Features
The COVID-19 Pandemic in Sri Lanka: Contextualising it geographically
By Dr. Nalani Hennayake and
Dr. Kumuduni Kumarihamy
(Continued from Friday)
The statistics and information aside, what this tells us is that the hope for immunization through a vaccine for the coronavirus could be far off than we think. Dynamics of vaccine politics exists within global politics and the capitalist economy. The Drug Controller General of India has approved the Oxford COVID-19 vaccine developed by AstraZeneca and another by the Indian manufacturer Bharat Biotech for emergency care. During his recent visit to Sri Lanka, India’s Foreign Minister had pledged that India would prioritize Sri Lanka when supplying vaccines to other countries. In the same meeting, the Indian Foreign Minister had reiterated “India’s backing for Sri Lanka’s reconciliation process and an ‘inclusive political outlook’ that encourages ethnic harmony while the Sri Lankan Foreign Minister rejoiced in the merits of ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’.” At the same time, it was reported that Sri Lanka is making plans to sign an agreement to secure the COVID-19 vaccine through the COVAX facility, which is already approved by the Cabinet.
Various news reports indicate that Sri Lanka is discussing whether to obtain the vaccines from the United States, Britain, or Sputnik V vaccine from Russia. However, it is clear that Sri Lanka has entered into world politics of vaccines. Such vaccine politics tells us that we need to steadily continue controlling strategies such as social distancing, contact tracing, antigen, and PCR testing, significantly raising awareness at the micro-community level. The kind of resilience that local people display when a family member undergoes an infectious disease such as measles and mumps are remarkable. People must be reminded of their resilience and caring. The communities must be made aware of the importance of safeguarding against the coronavirus, given its increased politicization and uneven possibilities of immunization and care.
While it is difficult to anticipate an equitable distribution of the vaccines globally, Sri Lanka’s situation will be determined by the number of vaccines received and the pandemic’s increased politicization. The WHO recognizes four categories of vulnerable persons/groups: Persons at risk of more serious illness from COVID-19, persons or groups with social vulnerabilities, persons or groups living in closed settings, and persons or groups with a higher occupational risk of exposure to the virus. What guarantees that these groups will be considered on a priority basis and the process of immunization will not be biased towards economic and political power? The global geographies of vaccines communicate to us two important messages. First are the difficulty and the disadvantaged position of obtaining vaccines for Sri Lanka as a less-developed country, and as a result, the COVID-19 pandemic can be protracted. Until the vaccines are obtained and a sizeable population of, at least, the risk category – including the frontline health care and security personal – are immunized, we will automatically be identified as vulnerable territories in terms of bio-security. Second, this vulnerability can be manipulated politically, both globally and nationally, to negotiate other deals with powerful countries to trade with vaccines.
The possibility of uneven geographies of care is a fact that should be anticipated given that a majority of the infected are from what we call ‘low-income, low-social status’ communities. There is now a tendency to identify COVID-19 as a disease of the impoverished. The local government bodies such as Municipal councils must reevaluate their position, not how they have acted to control the pandemic, but what they have failed to do in addressing the social welfare issues of the urban low-income communities.
As we look at the possible geographies of care, it is evident that the existence of a relatively good hospital network (at national, regional, and local levels) with relatively good coverage of the entire country has been immensely helpful in treating and caring for COVID-19 patients and those suspected. In addition to the already existing hospitals, the government has converted various government institutions into treatment centres in different parts of the island. This provides breathing space for the government hospitals when dealing with COVID-19 patients and patients who need critical medical care for other illnesses. It should also not be forgotten that the Public Health Inspectors were a category of lesser-known among the hierarchy of the health workers. Their role in curtailing the COVID-19 pandemic has been indispensable: Working not under the best of circumstances and with the minimum personal protective equipment. The average labourer who was entrusted with the strenuous task of sanitizing public places must be cared for too.
The public health system operationalized through MOH areas, a total of 347 MOH areas, as per the Annual Health Statistics Report 2017, is an essential component of controlling the pandemic now or in the future. The health sector generally receives only 1.59 percent of the GNP and 5.94 percent of the National Expenditure, a measly share for an essential sector. According to the same Report, Sri Lanka records an acute shortage of health personnel. There is a significant shortage of nurses and doctors: One doctor for 1083 people, one nurse per 471 people, one Public Health Midwife for 3533 people. As we look into the possible geographies of care, the significance of Primary Health Care Units, the MOH-based public health system, in maintaining a healthy country is indisputable.
Micro-geographies of COVID-19
In its interim guidance issued on May 18, 2020, the directive issued by the WHO is as follows: “Physical and social distancing measures in public spaces to prevent transmission between infected individuals and those who are not infected, and shield those at risk of developing serious illnesses. These measures include physical distancing, reduction or cancellation of mass gatherings and avoiding crowded spaces in different settings (e.g., public transport, restaurants, bars, theatres), working from home, and supporting adaptations to workplaces and educational institutions. For physical distancing, WHO recommends a minimum distance of at least one meter between people to limit the risk of interpersonal transmission.” Thus, the WHO recommendation includes two components: physical distancing of one meter between people and social distancing as much as possible in the social events, gatherings, etc.
This requirement was initially communicated as social distancing (සමාජ දුරස්ථභාවය) in Sri Lanka. The exercise of ‘physical and social distancing’ during COVID-19 reminded us of the work of two Political Geographers, Robert E. Norris, and L. Lloyd Haring. They argued that “every person has [is] a portable territory that is larger than the space s/he physically needs” (1980:9). They further wrote that “This territory is called personal space. It is similar in some ways to a political territory. Both personal space and political space are bounded, occupants of each type of space interact with each other of their kin, and uninvited intruders in both types of areas cause stress and behavioural changes within the intruded area.” It is imperative to understand that the personal space or the portable territory is unique to each individual in both size and shape, and they may vary over time and space, according to their specific individual requirements. In such a situation, how can we/how do we regiment this personal space in fear of the uninvited intruder of the coronavirus pathogen, through a standard measure of one or two meters between individuals? Until the COVID-19 pandemic emerged, this space, the portable territory of ours, had been taken for granted. We operated with a sense of relative autonomy over our portable territories. Now, we are told by the state and those in charge of controlling the pandemic how to operate these portable territories, maintaining a distance of one to two meters from each other. It is also expected that every person would carry out this ‘social distancing’ uniformly.
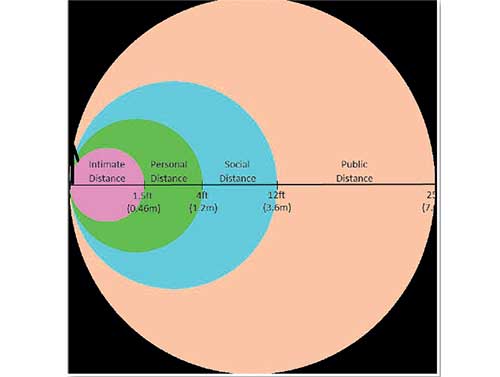
In early years, geographers were influenced by the science of spatial distancing, proxemics, introduced by the Cultural Anthropologist Edward T. Hall, who studied proxemics to understand human spatial behaviour at a micro-scale. In his famous book, “The Hidden Dimension,” published in 1966, he introduced a typology of human spatial distancing. This typology classifies the micro-spatiality of human beings into four types of spaces: intimate space, personal space, social space, and public space. Each type of space is demarcated with a specific distance, internally divided into a near phase and a far phase. The ‘portable territory’ mentioned above includes the intimate and personal spaces in this typology. According to Hall’s generalization, these portable territories end at four feet (1.2 meters), where social space begins. In his typology, ‘social space’ (See Diagram 01) spans between four to twelve feet, which is housed between personal and the public space. Edward T. Hall elaborates that “a proxemic feature of social distance is that it can be used to insulate or screen people from each other” (1966: 123). Social distance thus demarcates the end of physical dominion of an individual or, in other words, literally the jurisdiction of the portable territory.
Diagram 01: Distance Typology
In the case of COVID-19, hypothesizing that every person could be a possible carrier of the pathogen, one must maintain the one-metre distance. The distance of one-meter marks the outer boundary of the personal space and the inner boundary of the social space. An effective way to control the pathogens’ spread is to ensure that one strictly remains within one’s portable territory or, control people’s proxemic behaviour. This is very challenging since human beings have been civilized as social beings with defined and undefined social spaces!
Social distancing has become our new norm, and there is an undeniable need for this restriction. However, proxemic behaviour is not entirely an individual matter of concern. People of different cultures display different proxemic patterns; in other words, proxemic patterns are culturally highly conditioned. The concepts of ‘near’ and ‘distant’ are culturally different and relative. “The specific distance chosen (between two or more individuals) depends on the transaction, the relationship of the interacting individuals, how they feel and what they are doing… (Hall, 1969: 128). Human space requirements are generally influenced by his/her environment and surroundings and cultural norms. It is essential to understand the various elements in the immediate surroundings and the larger social context that contribute to our sense of spaces, distances, and relations. Implementers of social distancing may think that all people in a queue are potential carriers of the coronavirus, and therefore, one must maintain a distance of one meter. But some people may feel uncomfortable with social distancing simply because they may have socialized into different proxemic patterns.
Our proxemic behaviour may change, given the particular circumstances. For example, the need to feed a crying child at home, ailing parents, or one’s family overrides the fear of the virus, and the social distance is often contracted, in fear the person in front may grab what you may need. How people feel about each other at a particular time in a given space is a decisive factor in maintaining distance. In his study, Edward T. Hall explains that when people are angry and frustrated, they unknowingly tend to move closer. Some people often forget or become inconsiderate about maintaining social distance simply because of the urgency that being served in a regular queue entails. On such occasions, people are often characterized and labelled as irrational, undisciplined, and even unruly, whereas in political gatherings, opening ceremonies, personalized ‘bodhi pujas,’ etc., proxemic behaviour is often overlooked.
The standard proxemics required to control the COVID-19 pandemic are not realities for people who live in congested localities such as urban low-income areas and plantation areas where COVID-19 is fast spreading. Public services and commercial activities must be streamlined to facilitate a rational proxemic behaviour to maintain the social distance (see, for example, photograph no.1), with the understanding that the proxemic behaviour is culturally conditioned. It is very self-explanatory. Our discussion on proxemics here is not an argument against the requirement of one-meter restriction or any other form of social distancing. But understanding the cultural nuances of proxemics helps us be sensitive and intelligent when handling difficult situations rather than labelling people as irrational, undisciplined, and uncultured.
Few conclusive thoughts
What we have tried to emphasize in the article is the need and value of contextualizing the COVID-19 pandemic geographically. There are two aspects to this. First, it is imperative that the prevalence of the COVID-19 is mapped at the GN level with the available data focusing on individual MOH divisions. With our ‘sample’ exercise of Kandy, we have shown that a better spatial picture can be derived from GN level mapping. Since the MOH division, among others, is a crucial operational spatial unit for matters of public health, it is essential to map the number of COVID-19 patients at the MOH level, preferably even randomly locating them within GN divisions. The unintended benefit of such mapping would be that the existing health record systems (IMMR/eIMMR, etc.) will be further developed as a spatial health record system. A spatial health record system helps to understand the ecological dynamics of any disease and can be used as a real-time health monitoring and surveillance tool. The existing health record systems contain patients’ identity numbers (bed-head ticket number), age, gender, postal address, etc. If locational information such as GN, DSD, and district can be added, the data can easily be extracted at any spatial unit from the database for analysis in a crisis. Moreover, the postal addresses can be converted to Geographic Coordinates, indicating the patients’ geographical locations, using geocoding techniques.
Second, it is essential to understand the socioeconomic and ecological contexts of areas where the disease spreads at high intensity. Such a task is made difficult because of the unavailability of data relating to socioeconomic contexts at the GN level. However, the existing administrative system and its resources (Divisional Secretaries, Grama NIladharis, etc.) can be utilized to gather information about local areas. The process of controlling the pandemic must be localized with the MOH as the key operational spatial unit while adhering to national health guidelines and ethical concerns. It is time for the MOH-led system to take pro-active measures (i.e., creating awareness), in collaboration with the existing administrative setup, community organizations and networks, to safeguard the areas where the disease has not yet spread. Most importantly, this process needs to be monitored at the district level. Perhaps, district task forces need to be established to assess and take stock of the district’s current situation, preferably at the GN division level, and implement management and preventive measures.
In its recommendations, the WHO has repeatedly emphasized the need to adhere to both public health and social measures and, very importantly, select and ‘calibrate based on their local context.’ The WHO writes very clearly in its ‘COVID-19 Global Risk Communication and Community Engagement Strategy,’ that “COVID-19 is more than a health crisis; it is also an information and socioeconomic crisis.” It highlights the need to be ‘informed by data that cover the community needs, issues, and perceptions’ and engage with the communities. When the pandemic becomes protracted and the vaccines are not within reach, it is crucial to engage with the communities at the lower levels to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. The authorities must pay special attention to the areas that it has not yet spread and take pro-active measures to safeguard those areas, perhaps with the assistance of community organizations and institutions to create awareness among communities.
It appears that people are becoming complacent, and this can exacerbate the situation. Generally, people expect the government to control the second wave and are less inclined to take responsibility for individual behaviours and public health and social measures. On the other hand, the government seems to expect the full responsibility to be taken by the individuals. As the pandemic situation is drawn out, people tend to take risks for granted and assumes normalcy. Such complacency can be detrimental to the process of controlling the pandemic. Such complacency is also a result of poor or lack of communication about the disease, specially among vulnerable communities. Although the Ministry of Health has developed a comprehensive set of health guidelines, whether they are effectively communicated to the people is a matter of concern. Many people cannot grasp the severity of the disease and the significance of adhering to preventive health and social measures. Therefore, authorities must seriously consider sharing the responsibility of controlling the pandemic with the communities.
Finally, while we encourage mapping as a tool that can facilitate better decision making, it is important to understand that maps, and even charts and diagrams, etc., can become ‘political technologies.’ Such political technologies can instil a sense of concern, fear, and anxiety among the decision-makers and the public. We see that the pandemic is fast politicized in Sri Lanka. Mapping and geo-visualization of COVID-19 should not be ruled out either in fear of exposure or political manipulation, as it may suggest how the pandemic needs to be acted upon effectively at the local level.
Dr. Nalani Hennayake teaches a range of Human Geography courses) and Dr. Kumudini Kumarihamy teaches GIS and Health at the Department of Geography, University of Peradeniya.
(Concluded)
Features
A wage for housework? India’s sweeping experiment in paying women

In a village in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, a woman receives a small but steady sum each month – not wages, for she has no formal job, but an unconditional cash transfer from the government.
Premila Bhalavi says the money covers medicines, vegetables and her son’s school fees. The sum, 1,500 rupees ($16: £12), may be small, but its effect – predictable income, a sense of control and a taste of independence – is anything but.
Her story is increasingly common. Across India, 118 million adult women in 12 states now receive unconditional cash transfers from their governments, making India the site of one of the world’s largest and least-studied social-policy experiments.
Long accustomed to subsidising grain, fuel and rural jobs, India has stumbled into something more radical: paying adult women simply because they keep households running, bear the burden of unpaid care and form an electorate too large to ignore.
Eligibility filters vary – age thresholds, income caps and exclusions for families with government employees, taxpayers or owners of cars or large plots of land.
“The unconditional cash transfers signal a significant expansion of Indian states’ welfare regimes in favour of women,” Prabha Kotiswaran, a professor of law and social justice at King’s College London, told the BBC.
The transfers range from 1,000-2,500 rupees ($12-$30) a month – meagre sums, worth roughly 5-12% of household income, but regular. With 300 million women now holding bank accounts, transfers have become administratively simple.
Women typically spend the money on household and family needs – children’s education, groceries, cooking gas, medical and emergency expenses, retiring small debts and occasional personal items like gold or small comforts.
What sets India apart from Mexico, Brazil or Indonesia – countries with large conditional cash-transfer schemes – is the absence of conditions: the money arrives whether or not a child attends school or a household falls below the poverty line.

Goa was the first state to launch an unconditional cash transfer scheme to women in 2013. The phenomenon picked up just before the pandemic in 2020, when north-eastern Assam rolled out a scheme for vulnerable women. Since then these transfers have turned into a political juggernaut.
The recent wave of unconditional cash transfers targets adult women, with some states acknowledging their unpaid domestic and care work. Tamil Nadu frames its payments as a “rights grant” while West Bengal’s scheme similarly recognises women’s unpaid contributions.
In other states, the recognition is implicit: policymakers expect women to use the transfers for household and family welfare, say experts.
This focus on women’s economic role has also shaped politics: in 2021, Tamil actor-turned-politician Kamal Haasan promised “salaries for housewives”. (His fledgling party lost.) By 2024, pledges of women-focused cash transfers helped deliver victories to political parties in Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Odisha, Haryana and Andhra Pradesh.
In the recent elections in Bihar, the political power of cash transfers was on stark display. In the weeks before polling in the country’s poorest state, the government transferred 10,000 rupees ($112; £85) to 7.5 million female bank accounts under a livelihood-generation scheme. Women voted in larger numbers than men, decisively shaping the outcome.
Critics called it blatant vote-buying, but the result was clear: women helped the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)-led coalition secure a landslide victory. Many believe this cash infusion was a reminder of how financial support can be used as political leverage.
Yet Bihar is only one piece of a much larger picture. Across India, unconditional cash transfers are reaching tens of millions of women on a regular basis.
Maharashtra alone promises benefits for 25 million women; Odisha’s scheme reaches 71% of its female voters.
In some policy circles, the schemes are derided as vote-buying freebies. They also put pressure on state finances: 12 states are set to spend around $18bn on such payouts this fiscal year. A report by think-tank PRS Legislative Research notes that half of these states face revenue deficits – this happens when a state borrows to pay regular expenses without creating assets.
But many argue they also reflect a slow recognition of something India’s feminists have argued for decades: the economic value of unpaid domestic and care work.
Women in India spent nearly five hours a day on such work in 2024 – more than three times the time spent by men, according to the latest Time Use Survey. This lopsided burden helps explain India’s stubbornly low female labour-force participation. The cash transfers, at least, acknowledge the imbalance, experts say.
Do they work?
Evidence is still thin but instructive. A 2025 study in Maharashtra found that 30% of eligible women did not register – sometimes because of documentation problems, sometimes out of a sense of self-sufficiency. But among those who did, nearly all controlled their own bank accounts.

A 2023 survey in West Bengal found that 90% operated their accounts themselves and 86% decided how to spend the money. Most used it for food, education and medical costs; hardly transformative, but the regularity offered security and a sense of agency.
More detailed work by Prof Kotiswaran and colleagues shows mixed outcomes.
In Assam, most women spent the money on essentials; many appreciated the dignity it afforded, but few linked it to recognition of unpaid work, and most would still prefer paid jobs.
In Tamil Nadu, women getting the money spoke of peace of mind, reduced marital conflict and newfound confidence – a rare social dividend. In Karnataka, beneficiaries reported eating better, gaining more say in household decisions and wanting higher payments.
Yet only a sliver understood the scheme as compensation for unpaid care work; messaging had not travelled. Even so, women said the money allowed them to question politicians and manage emergencies. Across studies, the majority of women had full control of the cash.
“The evidence shows that the cash transfers are tremendously useful for women to meet their own immediate needs and those of their households. They also restore dignity to women who are otherwise financially dependent on their husbands for every minor expense,” Prof Kotiswaran says.
Importantly, none of the surveys finds evidence that the money discourages women from seeking paid work or entrench gender roles – the two big feminist fears, according to a report by Prof Kotiswaran along with Gale Andrew and Madhusree Jana.
Nor have they reduced women’s unpaid workload, the researchers find. They do, however, strengthen financial autonomy and modestly strengthen bargaining power. They are neither panacea nor poison: they are useful but limited tools, operating in a patriarchal society where cash alone cannot undo structural inequities.

What next?
The emerging research offers clear hints.
Eligibility rules should be simplified, especially for women doing heavy unpaid care work. Transfers should remain unconditional and independent of marital status.
But messaging should emphasise women’s rights and the value of unpaid work, and financial-literacy efforts must deepen, researchers say. And cash transfers cannot substitute for employment opportunities; many women say what they really want is work that pays and respect that endures.
“If the transfers are coupled with messaging on the recognition of women’s unpaid work, they could potentially disrupt the gendered division of labour when paid employment opportunities become available,” says Prof Kotiswaran.
India’s quiet cash transfers revolution is still in its early chapters. But it already shows that small, regular sums – paid directly to women – can shift power in subtle, significant ways.
Whether this becomes a path to empowerment or merely a new form of political patronage will depend on what India chooses to build around the money.
[BBC]
Features
People set example for politicians to follow

Some opposition political parties have striven hard to turn the disaster of Cyclone Ditwah to their advantage. A calamity of such unanticipated proportions ought to have enabled all political parties to come together to deal with this tragedy. Failure to do so would indicate both political and moral bankruptcy. The main issue they have forcefully brought up is the government’s failure to take early action on the Meteorological Department’s warnings. The Opposition even convened a meeting of their own with former President Ranil Wickremesinghe and other senior politicians who shared their experience of dealing with natural and man-made disasters of the past, and the present government’s failures to match them.
The difficulty to anticipate the havoc caused by the cyclone was compounded by the neglect of the disaster management system, which includes previous governments that failed to utilise the allocated funds in an open, transparent and corruption free manner. Land designated as “Red Zones” by the National Building Research Organisation (NBRO), a government research and development institute, were built upon by people and ignored by successive governments, civil society and the media alike. NBRO was established in 1984. According to NBRO records, the decision to launch a formal “Landslide Hazard Zonation Mapping Project (LHMP)” dates from 1986. The institutional process of identifying landslide-prone slopes, classifying zones (including what we today call “Red Zones”), and producing hazard maps, started roughly 35 to 40 years ago.
Indonesia, Thailand and the Philippines which were lashed by cyclones at around the same time as Sri Lanka experienced Cyclone Ditwah were also unprepared and also suffered enormously. The devastation caused by cyclones in the larger southeast Asian region is due to global climate change. During Cyclone Ditwah some parts of the central highlands received more than 500 mm of rainfall. Official climatological data cite the average annual rainfall for Sri Lanka as roughly 1850 mm though this varies widely by region: from around 900 mm in the dry zones up to 5,000 mm in wet zones. The torrential rains triggered by Ditwah were so heavy that for some communities they represented a rainfall surge comparable to a major part of their typical annual rainfall.
Inclusive Approach
Climate change now joins the pantheon of Sri Lanka’s challenges that are beyond the ability of a single political party or government to resolve. It is like the economic bankruptcy, ethnic conflict and corruption in governance that requires an inclusive approach in which the Opposition, civil society, religious society and the business community need to join rather than merely criticise the government. It will be in their self-interest to do so. A younger generation (Gen Z), with more energy and familiarity with digital technologies filled, the gaps that the government was unable to fill and, in a sense, made both the Opposition and traditional civil society redundant.
Within hours of news coming in that floods and landslides were causing havoc to hundreds of thousands of people, a people’s movement for relief measures was underway. There was no one organiser or leader. There were hundreds who catalysed volunteers to mobilise to collect resources and to cook meals for the victims in community kitchens they set up. These community kitchens sprang up in schools, temples, mosques, garages and even roadside stalls. Volunteers used social media to crowdsource supplies, match donors with delivery vehicles, and coordinate routes that had become impassable due to fallen trees or mudslides. It was a level of commitment and coordination rarely achieved by formal institutions.
The spontaneous outpouring of support was not only a youth phenomenon. The larger population, too, contributed to the relief effort. The Galle District Secretariat sent 23 tons of rice to the cyclone affected areas from donations brought by the people. The Matara District Secretariat made arrangements to send teams of volunteers to the worst affected areas. Just as in the Aragalaya protest movement of 2022, those who joined the relief effort were from all ethnic and religious communities. They gave their assistance to anyone in need, regardless of community. This showed that in times of crisis, Sri Lankans treat others without discrimination as human beings, not as members of specific communities.
Turning Point
The challenge to the government will be to ensure that the unity among the people that the cyclone disaster has brought will outlive the immediate relief phase and continue into the longer term task of national reconstruction. There will be a need to rethink the course of economic development to ensure human security. President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has spoken about the need to resettle all people who live above 5000 feet and to reforest those areas. This will require finding land for resettlement elsewhere. The resettlement of people in the hill country will require that the government address the issue of land rights for the Malaiyaha Tamils.
Since independence the Malaiyaha Tamils have been collectively denied ownership to land due first to citizenship issues and now due to poverty and unwillingness of plantation managements to deal with these issues in a just and humanitarian manner beneficial to the workers. Their resettlement raises complex social, economic and political questions. It demands careful planning to avoid repeating past mistakes where displaced communities were moved to areas lacking water, infrastructure or livelihoods. It also requires political consensus, as land is one of the most contentious issues in Sri Lanka, tied closely to identity, ethnicity and historical grievances. Any sustainable solution must go beyond temporary relocation and confront the historical exclusion of the Malaiyaha Tamil community, whose labour sustains the plantation economy but who remain among the poorest groups in the country.
Cyclone Ditwah has thus become a turning point. It has highlighted the need to strengthen governance and disaster preparedness, but it has also revealed a different possibility for Sri Lanka, one in which the people lead with humanity and aspire for the wellbeing of all, and the political leadership emulates their example. The people have shown through their collective response to Cyclone Ditwah that unity and compassion remain strong, which a sincere, moral and hardworking government can tap into. The challenge to the government will be to ensure that the unity among the people that the cyclone disaster has brought will outlive the immediate relief phase and continue into the longer term task of national reconstruction with political reconciliation.
by Jehan Perera
Features
An awakening: Revisiting education policy after Cyclone Ditwah

 In the short span of two or three days, Cyclone Ditwah, has caused a disaster of unprecedented proportions in our midst. Lashing away at almost the entirety of the country, it has broken through the ramparts of centuries old structures and eroded into areas, once considered safe and secure.
In the short span of two or three days, Cyclone Ditwah, has caused a disaster of unprecedented proportions in our midst. Lashing away at almost the entirety of the country, it has broken through the ramparts of centuries old structures and eroded into areas, once considered safe and secure.
The rains may have passed us by. The waters will recede, shops will reopen, water will be in our taps, and we can resume the daily grind of life. But it will not be the same anymore; it should not be. It should not be business as usual for any of us, nor for the government. Within the past few years, Sri Lankan communities have found themselves in the middle of a crisis after crisis, both natural and man-made, but always made acute by the myopic policies of successive governments, and fuelled by the deeply hierarchical, gendered and ethnicised divides that exist within our societies. The need of the hour for the government today is to reassess its policies and rethink the directions the country, as a whole, has been pushed into.
Neoliberal disaster
In the aftermath of the devastation caused by the natural disaster, fundamental questions have been raised about our existence. Our disaster is, in whole or in part, the result of a badly and cruelly managed environment of the planet. Questions have been raised about the nature of our economy. We need to rethink the way land is used. Livelihoods may have to be built anew, promoting people’s welfare, and by deveoloping a policy on climate change. Mega construction projects is a major culprit as commentators have noted. Landslides in the upcountry are not merely a result of Ditwah lashing at our shores and hills, but are far more structural and points to centuries of mismanagement of land. (https://island.lk/weather-disasters-sri-lanka-flooded-by-policy-blunders-weak-enforcement-and-environmental-crime-climate-expert/). It is also about the way people have been shunted into lands, voluntarily or involuntarily, that are precarious, in their pursuit of a viable livelihood, within the limited opportunities available to them.
Neo liberal policies that demand unfettered land appropriation and built on the premise of economic growth at any expense, leading to growing rural-urban divides, need to be scrutinised for their short and long term consequences. And it is not that any of these economic drives have brought any measure of relief and rejuvenation of the economy. We have been under the tyrannical hold of the IMF, camouflaged as aid and recovery, but sinking us deeper into the debt trap. In October 2025, Ahilan Kadirgamar writes, that the IMF programme by the end of 2027, “will set up Sri Lanka for the next crisis.” He also lambasts the Central Bank and the government’s fiscal policy for their punishing interest rates in the context of disinflation and rising poverty levels. We have had to devalue the rupee last month, and continue to rely on the workforce of domestic workers in West Asia as the major source of foreign exchange. The government’s negotiations with the IMF have focused largely on relief and infrastructure rebuilding, despite calls from civil society, demanding debt justice.
The government has unabashedly repledged its support for the big business class. The cruelest cut of them all is the appointment of a set of high level corporate personalities to the post-disaster recovery committee, with the grand name, “Rebuilding Sri Lanka.” The message is loud and clear, and is clearly a slap in the face of the working people of the country, whose needs run counter to the excessive greed of extractive corporate freeloaders. Economic growth has to be understood in terms that are radically different from what we have been forced to think of it as, till now. For instance, instead of investment for high profits, and the business of buy and sell in the market, rechannel investment and labour into overall welfare. Even catch phrases like sustainable development have missed their mark. We need to think of the economy more holistically and see it as the sustainability of life, livelihood and the wellbeing of the planet.
The disaster has brought on an urgency for rethinking our policies. One of the areas where this is critical is education. There are two fundamental challenges facing education: Budget allocation and priorities. In an address at a gathering of the Chamber of Commerce, on 02 December, speaking on rebuilding efforts, the Prime Minister and Minister of Education Dr. Harini Amarasuriya restated her commitment to the budget that has been passed, a budget that has a meagre 2.4% of the GDP allocated for education. This allocation for education comes in a year that educational reforms are being rolled out, when heavy expenses will likely be incurred. In the aftermath of the disaster, this has become more urgent than ever.
Reforms in Education
The Government has announced a set of amendments to educational policy and implementation, with little warning and almost no consultation with the public, found in the document, Transforming General Education in Sri Lanka 2025 published by the Ministry of Education. Though hailed as transformative by the Prime Minister (https://www.news.lk/current-affairs/in-the-prevailing-situation-it-is-necessary-to-act-strategically-while-creating-the-proper-investments-ensuring-that-actions-are-discharged-on-proper-policies-pm), the policy is no more than a regurgitation of what is already there, made worse. There are a few welcome moves, like the importance placed on vocational training. Here, I want to raise three points relating to vital areas of the curriculum that are of concern: 1) streamlining at an early age; relatedly 2) prioritising and privileging what is seen as STEM education; and 3) introducing a credit-based modular education.
1. A study of the policy document will demonstrate very clearly that streamlining begins with Junior Secondary Education via a career interest test, that encourages students to pursue a particular stream in higher studies. Further Learning Modules at both “Junior Secondary Education” and “Senior Secondary Education Phase I,” entrench this tendency. Psychometric testing, that furthers this goal, as already written about in our column (https://kuppicollective.lk/psychometrics-and-the-curriculum-for-general-education/) points to the bizarre.
2. The kernel of the curriculum of the qualifying examination of Senior Secondary Education Phase I, has five mandatory subjects, including First Language, Math, and Science. There is no mandatory social science or humanities related subject. One can choose two subjects from a set of electives that has history and geography as separate subjects, but a Humanities/Social Science subject is not in the list of mandatory subjects. .
3. A credit-based, modular education: Even in universities, at the level of an advanced study of a discipline, many of us are struggling with module-based education. The credit system promotes a fragmented learning process, where, depth is sacrificed for quick learning, evaluated numerically, in credit values.
Units of learning, assessed, piece meal, are emphasised over fundamentals and the detailing of fundamentals. Introducing a module based curriculum in secondary education can have an adverse impact on developing the capacity of a student to learn a subject in a sustained manner at deeper levels.
Education wise, and pedagogically, we need to be concerned about rigidly compartmentalising science oriented, including technological subjects, separately from Humanities and Social Studies. This cleavage is what has led to the idea of calling science related subjects, STEM, automatically devaluing humanities and social sciences. Ironically, universities, today, have attempted, in some instances, to mix both streams in their curriculums, but with little success; for the overall paradigm of education has been less about educational goals and pedagogical imperatives, than about technocratic priorities, namely, compartmentalisation, fragmentation, and piecemeal consumerism. A holistic response to development needs to rethink such priorities, categorisations and specialisations. A social and sociological approach has to be built into all our educational and development programmes.
National Disasters and Rebuilding Community
In the aftermath of the disaster, the role of education has to be rethought radically. We need a curriculum that is not trapped in the dichotomy of STEM and Humanities, and be overly streamlined and fragmented. The introduction of climate change as a discipline, or attention to environmental destruction cannot be a STEM subject, a Social Science/Humanities subject or even a blend of the two. It is about the vision of an economic-cum-educational policy that sees the environment and the economy as a function of the welfare of the people. Educational reforms must be built on those fundamentals and not on real or imagined short term goals, promoted at the economic end by neo liberal policies and the profiteering capitalist class.
As I write this, the sky brightens with its first streaks of light, after days of incessant rain and gloom, bringing hope into our hearts, and some cheer into the hearts of those hundreds of thousands of massively affected people, anxiously waiting for a change in the weather every second of their lives. The sense of hope that allows us to forge ahead is collective and social. The response by Lankan communities, to the disaster, has been tremendously heartwarming, infusing hope into what still is a situation without hope for many. This spirit of collective endeavour holds the promise for what should be the foundation for recovery. People’s demands and needs should shape the re-envisioning of policy, particularly in the vital areas of education and economy.
(Sivamohan Sumathy was formerly attached to the Department of English, University of Peradeniya)
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
By Sivamohan Sumathy
-
News6 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
 News5 days ago
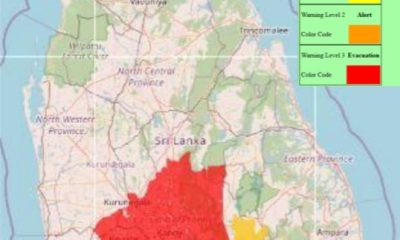
News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoHouse erupts over Met Chief’s 12 Nov unheeded warning about cyclone Ditwah













