Features
The Monk and Me
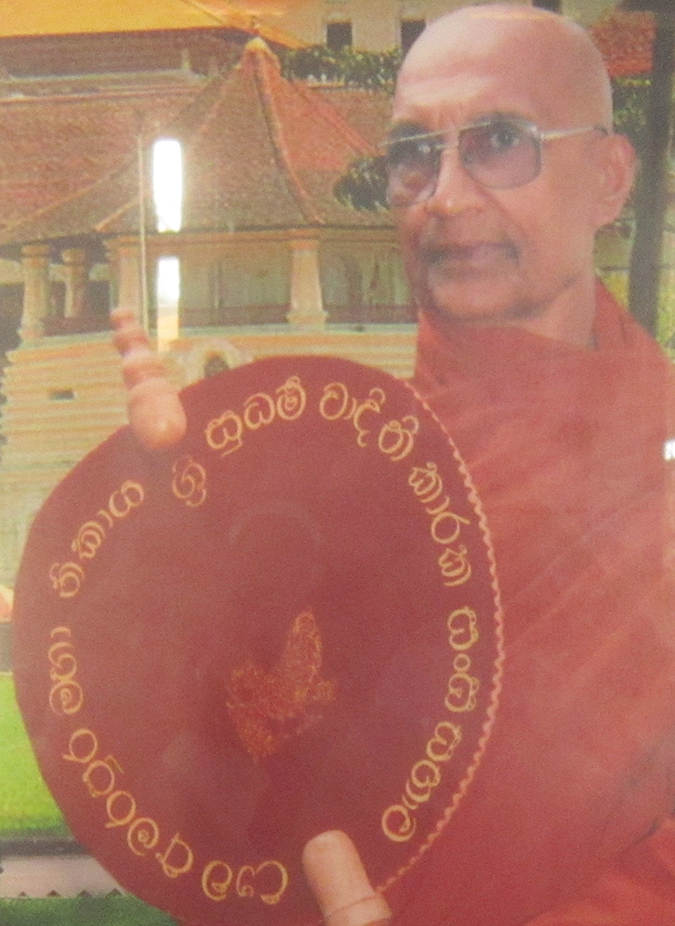

by Michael Patrick O’Leary
On October 13, 2017, we heard the sad news of the death of our very dear friend, the Most Venerable Meeriyabedde Upananda Mahanayaka Thera, the Mahanayaka of Uva Amarapura Nikaya. We knew the Most Venerable Upananda for a long time before we realized how eminent he was. We just knew that he was a special human being. As well as being the High Priest of the Pelgahattene temple, he was also responsible for 56 other temples.
It is difficult to find any information about our friend by Googling, although he was a monk for 80 years and at Pelgahattene for 50 years. He was not one of those celebrity monks who haunts the media, drawing attention to the man rather than the Dhamma. My information about him is mainly based on my personal contact with him over a period of 14 years
In Ireland they have the term “blow-in”. According to a Hiberno-English dictionary, a blow-in is a newcomer to an area, “someone who has been resident for less than 15 years”. When we settled in Sri Lanka from Ireland in 2002, we felt even more like interlopers than we had done in rural East Cork. In Colombo, we would attract little attention among the hordes of tourists (those were the days, my friend), but when we moved to our house in the mountains, we got strange, possibly hostile, looks as we passed through the nearby villages. We settled in one of the poorest areas of the country. Mine was the only white (or pink) face to be seen for many a mile. Even driving around in a clapped-out old car, we probably seemed rich, strange and privileged.
A Maniyo who knew my wife’s mother stayed with us soon after we moved in to our mountain retreat. She insisted that we must have pirith chanted to bring merit and protection to our household. She introduced us to the Most Venerable Upananda. Our Maniyo friend is a can-do kind of a person and soon arranged for a battalion of monks to come and perform rituals to help the house welcome and nurture us. Our life certainly changed for the better but this is probably not a result of the rituals but because the hamaduru wahansai became a very dear friend and some of the respect accorded to him reflected upon us.
The hostile frowns of the villagers turned to smiles and everyone offered to help us. We were invited to weddings and funerals and functions at the temple and generally felt that we were members of the community. I was given the honour of carrying the Buddha’s relics on my head at one ceremony. On another occasion, I sat beside the local police chief and the speaker of the Sri Lankan parliament presenting prizes to schoolchildren.
When we visited the high priest on his 90th birthday, he showed us a greeting card he had received from the then Head of State, President Mahinda Rajapaksa. The president had also telephoned him to give him his good wishes in person. He had also received a card from the then leader of the opposition and current president, Ranil Wickremesinghe.
The atmosphere around the temple was truly ecumenical. We saw our Muslim neighbours taking their small daughter to the Montessori school at the temple. The Most Venerable Upananda was a great friend of the priests at the Passara Catholic Church and joined them in many community projects. Many Hindu Tamils worked hard to maintain the premises and crops at the temple. We have seen them prostrating themselves at his feet in respect. The Most Venerable’s Tamil driver was tearful with grief at his demise. The Most Reverend won the love of all members of the community because he was upright with no hint of impropriety. He served the whole community, endlessly creating schemes to improve the lives of local people. He helped provide electricity, water and employment, and computer training; he devised schemes for growing mushrooms and producing cooking gas from waste.
The traditional expectation is that the laity provides and serves food to the clergy. We were happy to do this but also, thanks to the Most Venerable Upananda, we rarely had to buy rice or tea because he sent regular supplies to us. Whenever we visited him he insisted that we have breakfast and served us himself. He took particular pleasure in giving me the denture-threatening parippu vade that he knew I liked. “Mr Michael’s favourite!”
The Most Venerable Upananda had a reputation as a healer with special knowledge of traditional remedies. Anyone bitten by a snake went to him for the application of his snake stone to draw out the venom. There was a story, possibly apocryphal, that he was once kidnapped by the Tamil Tigers because of his healing powers and that he was offered a van as thanks for healing a senior cadre. He refused. He was also offered vehicles by mainstream politicians. He refused.
When we decided that we needed a new car, selling the old one was problematic. A potential buyer seemed to be trouble – he moaned about the price and however much we lowered it, we could foresee him coming back in perpetuity to complain about the car’s defects, of which there were many. Our friend Most Venerable Upananda offered to buy the car as it would be helpful to take him to his clinic appointments and various official functions. When she was president of Sri Lanka, Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga offered him a new jeep but he refused. We refused his offer and gave the car to him free of charge.
After we donated our car it became a community project. A local mechanic, without charging, put right many mechanical wrongs and spray-painted the car. He said how he can expect payment when we gave the car as a gift. Many little accoutrements and furbelows have been proudly added. A local builder constructed a new garage free of charge to house the vehicle and the completion of the structure was marked with a little ceremony with songs sung by small schoolchildren.
Our shorthand nickname for the Most Venerable Upananda was “The Don” because we saw him as the benevolent boss at the center of a benign mafia. The French sociologist Marcel Mauss, in his Essai sur le don, published in 1925, described how reciprocal gift-giving builds relationships between groups. The biologist, EO Wilson, coined the wonderful phrase, “the delicate web of reciprocity.” I tell the story of the donation of the car not in order to signal my own virtue. I do not want to engage in what Paul Newman called “noisy philanthropy”. Howard Jacobson coined the phrase “philanthropy – the last refuge of the scoundrel.”
I write not to boast of my own saintliness but to give readers an idea of what an ordinary person can achieve by small acts of direct giving. I challenged ethical philosopher Peter Singer’s idea of “making a difference”. Singer advocates regularly donating a percentage of one’s income to charitable institutions. He recognized that one could not always know how one’s donations were being spent. It seemed to me that this form of delegated compassion makes more of a difference to the giver’s self-esteem than to the welfare of the needy.
Bhikkhu Bodhi edited a small book of essays called Dāna – The Practice of Giving. In his introduction, he writes: “The goal of the path is the destruction of greed, hate and delusion, and the cultivation of generosity directly debilitates greed and hate, while facilitating the pliancy of mind that allows for the eradication of delusion”.
One would not be eradicating delusion if one merely set up a standing order to pay a percentage of one’s salary to an organization without finding out how the money is used. The Argentinian poet Antonio Porchia wrote: “I know what I have given you but I do not know what you have received”.
Andrew Carnegie wrote: “[O]f every thousand dollars spent in so-called charity today, it is probable that nine hundred and fifty dollars is unwisely spent—so spent, indeed, as to produce the very evils which it hopes to mitigate or cure.” Today it is much worse. Humanitarianism has become a billion-dollar industry. NGOs are huge corporate businesses ossified by management and career structures and bureaucracy. NGO workers can build up an image of saintliness as well as developing a lucrative CV.
Richard Titmuss, British social researcher and teacher, published The Gift Relationship in 1970. He compared blood donations in Britain (entirely voluntary) and the US (some bought and sold). Titmuss’ s conclusions concerned the quality of communities where people are encouraged to give to strangers. When blood becomes a commodity, he argued, its quality is corrupted (American blood was four times more likely to infect recipients with hepatitis than was British blood). Titmuss helped preserve the National Blood Service from Thatcherite privatisation.
Lewis Hyde also has examined the concept of the gift. He locates the origin of gift economies in the sharing of food. Many societies have strong prohibitions against turning gifts into trade. Hyde investigates the effect our delusion with the market economy has on our ability to give and receive. In a market economy, wealth is increased by ’saving’. In a gift economy, wealth is decreased by hoarding, for it is circulation within the community that generates increase in connections and strong relationships.
Andrew Carnegie warned successful men who failed to help others that “the man who dies thus rich dies disgraced.” Carnegie knew how to make money and he knew how to use it effectively. By the time he died in 1919, he had given away over $350 million ($ 494.2 billion in 2014 money) and he had established charitable organizations that are still active nearly a century after his death. Modern day rich givers like Warren Buffett and Bill Gates have expressed a Carnegie-like wish to divest themselves of their wealth.
Those of us with less wealth than Carnegie and co. can also benefit from giving. We can perhaps benefit more, because we can have the satisfaction of giving to the hand and looking in the eye. Clinging to material goods makes people selfish, struggling to satisfy insatiable desires with transitory pleasures. Dāna is the very practical act of giving; caga is the generous attitude ingrained in the mind by the repeated practice of dāna. The word caga in Pali means giving up, abandonment; the selfish grip one has on one’s possessions is loosened by caga. When we decide to give something of our own to someone else, we simultaneously reduce our attachment to the object; to make a habit of giving can thus gradually weaken the mental factor of craving. Giving is the antidote to cure the illness of egoism and greed.
You do not need to be as rich as Bill Gates is or as well-connected as Bono. You do not have to send money abroad. You do not even have to give money. Awareness is the most important thing. Look around your own area, talk to religious leaders and doctors, talk to your neighbours. They will advise you who is in need. By giving of your heart as well as your money, you can save yourself, make a difference and improve someone else’s life, by giving with wisdom.
It’s a bargain!
We travelled up to Uva from Colombo to pay our respects to our departed friend. We did not stay for the funeral itself on the afternoon of Monday October 16. There was to be a perehara from two o’clock in the afternoon. It was expected that 2,000 bhikkhus would attend. We attended and paid our respects early in the morning. Already, many people, including large parties of schoolchildren were there. Many people were in tears. We will miss him as will many others.
Features
Protection of Occupants Bill: Good, Bad and Ugly

I.Protection of Occupants Bill: The government has introduced two Bills, namely, the Rent (Repeal) Bill and the Protection of Occupants Bill which – if enacted – will have the effect of radically reforming the rent laws of our country. These two Bills were gazetted in September 2025 and tabled in Parliament on 20th January, 2026. Although several petitions were filed before the Supreme Court, challenging the constitutionality of these Bills, the Attorney-General informed the court that the two Bills would not be proceeded with in their present form, but would, instead, be referred to an expert committee for consideration. Accordingly, the petitions were withdrawn and the Supreme Court informed the Speaker that no formal determination would be made on the constitutionality of the said Bills in their present form. In parallel to these legal developments, the Ministry of Justice and National Integration has requested the members of the public to submit their comments, suggestions, or proposals regarding these Bills by 04th March, 2026. The Minister of Justice has also assured that he would not take any steps in relation to the two Bills until this consultative process is completed. Therefore, a clear need and opportunity has arisen for a vibrant public discussion on the proposed legislation. The purpose of this lecture is to contribute to this discussion by assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the two Bills in light of their historical, political, social and economic context.
II. The Rent Act and its objective
The Rent Act No. 7 of 1972 is a landmark piece of legislation which was introduced by Mr. Pieter Keuneman, the Minster of Housing at the time. The purpose of the Act was to confer significant protection on tenants through means such as restricting the increase of rent, giving security of tenure for the tenant and formalising the process of ejectment. The Rent Act of 1972 was a bold response to the lived realities of law in society. From a doctrinal perspective, the formation of a valid contract requires animus contrahendi (the intention to enter into a contract). However, it is widely acknowledged that parties to a contact may not be equal in terms of bargaining strength. One party may be stronger than the other, both economically and socially. In such situations, the function of the law is to protect the weaker party in his dealings with the stronger party. The assumption underlying the Rent Act was that the landlord was in a far stronger position than the tenant. Thus, the law was utilised to protect the interests of the more vulnerable party, namely the tenant. This objective of the Rent Act also closely aligned with the personal philosophy of Mr. Keuneman who was a prominent member of the Communist Party, of Sri Lanka. While the Rent Act was subsequently amended in 1976, 1977, 1980 and 2002, the original legislative scheme which safeguarded the rights of the tenants remained intact. What is proposed under the Protection of Occupants Bill, however, is a fundamental departure from the premises of that law.
III. Protection of Occupants Bill: An Overview
A close comparison between the Rent Act and the Protection of Occupants Bill shows that the safeguards afforded to the occupants under the latter (Clauses 3 (a), (b) and 4) are almost identical to the provisions of the former (Sections 13(1), 15 and 16). They both prevent the landlord from discontinuing or withholding the amenities previously provided to the tenant; damaging the premises to induce or compel the tenant to vacate the premises; and refusing to maintain the premises in proper condition. Yet, there is one crucial difference between the Rent Act and the Protection of Occupants Bill in relation to these safeguards. The rights and privileges enjoyed by a tenant under the Rent Act are not absolute. The tenant is being protected by the law only so long as he is complying with the terms and conditions of the tenancy agreement. The 1972 Act, therefore, operates on the assumption that a tenant is honouring his contractual obligations while enjoying the rights under the Act. The conditional nature of these safeguards is amply evident from the provisions of the Act.
For example, section 15 of the Rent Act prevents the landlord from discontinuing amenities provided to the tenant ‘without reasonable cause’. Thus, the landlord is not prevented from discontinuing the amenities at all times but only without reasonable cause. The breach of the contractual obligations by the tenant would surely constitute a reasonable cause for the landlord to discontinue the amenities provided by him to the tenant. By contrast, the language used in the Protection of Occupants Bill does not indicate any limitations on the exercise of the safeguards afforded by the Bill except the preliminary requirement under clause 2 that undisturbed and uninterrupted occupation for three months is necessary for the application of the Bill. In other words, any person who has been in lawful occupation of premises for three months acquires an accrued right to enjoy the safeguards mentioned in the Bill unless he is stopped from doing so by a court order.
Consequently, even if the tenancy agreement between landlord and tenant may have come to an end or the tenant may be in breach of the terms of the agreement, or he is using the premises for a completely different purpose, his rights and privileges remain unaffected. Recourse to the judicial process is the only avenue available for the landlord to revoke the safeguards given to the tenant even when the latter has blatantly breached the terms of his contract. Reciprocity and mutuality are the fundamental concepts that underlie the Rent Act, as the tenant’s protection under that Act is dependent on the reciprocity of obligations. Protection of Occupants Bill, on the other hand, provides a unilateral framework for the tenants to assert their rights without paying due regard to the interests of the landlord.
It is also important to mention, at this point, that the Protection of Occupants Bill makes an artificial and unjustifiable difference between the right of a tenant not to be ejected and the other safeguards provided to him under the Bill. In terms of clause 5, the landlord shall not eject an occupant in contravention of the terms and conditions of the lease agreement, or tenancy agreement. The necessary implication of this clause is that the landlord can eject an occupant in terms of the agreement between him and the tenant. Such a caveat is absent in the other provisions of the Bill that deal with the rights of an occupant.
Accordingly, there is a blanket prohibition on the landlord in discontinuing or withholding the amenities previously provided to the occupant or refusing to maintain the premises in proper condition. The landlord cannot take these actions even as per the agreement to which the tenant himself has given his consent. Apart from the absence of a rational basis to require the landlord to follow the tenancy agreement in ejecting a tenant but then to prevent him from doing the same with regard to the other less severe actions that he can resort to when the tenant is in breach of the contract, such a distinction also creates unfairness and inequality. Ejection of a tenant requires manpower and therefore, monetary resources as well. While a landlord who is capable of affording personnel to eject his tenant is benefited under the Bill, a landlord with modest means is left with no options other than a lengthy and cumbersome judicial process even when it is abundantly clear that his tenant is in violation of the tenancy agreement.
IV. Internal Inconsistencies in the Bill
The Protection of Occupants Bill is also poorly drafted and, thus, contains several internal inconsistencies. For example, clause 2 of the Bill provides that a person must be ‘in lawful occupation of a premises’ for him to invoke the provisions of the Bill. The term ‘occupation’ is defined in clause 13 which states that a person can be in occupation of a premises only ‘with the consent of the landlord.’ If a landlord has taken the actions mentioned above, such as discontinuing the amenities, the ‘aggrieved occupant’ is entitled to institute an action in a Court,
seeking the reliefs specified in that clause. Paradoxically, however, when a person goes to the Court to institute such actions, he is no longer ‘an occupant’ because all the eventualities against which a court order can be obtained, such as discontinuing amenities, refusing to maintain the premises, damaging the property, or ejecting the occupant, give an unmistakable indication that the person affected does not have the consent of the landlord to stay in the premises anymore. The withdrawal of the landlord’s consent is the irresistible conclusion that can be drawn from the aforementioned actions or omissions. Therefore, according to the definition of ‘occupation’ in clause 13, no person, who has faced the resistance of the landlord in the manner described in the Bill, can institute an action before the Court as he is no longer an ‘occupant’ with the landlord’s consent to stay in the premises.
V. A flawed rationale?
In addition to these structural flaws in the Protection of Occupants Bill, the rationale behind the same can also be questioned. It seems that the aim of the Bill is to bridge the gap between Haves and Have nots. It is assumed that the tenant is weaker than the landlord, both economically and socially. Thus, the Bill seeks to protect the rights of the weaker party i.e. the tenant from the arbitrary actions of the landlord. This is an extension of the political philosophy that influenced Mr. Keuneman to introduce the Rent Act. However, due to the unqualified protection given to the tenant, under the proposed new law, there is a serious question as to whether this political philosophy can truly be realised if the Bill is to be enacted in its present form. Suppose that there is a government servant who wants to build a house for his daughter. He may not be rich but manages to buy a land and build a house for his daughter with his salary. He may also want to rent the house until the daughter is married and collect the rent for his daughter’s marriage.
If the tenant, who lives in this house, stops paying the rent and also refuses to leave the property, there is nothing that this government servant can do except seeking a court order to eject him by spending more money and engaging in a lengthy trial that may take years to reach a final determination on the matter. He, of course, does not have the manpower to eject the tenant, but the Bill prevents him from engaging in unharmful actions, such as discontinuing amenities or refusing to maintain the premises, as well. He cannot collect the rent nor can he give the property to his daughter. In such a situation, the landlord becomes the victim as the Protection of Occupants Bill enables the tenant to abuse his rights. The theory of haves and have nots, which is supposed to be promoted by the Bill, breaks down at this point. The assumption that the have nots will be protected by this Act when they are pitted against the haves is simply not borne out when the provisions of the Bill are subject to pragmatic considerations of this kind.
VI. Impact on Banks
The Protection of Occupants Bill will also have a negative impact on the banking system of our country. Landlords often put their houses up as collateral for bank loans. Under the Recovery of loans by Banks (Special Provisions) Act No. 4 of 1990, the bank is empowered to sell such property at a public auction if the landlord fails to pay the money back to the bank, with the stipulated interest. It will be extremely difficult for the bank to exercise this right if the Protection of Occupants Bill is enacted without any amendments. Under the provisions of the Bill, a tenant may refuse to leave the premise, despite the breach of his contractual obligations. The bank then cannot sell the property with a tenant as it lacks vacua possessio (vacant possession). In any event, no person will buy a house with a tenant, specially when he knows that the presence of the tenant cannot be resisted under the proposed law. Thus, the bank loses its money due to its inability to sell the collateral and by extension, the members of the public, who deposited their money in the bank, will also suffer that loss.
VII. Impact on Condominium Property
With the increase of population in the urban areas, condominium property has become a convenient option for people who are looking for housing in major cities like Colombo, Kandy and Galle. Unfortunately, the Protection of Occupants Bill is bound to have a detrimental impact on at least three parties in a condominium. First, if the tenant of an apartment in the condominium does not pay his rent, the landlord, who owns the condominium, and expects to earn a certain profit from it, is undoubtedly affected. If a considerable number of tenants refuse to pay the rent, it will be difficult for the landlord to continue with his business. Second, in every condominium complex, there is a management committee which looks after the amenities and other facilities given to the apartments in that complex. However, if a tenant breaches the terms of his contract, the managers will be in a precarious position where they are compelled, under the proposed law, to provide those facilities to someone who has not honoured his contractual obligations towards to the maintenance of the condominium. Finally, the other residents in the condominium complex will be subject to grave injustice as there is a tenant who is immune from any deterrence for the breach of his contract while they continue to pay the rent and fulfil other obligations. Therefore, the condominium industry will severely be affected in multiple ways if the Protection of Occupants Bill is enacted in its current form.
VIII. Judicial process
The proponents of the Bill argue that the aim of the Bill is simply to formalise the actions that can be taken by the landlord when the tenant is in breach of the terms of his contract. It is, therefore, pointed out that if a tenant goes to the Court against the actions of the landlord, such as discontinuing the amenities or refusing to maintain the premises in proper condition, the latter can justify his actions by referring to the breach of the tenancy agreement. In fact, clause 7 (4) lays down time limits for the completion of cases that arise under the proposed legislation. In an uncontested case, the Court is required to deliver the final judgment within 3 months and if the claims of the occupant are contested by the landlord, 9 months are given for the completion of the case. What these provisions seem to have overlooked is the backlog of cases in District Courts which will be dealing with such cases if the Bill is enacted. It is highly doubtful whether these time limits can be adhered to by the District Courts in the midst of other civil actions, such as testamentary cases, divorce cases and property disputes which occupy a significant portion of the Courts’ daily schedule. In any event, a person aggrieved by an order of the court can appeal and no time limits have been prescribed for the appeal process. Most importantly, under clause 6(2), an occupant can obtain interim relief to maintain the status quo of the premises. The effect of this provision is that even an occupant, who is in breach of his contract, can obtain an interim order to maintain the status quo and thereby prevent the landlord from enforcing the contract until the completion of the case. It is convenient for the lawmakers to lay down time limits for cases in a statute but as the previous experiences have shown, the implementation of such limits, in practice, is exceedingly difficult.
IX. Social Impact
The Protection of Occupants Bill is likely to have a catastrophic impact on the social fabric of our country. With all the above hazards discussed above, nobody will buy a house and rent it out anymore. Renting a house, under the proposed legislation, will become a considerable risk which only very few people will be prepared to take. Consequently, there will be a drastic reduction of the housing stock and the number of houses and apartments available will fall drastically. In response, there will be an inevitable rise in rent values. The objective of the Bill to protect the rights of the tenants is most certainly commendable. However, the function of the law is to balance competing interests in society without conferring undue advantage or disadvantage on a particular social group. As former Dean of the Harvard Law School, Roscoe Pound, has argued, making of law is an exercise in social engineering. Law must balance different interests in society and come up with an equitable solution. However, the proposed legislation leads to unfairness towards landlords, banks, dispositors and several parties in condominiums. From all these perspectives, impact of the proposed legislation is negative. The cumulative effect of all these consequences makes the Protection of Occupants Bill a counter-productive law which fails to achieve its purpose. Therefore, significant amendments are required before the proposed Bill is enacted into law.
Guest lecture delivered in the Faculty of Law, University of Colombo,
by Emeritus Professor G. L. Peiris
on 16 February, 2026
Features
LOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer

From Aloka the Peace Dog to Manula the School Icon — Sri Lanka’s love for dogs is wholesome and beautiful. But, behind every wagging tail lurks a public health crisis that kills silently, swiftly, and without mercy.
Aloka and Manula: Stars with a Message
Sri Lanka fell in love, not once, but twice in the span of a few weeks. First came Aloka, the serene, soulful dog who walked alongside venerable Buddhist monks during their peace walk in the USA, matching their calm stride with a dignity that moved the nation to tears. By nightfall, Aloka was not just a Sri Lankan celebrity he was an international sensation, a symbol of compassion and coexistence that transcended borders. The world watched, and the world smiled.
Then came Manula. from the schoolyard of Tissa Vidyalaya, in the Kalutara district. A photograph went viral – a scruffy, joyful dog apparently “performing” alongside students at the school’s annual inter-house sports meet band performance. Manula, a school mascot born not by appointment but by the daily love of students and teachers, became an overnight hero.
Both dogs share something beyond their celebrity. Both are native breeds, the ancient indigenous dogs of India and Sri Lanka, lean and hardy, shaped by centuries of co-evolution with humans on this subcontinent. Both roam freely. Both are adored. And both, unknowingly, sit at the centre of a public health conversation that Sri Lanka urgently needs to have.
When Aloka walked among the crowds, children rushed forward, small hands reaching out, eager to touch this gentle, famous dog. Manula, it is safe to assume, is petted by dozens of schoolchildren every single day. These are acts of love instinctive, natural, beautifully human. But they are also, without the right precautions, potentially dangerous.
The disease these encounters could transmit is rabies. And, in Sri Lanka, rabies is not a distant theoretical threat. It is the country’s number one public health emergency one that kills, maims, and drains the economy, all while remaining almost entirely preventable.
What is Rabies? Understanding the Invisible Enemy
Rabies is a viral disease caused by the Rabies lyssavirus, a member of the Rhabdoviridae family. It is one of the oldest known infectious diseases in human history, described in ancient Mesopotamian texts over four thousand years ago. It is also one of the most terrifying: once symptoms appear in a human being, rabies is almost universally fatal. The mortality rate after symptom onset approaches 100%.
The virus attacks the central nervous system the brain and spinal cord causing progressive and irreversible neurological deterioration. There are two clinical forms. Furious rabies, the more common form, produces the haunting symptoms most people associate with the disease: extreme agitation, hydrophobia (an irrational, violent terror of water), aerophobia (fear of air currents), hallucinations, excessive salivation, and aggressive behaviour. Paralytic rabies, sometimes called “dumb rabies,” progresses more quietly with gradual muscle paralysis, weakness, and eventual coma and is often misdiagnosed.
Death typically follows within two to 10 days of the onset of symptoms, caused by respiratory failure or cardiac arrest. There is no cure once the virus reaches the brain.
How Rabies Travels from Dog to Human
The transmission route is straightforward but sobering. The rabies virus lives in the saliva of infected animals. It enters the human body through a bite, or when infectious saliva contacts broken skin, a scratch, or mucous membranes such as the eyes, nose, or mouth. A lick from an infected dog on an open wound or a child’s eyes can, in rare cases, be sufficient.
Once inside the body, the virus travels along nerve fibres towards the brain at a rate of approximately 12 to 24 millimetres per day. This journey, called the incubation period, is deceptively long. It typically ranges from one to three months, though it can be as short as a week or as long as a year, depending on the site of the bite (bites closer to the head are more dangerous), the severity of the wound, and the viral load introduced.
This long incubation period is simultaneously a tragedy and an opportunity. It is a tragedy because people often forget about or dismiss a dog bite weeks later, believing they are safe. It is an opportunity because there is a window, a precious, life-saving window during which post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), a series of rabies vaccinations, can prevent the virus from reaching the brain and save the patient’s life with near-complete certainty.
What To Do Immediately If a Dog Bites You
Every second matters. The following steps must be followed without hesitation:
Step 1 — Wash the wound immediately and thoroughly.
This is the single most important first-aid measure. Wash the bite site vigorously with soap and running water for a minimum of 15 minutes. The mechanical action of washing physically removes viral particles. Research shows that thorough wound washing alone reduces the risk of rabies transmission by up to 50%. Do not panic. Wash, wash and wash.
Step 2 — Apply an antiseptic.
After washing, apply povidone-iodine, ethanol, or another virucidal antiseptic to the wound if available. Do not cover the wound tightly and allow it to breathe.
Step 3 — Go to hospital or a rabies clinic immediately.
Do not wait. Do not adopt a “wait and see” approach. Do not be reassured by the dog appearing healthy as healthy animals can shed the rabies virus before showing symptoms. Present yourself to the nearest government hospital or Anti-Rabies Clinic (ARC). Sri Lanka has a nationwide network of these clinics.
Step 4 — Begin Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP).
A doctor will assess the category of exposure and recommend the appropriate PEP regimen. This typically involves a course of intramuscular rabies vaccines administered over 14 to 28 days. For severe bites (Category III), Rabies Immunoglobulin (RIG) will also be injected into the wound site to provide immediate passive immunity. PEP is safe, effective, and free of charge at government hospitals in Sri Lanka.
Step 5 — Complete the full vaccine course.
This is where many patients fail. The vaccines work only if the complete schedule is followed. Missing doses can leave a person unprotected. PEP must be completed, regardless of whether the dog is found, tested, or appears healthy afterward.
One critical caution: if you are bitten on the face, head, neck, or hands areas with rich nerve supply close to the brain treat this as the highest emergency and reach a hospital as fast as humanly possible.
Rabies in the World: A Disease That Refuses to Disappear
Despite being entirely vaccine-preventable, rabies remains a significant global public health challenge, responsible for an estimated 59,000 human deaths annually, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO). This figure is almost certainly an undercount; many deaths in rural areas of Africa and Asia go unreported or are misattributed. The WHO estimates that 99% of human rabies cases are caused by dog bites.
Africa and Asia bear the overwhelming burden of the disease, together accounting for approximately 95% of all global rabies deaths. The countries worst affected include India which alone accounts for roughly 36% of global rabies deaths, with an estimated 18,000 to 20,000 fatalities per year along with Bangladesh, Ethiopia, China, and the Philippines. Shockingly, children, under 15 years of age, account for up to 40% of all rabies victims, largely because they are more likely to engage with stray dogs and and are less likely to report bites.
The economic cost of rabies, globally, is staggering. A 2015 study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases estimated the annual global cost of rabies, including lost lives, healthcare expenditure, and livestock deaths, at over USD 8.6 billion.
The encouraging news is that rabies can be eliminated. Several countries, including Japan, the United Kingdom, Australia, and most of Western Europe, are certified rabies-free, having achieved this through sustained dog vaccination campaigns, stray dog management, and public education. The WHO, together with the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) and the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), has set the ambitious target of zero human deaths from dog-mediated rabies, globally, by 2030.
South Asia: A Region Under Threat
South Asia represents one of the world’s most severe rabies hotspots. India’s enormous burden has already been noted. Bangladesh has made significant progress in recent years through mass dog vaccination, reducing human rabies deaths substantially. Nepal continues to struggle with high exposure rates, particularly in rural areas. Bhutan has made commendable strides with its dog vaccination programme.
Sri Lanka stands at a critical juncture. While the country has reduced its annual rabies death toll, significantly, over the decades, from hundreds of deaths per year, in the 1970s and 1980s, to the current figures of approximately 20 to 40 deaths per year, this progress masks a troubling reality: the disease has not been eliminated. And every death from rabies is entirely preventable.
Sri Lanka’s Rabies Crisis: Dogs, Schools, and a Cultural Paradox
Sri Lanka’s relationship with dogs is ancient and complex. In Buddhist tradition the faith of the majority of Sri Lankans compassion extends to all living beings. Feeding stray animals is considered an act of merit (pin). Harming an animal is considered morally reprehensible. This cultural and religious fabric has, over centuries, created a society extraordinarily generous to stray dogs and, unintentionally, a society extraordinarily vulnerable to the diseases they carry.
Across Sri Lanka, from Colombo’s busy urban streets to the most remote village in the deep south or the far north, stray dogs are everywhere. They sleep in temple grounds. They loiter near marketplaces. They gather at rubbish dumps. And they congregate in numbers that would astonish any visitor — at school gates, school canteens, and school playgrounds.
The school dog phenomenon is perhaps the most acute expression of Sri Lanka’s rabies vulnerability. Across the country, virtually every school, urban or rural, large or small, has its unofficial resident pack of stray dogs. These animals are fed daily by students sharing their lunch, by teachers, and by school staff. They become familiar, named, beloved – like Manula. And because they are beloved and familiar, children touch them, play with them, hug them, and allow the dogs to lick their faces, all without any thought of risk.
This is not carelessness. This is kindness, rooted in culture and religion. But it is kindness, without knowledge, and that gap between compassion and information is where rabies lives and kills.
The Economic and Social Toll of Rabies in Sri Lanka
The cost of rabies in Sri Lanka is far greater than the death toll alone suggests. It exacts a profound economic and social price that touches families, the healthcare system, and the broader economy.
Each year, Sri Lanka’s Anti-Rabies Clinics manage an estimated 100,000 to 150,000 dog bite cases. The provision of Post-Exposure Prophylaxis vaccines and immunoglobulin for these patients imposes a massive and recurring burden on the public health budget. The cost of a single PEP course, if purchased privately, runs into tens of thousands of rupees. Multiply this across over a hundred thousand patients annually, and the numbers become daunting.
Beyond direct medical costs, there is the cost of lost productivity. Dog bite patients require multiple hospital visits for vaccine doses. Working adults lose workdays. Farmers and labourers in rural areas, often the most vulnerable to dog bites, face income losses that can devastate already fragile household economies. Children bitten during the school day lose schooling time and, in some cases, develop lasting psychological trauma and cynophobia (fear of dogs).
Then there is the immeasurable social cost: a rabies death in a family is uniquely devastating. It strikes with grotesque swiftness once symptoms appear. Families watch helplessly as a loved one, often a child, deteriorates into terror, agony, and death within days. The psychological scars endure for generations. And the cruel irony is that this death, had the family sought treatment promptly, was entirely and easily preventable.
Protecting Yourself: How to Avoid Dog Bites
Awareness and behavioural change are the first and most important shields against rabies. The following practices, especially when taught to children, can dramatically reduce the risk of dog bites:
Never approach a dog that is eating, sleeping, or caring for puppies. These are the moments when even gentle dogs are most likely to bite defensively. Never run towards or away from a stray dog — sudden movements trigger the chase instinct. Stand still, avoid eye contact, and back away slowly if a dog approaches aggressively.
Never attempt to pet a dog through a fence or gate. Never reach into a dog’s sleeping space. Do not disturb a dog that appears ill or injured without professional assistance. A sick dog is an unpredictable dog.
Teach children at home and at school that while loving animals is wonderful, there is a safe way to do so. Children must understand that they should always ask an adult before approaching an unfamiliar dog, and should never put their faces close to a dog’s face, however friendly the animal appears.
Good Practices When Petting a Dog with an Unknown History
For a dog like Aloka or Manula – a dog beloved by many but with an unknown vaccination history – some simple, common-sense practices can significantly reduce your risk:
Always let the dog come to you rather than approaching it forcefully. Extend the back of your hand slowly, at the dog’s nose level, and allow the dog to sniff and initiate contact. If the dog turns away or shows signs of discomfort ears flattened, tail tucked, growling does not persist.
Pet the dog on the sides of the neck, chest, or back. Avoid the top of the head, initially, and never reach over a dog’s head with a stranger this can feel threatening to the animal. Do not allow a stray dog to lick your face, lips, eyes, or any open wound or sore. After touching any stray or unfamiliar dog, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching your face or food.
If you have children with you, maintain physical supervision at all times. A child’s instinct is to rush forward, kneel down, and hug a dog all of which can be risky with an animal of unknown temperament and health. Channel the child’s love into safe, supervised interaction.
Being a Responsible Dog Owner in Sri Lanka
If you have a dog at home or if you are considering getting one, responsible pet ownership is not just an ethical commitment to your animal. It is a public health responsibility. Here is what every Sri Lankan dog owner must do:
Vaccinate against rabies every year, without exception.
A single dose of rabies vaccine for your dog costs a fraction of the cost of a human PEP course. Your vaccinated dog cannot transmit rabies. Vaccination is available at government veterinary offices island-wide, often at minimal or no cost during mass vaccination campaigns. There is no excuse to leave your dog unvaccinated.
Register your pet.
Dog registration with your local municipal or pradeshiya sabha authority is a legal requirement in Sri Lanka. Registration facilitates rabies vaccination tracking and helps authorities manage stray dog populations.
Sterilise your dog.
Population control is central to rabies elimination. Sterilised dogs do not reproduce, reducing the number of unowned, unvaccinated puppies on the street. Many government and NGO programmes offer low-cost or free sterilisation services.
Do not allow your dog to roam freely.
A dog that roams unsupervised can be bitten by other animals, exposed to rabies in the environment, and can itself bite others. Leashing and containing your dog within a secure space is a basic responsibility of ownership.
Monitor your dog’s health.
Know your dog. Watch for changes in behaviour, like sudden aggression, disorientation, excessive salivation, difficulty swallowing, or aversion to water and light. These can be early signs of rabies. If you suspect your dog has been bitten by an animal of unknown rabies status, contact a veterinarian immediately.
Educate your household and neighbours.
Share information about rabies, wound washing, and the importance of seeking medical attention after dog bites. In Sri Lanka, a significant proportion of dog bite victims, particularly in rural areas, do not seek treatment because they are unaware of the risk or fear stigma. Education saves lives.
Love Your Dog. Protect Your Community.
Aloka and Manula represent something genuine and beautiful about Sri Lankan character, a capacity for compassion, a willingness to extend kindness to creatures beyond our species, a recognition that every living being deserves love. These are not values to be abandoned. They are values to be celebrated, protected and informed.
The goal is not to make Sri Lankans fear dogs. The goal is to make Sri Lankans safer in the love they already give so freely. Wash your hands after petting a stray. Vaccinate your dog. Teach your children. Seek treatment immediately after a bite. These are small acts with life-saving consequences.
Aloka walked in peace. Manula played in joy. May every dog in Sri Lanka, stray or owned, campus icon or temple companion live in a country where they are loved safely, vaccinated consistently, and managed with the compassion and the wisdom that Sri Lanka’s great religious and cultural traditions have always, at their best, demanded.
And may every child who reaches out to touch a dog do so knowing they are safe because adults around them have done their duty.
by Dr. Niroshan Gamage
Director – Public Health Veterinary Services, Ministry of Health
Features
Zelensky tells BBC Putin has started World War 3 and must be stopped
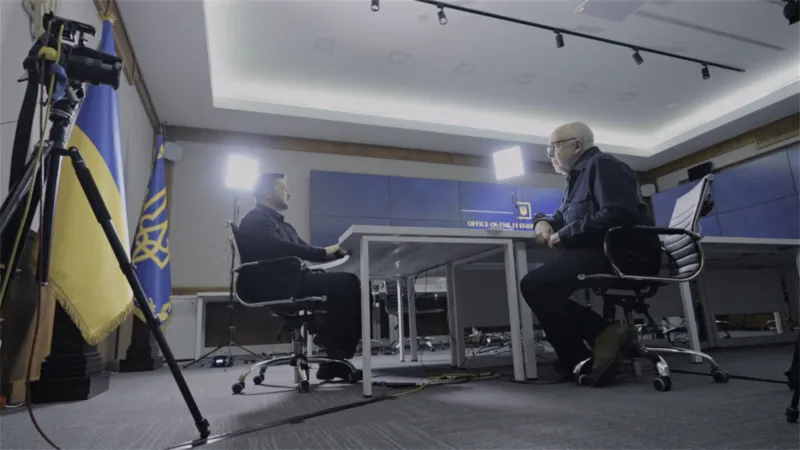

Ukraine’s President Volodymyr Zelensky continues to send out a firm message of defiance.
When we met this weekend in the government headquarters in Kyiv, he said that far from losing, Ukraine would end the war victorious. He was firmly against paying the price for a ceasefire deal demanded by President Vladimir Putin, which is withdrawing from strategic ground that Russia has failed to capture despite sacrificing tens of thousands of soldiers.
Putin, Zelensky said, has already started World War Three, and the only answer was intense military and economic pressure to force him to step back.
“I believe that Putin has already started it. The question is how much territory he will be able to seize and how to stop him… Russia wants to impose on the world a different way of life and change the lives people have chosen for themselves.”
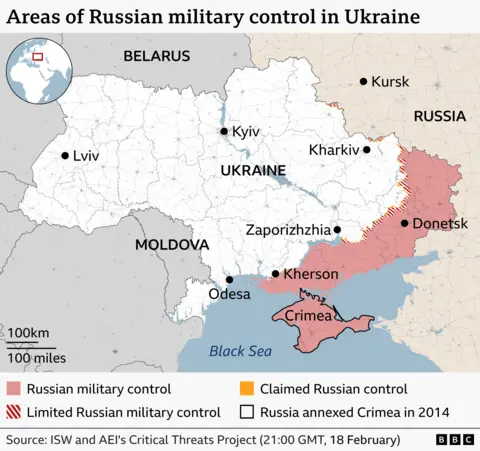
What about Russia’s demand for Ukraine to hand over the 20% of the eastern region of Donetsk that it still holds – a line of towns Ukraine calls “fortress cities” – as well as more land in the southern regions of Kherson and Zaporizhzhia? Isn’t that, I asked, a reasonable request if it produces a ceasefire?
“I see this differently. I don’t look at it simply as land. I see it as abandonment – weakening our positions, abandoning hundreds of thousands of our people who live there. That is how I see it. And I am sure that this ‘withdrawal’ would divide our society.”
But isn’t it a good price to pay if that satisfies President Putin? Do you think it would satisfy him?
“It would probably satisfy him for a while… he needs a pause… but once he recovers, our European partners say it could take three to five years. In my opinion, he could recover in no more than a couple of years. Where would he go next? We do not know, but that he would want to continue the war is a fact.”
I met Volodymyr Zelensky in a conference room inside the heavily-guarded government enclave in a well-to-do corner of central Kyiv. In the interview he spoke mostly in Ukrainian.
You get a sense of the weight of leadership carried by Zelensky from the diligence of his security guards.
Visiting any head of state requires rigorous checks. But entering the presidential buildings in Kyiv takes the process to a level I have rarely experienced before.
It is not surprising in a country at war, with a president who has already been targeted by Russia.
Despite all that, the man who started as an entertainer, who won the Ukrainian version of Strictly Come Dancing in 2006, and played the role of an unexpected president of Ukraine in a TV comedy, before becoming the real-life president of Ukraine, seems to be remarkably resilient.
US President Donald Trump said on the eve of the most recent ceasefire talks in Geneva that “Ukraine better come to the table fast”.
He continues to default to putting more pressure on Ukraine than on Russia.
Western diplomats have indicated since last summer that Trump agrees with Putin that territorial concessions from Ukraine to Russia are the key to the ceasefire Trump wants, ideally before this coming summer.
Plenty of analysts outside the White House also judge that Ukraine cannot win the war and, without making concessions to Moscow, will lose it.
I asked Zelensky whether Trump and the others had a point.
“Where are you now?” Zelensky asked in return. “Today you are in Kyiv, you are in the capital of our homeland, you are in Ukraine. I am very grateful for this. Will we lose? Of course not, because we are fighting for Ukraine’s independence.”
Zelensky has often said that Ukraine can win, but what would victory look like?
Of course, he said, victory meant restoring normal lives for Ukrainians and ending the killing. But the wider view of victory he presented was all about a global threat that he says comes from Putin.
“I believe that stopping Putin today and preventing him from occupying Ukraine is a victory for the whole world. Because Putin will not stop at Ukraine.”
You are not saying that victory is getting all the land back, are you?
“We’ll do it. That is absolutely clear. It is only a matter of time. To do it today would mean losing a huge number of people – millions of people – because the [Russian] army is large, and we understand the cost of such steps. You would not have enough people, you would be losing them. And what is land without people? Honestly, nothing.”
“And we also don’t have enough weapons. That depends not just on us, but on our partners. So as of now that’s not possible but returning to the just borders of 1991 [the year Ukraine declared its independence, precipitating the final collapse of the Soviet Union] without a doubt, is not only a victory, it’s justice. Ukraine’s victory is the preservation of our independence, and a victory of justice for the whole world is the return of all our lands.”
A year ago, Zelensky visited the White House and received a reception one senior Western diplomat described to me as a pre-planned public “diplomatic mugging” from Donald Trump and his Vice-President, JD Vance.
Their argument, in the presence of the world’s media, was watched by millions around the world.
Trump, just inaugurated as president for the second time, was sending the strongest possible signal that the era of support Zelensky and Ukraine had relied on from President Joe Biden was over. Nato members were already on notice from the new administration. Vance had just got back from shattering Western European illusions about the strength of the trans-Atlantic alliance.
Since then, reportedly coached by Britain’s National Security Adviser Jonathan Powell among others, Zelensky has avoided public confrontations with Trump.
The US president has stopped almost all shipments of military aid to Ukraine. But the US still provides vital intelligence, and European countries are spending billions buying weapons from the Americans to give to Ukraine.

I asked Ukraine’s president about Trump’s often contradictory statements, recalling that among the untruths he has uttered is the accusation that Zelensky is a dictator who started the war – a precise echo of claims made by Vladimir Putin.
Zelensky laughed.
“I am not a dictator, and I didn’t start the war, that’s it.”
But can you trust President Trump? If you extract a security guarantee from him, I asked, would he keep his word? He is after all a man who changes his mind.
“It is not only President Trump, we’re talking about America. We are all presidents for the appropriate terms. We want guarantees for 30 years for example. Political elites will change, leaders will change.”
He meant that US security guarantees needed approval from Congress in Washington DC to make them watertight.
“They will be voted on in Congress for a reason. It’s not just presidents. Congress is needed. Because the presidents change, but institutions stay.”
In other words, Donald Trump might be unreliable, but he will not be there for ever.
Zelensky says those security guarantees would have to be in place before he could consider another American demand – the US demand for Ukraine to hold a general election by the summer, echoing another Russian talking point that Zelensky is an illegitimate president. Trump has not demanded elections in Russia, where Putin became leader for the first time on the last day of the 20th Century.
Zelensky said he had not decided whether to stand again, whenever an election is held: “I might run and might not.”
Elections were due in 2024, but they could not be held under martial law that was introduced after Russia’s full-scale invasion.
Holding postponed elections, Zelensky said, was technically possible if they had time to change the law to allow them to happen. But he needed security guarantees for Ukraine first.
He went on to raise so many potential problems about holding an election with millions of Ukrainians abroad as refugees and significant tracts of the country occupied by Russia that I suggested that in reality he was against the idea.
“If this is a condition for ending the war, let’s do it. I said, ‘honestly, you constantly raise the issue of elections’. I told the partners, ‘you need to decide one thing: you want to get rid of me or you want to hold elections? If you want to hold elections, (even if you are not ready to tell me honestly even now), then hold these elections honestly. Hold them in a way that the Ukrainian people will recognise, first of all. And you yourself must recognise that these are legitimate elections'”.
Volodymyr Zelensky has opponents and harsh critics here in Ukraine.
His government was rocked last autumn by a corruption scandal that led to the departure of his closest adviser.
But Zelensky, with a new team, still commands approval ratings that most leaders in Western Europe can only dream about.
He has irritated his allies at times with constant demands for more and better equipment. One of the accusations directed at him in the Oval Office by Trump and Vance a year ago was that he was not sufficiently grateful.
The latest item on his list is permission to manufacture American weapons under licence, including Patriot air defence missiles.
“Today the issue is air defence. This is the most difficult problem. Unfortunately, our partners still do not grant licenses for us to produce systems ourselves, for example, Patriot systems, or even missiles for the systems we already have. So far, we have not achieved success in this.”
Why won’t they do that?
“I don’t know. I have no answer.”
At the end of the interview, he switched from Ukrainian to English.
Given everything he had said, I asked him whether we needed to get ready for an even longer war in Ukraine.
“No, no, no, it’s two parallel tracks… you are playing chess with a lot of leaders, not with Russia. There is not one right way. You have to choose a lot of parallel steps, parallel directions. And one of these parallel ways will, I think, bring success. For us, success is to stop Putin.”
But Vladimir Putin isn’t going to end this war, is he? Unless he’s under massive pressure and he doesn’t seem to be.
“Yes and no. We will see. Yes and no. He doesn’t want, but doesn’t want doesn’t mean he will not. God bless. God bless, we will be successful. Thank you.”
And with that, he posed for photographs, shook hands with the BBC team, and strode out of the room.
[BBC]
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoWhy does the state threaten Its people with yet another anti-terror law?
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoVictor Melder turns 90: Railwayman and bibliophile extraordinary
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoReconciliation, Mood of the Nation and the NPP Government
-

 Features17 hours ago
Features17 hours agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoVictor, the Friend of the Foreign Press
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoNew Zealand meet familiar opponents Pakistan at spin-friendly Premadasa
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTariffs ruling is major blow to Trump’s second-term agenda
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoECB push back at Pakistan ‘shadow-ban’ reports ahead of Hundred auction














