Features
A People in-between East and West

The Dutch Burghers in Sri Lanka:
by Prabhath de Silva
“We are a vanishing tribe in Sri Lanka. The first paternal ancestor of my father’s family who arrived in Sri Lanka in 1774 was Pieter Scharenguivel. He was a Quarter Master in the service of the United Dutch East India Company which ruled the maritime provinces of Sri Lanka from the middle of the 17th century to 1796. The Dutch Burgher identity and consciousness within the family I grew up was extremely significant. It played a role in the conversations, traditions, customs, food, perceptions and social interactions. During the British colonial rule, our community produced eminent surgeons, doctors, legal luminaries, judges, engineers, sportsmen, musicians , historians and artists etc.” , said Anne-Marie Scharenguivel, 65, a management accountant and a member of Sri Lanka’s tiny Dutch Burgher community of less than 30,000 people. The people known as ‘Dutch Burghers are descendants of the Europeans who arrived in Sri Lanka as servants of the United East India Company (Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie- VOC) which ruled Sri Lanka’s maritime provinces from 1656 to 1796 or merchants and married native women or women who were children of mixed marriages between European men and native women.
Sri Lanka’s largest ethnic group is the Sinhalese, constituting 74.9% of the population of 21 million. The Sri Lankan Tamils, who live predominantly in the north and east of the island, are the largest ethnic minority group at 11.1% of Sri Lanka’s population. The Muslims are the third largest ethnic group at 9.3% of the population. Indian Tamils comprise 4.1% of Sri Lanka’s population. Smaller minority groups include the Malays, Burghers, Chetties (an originally trading community whose ancestors arrived from the southern parts of India) and the Veddahs -Sri Lanka’s indigenous people. Malays are descendants of Malay settlers brought by the Dutch colonial rulers.
The Dutch Connection with Sri Lanka
The Portuguese were the first European colonial power to arrive in Sri Lanka in 1505 when Sri Lanka had been divided into three kingdoms, namely the Kingdom of Kotte, Kingdom of Jaffna and the interior Kingdom of Kandy. Their presence in Sri Lanka’s maritime provinces between 1505 and 1656 CE, which began as an interaction of trade and commerce, later developed into a colonial rule in the maritime provinces (sans eastern coast from Trincomalee) downwards from 1597. Admiral Joris van Spilbergen (1568-1629), the Dutch circumnavigator, who commanded the fleet of ships’ Ram’, ‘Schaap’, and ‘Lam’ belonging to the Dutch company named Balthazar de Moucheron (a trading company that had been in existence before the establishment of the United East India Company -VOC in March 1602 ), landed in Batticaloa in Sri Lanka’s eastern coast on May 31, 1602, after a 12 month voyage at sea. Van Spilbergen met King Vimaladharmasuriya I, the King of Kandy (interior native kingdom of Sri Lanka), and negotiated the possibilities of trade in cinnamon and pepper and of providing military assistance to the King of Kandy to expel the Portuguese from the coastal regions of the Island. Van Spilbergen’s visit was the first Dutch visit to the Island. Spilbergen was followed by the visits of the fleets of Dutch ships commanded by the Dutch navigator, Sebald de Weert in November 1602, Jacob Cornelisz in 1603 and Marcellus de Boschouwer in 1612.
On May 23, 1638, the Treaty of 1638 between the Kingdom of Kandy and the United East India Company was signed by King Rajasinghe II for the Kingdom of Kandy and Adam Westerwold and William Jacobsz Coster, a commander and vice commander of the Dutch Naval Forces representing the United East India Company (VOC) in Batticaloa. The treaty secured the terms under which the two nations would cooperate in defending the Kandyan Kingdom from the Portuguese. The writer vividly remembers visiting the Dutch State Archives in The Hague in 1985 accompanied by a Dutch Burgher lady friend (64 at that time) settled down in that city, to see one of the original copies of this treaty handwritten in medieval Dutch. This friend whose father was a Ceylonese Dutch Burgher named Kriekenbeek and whose mother was a native Dutch lady, having left Ceylon (Sri Lanka) in 1948 at the age of 24 and having lived in The Netherlands for almost 37 years, was able to translate the contents of the Treaty for me from Dutch to English. I can also remember the courtesy and kindness extended to me (then a 25 year old lawyer) by the Staff of the Dutch State Archives.
The key points of the 1638 Treaty were (a) the Dutch should provide the King of Kandy with military and naval assistance to drive the Portuguese from the Island; (b) the Kandyan King should fully settle the military and naval expenditure incurred by the Dutch for onslaughts against the Portuguese by way of providing the Dutch with commodities such as cinnamon and pepper etc (c) the King of Kandy should grant the Dutch the monopoly of collecting spices and other commodities except elephants from the territories that constituted the Kingdom of Kandy; and (d) the Dutch should vacate the fortresses that would be captured from the Portuguese if the King would desire to take them over. Between 1640 and 1658 the Dutch completely expelled the Portuguese from the maritime provinces of Sri Lanka and ruled until 1796 when the British in turn replaced the Dutch and eventually took the whole island, including its holdout interior Kingdom of Kandy.
The maritime provinces of Sri Lanka came under the rule of Dutch East India Company after its armies defeated the Portuguese in a series of battles between 1640 and 1658. When the Kandyan King, Rajasinghe II demanded the Dutch to vacate and hand over the captured Portuguese Fortresses and territories, the Dutch presented a bill of military and naval expenditure involved in the battles to oust the Portuguese and asked the King to settle the bill first. But Rajasinghe II who was unable to settle the bill, would say that the Dutch had exaggerated the expenditure. The Dutch would maintain that they could hold the territories and fortresses captured from the Portuguese until the King Rajasinghe II and his successors would fully settle their bill of military and naval expenditure of onslaughts against the Portuguese. This was the legal foundation upon which the Dutch justified their occupation of the maritime provinces in the southern, western and northern coastal areas. Later they formulated another legal argument in their search for a legal basis for their rule in those regions.
They argued that Rajasinghe’s Treaty of 1638 with them was a nullity with regard to the Kingdom of Kotte as King Don Jao Dharmapala had gifted it to the King of Portugal in 1591 and the Portuguese had acquired the sovereignty of the Kingdom of Jaffna by conquest by war 1621, and as such Rajasinghe II, the King of Kandy had legal status (locus standi) to sign a treaty claiming the sovereignty over former territories of the Kingdom of Kotte (south western coastal areas of Sri Lanka) and the Kingdom of Jaffna (northern coastal areas). After a war between the Kingdom of Kandy and the forces of the United East India Company, the dispute over the sovereignty of the maritime provinces was permanently settled by the Treaty of 1766, by which the King of Kandy conceded the territorial control of the western, southern, northern and eastern coastal areas to the Dutch. The maritime provinces were ruled by the Dutch East India Company from 1656 to 1796. During their period, a canal system was developed, a judicial system was introduced with the Roman-Dutch Law. The Roman-Dutch Law still remains to be the residuary common law in civil matters, though much of it has been replaced with English Law by statutes during the British rule.
A number of Dutch words have become naturalized in the Sinhalese language . Among many such words are: Kamaraya in Sinhalese is derived from the Dutch word ‘Kamer’ for the room, Kanthoruwa in Sinhalese for office is derived from the Dutch word ‘Kantoor” for office, ‘ boodalaya’ in Sinhalese is derived from the Dutch word ‘Boedel’ for the estate of a deceased person, ‘Kakkussiya” in Sinhalese for lavatory is derived from the Dutch word’ Kakhuis’. The British captured the maritime provinces of the Island in 1796. Among other legacies of the Dutch rule are Dutch forts and a few buildings preserved for posterity. The Dutch Burgher community in Sri Lanka is a living legacy of the Dutch period. When native feudal Chiefs ceded the sovereignty of the interior native Kandyan Kingdom to the British Empire by the Kandyan Convention of 1815, the whole Island came under the British rule. Sri Lanka gained independence from the British in1948.
Who are the Burghers and the Dutch Burghers?
The word ‘Burgher’ is derived from the Dutch word ‘Vrije Burgher ‘, meaning “free citizen” or “town dweller”. The Burghers in Sri Lanka are an Eurasian community of mixed origin, whose first paternal ancestors were European colonists (mainly from Portugal, The Netherlands and the UK) who had married native Sinhalese or Tamil women. The Portuguese men who opted to remain in Sri Lanka had married native Sinhalese or Tamil women because there were no Portuguese women in the Island. The children who were born in a marriage between the Portuguese colonists and native women in Portuguese colonies overseas were called Mesticos. The second and subsequent generations of Portuguese colonists who opted to remain in Sri Lanka preferred to marry the Mestico women and their second preference was the native women. The servants and soldiers of the Dutch East India who arrived in Sri Lanka were not only Dutch but belonged to other European nationalities too including German and French Protestants known as Huguenots, Scandinavian and Italian. Marriages between them and native women were less frequent with the passage of time.
The descendants of the European servants of the Dutch East India Company and Mestico women and native women ( Sinhalese and Tamil) became known as ‘Dutch Burghers’. In order to be considered as a Dutch Burgher, one’s father ought to have inherited an European family name from an European paternal ancestor who had come to Sri Lanka during the period Dutch East India Company ruled the maritime provinces of the Island. During the Dutch colonial period, the mother tongue or the lingua franca of the Dutch Burgher community in Sri Lanka was an Indo-Portuguese creole, though the Dutch Burghers later adopted English as their first language during the British colonial period.
Dutch Burghers during the British colonial rule in Sri Lanka
Although many portray British rule here as ‘exploitative’, of our country, they ignore the vast economic, social and educational developments that facilitated the transition from feudalism to capitalism and a parliamentary democracy. The contemporary progressive political trends in Britain with her social movements like utilitarianism, social, democratic and labour movements, too influenced colonial rule here. The British empire was an extension of British capitalism to the colonies including Ceylon. Lenin in his book “Colonialism: The Advanced Stage of Capitalism” presented a similar argument. Today, we beg for foreign investment. This is not a new phenomenon. During British colonial rule, British companies invested in the plantations and other sectors in Sri Lanka. These capitalists paid taxes to the British colonial government here on the profits they earned. Later parallel to the British and European capitalist class, an indigenous native entrepreneur class emerged. The colonial government managed the economy with its own tax revenue without borrowing from outside. The Dutch Burghers who were a sort of ‘people in between’ the west and the east were able to achieve eminent positions in the public service, medical profession, legal profession and judiciary during the British colonial period in Sri Lanka. They held a proportionately higher percentage of positions as clerks, engineers, surveyors, journalists, locomotive engine drivers and railway guards in the public service. Their presence was significant in the employment of mercantile sector. It was the eminent Dutch Burghers like Charles Ambrose Lorensz were the pioneer constitutionalists who agitated for more liberal and democratic constitutional reforms during the 19th century British colonial Sri Lanka.
The Dutch Burghers in Post -Independence Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka gained independence from the British in 1948 and inherited from the British a democratic form of government based on the Westminster parliamentary model. At the time of Independence, Sinhalese majority constituted 66% of Sri Lanka’s population and the Buddhists who were almost exclusively Sinhalese constituted 60% of the Sri Lanka’s population whilst the remaining 6% of the Sinhalese population were Christians. Sri Lanka’s ethno-religious and ethnic minorities ,at the time of independence constituted 34% of Sri Lanka’s population. Sri Lanka’s first Prime Minister, D. S. Senanayake, a Sinhalese Buddhist, was a pragmatic leader who did not want to upset the ethnic harmony prevalent at the time of Independence. He and his political party the United National Party formed coalition governments with the major Tamil and Muslim parties and formed the cabinet of ministers representing Sri Lanka’s majority Sinhalese Buddhist community and other ethno-linguistic and religious minorities.
He and his two immediate successors, Dudley Senanayake and Sir John Kotalawala after Senanayake’s resignation refused to accede to the demands of the Sinhalese Buddhist nationalists for making Sinhalese the only official language replacing English, making Buddhism the State religion and for immediate take over of Christian denominational schools by the State. The Sinhalese Buddhist nationalists approached Solomon West Ridgway Dias Bandaranaike, who had broke away from D. S. Senanayake’s United National Party and had formed a new political party named Sri Lanka Freedom Party. Bandaranaike promised to implement all these demands of the Sinhalese Buddhist nationalists in the event his party would come to power at the next General Election. Bandaranaike was a Sinhalese born to a highly anglicized Christian aristocratic family. Educated at Oxford (1919-1925), Bandaranaike was a Barrister-at-Law and an eloquent speaker at the Oxford Union. A few years after his return to the Island from Oxford, Bandaranaike adopted the national dress, learned the Sinhalese language and began to tread on a path of communal politics based on Sinhalese Buddhist nationalism.
In 1956, a coalition led by Bandaranaike’s on communal sentiments and slogans of the Sinhalese Buddhist nationalism and socialism, was elected to power and Bandaranaike became the Prime Minister. One of the first things his government hurriedly did was to enact an Official Language Act making Sinhalese the only official language disregarding the Tamil and English , and the demand for making both Sinhalese and Tamil as official languages put forward by the Tamil political parties and Marxist political parties were rejected. The enactment of this piece of legislation deprived the English educated intelligentsia of Tamils, Dutch Burghers and Sinhalese of public sector jobs unless they passed an examination to prove their proficiency in Sinhala language.
Bandaranaike who began to experience the initial destructive consequences of his short sighted policies ,could not live long to witness the long term consequence of the whirlwind of communal tensions he set in motion through his unwise initiatives.
In September 1959, Bandaranaike was assassinated by a Buddhist monk named Talduwe Somarama, a misguided instrument or a cat’s paw of a conspiracy by a group of Sinhalese Buddhists (led by a prominent Sinhalese Buddhist monk) who helped him come to power , but developed an enmity with him, when in power, Bandaranaike refused to help them form a shipping company. The enactment of Bandaranaike’s ‘Sinhala Only’ and the events that followed drastically changed the political landscape of Sri Lanka, with his SLFP’s rival, the UNP’s governments too pursuing the same policies when in power, resulting in communal riots of 1958, 1977 and 1983 disturbances and tensions culminating in a 30-year civil war. Mrs. Bandaranaike who became prime minister in 1960, pursued policies of her husband rigorously, and took over the denominational schools of which an overwhelming majority were Christian in 1961. This entailed further appeasing the demands of the Sinhalese Buddhist nationalists by withholding State grants and subsidies for such schools if they opted to remain private. As result only 51 Christian school out of hundreds could remain independent.
Christians, particularly Catholics considered the take over of their schools by the State a discriminatory blow. Mrs. Bandaranaike, elected to power again in 1970 with a two third majority in parliament, severed the constitutional links with the British monarch as the ceremonial head of the state and abolished right to appeal the decisions of the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. Her government enacted a Republican constitution granting Buddhism the foremost place in the Sri Lankan State, casting a constitutional duty upon the State to protect and foster Buddhism. Her government went further to perpetuate the Sinhala Only policy of her late husband by making Sinhala the only official language in the Sri Lankan State by incorporating provisions for such status in the new constitution of 1972. History has shown that issues of race, caste, religion, language and blind political affiliations have always been exploited by the leaders, and that these machinations have not originated from the ordinary people or peasants. Innocent peasants may be misled, misguided and mobilized by the leaders to achieve their narrow self–serving interests and ambitions by exploiting ethnicity, religion, caste and language in the South Asian political context. The Dutch Burghers, having experienced anxieties and insecurities of their future prospects, opted to emigrate mainly to Australia.
(To be continued next week)
Features
More state support needed for marginalised communities

Message from Malaiyaha Tamil community to govt:
Insights from SSA Cyclone Ditwah Survey
When climate disasters strike, they don’t affect everyone equally. Marginalised communities typically face worse outcomes, and Cyclone Ditwah is no exception. Especially in a context where normalcy is far from “normal”, the idea of returning to normalcy or restoring a life of normalcy makes very little sense.
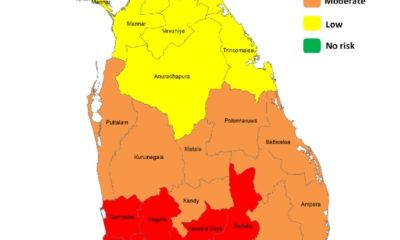
The island-wide survey (https://ssalanka.org/reports/) conducted by the Social Scientists’ Association (SSA), between early to mid-January on Cyclone Ditwah shows stark regional disparities in how satisfied or dissatisfied people were with the government’s response. While national satisfaction levels were relatively high in most provinces, the Central Province tells a different story.
Only 35.2% of Central Province residents reported that they were satisfied with early warning and evacuation measures, compared to 52.2% nationally. The gap continues across every measure: just 52.9% were satisfied with immediate rescue and emergency response, compared with the national figure of 74.6%. Satisfaction with relief distribution in the Central Province is 51.9% while the national figure stands at 73.1%. The figures for restoration of water, electricity, and roads are at a low 45.9% in the central province compared to the 70.9% in national figures. Similarly, the satisfaction level for recovery and rebuilding support is 48.7% in the Central Province, while the national figure is 67.0%.
A deeper analysis of the SSA data on public perceptions reveals something important: these lower satisfaction rates came primarily from the Malaiyaha Tamil population. Their experience differed not just from other provinces, but also from other ethnic groups living in the Central Province itself.
The Malaiyaha Tamil community’s vulnerability didn’t start with the cyclone. Their vulnerability is a historically and structurally pre-determined process of exclusion and marginalisation. Brought to Sri Lanka during British rule to work for the empire’s plantation economies, they have faced long-term economic exploitation and have repeatedly been denied access to state support and social welfare systems. Most estate residents still live in ‘line rooms’ and have no rights to the land they cultivate and live on. The community continues to be governed by an outdated estate management system that acts as a barrier to accessing public and municipal services such as road repair, water, electricity and other basic infrastructures available to other citizens.
As far as access to improved water sources is concerned, the Sri Lanka Demographic Health Survey (2016) shows that 57% of estate sector households don’t have access to improved water sources, while more than 90% of households in urban and rural areas do. With regard to the level of poverty, as the Department of Census and Statistics (2019) data reveals, the estate sector where most Malaiyaha Tamils live had a poverty headcount index of 33.8%; more than double the national rate of 14.3%. These statistics highlight key indicators of the systemic discrimination faced by the Malaiyaha Tamil community.
Some crucial observations from the SSA data collectors who enumerated responses from estate residents in the survey reveal the specific challenges faced by the Malaiyaha Tamils, particularly in their efforts to seek state support for compensation and reconstruction.
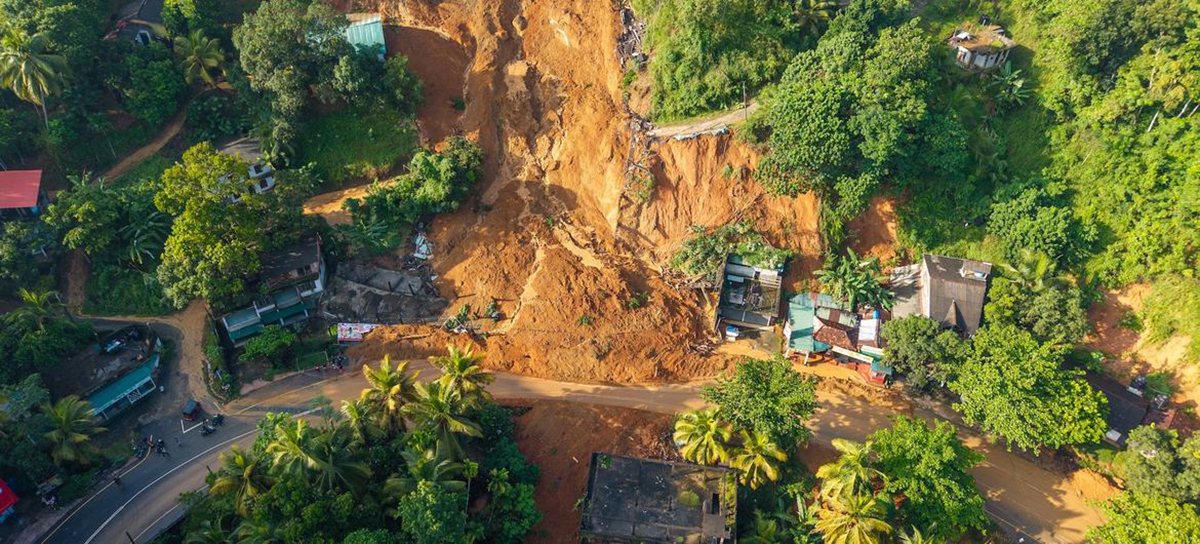
First, the Central Province experienced not just flooding but also the highest number of landslides in the island. As a result, some residents in the region lost entire homes, access roadways, and other basic infrastructures. The loss of lives, livelihoods and land was at a higher intensity compared to the provinces not located in the hills. Most importantly, the Malaiyaha Tamil community’s pre-existing grievances made them even more vulnerable and the government’s job of reparation and restitution more complex.
Early warnings hadn’t reached many areas. Some data collectors said they themselves never heard any warnings in estate areas, while others mentioned that early warnings were issued but didn’t reach some segments of the community. According to the resident data collectors, the police announcements reached only as far as the sections where they were able to drive their vehicles to, and there were many estate roads that were not motorable. When warnings did filter through to remote locations, they often came by word of mouth and information was distorted along the way. Once the disaster hit, things got worse: roads were blocked, electricity went out, mobile networks failed and people were cut off completely.
Emergency response was slow. Blocked roads meant people could not get to hospitals when they needed urgent care, including pregnant mothers. The difficult terrain and poor road conditions meant rescue teams took much longer to reach affected areas than in other regions.
Relief supplies didn’t reach everyone. The Grama Niladhari divisions in these areas are huge and hard to navigate, making it difficult for Grama Niladharis to reach all places as urgently as needed. Relief workers distributed supplies where vehicles could go, which meant accessible areas got help while remote communities were left out.
Some people didn’t even try to go to safety centres or evacuation shelters set up in local schools because the facilities there were already so poor. The perceptions of people who did go to safety centres, as shown in the provincial data, reveal that satisfaction was low compared to other affected regions of the country. Less than half were satisfied with space and facilities (42.1%) or security and protection (45.0%). Satisfaction was even lower for assistance with lost or damaged documentation (17.9%) and information and support for compensation applications (28.2%). Only 22.5% were satisfied with medical care and health services below most other affected regions.
Restoring services proved nearly impossible in some areas. Road access was the biggest problem. The condition of the roads was already poor even before the cyclone, and some still haven’t been cleared. Recovery is especially difficult because there’s no decent baseline infrastructure to restore, hence you can’t bring roads and other public facilities back to a “good” condition when they were never good, even before the disaster.
Water systems faced their own complications. Many households get water from natural sources or small community projects, and not the centralised state system. These sources are often in the middle of the disaster zone and therefore got contaminated during the floods and landslides.
Long-term recovery remains stalled. Without basic infrastructure, areas that are still hard to reach keep struggling to get the support they need for rebuilding.
Taken together, what do these testaments mean? Disaster response can’t be the same for everyone. The Malaiyaha Tamil community has been double marginalised because they were already living with structural inequalities such as poor infrastructure, geographic isolation, and inadequate services which have been exacerbated by Cyclone Ditwah. An effective and fair disaster response needs to account for these underlying vulnerabilities. It requires interventions tailored to the historical, economic, and infrastructural realities that marginalized communities face every day. On top of that, it highlights the importance of dealing with climate disasters, given the fact that vulnerable communities could face more devastating impacts compared to others.
(Shashik Silva is a researcher with the Social Scientists’ Association of Sri Lanka)
by Shashik Silva ✍️
Features
Crucial test for religious and ethnic harmony in Bangladesh

 Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
The apprehensions are mainly on the part of religious and ethnic minorities. The parliamentary poll of February 12th is expected to bring into existence a government headed by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and the Islamist oriented Jamaat-e-Islami party and this is where the rub is. If these parties win, will it be a case of Bangladesh sliding in the direction of a theocracy or a state where majoritarian chauvinism thrives?
Chief of the Jamaat, Shafiqur Rahman, who was interviewed by sections of the international media recently said that there is no need for minority groups in Bangladesh to have the above fears. He assured, essentially, that the state that will come into being will be equable and inclusive. May it be so, is likely to be the wish of those who cherish a tension-free Bangladesh.
The party that could have posed a challenge to the above parties, the Awami League Party of former Prime Minister Hasina Wased, is out of the running on account of a suspension that was imposed on it by the authorities and the mentioned majoritarian-oriented parties are expected to have it easy at the polls.
A positive that has emerged against the backdrop of the poll is that most ordinary people in Bangladesh, be they Muslim or Hindu, are for communal and religious harmony and it is hoped that this sentiment will strongly prevail, going ahead. Interestingly, most of them were of the view, when interviewed, that it was the politicians who sowed the seeds of discord in the country and this viewpoint is widely shared by publics all over the region in respect of the politicians of their countries.
Some sections of the Jamaat party were of the view that matters with regard to the orientation of governance are best left to the incoming parliament to decide on but such opinions will be cold comfort for minority groups. If the parliamentary majority comes to consist of hard line Islamists, for instance, there is nothing to prevent the country from going in for theocratic governance. Consequently, minority group fears over their safety and protection cannot be prevented from spreading.
Therefore, we come back to the question of just and fair governance and whether Bangladesh’s future rulers could ensure these essential conditions of democratic rule. The latter, it is hoped, will be sufficiently perceptive to ascertain that a Bangladesh rife with religious and ethnic tensions, and therefore unstable, would not be in the interests of Bangladesh and those of the region’s countries.
Unfortunately, politicians region-wide fall for the lure of ethnic, religious and linguistic chauvinism. This happens even in the case of politicians who claim to be democratic in orientation. This fate even befell Bangladesh’s Awami League Party, which claims to be democratic and socialist in general outlook.
We have it on the authority of Taslima Nasrin in her ground-breaking novel, ‘Lajja’, that the Awami Party was not of any substantial help to Bangladesh’s Hindus, for example, when violence was unleashed on them by sections of the majority community. In fact some elements in the Awami Party were found to be siding with the Hindus’ murderous persecutors. Such are the temptations of hard line majoritarianism.
In Sri Lanka’s past numerous have been the occasions when even self-professed Leftists and their parties have conveniently fallen in line with Southern nationalist groups with self-interest in mind. The present NPP government in Sri Lanka has been waxing lyrical about fostering national reconciliation and harmony but it is yet to prove its worthiness on this score in practice. The NPP government remains untested material.
As a first step towards national reconciliation it is hoped that Sri Lanka’s present rulers would learn the Tamil language and address the people of the North and East of the country in Tamil and not Sinhala, which most Tamil-speaking people do not understand. We earnestly await official language reforms which afford to Tamil the dignity it deserves.
An acid test awaits Bangladesh as well on the nation-building front. Not only must all forms of chauvinism be shunned by the incoming rulers but a secular, truly democratic Bangladesh awaits being licked into shape. All identity barriers among people need to be abolished and it is this process that is referred to as nation-building.
On the foreign policy frontier, a task of foremost importance for Bangladesh is the need to build bridges of amity with India. If pragmatism is to rule the roost in foreign policy formulation, Bangladesh would place priority to the overcoming of this challenge. The repatriation to Bangladesh of ex-Prime Minister Hasina could emerge as a steep hurdle to bilateral accord but sagacious diplomacy must be used by Bangladesh to get over the problem.
A reply to N.A. de S. Amaratunga
A response has been penned by N.A. de S. Amaratunga (please see p5 of ‘The Island’ of February 6th) to a previous column by me on ‘ India shaping-up as a Swing State’, published in this newspaper on January 29th , but I remain firmly convinced that India remains a foremost democracy and a Swing State in the making.
If the countries of South Asia are to effectively manage ‘murderous terrorism’, particularly of the separatist kind, then they would do well to adopt to the best of their ability a system of government that provides for power decentralization from the centre to the provinces or periphery, as the case may be. This system has stood India in good stead and ought to prove effective in all other states that have fears of disintegration.
Moreover, power decentralization ensures that all communities within a country enjoy some self-governing rights within an overall unitary governance framework. Such power-sharing is a hallmark of democratic governance.
Features
Celebrating Valentine’s Day …

 Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
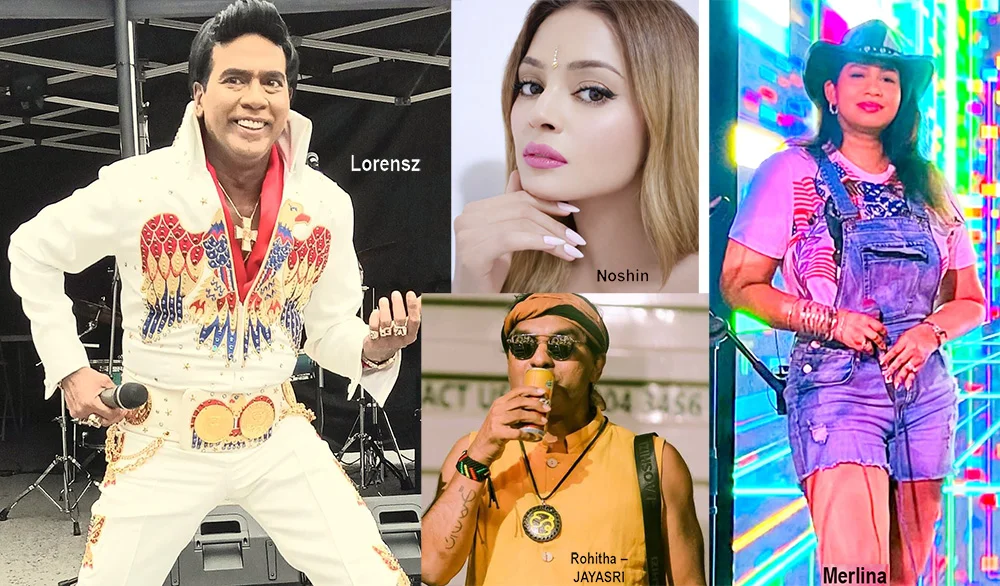
Merlina Fernando (Singer)
Yes, it’s a special day for lovers all over the world and it’s even more special to me because 14th February is the birthday of my husband Suresh, who’s the lead guitarist of my band Mission.
We have planned to celebrate Valentine’s Day and his Birthday together and it will be a wonderful night as always.
We will be having our fans and close friends, on that night, with their loved ones at Highso – City Max hotel Dubai, from 9.00 pm onwards.
Lorensz Francke (Elvis Tribute Artiste)
On Valentine’s Day I will be performing a live concert at a Wealthy Senior Home for Men and Women, and their families will be attending, as well.
I will be performing live with romantic, iconic love songs and my song list would include ‘Can’t Help falling in Love’, ‘Love Me Tender’, ‘Burning Love’, ‘Are You Lonesome Tonight’, ‘The Wonder of You’ and ‘’It’s Now or Never’ to name a few.
To make Valentine’s Day extra special I will give the Home folks red satin scarfs.
Emma Shanaya (Singer)
I plan on spending the day of love with my girls, especially my best friend. I don’t have a romantic Valentine this year but I am thrilled to spend it with the girl that loves me through and through. I’ll be in Colombo and look forward to go to a cute cafe and spend some quality time with my childhood best friend Zulha.
JAYASRI
Emma-and-Maneeka
This Valentine’s Day the band JAYASRI we will be really busy; in the morning we will be landing in Sri Lanka, after our Oman Tour; then in the afternoon we are invited as Chief Guests at our Maris Stella College Sports Meet, Negombo, and late night we will be with LineOne band live in Karandeniya Open Air Down South. Everywhere we will be sharing LOVE with the mass crowds.
Kay Jay (Singer)
I will stay at home and cook a lovely meal for lunch, watch some movies, together with Sanjaya, and, maybe we go out for dinner and have a lovely time. Come to think of it, every day is Valentine’s Day for me with Sanjaya Alles.
Maneka Liyanage (Beauty Tips)
On this special day, I celebrate love by spending meaningful time with the people I cherish. I prepare food with love and share meals together, because food made with love brings hearts closer. I enjoy my leisure time with them — talking, laughing, sharing stories, understanding each other, and creating beautiful memories. My wish for this Valentine’s Day is a world without fighting — a world where we love one another like our own beloved, where we do not hurt others, even through a single word or action. Let us choose kindness, patience, and understanding in everything we do.
Janaka Palapathwala (Singer)

Janaka
Valentine’s Day should not be the only day we speak about love.
From the moment we are born into this world, we seek love, first through the very drop of our mother’s milk, then through the boundless care of our Mother and Father, and the embrace of family.
Love is everywhere. All living beings, even plants, respond in affection when they are loved.
As we grow, we learn to love, and to be loved. One day, that love inspires us to build a new family of our own.
Love has no beginning and no end. It flows through every stage of life, timeless, endless, and eternal.
Natasha Rathnayake (Singer)
We don’t have any special plans for Valentine’s Day. When you’ve been in love with the same person for over 25 years, you realise that love isn’t a performance reserved for one calendar date. My husband and I have never been big on public displays, or grand gestures, on 14th February. Our love is expressed quietly and consistently, in ordinary, uncelebrated moments.
With time, you learn that love isn’t about proving anything to the world or buying into a commercialised idea of romance—flowers that wilt, sweets that spike blood sugar, and gifts that impress briefly but add little real value. In today’s society, marketing often pushes the idea that love is proven by how much money you spend, and that buying things is treated as a sign of commitment.
Real love doesn’t need reminders or price tags. It lives in showing up every day, choosing each other on unromantic days, and nurturing the relationship intentionally and without an audience.
This isn’t a judgment on those who enjoy celebrating Valentine’s Day. It’s simply a personal choice.
Melloney Dassanayake (Miss Universe Sri Lanka 2024)
 I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I’m incredibly blessed because, for me, every day feels like Valentine’s Day. My special person makes sure of that through the smallest gestures, the quiet moments, and the simple reminders that love lives in the details. He shows me that it’s the little things that count, and that love doesn’t need grand stages to feel extraordinary. This Valentine’s Day, perfection would be something intimate and meaningful: a cozy picnic in our home garden, surrounded by nature, laughter, and warmth, followed by an abstract drawing session where we let our creativity flow freely. To me, that’s what love is – simple, soulful, expressive, and deeply personal. When love is real, every ordinary moment becomes magical.
Noshin De Silva (Actress)
Valentine’s Day is one of my favourite holidays! I love the décor, the hearts everywhere, the pinks and reds, heart-shaped chocolates, and roses all around. But honestly, I believe every day can be Valentine’s Day.
It doesn’t have to be just about romantic love. It’s a chance to celebrate love in all its forms with friends, family, or even by taking a little time for yourself.
Whether you’re spending the day with someone special or enjoying your own company, it’s a reminder to appreciate meaningful connections, show kindness, and lead with love every day.
And yes, I’m fully on theme this year with heart nail art and heart mehendi design!
Wishing everyone a very happy Valentine’s Day, but, remember, love yourself first, and don’t forget to treat yourself.
Sending my love to all of you.
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Midweek Review4 days ago
Midweek Review4 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Midweek Review4 days ago
Midweek Review4 days agoTheatre and Anthropocentrism in the age of Climate Emergency