Features
Eradicating CKDu From Sri Lanka is Straightforward—What is Preventing it?
by Drs. Sunil J. Wimalawansa and Chandra B. Dissanayake
(Prof. of Medicine and Prof. of Geology)
Since identifying chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka in the mid-1990s, little progress has been made in aetiology and prevention. Despite the numerous hypotheses and conjectures—with more than 35—none have been thoroughly studied or substantiated as the definitive cause of CKDu.
The development of CKDu necessitates simultaneous exposure to various factors and conditions over an extended period. Hence, it is also called chronic kidney disease of multifactorial origin (CKDmfo). A recent newspaper article suggested that Chinese researchers re-confirmed the lack of association of agrochemicals, heavy metals, or arsenic (common postulated factors) with CKDu, consistent with our and other scientists’ publications over 15 years.
Comparatively, on a per-hectare basis of arable land, New Zealand and numerous other countries employ more than ten-fold the amount of agrochemicals and fertilisers containing heavy metals. Similarly, in Sri Lanka, in hilly country like Nuwara Eliya, and wet zones, farmers extensively utilize inorganic fertilisers, especially phosphates and pesticides—significantly more than in the dry zones. Surprisingly, there is little to no reported incidence of CKDu in these regions.
Research studies on hypothesis-driven causation are needed
The lack of conclusive evidence on CKDu stems from inadequately designed studies that fail to assess causes and test specific hypotheses. No CKDu study has rigorously applied Hill’s criteria for disease causation to distinguish casual association from causation. To address CKDu causes effectively, detailed empirical studies, not just descriptive ones, are essential. [For more details, refer to Hill, A.B., 1965, “The Environment and Disease: Association or Causation?”]
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14283879].
No credible scientific evidence supports the role of any of the mentioned postulated factors in contributing to or causing CKDu. Definitive conclusions necessitate well-conducted, unbiased studies with proper design and sufficient statistical power to thoroughly assess or rule out the potential effects of heavy metals, algal toxins, and agrochemicals on CKDu.
Critical causative criteria for establishing a link between a factor and a disease include the Strength of the association, Consistency, Specificity, Temporality, Biological gradient, Plausibility, Coherence, and Empirical data (Experiments). The presence of the majority of these factors is necessary to attribute causation. However, most studies on CKDu are heterogeneous and descriptive, offering limited value. Therefore, conducting meta-analyses using such data is scientifically unsound and inappropriate, as they will likely yield misleading conclusions.
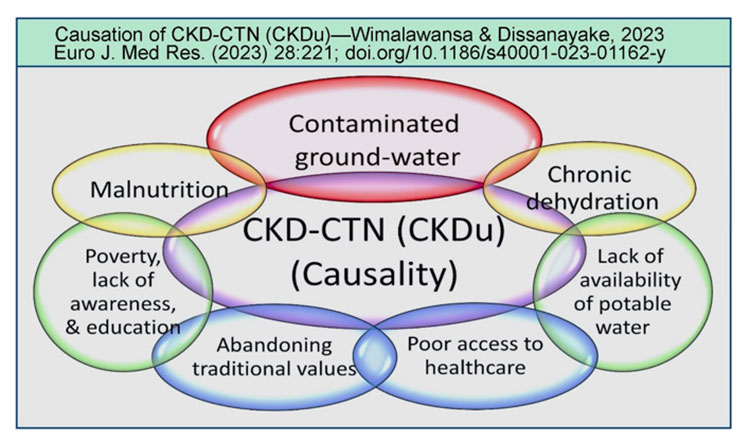
Because CKDu arises from forming nanocrystals and nanotubes in kidney tubules and tissues, a more fitting designation would be “CKD of crystal-tubular nephropathy” (CKD-CTN). The accompanying figure illustrates critical factors contributing to the CKD-CTN development (from Wimalwansa & Dissanayake, Euro. J. Med. Res., July 2023: https://rdcu.be/dgagf). (See Figure)
Poorly designed studies generated inconclusive data:
Compartmentalized research and poor study designs consistently fail to address research questions and test hypotheses related to CKDu. This lack of adherence to fundamental scientific principles, along with issues in improper sample collection and data integrity, has resulted in skewed and unreliable conclusions, muddling the progress and analyses of CKDu in the country.
Extrapolating such data to the overall status of CKDu in Sri Lanka and other tropical countries shifts attention away from identifying actual causative factors, proper fund allocation, and implementing essential remedies for CKDu prevention. Biased comments by Chinese scientists, such as ‘aristolochic acid,’ while relevant in rural China, are not pertinent to CKDu (CKD-CTN) in the dry zones of Sri Lanka.
Methodological and conceptual failures:
No conclusive evidence supports agrochemicals (glyphosate) or heavy metals causing CKDu. Claims linking slightly elevated magnesium in drinking water to CKDu lack reliability due to sampling and methodological errors. In contrast, over 750 international research articles establish magnesium as a “renal protector” in humans.
Detecting an isolated elevation of magnesium or extremely low levels of glyphosate in inconsistent studies is insufficient to establish even an association, let alone causation. Such findings meet only one of Hill’s Causation criteria. Inferences from random water samples and two rat studies lack reproducibility and conclusiveness. The flawed extrapolation of this data to assert that glyphosate or magnesium causes CKDu has diverted attention and national research funds to unproductive programmes. The crucial factor in drinking water is the “calcium to magnesium” ratio, not individual components alone.
Glyphosate or other chemicals used in intervention experiments, equivalent to body weight on a kg basis, are “astronomically” high—toxic. Such concentrations do not exist in water or soil under normal conditions. Such concentration exists when an individual ingests concentrated glyphosate. Therefore, conclusions from such experiments are misleading. Any toxicity dependent on the “dose and exposure” and real-world scenarios do not match the extreme concentrations used in intervention experiments.
Studies have consistently lacked rigorousness during sample collection, standardized methodology, and the use of controls. They also lack quality control during analyses and testing hypotheses. Methodological errors, such as smaller sample sizes and a lack of control experiments, introduce random- and Type-2 errors into the data. To obtain accurate insights, examining thousands of properly collected water samples across affected regions is crucial, as is comparing them with comparable but non-affected villages within the same region (e.g., subtractive analysis), even within ‘affected’ villages, pockets with good-quality drinking water (e.g., natural springs), thus clusters of unaffected families. Therefore, calling the entire area as CKDu affecting is a misnomer.
The neglect of already published data
Suppose one uses “CKD” as a keyword in the following URL: one can pull over a dozen research articles illustrating that CKDu is triggered by “natural” causes—hard water (Ca2+), excess phosphate in combination with fluoride” and chronic dehydration.
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sunil-Wimalawansa/publications
Peasants experiencing chronic dehydration due to daily exposure to hot climates and nightly alcohol intake, along with drinking water high in Calcium, Carbonate/ Phosphates, and Fluoride ions, etc., create a “conducive internal environment” for the formation of calcium phosphate (CaPO4) crystals within renal tissue. Additionally, hard water chelates glyphosate, eliminating its potential toxicity, if any, whereas fluoride has the opposite effect.
Chronic exposure to excess calcium, carbonate/phosphate (and other anions), and fluoride through the ingestion of hard water over a decade is necessary to induce CKD-CTN. Such extended exposure maintains the mentioned higher ionic concentrations in renal tissues. Chronic dehydration leads to consistently concentrated urine, enabling the precipitation of hydroxy- and oxalate-apatite nano-minerals in the kidneys. This process occurs with or without fluoride, but fluoride stabilizes these nano-mineral crystals, forming fluorapatite resistant to degradation, allowing crystals to grow. Fluorapatite nanocrystals are implicated in causing CKD-CTN, causing fatal renal failure. The detailed mechanism is illustrated in the following article: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3298/7/1/2
The way to prevent and eradicate CKDu:
Consuming potable water and avoiding prolonged dehydration can prevent persistent dehydration-associated CKD-CTN. This concept offers highly cost-effective and straightforward solutions to safeguard peasants, particularly farm laborers. This eliminates silent, deadly disease, without needing expensive medications, interventions, or the construction of dialysis centers and hospitals, which is especially crucial in financially strained circumstances.
Research, including ours, has shown that increasing daily access to clean water significantly reduces CKD-CTN incidence and associated morbidities and premature deaths. Unfortunately, once the disease progresses beyond CKD stage IIIB, the damage becomes irreversible. It leads to hardening and shrinkage of the kidney due to fibrosis—resulting in permanent damage.
The following two published articles provide a detailed methodology and cost-benefit analysis of ways to eradicate CKDu from Sri Lanka:—CKD-CTN.Public health interventions for chronic diseases: cost-benefit modelizations for eradicating chronic kidney disease of multifactorial origin (CKDmfo/ CKDu) from tropical countries. Heliyon 2019;5(10):e02309. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02309.And Strategic framework for managing non-communicable diseases: Preventing chronic kidney disease of multifactorial origin (CKDmfo/CKDu) as an Example. Chronic Dis Int 2015;2(2 (1018)):1-9 (https://austinpublishinggroup.com/chronic-diseases/fulltext/chronicdiseases-v2-id1018.php).
The direct approaches outlined in the above articles offer ways to mitigate and eradicate CKDu/CKD-CTN in Sri Lanka and other affected countries. Unfortunately, there has been a lack of political will to address the issue. For some, it has become an unscrupulous business. The mentioned scientific papers provide details on how implementing a multi-pronged approach can prevent CKD-CTN, reduce premature deaths, and minimize the socio-economic impact on affected families. For more information. More information in:
Environmental health and preventive medicine 2014;19(6):375-394. DOI: 10.1007/s12199-014-0395-5 (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25239006/).
Critical elements need to eradicate CKD-CTN from Sri Lanka
It is essential to systematically address peasants’ lifestyles and dietary habits, improve micro-nutrition, protect their renal and general health, and mitigate CKD-CTN. In addition to providing potable water, other interventions are also necessary to overcome this forgotten killer. Adhering to such would save the lives of people in CKD-CTN-affected tropical countries. They consume insufficient water due to the unpleasant taste of naturally contaminated hard water. Just because peasants do not have a voice is not an excuse to neglect them by the politicians and the government.
The key to eradicating CKD-CTN is prevention through education, lifestyle changes, and increased consumption of clean water—not in treating renal disease or expanding dialysis centers, hospitals, or transplantation services. To effectively prevent CKD-CTN, providing safe and affordable clean water in the affected and adjacent regions in the entire dry zone is essential rather than solely emphasizing aggressive treatment of end-stage renal diseases.
Historical evidence indicates that ancient Sri Lankan Kingdoms, like Anuradhapura, Polonnaruwa, Dambadeniys, Sigiriya, and Yapahuwa, were relocated, primarily within the dry zonal regions, now affected by CKD-CTN. The reasons for these relocations, whether protecting from invading armies, severe malarial epidemics, or deaths due to CKD-CTN, remain uncertain. Proposals to move the entire North Central Province (NCP) population elsewhere or replace the topsoil in the region are deemed impractical and absurd.
The current approach will continue to fail
The current strategy of expanding renal clinics, dialysis and transplantation services, coupled with reliance on aid from other countries, is an ineffective approach that falls short of “preventing and eradicating” CKD-CTN in Sri Lanka. This method is like holding a tail to tame a tiger. Even if the rates of deaths have somewhat slowed, it is likely because many of the most vulnerable individuals are already deceased. The focus should shift towards protecting the younger generation and families. Unfortunately, CKDu has become a business venture for many, akin to exploitation during the LTTE war.
In addressing CKD-CTN, vision, political will, and prioritization of programs that cost less than a few months of healthcare expenses for maintaining affected individuals and families are lacking. Sri Lanka possesses the necessary technology, know-how, and essential resources to implement a program for eradication without requiring international expertise. However, inherent conflicts of interest hinder the implementation of the right path and impede progress.
Our latest contribution on the subject [Title: Nanocrystal-induced Chronic Tubular-nephropathy in Tropical Countries: Diagnosis, Mitigation, and Eradication] published on July 2023 in a Nature Journal (EJMR)—PDF of the article available from the following links: https://rdcu.be/dgagf
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-023-01162-y
Features
Indian Ocean Security: Strategies for Sri Lanka

During a recent panel discussion titled “Security Environment in the Indo-Pacific and Sri Lankan Diplomacy”, organised by the Embassy of Japan in collaboration with Dr. George I. H. Cooke, Senior Lecturer and initiator of the Awarelogue Initiative, the keynote address was delivered by Prof Ken Jimbo of Kelo University, Japan (Ceylon Today, February 15, 2026).
The report on the above states: “Prof. Jimbo discussed the evolving role of the Indo-Pacific and the emergence of its latest strategic outlook among shifting dynamics. He highlighted how changing geopolitical realities are reshaping the region’s security architecture and influencing diplomatic priorities”.
“He also addressed Sri Lanka’s position within this evolving framework, emphasising that non-alignment today does not mean isolation, but rather, diversified engagement. Such an approach, he noted, requires the careful and strategic management of dependencies to preserve national autonomy while maintaining strategic international partnerships” (Ibid).
Despite the fact that Non-Alignment and Neutrality, which incidentally is Sri Lanka’s current Foreign Policy, are often used interchangeably, both do not mean isolation. Instead, as the report states, it means multi-engagement. Therefore, as Prof. Jimbo states, it is imperative that Sri Lanka manages its relationships strategically if it is to retain its strategic autonomy and preserve its security. In this regard the Policy of Neutrality offers Rule Based obligations for Sri Lanka to observe, and protection from the Community of Nations to respect the territorial integrity of Sri Lanka, unlike Non-Alignment. The Policy of Neutrality served Sri Lanka well, when it declared to stay Neutral on the recent security breakdown between India and Pakistan.
Also participating in the panel discussion was Prof. Terney Pradeep Kumara – Director General of Coast Conservation and Coastal Resources Management, Ministry of Environment and Professor of Oceanography in the University of Ruhuna.
He stated: “In Sri Lanka’s case before speaking of superpower dynamics in the Indo-Pacific, the country must first establish its own identity within the Indian Ocean region given its strategically significant location”.
“He underlined the importance of developing the ‘Sea of Lanka concept’ which extends from the country’s coastline to its 200nauticalmile Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Without firmly establishing this concept, it would be difficult to meaningfully engage with the broader Indian Ocean region”.
“He further stated that the Indian Ocean should be regarded as a zone of peace. From a defence perspective, Sri Lanka must remain neutral. However, from a scientific and resource perspective, the country must remain active given its location and the resources available in its maritime domain” (Ibid).
Perhaps influenced by his academic background, he goes on to state:” In that context Sri Lanka can work with countries in the Indian Ocean region and globally, including India, China, Australia and South Africa. The country must remain open to such cooperation” (Ibid).
Such a recommendation reflects a poor assessment of reality relating to current major power rivalry. This rivalry was addressed by me in an article titled “US – CHINA Rivalry: Maintaining Sri Lanka’s autonomy” ( 12.19. 2025) which stated: “However, there is a strong possibility for the US–China Rivalry to manifest itself engulfing India as well regarding resources in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While China has already made attempts to conduct research activities in and around Sri Lanka, objections raised by India have caused Sri Lanka to adopt measures to curtail Chinese activities presumably for the present. The report that the US and India are interested in conducting hydrographic surveys is bound to revive Chinese interests. In the light of such developments it is best that Sri Lanka conveys well in advance that its Policy of Neutrality requires Sri Lanka to prevent Exploration or Exploitation within its Exclusive Economic Zone under the principle of the Inviolability of territory by any country” ( https://island.lk/us- china-rivalry-maintaining-sri-lankas-autonomy/). Unless such measures are adopted, Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone would end up becoming the theater for major power rivalry, with negative consequences outweighing possible economic gains.
The most startling feature in the recommendation is the exclusion of the USA from the list of countries with which to cooperate, notwithstanding the Independence Day message by the US Secretary of State which stated: “… our countries have developed a strong and mutually beneficial partnership built on the cornerstone of our people-to-people ties and shared democratic values. In the year ahead, we look forward to increasing trade and investment between our countries and strengthening our security cooperation to advance stability and prosperity throughout the Indo-Pacific region (NEWS, U.S. & Sri Lanka)
Such exclusions would inevitably result in the US imposing drastic tariffs to cripple Sri Lanka’s economy. Furthermore, the inclusion of India and China in the list of countries with whom Sri Lanka is to cooperate, ignores the objections raised by India about the presence of Chinese research vessels in Sri Lankan waters to the point that Sri Lanka was compelled to impose a moratorium on all such vessels.
CONCLUSION
During a panel discussion titled “Security Environment in the Indo-Pacific and Sri Lankan Diplomacy” supported by the Embassy of Japan, Prof. Ken Jimbo of Keio University, Japan emphasized that “… non-alignment today does not mean isolation”. Such an approach, he noted, requires the careful and strategic management of dependencies to preserve national autonomy while maintaining strategic international partnerships”. Perhaps Prof. Jimbo was not aware or made aware that Sri Lanka’s Foreign Policy is Neutral; a fact declared by successive Governments since 2019 and practiced by the current Government in the position taken in respect of the recent hostilities between India and Pakistan.
Although both Non-Alignment and Neutrality are often mistakenly used interchangeably, they both do NOT mean isolation. The difference is that Non-Alignment is NOT a Policy but only a Strategy, similar to Balancing, adopted by decolonized countries in the context of a by-polar world, while Neutrality is an Internationally recognised Rule Based Policy, with obligations to be observed by Neutral States and by the Community of Nations. However, Neutrality in today’s context of geopolitical rivalries resulting from the fluidity of changing dynamics offers greater protection in respect of security because it is Rule Based and strengthened by “the UN adoption of the Indian Ocean as a Zone of peace”, with the freedom to exercise its autonomy and engage with States in pursuit of its National Interests.
Apart from the positive comments “that the Indian Ocean should be regarded as a Zone of Peace” and that “from a defence perspective, Sri Lanka must remain neutral”, the second panelist, Professor of Oceanography at the University of Ruhuna, Terney Pradeep Kumara, also advocated that “from a Scientific and resource perspective (in the Exclusive Economic Zone) the country must remain active, given its location and the resources available in its maritime domain”. He went further and identified that Sri Lanka can work with countries such as India, China, Australia and South Africa.
For Sri Lanka to work together with India and China who already are geopolitical rivals made evident by the fact that India has already objected to the presence of China in the “Sea of Lanka”, questions the practicality of the suggestion. Furthermore, the fact that Prof. Kumara has excluded the US, notwithstanding the US Secretary of State’s expectations cited above, reflects unawareness of the geopolitical landscape in which the US, India and China are all actively known to search for minerals. In such a context, Sri Lanka should accept its limitations in respect of its lack of Diplomatic sophistication to “work with” such superpower rivals who are known to adopt unprecedented measures such as tariffs, if Sri Lanka is to avoid the fate of Milos during the Peloponnesian Wars.
Under the circumstances, it is in Sri Lanka’s best interest to lay aside its economic gains for security, and live by its proclaimed principles and policies of Neutrality and the concept of the Indian Ocean as a Zone of Peace by not permitting its EEC to be Explored and/or Exploited by anyone in its “maritime domain”. Since Sri Lanka is already blessed with minerals on land that is awaiting exploitation, participating in the extraction of minerals at the expense of security is not only imprudent but also an environmental contribution given the fact that the Sea and its resources is the Planet’s Last Frontier.
by Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
Protecting the ocean before it’s too late: What Sri Lankans think about deep seabed mining

Far beneath the waters surrounding Sri Lanka lies a largely unseen frontier, a deep seabed that may contain cobalt, nickel and rare earth elements essential to modern technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Around the world, governments and corporations are accelerating efforts to tap these minerals, presenting deep-sea mining as the next chapter of the global “blue economy.”
For an island nation whose ocean territory far exceeds its landmass, the question is no longer abstract. Sri Lanka has already demonstrated its commitment to ocean governance by ratifying the United Nations High Seas Treaty (BBNJ Agreement) in September 2025, becoming one of the early countries to help trigger its entry into force. The treaty strengthens biodiversity conservation beyond national jurisdiction and promotes fair access to marine genetic resources.
Yet as interest grows in seabed minerals, a critical debate is emerging: Can Sri Lanka pursue deep-sea mining ambitions without compromising marine ecosystems, fisheries and long-term sustainability?
Speaking to The Island, Prof. Lahiru Udayanga, Dr. Menuka Udugama and Ms. Nethini Ganepola of the Department of Agribusiness Management, Faculty of Agriculture & Plantation Management, together with Sudarsha De Silva, Co-founder of EarthLanka Youth Network and Sri Lanka Hub Leader for the Sustainable Ocean Alliance, shared findings from their newly published research examining how Sri Lankans perceive deep-sea mineral extraction.
The study, published in the journal Sustainability and presented at the International Symposium on Disaster Resilience and Sustainable Development in Thailand, offers rare empirical insight into public attitudes toward deep-sea mining in Sri Lanka.
Limited Public Inclusion
“Our study shows that public inclusion in decision-making around deep-sea mining remains quite limited,” Ms. Nethini Ganepola told The Island. “Nearly three-quarters of respondents said the issue is rarely covered in the media or discussed in public forums. Many feel that decisions about marine resources are made mainly at higher political or institutional levels without adequate consultation.”
The nationwide survey, conducted across ten districts, used structured questionnaires combined with a Discrete Choice Experiment — a method widely applied in environmental economics to measure how people value trade-offs between development and conservation.
Ganepola noted that awareness of seabed mining remains low. However, once respondents were informed about potential impacts — including habitat destruction, sediment plumes, declining fish stocks and biodiversity loss — concern rose sharply.
“This suggests the problem is not a lack of public interest,” she told The Island. “It is a lack of accessible information and meaningful opportunities for participation.”
Ecology Before Extraction
Dr. Menuka Udugama said the research was inspired by Sri Lanka’s growing attention to seabed resources within the wider blue economy discourse — and by concern that extraction could carry long-lasting ecological and livelihood risks if safeguards are weak.
“Deep-sea mining is often presented as an economic opportunity because of global demand for critical minerals,” Dr. Udugama told The Island. “But scientific evidence on cumulative impacts and ecosystem recovery remains limited, especially for deep habitats that regenerate very slowly. For an island nation, this uncertainty matters.”
She stressed that marine ecosystems underpin fisheries, tourism and coastal well-being, meaning decisions taken about the seabed can have far-reaching consequences beyond the mining site itself.
Prof. Lahiru Udayanga echoed this concern.
“People tended to view deep-sea mining primarily through an environmental-risk lens rather than as a neutral industrial activity,” Prof. Udayanga told The Island. “Biodiversity loss was the most frequently identified concern, followed by physical damage to the seabed and long-term resource depletion.”
About two-thirds of respondents identified biodiversity loss as their greatest fear — a striking finding for an issue that many had only recently learned about.
A Measurable Value for Conservation
Perhaps the most significant finding was the public’s willingness to pay for protection.
“On average, households indicated a willingness to pay around LKR 3,532 per year to protect seabed ecosystems,” Prof. Udayanga told The Island. “From an economic perspective, that represents the social value people attach to marine conservation.”
The study’s advanced statistical analysis — using Conditional Logit and Random Parameter Logit models — confirmed strong and consistent support for policy options that reduce mineral extraction, limit environmental damage and strengthen monitoring and regulation.
The research also revealed demographic variations. Younger and more educated respondents expressed stronger pro-conservation preferences, while higher-income households were willing to contribute more financially.
At the same time, many respondents expressed concern that government agencies and the media have not done enough to raise awareness or enforce safeguards — indicating a trust gap that policymakers must address.
“Regulations and monitoring systems require social acceptance to be workable over time,” Dr. Udugama told The Island. “Understanding public perception strengthens accountability and clarifies the conditions under which deep-sea mining proposals would be evaluated.”
Youth and Community Engagement
Ganepola emphasised that engagement must begin with transparency and early consultation.
“Decisions about deep-sea mining should not remain limited to technical experts,” she told The Island. “Coastal communities — especially fishers — must be consulted from the beginning, as they are directly affected. Youth engagement is equally important because young people will inherit the long-term consequences of today’s decisions.”
She called for stronger media communication, public hearings, stakeholder workshops and greater integration of marine conservation into school and university curricula.
“Inclusive and transparent engagement will build trust and reduce conflict,” she said.
A Regional Milestone
Sudarsha De Silva described the study as a milestone for Sri Lanka and the wider Asian region.
“When you consider research publications on this topic in Asia, they are extremely limited,” De Silva told The Island. “This is one of the first comprehensive studies in Sri Lanka examining public perception of deep-sea mining. Organizations like the Sustainable Ocean Alliance stepping forward to collaborate with Sri Lankan academics is a great achievement.”
He also acknowledged the contribution of youth research assistants from EarthLanka — Malsha Keshani, Fathima Shamla and Sachini Wijebandara — for their support in executing the study.
A Defining Choice
As Sri Lanka charts its blue economy future, the message from citizens appears unmistakable.
Development is not rejected. But it must not come at the cost of irreversible ecological damage.
The ocean’s true wealth, respondents suggest, lies not merely in minerals beneath the seabed, but in the living systems above it — systems that sustain fisheries, tourism and coastal communities.
For policymakers weighing the promise of mineral wealth against ecological risk, the findings shared with The Island offer a clear signal: sustainable governance and biodiversity protection align more closely with public expectations than unchecked extraction.
In the end, protecting the ocean may prove to be not only an environmental responsibility — but the most prudent long-term investment Sri Lanka can make.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
How Black Civil Rights leaders strengthen democracy in the US

 On being elected US President in 2008, Barack Obama famously stated: ‘Change has come to America’. Considering the questions continuing to grow out of the status of minority rights in particular in the US, this declaration by the former US President could come to be seen as somewhat premature by some. However, there could be no doubt that the election of Barack Obama to the US presidency proved that democracy in the US is to a considerable degree inclusive and accommodating.
On being elected US President in 2008, Barack Obama famously stated: ‘Change has come to America’. Considering the questions continuing to grow out of the status of minority rights in particular in the US, this declaration by the former US President could come to be seen as somewhat premature by some. However, there could be no doubt that the election of Barack Obama to the US presidency proved that democracy in the US is to a considerable degree inclusive and accommodating.
If this were not so, Barack Obama, an Afro-American politician, would never have been elected President of the US. Obama was exceptionally capable, charismatic and eloquent but these qualities alone could not have paved the way for his victory. On careful reflection it could be said that the solid groundwork laid by indefatigable Black Civil Rights activists in the US of the likes of Martin Luther King (Jnr) and Jesse Jackson, who passed away just recently, went a great distance to enable Obama to come to power and that too for two terms. Obama is on record as owning to the profound influence these Civil Rights leaders had on his career.
The fact is that these Civil Rights activists and Obama himself spoke to the hearts and minds of most Americans and convinced them of the need for democratic inclusion in the US. They, in other words, made a convincing case for Black rights. Above all, their struggles were largely peaceful.
Their reasoning resonated well with the thinking sections of the US who saw them as subscribers to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, for instance, which made a lucid case for mankind’s equal dignity. That is, ‘all human beings are equal in dignity.’
It may be recalled that Martin Luther King (Jnr.) famously declared: ‘I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up, live out the true meaning of its creed….We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’
Jesse Jackson vied unsuccessfully to be a Democratic Party presidential candidate twice but his energetic campaigns helped to raise public awareness about the injustices and material hardships suffered by the black community in particular. Obama, we now know, worked hard at grass roots level in the run-up to his election. This experience proved invaluable in his efforts to sensitize the public to the harsh realities of the depressed sections of US society.
Cynics are bound to retort on reading the foregoing that all the good work done by the political personalities in question has come to nought in the US; currently administered by Republican hard line President Donald Trump. Needless to say, minority communities are now no longer welcome in the US and migrants are coming to be seen as virtual outcasts who need to be ‘shown the door’ . All this seems to be happening in so short a while since the Democrats were voted out of office at the last presidential election.
However, the last US presidential election was not free of controversy and the lesson is far too easily forgotten that democratic development is a process that needs to be persisted with. In a vital sense it is ‘a journey’ that encounters huge ups and downs. More so why it must be judiciously steered and in the absence of such foresighted managing the democratic process could very well run aground and this misfortune is overtaking the US to a notable extent.
The onus is on the Democratic Party and other sections supportive of democracy to halt the US’ steady slide into authoritarianism and white supremacist rule. They would need to demonstrate the foresight, dexterity and resourcefulness of the Black leaders in focus. In the absence of such dynamic political activism, the steady decline of the US as a major democracy cannot be prevented.
From the foregoing some important foreign policy issues crop-up for the global South in particular. The US’ prowess as the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ could be called in question at present but none could doubt the flexibility of its governance system. The system’s inclusivity and accommodative nature remains and the possibility could not be ruled out of the system throwing up another leader of the stature of Barack Obama who could to a great extent rally the US public behind him in the direction of democratic development. In the event of the latter happening, the US could come to experience a democratic rejuvenation.
The latter possibilities need to be borne in mind by politicians of the South in particular. The latter have come to inherit a legacy of Non-alignment and this will stand them in good stead; particularly if their countries are bankrupt and helpless, as is Sri Lanka’s lot currently. They cannot afford to take sides rigorously in the foreign relations sphere but Non-alignment should not come to mean for them an unreserved alliance with the major powers of the South, such as China. Nor could they come under the dictates of Russia. For, both these major powers that have been deferentially treated by the South over the decades are essentially authoritarian in nature and a blind tie-up with them would not be in the best interests of the South, going forward.
However, while the South should not ruffle its ties with the big powers of the South it would need to ensure that its ties with the democracies of the West in particular remain intact in a flourishing condition. This is what Non-alignment, correctly understood, advises.
Accordingly, considering the US’ democratic resilience and its intrinsic strengths, the South would do well to be on cordial terms with the US as well. A Black presidency in the US has after all proved that the US is not predestined, so to speak, to be a country for only the jingoistic whites. It could genuinely be an all-inclusive, accommodative democracy and by virtue of these characteristics could be an inspiration for the South.
However, political leaders of the South would need to consider their development options very judiciously. The ‘neo-liberal’ ideology of the West need not necessarily be adopted but central planning and equity could be brought to the forefront of their talks with Western financial institutions. Dexterity in diplomacy would prove vital.
-

 Life style7 days ago
Life style7 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoThailand to recruit 10,000 Lankans under new labour pact
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoNew Zealand meet familiar opponents Pakistan at spin-friendly Premadasa
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoECB push back at Pakistan ‘shadow-ban’ reports ahead of Hundred auction