Opinion
Bali Declaration: Is it the clarion call to #endTobacco?

By SHOBHA SHUKLA, BOBBY RAMAKANT – CNS
Tobacco use is among the unhealthy behaviours that result in preventable burden of cancers, strokes, and heart diseases, said Budi Gunadi Sadikin, Indonesia’s health minister. In Indonesia tobacco use is the second largest risk factor for untimely deaths, he added. World Health Organization had earlier underlined that without clamping tobacco use, we cannot deliver on the promises enshrined in the Sustainable Development Goals.
Indonesia has walked the talk on building a grounds-up movement against tobacco. In 2011, twelve Mayors had come together to forge a Mayors’ Alliance to advance tobacco control in their respective cities. Today in 2022, there are over 150 Mayors of different Indonesian cities that are part of this Alliance, who are adapting as well as enforcing local laws to reduce tobacco use, said Dr Bima Arya Sugiarto, Co-Chair of Asia Pacific Cities Alliance for Health and Development (APCAT) and Mayor of Bogor City in Indonesia. “Mayors’ Alliance has been the main driver for banning tobacco advertising and promotion, as well as preventing tobacco industry interference in public policy” he said.
Both were speaking at the opening ceremony of 7th Asia Pacific Summit of Mayors (7th APCAT Summit or #APCAT2022) being held in Bali, Indonesia.Another sterling example of grounds-up tobacco control movement in Indonesia is the fact that “as of November 2022, over 300 cities have adopted the local smokefree laws,” said Dr Bima Arya.
That is why Indonesian health minister called for stronger partnerships “to reduce tobacco use” and “expand the on-the-ground effective programmes for tobacco control.”
“I would like to extend my gratitude to Mayors who have passed local smokefree laws. It is important for central government to collaborate with local governments to achieve tobacco control,” said the Indonesian health minister.
Despite alarming levels of tobacco industry interference, it is indeed commendable that Mayors and sub-national leaders of Indonesia have been able to advance tobacco control.
Agrees Kelly Larson of Bloomberg Philanthropies: “We acknowledge the role of sub-national leaders in Indonesia and commend the Mayors of over 300 cities who have passed local smokefree laws, that protect 75% of the country’s population from the hazards of tobacco smoke.” Kelly Larson shared that prioritising tobacco control and public health in New York resulted in increased life expectancy of 2 years for its citizens.
Not surprisingly, tobacco industry and its front groups are trying to create hurdles when local sub-national leaders try to advance tobacco control and health promotion. Effective enforcement of strong tobacco control laws hurt the industry profits. For instance, in 2017, Bogor City had become the first Indonesian city to implement a point-of-sale tobacco display ban as part of its smokefree law. But soon after a legal battle ensued. Finally, in February 2020, the city of Bogor won the court case when Supreme Court had upheld its ban on the display of tobacco products at point-of-sale.
While exposing how tobacco industry approaches election candidates to influence public policy, Mayor of Bogor City Dr Bima Arya said in 7th APCAT Summit opening session that “every candidate of local elections was approached by the tobacco industry…”
#APCAT2022 Declaration gives hope for a better tomorrow
“We, the delegates of the 7th Asia Pacific Summit of Mayors, recognize that APCAT is a vital platform to share experiences, shape local actions, and secure greater leadership as well as look for synergistic actions between specific health and development programmes.
We commit to accelerate progress towards eventually ending tobacco use, as well as preventing the avoidable burden of NCDs, eliminating Tuberculosis, and improving synergy between health and development programmes and promoting integrated responses where possible, thereby reducing disease burden and averting untimely deaths, by:
– Leading effective implementation of tobacco control programmes that include smokefree environments; a complete ban on tobacco advertising, promotion, and sponsorship; promotion of larger graphic health warnings with plain packaging on tobacco packs; smoking cessation programmes; and a ban on electronic cigarettes, heated tobacco products, shisha, and other similar products;
– Working with national government and policy makers to raise taxes and prices on unhealthy commodities (such as, but not limited to, tobacco products, alcohol, sugary and sweetened beverages);
– Ensuring accountability to prevent interferences and rejecting funding, logistics, donations, or grants from, and partnerships with, any entity related to any unhealthy commodity industries (such as, but not limited to, tobacco, alcohol, sugary and sweetened beverages);
– Investing in tobacco control for prevention of tuberculosis, non-communicable disease, and stunting. It includes smoking cessation in TB and NCD clinics, and family health programs; universal screening for TB and NCDs
– Adopting One Health approaches and processes to ensure that “a healthy city is a resilient city”.
Every tobacco-related death is preventable
The 7th Asia Pacific Summit of Mayors, which opened today in Bali, Indonesia, is jointly organised by the Asia Pacific Cities Alliance for Health and Development (APCAT), Ministry of Health, Republic of Indonesia; Ministry of Home Affairs, Republic of Indonesia; National Centre for Health Promotion, Ministry of Health, Cambodia; Bloomberg Philanthropies; Cities of Bogor, Denpasar and Klungkung of Indonesia; Balanga City, Philippines; Association of All Health Offices Indonesia (ADINKES), Indonesia Mayor and Regent Alliance, Indonesian Public Health Association; Udayana Central; Campaign for Tobacco Free Kids, Vital Strategies; Tobacco Free Generation International, The International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease (The Union); APCAT Parliamentarians and Asia Pacific Media Alliance for Health and Development (APCAT Media).
Over 1000 national and sub-national leaders, public health experts are attending the 7th APCAT Summit in Bali, Indonesia in person and virtually. Participants include mayors, governors, ministers, members of parliament, tobacco control advocates, and media from across the Asia Pacific region.
Over 8.67 million people die of tobacco use every year (out of which one million die due to second and third-hand tobacco smoke). Despite the crippling onslaught of COVID-19 public health emergency and humanitarian crises, tobacco industry has heightened its deceptive strategies to protect and expand its markets. In addition to the mountainous death toll and avoidable disease burden, tobacco use has also resulted in an annual economic loss of nearly USD 2 trillion to the global economy.
.
Opinion
General Educational Reforms: To what purpose? A statement by state university teachers

One of the major initiatives of the NPP government is reforming the country’s education system. Immediately after coming to power, the government started the process of bringing about “transformational” changes to general education. The budgetary allocation to education has been increased to 2% of GDP (from 1.8% in 2023). Although this increase is not sufficient, the government has pledged to build infrastructure, recruit more teachers, increase facilities at schools and identified education reforms as an urgent need. These are all welcome moves. However, it is with deep concern that we express our views on the general education reforms that are currently underway.
The government’s approach to education reform has been hasty and lacking in transparency and public consultation. Announcements regarding the reforms planned for January 2026 were made in July 2025. In August, 2025, a set of slides was circulated, initially through unofficial sources. It was only in November 2025, just three months ahead of implementation, that an official policy document, Transforming General Education in Sri Lanka 2025, was released. The Ministry of Education held a series of meetings about the reforms. However, by this time the modules had already been written, published, and teacher training commenced.
The new general education policy shows a discrepancy between its conceptual approach and content. The objectives of the curriculum reforms include: to promote “critical thinking”, “multiple intelligences”, “a deeper understanding of the social and political value of the humanities and social sciences” and embed the “values of equity, inclusivity and social justice” (p. 9). Yet, the new curriculum places minimal emphasis on social sciences and humanities, and leaves little time for critical thinking or for molding social justice-oriented citizens. Subjects such as environment, history and civics, are left out at the primary level, while at the junior secondary level, civics and history are allocated only 10 and 20 hours per term. The increase in the number of “essential subjects” to 15 restricts the hours available for fundamentals like mathematics and language; only 30 hours are allocated to mathematics and the mother tongue, per term, at junior secondary level. Learning the second national language and about our conflict-ridden history are still not priorities despite the government’s pledge to address ethnic cohesion. The time allocation for Entrepreneurship and Financial Literacy, now an essential subject, is on par with the second national language, geography and civics. At the senior secondary level (O/L), social sciences and humanities are only electives. If the government is committed to the objectives that it has laid out, there should be a serious re-think of what subjects will be taught at each grade, the time allocated to each, their progress across different levels, and their weight in the overall curriculum.
A positive aspect of the reforms is the importance given to vocational training. A curriculum that recognises differences in students, whether in terms of their interest in subject matter, styles of learning, or their respective needs, and caters to those diverse needs, would make education more pluralistic and therefore democratic. However, there must be some caution placed on how difference is treated, and this should not be reflected in vocational training alone, but in all aspects of the curriculum. For instance, will the history curriculum account for different narratives of history, including the recent history of Sri Lanka and the histories of minorities and marginalised communities? Will the family structures depicted in textbooks go beyond conventional conceptions of the nuclear family? Addressing these areas too would allow students to feel more represented in curricula and enable them to move through their years of schooling in ways that are unconstrained by stereotypes and unjust barriers.
The textbooks for the Grade 6 modules on the National Institute of Education (NIE) website appear to have not gone through rigorous review. They contain rampant typographical errors and include (some undeclared) AI-generated content, including images that seem distant from the student experience. Some textbooks contain incorrect or misleading information. The Global Studies textbook associates specific facial features, hair colour, and skin colour, with particular countries and regions, and refers to Indigenous peoples in offensive terms long rejected by these communities (e.g. “Pygmies”, “Eskimos”). Nigerians are portrayed as poor/agricultural and with no electricity. The Entrepreneurship and Financial Literacy textbook introduces students to “world famous entrepreneurs”, mostly men, and equates success with business acumen. Such content contradicts the policy’s stated commitment to “values of equity, inclusivity and social justice” (p. 9). Is this the kind of content we want in our textbooks?
The “career interest test” proposed at the end of Grade 9 is deeply troubling. It is inappropriate to direct children to choose their career paths at the age of fourteen, when the vocational pathways, beyond secondary education, remain underdeveloped. Students should be provided adequate time to explore what interests them before they are asked to make educational choices that have a bearing on career paths, especially when we consider the highly stratified nature of occupations in Sri Lanka. Furthermore, the curriculum must counter the stereotyping of jobs and vocations to ensure that students from certain backgrounds are not intentionally placed in paths of study simply because of what their parents’ vocations or economic conditions are; they must also not be constrained by gendered understandings of career pathways.
The modules encourage digital literacy and exposure to new communication technologies. On the surface, this initiative seems progressive and timely. However, there are multiple aspects such as access, quality of content and age-appropriateness that need consideration before uncritical acceptance of digitality. Not all teachers will know how to use communication technologies ethically and responsibly. Given that many schools lack even basic infrastructure, the digital divide will be stark. There is the question of how to provide digital devices to all students, which will surely fall on the shoulders of parents. These problems will widen the gap in access to digital literacy, as well as education, between well-resourced and other schools.
The NIE is responsible for conceptualising, developing, writing and reviewing the general education curriculum. Although the Institution was established for the worthy cause of supporting the country’s general education system, currently the NIE appears to be ill-equipped and under-staffed, and seems to lack the experience and expertise required for writing, developing and reviewing curricula and textbooks. It is clear by now that the NIE’s structure and mandate need to be reviewed and re-invigorated.
In light of these issues, the recent Cabinet decision to postpone implementation of the reforms for Grade 6 to 2027 is welcome. The proposed general education reforms have resulted in a backlash from opposition parties and teachers’ and student unions, much of it, legitimately, focusing on the lack of transparency and consultation in the process and some of it on the quality and substance of the content. Embedded within this pushback are highly problematic gendered and misogynistic attacks on the Minister of Education. However, we understand the problems in the new curriculum as reflecting long standing and systemic issues plaguing the education sector and the state apparatus. They cannot be seen apart from the errors and highly questionable content in the old curriculum, itself a product of years of reduced state funding for education, conditionalities imposed by external funding agencies, and the consequent erosion of state institutions. With the NPP government in charge of educational reforms, we had expectations of a stronger democratic process underpinning the reforms to education, and attention to issues that have been neglected in previous reform efforts.
With these considerations in mind, we, the undersigned, urgently request the Government to consider the following:
* postpone implementation and holistically review the new curriculum, including at primary level.
* adopt a consultative process on educational reforms by holding public sittings across the country .
* review the larger institutional structure of the educational apparatus of the state and bring greater coordination within its constituent parts
* review the NIE’s mandate and strengthen its capacity to develop curricula, such as through appointexternal scholars an open and transparent process, to advise and review curriculum content and textbooks.
* consider the new policy and curriculum to be live documents and make space for building consensus in policy formulation and curriculum development to ensure alignment of the curriculum with policy.
* ensure textbooks (other than in language subjects) appear in draft form in both Sinhala and Tamil at an early stage so that writers and reviewers from all communities can participate in the process of scrutiny and revision from the very beginning.
* formulate a plan for addressing difficulties in implementation and future development of the sector, such as resource disparities, teacher training needs, and student needs.
A.M. Navaratna Bandara,
formerly, University of Peradeniya
Ahilan Kadirgamar,
University of Jaffna
Ahilan Packiyanathan,
University of Jaffna
Arumugam Saravanabawan,
University of Jaffna
Aruni Samarakoon,
University of Ruhuna
Ayomi Irugalbandara,
The Open University of Sri Lanka.
Buddhima Padmasiri,
The Open University of Sri Lanka
Camena Guneratne,
The Open University of Sri Lanka
Charudaththe B.Illangasinghe,
University of the Visual & Performing Arts
Chulani Kodikara,
formerly, University of Colombo
Chulantha Jayawardena,
University of Moratuwa
Dayani Gunathilaka,
formerly, Uva Wellassa University of Sri Lanka
Dayapala Thiranagama,
formerly, University of Kelaniya
Dhanuka Bandara,
University of Jaffna
Dinali Fernando,
University of Kelaniya
Erandika de Silva,
formerly, University of Jaffna
G.Thirukkumaran,
University of Jaffna
Gameela Samarasinghe,
University of Colombo
Gayathri M. Hewagama,
University of Peradeniya
Geethika Dharmasinghe,
University of Colombo
F. H. Abdul Rauf,
South Eastern University of Sri Lanka
H. Sriyananda,
Emeritus Professor, The Open University of Sri Lanka
Hasini Lecamwasam,
University of Peradeniya
(Rev.) J.C. Paul Rohan,
University of Jaffna
James Robinson,
University of Jaffna
Kanapathy Gajapathy,
University of Jaffna
Kanishka Werawella,
University of Colombo
Kasun Gajasinghe, formerly,
University of Peradeniya
Kaushalya Herath,
formerly, University of Moratuwa
Kaushalya Perera,
University of Colombo
Kethakie Nagahawatte,
formerly, University of Colombo
Krishan Siriwardhana,
University of Colombo
Krishmi Abesinghe Mallawa Arachchige,
formerly, University of Peradeniya
L. Raguram,
University of Jaffna
Liyanage Amarakeerthi,
University of Peradeniya
Madhara Karunarathne,
University of Peradeniya
Madushani Randeniya,
University of Peradeniya
Mahendran Thiruvarangan,
University of Jaffna
Manikya Kodithuwakku,
The Open University of Sri Lanka
Muttukrishna Sarvananthan,
University of Jaffna
Nadeesh de Silva,
The Open University of Sri Lanka
Nath Gunawardena,
University of Colombo
Nicola Perera,
University of Colombo
Nimal Savitri Kumar,
Emeritus Professor, University of Peradeniya
Nira Wickramasinghe,
formerly, University of Colombo
Nirmal Ranjith Dewasiri,
University of Colombo
P. Iyngaran,
University of Jaffna
Pathujan Srinagaruban,
University of Jaffna
Pavithra Ekanayake,
University of Peradeniya
Piyanjali de Zoysa,
University of Colombo
Prabha Manuratne,
University of Kelaniya
Pradeep Peiris,
University of Colombo
Pradeepa Korale-Gedara,
formerly, University of Peradeniya
Prageeth R. Weerathunga,
Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
Priyantha Fonseka,
University of Peradeniya
Rajendra Surenthirakumaran,
University of Jaffna
Ramesh Ramasamy,
University of Peradeniya
Ramila Usoof,
University of Peradeniya
Ramya Kumar,
University of Jaffna
Rivindu de Zoysa,
University of Colombo
Rukshaan Ibrahim,
formerly, University of Jaffna
Rumala Morel,
University of Peradeniya
Rupika S. Rajakaruna,
University of Peradeniya
S. Jeevasuthan,
University of Jaffna
S. Rajashanthan,
University of Jaffna
S. Vijayakumar,
University of Jaffna
Sabreena Niles,
University of Kelaniya
Sanjayan Rajasingham,
University of Jaffna
Sarala Emmanuel,
The Open University of Sri Lanka
Sasinindu Patabendige,
formerly, University of Jaffna
Savitri Goonesekere,
Emeritus Professor, University of Colombo
Selvaraj Vishvika,
University of Peradeniya
Shamala Kumar,
University of Peradeniya
Sivamohan Sumathy,
formerly, University of Peradeniya
Sivagnanam Jeyasankar,
Eastern University Sri Lanka
Sivanandam Sivasegaram,
formerly, University of Peradeniya
Sudesh Mantillake,
University of Peradeniya
Suhanya Aravinthon,
University of Jaffna
Sumedha Madawala,
University of Peradeniya
Tasneem Hamead,
formerly, University of Colombo.
Thamotharampillai Sanathanan,
University of Jaffna
Tharakabhanu de Alwis,
University of Peradeniya
Tharmarajah Manoranjan,
University of Jaffna
Thavachchelvi Rasan,
University of Jaffna
Thirunavukkarasu Vigneswaran,
University of Jaffna
Timaandra Wijesuriya,
University of Jaffna
Udari Abeyasinghe,
University of Peradeniya
Unnathi Samaraweera,
University of Colombo
Vasanthi Thevanesam,
Professor Emeritus, University of Peradeniya
Vathilingam Vijayabaskar,
University of Jaffna
Vihanga Perera,
University of Sri Jayewardenepura
Vijaya Kumar,
Emeritus Professor, University of Peradeniya
Viraji Jayaweera,
University of Peradeniya
Yathursha Ulakentheran,
formerly, University of Jaffna.
Opinion
Science at the heart of democracy: A blueprint for Sri Lanka

When Vikings arrived in Iceland towards the end of the 8th century, they gathered on a midsummer’s day to hear the laws of the land proclaimed, air grievances, and seek justice. This marked the beginning of the oldest known parliament in the world — the Althing, or Thingvellir — which still operates today.
The word “parliament” later came to describe the after-dinner discussions between monks in their cloisters. Modern parliaments trace their roots to 13th-century England, when King Edward I convened joint meetings of two governing bodies: the Great Council and the Curia Regis, a smaller body of semi-professional advisors.
The British Parliament, often called the “Mother of Parliaments,” consists of the Sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. Historically, such law-making institutions are designed to hear diverse views and facilitate informed debate. Access to up-to-date scientific and academic knowledge plays a crucial role in shaping these debates — enabling the UK to remain a world-leading economy with proactive decision-making.
Being an island nation influenced by British democratic traditions, Sri Lanka could also draw inspiration from such processes to remain agile in a fast-changing world.
From Medieval Advice to Modern Science in Governments
Providing advice — especially scientific advice — to lawmakers has evolved dramatically since the 13th century.
In 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, then the UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson often appeared alongside the Government Chief Scientific Advisor and the Government Chief Medical Advoser. Professor Jonathan Van-Tam, Deputy Chief Medical Officer at the time, became widely known for explaining complex public health messages using relatable football metaphors.
The Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE) guided the government on pandemic preparedness, supplying expert knowledge for critical decisions. Today, the UK Government Office for Science hosts Chief Scientific Advisers in each government department, typically senior academics from research-intensive universities appointed for three to five years.
Scrutiny and Evidence in Policymaking
The Parliament is the ultimate law-making body in the UK, holding the government accountable through debates and select committee inquiries. These committees — composed of MPs outside government and led by senior members — scrutinise policy decisions and monitor their implementation.
Support structures such as the Parliamentary Office for Science and Technology (POST) conduct ongoing research on topics of policy interest, identified through “horizon scanning” involving both internal and external experts. The Knowledge Exchange Unit maintains links with academic institutions, ensuring access to the latest evidence.
However, policy-making often happens under tight deadlines, reacting to both domestic and global developments. This demands quick access to authoritative expertise and knowledge — a need not always easy to meet.
Thematic Research Leads: A New Approach
To address this, the UK has introduced Thematic Research Leads (TRLs) — mid-career researchers embedded in Parliament three days a week while retaining their academic posts. TRLs act as impartial subject experts, bringing networks of research connections to parliamentary teams.
Their work includes organising expert briefings, running training sessions, hosting roundtables, and even simulating policy scenarios.
During my tenure as TRL for AI and Digital Technologies, I have supported this process in multiple ways.
* Supported multiple select committees by scoping inquiries, preparing briefing notes, and identifying expert witnesses.
* Delivered technical presentations — for example, explaining how social media algorithms operate, drawing directly from academic literature and open-source code.
* Collaborated with other TRLs, such as in crime and justice, to train parliamentary staff on AI’s role in surveillance and criminal justice.
Such efforts deepen Parliament’s technical understanding, enabling more informed, future-ready policy scrutiny.
Lessons for Sri Lanka: Integrating Science into Policymaking Infrastructure
There are few ways in which I believe Sri Lanka can utilise scientific and expert knowledge within the democratic processes.
1. Embed experts in Parliament
– Appoint Chief Scientific Advisors or Thematic Research Leads to bring impartial, up-to-date expertise directly into legislative debates.
2. Scan for niche opportunities
– Proactively identify sectors where Sri Lanka has unique strengths (e.g., agriculture, nanotechnology, AI) and link them to emerging global markets.
3. Build a “College of Experts”
– Create a formal network connecting the Sri Lankan scientific diaspora with local specialists to advise policymakers.
4. Strengthen research–policy links
– Develop units like the UK’s Parliamentary Office for Science and Technology to supply evidence-based briefings and horizon scanning. Then seek to collaborate with similar institutions around the world such as the POST.
5. Upskill policymakers
– Provide MPs and officials with targeted technical training so they can scrutinise policies with confidence and depth.
6. Move from reactive to proactive
– Use foresight tools and expert panels to anticipate global changes rather than only responding to crises.
In a world where artificial intelligence, bioengineering, and climate threats move faster than traditional politics, the ability to turn cutting-edge research into timely policy will decide which countries lead — and which fall behind.
Professor Varuna De Silva is the Chair of AI and Digital Technologies at Loughborough University, UK. He currently serves as the Thematic Research Lead to the UK Parliament, in the area of AI and Digital. He is a graduate of the University of Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, and received his Ph.D. from the University of Surrey in the UK in 2011.
by Professor Varuna De Silva
Opinion
Morning Star of Nursing Education in Sri Lanka
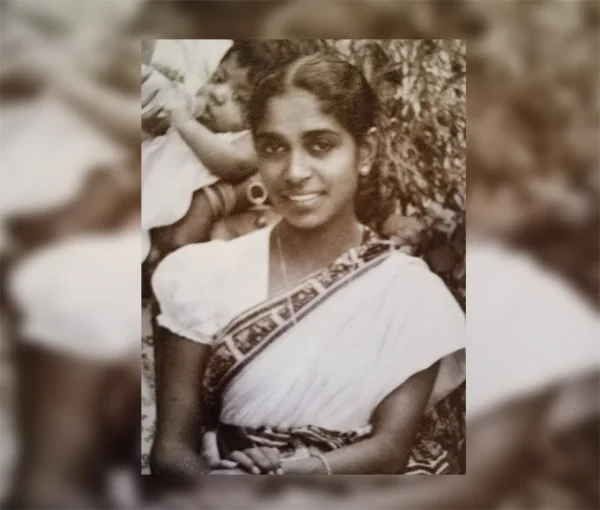

Chandra de Silva, 20th Death Anniversary
After a convulsive struggle for national liberation from British colonialism which tore the subcontinent apart, India gained its independence in 1947. Way ahead of Ceylon, on the cusp of this momentous event, it established a degree-awarding College of Nursing at the University of Delhi in 1946, a committee having visited and considered the best practices in nursing education in Canada, the USA, England and Scotland. It then carefully designed a course to meet the needs of India’s social and health requirements, and admitted its first batch of 13 students in July 1946, for a four-year BSc (Honors) degree in Nursing.
Soon after, they offered this advantage through a competitive interview to students from Ceylon.
In 1950, the year India adopted its first Republican Constitution, Chandra Samarasinghe was one of the three persons admitted to this course, and would go on to be the one who eventually introduced university education for Sri Lankan nurses in 1992, after a lifetime of campaigning.
When Chandra de Silva (nee Samarasinghe), much loved and respected by her students and colleagues alike, passed away 20 years ago on 28th January 2006, a former student wrote a moving tribute to her titled “The Morning Star of the World of Nursing Has Faded…” on the front page of the February 2006 issue of the magazine New Vision, a publication of the Graduate Nurses’ Foundation of Sri Lanka.
Describing Chandra as “the Nightingale of Sri Lanka”, a “most noble lady (Athi uththama kanthawa) filled with compassion”, “born for the good fortune of the nation” and “incomparable teacher-mother (guru mathawa) of hundreds of thousands of students”, the writer, Malini Ranasinghe, who was the President of the Graduate Nurses Foundation, confesses it is beyond her to set down in full Chandra’s life-long service of over 50 years to the profession. The magazine New Vision itself was one of Chandra’s many initiatives as was the encouragement for the Nursing Profession to obtain membership of the Sri Lanka Association of Professionals. Malini Ranasinghe promises in this heartfelt farewell, that Chandra’s legacy would be passed down the ages to each new batch of nursing students, to remain in their hearts through the course on the History of Nursing.
Chandra was Sri Lanka’s first Chief Nursing Education Officer (CNEO, now titled Director Nursing) at the Ministry of Health. She took up the pioneering role in 1967, having returned from Boston University, USA, after completing a Master’s degree in Education and Administration.
In her first year in the role, Chandra presented a comprehensive memorandum drawing the attention of the government of the day to the country’s need for a Bachelor’s degree in Nursing. She was the first to do so. It took decades before this dream came true, with Chandra having made several more proposals many years apart, before she was invited by a Canadian University in collaboration with the Open University of Sri Lanka (OUSL) to help set up the degree course in Nursing in 1992. Having spent most of her professional life in a battle to uplift the nursing profession in Sri Lanka to international standards, she was setting exam papers at the OUSL the day before she was admitted to hospital for kidney surgery, and passed away at the recovery unit. By then, she had seen not only several batches of undergraduate nurses don their robes, but also graduate nurses earn Master’s degrees with a PhD programme well on its way to being implemented.
When Delhi Built Bridges
It all started when three young ladies boarded a train with their Thomas Cooks travel documents, to Delhi in July 1950, having competed and won places at Delhi University to follow a BSc Honours degree, majoring in Nursing. Chandra Samarasinghe from Mahamaya College Kandy, dressed in a Kandyan Saree, Trixie Marthenesz from Ladies College and later Ananda College Colombo, and Shireen Packeer, also from Ananda College Colombo, in dresses, were the lucky ones selected, and became firm friends known as the “The Trio from Ceylon” at their university in India. They had “luxury accommodation” at their residential university campus at number 12, Jaswant Singh Road, New Delhi, and travelled everywhere on their bikes.
They had a blast during their four years there, not only completing their degrees but also able to experience the newly independent nation in transition, already forging a future for itself. Chandra continued to wear the Kandyan saree throughout her stay there, and when she had to introduce herself to the rest of the students, said “I am Chandra Samarasinghe from Kandy, in Lanka”, leaving a puzzled Trixie wondering why she didn’t say Ceylon. When they left the university after four years, the Principal, Dr. Margeretta Craig, O.B.E. told them “You three Ceylonese girls have been live wires!” They got on well with the staff including the Vice Principal Dr. Edith Buchanan, a Canadian from the Canadian Faculty of Nursing, who had an interesting experience with Chandra at their first encounter. When asked to explain the meaning of the term “prone position”, Chandra, always the first to offer an answer, piped up to say somewhat indelicately, “That’s the one with the backside up!” to giggles from the class. She was soon persuaded that “face-down” was a much more decorous way of saying it.
They sang and danced in the presence of Lady Edwina Mountbatten who graced the university’s annual concerts and had their names appear approvingly in the Indian newspaper report of the event. They were invited to Rashtrapati Bhavan in 1951 where they met India’s iconic first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and Dr. Rajendra Prasad, the first President. They made friends with J. Wijetunga, author of ‘Grass for my Feet’ fame who lived only a short distance away from their hostel, who gave them free access to his pantry and taught them the cultural history of India and also of Sri Lanka. They travelled to places of interest including a long-desired visit to Shanthi Nikethan, having developed a love for Rabindranath Tagore’s work, and took photos in front of the Taj Mahal.
When they first arrived in Delhi, they were thrilled to meet another Sri Lankan student in the senior year who had known them from Ceylon, Viola Perera. Viola introduced them to her friends, one of whom on obtaining her PhD became the Principal of the College of Nursing, University of Delhi.
It was clear that their time at Delhi University left a deep impression on the girls. They were being trained to take over from the departing British, and to maintain the required standards as well as to develop them further. The sense of patriotic duty they saw in India made an impression on them. They also had plenty of fun, and Chandra was able to keep Ceylon’s end up when the beautiful Bengali voices of Indian students sang at their gatherings, having herself been voice-trained by Saranagupta Amarasinghe, and according to Trixie Marthenesz’s reminiscences in her book, ‘Those Delhi Days”, also by Ananda Samarakoon (p143).
A Worthy Battle Waged
Back in Ceylon, Chandra tried many times to introduce the educational opportunities she herself had obtained, to others in her profession. And yet, unlike India at Independence, Ceylon and later even Sri Lanka, was not ready to accept such progress easily. With the Health Ministry decision makers being male and mostly doctors, they ignorantly regarded the role of the nurse as a minor one, needing just “a pair of hands”. It may have involved some insecurity which masqueraded as good sense, at the cost to the country for many decades. As CNEO, Chandra battled through it all, rewriting the curriculum to bring it up to international standards, doing what she could to send Nurses overseas for training. And she kept presenting proposals for a BSc programme, which fell on deaf ears. Decades later, she was rewarded for her unwavering commitment to the cause when she was asked to start the BSc Nursing programme at the Open University of Sri Lanka (OUSL), which is now a great asset to the country, with other universities also offering it.
In 2004, two years before she passed away, the first publication of New Vision by the Graduate Nurses Foundation of Sri Lanka was presented to her. In the 2005 issue, they reproduced on the front page her keynote address at their AGM on the 31st of October 2004, at which she was Chief Guest.
Her speech recounts the painfully hard journey that the profession (and she herself) had to endure to raise it to its current status. Chandra recalls with sadness that the three-year Nursing Diploma did not entitle Sri Lankan nurses to pursue higher education, qualifying them only to follow a few courses at the Post Basic School of Nursing:
“I had to fight a very hard battle to keep the 3 year programme intact because there was a very serious effort to downgrade the three year programme to two years, a step that would have prevented our nurses from obtaining any acceptance and recognition in a foreign country. There was intense official and political pressure for a long time to effect this change but with the assistance of a few other Nursing Leaders this retrograde step was suppressed, perhaps forever. Such dangers can arise in the future too. The price we nurses have to pay, is eternal vigilance to challenge and suppress any effort to downgrade the standard of Nursing Education in Sri Lanka.”
She happily announced that at that stage, there were 200 BSc graduates and 25 who had obtained their Master’s degree, with two heading for their PhD. She defined the lack of access to higher education for nurses as a “human right denied”. She also declared that for the first time, there was agreement across all nursing services to propose a nursing degree at conventional universities, disclosing that this was the “first time such consensus has manifested in the Nursing Services”. She called upon nurses to retain this unity “at whatever cost” and just as in other professions such an engineering, law, medicine, “it was time to rectify this anomaly” and “work together to achieve this new dimension in Nursing Education.”
A Mother to More Than Her Own
As I write this memorial to honour my mother Chandra for her life of service and unwavering dedication to provide for others the education she herself received at two of the best universities in the world (Delhi and Boston), her determination and grace under pressure, I know why I have focused on her professional life rather than her personal one. It is because I grew up sensing that she was truly a mother to a larger family, of nursing students and professionals she was responsible for. She never turned away any of them coming over to her home for special help with their dissertation topics or applications for scholarships. She encouraged the senior nursing staff to follow the degree course and helped them complete it when they were discouraged. Some who recognized me at the counters in private hospitals came up to declare their gratitude to her for this specific gesture of help, because their employment prospects had expanded greatly with that.
Though infinitely patient, graceful and ladylike, my mother was a fighter. I saw how she never gave up on her ambitions for her profession, although she was hardly ambitious for herself. I saw her pain, and her determination to fight on in a hostile environment of male dominated bureaucracy.
I am eternally grateful to Aunty Trixie (Trixie Marthenesz, her fellow student at Delhi Uni) for writing a delightful little booklet called “Those Delhi Days” (Tharanjee Prints, Maharagama, 2009), recounting their time from 1950 to 1954 at the University of Delhi, with wonderful photographs of their 4-year journey as undergraduates, including at the annual concert in creative costumes and also on their holidays around India. An especially charming photo on the first page is the one on Convocation Day 1954, which shows Chandra, Trixie and Shareen together with a few of their batch mates wearing their robes with the distinctive Delhi Uni Cap. The book recalls in such delicious detail their time during such an exciting period in India, just two years after Independence from the British. I found some of the facts for this article from that book. Aunty Trixie, whom my mother drew in, together with Aunty Viola (Viola Perera, the senior student at Delhi University) talking them both out of retirement to begin the work of setting up a new department of Nursing at the Open University, writes in her book, of the young student Chandra who screamed at witnessing the death of their first patient in a hospital in India, bringing “half the ward to the scene”, but who then turned into “a leader among professional nurses in Sri Lanka” which appellation Trixie says “befitted her”.
I see that others have now taken the profession to new heights. Her students are now the warriors at the forefront of the battle for even further professional and pedagogical development. She would be proud. I like to believe that she was as much a guiding light as a Morning Star, softly glowing in the memories of those who knew her, inspiring them to never give up, and to do things with grace. That’s why I share these memories of my exceptional, beloved mother with all those nurses who have known her personally, her colleagues, lecturers and students in white who lined the path throwing jasmine blossoms at the vehicle taking her on her final journey through Kanatte, Colombo’s the main cemetery, and those who have and will come to know her, and the contribution she made to their profession, through the History of Nursing in Sri Lanka.
By Sanja de Silva Jayatilleka
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank, UnionPay launch SplendorPlus Card for travelers to China
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoConference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”
-
 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoLuck knocks at your door every day
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days ago‘Building Blocks’ of early childhood education: Some reflections
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoDialog Brings the ICC Men’s T20 Cricket World Cup 2026 Closer to Sri Lankans
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRising climate risks and poverty in focus at CEPA policy panel tomorrow at Open University













