Latest News
Thailand warns clashes with Cambodia could ‘move towards war’
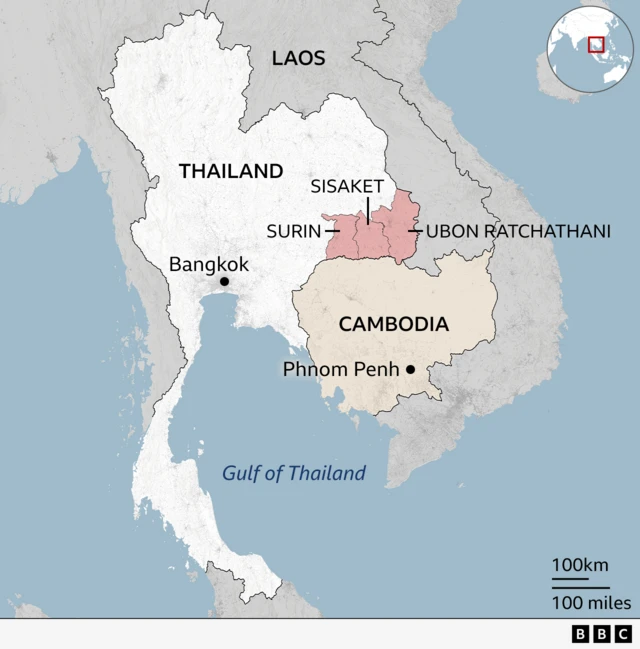
Thailand’s leader has warned that clashes between Thailand and Cambodia, which have killed at least 16 people and displaced tens of thousands in both countries, could “move towards war”.
Acting Prime Minister Phumtham Wechayachai added that the fighting now included heavy weapons and had spread to 12 locations along the border.
Thailand also accused Cambodia of firing into civilian areas and evacuated all villages deemed to be within the radius of its rockets.
Cambodia, for its part, accused Thailand of using cluster munitions. Cluster munitions are banned in much of the world because of their indiscriminate effect on civilian populations. Thailand has not responded to the allegations.
Meanwhile, Thailand’s foreign minister told the Reuters news agency that there was “no need” for third-party mediation in the conflict, even as global leaders appealed for an immediate ceasefire.
Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim, who chairs the Association of South East Asian Nations, or Asean, had earlier offered to facilitate talks between the two countries.
“I welcome the positive signals and willingness shown by both Bangkok and Phnom Penh to consider this path forward,” Anwar wrote on Facebook late Thursday.
But Thai foreign ministry spokesman Nikorndej Balankura told Reuters that the situation must be solved through bilateral means, adding that Phnom Penh must stop its offensive moves.
“I don’t think we need any mediation from a third country yet,” Nikorndej said.
The comments came as both countries updated the death toll from the fighting.
Thailand said 14 civilians and one soldier were killed in the fighting, while provincial authorities in Cambodia said at least one civilian in Oddar Meanchey was killed.
The US has also called for an “immediate cessation of hostilities, protection of civilians and a peaceful resolution of the conflict”.
“We are… gravely concerned by the escalating violence along the Thailand Cambodia border, and deeply saddened by reports of harm to civilians,” State Department spokesman Tommy Pigott said at a regular media briefing.
China, which has political and strategic ties with Cambodia and Thailand, said it is “deeply concerned” over the conflict and hopes both sides can resolve issues through dialogue and consultation.
Australia, the European Union and France have also called for peace.
The United Nations Security Council was expected to meet on Friday over the conflict.
In a letter to the council on Thursday, Cambodia’s Prime Minister Hun Manet had urged it to intervene to “stop Thailand’s aggression”.
Thailand and Cambodia have each accused the other of firing the first shots on Thursday.
Thailand claims the clash began with Cambodia’s military deploying drones to conduct surveillance of Thai troops near the border.
Cambodia says Thai soldiers initiated the conflict when they violated a prior agreement by advancing on a Khmer-Hindu temple near the border.
The dispute between the two countries dates back to more than a hundred years ago, when the borders of the two nations were drawn after the French occupation of Cambodia.
There were sporadic clashes over the years which saw soldiers and civilians killed on both sides.
The latest tensions ramped up in May after a Cambodian soldier was killed in a clash. This plunged bilateral ties to their lowest point in more than a decade.
At a sports complex that was converted into an evacuation centre in Thailand’s Surin province, evacuees – many of them children and elderly – said they were still shaken by the rocket and artillery attacks they witnessed on Thursday.
Older evacuees who had lived through bombardments during the Cambodian Civil War of the 1980s told the BBC the recent fighting was the worst they had experienced.
Joi Phasuwan, from the Phanom Dong Rak district, said she and her two grandchildren “waited a long time” before they finally got moved to the evacuation centre. They moved farther this time compared to past evacuations, she added.
Elsewhere, a small group of older men huddled around the entrance to a school about 10km (6.2 miles) from the border.
All the houses around them were deserted. The men stayed back to guard their homes and livestock, while all the women and children had been evacuated.
They stayed close to an improvised shelter, constructed last month from sections of concrete pipe and reinforced with sandbags and rows of sand-filled tires.
Artillery boomed across this small village all morning, and the Cambodian rocket attacks on Thursday unnerved the men.
The school was also being used by Thai soldiers, but they did not want to be filmed – nor did they want the school to be identified.
The roads were empty, apart from the occasional military lorry ferrying soldiers. Passing through village after village, there was no-one to be seen.
Life all along this border region has been brought to a halt by a dispute over a few old temples and some insignificant strips of forested land.
(BBC)
Latest News
Advisory for Heavy Rain issued for the Central, Uva and Sabaragamuwa provinces and in the Ampara, Batticaloa and Polonnaruwa districts

Advisory for Heavy Rain Issued by the Natural Hazards Early Warning Centre at 12.00 noon on 21 February 2026 valid for the period until 08.30 a.m. 22 February 2026
Due to the low level atmospheric disturbance in the vicinity of Sri Lanka, Heavy showers above 100 mm are likely at some places in the Central, Uva and Sabaragamuwa provinces and in the Ampara, Batticaloa and Polonnaruwa districts and fairly heavy showers above 75 mm are likely at some places elsewhere.
Therefore, the general public is advised to take adequate precautions to minimize damages caused by heavy rain, strong winds and lightning during thundershowers.
Latest News
Ranaweera’s four-for leads Sri Lanka to tense win over West Indies
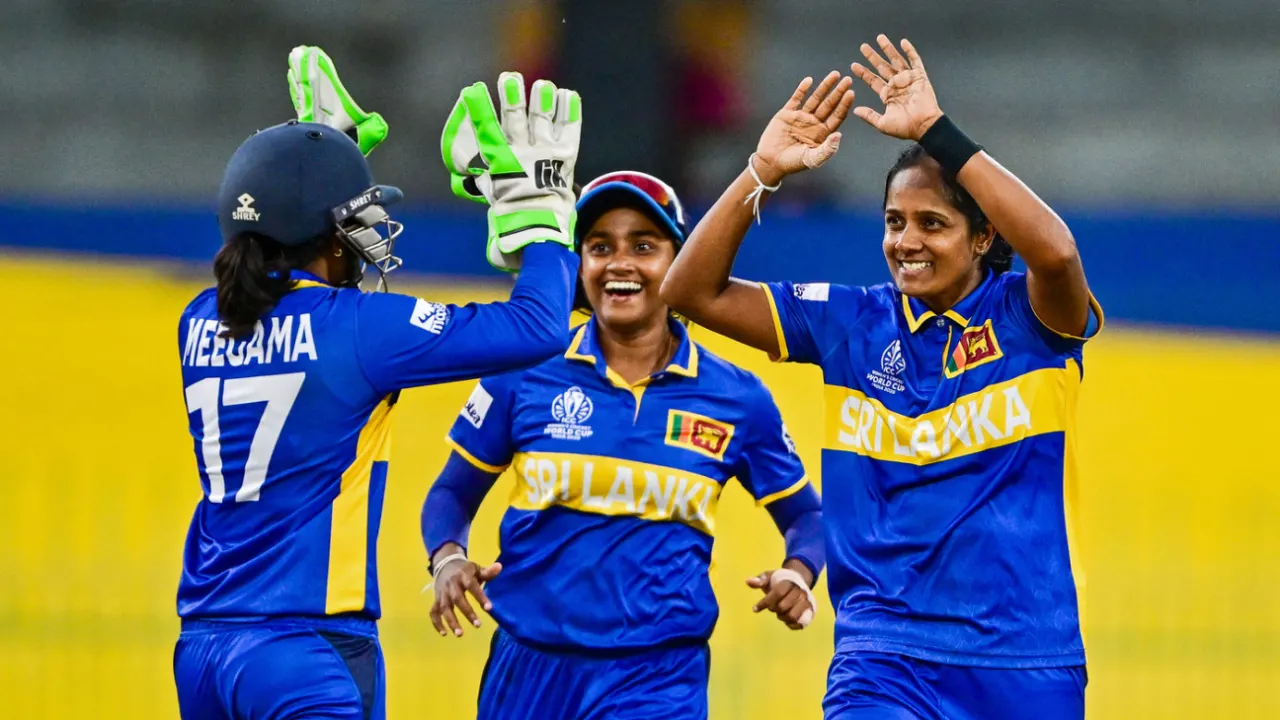

Sri Lanka took a 1-0 lead in the ODI series with a tense ten-run win over West Indies, thanks largely to a match-defining performance from Inoka Ranaweera.
After being asked to bat, Sri Lanka posted 240 for 6, built on half-centuries from Hasini Perera (61 off 86) and Harshitha Samarawickrema (66 off 105). Captain Chamari Athapaththu made 27, while useful middle-order contributions from Nilakshika Silva and Kavisha Dilhari kept the innings moving at a controlled rate. A late cameo from Dewmi Vihanga, who struck 14 off six balls, ensured Sri Lanka pushed towards a competitive total in St George’s in Grenada.
But it was Ranaweera who tilted the contest. The experienced left-arm spinner returned figures of 4 for 44 from her ten overs. She removed the No. 3 Shemaine Campbelle cheaply, dismissed Chinelle Henry soon after, and then returned to break the dangerous stand of 89 between Stefanie Taylor and Jannillea Glasgow in the 40th over, just as West Indies were threatening to surge ahead. Ranaweera also accounted for Shawnisha Hector at the death.
Taylor’s 66 off 83 balls and Glasgow’s 50 off 67 had revived West Indies from early setbacks, and with Aaliyah Alleyne in the middle, the chase remained alive deep into the game. West Indies needed 18 from the last two overs, and 12 from the last six balls. However, Sri Lanka’s spinners held firm, with Dilhari finishing with three wickets, including two in the final over, to complement Ranaweera’s starring role.
West Indies were eventually bowled out for 230 in 49.4 overs. Sri Lanka have now won four of their last five ODIs against West Indies since 2017.
Brief scores:
Sri Lanka Women 240 for 6 in 50 overs (Harshitha Samarawickrama 66, Hasini Perera 61; Hayley Matthews 2-46, Karishma Ramharak 2-57) beat West Indies Women 230 in 49.4 overs (Stefanie Taylor 66, Jannillea Glasgow 50; Inoka Ranaweera 4-44, Kavish Dilhari 3-49) by ten runs
[Cricinfo]
Latest News
Trump brings in new 10% tariff as Supreme Court rejects his global import taxes
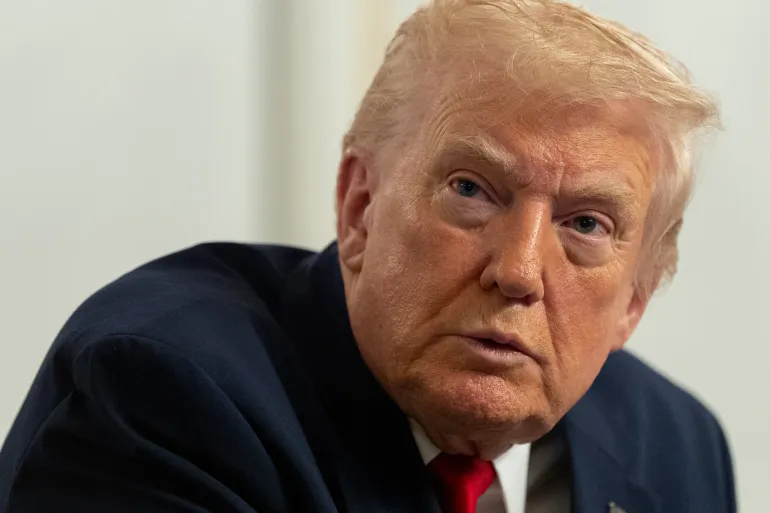

US President Donald Trump has imposed a new 10% global tariff to replace ones struck down by the Supreme Court, calling the ruling “terrible” and lambasting the justices who rejected his trade policy as “fools”.
The president unveiled the plan shortly after the justices outlawed most of the global tariffs the White House announced last year.
In a 6-3 decision, the court held that the president had overstepped his powers.
The decision was a major victory for businesses and US states that had challenged the duties, opening the door to potentially billions of dollars in tariff refunds, while also injecting new uncertainty into the global trade landscape.
Speaking from the White House on Friday, Trump indicated that refunds would not come without a legal battle, saying he expected the matter to be tied up in court for years.
He also said he would turn to other laws to press ahead with his tariffs, which he has argued encourage investment and manufacturing in the US.
“We have alternatives – great alternatives and we’ll be a lot stronger for it,” he said.
The court battle was focused on import taxes that Trump unveiled last year on goods from nearly every country in the world.
The tariffs initially targeted Mexico, Canada and China, before expanding dramatically to dozens of trade partners on what the president billed as “Liberation Day” last April.
The White House had cited a 1977 law, the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA), which gives the president power to “regulate” trade in response to an emergency.
But the measures sparked outcry at home and abroad from firms facing an abrupt rise in taxes on shipments entering the US, and fuelled worries that the levies would lead to higher prices.
Arguing before the court last year, lawyers for the challenging states and small businesses said that the law used by the president to impose the levies made no mention of the word “tariffs”.
They said that Congress did not intend to hand off its power to tax or give the president an “open-ended power to junk” other existing trade deals and tariff rules.
In his opinion, Chief Justice John Roberts, a conservative, sided with that view.
“When Congress has delegated its tariff powers, it has done so in explicit terms and subject to strict limits,” he wrote.
“Had Congress intended to convey the distinct and extraordinary power to impose tariffs, it would have done so expressly, as it consistently has in other tariff statutes.”
The decision to strike down the tariffs was joined by the court’s three liberal justices, as well as two justices nominated by Trump: Amy Coney Barrett and Neil Gorsuch.
Three conservative justices, Clarence Thomas, Brett Kavanaugh and Samuel Alito, dissented.
At the White House, Trump said he was “absolutely ashamed” of the Republican appointees on the court who voted against his trade policy.
He said they were “just being fools and lap dogs” and were “very unpatriotic and disloyal to our Constitution”.
Shares on Wall Street rose after the announcement, with the S&P 500 closing up about 0.7%, as businesses across the US cautiously welcomed the ruling.
“I feel… like a thousand-pound weight has been lifted off my chest,” said Beth Benike, the owner of Busy Baby products in Minnesota, which manufactures products in China.
Nik Holm, chief executive of Terry Precision Cycling, one of the small businesses involved in the case, called the ruling a “relief”.
“Though it will be many months before our supply chain is back up and running as normal, we look forward to the government’s refund of these improperly-collected duties,” he said.
The anticipated refunds and relief from tariff costs may prove elusive, however.
On Friday, Trump imposed the new 10% tariff under a never-used law known as Section 122, which gives the power to put in place tariffs up to 15% for 150 days, at which point Congress must step in.
Analysts expect the White House to consider other tools, such as Section 232 and Section 301, which allow import taxes to address national security risks and unfair trade practices.
Trump has previously used those tools for tariffs, including some announced last year on sectors such as steel, aluminium and cars. Those were untouched by the court ruling.
A White House official said countries that struck trade deals with the US, including the UK, India and the EU, will now face the global 10% tariff under Section 122 rather than the tariff rate they had previously negotiated.
The Trump administration expects those countries to keep abiding by the concessions they had agreed to under the trade deals, the official added.
“Things have only gotten more complicated and more messy today,” said Geoffrey Gertz, senior fellow at the Center for a New American Security in Washington.
Reaction by major trade partners was relatively muted.
“We take note of the ruling by the U.S. Supreme Court and are analysing it carefully,” European Commission spokesman Olof Gill wrote on social media.
The US has already collected at least $130bn in tariffs using the IEEPA law, according to the most recent government data.
In recent weeks, hundreds of firms, including retailer Costco, aluminium giant Alcoa and food importers like tuna fish brand Bumble Bee, have filed lawsuits contesting the tariffs, in a bid to get in line for a refund.
But the decision by the majority does not directly mention refunds, likely handing back the question of how that process might work to the Court of International Trade.
In his dissent, Justice Brett Kavanaugh warned the situation would be a “mess”.
Diane Swonk, chief economist at KPMG US, warned that the cost of litigation could make recouping funds difficult for smaller firms.
“Unfortunately, I’d say curb your enthusiasm, although I understand the desire for relief,” she said.
Steve Becker, head of the law firm Pillsbury, said the “best thing” for businesses would be if the government created a procedure that did not require filing a lawsuit.
[BBC]
“I think companies can be fairly confident that they’ll get their money back eventually,” he added. “How long it will take really is up to the government.”
-

 Life style7 days ago
Life style7 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoThailand to recruit 10,000 Lankans under new labour pact
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoMassive Sangha confab to address alleged injustices against monks
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoGiants in our backyard: Why Sri Lanka’s Blue Whales matter to the world













