Features
Viewing 20A through governance prisms

By Austin Fernando
(Former Secretary to the President)
Twentieth Amendment (20A) is reviewed by commentators from political, legal, journalistic, and religious angles. Not belonging to any such group, I do not venture to cover the multitude of discussions on 20A. My focus is to view 20A to understand how it affects governance and causes political contradictions.
In democratic good governance, there are essential elements, such as the rule of law, transparency, responsiveness, consensual oriented action, equity and inclusivity, accountability, and participation. Irrespectively, it is surprising to observe public administrators/their associations (except Auditors) in stoic silence on the 20A, though they will implement and experience fallouts of the 20A.
Ministerial Review Committee
The 20A created contradictory opinions even among the government ranks. Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapaksa appointed a Committee of Ministers to review 20A. When this Committee Report was handed over, the public expected a review by the Cabinet. But it did not happen. Responsiveness, inclusivity, and participation have been lost even before 20A is passed, with a presidential directive to discuss the revisions of the Ministerial Committee at the Committee Stage. Such directives are common in Executive Presidency though one may question the applicability of Article 42(2) – “collective responsibility.” Anyway, the revisions will hence lack prior legal or public scrutiny.
Drafting crucial law
Probably, the Minister of Justice, who coordinated abolishing 19A, would have ordered the drafters to revert to 18A. Due to the critical nature, the Legal Draftsman would have officially conveyed the Cabinet of the implications of the amendments. It would have been opportune if that had happened, and their views shared, least as an Annex to the Cabinet Memorandum, especially for the Cabinet to observe the weaknesses/adversities of 20A, independently. Let me view 20A to observe the effects on good governance in this scenario.
Post-conflict issues and President’s duty
One sensitive amendment is the deletion of Article 33(1)(b) “Promote national reconciliation and integration.” It entered the 19A from post-conflict demands and tagged as a presidential ‘duty.’ Not much to exceptionally disturb the President through this ‘duty’ happened during the last five years. Hence, this deletion wrongly orchestrates negativism that he may be averse to ‘reconciliation and integration.’ It is unfair by him and hence deserves review.
Constitutional Council vs Parliamentary Council
Chapter VIIA – The Executive, matters to good governance. The first important issue is the erasure of the Constitutional Council (CC) and replacement by the Parliamentary Council (PC). The membership of the PC is political, and the proposed processes in application are subjected to presidential whim, especially by the power to supersede PC’s observations. These dilute PC’s independence and restricts inclusive participation.
Audit and Procurement Commissions
Under the 19A, nine Commissions were established out of which 20A has deleted the Audit Services Commission and National Procurement Commission (NPC). Erasing the Audit Services Commission does not reflect well for good governance.
Worst is to selectively leave-out audit of the Presidential Secretariat and the Prime Minister’s Office by constitutional fiat [Article 154(1)- 20A]. The primary objective of auditing is to examine the accuracy of accounts and express opinions on financial statements. The secondary objective is to detect and prevent frauds, misuses, misappropriations, etc.
Preventing auditing cheekily endorses the reluctance to be transparent and accountable; and could motivate officers to deliberately committing errors, frauds, and corruption. More important is the impact on parliamentary control of state finances (Article 148). The President, PM, and their officials, immune to parliamentary financial control, predict an accountability disaster. This also ridicules the government’s “One Country, One Law” rhetoric because other Ministers and officials have no such immunity.
In the private sector, the shareholders decide who the Auditors are, to audit the Board, Chief Executive (CEO), and all transactions. The 20A wants everyone to be audited, but not Sri Lanka’s CEO and his deputy. If 20A equivalent had happened in the private sector, shareholders would have revolted, but 20A is Amurtha (elixir) for government supporters.
Article 156C directs the National Procurement Commission (NPC) to formulate fair, transparent, competitive, and cost-effective procedures and guidelines for government procurements. These are extremely positive objectives. It is surprising for 20A to push them aside because we hear of wrongdoings, worth millions of rupees, happening even while the 19A is operative, as alleged by government spokespersons. What can we predict without an NPC? If the NPC is slow performing, corrections should be followed, rather than to abolish it.
“Independent Commissions”
According to the 19A, members of the Commissions were appointed by the President. (Article 41B and 41C). There had been very few disagreements on appointments between the CC and the Executive, which had been sorted out proving the ability to cohabit.
Special concerns on the CC are projected regarding higher judicial appointments. We sometimes hear the complaint of the President’s inability to get judges appointed at will. These are probably related to the CC’s unanimous rejections of two judicial appointment recommendations. Nevertheless, these decisions were made with the participation of the representatives of the then Opposition and civil society. Thus, 20A will ignore the latter arrangements negating an existing democratic process. Under 20A, a President’s recommendations, though wrong, may stay on, irrespective of negative observations of the PC. Article 41C blocked this happening, post-19A. Therefore, are the 20A provisions democratic and hail good governance?
Proposed Article 111D permits the President to appoint two members of his wish to the Judicial Services Commission. When such open-ended appointments are possible it gives hope to the judiciary that they could manipulate their personal gains.
Therefore, reviewing these appointments by the CC will do justice to the judiciary.
Though the incumbent President, with a strong Parliament, and personality, may not sometimes succumb to such influencing, but a weaker President certainly will, to sustain power. Constitutions must be drafted with appropriate controls applicable to any President, and not person-centric to the incumbent. This mistake has been repeated by us and should end.
Even the Public Service Commission (PSC) is appointed by the President after receiving PC observations. Again, overruling these observations, like in other instances, could make the PSC also toothless.
The effects will be observed in the short, medium, and long terms in recruitment, promotion, discipline, transfers, etc. The future of public administration may effectively face dismal problems.
We hear from the Minister of Justice of the constraints to appointment an IGP. He castigated the “purpose” or “use” of a National Police Commission (NPC) based on this. But such an appointment is prohibited by Article 155G. The increased numbers of criminal incidents were referred to prove the ineffectiveness of the NPoC. He ignored that the NPoC does not have the power to fight criminality. (Article 155G)
Removal of Officers (Procedure) Act No. 5 of 2002 clearly states that IGP’s removal is possible only under specified circumstances, such as insolvency, ill health, ceasing to be a citizen, etc. None of these sins were proved and the incumbent government retired him with all attached perks. Factually, there was no vacancy until he formally retired to appoint a new IGP. But when such irresponsible criticisms happen others hang on to such arguments. Therefore, they also pray for NPoC’s demise!
Dual citizenry
By deleting Article 91 (d) (xiii), 20A permits dual citizen’s appointment as parliamentarians. The need to use this amendment will be at the next general election, after five years. But the government is in a mighty hurry. Urgent implementation will be required if the National List is to be tampered for special political gain. Some ministers stated that 19A – 91(d)(xii) should be repealed because it was incorporated by person-centric lawmaking and thus wrong. The irony is that the 19A deletion also appears to accommodate person-centricity.
The keen advocates of this amendment are those who argued against Singapore-rooted Arjuna Mahendran. They forget that the difficulties with Mahendran would arise with dual citizen politicians sinning after 20A. Politicians sin whichever the party they belong!
When a clerk, a Grama Sevaka, IGP or a Secretary must be a citizen, but not parliamentarians, Ministers, PMs, or Presidents, it is a joke. Since the President has shown how to solve the dual citizenship problem, individually, why mess with the Constitution without following the Leader?
Another important reason is that this amendment will apply to any other dual citizens while being members of international terror groups (e.g. ISIS) or Tiger remnants. This situation is worsened by repealing the administering of the Official Oath (Article 53) in Schedule 7 of the Constitution. We are assured that the President will not do underhand deals with LTTE remnants or the Islamic terror groups. But this amendment affecting security governance could be used by another President or Minister, supported by extremists, by being inactive, permitting “support, espouse, promote, encourage or advocate the establishment of a separate state.”
This freedom to engage in separatist agendas may motivate helpful activities for separatism and it will be the base for another conflict that has to be fought. Such motivators are mentioned of previous regimes and cannot it repeat with the current and future regimes? This country has suffered enough and hence this amendment needs erasure or at least modifying.
Election promises and constitutional amendments
That the incumbent President received nearly seven million votes at the presidential election and a 2/3 majority at the general election is used to validate the 20A. But were the electors told that these questionable changes (e. g. abolition of dual citizenship, Audit and Procurement Commissions, Article 53, immunity, and castrating the independence of the CC/Commissions, etc.) would follow? No!
We must also remember that these amendments cannot be repealed conveniently. A President in power with a lean margin or performing with a weak parliamentary alliance can use these amendments to the detriment of democratic governance/country, even militarily. Canvassers may emerge inviting political leaders to be autocrats using some of these amended powers. In such circumstances, what is the guarantee that an Idi Amin or Robert Mugabe will not emerge from among our politicians?
President must be the Minister of Defence
The 20A corrects a prohibition in the 19A. The incumbent President, while possessing the power to declare war and peace and appoint the three Services Chiefs, is disabled to be the Minister of Defence because he is not a parliamentarian. I reason to differ from 19A, without being person-centric on the incumbent President’s professional suitability to be the Minister of Defence.
To wit, Article 4 (b) of our Constitution stipulates that the “executive power of the people, including the defence of Sri Lanka,” must be exercised by the President. Only “defence” is specially chosen here, not Agriculture, industry, etc. Under Article 33A, (which will be deleted by 20A, included in Article 42), the President is accountable for “his powers” to the Parliament on laws applicable to public security. Public security always combines with defence.
At present, there is no Minister of Defence and there is a Secretary Defence. According to Article 52(1): “There shall be a Secretary for every Ministry of a Minister of the Cabinet of Ministers.” By Article 52(2) the Secretary shall act “subject to the directions and control of his Minister…’’ It is the Cabinet Minister of Defence and not the State Minister. This status is thus challengeable legally.
When these situations are bagged together, the Ministry of Defence/relevant institutions should come under the President. However, 20A permits him to hold even any other Ministry [reintroduced Article 44(2)] and sadly this “residual power” deviates from democratic governance elements.
The 20A has revisited the issue. Taking into consideration the above-mentioned reasons only the Ministry of Defence should be handled by the President.
President the Messiah
There is a school of thought that considers the incumbent President as the Messiah who has proven prowess to accelerate action and therefore wants to “strengthen his hands,” to bring in political stability and economic revival. The successful manner the President managed the COVID-19 issues showed that for him the 19A was not a hindrance to perform efficiently and effectively.
However, considering the challenges ahead, the President requiring concentrated power is not surprising. Evening TV news everyday shows that he is attempting it. Concurrently, it is a fact that pre-2015 when Presidents had these executive powers there was an ongoing 25-year conflict. Equal development outputs were not observed during the tenures of some Presidents. Exceptional performances were based on individualistic strengths. Hence, to tag the Executive Presidency as a panacea for stability and development is a misnomer.
Emerging political contradictions
There seem to be six major political contradictions that affect political governance.
One is how the incumbent PM would bear the amendments reducing his powers substantially. Tisaranee Gunasekara has explained this, as quoted below. Agreement or not is your choice.
“Rendering the post of PM powerless is a measure of protection, in case the family is compelled by circumstances to bestow the premiership on an outsider, as a stop-gap measure. If the 20th Amendment becomes law, such a premier will be a mere cipher and will not have the power or the authority to challenge Rajapaksa primacy in any serious sense. His role will be to warm that seat until the next Rajapaksa is ready to step in.”
If true, brilliant manoeuvrering!
The second contradiction is the stance of the United National Party and break away Samagi Janabalavegaya. For them to oppose the 20A is a cautious ride. It is because the 20A basics evolved from their original Jayewardene Constitution, tinkered with by others later.
The third political contradiction is from the politicians who now venerate 20A – the by-product of the Jayewardene Constitution – the “Bahubootha vyavasthaava” (Mayhem Constitution)
The fourth extremely embarrassing political contradiction is for President Sirisena to vote for 20A, having praised 19A as the apex of democratic governance. He was the major force behind its approval in 2015. He may vote for the 20A, but his conscience will bleed until his last breath.
The fifth contradiction will arise from the expectations of the Tamil political parties who will see 20A to be the majoritarian political steamroller.
The last contradiction emerges with the speculation that the Sri Lankan Muslim Congress may support the 20A, as they did in 2010, and the sufferings Muslims experienced. Maybe, for the SLMC governance is reborn!
A historical opportunity has been given to consider solutions for the contradictions through constitutional amendments with a 2/3 majority in the Parliament. The country wishes the government will give priority to the country’s needs over personal or political group needs. It is a difficult proposition, but the government was given the unusual power to face and overcome even worse difficulties.
A short article cannot discuss the vast array of issues arising out of the abolition of the 19A. Hence, issues such as the presidential immunity, appointment and removal of Ministers and the PM, dissolution of parliament, etc., are not dealt with here though those issues certainly affect good democratic governance extensively.
There are deep ramifications of issues arising from the proposed constitutional amendments. The President must first protect himself, politically. As a democratically elected person he need not camouflage himself with an anti-democratic cloak because he has a massive vantage value unlike anyone else in his government, to take correct steps. Hence, his actions need not be at the expense of democratic governance. Regrettably, the published amendments do not show such. The sacred principles of good governance will safeguard him, us and the country.
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
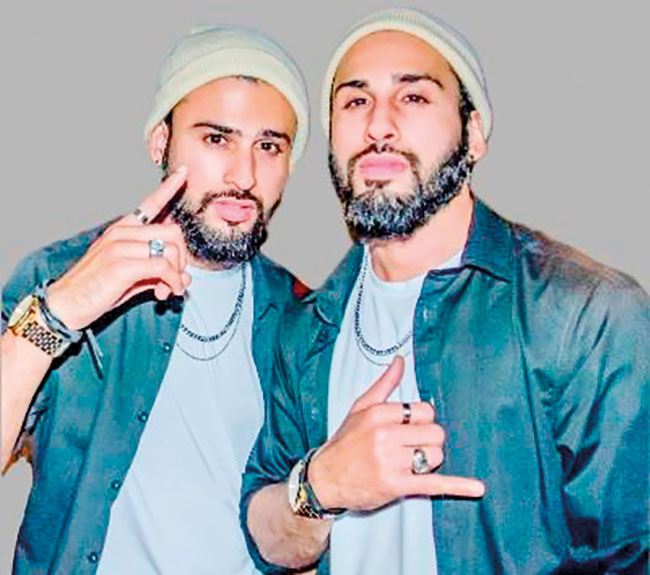

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans




















