meaning.
· The ordinary citizens are more faithful custodians of democracy than the elites:
Democratization is not a process confined to the activities of political elites as well as governments, as wrongly assumed in the mainstream democracy studies and assessments. The Sri Lankan case studies in the book show that democratization from below, at the level of the governed and the disempowered citizens, is most important in mapping paths of democratization in Sri Lanka. This thesis is valid to democracy’s liberal variant too.
The book shows that the dispossessed and the ordinary citizens, rather than the elites, have had a greater stake at defending and consolidating democracy. They have done it through the struggles of resistance against the elite-led de-democratization. The elites have domesticated, tamed, abandoned, and even became hostile to the liberal normative content of democracy.
People have also collaborated with backed the political elites in the latter’s projects of de-democratisation. However, in crucial moments of crisis the people, demos, have defended and deepened the idea and the normative content of even liberal democracy in Sri Lanka.
· Elite capture of liberal democracy has made democracy thin
: A lesson I have learned in the course of research for this book is that liberal democracy has the unintended consequence of dividing the population of Sri Lanka into two new classes in its own way: political elites and political non-elites. This has been a general pattern in other societies too.
Sri Lanka’s process of elite-led democratic backsliding has been paralleled with the introduction of representative government early last century. Elites who benefitted from the electoral, representative democracy have appropriated the liberal democracy and used it as an instrument for consolidating their social, economic, political and familial power.
Thus, the conception of democracy associated with Sri Lanka’s ruling elites has been a thin and truncated version of liberal democracy. Its role in democratization has now come to an effective end. Sri Lankan people await a strong democracy in terms of its social roots and normative commitments.
· Popular resistance to deprivations and unjust exercise of power has deepened the normative foundations of democracy in Sri Lanka
: The instrumentalist use of representative and parliamentary democracy by the elites is only one side of the story of democratization in Sri Lanka. In contrast, there is a subaltern story of democratization too.
The Left parties, working class, peasants, the working people, women’s groups, ethnic minorities, and student movements have contributed substantively to deepening the idea, the meaning, normative goals and the social relevance of Sri Lanka’s democracy. Through social practices of demands and direct political action for substantive equality and justice, they have shown how the limits of narrowly conceived and much abused representative democracy could be reformed. Thus, Sri Lanka’s democracy is not the monopolistic possession of the political elites. It is the inheritance of a plurality of non-elite social groups as well.
· Continuing conflict between democratic backsliding and popular demand for more democracy awaits a deep-democratic resolution:
Since independence, Sri Lanka’s democracy has evolved along two contradictory trajectories. The first is the path of democratic backsliding and de-democratization chosen by the elites. The second is the path of demanding and fighting for more democracy by the subordinate and non-elite social classes, trade unions and social movements, the civil society groups, and reformist elites.
The conflict between these two opposing paths is a major facet of the crisis of democratization in Sri Lanka. Its resolution presupposes a project of re-democratisation through radically substantive political and constitutional reforms.
What is Happening to Democracy
Let us briefly reflect on what is happening to democracy in Sri Lanka at present. Sri Lankan democracy seems to have entered a new phase of forced retreat engineered by the new ruling coalition. People of Sri Lanka who have yearend for the revival of democracy find themselves caught up in a new version of what our book calls the ‘de-democratization trap.
’ Its key feature has been the incorporation of ordinary citizens as disempowered voters to a deceitful social contract crafted by the political elites. As the citizen’s protests last year and this year have shown us, that deceitful social contract is now shattered. Citizens want to replace it with a deeply democratic and authentic social contract.
Meanwhile, there seems to be two processes of polarization of the Sri Lankan society into two hostile camps. The first is between the haves and have nots in the economic and social sense. The second is the growing enmity between the majority of the citizens who crave for more democracy and a minority of the elites who thrive on no democracy. The ways in which these polarities and contradictions will play themselves out are sure to shape the nature of politics of Sri Lanka in the months and years to come.
Returning to open democracy, more executive, legislative and judicial accountability, re-democratization of the constitution, the state, the government, and parliament, guaranteeing of economic and social justice to the poor, the working people and the middle classes are essential pre-conditions for resolving these contradictions peacefully with no recourse to violence by any side. That is also a message implicit in our book.
So, students of democracy in Sri Lanka will have a politically exciting time ahead. I and my collaborators sincerely hope that these two volumes will inspire a new interest in democracy studies among the young scholars in Sri Lanka. I am also hopeful that the readers will not fail to notice that the chapters have been written by a team of Sri Lankan scholars who have a deep passion for democracy.
Finally, let me thank a few people whose contribution to the success of this initiative warrants special acknowledgement. I have already referred to the inspiring and non-interventionist leadership provided by Madam Kumaratunga. Of course, it is our team of chapter contributors who have made these two volumes actually possible. They had the patience to tolerate the constant nagging by an impatient Editor and his support staff.
I must also mention the contribution made by our two copy-editors, Madara Rammunthugala and Nicola Perera, for refining the entire text. All reveiwers of the draft chapters also deserve my grateful acknowledgement for their contribution to ensuring the scholarly quality and standards of the publication. Suresh Amuhena designed the cover for us amidst many other commitments. Dr. Minna Taheer and Ms. Isuri Wickramaratna of the BCIS extended to me their assiatance throughout this project.
The BCIS staff Board of Academic Affairs and BMICH Board of Management ensured generous institutional support for the success of this entire intiative. Finally, Mr. Vijitha Yapa and his staff undertook the task of designing, printing and selling the book. All of them are partners of this worthy achievement. There are so many others who deserve my sincere thanks, and they are mentioned by name in the ‘Acknowledgements’ section book.
Finally, I am really happy that we have Professor Pratap Bhanu Mehta, an eminent scholar from India, as our keynote speaker. I will not take any more of your time to allow you to listen to his erudite presentation.
Opinion
Will computers ever be intelligent?

The Island has recently published various articles on AI, and they are thought-provoking. This article is based on a paper I presented at a London University seminar, 22 years ago.
Will computers ever be intelligent? This question is controversial and crucial and, above all, difficult to answer. As a scientist and student of philosophy, how am I going to answer this question is a problem. In my opinion this cannot be purely a philosophical question. It involves science, especially the new branch of science called “The Artificial Intelligence”. I shall endeavour to answer this question cautiously.
Philosophers do not collect empirical evidence unlike scientists. They only use their own minds and try to figure out the way the world is. Empirical scientists collect data, repeat and predict the behaviour of matter and analyse them.
We can see that the question—”Will computers ever be intelligent?”—comes under the branch of philosophy known as Philosophy of Mind. Although philosophy of mind is a broad area, I am concentrating here mainly on the question of consciousness. Without consciousness there is no intelligence. While they often coincide in humans and animals, they can exist independently, especially in AI, which can be highly intelligent without being conscious.
AI and philosophers
It appears that Artificial Intelligence holds a special attraction for philosophers. I am not surprised about this as Al involves using computers to solve problems that seem to require human reasoning. Apart from solving complicated mathematical problems it can understand natural language. Computers do not “understand” human language in the human sense of comprehension; rather, they use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to analyse patterns in data. Artificial Intelligence experts claim certain programmes can have the possibility of not only thinking like humans but also understanding concepts and becoming conscious.
The study of the possible intelligence of logical machines makes a wonderful test case for the debate between mind and brain. This debate has been going on for the last two and a half centuries. If material things, made up entirely of logical processes, can do exactly what the brain can, the question is whether the mind is material or immaterial.
Although the common belief is that philosophers think for the sake of thinking, it is not necessarily so. Early part of the 20th century brought about advances in logic and analytical philosophy in Britain. It was a philosopher (Ludwig Wittgenstein) who invented the truth table. This was a simple analytic tool useful in his early work. But this was absolutely essential to the conceptual basis of early computer science. Computer science and brain science have developed together and that is why the challenge of the thinking machine is so important for the philosophy of mind. My argument so far has been to justify how and why AI is important to philosophers and vice versa.
Looking at computers now, we can see that the more sophisticated the computer, the more it is able to emulate rather than stimulate our thought processes. Every time the neuroscientists discover the workings of the brain, they try to mimic brain activity with machines.
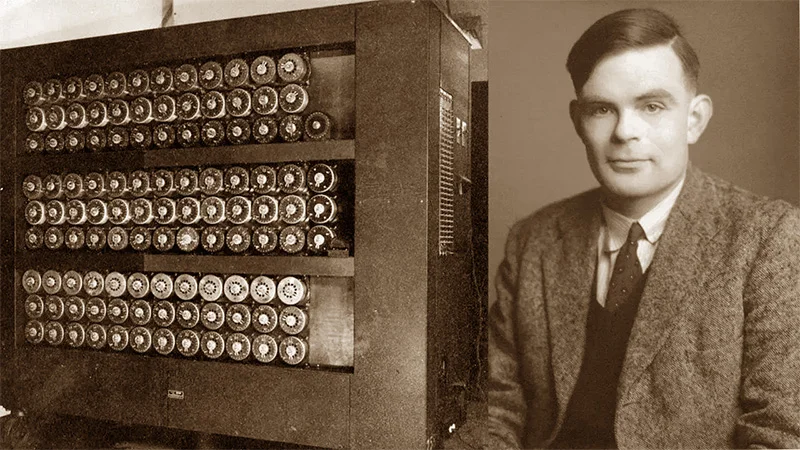
How can one tell if a computer is intelligent? We can ask it some questions or set a test and study its response and satisfy ourselves that there is some form of intelligence inside this box. Let us look at the famous Alan Turing Test. Imagine a person sitting at a terminal (A) typing questions. This terminal is connected to two other machines, (B) and (C). At terminal (B) sits another person (B) typing responses to the questions from person (A). (C) is not a human being, but a computer programmed to respond to the questions. If person (A) cannot tell the difference between person (B) and computer(C), then we can deduce that computer is as intelligent as person (B). Critics of this test think that there is nothing brilliant about it. As this is a pragmatic exercise and one need not have to define intelligence here. This must have amused the scientists and the philosophers in the early days of the computers. Nowadays, computers can do much more sophisticated work.
Chinese Room experiment
The other famous experiment is John Sealer’s Chinese room experiment. *He uses this experiment to debunk the idea that computers could be intelligent. For Searle, the mind and the brain are the same. But he warns us that we should not get carried away with the emulative success of the machines as mind contains an irreducible subjective quality. He claims that consciousness is a biological process. It is found in humans as well as in certain animals. It is interesting to note that he believes that the mind is entirely contained in the brain. And the empirical discovery of neural processes cannot be applied to outside the brain. He discards mind-body dualism and thinks that we cannot build a brain outside the body. More commonly, we believe the mind is totally in the brain, and all firing together and between, and what we call ‘thought’ comes from their multifarious collaboration.
Patricia and Paul Churchland are keen on neuroscientific methods rather than conventional psychology. They argue that the brain is really a processing machine in action. It is an amazing organ with a delicately organic structure. It is an example of a computer from the future and that at present we can only dream of approaching its processing speed. I think this is not something to be surprised about. The speed of the computer doubles every year and a half and in the distant future there will be machines computing faster than human beings. Further, the Churchlands’, strongly believe that through science one day we will replicate the human brain. To argue against this, I am putting forward the following true story.
I remember watching an Open University (London) education programme some years ago. A team of professors did an experiment on pavement hawkers in Bogota, Colombia. They were fruit sellers. The team bought a large number of miscellaneous items from these street vendors. This was repeated on a number of occasions. Within a few seconds, these vendors did mental calculations and came out with the amounts to be paid and the change was handed over equally fast. It was a success and repeatable and predictable. The team then took the sample population into a classroom situation and taught them basic arithmetic skills. After a few months of training they were given simple sums to do on selling fruit. Every one of them failed. These people had the brain structure that of ordinary human beings. They were skilled at their own jobs. But they could not be programmed to learn a set of rules. This poses the question whether we can create a perfect machine that will learn all the human transferable skills.
Computers and human brains excel at different tasks. For instance, a computer can remember things for an infinite amount of time. This is true as long as we don’t delete the computer files. Also, solving equations can be done in milliseconds. In my own experience when I was an undergraduate, I solved partial differential equations and it took me hours and a lot of paper. The present-day students have marvellous computer programmes for this. Let alone a mere student of mathematics, even a mathematical genius couldn’t rival computers in the above tasks. When it comes to languages, we can utter sentences of a completely foreign language after hearing it for the first time. Accents and slang can be decoded in our minds. Such algorithms, which we take for granted, will be very difficult for a computer.
I always maintain that there is more to intelligence than just being brilliant at quick thinking. A balanced human being to my mind is an intelligent person. An eccentric professor of Quantum Mechanics without feelings for life or people, cannot be considered an intelligent person. To people who may disagree with me, I shall give the benefit of the doubt and say most of the peoples’ intelligence is departmentalised. Intelligence is a total process.
Other limitations to AI
There are other limitations to artificial intelligence. The problems that existing computer programmes can handle are well-defined. There is a clear-cut way to decide whether a proposed solution is indeed the right one. In an algebraic equation, for example, the computer can check whether the variables and constants balance on both sides. But in contrast, many of the problems people face are ill-defined. As of yet, computer programmes do not define their own problems. It is not clear that computers will ever be able to do so in the way people do. Another crucial difference between humans and computers concerns “common sense”. An understanding of what is relevant and what is not. We possess it and computers don’t. The enormous amount of knowledge and experience about the world and its relevance to various problems computers are unlikely to have.
In this essay, I have attempted to discuss the merits and limitations of artificial intelligence, and by extension, computers. The evolution of the human brain has occurred over millennia, and creating a machine that truly matches human intelligence and is balanced in terms of emotions may be impossible or could take centuries
*The Chinese Room experiment, proposed by philosopher John Searle, challenges the idea that computers can truly “understand” language. Imagine a person locked in a room who does not know Chinese. They receive Chinese symbols through a slot and use an instruction manual to match them with other symbols to produce correct replies. To outsiders, it appears the person understands Chinese, but in reality, they are only following rules. Searle argues that similarly, a computer may process language convincingly without genuine understanding or consciousness.
by Sampath Anson Fernando
Opinion
Tradition, transformation, and China’s readiness as a global leader

Chinese New Year and the Spring Festival 2026:
The Chinese New Year, known domestically as the Spring Festival, is the most significant and widely celebrated cultural event in China. More than a public holiday, it represents a profound intersection of history, family, national identity, and future vision. As China prepares to celebrate Chinese New Year 2026, marking the Year of the Fire Horse, the nation does so with renewed confidence, cultural vitality, and strategic readiness, underpinned by the major achievements realized in 2025.
The festival reflects the harmony between continuity and change, demonstrating how traditions from thousands of years ago continue to guide and inspire the rhythm of modern life. It is a celebration not only of the calendar year but also of the enduring values of family, unity, renewal, and optimism.
Ancient Origins and Cultural Foundations
The origins of the Chinese New Year extend back more than 3,000 years, to early agrarian societies that organized their lives around lunar cycles. Early celebrations were closely linked to the agricultural calendar and seasonal transitions. Communities honored their ancestors, thanked nature for harvests, and performed rituals to seek prosperity, peace, and harmony in the coming year.
One of the most enduring and colorful legends associated with the festival is that of Nian, a mythical beast believed to appear at the turn of each year to terrorize villages. According to folklore, people discovered that Nian feared loud noises, fire, and the color red, which led to the invention of fireworks, firecrackers, lanterns, and red decorations—practices that remain central to the festival today.
The Spring Festival also follows the Chinese zodiac, a twelve-year cycle of animals, each symbolizing unique characteristics and influencing personality, fortune, and societal outlooks. These symbols continue to shape cultural expectations, social customs, and even business planning, illustrating the seamless blend of ancient wisdom with contemporary life. Despite centuries of change, the festival’s core values—family unity, respect for elders, gratitude, and hope for the future—remain unchanged.
The Year of the Fire Horse: Meaning, Dates, and Significance
Chinese New Year 2026 ushers in the Year of the Fire Horse, which will last from February 17, 2026, to February 5, 2027. The Horse is the seventh animal in the zodiac cycle and is traditionally associated with strength, independence, agility, vitality, and a pioneering spirit. The Fire element amplifies these qualities, symbolizing energy, courage, action, and transformation. Together, the Fire Horse embodies boldness, dynamism, and forward movement—traits mirrored in China’s economic, technological, and social aspirations.
Chinese New Year 2026 falls on Tuesday, February 17, 2026, with the official public holiday period in China running from February 15 to February 23, totaling nine days of national celebrations. The festivities extend beyond this period to 16 days, beginning on New Year’s Eve (February 16) and culminating with the Lantern Festival on March 3, 2026, when streets and public spaces glow with lanterns and dragon dances. Recent past and future Horse years include 1954, 1966, 1978, 1990, 2002, 2014, and 2026, each often associated with periods of significant movement, reform, or social transformation in Chinese history.
The Fire Horse year is regarded as particularly dynamic, characterized by rapid change, bold decisions, and a strong focus on independence—qualities that resonate with modern China’s trajectory toward global leadership.
Xiaonian: The Lively Prelude to the New Year
Before the Spring Festival itself, celebrations commence with Xiaonian (Little New Year), which marks the first stage of festive preparation. In northern China, Xiaonian falls on the 23rd day of the 12th lunar month, while in the south, it is celebrated on the 24th, reflecting centuries-old regional variations.
Xiaonian is traditionally linked to the Kitchen God, who reports the household’s deeds to heaven. Families offer sweets and symbolic foods, hoping for favorable blessings in the year ahead. Homes are cleaned thoroughly, sweeping away misfortune and making space for renewal. Though modern lifestyles have transformed certain rituals, Xiaonian retains its emotional significance, building anticipation and warmth for the grand reunion of the New Year. It represents the beginning of preparation, reflection, and hope.
Spring Festival Celebrations Across China
The Spring Festival spans 16 days, encompassing family reunions, regional fairs, cultural performances, and public spectacles.
Regional variations highlight China’s rich cultural diversity:
* Beijing and Northern China: Temple fairs are central, featuring folk music, opera performances, calligraphy, and crafts, alongside festive food stalls.
* Southern China (Guangdong, Fujian): Flower markets are a signature, with vibrant blooms symbolizing luck, prosperity, and renewal.
* Sichuan and Chongqing: Fireworks, spicy festival cuisine, and public performances dominate the celebrations.
* Historic provinces such as Shaanxi and Shanxi: Folk operas, paper-cutting, and drum performances preserve centuries-old traditions.
* Ethnic minority regions: Tibet, Yunnan, and Guangxi feature unique customs and performances that reflect cultural inclusivity.
Modern technology has amplified these traditions. Digital red envelopes (hongbao), livestreamed gala performances, and online marketplaces allow participation across cities and continents, showing how China merges heritage with contemporary innovation.
Key Traditions of Chinese New Year 2026
The Year of the Fire Horse comes alive through longstanding customs:
* Reunion Dinner: Families gather on New Year’s Eve, February 16, 2026, for sumptuous meals symbolizing unity and abundance.
* Home Decoration: Cleaning homes, hanging red lanterns, placing couplets, and displaying auspicious symbols prepare the household for a prosperous year.
* Red Envelopes (Hongbao): Elders gift children and unmarried adults money-filled red envelopes, wishing prosperity and good fortune.
* Fireworks and Firecrackers: A centuries-old tradition used to ward off evil spirits and invite good luck.
* Lantern Festival: Concluding the celebrations on March 3, 2026, communities showcase elaborate lantern displays, dragon dances, and family gatherings, emphasizing light, joy, and renewal.
Chunyun: The Spring Festival Travel Rush
An integral aspect of the Spring Festival is Chunyun, the annual travel rush marking the return of millions to their hometowns. Known as the world’s largest recurring human migration, it underscores the importance of family reunion in Chinese culture.
For 2026, Chunyun is expected to surpass previous records. Official projections estimate 9.5 billion cross-regional trips, including 540 million rail journeys and 95 million air trips. The peak travel period coincides with the official public holiday from February 15 to February 23, creating enormous pressure on transport networks.
China’s high-speed rail system, digital ticketing platforms, and smart logistics infrastructure manage this vast movement efficiently. Beyond logistics, Chunyun represents a remarkable societal phenomenon: a demonstration of national cohesion, familial bonds, and the scale of modern China’s capabilities.
China’s Achievements in 2025: Foundations for Leadership
As the nation celebrates the Year of the Fire Horse, it does so on the back of a remarkable year of progress in 2025:
* Economic Growth: China’s economy surpassed 140 trillion yuan (≈USD 20 trillion), achieving around 5 percent GDP growth despite trade tensions. This demonstrates resilience, scale, and structural stability.
* Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, quantum computing, high-speed rail, space exploration, and advanced manufacturing have propelled China into global leadership across key innovation sectors.
* Green and Sustainable Development: China reinforced its position as a leader in renewable energy, electric vehicles, low-carbon cities, and clean infrastructure, advancing the global energy transition.
* Global Engagement: Through trade, cultural diplomacy, and multilateral initiatives, China strengthened international cooperation, enhancing its role as a stabilizing global actor.
These accomplishments illustrate a nation capable of balancing tradition and innovation, social cohesion and global leadership.
Spring Festival as a Mirror of Modern China
The Spring Festival captures the essence of China’s evolution. From Xiaonian rituals to Chunyun, from the ancient zodiac to high-tech celebrations, the festival reflects a civilization that respects its past while confidently embracing the future.
The symbolism of the Fire Horse—energy, freedom, and action—resonates with the national trajectory: innovation-driven growth, inclusivity, cultural pride, and strategic global engagement. The festival highlights how tradition and modernity coexist, creating a society that is both rooted in history and prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.
Conclusion: Renewal, Reunion, and Global Readiness
Chinese New Year is more than a cultural event; it is a living manifestation of China’s identity and values. It represents family, tradition, renewal, and optimism, while showcasing the nation’s capacity for logistical sophistication, social coordination, and global engagement.
As lanterns glow in 2026, families reunite, communities celebrate, and cities shine—mirroring a nation that is culturally confident, economically resilient, technologically advanced, and globally influential. In the spirit of the Fire Horse, China embarks on the new year with bold energy, poised to act decisively, innovate continuously, and engage meaningfully with the world.
The Spring Festival of 2026 thus stands as a testament to China’s enduring cultural heritage and its readiness to contribute as a world leader in the decades ahead, combining the wisdom of tradition with the promise of a transformative future.
by Prasad Wijesuriya,
General Secretary, Sri Lanka – China Friendship Association
Opinion
The Walk for Peace in America a Sri Lankan initiative: A startling truth hidden by govt.

When we come to it
We, this people, on this wayward, floating body
Created on this earth, of this earth
Have the power to fashion for this earth
A climate where every man and every woman
Can live freely without sanctimonious piety
Without crippling fearWhen we come to it
We must confess that we are the possible
We are the miraculous, the true wonder of this world
That is when, and only when
We come to it.
· Concluding lines of the poem ‘A brave and startling truth’
(1995)
– Maya Angelou
Ven. Dr Melpitiye Wimalakitti Nayake Thera, Head Monk of the Wijesundararamaya, Asgiriya, Kandy, and the Chief Incumbent of the Gotama Viharaya Monastery, Fort Worth, Texas, USA, claims that the ongoing Texas to Washington Walk for Peace march led by the American monk of Vietnam origin Ven. Pannakara is ‘an initiative of ours’ (ape wedak). He made this claim during a recent podcast hosted by the well-known YouTuber and journalist Chamuditha Samarawickrema (CNB/February 5, 2026). The Huong Dao Monastery of Bhante Pannakara, who is leading the peace walk is close to the Gotama Viharaya Monastery of Wimalakitti Thera, who tells us that he has had a strong connection with Vietnamese monks and has already collaborated with them in many Buddhist activities.
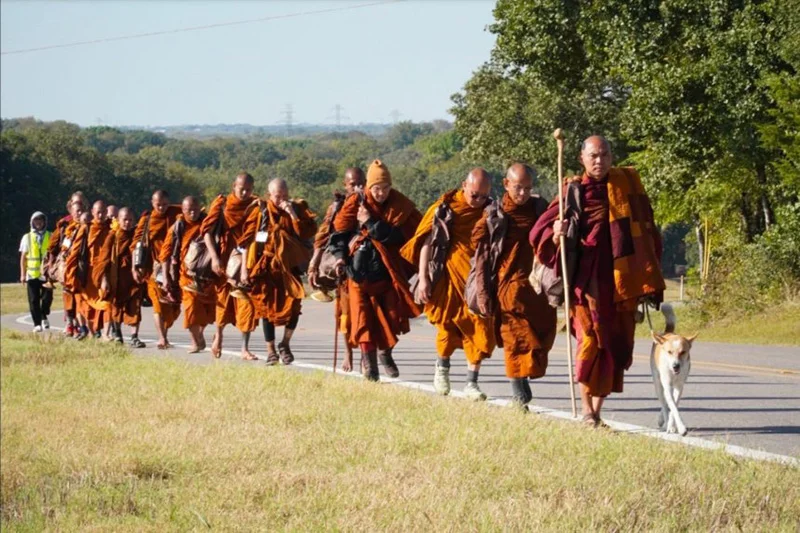
Talking about Ven. Pannakara, Ven. Wimalakitti says that he is a pupil of senior Vietnamese bhikkhu Ven. Ratanaguna of the same Huong Dao Monastery in Fort Worth Texas. He is leading a team of 24 Buddhist monks from different countries in the (Southeast Asian) region including Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, Bangladesh, Laos, etc., taking part in the Walk for Peace (from Fort Worth in Texas to Washington D.C.). It is going to be 2723 miles long according to Wimalakitti Thera. The Walk for Peace started on October 26, 2025 and is due to pass through 4 time zones and 10 states, braving extremes of weather and trekking through patches of harsh terrain.
It was 40 degrees Celsius in Texas, when they started. In seven days, the Peace Walkers reached Georgia in Atlanta. It was raining there. Then, they arrived in South Carolina, where it was cold, the temperature usually being under 20 degrees Celsius. By the time of the podcast with Chamuditha, the Walk for Peace was proceeding through the even colder North Carolina, the temperature barely rising above 1 or 2 degrees Celsius. Then, they reached Virginia with heavy snowfall, but the Walk went ahead nonstop.
The original plan was to walk 8 hours and cover 20 miles in a day. Now they want to do 10 hours a day and cover a targeted 40 miles. They hoped to have at least 20 participants in the Walk at any time. The whole Walk is expected to take 120 days and end on February 13, 2026.
America is a big democratic country, the monk says. The ordinary people are more interested in inner peace than in politics. There are 125 Sri Lankan Buddhist pansalas in America, 15 of which stand on the route of the continuing Walk for Peace. Sri Lankan monks resident in these monasteries, in partnership with monks from other countries, provide the Walkers with essential food, temporary lodgings, and hygienic facilities. They also work out security arrangements for the peace-walking monks in coordination with government and municipal authorities and Police.
Ven. Wimalakitti provides this information as a member and a director of the organising committee responsible for the Walk for Peace project. According to him, Ven. Pannakara takes part in an annual walk in India from Buddha Gaya to Kolkata (the capital city of India’s West Bengal state) as a dhutanga practice (one of the 13 strict ascetic practices recommended for bhikkhus in Theravada Buddhism that aim at perfecting austerity, mental purification, and renunciation). About 200 Buddhist monks join Bhikkhu Pannakara on this walk.
The dog now celebrated as Aloka started following Ven. Pannakara at Buddha Gaya and reached Kolkata with him. He followed the monk even to the airport. Bhikkhu Pannakara could not leave the dog behind in India and fly back to America. So, he canceled his flight and stayed back in India for eight months, during which he trained the dog and completed the paperwork necessary to take him to America with him. Once in America, Aloka sometimes started growling at people at first, because he was not used to the new environment. So, they put a pet cone around his neck to calm him while on the move. Now he participates in the Walk without the pet cone and walks beside Bhikkhu Pannakara at the head of the column of Walkers. The monk usually takes Aloka on a leash and occasionally, off-leash. Aloka had a paw injury during the walk and had to be hospitalised for a few days for surgery. He has rejoined the walk now. The dog has a car reserved for him to move with the walking party whenever he is unable to walk.
Ven. Wimalakitti Thera says he took part in six discussions held at the Huong Dao pansala when the peace walk was being planned. They had to discuss security matters with the Police. Concerns were raised about possible assassination attempts on Bhikkhu Pannakara. The dedicated monk said that he was ready to lay down his life for the cause of the Walk. Wimalakitti Thera said Bhikkhu Pannakara is only 37 years old.
At the beginning of the fourth week into the Walk, there was a serious traffic accident. The monks were walking along the shoulder of the road (near Dayton, Texas, east of Houston, on November 19, 2025) guided by a slow-moving escort vehicle (with hazard lights on). A truck hit the rear of the pilot car pushing it into the monks. The impact left two monks injured, one of them (Phra Ajarn Maha Dam Phommasan, aka Bhante Dam Phommasan) very seriously. The injured monks were airlifted to Houston for medical attention. Bhante Dam Phommasan had to undergo multiple surgeries, including the amputation of his leg. (The information given within parentheses in this piece of writing is added by me for clarity.)
On another occasion (in early January 2026, in Walton County, near Good Hope, Georgia) an unidentified protestor accompanied by a group of his supporters blocked the monks’ path (holding signs like ‘JESUS SAVES’, ‘Turn to Christ’; WARNING: ‘walking to hell’, ‘Hell awaits’, etc., but the people gathered there cheered on the monks, and asked the protestors to just move on). Ven. Wimalakitti (who was presumably on the scene) says that the police diverted them onto an alternative route. The unperturbed monks did not react to the disruptors and continued their walk in silence. The night routes were decided by the Police. The initial hostility petered out gradually, as thousands gathered on the roadsides to watch the monks walking and to listen to the sermons in the night.
(On Christmas Day 2025, the monks stopped at a church in Alabama, before entering into Georgia the next day.) Ven. Wimalakitti says that when Bhikkhu Pannakara made an address in the church that evening, it was filled to capacity, and his speech had to be broadcast on outdoor screens.
The Walk actually began as a dhutanga (please, see above) observance as Ven. Wimalakitti explains during the discursive podcast, which forms the basis of this essay. But, on the third day, the name was changed to ‘Walk for Peace’. Its purpose is non-religious and non-political. ‘Today is my day of peace’ is the theme. (Ven. Pannakara exhorts) “When you get up in the morning, say to yourself ‘Today is going to be my day of peace’”. When Wimalakitti Thera says “Ordinary Americans are really interested in Meditation (bhavana). They are much less interested in the dhamma”, he is making an obvious oversimplification that seems to be limited exclusively to the current Walk for Peace context.
WimalakittiThera claims that a single Pakistani individual from Texas ‘provides security for the Walk’. However much I tried, I couldn’t catch his name as the monk pronounced it. So I sought AI help. AI clarifies that ‘Based on the results of the 2025-2026 Walk for Peace from Texas to Washington D.C., the security and the logistics for the Buddhist monks are primarily handled by local law enforcement agencies (sheriffs and police departments) who secure the roads as the group walks’.(So, there is no mention of a Pakistani (American) providing security for the walk). The monk might be mistaken about the matter. But that piece of information is not so important. Though the monks have absolutely no political motives, the Sri Lankan monk thinks they expect (US President Donald) Trump to be there when they reach Washington, near the White House. A reception for the monks is scheduled to take place on that occasion with the participation of the Sri Lankan ambassador.
The highlight of the Chamuditha News Brief (CNB) podcast featuring Ven. Dr Melpitiye Wimalakitti uploaded on February 5, 2026 is his revelation of a well-kept secret, which is that the Sri Lankan monks living in America played the major pioneering role in organising the Walk for Peace across America project and that they wanted the Sri Lankan government to support it. The 17-member organising committee under the leadership of Ven. Wimalakitti, including the Vietnamese American bhikkhu Ven. Pannakara (who is now leading the Walk for Peace march) visited Sri Lanka in this connection in May 2025, that is, nine months ago. Ven. Wimalakitti showed the group photographs that the visiting monks took with prime minister Harini Amarasuriya, some ministers and other dignitaries. Still, ordinary Sri Lankans are unaware of this momentous event, it seems.
Unfortunately, there had not been any response to the monks’ request up to the day that Chamuditha did the podcast with Ven. Wimalakitti. The monk said that he broke off his participation in the Walk in order to visit Sri Lanka again for the express purpose of urging the Sri Lankan government’s participation in the Vesak celebration at Walk team leader Ven. Pannakara’s monastery in Texas in May. Ven. Wimalakitti said he gave the president and the prime minister (as I think he claimed) formal invitation cards requesting them to arrange for government delegates to attend the Vesak ceremony set to be held at the Huong Dao Monastery of Ven. Bhante Pannakara in Dallas, Fort Worth, Texas on May 26 this year (2026). He also wants them to grace the transport of relics from Sri Lanka. The monk was due to leave for America the night following the day of the programme with Chamuditha; but he had still got no reply from those important invitees. However,the Sri Lankan Ambassador in Washington is taking a great interest in this event, according to Ven. Wimalakitti.
At the end of the podcast, Ven. Wimalakitti voiced two important messages: “I want to say a word of diplomatic importance. This is a great opportunity for Sri Lanka, diplomatically speaking. This is a moment of awakening, not only for America but also for the whole world. All of you citizens of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka as a Theravada Buddhist state, can make your contribution to this global awakening. I urgently request that this great opportunity be not missed”. (The Walk for Peace, the peace pilgrimage across America, from Texas to Washington D.C., is performed by a group of Theravada Buddhist monks. It showcases the key Buddhist spiritual values of compassion, loving-kindness, non-violence, and peace that underlie Sri Lanka’s dominant religious culture. These values are a source of soft power for Sri Lanka in its diplomatic and cultural relations with the powerful United States of America.)
“Secondly, as Buddhists of Sri Lanka, please don’t criticise our monks or the Buddhist religion, simply because others do so. Please, think about this (insulting the monks and the Dhamma) with great equanimity. Both Buddhist monks and laypersons must keep updated about current trends. Some of our monks often attract criticism because they fail to adjust to changing times.”
By Rohana R. Wasala
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check