Business
External Sector Performance – December 2022
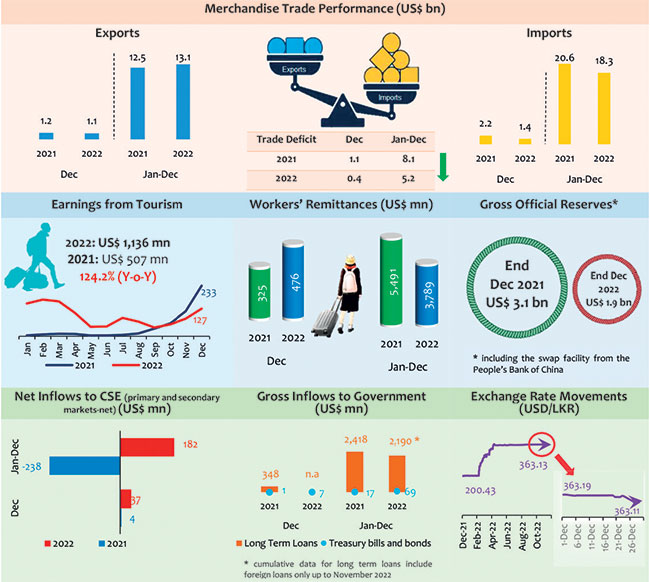
* Earnings from exports remained resilient during 2022 recording the highest ever exports,
while expenditure on imports declined significantly in 2022, compared to 2021.
* Merchandise trade deficit recorded the lowest in 2022, since 2010.
* Foreign investments in the government securities market and Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) recorded a notable net inflow during 2022 compared to net outflow in 2021.
* The recovery in earnings from tourism persisted in 2022 and marked a noticeable growth, although workers’ remittances moderated in 2022, compared to 2021.
Performance of Merchandise Trade in 2022
Earnings from exports in 2022 surpassed US dollars 13 billion per year for the first time, recording an increase of 4.9 per cent from the previous highest recorded in 2021. This improvement was a result of increased earnings from industrial exports, including garments, gems, diamonds and jewellery, machinery and mechanical appliances and petroleum products. Meanwhile, total import expenditure in 2022 amounted to US dollars 18,291 million, recording a decline of 11.4 per cent, year-on-year, resulted from measures to restrict non-urgent imports and liquidity constraints prevailed in the market for the most part of 2022. As a result, the deficit in the trade account in 2022 narrowed to the lowest level since 2010 to US dollars 5,185 million, from US dollars 8,139 million recorded in 2021.
The major contributory factors for the decline in the cumulative trade deficit in 2022 are shown in Merchandise Trade Balance The deficit in the merchandise trade account narrowed to US dollars 358 million in December 2022, from US dollars 1,085 million recorded in December 2021, helped by a larger decline in imports, compared to the decline in exports.
Performance of Merchandise Exports1 Overall exports:
Earnings from merchandise exports declined by 7.7 per cent in December 2022, over December 2021, to US dollars 1,068 million. The decline in earnings from industrial exports mainly contributed to the decline in export earnings in December 2022.
Industrial exports: Earnings from the export of industrial goods declined in December 2022, compared to December 2021, mainly due to the lower exports of garments resulted from reduced spending capacity associated with high inflation and recessionary concerns in most of the major markets (the USA, the EU and the UK). Similarly, earnings from rubber products continued to decline due to the lower exports of tires and household rubber gloves. Further, a sizable decline was recorded in the exports of food, beverages, and tobacco (mainly, manufactured tobacco), although earnings from gems, diamonds, and jewellery; and machinery and mechanical appliances (mainly, electronic equipment) increased.
Agricultural exports: Earnings from tea exports marginally declined with the higher average export prices of tea was offset by the decline in volume exported, resulted from the lag effect of the unavailability of adequate fertiliser. Earnings from the export of other agricultural goods declined in December 2022, compared to a year ago, resulted from lower export volumes of pepper, categorised under spices.
Mineral exports: Earnings from mineral exports increased in December 2022, compared to December 2021, mainly due to the increase in export of titanium ores.
Business
Cheaper credit expected to drive Sri Lanka’s business landscape in 2026

The opening weeks of 2026 are offering a glimmer of cautious hope for the business community weary from years of economic turbulence and steep financing costs. The Central Bank’s latest weekly economic indicators signal more than just macroeconomic stability. They point to early signs of a long-awaited trend; a measurable dip in borrowing costs.
“If sustained, this shift could transform steady growth into a robust, investment-led expansion,” a senior economist told The Island Financial Review.
The benchmark Average Weighted Prime Lending Rate (AWPR) declined by 21 basis points to 8.98% for the week ending 16 January, according to the Central Bank.
“For entrepreneurs and CEOs, this is not just another statistic. It could mean the difference between postponing an expansion and hiring new staff. Across boardrooms, the hope is that this marks the start of a sustained downward trend that holds through 2026,” he said.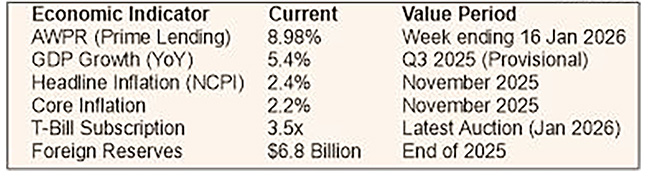
When asked about the instances where Treasury Bills are not fully subscribed by the investors, he replied,” Treasury Bill yields remained broadly stable, with only minimal movement across 91-day, 182-day, and 364-day tenors. Strong demand was clear, with the latest T-Bill auction oversubscribed by about 3.5 times. This sovereign-level stability creates room for the gradual easing of commercial lending rates, allowing the Central Bank to nurture a more growth-supportive monetary policy.”
Replying to a question on how he views the inflation numbers in this context, he said, “The year-on-year increase in the National Consumer Price Index stood at a manageable 2.4% in November, with core inflation at 2.2%. Such an environment should allow interest rates to fall without sparking a price spiral. For businesses, it means the real cost of borrowing adjusted for inflation, and it is becoming more favourable for them. While consumers still face weekly price shifts in vegetables and fish, the broader disinflation trend gives policymakers leeway to keep credit affordable.”
Referring to the growth trajectory, he mentioned, “With GDP growth provisionally at 5.4% in the third quarter of 2025 and Purchasing Managers’ Indices signalling expansion in both manufacturing and services, the economy is in a growth phase. However, to accelerate this momentum businesses need capital at lower cost to modernise machinery, boost export capacity, and spur innovation. Affordable credit is, therefore, not merely helpful, it is essential to shift growth into a higher gear.”
In conclusion , he said,” The coming months will be watched closely, because for Sri Lankan businesses, a sustained decline in borrowing costs isn’t just an indicator; it’s the foundation for growth. There’s hope that this easing in the cost of money will prevail through most of the year.”
By Sanath Nanayakkare ✍️
Business
Mercantile Investments expands to 90 branches, backed by strong growth

Mercantile Investments & Finance PLC has expanded its national footprint to 90 branches with a new opening in Tangalle, reinforcing its commitment to community accessibility. The trusted non-bank financial institution, with over 60 years of service, now supports diverse communities across Sri Lanka with leasing, deposits, gold loans, and tailored lending.
This physical expansion aligns with significant financial growth. The company recently surpassed an LKR 100 billion asset base, with its lending portfolio doubling to Rs. 75 billion and deposits growing to Rs. 51 billion, reflecting strong customer trust. It maintains a low NPL ratio of 4.65%.
Chief Operating Officer Laksanda Gunawardena stated the branch network is vital for building trust, complemented by ongoing digital investments. Managing Director Gerard Ondaatjie linked the growth to six decades of safeguarding depositor interests.
With strategic plans extending to 2027, Mercantile Investments aims to convert its scale into sustained competitive advantage, supporting both customers and Sri Lanka’s economic progress.
Business
AFASL says policy gap creates ‘uneven playing field,’ undercuts local Aluminium industry

A glaring omission in the Board of Investment’s (BOI) Negative List is allowing duty-free imports of fully fabricated aluminium products, severely undercutting Sri Lanka’s domestic manufacturers, according to a leading industry association.
The Aluminium Fabricators Association of Sri Lanka (AFASL) warns that this policy failure is threatening tens of thousands of jobs, draining foreign exchange, and stifling local industrial capacity.
“This has created an uneven playing field,” the AFASL said, adding that BOI-approved developers gain cost advantages over local fabricators, while government revenue and foreign exchange are lost through imports of products already made in Sri Lanka.
The core of the issue lies in a critical policy gap. While raw aluminium extrusions are protected on the BOI’s Negative List – which restricts duty-free imports – finished products like doors, windows, and façade systems are not. Furthermore, the list’s lack of specific Harmonised System (HS) codes allows these finished items to be imported under varying descriptions, slipping through duty-free.
This loophole, the AFASL argues, disadvantages a robust local industry that employs over 30,000 people directly and indirectly. Supported by five local extrusion manufacturers, a skilled NVQ-certified workforce, and a well-established glass-processing sector, the industry has been operational since the 1980s.
The association highlights that the damage extends beyond fabrication. The imported systems often include glass, hinges, locks, and accessories, all of which are produced locally, thereby cutting off demand across the entire domestic value chain. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), a segment government policy aims to support, are feeling the impact most acutely.
Since May 2025, the AFASL has been engaged in talks with the BOI, Finance Ministry, and Industries Ministry. Their key demand is to include specific HS codes on the Negative List and to list fabricated aluminium doors, windows, and curtain wall systems under HS Code 7610 to close the loophole.
While welcoming supportive recommendations from the Industries Ministry to add these products to an updated Negative List, the AFASL sounded a note of caution. It warned that proposed reductions in the CESS levy could further incentivise imports, undermining the sector’s recovery from the economic crisis.
The association also pointed to an inequity in the current framework. With most subsidies withdrawn, BOI-registered property developers continue to benefit from duty-free imports, while locally made products remain subject to heavy taxes for the general population.
The AFASL is urging policymakers to align investment incentives with national industrial policy, protect domestic manufacturing, and ensure fair competition across the construction supply chain to safeguard an industry vital to Sri Lanka’s economy.
By Sanath Nanayakkare ✍️
-

 Editorial1 day ago
Editorial1 day agoIllusory rule of law
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoUNDP’s assessment confirms widespread economic fallout from Cyclone Ditwah
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoKoaloo.Fi and Stredge forge strategic partnership to offer businesses sustainable supply chain solutions
-

 Editorial2 days ago
Editorial2 days agoCrime and cops
-

 Features1 day ago
Features1 day agoDaydreams on a winter’s day
-

 Editorial3 days ago
Editorial3 days agoThe Chakka Clash
-

 Features1 day ago
Features1 day agoSurprise move of both the Minister and myself from Agriculture to Education
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoSLT MOBITEL and Fintelex empower farmers with the launch of Yaya Agro App













