Features
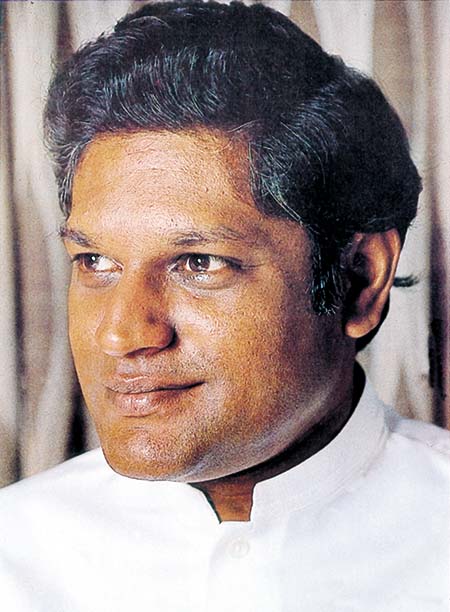
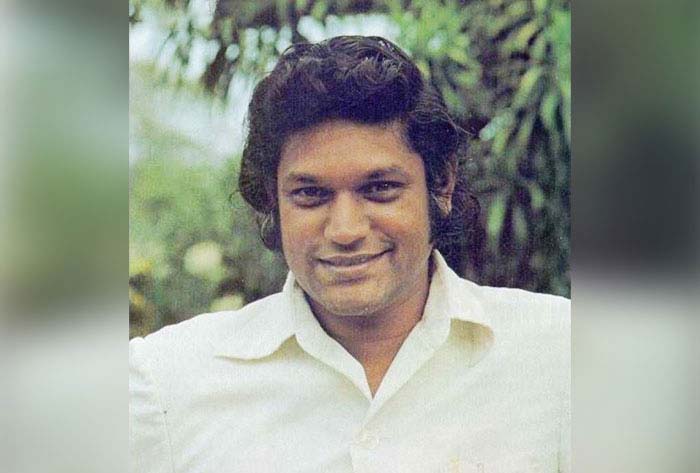
Upali Wijewardene – an enigma and a legend

by Ajith Samaranayake
Between Sri Lanka’s 35th independence anniversary and his birthday Upali Wijewardene boarded his executive Lear Jet at Kuala Lumpur and in a single fateful flash became solidified into an enigma and a legend. The flamboyant tycoon who had left with five others never arrived in Colombo. Somewhere over the Straits of Malacca the plane disappeared with not a clue or a trace.
The drama held the nation in its grip for months. Newspapers reported little else except the mystery of the disappearance. Speculation spread like a bush fire and as the days passed with no news the most fantastic cloak and dagger theories were spun. People gathered by the roadside to listen to the radio news bulletins and strangers become friends as they speculated about the fate of a man who was one of Sri Lanka’s most beloved sons.
Destined
For Philip Upali Wijewardene it was a strangely fitting apotheosis. It was as if his whole colourful career was destined for this final peak, this sudden and dramatic exit just as he was in the very centre of the public eye, a glorious accession to the heights of myth and legend.
For Upali’s life was of the kind which dreams are made of. Though born to one of the most distinguished families in Colombo and into a charmed circle which constituted Sri Lanka’s ruling elite, Upali had carved out a career in an area totally out of synch with that class. He did not take to law or medicine or pursue an academic career as the more favoured sons of this affluent, anglicised and genteel elite were wont to do. Neither did he take to politics.
On the contrary with nothing much except the most rudimentary capital and confidence in his own abilities he began a confectionery industry and business in a part of his ancestral home where such brushes with crude commerce had never before taken place. Down the years this fledgling business he was able to build and expand into a mighty conglomerate, Sri Lanka’s only multinational, until he acquired a worldwide reputation as Sri Lanka’s leading entrepreneur, an enterprising and shrewd businessman who could hold his own with the best of them in New York, London or Bonn.
But by February 13, that fateful day which again confirmed the hold of superstition, Upali’s mind was not preoccupied with his businesses alone. For about two years politics had replaced business as his central passion. The man who had conquered the commanding heights of commerce now wanted to conquer the commanding heights of politics. And like everything else he did, he wanted to do it soon.
In 1981 he had founded The Island and the Divaina which had immediately become the eye of the political storm. Their vigorous reporting and comments which did not spare even some of the most powerful politicians of the ruling UNP came as a stirring antidote to the flabby, tame-cat Lake House press which was then dominating journalism.
Readers lapped up the new offerings avidly. Upali Wijewardene’s name was bandied about freely in Parliament. He made no secret of the fact that he wanted to enter Parliament and become finance minister which raised the hackles of the Finance Minister, the fiercely combative Mr. Ronnie de Mel. It became quite commonplace for the bespectacled and owlish Minister to hurl fearsome thunderbolts at the absent Upali in Parliament while we parliamentary reporters of The Island in the absence of our owner became surrogates for the ministerial fury and the embarrassed focus of the eyes of our colleagues in the crowded press gallery of the old Parliament by the sea.
Following year
The following year was to be one of the most crucial in Sri Lanka’s politics. President Jayewardene, Upali’s cousin and mentor, called an early Presidential Election, and in the absence of his normal rival Mrs. Sirima Bandaranaike, incapacitated by her loss of civic rights, easily beat former Minister Hector Kobbekoduwa fielded by an SLFP in tatters.
Then claiming that there was a Naxalite conspiracy to assassinate him if he had lost and claiming further that if General Elections were held on schedule a sizeable number of these horrendous Naxalites would enter Parliament he held a Referendum which the UNP won amidst widespread claims of thuggery, ballot-rigging, etc.
Anyway Upali was loyally by Jayewardene’s side during both campaigns, campaigning vigorously for the UNP at Kamburupitiya, his mother’s ancestral village, for which he had done much through his Ruhunu Udanaya programme for improving the conditions of villages in the South. The south he considered his heartland and it was from the South that he sought to enter Parliament for which there were vacancies even as he boarded his Lear Jet that day in the Malaysian capital.
Elections
For what had happened was that Jayewardene had asked for and received the resignations of 17 members of Parliament who had lost their electorates at the Referendum. Parliament had just been convened for the new session of the Second Jayewardene Presidency and the guns had boomed and the Jayamangala Gathas had been chanted. As that irrepressible Communist MP, the much lamented late Sarath Muttettuwegama quipped, “There was a 21-gun salute only the other day. And now 17 of you are gone.” Among the vacancies were Kamburupitiya and Devinuwara either of which Upali was planning to contest.
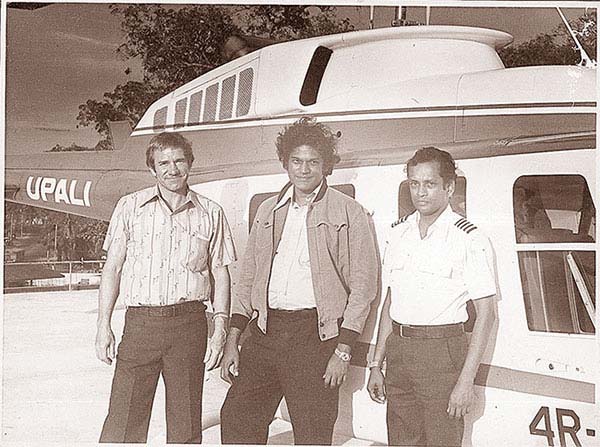
This was the backdrop to Upali’s destiny which during the next few weeks would hold the nation in its grip and virtually bring the country to a standstill. Among those on board with Upali in the plane which had left Malaysia’s Subang Airport at 8.41 p.m. on February 13 were Mr. Ananda Pelimuhandiram, the whiz kid Financial Director of the Upali Group and one of his most trusted lieutenants, a Malaysian lawyer Mr. S. M. Ratnam and Steward Mr. A. Senanayake. The jet was piloted by Capt. Noel Anandappa with Mr. Sidney de Zoysa as co-pilot.
They were to have reached Colombo by 9.45 p.m. that night but they did not come. Neither did they come the next day. By the morning of Monday February 14 Colombo was agog with the news. Soon it spread everywhere and the people paused in awe and wonderment as the enormity of the event sank into the public consciousness. Upali Wijewardene had mysteriously vanished with his three companions and two navigators leaving not a clue behind somewhere in that vast and empty night sky over Malaysia.
On Tuesday February 15 The Island, ‘Upali’s beloved flagship, broke the news soberly. Over a banner headline “Plane carrying Upali Wijewardene feared lost”. it told its readers that the jet had lost radio contact with the airport just 15 minutes after take off. The last message had said that the aircraft was at an altitude of 27,000 feet. Indonesia and Malaysia had launched a joint air and sea search operation but had failed to find any debris of an aircraft.
At The Island that Monday it was like something out of a novel by Kafka. We were in a daze. Was it possible that six people on board an aircraft in this miraculous age of technology could disappear without a trace? People huddled about the corridors talking, absorbing the news only slowly while the telephones rang incessantly as the other newspapers were getting in touch with us for the latest. But we could do little to shed light on the mystery. The most intensive search by several governments could not yield a single clue. These headlines from the papers which followed convey the flavour of those bizarre days.
February 16 —Air, sea search for Upali Wijewardene continues. Aussie plane may have seen missing jet
February 17— Three planes with sophisticated equipment comb the ocean. No results yet from seven-notion search
A flare and a weak signal but search proves negative. Search for missing plane in Andaman Island.
February 18 – Search for missing jet narrows to coastal area round Sumatra. Lear Jet reps suspect sabotage.
Wreckage
On the same day something happened which could well have been the tragic denouement of the whole drama but which was aborted at the last moment. On the afternoon of that Friday a Reuter report was received that the wreckage of the private jet and several bodies had been found off the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
I was in Fort at the time having taken a brief respite from the bleak house at Bloemendhal Road. With me at one of Fort’s many hospitable hostelries where we were drinking more than usual was Joe Segera, the Daymon Runyonesque Lake House story teller and chronicler of Canal Row and Chandra S. Perera, the always nattily-dressed NBC reporter and man about town.
Slowly the story spread through Canal Row, Hospital Street and Baillie Street and people reacted with shock and grief. More pints were drunk and our senses numbed somewhat by what we had taken Chandra who had known Upali in London and had common friends with him and I repaired to Bloemendhal Road.
There we were told by Editor Vijitha Yapa who had worked frenziedly during those days to bring out the paper in the midst of the tension that Reuter had denied the story within the hour. The next day The Island reported that it had been besieged with telephone calls following the story breaking. Reuters, Hong Kong had been contacted and The Island told ‘The story will be held back’, it reported.
And so the days passed. More headlines.
February 19 — Divers too join search near Sumatra. Another frustrating day of search
February 21 — Top Sri Lanka cops arrive in KL for investigation
Sabotage not ruled out
February 22 — Wheel found by fishermen did come from Lear Jet. Oil slick found near Kumana not from Lear Jet. February 23 —Minesweepers deployed in Indonesia today to find Jet Identification of Lear Jet wheel narrows search area. February 24 — If Lear Jet wheel was spare explosion may have occurred
February 25 —Fishermen cleared: Minesweeper move into find jet. There was no black box on missing Lear Jet. February 26 — PM answers questions on Upali
Unsolved
And so that unusually short month petered out sadly with the riddle unsolved. On the last day of February The Island headline was ‘Lalith thinks sabotage is likely cause of crash’. Under the by line of Lasantha Wickremetunge it said that the then Minister of Trade and Shipping Lalith Athulathmudali who had returned from Indonesia on February 26 as President Jayewardene’s special envoy had said that there were three possibilities for the disappearance of which the most likely was sabotage. Of the other possibilities, pilot error and a defect in the aircraft were most unlikely.
Mr. Athulathmudali also stressed that his investigations had shown that Mr. Wijewardene had no commercial enemies. In a box in the same story the paper reported ‘Temporary halt to search’ saying that since the area searched by the minesweeper had yielded no clues the search; was being abandoned and would resume if fresh evidence is uncovered. Only a single wheel — the right outbourne wheel — of the whole aircraft was found.
And so ended a drama which had electrified the country that cruel month of February and still continues to bemuse the people. What happened to Upali? is still the most popular question asked by friends and acquaintances from anybody connected with the Upali Group. Upali fascinated the people in life and now that he is no longer to be found, lost somewhere in the vast ethereal emptiness, he has become a legend and a cult which continues to enthral the people.
What would have happened if he had arrived in Colombo that February night with politics entering a fresh phase and plunged into what would have undoubtedly been a stormy political career will remain one of the most fascinating “Ifs”, of our contemporary political history.
Enigmatic fate
But what is clear is that the enigmatic fate of the man who built a commercial empire from nothing and captured a nation’s heart will always be looked upon with wonderment by them. Whether Upali could have stormed the commanding heights of politics by using the methods of advertising and self-promotion which he so successfully used in his business enterprises we will never know. Yet, like Icarus who flew but went too close to the sun so that his wings melted, the strange and fascinating destiny of Upali Wijewardene, Sri Lanka’s first tycoon who also chose the sun as his symbol, will always be a glorious legend of our times.
Newspaper
Looking back across ten more eventful years several memories crowd the mind. The memory which stands out most prominently is that of the collective effort to bring out the paper in the midst of the most terrible tension which could have pervaded any newspaper office. Editor Vijitha Yapa who was a loyal friend of Upali had to battle his feelings while he held the fort in the news room keeping in constant touch with the latest developments and answering the questions of local and foreign journalists.
For him and Deputy Editor and News Editor Gamini Weerakoon it was a trial of endurance which they magnificently stood up to. Looking at the paper to which thousands turned during that fateful month for news of its proprietor there is no sign of the almost unbearable tension with which we were working.
Upali Mahattaya
Several days on end we did not go home and the bleak reaches of the night were spent on the bare office tables with the late K. C. Kulasinghe as my companion. Or some nights would be spent in the grimy digs of D. B. S. Jeyaraj located quite close to the Premil Sports Club which was often the hub of our social life where the owner, the late Rajendra Mudalali, would approach us sombrely, always dressed in spotless white sarong and shirt and inquire ‘Any news of Upali Mahattaya?’ And in the morning the sun would rise over the splendid dome of St. Lucia’s Cathedral and we would search the vast sky for an answer.
(This article first appeared in a supplement to mark the 10th anniversary of the disappearance of Upali Wijewardene and party on Feb 13, 1993)
Features
Rebuilding Sri Lanka Through Inclusive Governance

In the immediate aftermath of Cyclone Ditwah, the government has moved swiftly to establish a Presidential Task Force for Rebuilding Sri Lanka with a core committee to assess requirements, set priorities, allocate resources and raise and disburse funds. Public reaction, however, has focused on the committee’s problematic composition. All eleven committee members are men, and all non-government seats are held by business personalities with no known expertise in complex national development projects, disaster management and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations. They belong to the top echelon of Sri Lanka’s private sector which has been making extraordinary profits. The government has been urged by civil society groups to reconsider the role and purpose of this task force and reconstitute it to be more representative of the country and its multiple needs.
The group of high-powered businessmen initially appointed might greatly help mobilise funds from corporates and international donors, but this group may be ill equipped to determine priorities and oversee disbursement and spending. It would be necessary to separate fundraising, fund oversight and spending prioritisation, given the different capabilities and considerations required for each. International experience in post disaster recovery shows that inclusive and representative structures are more likely to produce outcomes that are equitable, efficient and publicly accepted. Civil society, for instance, brings knowledge rooted in communities, experience in working with vulnerable groups and a capacity to question assumptions that may otherwise go unchallenged.
A positive and important development is that the government has been responsive to these criticisms and has invited at least one civil society representative to join the Rebuilding Sri Lanka committee. This decision deserves to be taken seriously and responded to positively by civil society which needs to call for more representation rather than a single representative. Such a demand would reflect an understanding that rebuilding after a national disaster cannot be undertaken by the state and the business community alone. The inclusion of civil society will strengthen transparency and public confidence, particularly at a moment when trust in institutions remains fragile. While one appointment does not in itself ensure inclusive governance, it opens the door to a more participatory approach that needs to be expanded and institutionalised.
Costly Exclusions
Going down the road of history, the absence of inclusion in government policymaking has cost the country dearly. The exclusion of others, not of one’s own community or political party, started at the very dawn of Independence in 1948. The Father of the Nation, D S Senanayake, led his government to exclude the Malaiyaha Tamil community by depriving them of their citizenship rights. Eight years later, in 1956, the Oxford educated S W R D Bandaranaike effectively excluded the Tamil speaking people from the government by making Sinhala the sole official language. These early decisions normalised exclusion as a tool of governance rather than accommodation and paved the way for seven decades of political conflict and three decades of internal war.
Exclusion has also taken place virulently on a political party basis. Both of Sri Lanka’s post Independence constitutions were decided on by the government alone. The opposition political parties voted against the new constitutions of 1972 and 1977 because they had been excluded from participating in their design. The proposals they had made were not accepted. The basic law of the country was never forged by consensus. This legacy continues to shape adversarial politics and institutional fragility. The exclusion of other communities and political parties from decision making has led to frequent reversals of government policy. Whether in education or economic regulation or foreign policy, what one government has done the successor government has undone.
Sri Lanka’s poor performance in securing the foreign investment necessary for rapid economic growth can be attributed to this factor in the main. Policy instability is not simply an economic problem but a political one rooted in narrow ownership of power. In 2022, when the people went on to the streets to protest against the government and caused it to fall, they demanded system change in which their primary focus was corruption, which had reached very high levels both literally and figuratively. The focus on corruption, as being done by the government at present, has two beneficial impacts for the government. The first is that it ensures that a minimum of resources will be wasted so that the maximum may be used for the people’s welfare.
Second Benefit
The second benefit is that by focusing on the crime of corruption, the government can disable many leaders in the opposition. The more opposition leaders who are behind bars on charges of corruption, the less competition the government faces. Yet these gains do not substitute for the deeper requirement of inclusive governance. The present government seems to have identified corruption as the problem it will emphasise. However, reducing or eliminating corruption by itself is not going to lead to rapid economic development. Corruption is not the sole reason for the absence of economic growth. The most important factor in rapid economic growth is to have government policies that are not reversed every time a new government comes to power.
For Sri Lanka to make the transition to self-sustaining and rapid economic development, it is necessary that the economic policies followed today are not reversed tomorrow. The best way to ensure continuity of policy is to be inclusive in governance. Instead of excluding those in the opposition, the mainstream opposition in particular needs to be included. In terms of system change, the government has scored high with regard to corruption. There is a general feeling that corruption in the country is much reduced compared to the past. However, with regard to inclusion the government needs to demonstrate more commitment. This was evident in the initial choice of cabinet ministers, who were nearly all men from the majority ethnic community. Important committees it formed, including the Presidential Task Force for a Clean Sri Lanka and the Rebuilding Sri Lanka Task Force, also failed at first to reflect the diversity of the country.
In a multi ethnic and multi religious society like Sri Lanka, inclusivity is not merely symbolic. It is essential for addressing diverse perspectives and fostering mutual understanding. It is important to have members of the Tamil, Muslim and other minority communities, and women who are 52 percent of the population, appointed to important decision making bodies, especially those tasked with national recovery. Without such representation, the risk is that the very communities most affected by the crisis will remain unheard, and old grievances will be reproduced in new forms. The invitation extended to civil society to participate in the Rebuilding Sri Lanka Task Force is an important beginning. Whether it becomes a turning point will depend on whether the government chooses to make inclusion a principle of governance rather than treat it as a show of concession made under pressure.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Reservoir operation and flooding

Former Director General of Irrigation, G.T. Dharmasena, in an article, titled “Revival of Innovative systems for reservoir operation and flood forecasting” in The Island of 17 December, 2025, starts out by stating:
“Most reservoirs in Sri Lanka are agriculture and hydropower dominated. Reservoir operators are often unwilling to acknowledge the flood detention capability of major reservoirs during the onset of monsoons. Deviating from the traditional priority for food production and hydropower development, it is time to reorient the operational approach of major reservoirs operators under extreme events, where flood control becomes a vital function. While admitting that total elimination of flood impacts is not technically feasible, the impacts can be reduced by efficient operation of reservoirs and effective early warning systems”.
Addressing the question often raised by the public as to “Why is flooding more prominent downstream of reservoirs compared to the period before they were built,” Mr. Dharmasena cites the following instances: “For instance, why do (sic) Magama in Tissamaharama face floods threats after the construction of the massive Kirindi Oya reservoir? Similarly, why does Ambalantota flood after the construction of Udawalawe Reservoir? Furthermore, why is Molkawa, in the Kalutara District area, getting flooded so often after the construction of Kukule reservoir”?
“These situations exist in several other river basins, too. Engineers must, therefore, be mindful of the need to strictly control the operation of the reservoir gates by their field staff. (Since) “The actual field situation can sometimes deviate significantly from the theoretical technology… it is necessary to examine whether gate operators are strictly adhering to the operational guidelines, as gate operation currently relies too much on the discretion of the operator at the site”.
COMMENT
For Mr. Dharmasena to bring to the attention of the public that “gate operation currently relies too much on the discretion of the operator at the site”, is being disingenuous, after accepting flooding as a way of life for ALL major reservoirs for decades and not doing much about it. As far as the public is concerned, their expectation is that the Institution responsible for Reservoir Management should, not only develop the necessary guidelines to address flooding but also ensure that they are strictly administered by those responsible, without leaving it to the arbitrary discretion of field staff. This exercise should be reviewed annually after each monsoon, if lives are to be saved and livelihoods are to be sustained.
IMPACT of GATE OPERATION on FLOODING
According to Mr. Dhamasena, “Major reservoir spillways are designed for very high return periods… If the spillway gates are opened fully when reservoir is at full capacity, this can produce an artificial flood of a very large magnitude… Therefore, reservoir operators must be mindful in this regard to avoid any artificial flood creation” (Ibid). Continuing, he states: “In reality reservoir spillways are often designed for the sole safety of the reservoir structure, often compromising the safety of the downstream population. This design concept was promoted by foreign agencies in recent times to safeguard their investment for dams. Consequently, the discharge capacities of these spill gates significantly exceed the natural carrying capacity of river(s) downstream” (Ibid).
COMMENT
The design concept where priority is given to the “sole safety of the structure” that causes the discharge capacity of spill gates to “significantly exceed” the carrying capacity of the river is not limited to foreign agencies. Such concepts are also adopted by local designers as well, judging from the fact that flooding is accepted as an inevitable feature of reservoirs. Since design concepts in their current form lack concern for serious destructive consequences downstream and, therefore, unacceptable, it is imperative that the Government mandates that current design criteria are revisited as a critical part of the restoration programme.
CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN GATE OPENINGS and SAFETY MEASURES
It is only after the devastation of historic proportions left behind by Cyclone Ditwah that the Public is aware that major reservoirs are designed with spill gate openings to protect the safety of the structure without factoring in the consequences downstream, such as the safety of the population is an unacceptable proposition. The Institution or Institutions associated with the design have a responsibility not only to inform but also work together with Institutions such as Disaster Management and any others responsible for the consequences downstream, so that they could prepare for what is to follow.
Without working in isolation and without limiting it only to, informing related Institutions, the need is for Institutions that design reservoirs to work as a team with Forecasting and Disaster Management and develop operational frameworks that should be institutionalised and approved by the Cabinet of Ministers. The need is to recognize that without connectivity between spill gate openings and safety measures downstream, catastrophes downstream are bound to recur.
Therefore, the mandate for dam designers and those responsible for disaster management and forecasting should be for them to jointly establish guidelines relating to what safety measures are to be adopted for varying degrees of spill gate openings. For instance, the carrying capacity of the river should relate with a specific openinig of the spill gate. Another specific opening is required when the population should be compelled to move to high ground. The process should continue until the spill gate opening is such that it warrants the population to be evacuated. This relationship could also be established by relating the spill gate openings to the width of the river downstream.
The measures recommended above should be backed up by the judicious use of the land within the flood plain of reservoirs for “DRY DAMS” with sufficient capacity to intercept part of the spill gate discharge from which excess water could be released within the carrying capacity of the river. By relating the capacity of the DRY DAM to the spill gate opening, a degree of safety could be established. However, since the practice of demarcating flood plains is not taken seriously by the Institution concerned, the Government should introduce a Bill that such demarcations are made mandatory as part of State Land in the design and operation of reservoirs. Adopting such a practice would not only contribute significantly to control flooding, but also save lives by not permitting settlement but permitting agricultural activities only within these zones. Furthermore, the creation of an intermediate zone to contain excess flood waters would not tax the safety measures to the extent it would in the absence of such a safety net.
CONCLUSION
Perhaps, the towns of Kotmale and Gampola suffered severe flooding and loss of life because the opening of spill gates to release the unprecedented volumes of water from Cyclone Ditwah, was warranted by the need to ensure the safety of Kotmale and Upper Kotmale Dams.
This and other similar disasters bring into focus the connectivity that exists between forecasting, operation of spill gates, flooding and disaster management. Therefore, it is imperative that the government introduce the much-needed legislative and executive measures to ensure that the agencies associated with these disciplines develop a common operational framework to mitigate flooding and its destructive consequences. A critical feature of such a framework should be the demarcation of the flood plain, and decree that land within the flood plain is a zone set aside for DRY DAMS, planted with trees and free of human settlements, other than for agricultural purposes. In addition, the mandate of such a framework should establish for each river basin the relationship between the degree to which spill gates are opened with levels of flooding and appropriate safety measures.
The government should insist that associated Agencies identify and conduct a pilot project to ascertain the efficacy of the recommendations cited above and if need be, modify it accordingly, so that downstream physical features that are unique to each river basin are taken into account and made an integral feature of reservoir design. Even if such restrictions downstream limit the capacities to store spill gate discharges, it has to be appreciated that providing such facilities within the flood plain to any degree would mitigate the destructive consequences of the flooding.
By Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
Listening to the Language of Shells

The ocean rarely raises its voice. Instead, it leaves behind signs — subtle, intricate and enduring — for those willing to observe closely. Along Sri Lanka’s shores, these signs often appear in the form of seashells: spiralled, ridged, polished by waves, carrying within them the quiet history of marine life. For Marine Naturalist Dr. Malik Fernando, these shells are not souvenirs of the sea but storytellers, bearing witness to ecological change, resilience and loss.
“Seashells are among the most eloquent narrators of the ocean’s condition,” Dr. Fernando told The Island. “They are biological archives. If you know how to read them, they reveal the story of our seas, past and present.”
A long-standing marine conservationist and a member of the Marine Subcommittee of the Wildlife & Nature Protection Society (WNPS), Dr. Fernando has dedicated much of his life to understanding and protecting Sri Lanka’s marine ecosystems. While charismatic megafauna often dominate conservation discourse, he has consistently drawn attention to less celebrated but equally vital marine organisms — particularly molluscs, whose shells are integral to coastal and reef ecosystems.
“Shells are often admired for their beauty, but rarely for their function,” he said. “They are homes, shields and structural components of marine habitats. When shell-bearing organisms decline, it destabilises entire food webs.”
Sri Lanka’s geographical identity as an island nation, Dr. Fernando says, is paradoxically underrepresented in national conservation priorities. “We speak passionately about forests and wildlife on land, but our relationship with the ocean remains largely extractive,” he noted. “We fish, mine sand, build along the coast and pollute, yet fail to pause and ask how much the sea can endure.”
Through his work with the WNPS Marine Subcommittee, Dr. Fernando has been at the forefront of advocating for science-led marine policy and integrated coastal management. He stressed that fragmented governance and weak enforcement continue to undermine marine protection efforts. “The ocean does not recognise administrative boundaries,” he said. “But unfortunately, our policies often do.”
He believes that one of the greatest challenges facing marine conservation in Sri Lanka is invisibility. “What happens underwater is out of sight, and therefore out of mind,” he said. “Coral bleaching, mollusc depletion, habitat destruction — these crises unfold silently. By the time the impacts reach the shore, it is often too late.”
 Seashells, in this context, become messengers. Changes in shell thickness, size and abundance, Dr. Fernando explained, can signal shifts in ocean chemistry, rising temperatures and increasing acidity — all linked to climate change. “Ocean acidification weakens shells,” he said. “It is a chemical reality with biological consequences. When shells grow thinner, organisms become more vulnerable, and ecosystems less stable.”
Seashells, in this context, become messengers. Changes in shell thickness, size and abundance, Dr. Fernando explained, can signal shifts in ocean chemistry, rising temperatures and increasing acidity — all linked to climate change. “Ocean acidification weakens shells,” he said. “It is a chemical reality with biological consequences. When shells grow thinner, organisms become more vulnerable, and ecosystems less stable.”
Climate change, he warned, is no longer a distant threat but an active force reshaping Sri Lanka’s marine environment. “We are already witnessing altered breeding cycles, migration patterns and species distribution,” he said. “Marine life is responding rapidly. The question is whether humans will respond wisely.”
Despite the gravity of these challenges, Dr. Fernando remains an advocate of hope rooted in knowledge. He believes public awareness and education are essential to reversing marine degradation. “You cannot expect people to protect what they do not understand,” he said. “Marine literacy must begin early — in schools, communities and through public storytelling.”
It is this belief that has driven his involvement in initiatives that use visual narratives to communicate marine science to broader audiences. According to Dr. Fernando, imagery, art and heritage-based storytelling can evoke emotional connections that data alone cannot. “A well-composed image of a shell can inspire curiosity,” he said. “Curiosity leads to respect, and respect to protection.”
Shells, he added, also hold cultural and historical significance in Sri Lanka, having been used for ornamentation, ritual objects and trade for centuries. “They connect nature and culture,” he said. “By celebrating shells, we are also honouring coastal communities whose lives have long been intertwined with the sea.”
However, Dr. Fernando cautioned against romanticising the ocean without acknowledging responsibility. “Celebration must go hand in hand with conservation,” he said. “Otherwise, we risk turning heritage into exploitation.”
He was particularly critical of unregulated shell collection and commercialisation. “What seems harmless — picking up shells — can have cumulative impacts,” he said. “When multiplied across thousands of visitors, it becomes extraction.”
As Sri Lanka continues to promote coastal tourism, Dr. Fernando emphasised the need for sustainability frameworks that prioritise ecosystem health. “Tourism must not come at the cost of the very environments it depends on,” he said. “Marine conservation is not anti-development; it is pro-future.”

Dr. Malik Fernando
Reflecting on his decades-long engagement with the sea, Dr. Fernando described marine conservation as both a scientific pursuit and a moral obligation. “The ocean has given us food, livelihoods, climate regulation and beauty,” he said. “Protecting it is not an act of charity; it is an act of responsibility.”
He called for stronger collaboration between scientists, policymakers, civil society and the private sector. “No single entity can safeguard the ocean alone,” he said. “Conservation requires collective stewardship.”
Yet, amid concern, Dr. Fernando expressed cautious optimism. “Sri Lanka still has immense marine wealth,” he said. “Our reefs, seagrass beds and coastal waters are resilient, if given a chance.”
Standing at the edge of the sea, shells scattered along the sand, one is reminded that the ocean does not shout its warnings. It leaves behind clues — delicate, enduring, easily overlooked. For Dr. Malik Fernando, those clues demand attention.
“The sea is constantly communicating,” he said. “In shells, in currents, in changing patterns of life. The real question is whether we, as a society, are finally prepared to listen — and to act before silence replaces the story.”
By Ifham Nizam
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoBritish MP calls on Foreign Secretary to expand sanction package against ‘Sri Lankan war criminals’
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoChief selector’s remarks disappointing says Mickey Arthur
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoStreet vendors banned from Kandy City
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoSri Lanka’s coastline faces unfolding catastrophe: Expert
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoDisasters do not destroy nations; the refusal to change does
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLankan aircrew fly daring UN Medevac in hostile conditions in Africa
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoLife after the armband for Asalanka
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoYear ends with the NPP govt. on the back foot