Features
Will our large dams last forever?

By Eng. Thushara Dissanayake
Today, dams are indispensable structures for human prosperity and play a considerable role in the world economy and Sri Lanka without exception. There are more than 59,000 large dams all over the world according to registered data of the International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD). A dam is categorized as a large dam if the height of a dam is greater than 15 m. A dam of height 5 – 15 m is also considered a large dam if its storage capacity is more than 3 MCM. Accordingly, Sri Lanka has got around 94 large dams, 270 medium dams, and over 10,000 small dams. According to the ICOLD, China has the highest number of large dams numbering 23,841 while the USA and India rank second and third respectively. When dam type is concerned 65% of large dams are earthen dams and the main purpose of 47% of dams is to provide irrigation water.
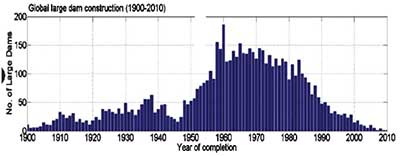
Similar to many other man-made structures dams too have a finite lifetime. In technical terms, it is defined as the design lifetime, which is generally, 100 years. However, many dams may exist longer than the design lifetime while some may fail even a short time after the commissioning owing to design or construction faults and natural calamities as well. Many large dams in the world have been built during 1950-90 being an era of intensive dam construction. In Sri Lanka too, except  Kaluganga and Moragahakanda dams, many of the other Mahaweli multi-purpose reservoirs were commissioned in the 1980s under the accelerated Mahaweli development programme. But the question is if the lifespan of a dam is 100 years how many of those dams will be left for us by the year 2100. The awful, though speculative, answer is nearly zero. Nevertheless, many dams will exist beyond their projected lifetime if we take care of them properly as discussed in detail below.
Kaluganga and Moragahakanda dams, many of the other Mahaweli multi-purpose reservoirs were commissioned in the 1980s under the accelerated Mahaweli development programme. But the question is if the lifespan of a dam is 100 years how many of those dams will be left for us by the year 2100. The awful, though speculative, answer is nearly zero. Nevertheless, many dams will exist beyond their projected lifetime if we take care of them properly as discussed in detail below.
Source: Global Reservoir and Dam Database
Factors affecting the lifetime
The basic determinant factors of the lifetime of a dam are either the structural failure of the dam or siltation that makes it no more usable due to loss in active water holding capacity. However, dam failures are rare yet disastrous. There is a growing concern about the seismic safety of dams with the recent earth tremors that occurred around Victoria dam. However, according to the reports, the main cause of dam failure in the world is foundation problems while inadequate spillway capacity being the next. Although earthquakes cause huge damages to the manmade infrastructure, only less than one percent of dams have failed as consequences of earthquakes.
In the context of ongoing climate change, there will be more intensive rains that generate unprecedented inflows to reservoirs. Unless the reservoirs’ spillway capacities are adequate or augmented to cater to the future requirements of changed rainfall characteristics, there will be high chances of dam failures due to overtopping.
When a dam is no more usable due to either safety reasons or loss of capacity after excessive siltation it would have to be decommissioned. Sometimes the purpose of such decommissioning may be restoring the ecosystem or preventing harmful effects. In Sri Lanka, many small dams at the village level have been abandoned due to breaching or natural effects like insufficient rainfall or for reasons unknown. However, we are yet to experience a purposeful decommissioning of a dam. In contrast, nearly 800 dams have been removed in the US in the last 100 years.
The plight of major dams in Sri Lanka
Today, modern technology helps us to monitor the health of the dams properly. Some of the recent projects implemented by the government intended to assure the safety of the major dams by carrying out necessary improvements. Hence, it is unlikely that we will witness another dam failure disaster in our country like that of the Kantale dam in 1986, which is considered the biggest dam failure event in the recent past. Hence, it is not the safety of the dams that is critical now but their sustainability.
Many recently built major dams of the country that hold big water storage lie in the mountainous areas in the upcountry. Most of them will reach the end of the designed lifetime by the end of this century when the excessive soil erosion-led siltation is considered. As a rule of thumb, the reduction in the active capacity of a reservoir per annum is 1%. However, the rate will further escalate if the catchment areas of such tanks are prone to deforestation, which would result in more and more soil erosion. Eventually, the water holding capacities of the reservoirs will irrevocably decrease. For instance, the Rantambe dam has lost its capacity by 45% due to siltation during 34-year lifetime according to Prof. S.B. Weerakoon. The majority of these reservoirs are serving agricultural land by providing water for irrigation while some are multipurpose contributing to hydropower generation. The installed hydropower generation capacity of these dams is about 33% of the total power generation capacity of the country while the actual generation remains around 23%. The reduction in generation potential is mainly due to variation in rainfall and that would be further worsened as an impact of climate change.
In the meantime, many of our dams in the low country may experience fewer siltation issues. A recent bathymetric survey carried out by the Climate Resilience Improvement Project of the Ministry of Irrigation has revealed that capacity loss in the Nachchaduwa dam due to siltation is almost zero. Presumably, the reasons for less siltation are the flatter watershed consisting of ample forest cover with less soil erosion potential and the cascade minor tanks system in the watershed area that retains the silt transported with the rainfall-runoff. Hence, we can assume that many of our l
ow country dams are still maintaining their original capacities if similar conditions prevail as those of Nachchaduwa.
Present challenges
With these ongoing natural and manmade environmental changes, we cannot take all our dams for granted. If the total storage capacity of our dams is reduced, the potential for providing irrigation water, drinking water and generating hydropower will also go down. So, we have to pay attention to this imminent issues and challenges sooner than later. We will have to switch to alternatives ways of managing our water resources in order to sustain our irrigated agriculture. Further, a considerable portion of hydropower will have to be replaced with alternative sources preferably renewable energy.
There are only a few lucrative options left for us to manage the impending crisis; the option of reservoir desilting is not discussed here as it is a reactive measure, probably the last resort, which goes against the objective of this write-up.
Firstly, we have to protect the existing dams not only by doing structural renovations but also by conserving the whole watershed areas of them against deforestation and activities that increase soil erosion to minimize the capacity loss due to siltation. Secondly, we have to increase the water use efficiencies of our irrigated agriculture to the best possible level in line with the concept of more crop per drop. Thirdly, we have to switch to other renewable energy sources, which could compensate for the decreasing hydropower capacity in the future amidst the growing demand. The success of all these actions depends on the genuine understanding of the challenges ahead and prompt actions of all the stakeholders.
(Eng. Thushara Dissanayake is a Chartered Engineer specialising in water resources engineering with over 20 years of experience)
Features
Rethinking post-disaster urban planning: Lessons from Peradeniya

A recent discussion by former Environment Minister, Eng. Patali Champika Ranawaka on the Derana 360 programme has reignited an important national conversation on how Sri Lanka plans, builds and rebuilds in the face of recurring disasters.
His observations, delivered with characteristic clarity and logic, went beyond the immediate causes of recent calamities and focused sharply on long-term solutions—particularly the urgent need for smarter land use and vertical housing development.
Ranawaka’s proposal to introduce multistoried housing schemes in the Gannoruwa area, as a way of reducing pressure on environmentally sensitive and disaster-prone zones, resonated strongly with urban planners and environmentalists alike.
It also echoed ideas that have been quietly discussed within academic and conservation circles for years but rarely translated into policy.
One such voice is that of Professor Siril Wijesundara, Research Professor at the National Institute of Fundamental Studies (NIFS) and former Director General of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Peradeniya, who believes that disasters are often “less acts of nature and more outcomes of poor planning.”
“What we repeatedly see in Sri Lanka is not merely natural disasters, but planning failures,” Professor Wijesundara told The Island.
“Floods, landslides and environmental degradation are intensified because we continue to build horizontally, encroaching on wetlands, forest margins and river reservations, instead of thinking vertically and strategically.”
The former Director General notes that the University of Peradeniya itself offers a compelling case study of both the problem and the solution. The main campus, already densely built and ecologically sensitive, continues to absorb new faculties, hostels and administrative buildings, placing immense pressure on green spaces and drainage systems.
“The Peradeniya campus was designed with landscape harmony in mind,” he said. “But over time, ad-hoc construction has compromised that vision. If development continues in the same manner, the campus will lose not only its aesthetic value but also its ecological resilience.”
Professor Wijesundara supports the idea of reorganising the Rajawatte area—located away from the congested core of the university—as a future development zone. Rather than expanding inward and fragmenting remaining open spaces, he argues that Rajawatte can be planned as a well-designed extension, integrating academic, residential and service infrastructure in a controlled manner.
Crucially, he stresses that such reorganisation must go hand in hand with social responsibility, particularly towards minor staff currently living in the Rajawatte area.
“These workers are the backbone of the university. Any development plan must ensure their dignity and wellbeing,” he said. “Providing them with modern, safe and affordable multistoried housing—especially near the railway line close to the old USO premises—would be both humane and practical.”
According to Professor Wijesundara, housing complexes built near existing transport corridors would reduce daily commuting stress, minimise traffic within the campus, and free up valuable land for planned academic use.
More importantly, vertical housing would significantly reduce the university’s physical footprint.
Drawing parallels with Ranawaka’s Gannoruwa proposal, he emphasised that vertical development is no longer optional for Sri Lanka.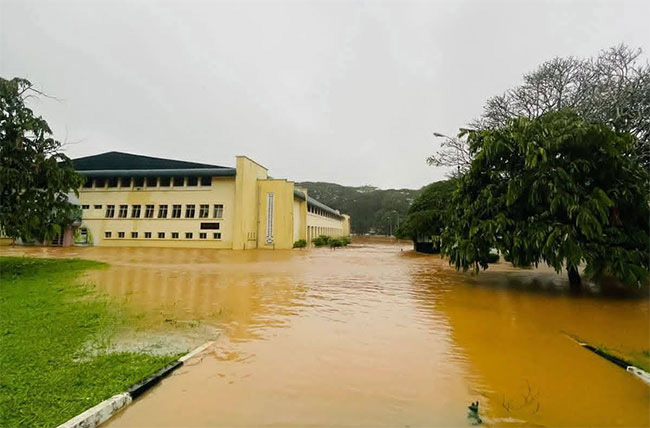
“We are a small island with a growing population and shrinking safe land,” he warned.
“If we continue to spread out instead of building up, disasters will become more frequent and more deadly. Vertical housing, when done properly, is environmentally sound, economically efficient and socially just.”
The veteran botanist also highlighted the often-ignored link between disaster vulnerability and the destruction of green buffers.
“Every time we clear a lowland, a wetland or a forest patch for construction, we remove nature’s shock absorbers,” he said.
“The Royal Botanic Gardens has survived floods for over a century precisely because surrounding landscapes once absorbed excess water. Urban planning must learn from such ecological wisdom.”
Professor Wijesundara believes that universities, as centres of knowledge, should lead by example.
“If an institution like Peradeniya cannot demonstrate sustainable planning, how can we expect cities to do so?” he asked. “This is an opportunity to show that development and conservation are not enemies, but partners.”
As climate-induced disasters intensify across the country, voices like his—and proposals such as those articulated by Patali Champika Ranawaka—underscore a simple but urgent truth: Sri Lanka’s future safety depends not only on disaster response, but on how and where we build today.
The challenge now lies with policymakers and planners to move beyond television studio discussions and academic warnings, and translate these ideas into concrete, people-centred action.
By Ifham Nizam ✍️
Features
Superstition – Major barrier to learning and social advancement

At the initial stage of my six-year involvement in uplifting society through skill-based initiatives, particularly by promoting handicraft work and teaching students to think creatively and independently, my efforts were partially jeopardized by deep-rooted superstition and resistance to rational learning.
Superstitions exerted a deeply adverse impact by encouraging unquestioned belief, fear, and blind conformity instead of reasoning and evidence-based understanding. In society, superstition often sustains harmful practices, social discrimination, exploitation by self-styled godmen, and resistance to scientific or social reforms, thereby weakening rational decision-making and slowing progress. When such beliefs penetrate the educational environment, students gradually lose the habit of asking “why” and “how,” accepting explanations based on fate, omens, or divine intervention rather than observation and logic.
Initially, learners became hesitant to challenge me despite my wrong interpretation of any law, less capable of evaluating information critically, and more vulnerable to misinformation and pseudoscience. As a result, genuine efforts towards social upliftment were obstructed, and the transformative power of education, which could empower individuals economically and intellectually, was weakened by fear-driven beliefs that stood in direct opposition to progress and rational thought. In many communities, illnesses are still attributed to evil spirits or curses rather than treated as medical conditions. I have witnessed educated people postponing important decisions, marriages, journeys, even hospital admissions, because an astrologer predicted an “inauspicious” time, showing how fear governs rational minds.
While teaching students science and mathematics, I have clearly observed how superstition acts as a hidden barrier to learning, critical thinking, and intellectual confidence. Many students come to the classroom already conditioned to believe that success or failure depends on luck, planetary positions, or divine favour rather than effort, practice, and understanding, which directly contradicts the scientific spirit. I have seen students hesitate to perform experiments or solve numerical problems on certain “inauspicious” days.
In mathematics, some students label themselves as “weak by birth”, which creates fear and anxiety even before attempting a problem, turning a subject of logic into a source of emotional stress. In science classes, explanations based on natural laws sometimes clash with supernatural beliefs, and students struggle to accept evidence because it challenges what they were taught at home or in society. This conflict confuses young minds and prevents them from fully trusting experimentation, data, and proof.
Worse still, superstition nurtures dependency; students wait for miracles instead of practising problem-solving, revision, and conceptual clarity. Over time, this mindset damages curiosity, reduces confidence, and limits innovation, making science and mathematics appear difficult, frightening, or irrelevant. Many science teachers themselves do not sufficiently emphasise the need to question or ignore such irrational beliefs and often remain limited to textbook facts and exam-oriented learning, leaving little space to challenge superstition directly. When teachers avoid discussing superstition, they unintentionally reinforce the idea that scientific reasoning and superstitious beliefs can coexist.
To overcome superstition and effectively impose critical thinking among students, I have inculcated the process to create a classroom culture where questioning was encouraged and fear of being “wrong” was removed. Students were taught how to think, not what to think, by consistently using the scientific method—observation, hypothesis, experimentation, evidence, and conclusion—in both science and mathematics lessons. I have deliberately challenged superstitious beliefs through simple demonstrations and hands-on experiments that allow students to see cause-and-effect relationships for themselves, helping them replace belief with proof.
Many so-called “tantrik shows” that appear supernatural can be clearly explained and exposed through basic scientific principles, making them powerful tools to fight superstition among students. For example, acts where a tantrik places a hand or tongue briefly in fire without injury rely on short contact time, moisture on the skin, or low heat transfer from alcohol-based flames rather than divine power.
“Miracles” like ash or oil repeatedly appearing from hands or idols involve concealment or simple physical and chemical tricks. When these tricks are demonstrated openly in classrooms or science programmes and followed by clear scientific explanations, students quickly realise how easily perception can be deceived and why evidence, experimentation, and critical questioning are far more reliable than blind belief.
Linking concepts to daily life, such as explaining probability to counter ideas of luck, or biology to explain illness instead of supernatural causes, makes rational explanations relatable and convincing.
Another unique example that I faced in my life is presented here. About 10 years ago, when I entered my new house but did not organise traditional rituals that many consider essential for peace and prosperity as my relatives believed that without them prosperity would be blocked. Later on, I could not utilise the entire space of my newly purchased house for earning money, largely because I chose not to perform certain rituals.
While this decision may have limited my financial gains to some extent, I do not consider it a failure in the true sense. I feel deeply satisfied that my son and daughter have received proper education and are now well settled in their employment, which, to me, is a far greater achievement than any ritual-driven expectation of wealth. My belief has always been that a house should not merely be a source of income or superstition-bound anxiety, but a space with social purpose.
Instead of rituals, I strongly feel that the unused portion of my house should be devoted to running tutorials for poor and underprivileged students, where knowledge, critical thinking, and self-reliance can be nurtured. This conviction gives me inner peace and reinforces my faith that education and service to society are more meaningful measures of success than material profit alone.
Though I have succeeded to some extent, this success has not been complete due to the persistent influence of superstition.
by Dr Debapriya Mukherjee
Former Senior Scientist
Central Pollution Control Board, India ✍️
Features
Race hate and the need to re-visit the ‘Clash of Civilizations’

 Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese has done very well to speak-up against and outlaw race hate in the immediate aftermath of the recent cold-blooded gunning down of several civilians on Australia’s Bondi Beach. The perpetrators of the violence are believed to be ardent practitioners of religious and race hate and it is commendable that the Australian authorities have lost no time in clearly and unambiguously stating their opposition to the dastardly crimes in question.
Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese has done very well to speak-up against and outlaw race hate in the immediate aftermath of the recent cold-blooded gunning down of several civilians on Australia’s Bondi Beach. The perpetrators of the violence are believed to be ardent practitioners of religious and race hate and it is commendable that the Australian authorities have lost no time in clearly and unambiguously stating their opposition to the dastardly crimes in question.
The Australian Prime Minister is on record as stating in this connection: ‘ New laws will target those who spread hate, division and radicalization. The Home Affairs Minister will also be given new powers to cancel or refuse visas for those who spread hate and a new taskforce will be set up to ensure the education system prevents, tackles and properly responds to antisemitism.’
It is this promptness and single-mindedness to defeat race hate and other forms of identity-based animosities that are expected of democratic governments in particular world wide. For example, is Sri Lanka’s NPP government willing to follow the Australian example? To put the record straight, no past governments of Sri Lanka initiated concrete measures to stamp out the evil of race hate as well but the present Sri Lankan government which has pledged to end ethnic animosities needs to think and act vastly differently. Democratic and progressive opinion in Sri Lanka is waiting expectantly for the NPP government’ s positive response; ideally based on the Australian precedent to end race hate.
Meanwhile, it is apt to remember that inasmuch as those forces of terrorism that target white communities world wide need to be put down their counterpart forces among extremist whites need to be defeated as well. There could be no double standards on this divisive question of quashing race and religious hate, among democratic governments.
The question is invariably bound up with the matter of expeditiously and swiftly advancing democratic development in divided societies. To the extent to which a body politic is genuinely democratized, to the same degree would identity based animosities be effectively managed and even resolved once and for all. To the extent to which a society is deprived of democratic governance, correctly understood, to the same extent would it experience unmanageable identity-bred violence.
This has been Sri Lanka’s situation and generally it could be stated that it is to the degree to which Sri Lankan citizens are genuinely constitutionally empowered that the issue of race hate in their midst would prove manageable. Accordingly, democratic development is the pressing need.
While the dramatic blood-letting on Bondi Beach ought to have driven home to observers and commentators of world politics that the international community is yet to make any concrete progress in the direction of laying the basis for an end to identity-based extremism, the event should also impress on all concerned quarters that continued failure to address the matters at hand could prove fatal. The fact of the matter is that identity-based extremism is very much alive and well and that it could strike devastatingly at a time and place of its choosing.
It is yet premature for the commentator to agree with US political scientist Samuel P. Huntingdon that a ‘Clash of Civilizations’ is upon the world but events such as the Bondi Beach terror and the continuing abduction of scores of school girls by IS-related outfits, for instance, in Northern Africa are concrete evidence of the continuing pervasive presence of identity-based extremism in the global South.
As a matter of great interest it needs mentioning that the crumbling of the Cold War in the West in the early nineties of the last century and the explosive emergence of identity-based violence world wide around that time essentially impelled Huntingdon to propound the hypothesis that the world was seeing the emergence of a ‘Clash of Civilizations’. Basically, the latter phrase implied that the Cold War was replaced by a West versus militant religious fundamentalism division or polarity world wide. Instead of the USSR and its satellites, the West, led by the US, had to now do battle with religion and race-based militant extremism, particularly ‘Islamic fundamentalist violence’ .
Things, of course, came to a head in this regard when the 9/11 calamity centred in New York occurred. The event seemed to be startling proof that the world was indeed faced with a ‘Clash of Civilizations’ that was not easily resolvable. It was a case of ‘Islamic militant fundamentalism’ facing the great bulwark, so to speak, of ‘ Western Civilization’ epitomized by the US and leaving it almost helpless.
However, it was too early to write off the US’ capability to respond, although it did not do so by the best means. Instead, it replied with military interventions, for example, in Iraq and Afghanistan, which moves have only earned for the religious fundamentalists more and more recruits.
Yet, it is too early to speak in terms of a ‘Clash of Civilizations’. Such a phenomenon could be spoken of if only the entirety of the Islamic world took up arms against the West. Clearly, this is not so because the majority of the adherents of Islam are peaceably inclined and want to coexist harmoniously with the rest of the world.
However, it is not too late for the US to stop religious fundamentalism in its tracks. It, for instance, could implement concrete measures to end the blood-letting in the Middle East. Of the first importance is to end the suffering of the Palestinians by keeping a tight leash on the Israeli Right and by making good its boast of rebuilding the Gaza swiftly.
Besides, the US needs to make it a priority aim to foster democratic development worldwide in collaboration with the rest of the West. Military expenditure and the arms race should be considered of secondary importance and the process of distributing development assistance in the South brought to the forefront of its global development agenda, if there is one.
If the fire-breathing religious demagogue’s influence is to be blunted worldwide, then, it is development, understood to mean equitable growth, that needs to be fostered and consolidated by the democratic world. In other words, the priority ought to be the empowerment of individuals and communities. Nothing short of the latter measures would help in ushering a more peaceful world.
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoMembers of Lankan Community in Washington D.C. donates to ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka’ Flood Relief Fund
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoBritish MP calls on Foreign Secretary to expand sanction package against ‘Sri Lankan war criminals’
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoBrowns Investments sells luxury Maldivian resort for USD 57.5 mn.
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoAir quality deteriorating in Sri Lanka
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCardinal urges govt. not to weaken key socio-cultural institutions
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoHatton Plantations and WNPS PLANT Launch 24 km Riparian Forest Corridor
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoAnother Christmas, Another Disaster, Another Recovery Mountain to Climb
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoGeneral education reforms: What about language and ethnicity?















