Features
History of St. Sebastian’s Shrine Kandana

By Godfrey Cooray
Senior Attorney-at-Law
President, National Catholic Writers’ Association
According to legend, St. Sebastian was born at Narbonne, in Gaul. He became a soldier in Rome and encouraged Marcellian and Marcus, who were sentence of death, to remain firm in their faith. St. Sebastian made several converts; among them were master of the rolls Nicostratus, who was in charge of prisoners, and his wife Zoe, a deaf mute whom he cured.
Sebastian was named captain in the Roman Army by Emperor Diocletian, as by Emperor Maximian when Diocletian went to the east. Neither knew that Sebastian was a Christian. When it was discovered that Sebastian was, indeed, a Christian, he was ordered to be executed. He was shot with arrows and left to die but when the widow of St. Castulas went to recover his body, she found that he was still alive and nursed him back to health. Soon after his recovery, St. Sebastian intercepted the Emperor; denounced him for his cruelty to Christians and was beaten to death on the Emperor’s order.
St. Sebastian was venerated in Milan as early as the time of St. Ambrose. St. Sebastian is the patron of archers, athletes, soldiers, the Saint of the youths and is appealed to protection against plagues. St. Ambrose reveals that the parents, that young Sebastian were living with in Milan, were a noble family. St. Ambrose further says that Sebastian, along with his three friends, Pankasi, Pulvius and Thorvinus, completed his education successfully with the blessing of his mother, Luciana. Rev. Fr. Dishnef guided him through his spiritual life. From his childhood, Sebastian wanted to join the Roman Army. With the help of King Karnus, young Sebastian became a soldier. Within as short span of time, he was appointed as the Commander of the Army of king Karnus.
Emperor Diocletian declared Christians the enemy of the Roman Empire and instructed judges to punish Christians who have embraced the Catholic Church. Young Sebastian, as one of the servants of Christ, converted thousands of other believers into Christians. When Emperor Diocletian revealed that Sebastian had become a Catholic, the anger Emperor ordered for Sebastian to be shot with arrows to death. After being shot by arrows, one of Sebastian supporters, Irane, treated him and cured him. When Sebastian was cured, he came to Emperor Diocletian and professed his faith for the second time disclosing that he is a servant of the Christ. Astounded by the fact that Sebastian is a Christian, Emperor Diocletian ordered the Roman Army to kill Sebastian with club blows.
In the liturgical calendar of the church, the feast of St. Sebastian is celebrated on the 20th of January. This day is, indeed, a mini Christmas to the people of Kandana, irrespective of their religion. The feast commence with the hoisting of the flag staff on the 11th of January at 4 p.m. at the Kandana junction, along the Colombo-Negombo road. There is a long history attached to the flag staff. The first flag staf,f which was an arieca nut tree, 25 feet tall, was hoisted by the Aththidiya family of Kandana and today their descendants continue the hoisting of the flag staff as a tradition. This year’s flag staff, too, was hoisted by the Raymond Aththidiya family. Several processions, originating from different directions carrying flags, meet at this flag staff junction. The pouring of milk on the flag staff has been a tradition in existence for a long time. The Nagasalan band was introduced by a well-known Jaffna businessman that had engaged in business in Kandana in the 1950s. The famous Kandaiyan Pille’s Nagasalan group takes the lead even today in the procession. Kiribath Dane in the Kandana town had been a tradition from time immemorial.
According to available history from the Catholic archives and volume III of the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka, the British period of vicariates of Colombo, written by Rev. Ft. Vito Perniola SJ, in 1806, states that the British government granted the freedom of conscious and religion to the Catholics in Ceylon and abolished all the anti-Catholic legislation enacted by the Dutch. The proclamation was declared and issued on the 3rd of August 1796 by Colonel James Stuart, the officer commanding the British forces of Ceylon as stated instated “Freedom granted to Catholics” (Sri Lanka national archives 20/5).
Before the Europeans, the missioners were all Goans from South India. In the year 1834, on the 3rd of December, XVI Gregory the Pope, issued a document Ex Muwere pastoralis ministeric, after which the Ceylon Catholic Church was made under the south Indian Cochin diocese. Very Rev. Fr. Vincent Rosario, the apostolic vicar general, was appointed along with 18 Goan priests (The Oratorion Mission in Sri Lanka being a history of the Catholic Chruch 1796-1874 by Arthur C Dep Chapter 11 pg 12). Rev Fr. Joachim Alberto arrived in Sri Lanka as missionary on the 6th of March 1830 when he was 31 years old and he was appointed to look after Catholics in Aluthkuru Korale, consisting Kandana, Mabole, Nagodaa and Ragama. There has been one Church built in 1810 in Wewala, about three miles away from Kandana. Wewala Chruch was situated bordering Muthurajawela which rose to fame for its granary. History reveals that the entire area was under paddy cultivation of which most of them were either farmers or toddy tappers. History further reveals that there has been an old canal built by King Weera Parakrama Bahu. Later it was built to flow through the Kelani River and Muthurajawela up to Negombo which was named as the Dutch Canal (RL Brohier historian). During the British time this canal was named as Hamilton Canal and was used to transport toddy, spices, paddy and tree planks. The tree planks were stored in Kandana. Therefore, the name Kandana derives from “Kandan Aana”.
 Rev. Fr. Joachim Alberto purchased a small piece of land called Haamuduruwange watte at Nadurupititya in Kandana and put up a small cadjan chapel and placed a picture of St. Sebastian for the benefit of his small congregation. In 1837 with the help of the devotees, he dug a small well and the water was used for tdrinking and bathing and today this well is still operative. He bought several acres of land, including the present cemetery premises. Moreover, he had put up the Church at Kalaeliya in honour of his patron St. Joachim where his body has been laid to rest according to his wish of the Last will attested by Weerasinghe Arachchige Brasianu Thilakaratne. Notary public dated 19th of July 1855. The present Church was built on the property bought on the 13th of August 1875 on deed no. 146 attested by Graciano Fernando. Notary public of the land Gorakagahawatta Aluthkuru Korale Ragam Pattu in Kandana within the extend ¼ acre from and out of the 16 acres. According to the old plan number 374 made by P.A. H. Philipia, Licensed surveyor , 9 acres and 25 perches belonged to St. Sebastian Church. However, today only 3 acres, 3 roods and 16.5 perches are left, according to plan number 397, surveyed by the same surveyor, while the rest had been sold to the villagers. According to the survey conducted by an Orithorian priest on 12th of February 1844 there were only 18 school-going Catholic students in AluthKuru Korale and one Antonio was the teaching for all classes. In 1844 there was no schools at Kandana (APF SCG India Volume 9829).
Rev. Fr. Joachim Alberto purchased a small piece of land called Haamuduruwange watte at Nadurupititya in Kandana and put up a small cadjan chapel and placed a picture of St. Sebastian for the benefit of his small congregation. In 1837 with the help of the devotees, he dug a small well and the water was used for tdrinking and bathing and today this well is still operative. He bought several acres of land, including the present cemetery premises. Moreover, he had put up the Church at Kalaeliya in honour of his patron St. Joachim where his body has been laid to rest according to his wish of the Last will attested by Weerasinghe Arachchige Brasianu Thilakaratne. Notary public dated 19th of July 1855. The present Church was built on the property bought on the 13th of August 1875 on deed no. 146 attested by Graciano Fernando. Notary public of the land Gorakagahawatta Aluthkuru Korale Ragam Pattu in Kandana within the extend ¼ acre from and out of the 16 acres. According to the old plan number 374 made by P.A. H. Philipia, Licensed surveyor , 9 acres and 25 perches belonged to St. Sebastian Church. However, today only 3 acres, 3 roods and 16.5 perches are left, according to plan number 397, surveyed by the same surveyor, while the rest had been sold to the villagers. According to the survey conducted by an Orithorian priest on 12th of February 1844 there were only 18 school-going Catholic students in AluthKuru Korale and one Antonio was the teaching for all classes. In 1844 there was no schools at Kandana (APF SCG India Volume 9829).
According to Sri Lanka National Archives (The Ceylon Almanac page 185), in the year 1852 there were 982 Catholics, According to the census reports in 2014 prepared by Rev. Ft. Sumeda Dissanayake TOR, the Director Franciscan Preaching group, Kadirana Negombo a survey revealed that there are 13,498 Catholics in Kandana.
According to the appointment of the Missionaries in the year 1866-1867 by Bishop Hillarien Sillani, Rev. Fr. Clement Pagnani OSB was sent to look after the missions in Negoda, Ragama, Batagama, Thudella, Kandana, Kala Eliya and Mabole. On the 18th of April 1866, the building of the new church commenced with a written agreement by and between Rec. Fr. Clement Pagnani and the then leaders of the Kandana Catholic Village Committee. This committee consisted of Kanugalawattage Savial Perera Samarasinghe Welwidane, Amarathunga Arachchige Issak Perera Appuhamy, Jayasuriya Arachchige Don Isthewan Appuhamy, Jayasuriya Appuhamylage Elaris Perera Muhuppu, Padukkage Andiris Perera Opisara, Kanugalawattage Peduru Perera Annavi and Mallawa Arachchige Don Peduru Appujamy. The said agreement stated that they will give a written undertaking that their labour and money will be utilized to build the new church of St. Sebastian and if they failed to do so they were ready to bear any punishment which will be imposed by the Catholic Church.
Rev. Fr. Bede Bercatta’s book “A History of the Vicariate of Colombo (page 359) says that Rev. Fr. Stanislaus Tabarani had problems of finding rock stones to lay the foundation. He was greatly worried over this and placed his due trust in divine providence. He prayed for days to St. Sebastian for his intercession. One morning after mass, he was informed by some people that they had seen a small patch of granite at a place in Rilaulla, close to the cChurch premises, although such stones were never seen there earlier, and requested him to inspect the place. The Parish Priest visited the location and was greatly delighted as his prayers has been answered.
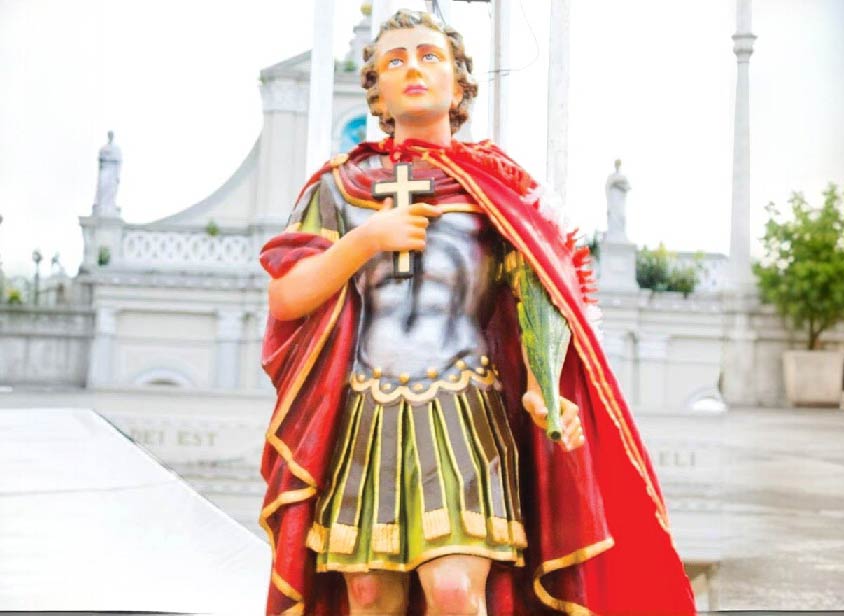
This small amount of granite rock provided enough granite blocks for the full foundation of the present Church. This place still known as “Rilaulla galwala”. The work on the building proceeded under successive parish priests but Rev. Fr. Stouter was responsible for much of it. The façade of the Church was built so high that it crashed on the 2nd of April of 1893. The present façade was then built and completed in the year 1905. The statue of St. Sebastian, which is behind the altar, had been carved off a “Madan tree”. It was done by a Paravara man named Costa Mama, who was staying with a resident named Miguel Baas at Ridualle, Kandana.
This statue was made at the request of Pavistina Perera Amaratunge, mother of former Member of Parliament gate mudaliyar D. Panthi Jayasuirya. The Church was completed during the time of Rev. Fr. Keegar and was blessed by then Archbishop of Colombo, Dr. Anthony Courdert OMI on 20th January 1912. In 1926, Rev. Fr. Romauld Fernando was appointed as the Parish Priest to the Kandana Church. He was an educationalist and a social worker. Without any hesitation he can be called as the father of education to Kandana. He was the pioneer to build three schools in Kandana: Kandana St. Sebastian Boys School, Kandana St. Sebastian English Girls School and Mazenod College Kandana.
Later he was appointed as the principal of St. Sebastian Boys English School. He bought a property at Kandana, close to the Ganemulla road, and started De Mazenod College. Later, it was given officially to Christian Brothers of Sri Lanka, by the then Archbishop of Colombo, Peter Mark. In 1931, there were 300 students (history of De Lasalle brothers by Rev. Fr. Bro Michael Robert). Today, there are over 3,500 students and is one of the leading Catholic schools in Sri Lanka. In 1924, one Karolis Jayasuriya Widanage donated two acres for the extension of De Mazenod College.
The frist priest from Kandana to be ordained was Rev. Fr. William Perera in 1904. With the help of Rev. Fr. Marcelline Jayakody, he composed the famous hymn “the Vikshopa Geethaya”, the hymn of our Lady of Sorrow.
The Life story of St. Sebastian was portrayed through a stage play called “Wasappauwa” and the world famous German passion play ‘’Obar Amargave wchi’’ was a sensation, initiated by Rev. Fr. Nicholas Perera. Legend reveals that in the year 1845, a South Indian Catholic on his way to meet his relatives in Colombo had brought a wooden statue of St. Sebastian, one and half feet tall, to be sold in Sri Lanka. When he reached Kalpitiya he had unexpectedly contracted malaria. He had made a vow at St. Anne’s Church. Thalawila, expecting a full recovery. En route to Colombo, he had come to know about the Church in Kandana and dedicated to St. Sebastian. In the absence of the then Parish Priest Rev. Fr. Joachim Alberto, the Muhuppu of the Church, with the help of others, had agreed to buy the statue for 75 pathagas (one pahtaga was 75 cents). Even though the seller had left the money in the hands of the “Muhuppu” to be collected, he never returned.
On the 19th of January 2006, Archbishop Oswald Gomis declared St. Sebastian Church as “St. Sebastian Shrine” by way of special notification and handed over the declaration to Rev. Fr. Susith Perera, the Parish Priest of Kandana.
On the 12th of January 2014, Catholics in Sri Lanka celebrated the reception of a reliquary containing a fragment of the arm of St. Sebastian. The reliquary was gifted from the administrator of the Basilica of St. Anthony of Padua and was brought to Sri Lanka by Monsignor Neville Perera. His Eminence Cardinal Malcolm Ranjit, Archbishop of Colombo, accompanied by priests and a large gathering, received the relic at the Katunayake International Airport, and brought it to Kandana led by a procession, and was enthroned at the St. Sebastian Shrine.
Rev. Fr. Lalith Expeditus, the present administrator of the shrine, and two other assistant priests, Rev. Fr. Anura Dias and Rev. Fr. Asela Mario, have finalized all arrangements to conduct the feast of St. Sebastian on a grand scale.
The latest book, written by Godfrey Cooray, named “Santha Sebastian Puranaya Saha Kandana (The history of St. Sebastian and Kandana), was launched at De La Salle Auditorium De Mazenod College, Kandana.
The Archbishop of Colombo His Eminence Most Rev. Cardinal Malcolm Ranjith was the Chief Guest.
The book discusses about the buried history of Muthurajawela and Aluth Kuru Korale civilisation, the history of Kandana and St. Sebastian. The author discusses the historical and archaeological values and culture.
The 157th Annual Feast of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine, Kandana, will be held on 20th January 2025. On the 19th of January, Sunday at 7 pm, Solemn Vespers will be presided by His Eminence Most Rev. Cardinal Malcolm Ranjith, the Archbishop of Colombo. Festive High Mass will be presided by His Lordship Most Rev. Dr. J. D. Anthony, the Auxiliary Bishop of Colombo, on 20th of January at 8pm.
Features
RIDDHI-MA:

A new Era of Dance in Sri Lanka
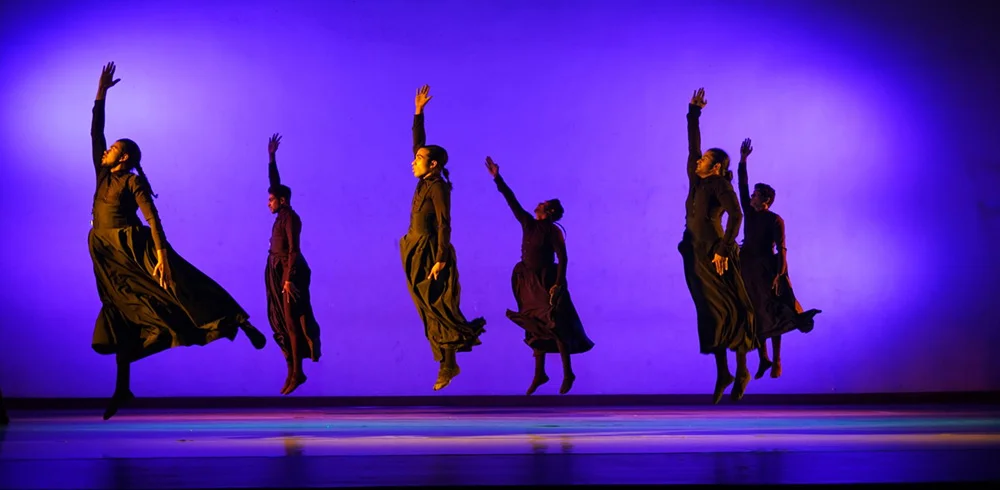
Kapila Palihawadana, an internationally renowned dancer and choreographer staged his new dance production, Riddhi-Ma, on 28 March 2025 at the Elphinstone theatre, which was filled with Sri Lankan theatregoers, foreign diplomats and students of dance. Kapila appeared on stage with his charismatic persona signifying the performance to be unravelled on stage. I was anxiously waiting to see nATANDA dancers. He briefly introduced the narrative and the thematic background to the production to be witnessed. According to him, Kapila has been inspired by the Sri Lankan southern traditional dance (Low Country) and the mythologies related to Riddhi Yâgaya (Riddi Ritual) and the black magic to produce a ‘contemporary ballet’.
Riddhi Yâgaya also known as Rata Yakuma is one of the elaborative exorcism rituals performed in the southern dance tradition in Sri Lanka. It is particularly performed in Matara and Bentara areas where this ritual is performed in order to curb the barrenness and the expectation of fertility for young women (Fargnoli & Seneviratne 2021). Kapila’s contemporary ballet production had intermingled both character, Riddi Bisaw (Princes Riddhi) and the story of Kalu Kumaraya (Black Prince), who possesses young women and caught in the evil gaze (yaksa disti) while cursing upon them to be ill (De Munck, 1990).
Kapila weaves a tapestry of ritual dance elements with the ballet movements to create visually stunning images on stage. Over one and a half hours of duration, Kapila’s dancers mesmerized the audience through their virtuosic bodily competencies in Western ballet, Sri Lankan dance, especially the symbolic elements of low country dance and the spontaneity of movements. It is human bodily virtuosity and the rhythmic structures, which galvanised our senses throughout the performance. From very low phases of bodily movements to high speed acceleration, Kapila managed to visualise the human body as an elevated sublimity.
Contemporary Ballet
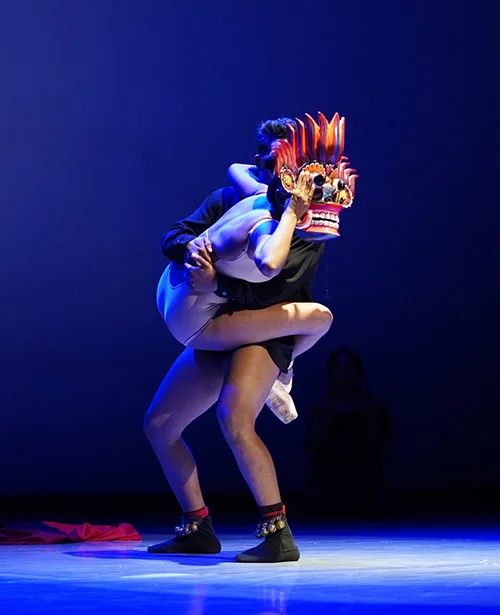

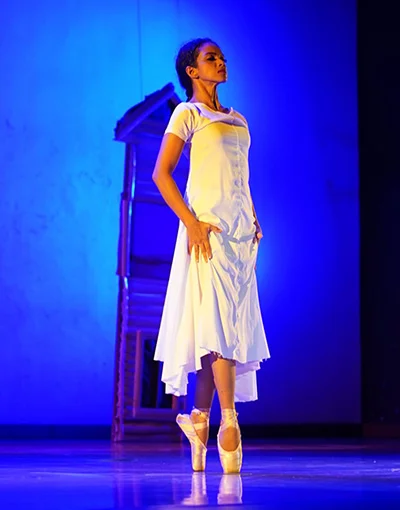
Figure 2 – (L) Umesha Kapilarathna performs en pointe, and (R) Narmada Nekethani performs with Jeewaka Randeepa, Riddhi-Ma, at Elphinstone Theatre, Maradana, 28th March 2025. Source:
Malshan Witharana
The dance production Riddhi-Ma was choreographed in several segments accompanied by a flow of various music arrangements and sound elements within which the dance narrative was laid through. In other words, Kapila as a choreographer, overcomes the modernist deadlock in his contemporary dance work that the majority of Sri Lankan dance choreographers have very often succumbed to. These images of bodies of female dancers commensurate the narrative of women’s fate and her vulnerability in being possessed by the Black Demon and how she overcomes and emancipates from the oppression. In this sense, Kapila’s dancers have showcased their ability to use the bodies not much as an object which is trained to perform a particular tradition but to present bodily fluidity which can be transformed into any form. Kapila’s performers possess formlessness, fluid fragility through which they break and overcome their bodily regimentations.
It was such a highly sophisticated ‘contemporary ballet’ performed at a Sri Lankan theatre with utmost rigour and precision. Bodies of all male and female dancers were highly trained and refined through classical ballet and contemporary dance. In addition, they demonstrated their abilities in performing other forms of dance. Their bodies were trained to achieve skilful execution of complex ballet movements, especially key elements of traditional ballet namely, improvisation, partnering, interpretation and off-balance and the local dance repertoires. Yet, these key ballet elements are not necessarily a part of contemporary ballet training (Marttinen, 2016). However, it is important for the dance students to learn these key elements of traditional ballet and use them in the contemporary dance settings. In this sense, Kapila’s dancers have achieved such vigour and somatic precision through assiduous practice of the body to create the magic on stage.
Pas de deux

Among others, a particular dance sequence attracted my attention the most. In the traditional ballet lexicon, it is a ‘pas de deux’ which is performed by the ‘same race male and female dancers,’ which can be called ‘a duet’. As Lutts argues, ‘Many contemporary choreographers are challenging social structures and norms within ballet by messing with the structure of the pas de deux (Lutts, 2019). Pas de Deux is a dance typically done by male and female dancers. In this case, Kapila has selected a male and a female dancer whose gender hierarchies appeared to be diminished through the choreographic work. In the traditional pas de deux, the male appears as the backdrop of the female dancer or the main anchorage of the female body, where the female body is presented with the support of the male body. Kapila has consciously been able to change this hierarchical division between the traditional ballet and the contemporary dance by presenting the female dominance in the act of dance.
The sequence was choreographed around a powerful depiction of the possession of the Gara Yakâ over a young woman, whose vulnerability and the powerful resurrection from the possession was performed by two young dancers. The female dancer, a ballerina, was in a leotard and a tight while wearing a pair of pointe shoes (toe shoes). Pointe shoes help the dancers to swirl on one spot (fouettés), on the pointed toes of one leg, which is the indication of the ballet dancer’s ability to perform en pointe (The Kennedy Centre 2020).
The stunning imagery was created throughout this sequence by the female and the male dancers intertwining their flexible bodies upon each other, throwing their bodies vertically and horizontally while maintaining balance and imbalance together. The ballerina’s right leg is bent and her toes are directed towards the floor while performing the en pointe with her ankle. Throughout the sequence she holds the Gara Yakâ mask while performing with the partner.
The male dancer behind the ballerina maintains a posture while depicting low country hand gestures combining and blurring the boundaries between Sri Lankan dance and the Western ballet (see figure 3). In this sequence, the male dancer maintains the balance of the body while lifting the female dancer’s body in the air signifying some classical elements of ballet.
Haptic sense

Figure 3: Narmada Nekathani performs with the Gara Yaka mask while indicating her right leg as en pointe. Male dancer, Jeewaka Randeepa’s hand gestures signify the low country pose. Riddhi-Ma, Dance Theatre at Elphinstone Theatre, 28th March 2025. Source: Malshan Witharana.
One significant element of this contemporary ballet production is the costume design. The selection of colour palette, containing black, red and while combining with other corresponding colours and also the costumes which break the traditional rules and norms are compelling. I have discussed in a recent publication how clothes connect with the performer’s body and operate as an embodied haptic perception to connect with the spectators (Liyanage, 2025). In this production, the costumes operate in two different ways: First it signifies sculpted bodies creating an embodied, empathic experience.
Secondly, designs of costumes work as a mode of three dimensional haptic sense. Kapila gives his dancers fully covered clothing, while they generate classical ballet and Sinhalese ritual dance movements. The covered bodies create another dimension to clothing over bodies. In doing so, Kapila attempts to create sculpted bodies on stage by blurring the boundaries of gender oriented clothing and its usage in Sri Lankan dance.
Sri Lankan female body on stage, particularly in dance has been presented as an object of male desire. I have elsewhere cited that the lâsya or the feminine gestures of the dance repertoire has been the marker of the quality of dance against the tândava tradition (Liyanage, 2025). The theatregoers visit the theatre to appreciate the lâsya bodies of female dancers and if the dancer meets this threshold, then she becomes the versatile dancer. Kandyan dancers such as Vajira and Chithrasena’s dance works are explored and analysed with this lâsya and tândava criteria. Vajira for instance becomes the icon of the lâsya in the Kandyan tradition. It is not my intention here to further discuss the discourse of lâsya and tândava here.
But Kapila’s contemporary ballet overcomes this duality of male-female aesthetic categorization of lâsya and tândava which has been a historical categorization of dance bodies in Sri Lanka (Sanjeewa 2021).

Figure 4: Riddhi-Ma’s costumes creates sculpted bodies combining the performer and the audience through empathic projection. Dancers, Sithija Sithimina and Senuri Nimsara appear in Riddhi-Ma, at Elphinstone Theatre, 28th March 2025, Source, Malshan Witharana.
Conclusion
Dance imagination in the Sri Lankan creative industry exploits the female body as an object. The colonial mind set of the dance body as a histrionic, gendered, exotic and aesthetic object is still embedded in the majority of dance productions produced in the current cultural industry. Moreover, dance is still understood as a ‘language’ similar to music where the narratives are shared in symbolic movements. Yet, Kapila has shown us that dance exists beyond language or lingual structures where it creates humans to experience alternative existence and expression. In this sense, dance is intrinsically a mode of ‘being’, a kinaesthetic connection where its phenomenality operates beyond the rationality of our daily life.
At this juncture, Kapila and his dance ensemble have marked a significant milestone by eradicating the archetypical and stereotypes in Sri Lankan dance. Kapila’s intervention with Riddi Ma is way ahead of our contemporary reality of Sri Lankan dance which will undoubtedly lead to a new era of dance theatre in Sri Lanka.
References
De Munck, V. C. (1990). Choosing metaphor. A case study of Sri Lankan exorcism. Anthropos, 317-328. Fargnoli, A., & Seneviratne, D. (2021). Exploring Rata Yakuma: Weaving dance/movement therapy and a
Sri Lankan healing ritual. Creative Arts in Education and Therapy (CAET), 230-244.
Liyanage, S. 2025. “Arts and Culture in the Post-War Sri Lanka: Body as Protest in Post-Political Aragalaya (Porattam).” In Reflections on the Continuing Crises of Post-War Sri Lanka, edited by Gamini Keerawella and Amal Jayawardane, 245–78. Colombo: Institute for International Studies (IIS) Sri Lanka.
Lutts, A. (2019). Storytelling in Contemporary Ballet.
Samarasinghe, S. G. (1977). A Methodology for the Collection of the Sinhala Ritual. Asian Folklore Studies, 105-130.
Sanjeewa, W. (2021). Historical Perspective of Gender Typed Participation in the Performing Arts in Sri Lanka During the Pre-Colonial, The Colonial Era, and the Post-Colonial Eras. International Journal of Social Science And Human Research, 4(5), 989-997.
The Kennedy Centre. 2020. “Pointe Shoes Dancing on the Tips of the Toes.” Kennedy-Center.org. 2020 https://www.kennedy-center.org/education/resources-for-educators/classroom-resources/media- and-interactives/media/dance/pointe-shoes/..
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Himansi Dehigama for proofreading this article.
About the author:
Saumya Liyanage (PhD) is a film and theatre actor and professor in drama and theatre, currently working at the Department of Theatre Ballet and Modern Dance, Faculty of Dance and Drama, University of the Visual and Performing Arts (UVPA), Colombo. He is the former Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies and is currently holding the director position of the Social Reconciliation Centre, UVPA Colombo.
Features
Sri Lanka’s Foreign Policy amid Geopolitical Transformations: 1990-2024 – Part II
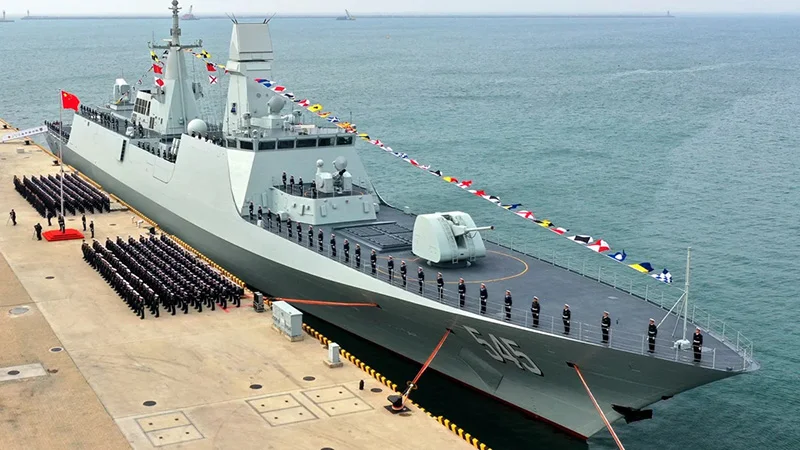

Chinese Naval Entry and End of Post-War Unipolarity
The ascendancy of China as an emerging superpower is one of the most striking shifts in the global distribution of economic and political power in the 21st century. With its strategic rise, China has assumed a more proactive diplomatic and economic role in the Indian Ocean, signalling its emergence as a global superpower. This new leadership role is exemplified by initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the establishment of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB). The Economist noted that “China’s decision to fund a new multilateral bank rather than give more to existing ones reflects its exasperation with the glacial pace of global economic governance reform” (The Economist, 11 November 2014). Thus far, China’s ascent to global superpower status has been largely peaceful.
In 2025, in terms of Navy fleet strength, China became the world’s largest Navy, with a fleet of 754 ships, thanks to its ambitious naval modernisation programme. In May 2024, the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) further strengthened its capabilities by commissioning the Fujian, its latest aircraft carrier. Equipped with an advanced electromagnetic catapult system, the Fujian can launch larger and heavier aircraft, marking a significant upgrade over its predecessors.
Driven by export-led growth, China sought to reinvest its trade surplus, redefining the Indian Ocean region not just as a market but as a key hub for infrastructure investment. Notably, over 80 percent of China’s oil imports from the Persian Gulf transit to the Straits of Malacca before reaching its industrial centres. These factors underscore the Indian Ocean’s critical role in China’s economic and naval strategic trajectories.
China’s port construction projects along the Indian Ocean littoral, often associated with the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), exemplify its deepening geopolitical and economic engagement in the region. These initiatives encompass multipurpose berth development, deep-sea port construction, and supporting infrastructure projects aimed at enhancing maritime connectivity and trade. Key projects include the development of Gwadar Port in Pakistan, a strategic asset for China’s access to the Arabian Sea; Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka, which became a focal point of debt diplomacy concerns; the Payra deep-sea port in Bangladesh; as well as port and road infrastructure development in Myanmar’s Yunnan and Kyaukphyu regions and Cambodia’s Koh Kong.
While these projects were promoted as avenues for economic growth and regional connectivity, they also triggered geopolitical tensions and domestic opposition in several host countries. Concerns over excessive debt burdens, lack of transparency, and potential dual-use (civilian and military) implications of port facilities led to scrutiny from both local and external stakeholders, including India and Western powers. As a result, some projects faced significant pushback, delays, and, in certain cases, suspension or cancellation. This opposition underscores the complex interplay between economic cooperation, strategic interests, and sovereignty concerns in China’s Indian Ocean engagements.
China’s expanding economic, diplomatic, and naval footprint in the Indian Ocean has fundamentally altered the region’s strategic landscape, signalling the end of early post-Cold War unipolarity. Through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) initiatives, China has entrenched itself economically, financing. Diplomatically, Beijing has deepened its engagement with littoral states through bilateral agreements, security partnerships, and regional forums, challenging traditional Western and Indian influence.
China’s expanding naval deployments in the Indian Ocean, including its military base in Djibouti, and growing security cooperation with regional states, mark the end of unchallenged US dominance in the region. The Indian Ocean is now a contested space, where China’s presence compels strategic recalibrations by India, the United States, and other regional actors. The evolving security landscape in the Indian Ocean—marked by intensifying competition, shifting alliances, and the rise of a multipolar order—has significant implications for Sri Lanka’s geopolitical future.
India views China’s growing economic, political, and strategic presence in the Indian Ocean region as a key strategic challenge. In response, India has pursued a range of strategic, political, and economic measures to counterbalance Chinese influence, particularly in countries like Sri Lanka through infrastructure investment, defense partnerships, and diplomatic engagements.
Other Extra-Regional powers
Japan and Australia have emerged as significant players in the post-Cold War strategic landscape of the Indian Ocean. During the early phases of the Cold War, Australia played a crucial role in Western ‘Collective Security Alliances’ (ANZUS and (SEATO). However, its direct engagement in Indian Ocean security remained limited, primarily supporting the British Royal Navy under Commonwealth obligations. Japan, meanwhile, refrained from deploying naval forces in the region after World War II, adhering to its pacifist constitution and post-war security policies. In recent decades, shifting strategic conditions have prompted both Japan and Australia to reassess their roles in the Indian Ocean, leading to greater defence cooperation and a more proactive regional presence.
In the post-Cold War era, Australia has progressively expanded its naval engagements in the Indian Ocean, driven by concerns over maritime security, protection of trade routes, and China’s growing influence. Through initiatives, such as the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) and deeper defence partnerships with India and the United States, Australia has bolstered its strategic presence in the Indian Ocean region.
Recalibration of Japan’s approach
Japan, too, has recalibrated its approach to Indian Ocean security in response to geopolitical shifts. Recognising the Indian Ocean’s critical importance for its energy security and trade, Japan has strengthened its naval presence through port visits, joint exercises, and maritime security cooperation. The Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force (JMSDF) has taken on a more active role in anti-piracy operations, freedom of navigation operations (FONOPS), and strategic partnerships with Indian Ocean littoral states. This shift aligns with Japan’s broader strategy of contributing to regional stability while balancing its constitutional constraints on military force projection.
Japan’s proactive role in the Indian Ocean region is evident in its diplomatic and defence engagements. In January 2019, Japan sent its Foreign Minister, Taro Kono, and Chief of Staff, Joint Staff, Katsutoshi Kawano, to the Raisina Dialogue, a high-profile geopolitical conference in India. Japan’s National Security Strategy, released in December 2022, identifies China’s growing assertiveness as its greatest strategic challenge and underscores the need to deepen bilateral ties and multilateral defence cooperation in the Indian Ocean. It also emphasises the importance of securing stable access to sea-lanes, through which more than 80 percent of Japan’s oil imports pass. In recent years, Japan has expanded its port investment portfolio across the Indian Ocean, with major projects in Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In 2021, Japan participated for the first time in CARAT-Sri Lanka (Cooperation Afloat Readiness and Training), a bilateral naval exercise. Japan’s Maritime Self-Defence Force returned for the exercise in January 2023, held at Trincomalee Port and Mullikulam Base.
Japan’s strategic interests in the Indian Ocean have been most evident in its involvement in port infrastructure development projects. Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar are key countries where early Chinese-led port construction faced setbacks. Unlike India, which carries historical and political complexities in its relations with these countries, Japan is better positioned to compete with China. In December 2021, a Japanese company established a ship repair and rebuilding facility in Trincomalee, complementing the already well-established Tokyo Cement factory. When the Sri Lanka Ports Authority announced plans in mid-2022 to develop Trincomalee as an industrial port—inviting expressions of interest from investors to utilise port facilities and up to 2,400 hectares of surrounding land—Trincomalee regained strategic attention.
The Colombo Dockyard, in collaboration with Japan’s Onomichi Dockyard, has established a rapid response afloat service in Trincomalee, marking a significant development in Japan’s engagement with Sri Lanka’s maritime infrastructure. This initiative aligns with Japan’s broader strategic interests in the Bay of Bengal, a region of critical economic and security importance. A key Japanese concern appears to be limiting China’s ability to establish a permanent presence in Trincomalee. This initiative underscores the broader strategic competition in the Indian Ocean. Trincomalee, with its deep-water harbour, has long been regarded as a critical maritime asset. Japan’s involvement reflects its efforts to deepen economic and strategic engagement with Sri Lanka amid growing regional competition. The challenge before Sri Lanka is how to navigate this strategic contest while maximising its national interests.
Other Regional Powers
In analyzing the evolving naval security architecture of the post-Cold War Indian Ocean, particular attention should be given to the naval developments of regional powers such as Pakistan, Indonesia, and Malaysia. In 2012, Pakistan established the Naval Strategic Force Command (NSFC) to strengthen Pakistan’s policy of Credible Minimum Deterrence (CMD). The creation of the NSFC suggests a shift toward sea-based deterrence, complementing Pakistan’s broader military strategy. In December 2012, Pakistan conducted a series of cruise missile tests from naval platforms in the Arabian Sea. Given India’s expanding maritime capabilities, which Pakistan views as a significant threat, the Pakistan Navy may consider deploying tactical nuclear weapons on surface ships as part of its evolving deterrence strategy. Sri Lanka’s foreign policy cannot overlook this development.
Indonesia also emerged as a significant player in the evolving naval security landscape of the Indian Ocean. In 2010, it launched a military modernisation programme aimed at achieving a ‘Minimum Essential Force’ (MEF) by 2024. As part of this initiative, Indonesia sought to build a modern Navy with 247 surface vessels and 12 submarines. One of the primary challenges faced by the Indonesian Navy (TNI-AL) is piracy. To enhance maritime security, Indonesia and Singapore signed the SURPIC Cooperation Arrangement in Bantam in May 2005, enabling real-time sea surveillance in the Singapore Strait for more effective naval patrols. In 2017, Indonesia introduced the Indonesian Ocean Policy (IOP) and subsequently incorporated blue economy strategies into its national development agenda, reinforcing its maritime vision. According to projections from the Global Firepower Index, published in 2025, the Indonesian Navy is ranked fourth in global ranking and second in Asia in terms of Navy fleet strength (Global Firepower, 2025).
In October 2012, the Royal Malaysian Navy (RMN) announced plans to build a second Scorpène simulator training facility at its base in Kota Kinabalu, in addition to submarine base in Sepanggar, Sabah, constructed in 2002. To enhance its naval capabilities, the RMN planned to procure 18 Littoral Mission Ships (LMS) for maritime surveillance and six Littoral Combat Ships (LCS) between 2019 and 2023. Malaysia and China finalised their first major defence deal during Prime Minister Najib Razak’s visit to Beijing in November 2016. During this visit, Malaysia’s Defence Ministry signed a contract to procure LMS from China, as reported by The Guardian. Despite this agreement, Malaysia continues to maintain amicable relations with both China and India, as does Indonesia.
The increasing presence of major naval powers, the rise of regional stakeholders, and the growing significance of trade routes and maritime security have transformed the Indian Ocean into a central pivot of both regional and global politics, with Sri Lanka positioned at its heart. (To be Continued)
by Gamini Keerawella
Features
More excitement for Andrea Marr…
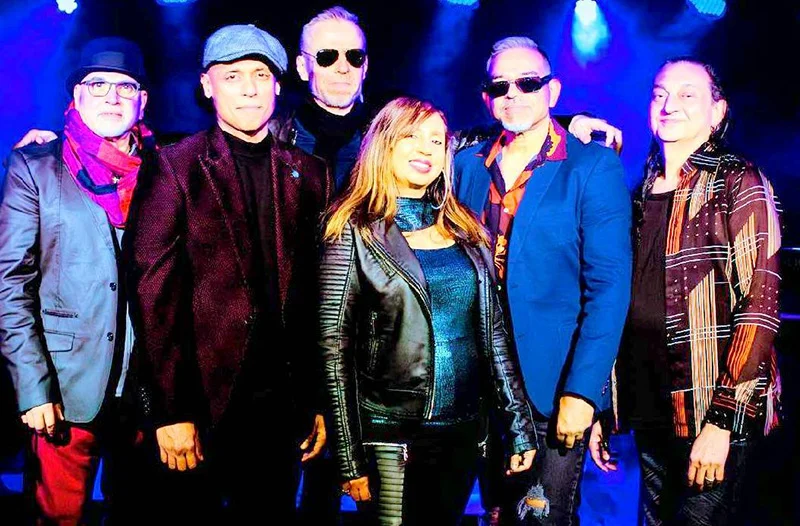

Sri Lankan Andrea Marr, now based in Australia, is in the spotlight again. She says she has teamed up with a fantastic bunch of Sri Lankan musicians, in Melbourne, and the band is called IntoGroove.
“The band has been going strong for many years and I have been a fan of this outfit for quite a few years; just love these guys, authentic R&B and funk.”
Although Andrea has her original blues band, The McNaMarr Project, and they do have a busy schedule, she went on to say that “when the opportunity came up to join these guys, I simply couldn’t refuse … they are too good.”
IntoGroove is Jude Nicholas (lead vocals), Peter Menezes (bass), Keith Pereira (drums), Blaise De Silva (keyboards) and and Steve Wright (guitar).

Andrea Marr: Powerhouse of the blues
“These guys are a fantastic band and I really want everyone to hear them.”
Andrea is a very talented artiste with many achievements to her credit, and a vocal coach, as well.
In fact, she did her second vocal coaching session at Australian Songwriters Conference early this year.
Her first student showcase for this year took place last Sunday, in Melbourne, and it brought into the spotlight the wonderful acts she has moulded, as teacher and mentor.
What makes Andrea extra special is that she has years of teaching experience and is able to do group vocal coaching for all styles, levels and genres.
In January, this year, she performed at the exclusive ‘Women In Blues’ showcase at Alfred’s On Beale Street (rock venue with live entertainment), in Memphis, in the USA, during the International Blues Challenge when bands from all over the world converge on Memphis for the ‘Olympics of the Blues.’
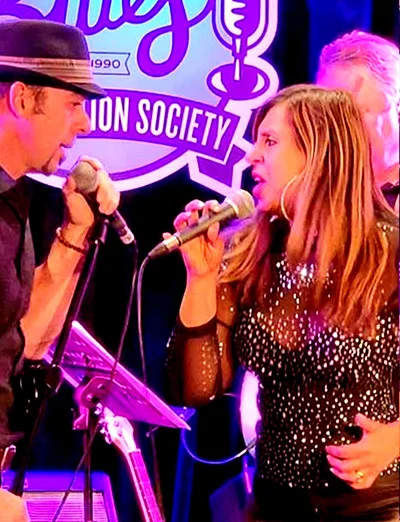

The McNaMarr Project with Andrea and Lindsay Marr in the
vocal spotlight
This was her fourth performance in the home of the blues; she has represented Australian Blues three times and, on this occasion, she went as ambassador for Blues Music Victoria, and The Melbourne Blues Appreciation Society’s ‘Women In Blues’ Coordinator.
Andrea was inducted into the Blues Music Victoria Hall of Fame in 2022 and released her 10th album which hit #1 on the Australian Blues Charts.
Known as ‘the pint-sized powerhouse of the blues’ for her high energy, soulful, original music, Andrea is also a huge fan of the late Elvis Presley and has checked out Graceland, in Memphis, Tennessee, USA, many times.
In Melbourne, the singer also plays a major role in helping Animal Rescue organisations find homes for abandoned cats.
Andrea Marr’s wish, at the moment, is that the Lankan audience, in Melbourne, would get behind this band, IntoGroove. They are world class, she added.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoColombo Coffee wins coveted management awards
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoStarlink in the Global South
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoDaraz Sri Lanka ushers in the New Year with 4.4 Avurudu Wasi Pro Max – Sri Lanka’s biggest online Avurudu sale
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoStrengthening SDG integration into provincial planning and development process
-
 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoNew SL Sovereign Bonds win foreign investor confidence
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoTo play or not to play is Richmond’s decision
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoModi’s Sri Lanka Sojourn
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoNew Zealand under 85kg rugby team set for historic tour of Sri Lanka











