Features
Black July 1983 – and some inside stories from wartime politics in Colombo and Delhi

(Excerpted from volume ii of the Sarath Amunugama autobiography)
I had undertaken a mission to South Korea on behalf of the DG of UNESCO to participate in a conference organized by the Korean Broadcasting Service [KBS] in Seoul. The South Koreans who were developing communications technology were keen to join the International Programme for Development Communication (IPDC). Due to political bickering they had been kept out of office in the UN system.
This conference was a well-planned attempt at breaking the log jam and taking their rightful place in the global community. The apotheosis of that attempt was the election of Ban Ki Moon as Secretary General of the UN several years later. After this meeting, as customary, I broke journey in Colombo on my way back to Paris. But it was not to be the pleasant holiday that I had planned for.
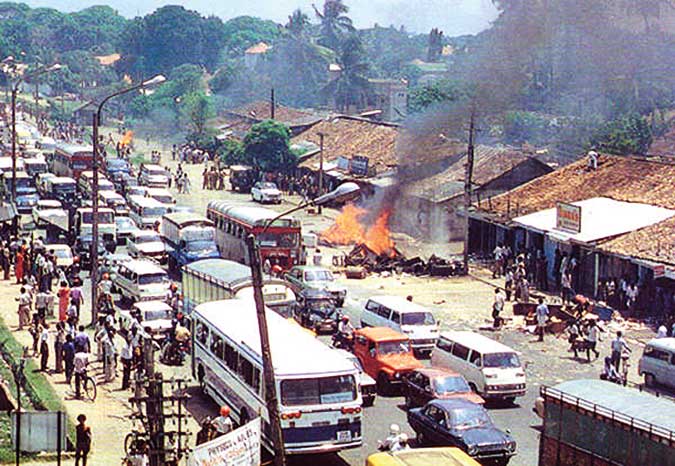
Following the killing of an army patrol in the North by the LTTE which had been trained by RAW, riots broke out in Colombo and spread throughout the country for over a week and I was forced to remain to witness those horrific days. I had driven to Bentota on that day and on my way back was an eyewitness to the fact that the violence was the result of a government inspired program.
Many of the looters, at least on the first day, were workers of state institutions like the Electricity Board and the Port Corporation. They were going about in Government vehicles. The first wave of rioting and looting was organized by Minister Cyril Mathew who had deployed the goons of the Corporations under him, with the seeming concurrence of the President.
This attempt to threaten the Colombo Tamils, who were no doubt surreptitiously supporting the ‘boys’, went terribly wrong and the country entered a 30 year-long armed conflict. It spelt the doom of the growth-oriented policies of the JRJ administration which was sucked into a wasteful war of attrition and a path of confrontation with our closest neighbor, India.
It helped the Tamil armed groups to gain more recruits, funding and foreign support. The first attempt to break the shackles of outdated ideologies and enter the path of economic growth – a pattern soon to be adopted worldwide – thereby got sidetracked and the country’s resources were needlessly squandered. It spelt the end of JRJ’s dreams and we began to slide towards greater violence and repression.
This unexpected self-inflicted turn of events caught the world by surprise. The western world which was supporting the new regime for its dismantling of the ineffectual socialist policies of the Bandaranaikes was taken aback when the July events led to a mass exodus of Tamils to their countries and India. These expatriates were well received at that time by the west that now has had second thoughts after mass migrations of refugees from Africa, the Middle East and Latin American countries.
The first wave of Tamil refugees was welcomed in Europe which was entering a phase of manpower shortage. Their displacement helped the migrants to benefit from the liberal policies of Europe at that time which greeted ‘Guest Arbiters’ with open arms. In Berlin for example they were found housing and jobs as the old residents were moving out to West Germany and the city was facing a shortage of manpower.
I remember visiting Berlin for a short visit and being offered an immediate working visa. The Turks and Tamils became welcome communities that helped the west in thwarting the Communist attempt to depopulate Berlin with threats to their security. Berliners who had borne the brunt of the damage at the end of Second World War were leaving the beleaguered city in droves fearing a Soviet invasion.
Indian Intervention
The killing of Sinhala troops in the North which led to the riots of 1983 was by the exploding of a land mine. The rag tag rebels of the North had been provided landmines and modern weapons training by India notwithstanding their formal denials. At first this was done surreptitiously while our intelligence services and Foreign Service remained deaf and dumb.
But while these services dithered, Indian media blew up the story and the two countries were drawn into a protracted conflict. The exposure of LTTE training camps located in Dehra Dun by ‘India Today’ magazine in a special issue set off shock waves in both Colombo and New Delhi. In the events that followed the political and psychological needs of Indira Gandhi played a pivotal role.
By this time she had achieved the popularity she craved for by marching into East Bengal and bifurcating Pakistan. Bangladesh became an independent country in 1972. The influx of refugees into Bengal from East Pakistan due to the repressive policies of Bhutto and his Punjabi Generals had created many difficulties for the Indian economy, already in the doldrums because of Indira’s quasi-socialist policies.
The world watched with horror as Bengali Muslims were slaughtered by their Punjabi countrymen. East Pakistanis had to flee ‘en masse’ over the border into Indian territory. Now another mass of refugees from Sri Lanka were pouring into Tamil Nadu raising the spectre of disrupting the already fragile economy of the south.
Coincidentally Indira and the Congress was keen to establish their presence in the South of India, particularly in Tamil Nadu to balance their fading fortune in the North. Her father Jawaharlal Nehru had been forced to accept the concept of linguistic states in the Indian Union after the South had started rioting against the imposition of Hindi as the national language.
Even the famous Tamil Nadu films industry had started to boycott Hindi films. It was this agitation that drew bigwigs of the Tamil film industry into politics, which has remained a characteristic of TN politics till today. On being rejected in the North, including the family electorate of Raibareli in Uttar Pradesh, Indira turned to the South and entered Parliament from Chikmagalur electorate in Bangalore district.
The influx of refugees from the North and East of Sri Lanka to the southern Indian states was adding to the pressure on Indira to adopt a hawkish stance and use the popular ‘Bangladesh option’. Indira had another reason for disliking the JRJ administration. She was clearly on Sirimavo’s side and unlike her father Nehru who maintained a strict neutrality, agreed to an expanded Indian role in the Sri Lankan conflict, against JRJ whom she perceived as Morarji Desai’s ‘alter ego’.
She hated Desai and the aging ex-PM hated her in return. JRJ was caught in the middle. He tried to placate Indira by using the good offices of a Congress oriented businessman to bring about a reconciliation but to no avail. Indira’s advisors who were mainly leftists criticized JRJ for his links with the US, Pakistan and Israel. Following the July riots, she sent her Foreign Minister Rao to Colombo thereby creating a precedent for later interventions.
JRJ and the UNP establishment then began to realize the gravity of the situation, but the scenario had changed perhaps irrevocably. I flew back to Paris to find the media and academia greatly agitated and turning their attention to the Tamil issue in Sri Lanka which did not earlier hold centre stage. It had become world news.
I remember journalists crowding into the Paris airport to meet returning passengers from Sri Lanka offering good money for photos and video clips of Colombo burning. It showed that this was an event that they had not anticipated, and were now searching for quick answers. From now on Sri Lanka and her ethnic conflict drew worldwide attention much to the detriment of Sri Lanka and JRJ personally.
Back in Paris
I returned to my home in Paris in late July 1983 to find friends and colleagues anxious to know about my experiences during those fatal days. DG M’bow was good enough to consider my sojourn in Colombo as leave with pay thinking that my life was in danger, thanks to the media hype that marked that ‘silly season’ meaning that it was a period when western media was hunting for news when their own news makers were on summer vacation.
The French media was ignorant of the meaning of the events in Colombo and turned to ‘Sri Lanka specialists’ in French academia for information. Our high commissioner in London and ambassador in Paris were ill informed and tongue tied adding to the confusion. Their performance before TV cameras, for which they had no training, was pathetic.
I was met by my friend and academic Eric Meyer who had been asked by ‘Le Monde’ to contribute an explanatory essay. I briefed him and Eric’s article appeared in ‘Le Monde Diplomatique’ in which he acknowledged my role in interpreting the July events. This essay is still a standard reference on the issue and has been reproduced several times, including in a collection of essays on this subject compiled by James Manor. I interacted with many French intellectuals and journalists who were now looking on Sri Lanka as a new ‘story’ which was replacing the old chestnuts of Africa and the Middle East which had been their main focus of interest till now.
While I got back to my duties in IPDC I had to interact with the Indian delegation on a regular basis on official matters after our New Delhi meeting. This meant interaction with Parathasarathy who was the head of the Indian delegation. Indira Gandhi had appointed him as the head of her foreign policy advisory team. From him I could elicit the official Indian view of the recent events in Sri Lanka at a very high level.
Indira relied on GP because he was a Tamil from Chennai [then Madras] and she wanted the South to be comfortable with her decisions on Sri Lanka. Parathasarathy became the virtual spokesman of the TULF whose leaders had fled to Delhi thanks to the July riots. The Indian central government had earlier concerned itself mainly with the fate of the ‘Indian Tamils’. It was now dragged in to creating a trilateral relationship which added the concerns of Tamil Nadu to those of Colombo and New Delhi.
The Indian Foreign Office which handled this issue earlier, with assistance from RAW, was compelled to factor in the concerns of South India in a big way. The Nehruvian assurances regarding noninterference in the internal affairs of neighboring countries was abandoned in the face of ‘real politik’, necessitated by the political and electoral changes in India. Indira Gandhi symbolized that transformation of Indian policy and she introduced a lack of warmth in our mutual relations unlike in the time of Jawaharlal Nehru. Indira’s legacy became embedded in the relationship between our two countries from then on and became a crucial part of the foreign relations problems of Sri Lanka. A warm relationship had suddenly turned very cold.
Tamil Nadu
The first need of an armed insurgency is a proximate ‘safe haven’. Without such a ‘strategic rear’, as the JVP discovered to their cost, an armed uprising will not succeed except in very special circumstances. North Korea had Red China as its sanctuary. Vietnam had Cambodia and Laos as safe havens before the US began bombing Cambodia to interdict the movements of liberation fighters and war material from the war zone.
The LTTE could fight for such a long time because the coastal villagers in Tamil Nadu became their sanctuary and a ‘No Go’ zone for our armed forces. They also could elicit much sympathy from Tamil
politicians in South India. A turning point in the defeat of the LTTE was their assassination of Rajiv Gandhi and the subsequent rapprochement of India with the Sri Lankan Government and the military.
The attacks on the IPKF by LTTE fighters removed that vital Tamil Nadu ‘sanctuary’ in the latter’s military strategy. With no safe havens and the sharing of vital intelligence between the Indian and Sri Lankan armed forces the LTTEs days were numbered. But that was to happen many years later. At this point of time the cards were stacked against Sri Lanka.
The Tamil Nadu government became a vital support group for the insurgents. Tamil Nadu politicians pressurized the central government in New Delhi largely because of the influx of refugees to their territory which was making it both a national and international issue. There was a wide disparity in the estimate of Tamil refugees in India. While Sri Lankan estimates put it at 35,000, Indian authorities proclaimed it to be 125,000.
As in the case of Bangladesh, Indian “hawks” were exaggerating the numbers of refugees to promote a more aggressive policy from Delhi towards Sri Lanka. What was a bilateral issue became a trilateral relationship. Many of Indira Gandhi’s advisors including G. Parthasarathy, Chidambaram, Venketeswaram and another senior official also named Parathsarathy became strong defenders of Tamil rights and were pushing the Indian Government to intervene forcefully on the Sri Lankan Tamil issue.
They were all lining up behind the TULF-inspired ‘Parathasarathy proposals’ that came to be referred to as ‘Annexure C’, which envisaged the setting up of a second tier of administration called Provincial Councils and the merger of the North and East. It was my experience that the somewhat ordinary Tamil Foreign Service officials tended to model themselves on Krishna Menon, the arrogant Indian Minister who was an advisor to Nehru on Foreign Affairs and a “hawk”.
Menon finally ruined his patron Nehru by tendering wrong advice on the question of “India’s China War’. The Tamil FS officers imitated Menon in dress and bad manners. It became necessary to reach beyond them to political and business interests to break the stranglehold of the ‘Tamil Brahmins’ of the FO. I conveyed the need for such an approach to JRJ and assured him, as I was to prove later, that the big Indian businessmen who had invested in Sri Lanka like the Tatas, Oberois, Hindujas and Jains were much more sympathetic to us than the South Block’s `Tamil lobby’.
All of these businessmen knew JRJ personally and were full of admiration for him and his free market policies. But they had not been brought into play by our Foreign Ministry which was obsessed with protocol, a sure sign of their incompetence. A senior FS man who was our representative, was constantly complaining that he was not being taken seriously by the Indian establishment. To make matters worse he established a direct link with Premadasa and began to indoctrinate him with a rabid anti–Indianism, little realizing that he was creating a split in the Cabinet on this issue and subverting JRJ’s initiatives. In a way JRJ brought it on himself because he treated FO officers with scant respect which sent them scurrying to Premadasa who received them with open arms. It also helped that this officer was married to a lady from the Colombo ‘Mudalali elite’ which was admired by Premadasa.
Back Channels
During Esmond’s visits to Paris he told us of a back channel he had set up to brief Indira Gandhi of our case. As referred to in passing earlier in these pages, this unlikely conduit was an American Professor of Sri Lankan origin called Ralph Buultjens. He was a teacher of political science at a New York University, who had managed to earn Indira’s confidence during their meetings in New York and New Delhi.
He was a suave operator who played on the vanity of important middle-aged ladies including many in Colombo Seven. He befriended Esmond who too was a no mean admirer of middle-aged ladies, particularly if they were white in color. This odd couple persuaded JRJ that his messages to the Indian PM were having its effect. I remember JRJ mentioning his friendship with Yunus, one of Jawarharlal’s confidantes and now an old man, who was invited to visit Colombo by him in order to influence Indira.
In spite of Buultjens’ assurances, the Northern situation was becoming worse and plans to develop the country’s economy were being sidelined much to the chagrin of Finance Minister Ronnie de Mel who advocated a conciliatory approach. While Buultjens could make no impact on our ethnic conflict he certainly created havoc in our Foreign Ministry and with the President. With the hope of being our Permanent Representative in the UN he began to bad mouth the incumbent UN Ambassador B.J. Fernando, who was a confidante of Premadasa and a long standing UNP supporter.
Letters purporting to be copies of correspondence between BJ and Premadasa denigrating JRJ were distributed among the political elite of Colombo. The Government which was already facing many difficulties was further embarrassed when BJ was summarily dismissed from his post as our representative in the UN. It was a sordid affair and Premadasa who was the ultimate target moved adroitly and overcame the crisis in which he could have suffered collateral damage.
The celebrated Buultjens ‘back channel’ brought nothing but trouble for JRJ and the country. I will later recount the `Buultjens affaire’ which shook up the UNP and created a lasting enmity between Premadasa and Gamini Dissanayake, which ended only with the tragic death of the new President. But with the accession of Rajiv Gandhi, efforts were made by Gamini and Lalith to reach out to influential friends of the Indian PM from among the `technocrats’ who were his closest friends, many of them Harvard graduates.
These overtures were more successful, and Rajiv began to hew his own line much to the consternation of the old guard and the Foreign Service officials. Rajiv replaced Parathasarathy and Venketeshwaran and brought in Foreign Secretary Romesh Bandari who struck up a cordial relationship with JRJ and was able to move the negotiations forward. Once when the negotiations were held up, I flew to New Delhi at JRJs request to meet Biki’ Oberoi with a message from him.
Oberoi was my friend from the time I was Permanent Secretary in charge of Tourism and an ex-officio member of the Board of the Hotel Colombo Oberoi. Biki and his brother-in-law, Gautam Khanna were great friends of Sri Lanka and were ready and willing to deploy their considerable clout among the business and political elite of Delhi to support our cause. Biki drove me from the Delhi airport to his magnificent farm on the outskirts of the city and invited Romesh Bandhari for lunch. We had lunch together and he suggested that JRJ should reconvene the All-party Conference and India would ensure the participation of the TULF.
JRJ agreed and the conference was reconvened. At that time the great fear of the Delhi ‘Tamil lobby’ was that we would reach out to Rajiv and exclude them. Chidambaram gave expression to this fear when he complained, referring to JRJ, “One of the difficulties was that he always tried to undermine whoever he was negotiating with by using his back channel connections to New Delhi. I was afraid that the PM [Rajiv] would be taken in by this beguiling man, and that is exactly what happened” [quoted in “J.R. Jayewardene of Sri Lanka-Biography Volume Two’; p624].
The worsening ethnic conflict was felt even by us expatriates at that time. The flights to Colombo from Charles De Gaulle and Heathrow in London had to be security checked several times before we boarded the plane. On many occasions our flight to Colombo had to be diverted to airports on the way and rechecked as there were messages, usually fake, of bombs on board. These leads had to be taken seriously as on one occasion the Air Lanka trident was blown up while on the ground at Katunayake.
The plan was to blow up the plane in the air while carrying 140 passengers. Tourism took a nosedive. Many tourism projects which we negotiated in Paris with Club Meditaranee and the Meridian group were put on hold. Fortunately UTA continued with their flights to the South Pacific via Colombo and with our friend Daniel Leferve as manager we could always get a seat at short notice.
As the LTTE grew in strength the powers of the central government in the North began to wane. The army which had not increased its strength and obtained the latest equipment was being confronted successfully by the terrorists. Even the Army top brass comprised of those drawn from privileged families in Colombo were not ready for combat duties. The President was getting increasingly frustrated as the situation both domestic and external seemed to be spinning out of control.
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
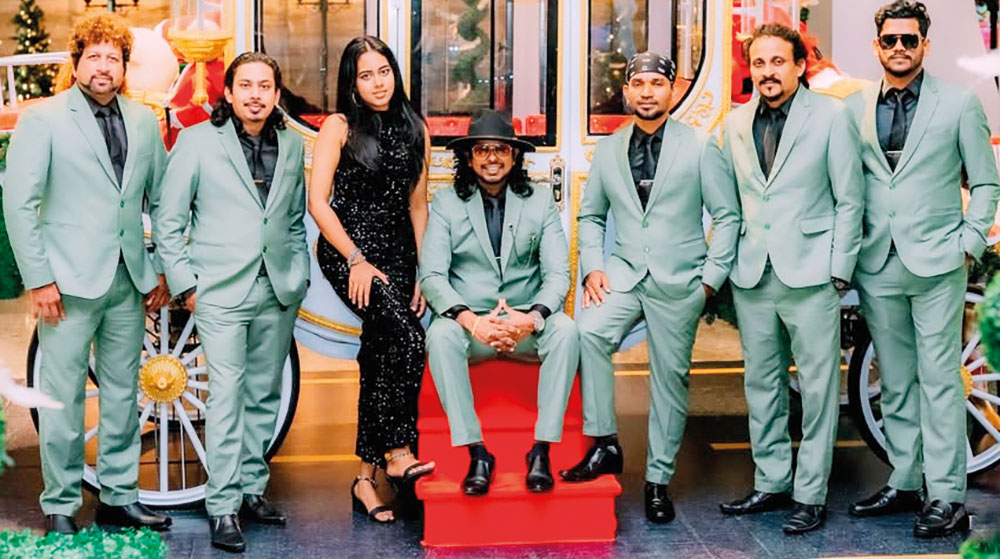
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
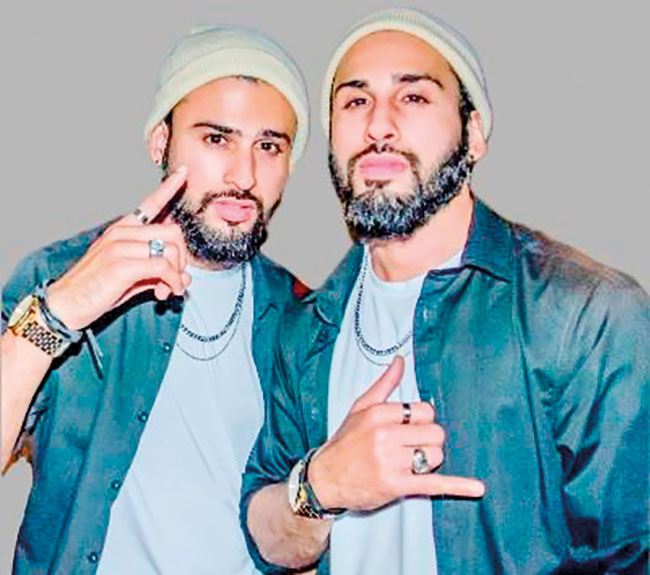

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-
 Features7 days ago
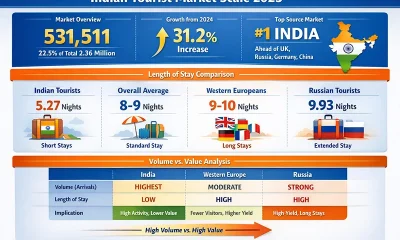
Features7 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans




























