Features
2020 was the year of doctors, which profession would it be in 2021?
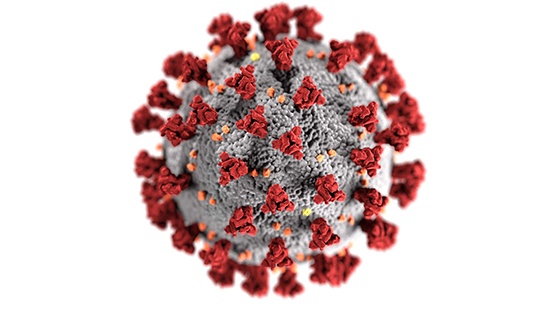
by Krishantha Prasad Cooray
One year ago, so-called astrologers took to two television stations to tell the nation what to expect in 2020. A person going by the name Chandrasiri Bandara explained that the stars were so moved by political developments in Sri Lanka that 2020 would be an extraordinarily prosperous year. At the same time, someone called Manjula Peiris was on TV explaining that the election results caused a planetary alignment that would open the floodgates of foreign investment in 2020. Indeed, Bandara was so specific as to say that that bulk of the prosperity would come after March 2020. To put it mildly, either they or their planets seem to have got their wires crossed.
There is no shame in forecasting the fate of the nation based on a political perspective or ideology. Indeed, many Sri Lankan professionals and business people also predicted that 2020 would be a good year for our country. The difference is that their conviction flowed from faith in a leader untarnished by politics who they saw as a breath of fresh air, and anticipation of a political culture that would shake up the public service.
Their miscalculation and disappointment could have been lessened if not for the pandemic, but this article is not intended to chronicle the many failures of the government. The fact is that no one could have predicted the economic devastation and paralysis that Covid-19 would cause not just in Sri Lanka but throughout the world. Success has been the exception, not the rule. Outside of Taiwan, Australia, New Zealand, South Korea, Singapore and Japan, it is hard to find a country that has not been ground to a halt by this deadly virus.
With over 40,000 people testing positive in Sri Lanka and nearly 200 fatalities, there is no gainsaying we could have done better. However, the same could be said of nearly every country in the world. What we do know is that if not for the knowledge, courage and professionalism of our frontline workers and first responders, we could easily have had over 10 times as much suffering.
Sri Lanka is blessed with one of the finest healthcare systems in the world. Despite spending under 4% of our GDP on health, we boast some of the best health outcomes to be had, including low infant mortality, high vaccination rates and free access to healthcare as a right to all citizens. As a country we think of success and failure in terms of political parties and politicians. Partisanship aside, every government and every party has done their part to strengthen our national health service, but our healthcare system is not the making of politicians.
It is a system composed of thousands of doctors, nurses, public health inspectors (PHIs), epidemiologists and other administrators who, even before Covid-19, shunned opportunities for employment in a world short of doctors, nurses and healthcare professionals. They chose instead to remain in Sri Lanka and make its people well, for a fraction of the compensation they could earn abroad.
Long before Covid-19 struck, they were our front line of defence. The Health Service’s epidemiology unit is no stranger to fighting and eradicating deadly diseases. It worked with the World Health Organisation (WHO) and United Nations (UN) to eradicate polio from our island by 1993, and to rid the country of Malaria by 2016. Just as our national intelligence services stand vigilant against the resurgence of the LTTE, the professionals of the epidemiology unit have guarded the country against the resurgence of diseases that are in our past.
When the global pandemic struck, our health professionals knew what to do. They wanted to lock down the island to contain the virus and use that precious time to trace those who may have been exposed and educate the public on the essential rules for curtailing the virus: frequently wash your hands, avoid touching your face, wear face coverings and keep one and a half metres apart from others.
Sadly, the public health narrative was hijacked from all quarters, and a strong, clear message on social distancing and hygiene quickly gave way to superstition, politics, religious extremism and militarization. The result was that the front-line workers and healthcare professionals who knew how to protect us were side-lined, and yet they silently did their jobs at great risk to themselves.
PHIs worked in communities without returning home for weeks, even sleeping in their offices without overtime pay, to trace and isolate potential Covid patients. Our nurses implemented ruthlessly efficient hygiene protocols at every health facility in the country and worked tirelessly to continue administering wards even amid shortages of personal protective equipment.
Our physicians and other doctors monitored patients and those under quarantine and provided a quality of care that contributed to one of the world’s lowest Covid-19 mortality rates, at just 0.4%. Of every 1,000 people infected with Covid-19 in Sri Lanka, only four have succumbed to the virus. In Sri Lanka, whether you are a peasant, prisoner or professional, our doctors have honoured their Hippocratic oath to ensure that you receive the best possible medical outcome.
Even once the virus spread through the country, and it was not considered safe for anyone to walk the streets, our police and military personnel put their lives on line to protect the rest of us. To date, over 1,500 police officers and nearly 1,000 navy personnel have been infected with Covid-19 in the line of duty. Many of these infections could have been avoided if senior policy and military officers had bowed to health professionals, instead of making doctors and professionals bow to them.
In other countries, it was the doctors who made decisions, and the military and police who implemented those decisions. Only in Sri Lanka did we try the reverse. There is no matching the efficiency and logistical prowess of our military and police department. Against an unknown enemy like a virus, it is for their own sake that they should have been allowed to benefit from deferring to the professionals who have studied the art of medicine for even longer than most soldiers have studied the art of war.
The role of doctors in fighting the war against the LTTE was restricted to field hospitals and operating theatres. Just as surgeons had no role to play in strategizing the fall of Kilinochchi or the retaking of the Jaffna peninsula, it is futile to expect generals to learn epidemiology overnight to manage a public health crisis like the world has never seen.
But whether doctors, nurses, police officers or soldiers, it is to all these front-line workers that we should dedicate the year 2020. This was their year. If not for them, Sri Lanka would be suffering beyond comprehension today. Had we listened to the public health experts and given them a role in leading these brave men and women, perhaps we would have ranked among the countries that successfully defeated Covid-19 and prevented its resurgence. Alas, a willingness to defer to professionals over politicians and charlatans is all that separated Sri Lanka from those countries that managed to beat back the pandemic.
Covid-19 does not care what goes into a pot or who throws it into a river, nor will the virus be deterred in the slightest by any ingredient of this ridiculous ‘paniya’ that is being peddled in the halls of Parliament and receiving a shocking amount of tacit endorsement from officials and public figures who should know better. It was horrifying to watch political leaders, members of the clergy and media institutions promote a completely untested concoction and encourage people to gather in crowds at great risks to themselves and the public unchallenged, all while the police continue to arrest those who break quarantine and social distancing rules for the far more noble purpose of providing for their families.
The fact that none but a few brave doctors has stood up to condemn this charade painted a very bleak picture of not just our country but its one-of-a-kind healthcare system. Our country built this exemplary healthcare system on a foundation of science, rationalism and professionalism. It should be the pride of our people. It is the duty of all patriotic professionals to condemn and shun any swindler or witchdoctor who undermines our health services by peddling such dangerous miracle cures or concoctions. Doctors have a particular duty to speak out against such superstition when it will put the lives of their own colleagues and patients in peril.
With the new year comes new opportunities to put our past failures and mistakes behind us and chart a new course. 2021 can be a different, prosperous year, if we resolve as a country to insist that our leaders put professionals first and promote rationalism over junk science. Now that several options for Covid-19 vaccines will be available in 2021, our public health service will have an opportunity this year to flex its muscles and deploy one of the most efficient mass immunization programs in the world.
Anyone who is even contemplating taking this responsibility away from the national health service and entrusting it to some new ‘task force’ or other body should know that Sri Lanka’s national immunization program, run by the health service, has long been one of the most efficient of any country. Even if Sri Lanka is late to get stocks of the vaccine, we have an opportunity to put ‘paniyas’ behind us by efficiently immunizing every single Sri Lankan against Covid-19.
As a nation that cares for its people, wherever they may live, Sri Lanka even has an opportunity to do right by those of our countrymen stranded abroad with no way to return, by efficiently deploying vaccine stocks and coordinating the immunization of Sri Lankans worldwide through our network of embassies and consulates. It is by doing such things that the government can redeem the confidence of its people and assert a role on the world stage as a country that nurtures its citizens and takes its responsibilities seriously.
2020 was marred by deception, partisan politics and economic uncertainty on top of Covid-19, making it one of the darkest years in living memory. While the poorest of poor took the brunt of the suffering, there was no shortage of fly-by-night businessmen who lost no time in taking advantage of your suffering, to pull off quick deals and make a fast buck, whether by manipulation of tariffs, tourism or other short-sighted tomfoolery with no regard for the credibility of our country.
Hopefully, in 2021, we can look forward to a culture of business leaders who earn and grow their fortunes by investing in the country, building a product or providing a service by employing Sri Lankans, rather than running behind wheeler dealers who use political connections to manipulate markets and regulations and score a quick buck at the cost of the public coffers.
For Sri Lanka to recover and transform its economy in a post-Covid world, we need to see fewer dirty deals and conmen healers and hear fewer ‘gotcha’ soundbites from politicians. In December 2019, many professionals and business leaders expected politicians to magically turn the country around in 2020. In 2021, it is their time to step up and make it happen. If they lead, politicians and officials will follow.
Last year, our doctors, nurses and PHIs stepped up to the plate and earned their role in history by putting their professionalism and duty above all other considerations and refusing to bow to pressure from any quarter. In 2021, let us hope that all professionals and leaders, whether in business, politics, the public service, judiciary, media or prosecutors, follow the example set by our doctors and make 2021 the year for all Sri Lankan professionals.
When I am writing for January 1, 2022, I am hopeful that this year will bring so many acts of courage, professionalism, integrity, conscience and ingenuity that I will be hard pressed to single out any single class of professionals to dedicate the year 2021 to.
Features
Beyond Left and Right: From Populism to Pragmatism and Recalibrating Democracy

The world is going through a political shake-up. Everywhere you look—from Western democracies to South Asian nations—people are choosing leaders and parties that seem to clash in ideology. One moment, a country swings left, voting for progressive policies and climate action. The next, a neighbouring country rushes into the arms of right-wing populism, talking about nationalism and tradition.
It’s not just puzzling—it’s historic. This global tug of war between opposing political ideas is unlike anything we’ve seen in recent decades. In this piece, I explore this wave of political contradictions, from the rise of labour movements in Australia and Canada, to the continued strength of conservative politics in the US and India, and finally to the surprising emergence of a radical leftist party in Sri Lanka.
Australia and Canada: A Comeback for Progressive Politics
Australia recently voted in the Labour Party, with Anthony Albanese becoming Prime Minister after years of conservative rule under Scott Morrison. Albanese brought with him promises of fairer wages, better healthcare, real action on climate change, and closing the inequality gap. For many Australians, it was a fresh start—a turn away from business-as usual politics.
In Canada, a political shift is unfolding with the rise of The Right Honourable Mark Carney, who became Prime Minister in March 2025, after leading the Liberal Party. Meanwhile, Jagmeet Singh and the New Democratic Party (NDP) are gaining traction with their progressive agenda, advocating for enhanced social safety nets in healthcare and housing to address growing frustrations with rising living costs and a strained healthcare system..
But let’s be clear—this isn’t a return to old-school socialism. Instead, voters seem to be leaning toward practical, social-democratic ideas—ones that offer government support without fully rejecting capitalism. People are simply fed up with policies that favour the rich while ignoring the struggles of everyday families. They’re calling for fairness, not radicalism.
America’s Rightward Drift: The Trump Effect Still Lingers
In contrast, the political story in the United States tells a very different tale. Even after Donald Trump left office in 2020, the Republican Party remains incredibly powerful—and popular.
Trump didn’t win hearts through traditional conservative ideas. Instead, he tapped into a raw frustration brewing among working-class Americans. He spoke about lost factory jobs, unfair trade deals, and an elite political class that seemed disconnected from ordinary life. His messages about “America First” and restoring national pride struck a chord—especially in regions hit hard by globalisation and automation.
Despite scandals and strong opposition, Trump’s brand of politics—nationalist, anti-immigration, and skeptical of global cooperation—continues to dominate the Republican Party. In fact, many voters still see him as someone who “tells it like it is,” even if they don’t agree with everything he says.
It’s a sign of a deeper trend: In the US, cultural identity and economic insecurity have merged, creating a political environment where conservative populism feels like the only answer to many.
India’s Strongman Politics: The Modi Era Continues
Half a world away, India is witnessing its own version of populism under Prime Minister Narendra Modi. His party—the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)—has ruled with a blend of Hindu nationalism, economic ambition, and strong leadership.
Modi is incredibly popular. His supporters praise his development projects, digital push, and efforts to raise India’s profile on the global stage. But critics argue that his leadership is dividing the country along religious lines and weakening its long-standing secular values.
Still, for many Indians—especially the younger generation and the rural poor—Modi represents hope, strength, and pride. They see him as someone who has delivered where previous leaders failed. Whether it’s building roads, providing gas connections to villages, or cleaning up bureaucracy, the BJP’s strong-arm tactics have resonated with large sections of the population.
India’s political direction shows how nationalism can be powerful—especially when combined with promises of economic progress and security.
A Marxist Comeback? Sri Lanka’s Political Wild Card
Then there’s Sri Lanka—a country in crisis, where politics have taken a shocking turn.
For decades, Sri Lanka was governed by familiar faces and powerful families. But after years of financial mismanagement, corruption, and a devastating economic collapse, public trust in mainstream parties has plummeted. Into this void stepped a party many thought had been sidelined for good—the Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP), a Marxist-Leninist group with a history of revolutionary roots.
Once seen as radical and even dangerous, the JVP has rebranded itself as a disciplined, modern political force. Today, it speaks directly to the country’s suffering masses: those without jobs, struggling to buy food, and fed up with elite corruption.
The party talks about fair wealth distribution, workers’ rights, and standing up to foreign economic pressures. While their ideas are left-leaning, their growing support is driven more by public frustration with current political leaders than by any shift toward Marxism by the public or any move away from it by the JVP.
Sri Lanka’s case is unique—but not isolated. Across the world, when economies collapse and inequality soars, people often turn to ideologies that offer hope and accountability—even if they once seemed extreme.
A Global Puzzle: Why Are Politics So Contradictory Now?
So what’s really going on? Why are some countries swinging left while others turn right?
The answer lies in the global crises and rapid changes of the past two decades. The 2008 financial crash, worsening inequality, mass migrations, terrorism fears, the COVID-19 pandemic, and now climate change have all shaken public trust in traditional politics.
Voters everywhere are asking the same questions: Who will protect my job? Who will fix healthcare? Who will keep us safe? The answers they choose depend not just on ideology, but on their unique national experiences and frustrations.
In countries where people feel abandoned by global capitalism, they may choose left-leaning parties that promise welfare and fairness. In others, where cultural values or national identity feel under threat, right-wing populism becomes the answer.
And then there’s the digital revolution. Social media has turbocharged political messaging. Platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube allow both left and right movements to reach people directly—bypassing traditional media. While this has given power to progressive youth movements, it’s also allowed misinformation and extremist views to flourish, deepening polarisation.
Singapore: The Legacy of Pragmatic Leadership and Technocratic Governance
Singapore stands as a unique case in the global political landscape, embodying a model of governance that blends authoritarian efficiency with capitalist pragmatism. The country’s political identity has been shaped largely by its founding Prime Minister, Lee Kuan Yew, often regarded as a political legend for transforming a resource-poor island into one of the most prosperous and stable nations in the world. His brand of leadership—marked by a strong central government, zero tolerance for corruption, and a focus on meritocracy—has continued to influence Singapore’s political ideology even after his passing. The ruling People’s Action Party (PAP), which has been in power since independence, remains dominant, but it has had to adapt to a new generation of voters demanding more openness, transparency, and participatory governance.
Despite criticisms of limited political pluralism, Singapore’s model is often admired for its long-term planning, public sector efficiency, and ability to balance rapid economic development with social harmony. In an era of rising populism and political fragmentation elsewhere, Singapore’s consistent technocratic approach provides a compelling counter-narrative—one that prioritises stability, strategic foresight, and national cohesion over ideological extremes.
What the Future Holds
We are living in a time where political boundaries are blurring, and old labels don’t always fit. Left and right are no longer clear-cut. Populists can be socialist or ultra-conservative. Liberals may support strong borders. Conservatives may promote welfare if it wins votes.
What matters now is trust—people are voting for those who seem to understand their pain, not just those with polished manifestos.
As economic instability continues and global challenges multiply, this ideological tug-of-war is likely to intensify. Whether we see more progressive reforms or stronger nationalist movements will depend on how well political leaders can address real issues, from food security to climate disasters.
One thing is clear: the global political wave is still rising. And it’s carrying countries in very different directions.
Conclusion
The current wave of global political ideology is defined by its contradictions, complexity, and context-specific transformations. While some nations are experiencing a resurgence of progressive, left-leaning movements—such as Australia’s Labour Party, Canada’s New Democratic Party, and Sri Lanka’s Marxist-rooted JVP—others are gravitating toward right-wing populism, nationalist narratives, and conservative ideologies, as seen in the continued strength of the US Republican Party and the dominant rule of Narendra Modi’s BJP in India. Amid this ideological tug-of-war, Singapore presents a unique political model. Eschewing populist swings, it has adhered to a technocratic, pragmatic form of governance rooted in the legacy of Lee Kuan Yew, whose leadership transformed a struggling post-colonial state into a globally admired economic powerhouse. Singapore’s emphasis on strategic planning, meritocracy, and incorruptibility provides a compelling contrast to the ideological turbulence in many democracies.
What ties these divergent trends together is a common undercurrent of discontent with traditional politics, growing inequality, and the digital revolution’s impact on public discourse. Voters across the world are searching for leaders and ideologies that promise clarity, security, and opportunity amid uncertainty. In mature democracies, this search has split into dual pathways—either toward progressive reform or nostalgic nationalism. In emerging economies, political shifts are even more fluid, influenced by economic distress, youth activism, and demands for institutional change.
Ultimately, the world is witnessing not a single ideological revolution, but a series of parallel recalibrations. These shifts do not point to the triumph of one ideology over another, but rather to the growing necessity for adaptive, responsive, and inclusive governance. Whether through leftist reforms, right-wing populism, or technocratic stability like Singapore’s, political systems will increasingly be judged not by their ideological purity but by their ability to address real-world challenges, unite diverse populations, and deliver tangible outcomes for citizens. In that respect, the global political wave is not simply a matter of left vs. right—it is a test of resilience, innovation, and leadership in a rapidly evolving world.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT , Malabe. He is also the author of the “Doing Social Research and Publishing Results”, a Springer publication (Singapore), and “Samaja Gaveshakaya (in Sinhala). The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the institution he works for. He can be contacted at saliya.a@slit.lk and www.researcher.com)
Features
An opportunity to move from promises to results

The local government elections, long delayed and much anticipated, are shaping up to be a landmark political event. These elections were originally due in 2023, but were postponed by the previous government of President Ranil Wickremesinghe. The government of the day even defied a Supreme Court ruling mandating that elections be held without delay. They may have feared a defeat would erode that government’s already weak legitimacy, with the president having assumed office through a parliamentary vote rather than a direct electoral mandate following the mass protests that forced the previous president and his government to resign. The outcome of the local government elections that are taking place at present will be especially important to the NPP government as it is being accused by its critics of non-delivery of election promises.
Examples cited are failure to bring opposition leaders accused of large scale corruption and impunity to book, failure to bring a halt to corruption in government departments where corruption is known to be deep rooted, failure to find the culprits behind the Easter bombing and failure to repeal draconian laws such as the Prevention of Terrorism Act. In the former war zones of the north and east, there is also a feeling that the government is dragging its feet on resolving the problem of missing persons, those imprisoned without trial for long periods and return of land taken over by the military. But more recently, a new issue has entered the scene, with the government stating that a total of nearly 6000 acres of land in the northern province will be declared as state land if no claims regarding private ownership are received within three months.
The declaration on land to be taken over in three months is seen as an unsympathetic action by the government with an unrealistic time frame when the land in question has been held for over 30 years under military occupation and to which people had no access. Further the unclaimed land to be designated as “state land” raises questions about the motive of the circular. It has undermined the government’s election campaign in the North and East. High-level visits by the President, Prime Minister, and cabinet ministers to these regions during a local government campaign were unprecedented. This outreach has signalled both political intent and strategic calculation as a win here would confirm the government’s cross-ethnic appeal by offering a credible vision of inclusive development and reconciliation. It also aims to show the international community that Sri Lanka’s unity is not merely imposed from above but affirmed democratically from below.
Economic Incentives
In the North and East, the government faces resistance from Tamil nationalist parties. Many of these parties have taken a hardline position, urging voters not to support the ruling coalition under any circumstances. In some cases, they have gone so far as to encourage tactical voting for rival Tamil parties to block any ruling party gains. These parties argue that the government has failed to deliver on key issues, such as justice for missing persons, return of military-occupied land, release of long-term Tamil prisoners, and protection against Buddhist encroachment on historically Tamil and Muslim lands. They make the point that, while economic development is important, it cannot substitute for genuine political autonomy and self-determination. The failure of the government to resolve a land issue in the north, where a Buddhist temple has been put up on private land has been highlighted as reflecting the government’s deference to majority ethnic sentiment.
The problem for the Tamil political parties is that these same parties are themselves fractured, divided by personal rivalries and an inability to form a united front. They continue to base their appeal on Tamil nationalism, without offering concrete proposals for governance or development. This lack of unity and positive agenda may open the door for the ruling party to present itself as a credible alternative, particularly to younger and economically disenfranchised voters. Generational shifts are also at play. A younger electorate, less interested in the narratives of the past, may be more open to evaluating candidates based on performance, transparency, and opportunity—criteria that favour the ruling party’s approach. Its mayoral candidate for Jaffna is a highly regarded and young university academic with a planning background who has presented a five year plan for the development of Jaffna.
There is also a pragmatic calculation that voters may make, that electing ruling party candidates to local councils could result in greater access to state funds and faster infrastructure development. President Dissanayake has already stated that government support for local bodies will depend on their transparency and efficiency, an implicit suggestion that opposition-led councils may face greater scrutiny and funding delays. The president’s remarks that the government will find it more difficult to pass funds to local government authorities that are under opposition control has been heavily criticized by opposition parties as an unfair election ploy. But it would also cause voters to think twice before voting for the opposition.
Broader Vision
The government’s Marxist-oriented political ideology would tend to see reconciliation in terms of structural equity and economic justice. It will also not be focused on ethno-religious identity which is to be seen in its advocacy for a unified state where all citizens are treated equally. If the government wins in the North and East, it will strengthen its case that its approach to reconciliation grounded in equity rather than ethnicity has received a democratic endorsement. But this will not negate the need to address issues like land restitution and transitional justice issues of dealing with the past violations of human rights and truth-seeking, accountability, and reparations in regard to them. A victory would allow the government to act with greater confidence on these fronts, including possibly holding the long-postponed provincial council elections.
As the government is facing international pressure especially from India but also from the Western countries to hold the long postponed provincial council elections, a government victory at the local government elections may speed up the provincial council elections. The provincial councils were once seen as the pathway to greater autonomy; their restoration could help assuage Tamil concerns, especially if paired with initiating a broader dialogue on power-sharing mechanisms that do not rely solely on the 13th Amendment framework. The government will wish to capitalize on the winning momentum of the present. Past governments have either lacked the will, the legitimacy, or the coordination across government tiers to push through meaningful change.
Obtaining the good will of the international community, especially those countries with which Sri Lanka does a lot of economic trade and obtains aid, India and the EU being prominent amongst these, could make holding the provincial council elections without further delay a political imperative. If the government is successful at those elections as well, it will have control of all three tiers of government which would give it an unprecedented opportunity to use its 2/3 majority in parliament to change the laws and constitution to remake the country and deliver the system change that the people elected it to bring about. A strong performance will reaffirm the government’s mandate and enable it to move from promises to results, which it will need to do soon as mandates need to be worked at to be long lasting.
by Jehan Perera
Features
From Tank 590 to Tech Hub: Reunited Vietnam’s 50-Year Journey

 The fall of Saigon (now Ho Chi Minh City – HCM) on 30 April 1975 marked the end of Vietnam’s decades-long struggle for liberation—first against French colonialism, then U.S. imperialism. Ho Chi Minh’s Viet Minh, formed in 1941, fought Japanese occupiers and later defeated France at Dien Bien Phu (1954). The Geneva Accords temporarily split Vietnam, with U.S.-backed South Vietnam blocking reunification elections and reigniting conflict.
The fall of Saigon (now Ho Chi Minh City – HCM) on 30 April 1975 marked the end of Vietnam’s decades-long struggle for liberation—first against French colonialism, then U.S. imperialism. Ho Chi Minh’s Viet Minh, formed in 1941, fought Japanese occupiers and later defeated France at Dien Bien Phu (1954). The Geneva Accords temporarily split Vietnam, with U.S.-backed South Vietnam blocking reunification elections and reigniting conflict.
The National Liberation Front (NLF) led resistance in the South, using guerrilla tactics and civilian support to counter superior U.S. firepower. North Vietnam sustained the fight via the Ho Chi Minh Trail, despite heavy U.S. bombing. The costly 1968 Tet Offensive exposed U.S. vulnerabilities and shifted public opinion.
Of even more import, the Vietnam meat-grinder drained the U.S. military machine of weapons, ammunition and morale. By 1973, relentless resistance forced U.S. withdrawal. In March 1975, the Vietnamese People’s Army started operations in support of the NLF. The U.S.-backed forces collapsed, and by 30 April the Vietnamese forces forced their way into Saigon.
At 11 am, Soviet-made T-54 tank no. 843 of company commander Bui Quang Than rammed into a gatepost of the presidential palace (now Reunification Palace). The company political commissar, Vu Dang Toan, following close behind in his Chinese-made T-59 tank, no. 390, crashed through the gate and up to the palace. It seems fitting that the tanks which made this historic entry came from Vietnam’s principal backers.
Bui Quang Than bounded from his tank and raced onto the palace rooftop to hoist the NLF flag. Meanwhile, Vu Dang Toan escorted the last president of the U.S.-backed regime, Duong Van Minh, to a radio station to announce the surrender of his forces. This surrender meant the liberation not only of Saigon but also of the entire South, the reunification of the country, and a triumph of perseverance—a united, independent nation free from foreign domination after a 10,000-day war.
Celebrations
On 30 April 2025, Vietnam celebrated the 50th anniversary of the Liberation of the South and National Reunification. HCM sprouted hundreds of thousands of national flags and red hammer-and-sickle banners, complemented by hoardings embellished with reminders of the occasion – most of them featuring tank 590 crashing the gate.
Thousands of people camped on the streets from the morning of 29 April, hoping to secure good spots to watch the parade. Enthusiasm, especially of young people, expressed itself by the wide use of national flag t-shirts, ao dais (traditional long shirts over trousers), conical hats, and facial stickers. This passion may reflect increasing prosperity in this once impoverished land.
The end of the war found Vietnam one of the poorest countries in the world, with a low per capita income and widespread poverty. Its economy struggled due to a combination of factors, including wartime devastation, a lack of foreign investment and heavy reliance on subsistence agriculture, particularly rice farming, which limited its potential for growth. Western sanctions meant Vietnam relied heavily on the Soviet Union and its socialist allies for foreign trade and assistance.
The Vietnamese government launched Five-Year Plans in agriculture and industry to recover from the war and build a socialist nation. While encouraging family and collective economies, it restrained the capitalist economy. Despite these efforts, the economy remained underdeveloped, dominated by small-scale production, low labour productivity, and a lack of modern technology. Inflexible central planning, inept bureaucratic processes and corruption within the system led to inefficiencies, chronic shortages of goods, and limited economic growth. As a result, Vietnam’s economy faced stagnation and severe hyperinflation.
These mounting challenges prompted the Communist Party of Vietnam to introduce Đổi Mới (Renovation) reforms in 1986. These aimed to transition from a centrally planned economy to a “socialist-oriented market economy” to address inefficiencies and stimulate growth, encouraging private ownership, economic deregulation, and foreign investment.
Transformation
Đổi Mới marked a historic turning point, unleashing rapid growth in agricultural output, industrial expansion, and foreign direct investment. Early reforms shifted agriculture from collective to household-based production, encouraged private enterprise, and attracted foreign investment. In the 2000s, Vietnam became a top exporter of textiles, electronics, and rice, shifting towards high-tech manufacturing (inviting Samsung and Intel factories). By the 2020s, it emerged as a global manufacturing hub, the future focus including the digital economy, green energy, and artificial intelligence.
In less than four decades, Vietnam transformed from a poor, agrarian nation into one of Asia’s fastest-growing economies, though structural reforms are still needed for sustainable development. Growth has remained steady, at 5-8% per year.
Vietnam’s reforms lifted millions out of poverty, created a dynamic export-driven economy, and improved education, healthcare, and infrastructure. This has manifested itself in reducing extreme poverty from 70% to 1%, increasing literacy to 96%, life expectancy from 63 to 74 years, and rural electrification from less than 50% to 99.9%. Industrialisation drove urbanisation, which doubled from 20% in 1986 to 40% now.
This change displayed itself during the celebrations in HCM, amid skyscrapers, highways and the underground metro system. Everybody dressed well, and smartphones could be seen everywhere – penetration has reached three-fourths of the population. Thousands turned out on motorbikes and scooters (including indigenous electric scooters) – two-wheeler ownership is over 70%, the highest rate per capita in ASEAN. Traffic jams of mostly new cars emphasised the growth of the middle class.
At the same time, street food vendors and makeshift pavement bistro owners joined sellers of patriotic hats, flags and other paraphernalia to make a killing from the revellers. This reflects the continuance of the informal sector– currently representing 30% of the economy.
The Vietnamese government channelled tax income from booming sectors into underdeveloped regions, investing in rural infrastructure and social welfare to balance growth and mitigate urban-rural inequality during rapid economic expansion. Nevertheless, this economic transformation came with unequal benefits, exacerbating income inequality and persistent gender gaps in wages and opportunities. Sustaining growth requires tackling corruption, upgrading workforce skills, and balancing development with inequality.
NLF flag

Tank 390 courtesy Bao Hai Duong
The parade itself, meticulously carried out (having been rehearsed over three days), featured cultural pageants and military displays and drew admiration. Of special note, the inclusion of foreign military contingents from China, Laos, and Cambodia for the first time signalled greater regional solidarity, acknowledging their historical support while maintaining a balanced foreign policy approach.
Veteran, war-era foreign journalists noted another interesting fact: the re-emergence of the NLF flag. Comprising red and blue stripes with a central red star, this flag had never been prominent at the ten-year anniversary celebrations. The journalists questioned its sudden reappearance. It may be to give strength to the idea of the victory being one of the South itself, part of a drive to increase unity between North and South.
Before reunification in 1975, North and South Vietnam embodied starkly contrasting economic and social models. The North operated under a centrally planned socialist system, with collectivised farms and state-run industries. It emphasised egalitarianism, mass education, and universal healthcare while actively preserving traditional Vietnamese culture. The South, by contrast, maintained a market-oriented economy heavily reliant on agricultural exports (rice and rubber) and foreign aid. A wealthy elite dominated politics and commerce, while Western—particularly American—cultural influence grew pervasive during the war years.
Following reunification under the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (1976), the government moved swiftly to integrate the two regions. In 1978, it introduced a unified national currency (the đồng, VND), merging the North’s and South’s financial systems into a single, state-controlled framework. The unification of monetary policy symbolised the broader ideological project: to erase colonial and capitalist legacies.
Unity and solidarity
However, the economic disparities and cultural divides between regions persist, though less pronounced than before. The South, particularly HCM, remains Vietnam’s economic powerhouse, with a stronger private sector and international trade connections. The North, including Hanoi, has a more government-driven economy. Southerners tend to have a more entrepreneurial mindset, while Northerners are often seen as more traditional and rule-bound. Conversely, individuals from the North occupy more key government positions.
Studies suggest that people in the South exhibit lower trust in the government compared to those in the North. HCM tends to have stronger support for Western countries like the United States, while Hanoi has historically maintained closer ties with China. People in HCM tend to use the old “Saigon” city name.
Consequently, the 50th anniversary celebrations saw a focus on reconciliation and unity, reflecting a shift in perspective towards peace and friendship, as well as accompanying patriotism with international solidarity.
The exuberant crowds, modern infrastructure, and thriving consumer economy showcased the transformative impact of Đổi Mới—yet lingering regional disparities, informal labour challenges, and unequal gains remind the nation that sustained progress demands inclusive reforms. The symbolic return of the NLF flag and the emphasis on unity underscored a nuanced reconciliation between North and South, honouring shared struggle while navigating enduring differences.
As Vietnam strides forward as a rising Asian economy, it balances its socialist legacy with global ambition, forging a path where prosperity and patriotism converge. The anniversary was not just a celebration of the past but a reflection on the complexities of Vietnam’s ongoing evolution.
(Vinod Moonesinghe read mechanical engineering at the University of Westminster, and worked in Sri Lanka in the tea machinery and motor spares industries, as well as the railways. He later turned to journalism and writing history. He served as chair of the Board of Governors of the Ceylon German Technical Training Institute. He is a convenor of the Asia Progress Forum, which can be contacted at asiaprogressforum@gmail.com.)
By Vinod Moonesinghe
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoOTRFU Beach Tag Rugby Carnival on 24th May at Port City Colombo
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoRanil’s Chief Security Officer transferred to KKS
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoRemembering Dr. Samuel Mathew: A Heart that Healed Countless Lives
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAitken Spence Travels continues its leadership as the only Travelife-Certified DMC in Sri Lanka
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe Broken Promise of the Lankan Cinema: Asoka & Swarna’s Thrilling-Melodrama – Part IV
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoRadisson Blu Hotel, Galadari Colombo appoints Marko Janssen as General Manager
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoCCPI in April 2025 signals a further easing of deflationary conditions
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA piece of home at Sri Lankan Musical Night in Dubai












