Features
Back to school anxiety

Adverse effect of diving headlong into schooling
After a year and a half of being cooped up in homes, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, children are set to go back to school, if they are not already. While some kids will be excited about meeting their peers and teachers, others, particularly the younger children, may feel overwhelmed in a new social environment. In some, forced out of their comfort zone, this may create separation anxiety. The anxiety about being separated from families, after being together for so long will only be compounded by fears of loved ones falling prey to the virus. To top it all off these kids have drilled into them various health precautions such as to not get too close to other people, to keep their masks on, use sanitizer and to wash their hands repeatedly. Anxiety is in the air and kids cannot help but feel it. Hopefully, the excitement of going back will outweigh the potential anxiety. In any case, it is bound to be a tough re-entry.
by Sajitha Prematunge
Ferdinando was apprehensive about the reopening of schools, and the fear of contracting COVID-19 had little to do with it. Her school is due to reopen next week and for teachers like her, student social anxiety is very real. The previous lockdowns set many of her students at the S. Mahinda Vidyalaya, Kalutara, several steps back in terms of education, as well as social interaction.
“Most of these kids are eager to come back to school since they are not well provided for at home,” said Nadee Ferdinando. It is heartbreaking to see kids turn up at school, after a year and a half long lockdown, emaciated. “When they are at school their friends share their food with them.” She observed that this is most pronounced in remote schools. Emotional and nutritional needs of students’ of such schools, are often neglected by parents who are low income earners. She observed a general lethargy and lack of concentration, immediately after the reopening of schools, after previous lockdowns. “It set them back several steps. They find it difficult to concentrate, they don’t answer questions and can’t absorb anything in the first few days. Some of them just sat there stupefied. It took time for them to come back to normal, after the previous lockdowns,” said Ferdinando.
 From her experience of previous lockdowns, she knows better than to dive headlong into academic activities. “So, we just stick to activities, like singing and dancing.” Ferdinando observed that it is not only the younger kids who are affected. After a stifling lockdown, cooped in their homes, kids as old as 13 require to be coaxed out of their shells with mundane gossip. “Above all they need to socialise and interact,” said Ferdinando.
From her experience of previous lockdowns, she knows better than to dive headlong into academic activities. “So, we just stick to activities, like singing and dancing.” Ferdinando observed that it is not only the younger kids who are affected. After a stifling lockdown, cooped in their homes, kids as old as 13 require to be coaxed out of their shells with mundane gossip. “Above all they need to socialise and interact,” said Ferdinando.
Psychological perspective
Karapitiya Teaching Hospital, Consultant Psychiatrist, Dr. Rumi Ruben pointed out that children are the group most adversely affected by the pandemic. “Being homebound, due to various regulations, lockdowns, restrictions in movement and health concerns, has been most stressful for children,” said Ruben. He pointed out that lockdowns have both pros and cons, pros being, being able to spend a lot of time with other family members, and cons also being, having to spend a lot of time with other family members, cooped up in a small house. “Kids of all ages, in the same house, can lead to fighting over resources,” said Ruben. Add to the mix sibling rivalry and it would be enough to drive any sane kid slowly mad.
He explained that during the past one and half years since school was out, apart from being deprived of education in the conventional sense, kids have been starved of recreation and time with peers. This is detrimental to kids’ personal development. Social interaction, reduced due to lockdowns, has blunted kids’ social and communication skills, which in turn has hampered their ability to express emotions. In this context, Ruben emphasises the significance of student-teacher interactive communication.
Online education
Online education cannot compare with the physical proximity afforded by a classroom. “Neither can teachers monitor the progress of students nor can students, counter question teachers,” Ruben pointed out. Besides, at school kids play with others their age and even fight. They also missed out on all the extracurricular activities, such as dancing and singing. “The deprivation of all this hampers social learning, which is vital for personal development.”
Inequality
The pandemic provided an ideal opportunity to gauge the inequality in our so-called free education. Laptops, tabs or mobile phones and internet access to take part in online classes did not come free and was beyond the capacity of most daily wage earners, the worst affected, economically, by the pandemic. The same extends to provision of basic needs such as food and nutritional needs as well as keeping children happy in general by meeting their emotional needs, such as by buying them toys and other trinkets. “Such circumstances invariably affect children’s psychology,” said Ruben.
“Another adverse effect of online education was the exposure to sexual material and addiction to gaming, now recognised by the WHO as a mental illness. “Gaming addiction entails withdrawal symptoms such as lack of concentration, anger management issues and withdrawal from other social activities.” Ruben pointed out that all these affect children’s communication.
Illness phobia
According to him, illness phobia, the fear of falling sick and dying or losing loved ones to an illness, in the current context, exacerbated by media coverage of the pandemic, and harping on the death toll, could lead to emotional neediness in children. “Clinginess in such children could lead to reluctance to separate from parents; separation anxiety. Children may refuse to go to school outright,” said Ruben. Such conditions could manifest in the form of social anxiety as well, characterised by irritability, loss of appetite and quarrelling with siblings.
In turn, social anxiety can manifest in the form of depressive symptoms. “Kids may refuse to study, may be irritable and may have difficulty falling asleep or have nightmares. These can exacerbate into medically unexplainable physical symptoms, such as stomach aches or headaches.” So the usual excuse for not wanting to go to school cannot be idly brushed aside. Ruben indicated that they could get physical if forced to conform to the new norm. “They could turn physically violent if parents force them to study or go to school. They may start to consider parents as enemies,” said Ruben. He suggested that phobic symptoms towards COVID-19 should be alleviated by reassurance and providing accurate information.
Adjustment period
Ruben reiterated the importance of allocating an adjustment period so that students could be afforded adequate time to adjust to the new environment. He warned against overburdening kids too early. “What all parties concerned; parents, teachers, education authorities, must understand is that covering the syllabus, should not be the priority. During this adjustment period students must not be overloaded.” Lest it turns into a sort of ‘school phobia’. Ruben recommended that education authorities formulate a revised syllabus to include only vital aspects.
“This adjustment period must be used to monitor students and identify those who display troubling symptoms, so that through parental mediation, they could be referred to a doctor for psychological support.”
Changes to a child’s environment, and stress, are risk factors for developing anxiety and going back to school after a long hiatus have all the right ingredients for anxiety. Some kids are too young to grasp the concept of acceptable risk. In this context it is also the parents’ responsibility to placate any lingering misgivings children may have about going back to school.
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
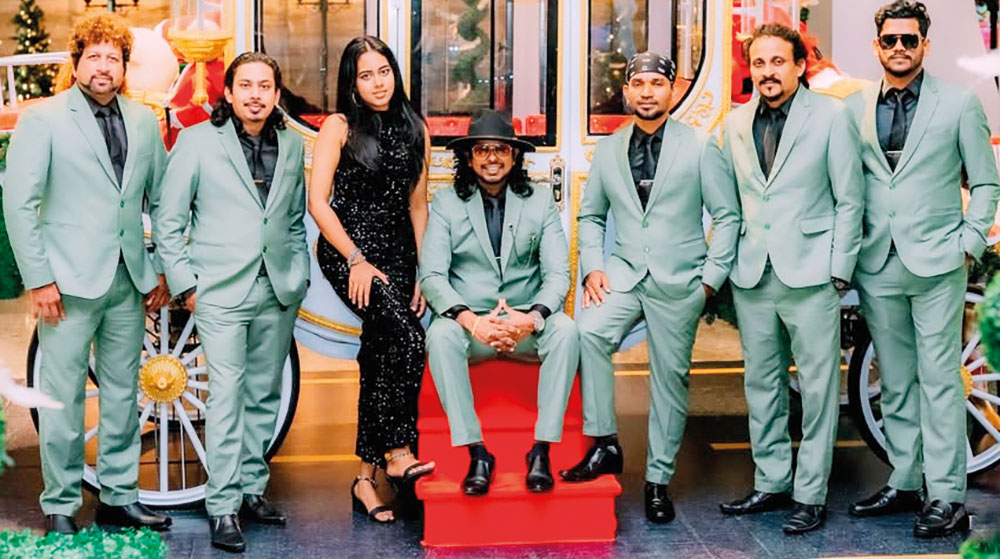
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
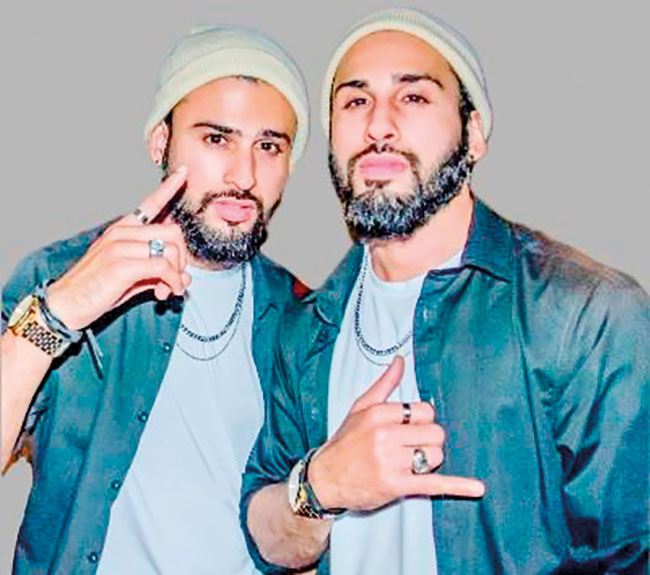

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans






















