Business
New IPS publication, ‘Palm Oil Industry in Sri Lanka: An Economic Analysis’
Q&A Explainer with Author
Featuring:Dr Erandathie Pathiraja
Research Fellow – Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka
- The palm oil industry in Sri Lanka saves USD 17 million annually in foreign exchange and contributes to the economy through employment and capital investments.
- Oil palm cultivation was allowed initially to reduce reliance on imported palm oil, but concerns over environmental and health impacts led to a decision to phase out cultivation within ten years.
- Environmental concerns associated with oil palm cultivation involve deforestation and water degradation and health risks from edible oil consumption include concerns on cardiovascular diseases.
- While the evidence remains inconclusive, there is clearly a need for robust and unbiased technical analysis on this hotly disputed issue.
Dr Erandathie Pathiraja, Research Fellow at the Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka (IPS), provides valuable insights into the recently published IPS study, ‘Palm Oil Industry in Sri Lanka: An Economic Analysis’. The study authored by Dr. Erandathie Pathiraja, Ruwan Samaraweera, Hiruni Fernando, and Jaan Bogodage, offers a comprehensive analysis of the economic and environmental impacts of the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka.
In the following Q&A session, Dr Pathiraja shares her perspectives on the reasons behind the ban on oil palm cultivation, the potential impact on the economy and environment, the industry’s economic contributions, environmental concerns and their mitigation, health issues related to edible oil consumption, and alternative solutions to meet the local edible oil demand.
Q: In light of the recent ban on oil palm cultivation in Sri Lanka, there has been much debate surrounding the decision. Could you share your insights on the reasons behind the ban and its potential impact on the economy and environment?
The palm oil industry in Sri Lanka has been an import substitution policy initiative aimed at reducing palm oil imports and boosting the economy. The 2021 ban on oil palm cultivation in Sri Lanka was primarily driven by concerns over its long-term environmental impact, owing to “soil erosion, drying of springs thus, affecting biodiversity and life of the community”. The policy further directs systematically removing the existing plantations and nurseries at an annual rate of 10% and replacing these with rubber or any other cultivation favourable for water resources.
The ban aims to shift the country towards more sustainable agricultural practices and protect Sri Lanka’s natural resources. In addition, by diversifying agricultural production, Sri Lanka aims to reduce its dependence on palm oil imports and strengthen domestic industries.
The ban on oil palm cultivation has generated mixed opinions and sparked debates. Some argue it could negatively affect the economy, as palm oil contributes to Sri Lanka’s edible oil requirements. The ban may increase reliance on imports, potentially impacting the country’s trade balance and food security. Furthermore, the ban has raised concerns among the Regional Plantation Companies (PRCs), who have already invested in cultivation and processing. Against such a backdrop, our study aims to revisit the reasons for the ban on oil palm cultivation and arguments against the ban focusing on economic, environmental, health and social factors.
Q: The study reveals that the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka contributes significantly to the economy. Could you shed some light on the economic aspects highlighted in the study and the potential benefits to the country?
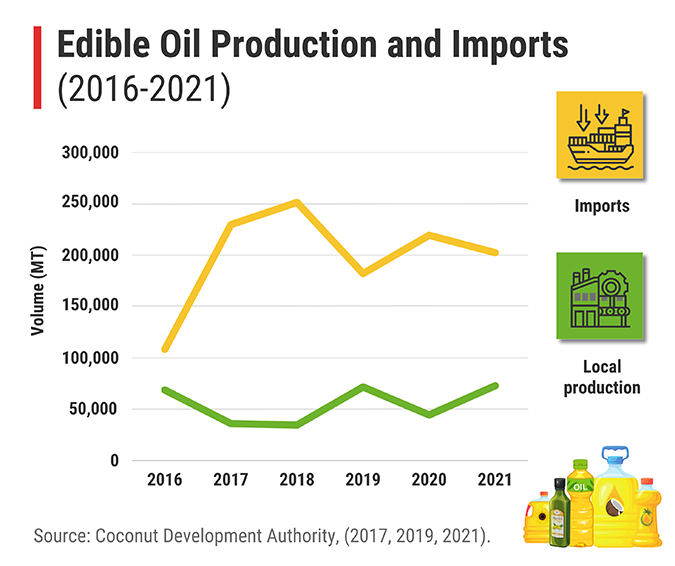
Certainly, the study demonstrates that the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka currently saves approximately USD 17 million annually in foreign exchange outflows and meets around 6% of the domestic edible oil demand. Moreover, it generates employment for over 33,000 individuals and attracts a capital investment of LKR 23 billion. These numbers illustrate the industry’s positive economic impact, but we must also consider the long-term sustainability and environmental impacts.
Q: Environmental concerns surrounding oil palm cultivation have been a major point of contention. What are some of the specific environmental issues associated with the industry, and how can they be addressed?
Oil Palm cultivation has faced criticism globally due to its environmental impacts primarily linked to deforestation. Some of the specific criticisms include groundwater depletion, water quality degradation, regeneration, siltation, floods, landslides, and palm oil mill effluent handling. These issues directly affect the surrounding communities and ecosystems.
In Sri Lanka, RPCs were allowed to cultivate oil palms in marginal rubber lands. Therefore, deforestation is not relevant unless rubber is considered a forest tree. Environmental issues are common to any agricultural land use and are observed in oil palm cultivation. However, the degree of impact varies depending on factors such as high input consumption (due to high oil productivity), vertical and horizontal root systems, and management practices. Global literature on these studies remains inconclusive due to their context-specific nature and lobby group research. Therefore, conducting further investigations and closely monitoring these issues within the local context is crucial to make informed decisions.
Implementing sustainable management practices, periodic monitoring, and potentially financing the environmental costs through mechanisms like import Cess or domestic levy can mitigate the negative externalities. However, monitoring smallholder cultivations would be challenging in the absence of policy provisions. Balancing economic benefits with environmental sustainability is key to a responsible palm oil industry.
Q: The study also mentions health concerns related to edible oil consumption. Could you elaborate on these concerns and propose possible solutions to address them effectively?
The study highlights that local edible oil consumption in Sri Lanka poses serious health risks due to improper processing, storage, and potential adulteration with repeatedly used oils. Therefore, addressing these issues at the forefront is crucial to overcome these hazards. This can be achieved by enforcing proper quality checks during importation and local edible oil production, ensuring adherence to processing and storage regulations, and avoiding repeatedly used oils. Additionally, it is equally important to raise public awareness about these aspects. By prioritising these measures, we can mitigate the health hazards associated with edible oil consumption and ensure public safety.
Q: Given the ban on oil palm cultivation, what alternatives exist to meet the local edible oil demand in Sri Lanka?
Meeting the local edible oil demand in Sri Lanka is indeed a challenge without imports. Nearly 74% of the demand is met through imports. Local palm oil supplies 6% and the rest is through local coconut oil, which varies with annual coconut production. While coconut oil is often considered a substitute, the current coconut production capacity is inadequate and does not remain a perfect substitute for industrial needs owing to different properties and prices. Given the limited land availability for expanding commercial cultivations in Sri Lanka for coconut and oil palm, productivity improvements would support partially bridging the gap. This can be facilitated by lowering the import tariff on edible oils, easing the burden on consumers. Adopting modern and safe oil production technologies such as virgin coconut oil and promoting high value-added products such as lauric acid for the export market are crucial to mitigate the impact on the coconut oil industry. Considering the economic crisis and foreign exchange deficit, a comprehensive evaluation of feasible alternatives is necessary.
Erandathie Pathiraja is a Research Economist at the Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka (IPS) with research interests in the analysis of industries and markets, competitiveness and SMEs. She holds a BSc in Agriculture from the University of Peradeniya, an MPhil in Agricultural Economics from the Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture, and a PhD in Agricultural Economics from The University of Melbourne, Australia. (Talk with Erandathie – erandathie@ips.lk)
Business
Janashakthi Life records over LKR 5 billion in profits for second consecutive year

Janashakthi Life, one of the fastest growing Life insurers in Sri Lanka has recorded a massive LKR 5.7 Billion Profit Before Tax for the period under review. This is the second consecutive year the company has surpassed the LKR 5 billion mark in PBT.
Reflecting on the company’s achievements, Ravi Liyanage, Director / CEO of Janashakthi Insurance PLC, said, “Our strong financial performance in 2024 is a testament to our strategic focus, operational excellence, and steadfast commitment to serving our policyholders. Despite market uncertainties, we have continued to grow, delivering exceptional value to our policyholders and all the stakeholders. Our exponential growth trajectory was double the size of the industry growth to reach 44% in revenue growth surpassing over LKR 6.6 Billion premium income whilst not compromising the value creation to our investors and shareholders recording over LKR 5.7 Billion PBT.
“Looking ahead, the company is well-poised to maintain its momentum as the fastest-growing insurance provider in 2025. The company has already deployed well focused strategies for market and distribution expansion in keeping with product / market as a matrix for growth. Some of the innovative products are being developed for emerging segments of the life insurance market in 2025. Further, plans are already in place to deliver best-in-class service through focused customer lifecycle management. The company is also executing robust digitalization initiatives to strengthen its position as a pioneer in digital innovation. Janashakthi Life’s total assets amount to LKR 38 billion at the close of 2024, reflecting robust growth. This underscores the financial strength and stability of the company, ensuring long-term security and sustainability for its stakeholders. Further, A key financial indicator, the Capital Adequacy Ratio of over 277%, highlights the company’s prudent financial management and reinforces confidence among all stakeholders”, added Liyanage.
Annika Senanayake, Chairperson of Janashakthi Insurance PLC, commented on the performance, “At Janashakthi Life, our resolute focus is on creating sustainable value for all stakeholders. Our performance in 2024 reflects not only our financial strength but also our deep commitment to supporting our policyholders when it matters most. The significant increase in claims paid denotes our dedication to being a reliable partner in our customers’ lives, providing them with financial security and peace of mind. As we look to the future, we are committed to invest in our human resource, technology, and product innovation to continue delivering customer-centric solutions, strengthening our market position, and driving long-term growth in Sri Lanka’s life insurance sector”.
“In 2024, we provided over LKR 4.2 billion in benefits to our policyholders through claims and maturities. The company’s prudent financial management and planning paved the way during this period to stay strong and tall irrespective of economic challenges”, Senanayake added.
The year under review saw many outstanding achievements in the company’s operations, including the highest growth in lives protected, new business premium growth of over 63%, which reflects the success of our business acquisition efforts. Additionally, we received numerous industry recognitions, such as Asia’s Best Insurance Company for Innovations at the Fifth Asia’s Best and Emerging Insurance Company Awards, the International Finance Awards, the Business Pinnacle Awards, the Business Tabloid Awards, the Global Banking Finance Awards 2024, the SLITAD People Development Awards, and the TAGS Awards, all of which highlight our commitment to employee development and industry leadership, to name just a few.
Founded in 1994 as a Life Insurance company, Janashakthi Insurance PLC (Janashakthi Life) made its mark in the industry as an innovator and household name over a span of over 30 years. Janashakthi Life has a strong presence across the island, with an expanding network of over 75 branches and a dedicated call centre that covers every corner of Sri Lanka. In line with its purpose of ‘Uplifting Lives and Empowering Dreams’, Janashakthi Life remains committed to becoming a leader in the Life Insurance industry by delivering a service beyond Insurance to its customers and stakeholders. Janashakthi Insurance PLC is a member of the JXG (Janashakthi Group), Sri Lanka’s emerging financial conglomerate that operates in the Insurance, Finance, and Investment sectors.
Business
Drop in HNB share price retards stock market trading; turnover dips

CSE trading was of a negative orientation and a low turnover level was recorded yesterday. A drop in the price of HNB shares contributed to this development in considerable measure.
HNB’s initial share price was Rs 314.75 but subsequently it dropped to Rs 305. HNB thus contributed 24 negative points to both indices.
The All Share Price Index went down by 67 points, while the S and P SL20 declined by 19.4 points. Turnover stood at Rs 1.66 billion with six crossings.
Those crossings were reported in Lankem Ceylon where 1 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 85 million; its shares traded at Rs 85, Commercial Bank 500,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 74 million; its shares sold at Rs 148, Richard Peiris 2.6 million shares crossed for Rs 68.9 million; its shares traded at Rs 26, Agarapathana Plantations 4 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 52.4 million; its shares traded at Rs 13.10, Hemas Holdings 200,000 shares crossed for Rs 24 million; its shares traded at Rs 120 and JKH 1 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 20.3 million; its shares traded at Rs 20.3.
In the retail market top six companies that mainly contributed to the turnover were; Sampath Bank Rs 183 million (1.5 million shares traded), JKH Rs 172 million (8.5 million shares traded), Commercial Bank Rs 138 million (931,000 shares traded), HNB Rs 122 million (403,000 shares traded), TJ Lanka Rs 57.4 million (1.1 million shares traded) and Commercial Credit Rs 33.3 million (593,000 shares traded). During the day 52.9 million share volumes changed hands in 11112 transactions.
It is said that the banking sector counter was the main contributor to the turnover followed by the manufacturing sector, especially JKH. The plantations sector counters were also a bit active especially with Agarapathana Plantations featuring.
The rupee was quoted at Rs 296.30/40 to the US dollar in the spot market, stronger from 296.35/45 on the previous day, dealers said, while bond yields were up steeply.
A bond maturing on 15.09.2027 was quoted at 9.55/65 percent, up from 9.47/50 percent. A bond maturing on 15.03.2028 was quoted at 9.97/10.05 percent. A bond maturing on 15.12.2028 was quoted at 10.20/30 percent. A bond maturing on 15.09.2029 was quoted at 10.35/45 percent, up from 10.30/35 percent. A bond maturing on 15.12.2032 was quoted at 10.75/85 percent, down from 10.75/90 percent.
The Central Bank was quoting a rate of Rs 292.0669 for buying and Rs 300.5806 for selling for US dollar telegraphic transfers; a rate of Rs 313.3986 for buying and Rs 326.1557 for selling for Euro; Rs 376.5107 buying and Rs 390.7131 selling for the British pound and Rs 1.9269 buying and Rs 2.0037 selling for the Japanese yen.
By Hiran H.Senewiratne
Business
British Council Sri Lanka marks Commonwealth Day by hosting latest cohort of returning Commonwealth and Chevening Scholars from Sri Lanka

The British Council in Sri Lanka hosted its annual networking event to welcome home the latest batch of Sri Lanka’s Commonwealth and Chevening Scholars returning from the UK on completion of their studies.
This year’s event, organized together with the British High Commission Colombo, was also the 65th anniversary of the Commonwealth Scholarships, and took place on Commonwealth Day—the first-ever “Welcome Home” event that celebrated both Commonwealth and Chevening Scholars. The scholarships enable outstanding emerging leaders from all over the world to pursue advance studies in the UK.
HE Andrew Patrick, British High Commissioner, Orlando Edwards, Country Director of British Council Sri Lanka, and Philip Everest, Policy Lead from the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development (FCDO) Commonwealth & Marshall Scholarship Unit, together with Commonwealth and Chevening Scholarship alumni attended.
Commonwealth Day was celebrated across 56 Commonwealth member countries on 10March under this year’s theme ‘Together We Thrive’, demonstrating how working together can build a future defined by opportunity and resilience. During his Commonwealth Day Message, His Majesty The King, Head of the Commonwealth stated, “The Commonwealth’s ability to bring together people from all over the world has stood the test of time and remains as ever-important today.
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoSeniors welcome three percent increase in deposit rates
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoThe US, Israel, Palestine, and Mahmoud Khalil
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoScholarships for children of estate workers now open
-

 Foreign News5 days ago
Foreign News5 days agoBuddhism’s holiest site erupts in protests over Hindu ‘control’ of shrine
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoJapanese Defence Delegation visits Pathfinder
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoCelebrating 25 Years of Excellence: The Silver Jubilee of SLIIT – PART I
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoWhen tractors become cars!
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAIA Higher Education Scholarships Programme celebrating 30-year journey
























