Features
In bid to counter China, US ramps up effort to boost military ties in Asia
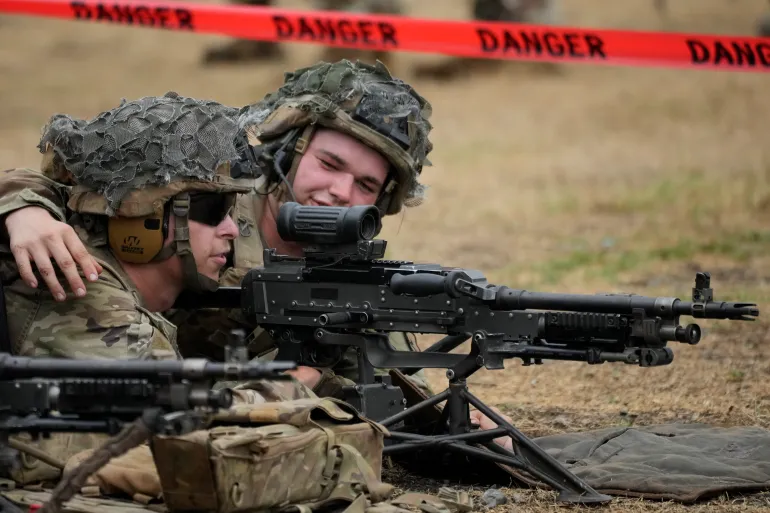

On May 30, the United States accused China of intercepting one of its spy planes in an “unnecessarily aggressive manoeuvre” over the South China Sea. The American RC-135 plane, according to the US military, was conducting routine operations over the sensitive waterway when the Chinese fighter jet flew directly in front of its nose.
A video shared by the US Indo-Pacific Command showed the cockpit of the RC-135 shaking in the wake of turbulence of the Chinese jet.
Days later, on June 5, the US again accused China of carrying out what it said was an ‘unsafe’ manouver near one of its vessels. This time it was around a warship in the Taiwan Strait. The US Indo-Pacific Command again released a video of the incident, showing a Chinese navy vessel cutting sharply across the path of a US destroyer at a distance of some 137 metres (150 yards), forcing the latter to slow down to avoid a collision.
Washington said the near misses showed China’s “growing aggressiveness”, but Beijing said the US was to blame, accusing its rival of deliberately “provoking risk” by sending aircraft and vessels for “close in reconnaissance” near its shores – moves it said posed a serious danger to its national security.
The close calls evoked memories of a deadly incident on April 1, 2001, when a Chinese fighter jet and a US surveillance plane collided in the sky over the South China Sea. The impact caused the Chinese jet to crash and killed the pilot, while the US plane was forced to make an emergency landing in China’s Hainan. Beijing held the 24 American aircrew members for 11 days and only released them when Washington apologised for the incident.
While the two countries were able to de-escalate tensions then, there are worries that a similar mishap today could widen into a bigger conflict due to the deterioration in relations between the rivals.
The US views China as the biggest challenge to the Western-dominated international order, pointing to Beijing’s rapid military buildup – the biggest in peacetime history – as well as its claims over the self-governed island of Taiwan and in the East and South China Seas. The US military’s so-called “freedom of navigation exercises” in the contested waterways near China are part of a push by the administration of President Joe Biden to deepen and expand its diplomatic and military presence in the Asia Pacific.
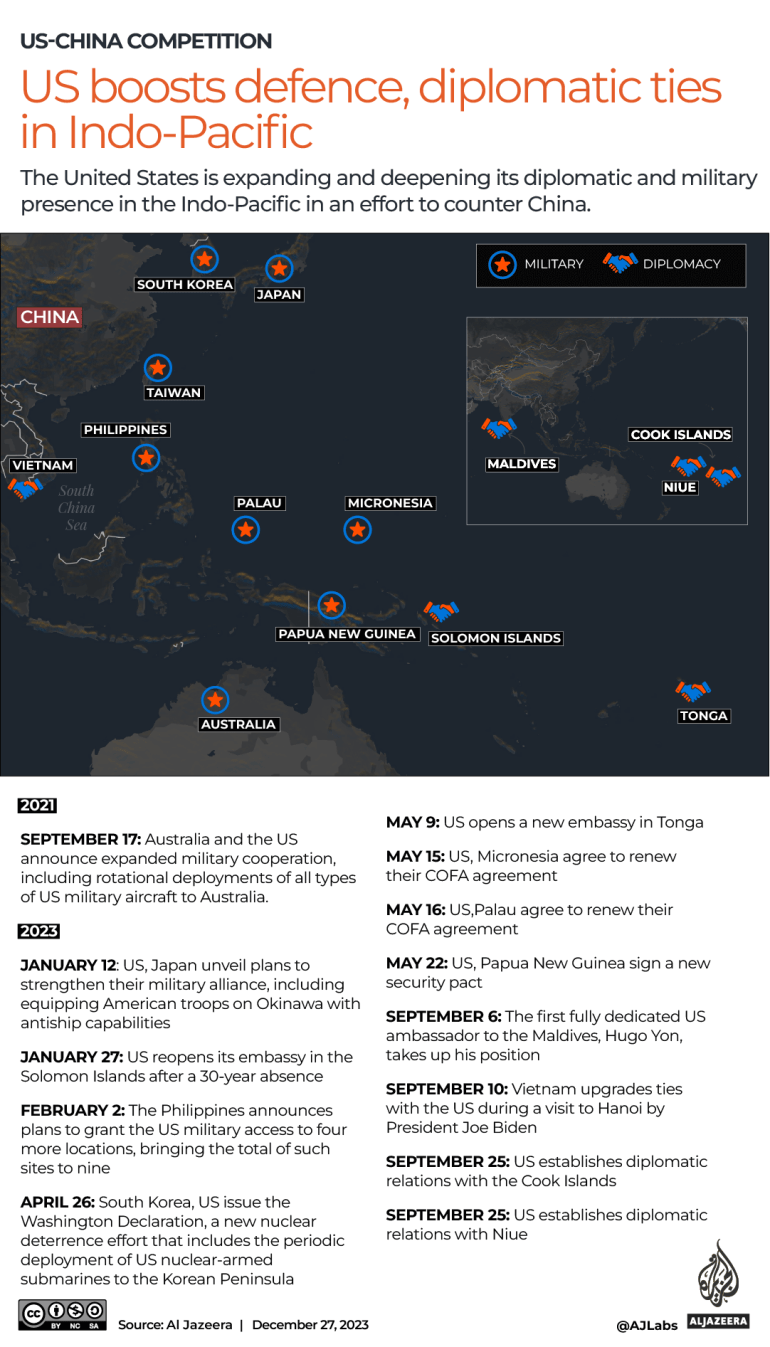
The campaign – which has accelerated over the past year – stretches from Japan to the Philippines and Australia, and from India to Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The “once in a generation effort,” as Gregory Poling, director of the Southeast Asia Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, puts it, involves the opening of new embassies in the region, deployment of troops and more advanced military assets, as well as obtaining access to sites in key areas facing the South China Sea and the Taiwan Strait.
For its part, China accuses the US of pursuing a policy of “containment, encirclement and suppression”, all aimed at holding back its economic development. And its leaders have pledged to resist.
Chinese President Xi Jinping said the US campaign has “brought unprecedented sever challenges to our country’s development”, and in a speech in March called on his countrymen to “dare to fight”. His former Defence Minister Li Shangfu, during an address at the Shangri-La Dialogue in Singapore, condemned what he called Washington’s “Cold War mentality”, and said Beijing would not be intimidated and would “resolutely safeguard national sovereignty and territorial integrity, regardless of any cost”.
Analysts say tensions will only heighten further as competition between China and the US – a contest about who gets to set the rules on the global stage – intensifies. While the superpower rivalry could bring benefits to countries in the Asia Pacific in the short term – particularly in the form of infrastructure loans and foreign direct investments – these nations could, in the future, find having to navigate between China and the US more challenging.
“This is a competition over what the rules-based order looks like, at least in Asia,” Poling told Al Jazeera. “It’s about whether or not the existing global rules continue to apply to Asia or whether China gets to carve out a huge area of exemption in which its preferred rules predominate.
“Clearly, the next couple of decades at least are going to be characterised by this growing competition. Unless China changes its strategy on this … then we’re going to see competition continue to heighten and tensions continue to heighten not just between the US and China, but also between China and most of its neighbours.”
China’s rise
Japan’s defeat in World War II ushered in an age of US dominance in Asia. But in recent decades, China’s growing military and economic might has brought an end to that uncontested primacy.
Under Xi, who took office in 2012 championing what he calls the “Chinese dream of national rejuvenation”, a vision to restore China’s great-power status, Beijing has invested heavily in modernising its military. According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies, a London-based think tank, China has more than doubled its military spending over the past decade, with expenditure reaching $219bn in 2022 although this is still less than a third of US spending during the same year.
China has also embarked on a naval shipbuilding programme that has put more vessels to sea between 2014 and 2018 than the total number of ships in the German, Indian, Spanish and British navies combined. The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has since also commissioned guided missile cruisers as well as nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines. In June 2022, it launched its third aircraft carrier, the Fujian. The PLA’s rocket force has also modernised its capabilities, including with the development of hypersonic missiles and anti-ship ballistic missiles. According to the US military, the PLA also plans to accelerate the expansion of its nuclear arsenal to as many as 700 nuclear warheads by 2027 and at least 1,000 by 2030.
Along with the military build-up, China has also become increasingly assertive in enforcing its territorial claims in crucial waterways off its coast.
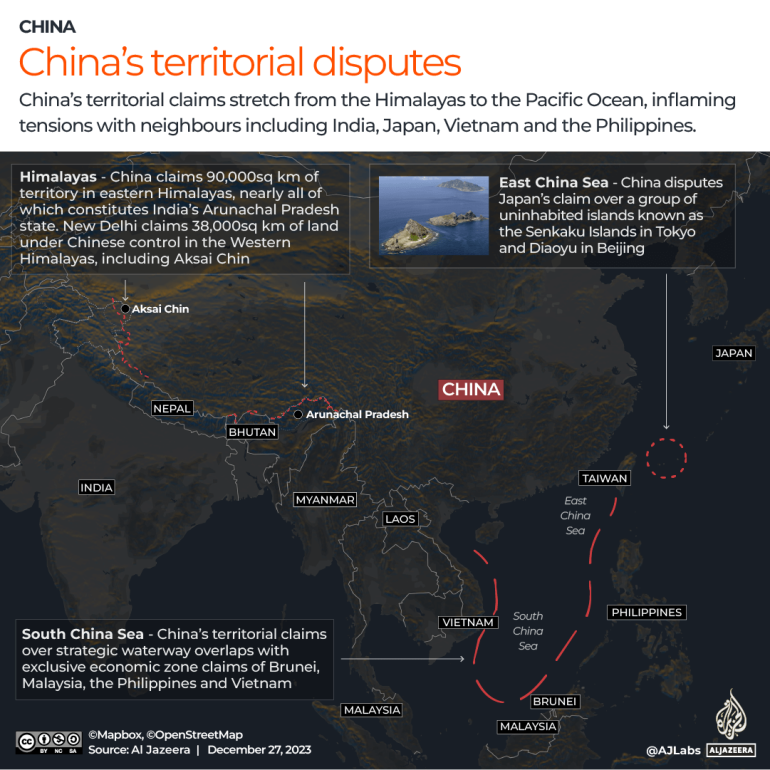
In the East China Sea, Beijing lays claim to a group of Japanese-administered islands known as Diaoyu in China and Senkaku in Japan and has increased naval and aerial patrols in the area, drawing protest from Tokyo.
China also lays claim to the entire South China Sea, via its nine-dash line, much to the ire of neighbouring Philippines, Vietnam, Taiwan, Brunei and Malaysia. To shore up those claims, China has built artificial islands in disputed waters, including in the Spratly Islands which it seized from the Philippines in 1996, and expanded its presence in the Paracel Islands which it seized from Vietnam in 1976. China now operates four large outposts with 10,000-foot runways on Woody Island, Fiery Cross Reef, Mischief Reef and Subi Reef. It has also deployed substantial military assets to the islands, including anti-ship missiles, and hangars capable of housing military transport, patrol and combat aircraft.
At the same time, China has faced off with India over their disputed border in the Himalayas. Tensions in the region boiled over in June 2020, when Chinese and Indian troops fought each other with sticks and clubs. At least 20 Indian and four Chinese soldiers died.
Xi has also stepped up rhetoric around Taiwan.
During the Chinese Communist Party’s Congress in September, Xi called unification with the democratically-governed island a “historic mission” and an “unshakable commitment”. The PLA has meanwhile normalised incursions into Taiwan’s Air Defence Identification Zone, the airspace in which Taiwan attempts to identify and control all aircraft.
On the economic front, too, China has grown increasingly powerful.
It is the most important trading partner for more than 120 countries in the world and has sought to expand its economic influence through the ambitious Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Under the project, sometimes known as the New Silk Road, China has financed physical infrastructure, such as ports, bridges and railways across Asia, Africa and Europe and funded hundreds of special economic zones, or industrial areas designed to create jobs. To date, some 147 countries have signed on to BRI projects or indicated an interest in doing so. In total, China has already disbursed an estimated $1 trillion on such efforts and may spend as much as $8 trillion over the life of the project.
Arc of alliances
The US has sounded the alarm over China’s growing clout.
Biden has called Xi a ‘dictator’, while his administration has accused Beijing of leveraging its commercial, military and technological might to “pursue a sphere of influence in the Indo-Pacific” and “become the world’s most influential power”.
Biden’s Secretary of State Antony Blinken, unveiling the US’s China strategy last year, described the Asian power as “the only country with both the intent to reshape the international order and, increasingly, the economic, diplomatic, military and technological power to do it”.
A key pillar in the US’s campaign to counter China has been its efforts to deepen and expand its military and diplomatic ties with countries in the Indo-Pacific. The campaign – which includes boosting relations with allies such as Australia, Japan and South Korea, and non-allies such as India and Vietnam – has arguably resulted in the most robust US diplomatic and military posture in the Asia Pacific in recent decades.
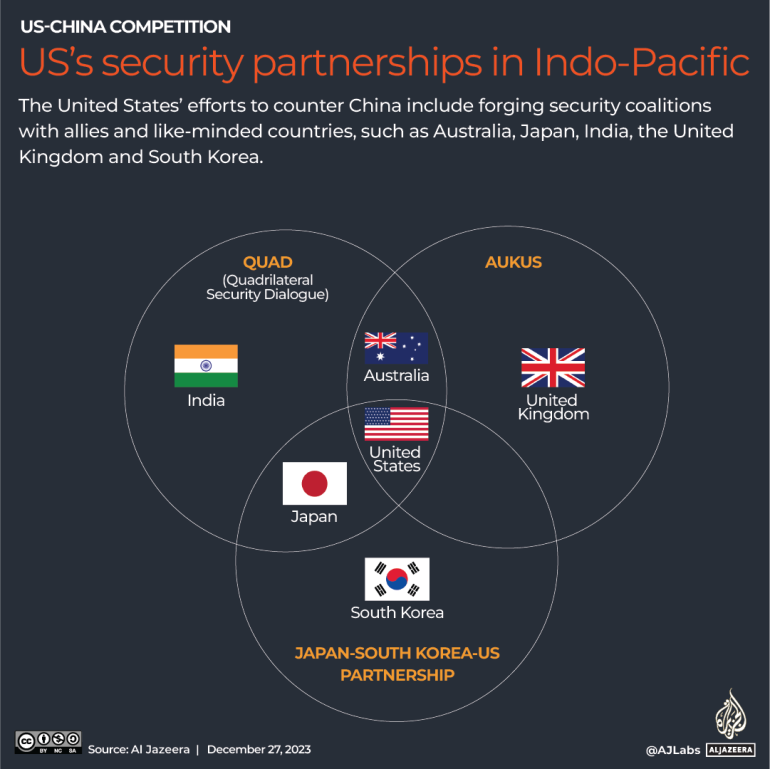
In Australia, the US, along with the United Kingdom, has announced a historic security partnership to equip Canberra with up to five nuclear-powered attack submarines by the early 2030s. These vessels, which are equipped with long-range missiles, are much harder to detect and can stay underwater far longer than conventional submarines, “making them one of the most effective ways to complicate Chinese military planning and give Beijing a reason to take pause before using force”, according to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Australia and the US have also announced plans to increase the rotational presence of US air, land and sea forces on the island continent, and build airfields to operate nuclear-capable B52 bombers from northern Australia.
In Japan, the US has announced plans to overhaul its troop presence on the Okinawa Islands, including equipping its maritime units there with long-range fire abilities that can hit ships – something that would be key in the event of a Chinese invasion of Taiwan.
In South Korea, which has grown increasingly anxious about neighbouring North Korea’s accelerating nuclear and missile programme, the US has announced new security assurances including the deployment of a nuclear-armed submarine to the Korean peninsula for the first time in four decades. More significantly, the US has announced a new trilateral security partnership with Seoul and Tokyo, a historic achievement given the long history of mutual acrimony between the two countries. At a summit in Camp David in the US in August, the three nations condemned China’s “dangerous and aggressive behaviours” in the South China Sea and pledged to deepen military and economic cooperation to tackle regional challenges.
In the Philippines, another US ally, the government of President Ferdinand Marcos Jr – incensed by Chinese harassment of its vessels in the South China Sea – has granted the Pentagon access to four more sites in the country. This brings to nine the number of locations that US forces have access to in the country – albeit on a rotational basis. Three of the four new sites are in the provinces of Cagayan and Isabela in northern Philippines, facing Taiwan, and the other in eastern Palawan, near the disputed Spratly Islands in the South China Sea. The Philippines and the US have also stepped up the scope and scale of their military exercises, and Washington has reinforced its commitment to defend Manila from an attack at sea. The navies of the two countries are eyeing joint naval patrols in the South China Sea, while the US has also increased freedom of navigation exercises in the waterway.
Vietnam, too, has upgraded its ties with the US. Alarmed by China’s actions in the South China Sea, Hanoi in September elevated the US’s diplomatic status to that of a comprehensive strategic partner – on par with that of China and Russia. The move came during a historic visit to the Vietnamese capital by Biden, and experts say it is indicative of the depth of its concern over its territorial dispute with China in the South China Sea.
On Taiwan, Biden has said on several occasions that the US would come to the island’s aid if there was a Chinese attack. While the White House has since walked back those statements, the Biden administration has continued arms sales to Taiwan, approving more than $3bn in weapons transfers and also allowing US officials to meet more freely with Taiwanese counterparts.
In the Pacific Islands, too, the US has expanded its military and diplomatic footprint.
In May, it signed a security deal with Papua New Guinea that gives it “unimpeded access” to several key airports and seaports in the Pacific nation and re-opened an embassy in the Solomon Islands after a 30-year absence. It has also opened an embassy in Tonga and is in talks with Kiribati and Vanuatu to establish a diplomatic presence there. Biden has also hosted historic summits for Pacific Island leaders in Washington, DC, pledging $810m in new aid for the Pacific Islands over the next decade, including to tackle the existential threat of climate change.
Non-aligned India, too, has stepped up cooperation with the US.
The two countries, along with Australia and Japan have revived an informal alliance known as the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, or Quad, in a bid to counter China and deliver public goods to countries in the Global South. Quad pledges include a key initiative to help countries protect maritime resources from predatory illegal fishing and promises to invest more than $50bn in developing infrastructure in the Indo-Pacific.
‘Desperation’
Analysts say the US campaign has stirred anger and concern in Beijing.
“This latest phase really just shows an increase in desperation on the part of the US because taking military measures usually is a last resort. Because it’s risky and it’s expensive. It’s also very dangerous. A country that has to resort to these measures, I think, clearly feels it is running out of options and is increasingly desperate to protect its rapidly eroding position in the world,” said Andy Mok, senior research fellow at the Center for China and Globalization in Beijing.
“We only need to look at a map of US military assets to see who’s the aggressor. It’s not that China has numerous military bases surrounding the United States. It’s exactly the opposite. So I think any reasonable observer would question this assertion whether China is really engaging in any sort of military provocations here.”
Mok said China is responding to the US’s efforts by continuing its military modernisation as well as strengthening its own ties.
The military modernisation efforts “include everything from the development of hypersonic missiles to a much stronger navy that is effective not just close to China’s shores, which would include Taiwan, of course, but much broader,” he said. “It includes cyber, includes space from the military perspective. So, becoming a much more comprehensive military force able to respond to threats a number of different ways.”
On the diplomatic front, Mok said China will look to strengthen multilateral initiatives such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, the world’s largest free trade agreement that brings together 15 countries, the BRICs group that includes Brazil, Russia and India, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), a nine-member Eurasian group that counts Pakistan and Iran among its members.
“These are all attempts to create a more humane and just global order, where these types of issues are, again, not decided by one country and not decided through coercion, whether that’s primarily military coercion or other forms of coercion, including economic sanctions,” he added.
Heightened tensions
For countries in the Asia Pacific, especially in Southeast Asia, the increased US-China competition has brought some economic benefits. To compete with China’s BRI, the US has pledged to step up investment in infrastructure, though much of this investment has yet to bear fruit, while the trade war between the superpowers has resulted in some Southeast Asian countries marketing themselves as alternative production destinations.
“In Southeast Asia, I think the emphasis is on autonomy. And to the extent that they can invite more actors in to have a stake – whether this is the United States, whether this is Korea, Japan, the EU or Australia – that is somewhat more preferred because it dilutes the presence of any single actor,” said Ja-Ian Chong, associate professor at the National University of Singapore.
“With the diversification of investment from the United States, South Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Australia, some Southeast Asian states will be big beneficiaries. So Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, and to some degree, the Philippines and Malaysia have seen investment that might otherwise go to China go to them.”
China, Chong said, sees the robustness of US presence in the region as a bit of a challenge.
“The question is, how they will respond? It is possible that they may respond with more caution, which could be stabilising, but there’s also a possibility that they could react even more strongly. But that’s not easy to predict at this point in time.”
So far, it appears that Beijing is seeking to contest the US’s presence.
That is evident not just in the confrontations between US and Chinese vessels and aircraft over the South China Sea and the Taiwan Strait, but also in Beijing’s standoffs with Philippine military boats in the South China Sea. These include incidents in August and earlier this month when the Chinese Coast Guard used water cannon to prevent the Philippine military from resupplying its troops living on a grounded warship on the disputed Second Thomas Shoal.
On Taiwan, too, China’s navy this year launched its largest-ever exercises in the Pacific Ocean, deploying an aircraft carrier and dozens of naval ships and warplanes, in a move analysts said was probably practice for enforcing a blockade around the island. Beijing said the purpose of the drills was to “resolutely combat the arrogance of Taiwan independence separatist forces and their actions to seek independence”.
Chong said the tensions were likely to pose new challenges to countries in the region.
“I expect the contestation to become more intense. Meaning to say that trying to navigate between the two major powers will become more challenging, not impossible, but certainly more challenging. To expect that you can act in ways that get benefits from both sides may become more difficult. It may be the case that working with one more will invite pressure from the other,” said Chong. “That is likely to be a challenge facing Southeast Asia unless they are more able to set up their own direction.”
(Aljazeera)
Features
Minds and Memories picturing 65 years of Sri Lankan Politics and Society

Last week I made mention of a gathering in Colombo to remember Kumar David, who passed away last October, as Comrade, Professor and Friend. The event was held on Saturday, April 5th, a day of double significance, first as the anniversary of the JVP insurrection on 5th April 1971, and now the occasion of the official welcome extended to visiting Indian Prime Narendra Modi by the still new JVP-NPP government. The venue was the Ecumenical Institute for Study and Dialogue (EISD) on Havelock Road, which has long been a forum for dialogues and discussions of topics ranging from religious ecumenism, Liberation Theology and Marxist politics. Those who gathered to remember Kumar were also drawn from many overlapping social, academic, professional and political circles that intersected Kumar’s life and work at multiple points. Temporally and collectively, the gathering spanned over six decades in the evolution of post-independence Sri Lanka – its politics, society and the economy.
Several spoke and recalled memories, and their contributions covered from what many of us have experienced as Sri Lankans from the early 1960s to the first two and a half decades of the 21st century. The task of moderating the discussion fell to Prof. Vijaya Kumar, Emeritus Professor of Chemistry at Peradeniya, who was a longtime friend of Kumar David at the university and a political comrade in the LSSP – especially in the Party’s educational and publication activities.
Vijaya Kumar recalled Kumar David’s contributions not only to Marxist politics but also to the popularization of Science that became a feature in several of KD’s weekly contributions to the Sunday Island and the Colombo Telegraph. Marshal Fernando, former and longtime Director of the EISD welcomed the participants and spoke of Kumar David’s many interactions with the Institute and his unflinching offer of support and advice to its activities. EISD’s current Director, Fr. Jayanath Panditharatne and his staff were extremely helpful.
Rohini David, Kumar’s wife of over 50 years, flew in specially for the occasion from Los Angeles and spoke glowingly of Kumar’s personal life as a husband and a father, and of his generosity for causes that he was committed to, not only political, but also, and more importantly, educational. An interesting nugget revealed by Rohini is the little known fact that Kumar David was actually baptized twice – possibly as a Roman Catholic on his father’s side, and as an Anglican on his mother’s side. Yet he grew to see an altogether different light in all of his adult life. Kumar’s father was Magistrate BGS David, and his maternal grandfather was a District Judge, James Joseph.
Kumar had an early introduction to politics as a result of his exposure to some of the political preparations for the Great Hartal of 1953. Kumar was 12 years old then, and the conduit was his step-father, Lloyd de Silva an LSSPer who was close to the Party’s frontline leaders. From a very young age, Kumar became familiar with all the leaders and intellectuals of the LSSP. Lloyd was known for his sharp wit and cutting polemics. One of my favourite lines is his characterization of Bala Tampoe as a “Lone Ranger in the Mass Movement.” Lloyd’s polemics may have rubbed on Kumar’s impressionable mind, but the more enduring effect came from Lloyd’s good collection of Marxist books that Kumar self-admittedly devoured as much as he could as a teenager and an undergraduate.
Electric Power and Politics
Early accounts of Kumar’s public persona came from Chris Ratnayake, Prof. Sivasegaram and Dr. K. Vigneswaran, all Kumar’s contemporaries at the Engineering Faculty that was then located in Colombo. From their university days in the early 1960s, until now, they have witnessed, been a part of and made their own contributions to politics and society in Sri Lanka. Chris, a former CEB and World Bank Electrical Engineer, was part of the Trotskyite LSSP nucleus in the Engineering Faculty, along with Bernard Wijedoru, Kumar David, Sivaguru Ganesan, MWW Dharmawardana, Wickramabahu Karunaratne and Chris Rodrigo. Of that group only Chris and MWW are alive now.
Chris gave an accurate outline of their political involvement as students, Kumar’s academic brilliance and his later roles as a Lecturer and Director of the CEB under the United Front Government. Chris also described Kumar’s later academic interest and professional expertise in the unbundling of power systems and opening them to the market. Even though he was a Marxist, or may be because of it, Kumar had a good understanding of the operation of the market forces in the electricity sector.
Chris also dealt at length on Sri Lanka’s divergent economic trajectories before and after 1977, and the current aftermath of the recent economic crisis. As someone who has worked with the World Bank in 81 countries and has had the experience of IMF bailout programs, Chris had both warning and advice in light of Sri Lanka’s current situation. No country, he said, has embarked on an economic growth trajectory by following standard IMF prescriptions, and he pointed out that countries like the Asian Tigers have prospered not by following the IMF programs but by charting their own pathways.
Prof. S. Sivasegaram and Dr. K. Vigneswaran graduated in 1964, one year after Kumar David, with first classes in Mechanical Engineering and Civil Engineering, respectively. Sivasegaram joined the academia like Kumar David, while Vigneswaran joined the Irrigation Department but was later drawn into the vortex of Tamil politics where he has been a voice of reason and a source for constructive alternatives. As Engineering students, they were both Federal Party supporters and were not aligned with Kumar’s left politics.
It was later at London Imperial College, Sivasegaram said, he got interested in Marxism and he credited Kumar as one of the people who introduced him to Marxism and to anti-Vietnam protests. But Kumar could not persuade Sivasegaram to be a Trotskyite. Sivasegaram has been a Maoist in politics and apart from his Engineering, he is also an accomplished poet in Tamil. Vigneswaran recalled Kumar’s political involvement as a Marxist in support of the right of self-determination of the Tamils and his accessibility to Tamil groups who were looking for support from the political left.
K. Ramathas and Lal Chandranath were students of Kumar David at Peradeniya, and both went on to become established professionals in the IT sector. Ramathas passionately recalled Kumar’s effectiveness as a teacher and described his personal debt of gratitude for helping him to get a lasting understanding of the concept and application of power system stability. This understanding has helped him deal with other systems, said Ramathas, even as he bemoaned the lack of understanding of system stability among young Engineers and their failure to properly explain and address recurrent power failures in Sri Lanka.
Left Politics without Power
The transition from Engineering to politics in the discussion was seamlessly handled by veterans of left politics, viz., Siritunga Jayasuriya, Piyal Rajakaruna and Dishan Dharmasena, and by Prof. Nirmal Dewasiri of the History Department at the University of Colombo. Siritunga, Piyal and Dishan spoke to the personal, intellectual and organizational aspects of Kumar David in the development of left politics after Kumar David, Vasudeva Nanayakkara and Bahu were no longer associated with the LSSP. Dewasiri reflected on the role of the intellectuals in left political parties and the lost to the left movement as a whole arising from the resignation or expulsion of intellectuals from left political organizations.
While Kumar David’s academic and professional pre-occupation was electric power, pursuing power for the sake of power was not the essence of his politics. That has been the case with Bahu and Sivasegaram as well. They naturally had a teaching or educational role in politics, but they shared another dimension that is universally common to Left politics. Leszek Kolakowski, the Polish Marxist who later became the most celebrated Marxist renegade, has opined that insofar as leftists are generally ahead of their times in advocating fundamental social change and promoting ideas that do not resonate with much of the population, they are unlikely to win power through electoral means.
Yet opposition politics predicated on exposing and decrying everything that is wrong with the system and projecting to change the system is fundamentally the most moral position that one can take in politics. So much so it is worth pursuing even without the prospect of power, as Hector Abhayavardhana wrote in his obituaries for LSSP leaders like NM Perera and Colvin R de Silva. By that token, the coalition politics of the 1960s could be seen as privileging a shared parliamentary path to power while dismissing as doctrinaire the insistence on a sole revolutionary path to power.
The two perspectives clashed head on and splintered the LSSP at its historic 1964 Conference. Kumar David and Lal Wijenayake were the youngest members at that conference, and the political genesis of Kumar David and others at the Engineering faculty that Chris Ratnayake outlined was essentially post-coalition politics. In later years, Vasudeva Nanayakkara, Bahu and Kumar David set about creating a left-opposition (Vama) tendency within the LSSP.
This was considered a superior alternative to breaking away from the Party that had been the experience of 1964. Kumar David may have instinctively appreciated the primacy of the overall system stability even if individual components were getting to be unstable! But their internal efforts were stalled, and they were systematically expelled from the Party one by one. Kumar David recounted these developments in the obituary he wrote for Bahu.
As I wrote last week, after 1977 and with the presidential system in place, the hitherto left political parties and organizations generally allied themselves with one or the other of the three main political alliances led by the SLFP, the SLPP and even the UNP. A cluster of them gravitated to the NPP that has been set up by the JVP under the leadership of Anura Kumara Dissanayake. Kumar David supported the new JVP/NPP initiative and was optimistic about its prospects. He wrote positively about them in his weekly columns in the Sunday Island and the Colombo Telegraph.
The Social Circles of Politics
Sometime in late 2006, Rohan Edrisinha introduced Kumar and me to Rajpal Abeynayake, who was then the Editor of the Sunday Observer, for the purpose of writing weekly columns for the Paper. Bahu was already writing for the Sunday Observer and for almost an year, Bahu, Kumar and I were Sunday Island columnists, courtesy of Rajpal Abeynayake. In 2007, Prof. Vijaya Kumar introduced us to Manik de Silva, already the doyen of Sri Lanka’s English medium editors, and Kumar and I started writing for the Sunday Island edited by Manik. It has been non-stop weekly writing a full 18 years. For a number of years, we have also been publishing modified versions of our articles in the Colombo Telegraph, the online journal edited by the inimitable Uvindu Kurukulasuriya.
Writing mainstream rekindled old friendships and created new ones. It was gratifying to see many of them show up at the celebration of life for Kumar. That included Rajpal Abeynayake, Bunchy Rahuman, Gamini Kulatunga, Ranjith Galappatti, Tissa Jayatilaka, NG (Tanky) Wickremeratne, and Manik de Silva. Vijaya Chandrasoma, who unfortunately could not attend the meeting, was particularly supportive of the event along with Tanky and Ramathas. Tissa and Manik spoke at the event and shared their memories of Kumar.
Dr. Santhushya Fernando of the Colombo Medical Faculty provided organizational support and created two superb video montages of Kumar’s life in pictures to background theme songs by Nat King Cole and Frank Sinatra. Manoj Rathnayake produced a Video Recording of the event.
In a quirky coincidence, five of those who attended the event, viz. Manik de Silva, Vijaya Kumar, Chris Ratnayake, S. Sivasegaram and K. Vigneswaran were all classmates at Royal College. On a personal note, I have been associated with every one of them in one way or another. Chris and I were also Engineers at the Hantana Housing Development in the early 1980s, for which the late Suren Wickremesinghe and his wife Tanya were the Architects. And Suren was in the same Royal College class as the other five mentioned here.
In the last article he wrote before his passing, Kumar David congratulated Anura Kumara Dissanayake for his magnificent political achievement and expressed cautious optimism for the prospects under an NPP government. Many in the new government followed Kumar David’s articles and opinions and were keen to participate in the celebration of life that was organized for him. That was not going to be possible anyway with the visit of Prime Minister Modi falling on the same day. Even so, Prof. Sunil Servi, Minister of Buddha Sasana, and Religious and Cultural Affairs, was graciously present at the event and expressed his appreciation of Kumar David’s contributions to Sri Lankan politics and society.
by Rajan Philips
Features
53 Years of HARTI- Looking Back and Looking Ahead
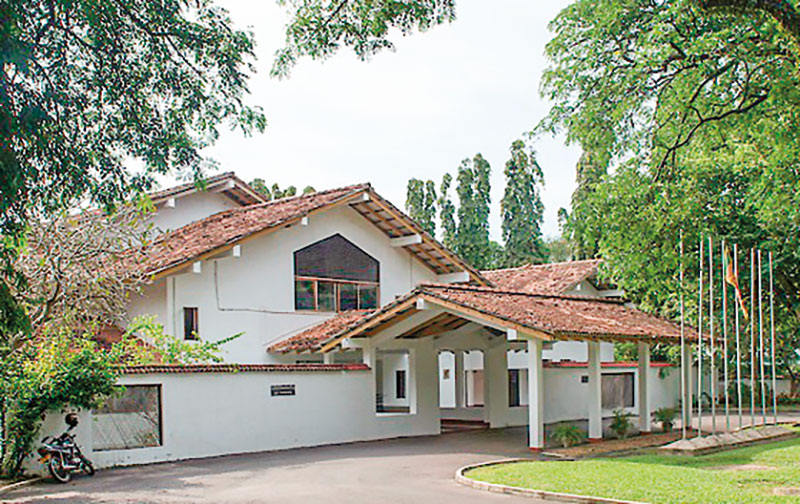

C. Narayanasuwami, the first Director of the then Agrarian Research and Training Institute (ARTI).
I am delighted to be associated with the fifty third anniversary celebrations of HARTI. I cherish pleasant memories of the relentless efforts made as the First Director to establish, incorporate, develop, direct, and manage a nascent institute in the 1970s amidst many challenges. The seven-year period as Director remains as the most formidable and rewarding period in my career as a development professional. I have been fortunate to have had a continuing relationship with HARTI over the last five decades. It is rarely that one who played a significant role in the establishment and growth of an institution gets an opportunity to maintain the links throughout his lifetime and provide messages on the completion of its fifth (I was still the director then), the 15th, 50th and 53rd anniversaries.
I had occasion also to acknowledge the contribution of the Institute on its 46th year when I released my book, ‘Managing Development: People, Policies and Institutions’ using HARTI auditorium and facilities, with the able support of the then director and staff who made the event memorable. The book contains a special chapter on HARTI.
On HARTI’s 15th anniversary I was called upon to offer some thoughts on the Institute’s future operations. The following were some of my observations then, “ARTI has graduated from its stage of infancy to adolescence….Looking back it gives me great satisfaction to observe the vast strides it has made in developing itself into a dynamic multidisciplinary research institution with a complement of qualified and trained staff. The significant progress achieved in new areas such as marketing and food policy, data processing, statistical consultancies, information dissemination and irrigation management, highlights the relevance and validity of the scope and objectives originally conceived and implemented”.
It may be prudent to review whether the recommendations contained in that message, specifically (a) the preparation of a catalogue of research findings accepted for implementation partially or fully during policy formulation, (b) the relevance and usefulness of information services and market research activities in enhancing farmer income, and (c) the extent to which the concept of interdisciplinary research- a judicious blend of socio-economic and technical research considered vital for problem-oriented studies- was applied to seek solutions to problems in the agricultural sector.
The thoughts expressed on the 15th anniversary also encompassed some significant management concerns, specifically, the need to study the institutional capabilities of implementing agencies, including the ‘human factor’ that influenced development, and a critical review of leadership patterns, management styles, motivational aspects, and behavioural and attitudinal factors that were considered vital to improve performance of agrarian enterprises.
A review of HARTI’s current operational processes confirm that farmer-based and policy-based studies are given greater attention, as for example, providing market information service for the benefit of producers, and undertaking credit, microfinance, and marketing studies to support policy changes.
The changes introduced over the years which modified the original discipline-based research units into more functional divisions such as agricultural policy and project evaluation division, environmental and water resources management division, and agricultural resource management division, clearly signified the growing importance attached to functional, action-oriented research in preference to the originally conceived narrowly focused discipline-based research activities.
HARTI has firmly established its place as a centre of excellence in socio-economic research and training with a mature staff base. It is pertinent at this juncture to determine whether the progress of HARTI’s operations was consistently and uniformly assessed as successful over the last five decades.
Anecdotal evidence and transient observations suggest that there were ups and downs in performance standards over the last couple of decades due to a variety of factors, not excluding political and administrative interventions, that downplayed the significance of socio-economic research. The success of HARTI’s operations, including the impact of policy-based studies, should be judged on the basis of improved legislation to establish a more structured socio-economic policy framework for agrarian development.
Looking Ahead
Fifty-three years in the life of an institution is substantial and significant enough to review, reflect and evaluate successes and shortcomings. Agrarian landscapes have changed over the last few decades and national and global trends in agriculture have seen radical transformation. Under these circumstances, such a review and reflection would provide the basis for improving organisational structures for agricultural institutions such as the Paddy Marketing Board, development of well-conceived food security plans, and above all, carefully orchestrated interventions to improve farmer income.
New opportunities have arisen consequent to the recent changes in the political horizon which further validates the role of HARTI. HARTI was born at a time when Land Reform and Agricultural Productivity were given pride of place in the development programs of the then government. The Paddy Lands Act provided for the emancipation of the farming community but recent events have proven that the implementation of the Paddy Lands Act has to be re-looked at in the context of agricultural marketing, agricultural productivity and income generation for the farming community.
Farmers have been at the mercy of millers and the price of paddy has been manipulated by an oligopoly of millers. This needs change and greater flexibility must be exercised to fix a guaranteed scale of prices that adjust to varying market situations, and provide adequate storage and milling facilities to ensure that there is no price manipulation. It is time that the Paddy Lands Act is amended to provide for greater flexibility in the provision of milling, storage and marketing services.
The need for restructuring small and medium scale enterprises (SMEs) recently announced by the government warrants greater inputs from HARTI to study the structure, institutional impediments and managerial constraints that inflict heavy damages leading to losses in profitability and organisational efficiency of SMEs.
Similarly, HARTI should look at the operational efficiency of the cooperative societies and assess the inputs required to make them more viable agrarian institutions at the rural level. A compact research exercise could unearth inefficiencies that require remedial intervention.
With heightened priority accorded to poverty alleviation and rural development by the current government, HARTI should be in the forefront to initiate case studies on a country wide platform, perhaps selecting areas on a zonal basis, to determine applicable modes of intervention that would help alleviate poverty.
The objective should be to work with implementing line agencies to identify structural and institutional weaknesses that hamper implementation of poverty reduction and rural development policies and programs.
The role played in disseminating marketing information has had considerable success in keeping the farming community informed of pricing structures. This should be further expanded to identify simple agricultural marketing practices that contribute to better pricing and income distribution.
HARTI should consider setting up a small management unit to provide inputs for management of small-scale agrarian enterprises, including the setting up of monitoring and evaluation programs, to regularly monitor and evaluate implementation performance and provide advisory support.
Research and training must get high level endorsement
to ensure that agrarian policies and programs constitute integral components of the agricultural development framework. This would necessitate a role for HARTI in central planning bodies to propose, consider and align research priorities in line with critical agricultural needs.
There is a felt need to establish links with universities and co-opt university staff to play a role in HARTI research and training activities-this was done during the initial seven-year period. These linkages would help HARTI to undertake evaluative studies jointly to assess impacts of agrarian/agricultural projects and disseminate lessons learned for improving the planning and execution of future projects in the different sectors.
In the overall analysis, the usefulness of HARTI remains in articulating that research and analysis are crucial to the success of implementation of agrarian policies and programs.
In conclusion, let us congratulate the architects and the dynamic management teams and staff that supported the remarkable growth of HARTI which today looks forward to injecting greater dynamism to build a robust institution that would gear itself to meeting the challenges of a new era of diversified and self-reliant agrarian society. As the first director of the Institute, it is my wish that it should grow from strength to strength to maintain its objectivity and produce evidence-based studies that would help toward better policies and implementation structures for rural transformation.
Features
Keynote Speech at the Launch of The Ceylon Journal, by Rohan Pethiyagoda

“How Rubber Shaped our Political Philosophy”
The Ceylon Journal was launched last August. Its first issue is already out of print. Only a handful of the second issue covering new perspectives of history, art, law, politics, folklore, and many other facets of Sri Lanka is available. To reserve your very own copy priced Rs. 2000 call on 0725830728.
Congratulations, Avishka [Senewiratne]. I am so proud of what you have done. Especially, Ladies and Gentlemen, to see and hear all of us stand up and actually sing the National Anthem was such a pleasure. Too often on occasions like this, the anthem is played, and no one sings. And we sang so beautifully this evening that it brought tears to my eyes. It is not often we get to think patriotic thoughts in Sri Lanka nowadays: this evening was a refreshing exception.
I’m never very sure what to say on an occasion like this, in which we celebrate history, especially given that I am a scientist and not a historian. It poses something of a challenge for me. Although we are often told that we must study history because it repeats itself, I don’t believe it ever does. But history certainly informs us: articles such as those in The Ceylon Journal, of which I read an advance copy, help us understand the context of our past and how it explains our present.
I want to take an example and explain what I am on about. I’m going to talk about rubber. Yes rubber, as in ‘eraser’, and how it crafted our national political identity, helping, even now seven decades later, to make ‘capitalism’ a pejorative.
As I think you know already, rubber came into general use in the middle of the 19th century. Charles Macintosh invented the raincoat in 1824 by placing a thin sheet of rubber between two sheets of fabric and pressing them together. That invention transformed many things, not least warfare. Just think of Napoleon’s invasion of Russia in the winter of 1812. His troops did that without any kind of waterproof clothing. Some 200,000 of them perished, not from bullets but from hypothermia. Waterproof raincoats could have saved thousands of lives. Not long after rubber came to be used for waterproofing, we saw the first undersea telegraph cable connecting Europe to North America being laid in the 1850s. When the American civil war broke out in 1860, demand for rubber increased yet further: the troops needed raincoats and other items made from this miracle material.
At that time rubber, used to be collected from the wild in the province of Pará in Northern Brazil, across which the Amazon drains into the Atlantic. In 1866, steamers began plying thousands of kilometres upriver, to return with cargoes of rubber harvested from the rainforest. Soon, the wild trees were being tapped to exhaustion and the sustainability of supply became doubtful.
Meanwhile, England was at the zenith of its colonial power, and colonial strategists thought rather like corporate strategists do today. The director of the Kew Gardens at the time, Joseph Hooker, felt there might be one day be a greater potential for rubber. He decided to look into the possibility of cultivating the rubber tree, Hevea brasiliensis, in Britain’s Asian colonies. So, he dispatched a young man called Henry Wickham to the Amazon to try to secure some seeds. In 1876, Wickham returned to Kew with 70,000 rubber seeds. These were planted out in hothouses in Kew and by the end of that year, almost 2000 of them had germinated.
These were dispatched to Ceylon, only a few weeks’ voyage away now, thanks to steamships and the Suez Canal. The director of the Peradeniya Botanic Garden at the time was George Henry Kendrick Thwaites, a brilliant systematic botanist and horticulturalist. Thwaites received the seedlings and had to decide where to plant them. He read the available literature—remember, this was 1876: there was no internet—and managed to piece together a model of the climatic conditions in the region of the Amazonian rainforest to which rubber was native. He decided that the plants would need an elevation of less than 300 metres and a minimum annual rainfall of at least 2000mm. In other words, the most suitable region for rubber would be an arc about 30 kilometres wide, extending roughly from Ambalangoda to Matale. Despite his never having seen a rubber plant until then, astonishingly, he got it exactly right.
Thwaites settled on a site in the middle of the arc, at Henarathgoda near Gampaha. That became the world’s first rubber nursery: the first successful cultivation of this tree outside Brazil. The trees grew well and, eight years later, came into seed. Henry Trimen, Thwaites’ successor, used the seeds to establish an experimental plantation near Polgahawela and also shared seeds with the Singapore Botanic Garden. Those would later become the foundation of the great Malaysian rubber industry.
But up to that time, Sri Lanka’s rubber plantation remained a solution looking for a problem. Then, in 1888, the problem arrived, and from a completely unexpected quarter: John Dunlop invented the pneumatic tire. Soon, bicycles came to be fitted with air-filled tires, followed by motorcars. In 1900, the US produced just 5,000 motorcars; by 1915, production had risen to half a million. The great rubber boom had begun.
Meanwhile, the colonial administration in Ceylon had invited investors to buy land and start cultivating rubber to feed the growing international demand. But by the early 1890s, three unusual things had happened. First, with the collapse of the coffee industry in the mid-1870s, many British investors had been bankrupted. Those who survived had to divert all their available capital into transitioning their failing coffee plantations into tea. They were understandably averse to risk. As a result, the British showed little interest in this strange tree called rubber that had been bought from Brazil.
Second, a native Sri Lankan middle class had by then emerged. The Colebrooke-Cameron reforms had led to the establishment of the Royal academy, later Royal College, by 1835. Other great schools followed in quick succession. From the middle of the 19th century, it was possible for Sri Lankans to get an education and get employment in government service, become professionals, doctors, lawyers, engineers, civil servants, clerks, and so on. And so, by the 1890s, a solid native middle class had emerged. The feature that defines a middle class, of course, is savings, and these savings now came to be translated into the capital that founded the rubber industry.
Third, the British had by then established a rail and road network and created the legal and commercial institutions for managing credit and doing business—institutions like banks, financial services, contract law and laws that regulated bankruptcy. They had made the rules, but by now, Sri Lankans had learned to play the game. And so, it came to be that Sri Lankans came to own a substantial part of the rubber-plantation industry very early in the game. By 1911, almost 200,000 acres of rubber had been planted and world demand was growing exponentially.
In just one generation, investors in rubber were reaping eye-watering returns that in today’s money would equate to Rs 3.6 million per acre per year. It was these people who, together with the coconut barons, came to own the grand mansions that adorn the poshest roads in Cinnamon Gardens: Ward Place, Rosmead Place, Barnes Place, Horton Place, and so on. There was an astonishingly rapid creation of indigenous wealth. By 1911, the tonnage at shipping calling in Sri Lankan ports—Colombo and Trincomalee—exceeded nine million tons, making them collectively the third busiest in the British Empire and the seventh busiest in the world. By comparison, the busiest port in Europe is now Rotterdam, which ranks tenth in the world.
 We often blame politicians for things that go wrong in our country and God knows they are responsible for most of it. But unfortunately for us, the first six years of independence, from 1948 to 1954, were really unlucky years for Sri Lanka. As if successive failed monsoons and falling rice crops weren’t bad enough, along came the Korean war. In the meantime, the Sri Lankan people had got used to the idea of food rations during the war and they wanted rations to be continued as free handouts. Those demands climaxed in the ‘Hartal’ of 1953, a general strike demanding something for nothing. Politicians were being forced to keep the promises they had made when before independence, that they would deliver greater prosperity than under the British.
We often blame politicians for things that go wrong in our country and God knows they are responsible for most of it. But unfortunately for us, the first six years of independence, from 1948 to 1954, were really unlucky years for Sri Lanka. As if successive failed monsoons and falling rice crops weren’t bad enough, along came the Korean war. In the meantime, the Sri Lankan people had got used to the idea of food rations during the war and they wanted rations to be continued as free handouts. Those demands climaxed in the ‘Hartal’ of 1953, a general strike demanding something for nothing. Politicians were being forced to keep the promises they had made when before independence, that they would deliver greater prosperity than under the British.
So, by 1949, D. S. Senanayake was forced to devalue the rupee, leading to rapid price inflation. Thankfully we didn’t have significant foreign debt then, or we might have had to declare insolvency much earlier than we finally did, in 2022. And then, because of failing paddy harvests, we were forced to buy rice
from China, which was in turn buying our rubber. But as luck would have it, China entered the Korean war, causing the UN, at the behest of the US, to embargo rubber exports to China.
This placed the D. S. Senanayake and John Kotelawala governments in an impossible predicament. There was a rice shortage; people were demanding free rice, and without rubber exports, there was no foreign exchange with which to buy rice. Kotelawala flew to Washington, D.C., to meet with President Eisenhower and plead for either an exemption from the embargo or else, for the US to buy our rubber. Despite Sri Lanka having provided rubber to the Allies at concessionary prices during the war and having supported the Allies, Eisenhower refused. British and American memories were short indeed. In India, Mahatma Gandhi and the Congress Party had chosen the moment, in August 1942 when Japan invaded Southeast Asia and were poised to invade Bengal, to demand that the British quit India, threatening in the alternative that they would throw their lot in with the Japanese. The Sri Lankan government, by contrast, had stood solidly by the Allies. But now, those same allies stabbed the fledgling nation in the chest. Gratitude, it seemed, was a concept alien to the West.
In these circumstances, Sri Lanka had no choice but to break the UN embargo and enter into a rice-for-rubber barter agreement with China. This resulted not only in the US suspending aid and the supply of agricultural chemicals to Sri Lanka, but also invoking the Battle Act and placing restrictions on US and UK ships calling at the island’s ports.
Understandably, by 1948, Sri Lankans entertained a strong disdain for colonialism. With the Cold War now under way, the USSR and China did all they could to split countries like Sri Lana away not just from their erstwhile colonial masters but also the capitalist system. If any doubt persisted in the minds of Sri Lankan politicians, Western sanctions put an end to that. The country fell into the warm embrace of the communist powers. China and the USSR were quick to fill the void left by the West, and especially in the 1950s, there was good reason to believe that the communist system was working. The Soviet economy was seeing unprecedented growth, and that decade saw them producing hydrogen bombs and putting the first satellite, dog and man in space.
As a consequence of the West’s perfidy in the early 1950s, ‘Capitalism’ continues to have pejorative connotations in Sri Lanka to this day. And it resulted in us becoming more insular, more inward looking, and anxious to assert our nationalism even when it cost us dearly.
Soon, we abolished the use of English, and we nationalized Western oil companies and the plantations. None of these things did us the slightest bit of good. We even changed the name of the country in English from Ceylon to Sri Lanka. Most countries in the world have an international name in addition to the name they call themselves. Sri Lanka had been ‘Lanka’ in Sinhala throughout the colonial period, even as its name had been Ceylon in English. The Japanese don’t call themselves Japan in their own language, neither do the Germans call themselves Germany. These are international names for Nihon and Deutschland, just like Baharat or Hindustan is what Indians call India. But we insisted that little Sri Lanka will assert itself and insist what the world would call us, the classic symptom of a massive inferiority complex. While countries like Singapore built on the brand value of their colonial names, we erased ours from the books. Now, no one knows where Ceylon tea or Ceylon cinnamon comes from.
Singapore is itself a British name: it should be Sinha Pura, the Lion City, a Sanskrit name. But Singapore values its bottom line more than its commitment to terminological exactitude. Even the name of its first British governor, Sir Stamford Raffles, has become a valued national brand. But here in Sri Lanka, rather than build on our colonial heritage, not the least liberal values the British engendered in us, together with democracy and a moderately regulated economy, we have chosen to deny it and seek to expunge it from our memory. We rejected the good values of the West along with the bad: like courtesy, queuing, and the idea that corruption is wrong.
We have stopped fighting for the dignity of our land, and I hope that as you read the articles in The Ceylon Journal that are published in the future, we will be reminded time and time again of the beautiful heritage of our country and how we can once again find it in ourselves to be proud of this wonderful land.
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoSuspect injured in police shooting hospitalised
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoRobbers and Wreckers
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoSri Lanka’s Foreign Policy amid Geopolitical Transformations: 1990-2024 – Part III
-

 Midweek Review5 days ago
Midweek Review5 days agoInequality is killing the Middle Class
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoSanjiv Hulugalle appointed CEO and General Manager of Cinnamon Life at City of Dreams Sri Lanka
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA brighter future …
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoNational Anti-Corruption Action Plan launched with focus on economic recovery
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoIChemC signs MoU with KIIT, India























