Features
The Rajapaksa Brothers’ Return is Not a Victory for All

President Gotabaya Rajapaksa however decided that he could still meet the challenges with the powers vested in him. True to his word, the infected clusters were quickly contained. Sri Lanka is yet to face the dreaded second wave that had engulfed most other countries. Though imports were severely controlled, his Administration ensured that there were no shortages of any essentials
by Shivanthi Ranasinghe
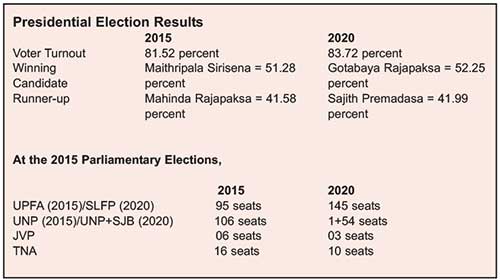
Sri Lanka is the first country to defeat “Regime Change”. The fact that this whole operation was reversed by the ballot makes this accomplishment irrefutable. It is after all in the guise of strengthening democracy that this “Regime Change” Operation was launched. Critics have tried to downplay this turn of events by claiming that the voter turnout was the lowest in the decade. With a voter turnout of over 71 percent however, the recently concluded general elections can hardly be considered to have been apathetic.
This election was held at a time that is trying for the whole world. There was an attempt within the country to postpone elections indefinitely and instead for the dissolved Parliament to be recalled. This would have allowed those politicians whose popularity that had nosedived to remain as decision-makers without a people’s mandate.
It is interesting that advocates of democracy found fault with President Gotabaya. They accused him of running the country without a Parliament. However, instead of taking the ground situation into account or exploring ways of safely conducting elections, their expectations were also for the dissolved parliament to be recalled and elections to be postponed. Surprisingly, it did not bother them that such an act would violate the people’s franchise.
President Gotabaya Rajapaksa however decided that he could still meet the challenges with the powers vested in him. True to his word, the infected clusters were quickly contained. Sri Lanka is yet to face the dreaded second wave that had engulfed most other countries. Though imports were severely controlled, his Administration ensured that there were no shortages of any essentials.
The Supreme Courts agreed with the President that he had taken the right steps in dissolving Parliament and calling for general elections. Therefore, the onus of holding elections were with the Elections Commission.
The EC that had already postponed elections twice had no other choice but to proceed. By this time, since the Kandakadu cluster, not a single new patient had been identified from within the Island.
It is also noteworthy that independent observers have declared this election to have been both fair and peaceful. Therefore, no one can interpret the two third majority that the Gotabaya Rajapaksa Administration received as anything but a clear mandate from the people.
A healthy voter turnout, elections conducted in a peaceful environment despite the trying circumstances and a clear message from the people attests to the strength of the democracy in Sri Lanka. Yet, the silence from the so-called proponents of democracy is deafening.
Mandate Received in
2015n & in 2020
After the 2015 presidential and parliamentary elections, many international players as well as independent bodies applauded Sri Lanka for reestablishing democracy. Some even took credit for it. The then US State Secretary John Kerry revealed that nearly USD 800 million of American taxpayers’ money was invested to change the governments of four countries. Sri Lanka was one of them.
 Yet, none of the countries that propelled the Yahapalana Government into power enthusiastically extended its support for the 2019 presidential elections. India’s lackluster approach is understandable. As far as India is concerned, the betrayal of leasing of the Hambantota Port to China for 99 years, which can be extended for another 99 years is equivalent to LTTE assassinating Rajiv Gandhi.
Yet, none of the countries that propelled the Yahapalana Government into power enthusiastically extended its support for the 2019 presidential elections. India’s lackluster approach is understandable. As far as India is concerned, the betrayal of leasing of the Hambantota Port to China for 99 years, which can be extended for another 99 years is equivalent to LTTE assassinating Rajiv Gandhi.
During the Mahinda Rajapaksa Administration, the ambitious Chinese-funded projects made India uneasy. The occasional visits from Chinese nuclear subs hardly compares though to the permanent residency Yahapalana Government granted to China with th leasing of the Port.
Absurd amounts of money were spent on the elections by all parties, especially on social media. However, it is not clear if the Yahapalana candidate, Sajith Premadasa received the same or similar support that Maithripala Sirisena did from external bodies.
In 2015, the Yahapalana Government came to power after receiving much support and assistance, especially in social media, from external sources. This was somewhat reminiscent to the LTTE days when the Government troops struggled without weapons comparable to those of the enemy. Likewise, the Mahinda Rajapaksa Administration too could not counter the social media onslaught.
Yet, the mandate the Yahapalana Government received in 2015 was not as clear as that received by the Gotabaya Administration in 2019-2020. By this time, the playing field in social media had leveled out. This allowed the Rajapaksa camp to effectively counter disinformation as well as carry out their own campaigns. Therefore, it is possible to surmise that the voters’ decision was less manipulated in 2019.
Manipulations for a
Democratic Majority
After Maithripala Sirisena won the 2015 Presidential Elections, he took control of the SLFP. This was a bizarre situation as the SLFP was the main party of the United People’s Freedom Alliance (UPFA). As such, backed by the UNP, Maithripala Sirisena contested against the UPFA. Thus, when he took over the SLFP, he effectively became the Head of the Government as well as that of the legitimate Opposition.
Sirisena came to power on the UNP vote base on an “apolitical” platform. Hence, the UNP voter was rather taken aback when he become the leader of their arch rival. They however calmed as Sirisena was then able to exert influence over the UPFA, enabling Ranil Wickremesinghe’s minority government to plough ahead unhindered. This allowed the minority government to even tinker with the Constitution.
Except for Rear Admiral Sarath Weerasekara, the new Opposition was in a confused daze and somewhat cowered by Mahinda Rajapaksa’s defeat. Therefore, they offered zero resistance. Their failure resulted in the 19th Amendment which they too supported. In the course of the next four years, the country was to suffer immensely because of an amendment without due democratic process.
To overcome the failure of obtaining a majority at the 2015 General Elections, Ranil Wickremesinghe formed a National Government. Maithripala Sirisena too helped in this manipulation by convincing about 40 UPFA MPs to join this union. He even replaced the names of those on the list placed before the electorate as National List nominees with defeated candidates who were loyal to him.
This violated the people’s mandate. Candidates rejected by the people do not have the moral right to represent them. Moreover, the National List is a means to bolster the intellectual capacity of the Parliament by inviting highly respected personalities and subject experts with a proven track record. It is most definitely not for candidates scorned by voters. The voters were in effect cuckolded twice because the promised National List was not the one that eventually materialized.
Maithrpala Sirisena’s actual motive was self preservation. Had he not got his own team, he would have been a mere puppet of the UNP. Yahapalana Government supporters argued that this as a progressive move that would end the era of divisive politics with both main parties on the same side.
In reality however, Maithripala Sirisena fortified with a team of his own began to assert his own independence. As a result, the two factions – one led by Sirisena and the other by Wickremesinghe – could not agree on many issues. This indecisiveness led to nine different economic policies within three years. By the fourth year, a Cold War of sorts had set in between the two camps, which led to the catastrophic Easter Sunday massacres.
Before this fission became apparent, the extraordinary lengths the Yahapalana Government went to ensure its dominance in Parliament were heralded as democratic. The various western agents who “dropped in” heaved a sigh of relief “that the era of Mahinda Rajapaksa authoritarianism is over”. It was only after Donald Trump became the US President that ended these visits, which in reality were a trespassing of our sovereignty.
These agents who “oohed” and “ahhed” over the “democratic reforms” ushered in with the Regime Change Operation, refused to see just how much the democratic norms were been violated. Maithripala Sirisena was able to lure only about half of the UPFA MPs. The corruption charges against these MPs miraculously disappeared. Despite the lure of power and perks, 55 MPs refused to be part of the Yahapalana Government. They continued to be persecuted by a special criminal investigation division directed by the then Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe.
This group presented themselves as the Joint Opposition (JO) as they contested against the Yahapalana Government. As such, the mandate JO received from their voters was to oppose the Yahapalana Government. Therefore, none of the UPFA MPs had a right to sit with the Yahapalana Government.
JO was the largest group in Parliament as an opposition. Together, this group represented eight of the nine provinces. Yet, Maithripala Sirisena as the President and Karu Jayasuriya as the Speaker refused to acknowledge the JO as the Opposition. Instead, the TNA with its meager presence in the Parliament, representing only two of the provinces was appointed as the Opposition Leader.
While Karu Jayasuriya agreed to treat the ostracized group as a separate entity, he refused to acknowledge the large number in the group. As such, he refused to allocate a reasonable time for the JO to speak in Parliament.
An Opposition Protective of Its Government
The TNA, while accepting the prestige of the position of the Leader of the Opposition, never spoke on any of the National issues. In fact, they barely disguised their complicit partnership with the Government. They never raised an issue over the Central Bank bond scams, even as the interests rates began to rise as a direct rippled effect of these scams. The economic repercussions were enormous as businesses collapsed and cost of living soared. As imports increased while the export markets struggled, the rupee came under intense pressure. The sudden devaluation of the rupee by 31 percent was unprecedented. This in turn increased our debt burden, causing our interest rates to rise even more.
During the tenure of the Yahapalana Government, Sri Lanka experienced a number of tragedies. Droughts and floods are common phenomenon in Sri Lanka. Apart from these, the Salawa explosion, the Meetotamulla garbage disaster and the massive Aranayaka landslide took place while the TNA sat as the Opposition. Not a single TNA MP visited any of these disaster sites, nor raised in Parliament the delay in compensating the victims. They did not even raise the issue faced by the Northern fishermen due to poaching by the South Indian fishing trawlers.
The TNA’s focus was holding the Sri Lankan Military accountable for alleged war crimes and gaining more autonomy. These were also the very objectives of the Yahapalana Government. As such, both the Yahapalana Government and the TNA were working in partnership.
While the Yahapalana Government co-sponsored the UNHRC Resolution 30/1, the TNA was formulating a new constitution with irreversible conditions to strengthen the provinces at the cost of the central government. They were thus working on the same project.
Even as the TNA were pushing for more autonomy, they failed to protect the powers they already have at hand. One by one the Provincial Councils became defunct as the PC elections were postponed indefinitely. The very reasons Provincial Councils were created was as a step to redress the grievances of the Tamils in the North and East. Yet, to date they have not expressed any distress over the fact that these councils are no longer functioning. It is ironic indeed that since the expiration of these councils, the provinces are being run by the Government.
It was indeed eyebrow raising when the TNA tried to protect the Yahapalana Government. As the popularity of the Yahapalana Government plummeted, a petrified TNA beseeched India to protect the government. By doing so, TNA must have become the first Opposition to want to protect the sitting government.
Democracy Advocators Break their Silence
Not a single West mentored entity was bothered by these vulgarities that shammed democracy. They continued to be relieved that the Rajapaksas were not at the helm. However, the people have voted with an overwhelming majority the Rajapaksa brothers back to power.
This is very alarming to the West-led foreign media as well as civil groups. They refuse to acknowledge any positive stride taken by the new Rajapaksa headed Administration. Even Sri Lanka’s superb management of the COVID-19 pandemic is met with countless criticism and without a single word of praise or acknowledgment of its remarkable successes. They worry that the “democratic reforms” introduced by the previous government will be rolled back.
Sri Lanka can be assured that the next four years will be a never ending complaint from these entities as they nitpick over isolated incidents and make mountains out of molehills. They may moan and groan, but it is the people in Sri Lanka who has to live with the situation. Therefore, it is the Sri Lankan citizen who must decide what is right and not for Sri Lanka.
(ranasingheshivanthi@gmail.com)
Features
Indian Ocean Security: Strategies for Sri Lanka

During a recent panel discussion titled “Security Environment in the Indo-Pacific and Sri Lankan Diplomacy”, organised by the Embassy of Japan in collaboration with Dr. George I. H. Cooke, Senior Lecturer and initiator of the Awarelogue Initiative, the keynote address was delivered by Prof Ken Jimbo of Kelo University, Japan (Ceylon Today, February 15, 2026).
The report on the above states: “Prof. Jimbo discussed the evolving role of the Indo-Pacific and the emergence of its latest strategic outlook among shifting dynamics. He highlighted how changing geopolitical realities are reshaping the region’s security architecture and influencing diplomatic priorities”.
“He also addressed Sri Lanka’s position within this evolving framework, emphasising that non-alignment today does not mean isolation, but rather, diversified engagement. Such an approach, he noted, requires the careful and strategic management of dependencies to preserve national autonomy while maintaining strategic international partnerships” (Ibid).
Despite the fact that Non-Alignment and Neutrality, which incidentally is Sri Lanka’s current Foreign Policy, are often used interchangeably, both do not mean isolation. Instead, as the report states, it means multi-engagement. Therefore, as Prof. Jimbo states, it is imperative that Sri Lanka manages its relationships strategically if it is to retain its strategic autonomy and preserve its security. In this regard the Policy of Neutrality offers Rule Based obligations for Sri Lanka to observe, and protection from the Community of Nations to respect the territorial integrity of Sri Lanka, unlike Non-Alignment. The Policy of Neutrality served Sri Lanka well, when it declared to stay Neutral on the recent security breakdown between India and Pakistan.
Also participating in the panel discussion was Prof. Terney Pradeep Kumara – Director General of Coast Conservation and Coastal Resources Management, Ministry of Environment and Professor of Oceanography in the University of Ruhuna.
He stated: “In Sri Lanka’s case before speaking of superpower dynamics in the Indo-Pacific, the country must first establish its own identity within the Indian Ocean region given its strategically significant location”.
“He underlined the importance of developing the ‘Sea of Lanka concept’ which extends from the country’s coastline to its 200nauticalmile Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Without firmly establishing this concept, it would be difficult to meaningfully engage with the broader Indian Ocean region”.
“He further stated that the Indian Ocean should be regarded as a zone of peace. From a defence perspective, Sri Lanka must remain neutral. However, from a scientific and resource perspective, the country must remain active given its location and the resources available in its maritime domain” (Ibid).
Perhaps influenced by his academic background, he goes on to state:” In that context Sri Lanka can work with countries in the Indian Ocean region and globally, including India, China, Australia and South Africa. The country must remain open to such cooperation” (Ibid).
Such a recommendation reflects a poor assessment of reality relating to current major power rivalry. This rivalry was addressed by me in an article titled “US – CHINA Rivalry: Maintaining Sri Lanka’s autonomy” ( 12.19. 2025) which stated: “However, there is a strong possibility for the US–China Rivalry to manifest itself engulfing India as well regarding resources in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While China has already made attempts to conduct research activities in and around Sri Lanka, objections raised by India have caused Sri Lanka to adopt measures to curtail Chinese activities presumably for the present. The report that the US and India are interested in conducting hydrographic surveys is bound to revive Chinese interests. In the light of such developments it is best that Sri Lanka conveys well in advance that its Policy of Neutrality requires Sri Lanka to prevent Exploration or Exploitation within its Exclusive Economic Zone under the principle of the Inviolability of territory by any country” ( https://island.lk/us- china-rivalry-maintaining-sri-lankas-autonomy/). Unless such measures are adopted, Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone would end up becoming the theater for major power rivalry, with negative consequences outweighing possible economic gains.
The most startling feature in the recommendation is the exclusion of the USA from the list of countries with which to cooperate, notwithstanding the Independence Day message by the US Secretary of State which stated: “… our countries have developed a strong and mutually beneficial partnership built on the cornerstone of our people-to-people ties and shared democratic values. In the year ahead, we look forward to increasing trade and investment between our countries and strengthening our security cooperation to advance stability and prosperity throughout the Indo-Pacific region (NEWS, U.S. & Sri Lanka)
Such exclusions would inevitably result in the US imposing drastic tariffs to cripple Sri Lanka’s economy. Furthermore, the inclusion of India and China in the list of countries with whom Sri Lanka is to cooperate, ignores the objections raised by India about the presence of Chinese research vessels in Sri Lankan waters to the point that Sri Lanka was compelled to impose a moratorium on all such vessels.
CONCLUSION
During a panel discussion titled “Security Environment in the Indo-Pacific and Sri Lankan Diplomacy” supported by the Embassy of Japan, Prof. Ken Jimbo of Keio University, Japan emphasized that “… non-alignment today does not mean isolation”. Such an approach, he noted, requires the careful and strategic management of dependencies to preserve national autonomy while maintaining strategic international partnerships”. Perhaps Prof. Jimbo was not aware or made aware that Sri Lanka’s Foreign Policy is Neutral; a fact declared by successive Governments since 2019 and practiced by the current Government in the position taken in respect of the recent hostilities between India and Pakistan.
Although both Non-Alignment and Neutrality are often mistakenly used interchangeably, they both do NOT mean isolation. The difference is that Non-Alignment is NOT a Policy but only a Strategy, similar to Balancing, adopted by decolonized countries in the context of a by-polar world, while Neutrality is an Internationally recognised Rule Based Policy, with obligations to be observed by Neutral States and by the Community of Nations. However, Neutrality in today’s context of geopolitical rivalries resulting from the fluidity of changing dynamics offers greater protection in respect of security because it is Rule Based and strengthened by “the UN adoption of the Indian Ocean as a Zone of peace”, with the freedom to exercise its autonomy and engage with States in pursuit of its National Interests.
Apart from the positive comments “that the Indian Ocean should be regarded as a Zone of Peace” and that “from a defence perspective, Sri Lanka must remain neutral”, the second panelist, Professor of Oceanography at the University of Ruhuna, Terney Pradeep Kumara, also advocated that “from a Scientific and resource perspective (in the Exclusive Economic Zone) the country must remain active, given its location and the resources available in its maritime domain”. He went further and identified that Sri Lanka can work with countries such as India, China, Australia and South Africa.
For Sri Lanka to work together with India and China who already are geopolitical rivals made evident by the fact that India has already objected to the presence of China in the “Sea of Lanka”, questions the practicality of the suggestion. Furthermore, the fact that Prof. Kumara has excluded the US, notwithstanding the US Secretary of State’s expectations cited above, reflects unawareness of the geopolitical landscape in which the US, India and China are all actively known to search for minerals. In such a context, Sri Lanka should accept its limitations in respect of its lack of Diplomatic sophistication to “work with” such superpower rivals who are known to adopt unprecedented measures such as tariffs, if Sri Lanka is to avoid the fate of Milos during the Peloponnesian Wars.
Under the circumstances, it is in Sri Lanka’s best interest to lay aside its economic gains for security, and live by its proclaimed principles and policies of Neutrality and the concept of the Indian Ocean as a Zone of Peace by not permitting its EEC to be Explored and/or Exploited by anyone in its “maritime domain”. Since Sri Lanka is already blessed with minerals on land that is awaiting exploitation, participating in the extraction of minerals at the expense of security is not only imprudent but also an environmental contribution given the fact that the Sea and its resources is the Planet’s Last Frontier.
by Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
Protecting the ocean before it’s too late: What Sri Lankans think about deep seabed mining

Far beneath the waters surrounding Sri Lanka lies a largely unseen frontier, a deep seabed that may contain cobalt, nickel and rare earth elements essential to modern technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Around the world, governments and corporations are accelerating efforts to tap these minerals, presenting deep-sea mining as the next chapter of the global “blue economy.”
For an island nation whose ocean territory far exceeds its landmass, the question is no longer abstract. Sri Lanka has already demonstrated its commitment to ocean governance by ratifying the United Nations High Seas Treaty (BBNJ Agreement) in September 2025, becoming one of the early countries to help trigger its entry into force. The treaty strengthens biodiversity conservation beyond national jurisdiction and promotes fair access to marine genetic resources.
Yet as interest grows in seabed minerals, a critical debate is emerging: Can Sri Lanka pursue deep-sea mining ambitions without compromising marine ecosystems, fisheries and long-term sustainability?
Speaking to The Island, Prof. Lahiru Udayanga, Dr. Menuka Udugama and Ms. Nethini Ganepola of the Department of Agribusiness Management, Faculty of Agriculture & Plantation Management, together with Sudarsha De Silva, Co-founder of EarthLanka Youth Network and Sri Lanka Hub Leader for the Sustainable Ocean Alliance, shared findings from their newly published research examining how Sri Lankans perceive deep-sea mineral extraction.
The study, published in the journal Sustainability and presented at the International Symposium on Disaster Resilience and Sustainable Development in Thailand, offers rare empirical insight into public attitudes toward deep-sea mining in Sri Lanka.
Limited Public Inclusion
“Our study shows that public inclusion in decision-making around deep-sea mining remains quite limited,” Ms. Nethini Ganepola told The Island. “Nearly three-quarters of respondents said the issue is rarely covered in the media or discussed in public forums. Many feel that decisions about marine resources are made mainly at higher political or institutional levels without adequate consultation.”
The nationwide survey, conducted across ten districts, used structured questionnaires combined with a Discrete Choice Experiment — a method widely applied in environmental economics to measure how people value trade-offs between development and conservation.
Ganepola noted that awareness of seabed mining remains low. However, once respondents were informed about potential impacts — including habitat destruction, sediment plumes, declining fish stocks and biodiversity loss — concern rose sharply.
“This suggests the problem is not a lack of public interest,” she told The Island. “It is a lack of accessible information and meaningful opportunities for participation.”
Ecology Before Extraction
Dr. Menuka Udugama said the research was inspired by Sri Lanka’s growing attention to seabed resources within the wider blue economy discourse — and by concern that extraction could carry long-lasting ecological and livelihood risks if safeguards are weak.
“Deep-sea mining is often presented as an economic opportunity because of global demand for critical minerals,” Dr. Udugama told The Island. “But scientific evidence on cumulative impacts and ecosystem recovery remains limited, especially for deep habitats that regenerate very slowly. For an island nation, this uncertainty matters.”
She stressed that marine ecosystems underpin fisheries, tourism and coastal well-being, meaning decisions taken about the seabed can have far-reaching consequences beyond the mining site itself.
Prof. Lahiru Udayanga echoed this concern.
“People tended to view deep-sea mining primarily through an environmental-risk lens rather than as a neutral industrial activity,” Prof. Udayanga told The Island. “Biodiversity loss was the most frequently identified concern, followed by physical damage to the seabed and long-term resource depletion.”
About two-thirds of respondents identified biodiversity loss as their greatest fear — a striking finding for an issue that many had only recently learned about.
A Measurable Value for Conservation
Perhaps the most significant finding was the public’s willingness to pay for protection.
“On average, households indicated a willingness to pay around LKR 3,532 per year to protect seabed ecosystems,” Prof. Udayanga told The Island. “From an economic perspective, that represents the social value people attach to marine conservation.”
The study’s advanced statistical analysis — using Conditional Logit and Random Parameter Logit models — confirmed strong and consistent support for policy options that reduce mineral extraction, limit environmental damage and strengthen monitoring and regulation.
The research also revealed demographic variations. Younger and more educated respondents expressed stronger pro-conservation preferences, while higher-income households were willing to contribute more financially.
At the same time, many respondents expressed concern that government agencies and the media have not done enough to raise awareness or enforce safeguards — indicating a trust gap that policymakers must address.
“Regulations and monitoring systems require social acceptance to be workable over time,” Dr. Udugama told The Island. “Understanding public perception strengthens accountability and clarifies the conditions under which deep-sea mining proposals would be evaluated.”
Youth and Community Engagement
Ganepola emphasised that engagement must begin with transparency and early consultation.
“Decisions about deep-sea mining should not remain limited to technical experts,” she told The Island. “Coastal communities — especially fishers — must be consulted from the beginning, as they are directly affected. Youth engagement is equally important because young people will inherit the long-term consequences of today’s decisions.”
She called for stronger media communication, public hearings, stakeholder workshops and greater integration of marine conservation into school and university curricula.
“Inclusive and transparent engagement will build trust and reduce conflict,” she said.
A Regional Milestone
Sudarsha De Silva described the study as a milestone for Sri Lanka and the wider Asian region.
“When you consider research publications on this topic in Asia, they are extremely limited,” De Silva told The Island. “This is one of the first comprehensive studies in Sri Lanka examining public perception of deep-sea mining. Organizations like the Sustainable Ocean Alliance stepping forward to collaborate with Sri Lankan academics is a great achievement.”
He also acknowledged the contribution of youth research assistants from EarthLanka — Malsha Keshani, Fathima Shamla and Sachini Wijebandara — for their support in executing the study.
A Defining Choice
As Sri Lanka charts its blue economy future, the message from citizens appears unmistakable.
Development is not rejected. But it must not come at the cost of irreversible ecological damage.
The ocean’s true wealth, respondents suggest, lies not merely in minerals beneath the seabed, but in the living systems above it — systems that sustain fisheries, tourism and coastal communities.
For policymakers weighing the promise of mineral wealth against ecological risk, the findings shared with The Island offer a clear signal: sustainable governance and biodiversity protection align more closely with public expectations than unchecked extraction.
In the end, protecting the ocean may prove to be not only an environmental responsibility — but the most prudent long-term investment Sri Lanka can make.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
How Black Civil Rights leaders strengthen democracy in the US
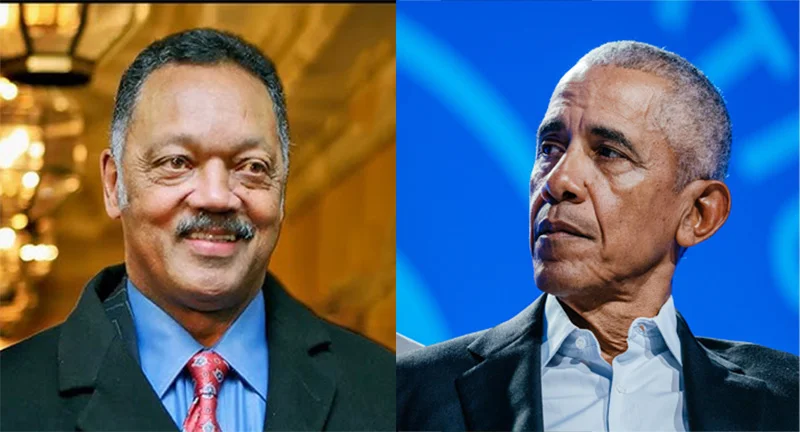

 On being elected US President in 2008, Barack Obama famously stated: ‘Change has come to America’. Considering the questions continuing to grow out of the status of minority rights in particular in the US, this declaration by the former US President could come to be seen as somewhat premature by some. However, there could be no doubt that the election of Barack Obama to the US presidency proved that democracy in the US is to a considerable degree inclusive and accommodating.
On being elected US President in 2008, Barack Obama famously stated: ‘Change has come to America’. Considering the questions continuing to grow out of the status of minority rights in particular in the US, this declaration by the former US President could come to be seen as somewhat premature by some. However, there could be no doubt that the election of Barack Obama to the US presidency proved that democracy in the US is to a considerable degree inclusive and accommodating.
If this were not so, Barack Obama, an Afro-American politician, would never have been elected President of the US. Obama was exceptionally capable, charismatic and eloquent but these qualities alone could not have paved the way for his victory. On careful reflection it could be said that the solid groundwork laid by indefatigable Black Civil Rights activists in the US of the likes of Martin Luther King (Jnr) and Jesse Jackson, who passed away just recently, went a great distance to enable Obama to come to power and that too for two terms. Obama is on record as owning to the profound influence these Civil Rights leaders had on his career.
The fact is that these Civil Rights activists and Obama himself spoke to the hearts and minds of most Americans and convinced them of the need for democratic inclusion in the US. They, in other words, made a convincing case for Black rights. Above all, their struggles were largely peaceful.
Their reasoning resonated well with the thinking sections of the US who saw them as subscribers to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, for instance, which made a lucid case for mankind’s equal dignity. That is, ‘all human beings are equal in dignity.’
It may be recalled that Martin Luther King (Jnr.) famously declared: ‘I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up, live out the true meaning of its creed….We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’
Jesse Jackson vied unsuccessfully to be a Democratic Party presidential candidate twice but his energetic campaigns helped to raise public awareness about the injustices and material hardships suffered by the black community in particular. Obama, we now know, worked hard at grass roots level in the run-up to his election. This experience proved invaluable in his efforts to sensitize the public to the harsh realities of the depressed sections of US society.
Cynics are bound to retort on reading the foregoing that all the good work done by the political personalities in question has come to nought in the US; currently administered by Republican hard line President Donald Trump. Needless to say, minority communities are now no longer welcome in the US and migrants are coming to be seen as virtual outcasts who need to be ‘shown the door’ . All this seems to be happening in so short a while since the Democrats were voted out of office at the last presidential election.
However, the last US presidential election was not free of controversy and the lesson is far too easily forgotten that democratic development is a process that needs to be persisted with. In a vital sense it is ‘a journey’ that encounters huge ups and downs. More so why it must be judiciously steered and in the absence of such foresighted managing the democratic process could very well run aground and this misfortune is overtaking the US to a notable extent.
The onus is on the Democratic Party and other sections supportive of democracy to halt the US’ steady slide into authoritarianism and white supremacist rule. They would need to demonstrate the foresight, dexterity and resourcefulness of the Black leaders in focus. In the absence of such dynamic political activism, the steady decline of the US as a major democracy cannot be prevented.
From the foregoing some important foreign policy issues crop-up for the global South in particular. The US’ prowess as the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ could be called in question at present but none could doubt the flexibility of its governance system. The system’s inclusivity and accommodative nature remains and the possibility could not be ruled out of the system throwing up another leader of the stature of Barack Obama who could to a great extent rally the US public behind him in the direction of democratic development. In the event of the latter happening, the US could come to experience a democratic rejuvenation.
The latter possibilities need to be borne in mind by politicians of the South in particular. The latter have come to inherit a legacy of Non-alignment and this will stand them in good stead; particularly if their countries are bankrupt and helpless, as is Sri Lanka’s lot currently. They cannot afford to take sides rigorously in the foreign relations sphere but Non-alignment should not come to mean for them an unreserved alliance with the major powers of the South, such as China. Nor could they come under the dictates of Russia. For, both these major powers that have been deferentially treated by the South over the decades are essentially authoritarian in nature and a blind tie-up with them would not be in the best interests of the South, going forward.
However, while the South should not ruffle its ties with the big powers of the South it would need to ensure that its ties with the democracies of the West in particular remain intact in a flourishing condition. This is what Non-alignment, correctly understood, advises.
Accordingly, considering the US’ democratic resilience and its intrinsic strengths, the South would do well to be on cordial terms with the US as well. A Black presidency in the US has after all proved that the US is not predestined, so to speak, to be a country for only the jingoistic whites. It could genuinely be an all-inclusive, accommodative democracy and by virtue of these characteristics could be an inspiration for the South.
However, political leaders of the South would need to consider their development options very judiciously. The ‘neo-liberal’ ideology of the West need not necessarily be adopted but central planning and equity could be brought to the forefront of their talks with Western financial institutions. Dexterity in diplomacy would prove vital.
-

 Life style5 days ago
Life style5 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoThailand to recruit 10,000 Lankans under new labour pact
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoMassive Sangha confab to address alleged injustices against monks
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoIMF MD here



















