News
China poised for diplomatic windfall in Sri Lanka elections

Beijing backs politicians and influential Buddhist leaders, expert says
MARWAAN MACAN-MARKAR, Asia regional correspondent, Nikkei Asian Review
BANGKOK — China is cultivating a wide swathe of political allies in Sri Lanka ahead of the nation’s general elections on Aug. 5, marking a break from throwing its lot in with one dominant political camp.
Foreign policy insiders in the small South Asian nation reckon the strategy fortifies the edge China has over geopolitical adversaries India, Japan and the U.S. when it comes to influencing a country that straddles an increasingly contested stretch of the Indian Ocean.
This diplomatic shift, the insiders say, has been marked by quiet, behind-the-scenes meetings between Chinese emissaries and the leading political parties vying for votes ahead of elections that in a little more than two weeks will determine parliament’s 225 lawmakers.
The coronavirus’s impact in Sri Lanka provided China with an opening to demonstrate its newly tuned diplomacy. Song Tao, minister of the international department of the Chinese Communist Party’s Central Committee, in June hosted a video conference with leaders of Sri Lanka’s major political parties to cultivate bipartisan bonds under the guise of fighting COVID-19.
The island nation has reported 2,674 infections and 11 deaths. According to Luo Chong, a spokesperson of the Chinese embassy in Colombo, the meeting was a goodwill gesture that has been repeated with other allies in the wake of the pandemic. “The International Department of the Communist Party of China conducted several joint-video conferences with different parties in Sri Lanka, Nepal, [the] Philippines, Indonesia and Arab counties, which is a common practice, especially under the current COVID-19 situation,” he told the Nikkei Asian Review.
The pandemic has boosted China’s influence in Sri Lanka, a veteran Sri Lankan diplomat said, referring to a $500 million loan President Gotabaya Rajapaksa desperately sought from China to help fight COVID-19.
“China is the only international player who has the funds to help with such emergencies,” the diplomat said. “Beijing was prompt because it knows which political players it is closer to in Sri Lanka — the Rajapaksas,” referring to the president and his elder brother Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapaksa, a former president.
But seasoned observers of Chinese diplomacy read more into Beijing’s preelection encounters with parties across Sri Lanka’s political spectrum.
Patrick Mendis, a visiting professor of global affairs at the National Chengchi University, based in Taiwan, said the CCP constantly adjusts its diplomacy based on previous outcomes. “It has remarkable agility to change as China learns from its past mistakes in Sri Lanka,” Mendis said. “Now, it supports not only political parties but influential Buddhist leaders, as China realizes the power of the Buddhist clergy in domestic politics.”
In 2015, China was perceived as backing then incumbent President Mahinda Rajapaksa. But Mahinda lost his reelection bid in a shock setback for the country’s most politically influential clan, the Rajapaksas, who had displayed signs of dynastic ambitions.
That 2015 poll, the second after the Rajapaksas presided over the end of a nearly 30-year Civil War, was marked by allegations that India, the regional power in South Asia, and China were bankrolling competing campaigns.
The Rajapaksa camp accused the Research and Analysis Wing, India’s spy agency, of pouring funds into a coalition of anti- Rajapaksa political parties to defeat Mahinda in his run for a third term.
Former President Maithripala Sirisena ended up winning, and his camp accused a Chinese company with investments in Sri Lanka of financing the Rajapaksa campaign.
Last year, in November, Gotabaya Rajapaksa, a former military lieutenant colonel, won a decisive mandate in the presidential poll, signaling voter appetite for a strongman leader after five years of a divisive and dysfunctional administration under an anti-Rajapaksa coalition.
While China burrowed deep into Sri Lankan politics — it has even commissioned local pollsters to gauge voter sentiment — it was also lavishing multibillion-dollar loans on the country for large infrastructure projects ranging from a new harbor and airport to highways. Not surprisingly, China accounts for 10% of Sri Lanka’s ballooning external debt of $55 billion. Compare that number to $88 billion, the size of the island’s economy
The China-funded projects have become a hot-button issue during election cycles as some Sri Lankan voters take a dislike to foreign money paying for strategic assets. “This was never the case before,” a senior South Asian diplomat said. “Foreign policy and foreign investment [used to have] bipartisan backing no matter which party won, but that has changed over the last few years, and strategic investments have become campaign fodder.”
As for Japan, for decades Sri Lanka’s largest bilateral lender and development partner, it now must deal with the Rajapaksa tilt toward China. Mere months into his first term, Gotabaya Rajapaksa has sent mixed messages to Japan about the fate of two multibillion-dollar infrastructure projects, both of which were championed by the previous coalition government.
One is an elevated light railway system through parts of Greater Colombo, the island’s largest commercial city. The new government says the rail will have to be delayed.
The other is an expanded container terminal in Colombo Port, which also has Indian and Sri Lankan backers. The tripartite agreement, signed in 2019 by the previous government, is also at the whim of the Rajapaksa government, which wants new terms. Japan appears unmoved for now. “There is no such fact that Japan and Sri Lanka have agreed to revise the plan of the LRT project,” an official at the Japanese Embassy in Colombo told Nikkei, referring to the Light Railway Transit project. “We understand that this project has so far been implemented as planned by the Sri Lankan implementing agency.”
But India’s government is fuming over the matter, especially now that the Rajapaksa camp is turning the Colombo Port container terminal project into an anti-India campaign issue.
Diplomatic sources in Colombo say India eyed a stake in the Colombo Port as a counterweight to China’s growing dominance in Sri Lanka’s maritime economy.
“The Indians don’t trust the Rajapaksas,” said a diplomat from a Western embassy in Sri Lanka’s former capital. “They see them as doubled-tongued. A reversal on the port project would see India returning to the pre-2015 days of distrusting Colombo.”
The U.S. faces a similar quandary. A $480 million grant under Washington’s so-called Millennium Challenge Corporation was partially meant to help upgrade Sri Lanka’s transport and logistics infrastructure, but it too has become an electoral football, as it was during the presidential election in November. Rajapaksa has profited from the anti-MCC campaign rhetoric of his ultranationalist constituency among the country’s Sinhala-Buddhist ethnic majority.
The U.S. may have to bite this political bullet to achieve its longer-termstrategic vision in the Indian Ocean, which includes Sri Lanka.
“Washington’s attention to Sri Lanka appears to be increasingly fueled by geostrategic concerns about China,” said Nilanthi Samaranayake, director for strategy and policy analysis at the Center for Naval Analysis, a Washington-based think tank. “[There is more] attention on Sri Lanka than ever before… [and there willbe] questions [after the elections] about which direction Sri Lankawill move in regarding its policies toward India, the U.S. and China.”
News
Health authorities on high alert over Nipah Virus threat
Sri Lanka has stepped up efforts to detect and respond to a potential outbreak of the deadly Nipah virus (NiV), with health authorities enhancing surveillance and laboratory readiness amid growing concerns in the region.
The Medical Research Institute (MRI), the country’s premier laboratory, has upgraded its testing capacity with the latest technology to identify the Nipah virus, enabling early detection of suspected cases, an MRI source said.
Nipah virus is a highly infectious zoonotic disease that can spread from animals
to humans and also through human-to-human contact. Fruit bats are the natural hosts of the virus.
First identified in Malaysia in 1988, the virus has since caused deadly outbreaks in countries including India and Bangladesh. Experts warn that Sri Lanka, with its close human-animal interactions and tropical climate, must remain vigilant against such emerging infectious diseases.
The case fatality rate of Nipah virus ranges from 40% to 75%, making it one of the most lethal viral infections affecting humans. There are currently no specific drugs or vaccines, with treatment relying mainly on intensive supportive care, health specialists say.
Symptoms of infection initially include fever, headaches, muscle pain, vomiting, and sore throat, followed by dizziness, drowsiness, altered consciousness, and neurological signs indicating acute encephalitis. Severe cases may progress to atypical pneumonia, acute respiratory distress, seizures, and coma within 24 to 48 hours.Authorities continue to urge heightened awareness and precautionary measures, emphasizing that early detection and rapid response are key to preventing outbreaks.
by Chaminda Silva ✍️
News
Free Media Movement demands govt. accountability on free speech issues

The Free Media Movement (FMM) has demanded government accountability on many freedom of expression issues referred to in a statement issued by the Human Rights Commission in a statement issued last week.
The statement under the hands of FMM Convener Lasantha De Silva and Secretary Dileesha Abeysundera says FMM has paid close attention to the statement issued by the Human Rights Commission (HRC) under reference number HRC/S/i/E/03/02/26. It has also informed that global stakeholders, including the International Federation of Journalists—of which it is a member—that are already closely monitoring this matter.
In its statement, HRC has elaborated at length on the issues that have arisen in Sri Lanka concerning freedom of expression and online safety. It specifically points out that the actions of the Sri Lanka Police have been a major contributing factor to these concerns. The Commission notes that recent conduct of the police has indirectly interfered even with the professional activities of journalists.
HRC has also drawn attention to the practice of summoning journalists and other activists before the police without providing clear reasons, in violation of circulars issued by the IGP. In certain instances, the police have stated that journalists were summoned due to alleged defamation arising from media activities.
However, freedom of expression guaranteed by the Constitution is restricted only within constitutionally prescribed limits. Accordingly, defamation that is no longer a criminal offence cannot be acted upon by the police. Such matters constitute civil offences that must be resolved before courts of law. The Commission further observes that attempts by politicians and others to lodge complaints with the Criminal Investigation Department regarding defamation are efforts to portray defamation as a criminal offence.
The HRC statement also addresses the Online Safety Act. While emphasizing the need to be mindful of online safety, the Commission points out that the current law does not address genuine needs. Therefore, as already demanded by many stakeholders, the government has the option to repeal this Act.
In addition, HRC has outlined a three-pronged approach that should be adopted to safeguard freedom of expression, as guaranteed by the Constitution and in line with Sri Lanka’s commitments under the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of the United Nations.
FMM said it is of the view that the Government of Sri Lanka must give serious consideration to this statement and to the recommendations emphasized therein. “This is a moment in which the accountability of the Sri Lankan government is being questioned. Accordingly, the Free Media Movement urges the government to take immediate steps to implement the recommendations set out in this statement,” it said.
News
Opposition alleges Govt deliberately delaying PC polls
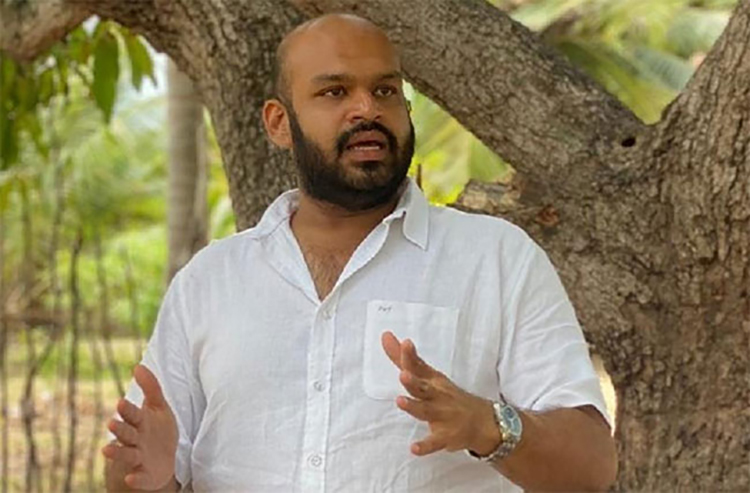

ITAK Batticaloa District MP Shanakiyan Rasamanickam accused the government in Parliament on Friday of deliberately delaying Provincial Council elections, pointing to its failure to nominate members to a Parliamentary Select Committee.
The committee, tasked with considering matters related to Provincial Council polls, was announced on 6 January 2026. Opposition parties submitted their nominees promptly.
However, a month later, the government has yet to name its eight members, preventing the committee from being constituted and from commencing its work, Rasamanickam alleged.
Opposition representatives argue that this delay represents intentional inaction aimed at postponing elections. They urged the government to appoint its nominees without further delay to allow the committee to proceed.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoSLIM-Kantar People’s Awards 2026 to recognise Sri Lanka’s most trusted brands and personalities
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoAll set for Global Synergy Awards 2026 at Waters Edge
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAPI-first card issuing and processing platform for Pan Asia Bank
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
-

 Editorial4 days ago
Editorial4 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoPhew! The heat …













