Foreign News
Thailand deports dozens of Uyghurs to China

At least 40 Uyghurs have been deported to China, the Thai authorities have confirmed, despite warnings from rights groups that they face possible torture and even death.
The group is thought to have been flown back to China’s Xinjiang region on Thursday, after being held for 10 years in a Bangkok detention centre.
China has been accused of committing crimes against humanity and possibly genocide against the Uyghur population and other mostly Muslim ethnic groups in the north-western region of Xinjiang. Beijing denies all of the allegations.
It is the first time Thailand has deported Uyghurs since 2015.
The deportation has been shrouded in secrecy after serious concerns were raised by the United States and United Nations.
Thai media reported that several trucks, some with windows blocked with sheets of black plastic, left Bangkok’s main immigration detention centre in the early hours of Thursday morning.
Hours later, tracker Flightrader24 showed an unscheduled China Southern Airlines flight leaving Bangkok, eventually arriving in Xinjiang. It was not immediately clear how many people had been deported.
The Thai defence minister told Reuters news agency that Beijing had given assurances the deportees would be looked after.
Beijing said that 40 Chinese illegal immigrants were repatriated from Thailand, but refused to confirm that the group were Uyghurs.
“The repatriation was carried out in accordance with the laws of China and Thailand, international law and international practice,” the foreign ministry said.
Chinese state media said the group had been bewitched by criminal organisations and were stranded in Thailand after illegally leaving the country.
Thailand’s Prime Minister Paetongtarn Shinawatra did not initially confirm any deportations had taken place when asked by reporters.
“In any country in the world actions must adhere to the principles of law, international processes, and human rights,” she said.
The group is thought to be the last of more than 300 Uyghurs who were detained at the Thai border in 2014 after fleeing repression in Xinjiang.
Many were sent to Turkey, which usually offers Uyghurs asylum, while others were deported back to China in 2015 – prompting a storm of protest from governments and human rights groups.
“What is the Thai government doing?” asked opposition lawmaker Kannavee Suebsang on social media on Thursday.
“There must not be Uyghur deportation to face persecution. They were jailed for 11 years. We violated their human rights for too long.”
The detention centre where the Uyghurs – who had been charged with no crime, apart from entering Thailand without a visa – were kept was known to be unsanitary and overcrowded. Five Uyghurs died in custody.
In a statement on Thursday, Human Rights Watch said the group now face a high risk of torture, enforced disappearance and long-term imprisonment.
“Thailand’s transfer of Uyghur detainees to China constitutes a blatant violation of Thailand’s obligations under domestic and international laws,” said the organisation’s Asia director, Elaine Pearson.
“Until yesterday [Wednesday], senior Thai officials had made multiple public assurances that these men would not be transferred, including to allies and UN officials.”
Phil Robertson, director of the Asia Human Rights and Labour Advocates (AHRLA) group, said that the deportations “totally destroyed” the “charade” that the current Thai government was different to the previous one “when it comes to transnational repression and cooperating with authoritarian neighbours”.
Amnesty International described the deportations as “unimaginably cruel”.
Bipartisan members of the US House China Committee on Wednesday issued a statement warning that the deportations “would constitute a clear violation of international human rights norms to which the Kingdom of Thailand is obligated under international law”.
The UN said that it “deeply regrets” the deportations.
There are about 12 million Uyghurs, mostly Muslim, living in Xinjiang, which is officially known as the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR).
The Uyghurs speak their own language, which is similar to Turkish, and see themselves as culturally and ethnically close to Central Asian nations. They make up less than half of the Xinjiang population.
Recent decades have seen a mass migration of Han Chinese (China’s ethnic majority) into Xinjiang, allegedly orchestrated by the state to dilute the minority population there.
China has also been accused of targeting Muslim religious figures and banning religious practices in the region, as well as destroying mosques and tombs.
[BBC]
Foreign News
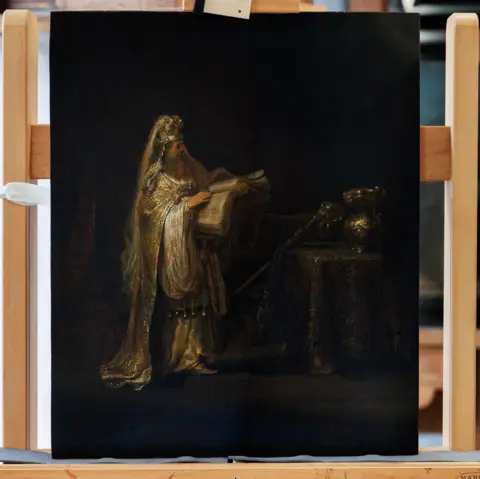
Rembrandt painting worth millions rediscovered after 65 years

A long lost painting by Rembrandt has been rediscovered and authenticated by experts, after its whereabouts were unknown for decades.
Rembrandt’s Vision of Zacharias in the Temple, from 1633, was excluded from a list of the Dutch master’s works in 1960, and disappeared after being sold to a private collector the following year.
But it resurfaced when its owners presented it for tests at the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, which undertook a two-year examination.
“When I saw it in our studio when it was restored, I was immediately struck by the incredible power it has,” Rijksmuseum director Taco Dibbits said.

The Rijksmuseum receives many emails from people asking for information about paintings they have inherited or bought, Dibbits said. In this case, they knew it could be something special.
“It came to us via email and one of our curators thought, this is really an interesting image, we’ve known about the painting for over 100 years but we’ve never seen it.”
The museum confirmed the authenticity after studying the paints, which fit with those used by Rembrandt during that period, and the painting technique and build-up of layers, which are also comparable with his other early works.
The signature is original and the wooden panel dates from the correct period, the researchers said.
“Materials analysis, stylistic and thematic similarities, alterations made by Rembrandt, and the overall quality of the painting all support the conclusion that this painting is a genuine work,” the gallery said.
The painting has all the hallmarks of Rembrandt at the “peak” of the early part of his career, Dibbits said.
“It’s very high quality. Sometimes with Rembrandt’s portraits you feel that he’s producing in quantity, but with this painting you really feel that he dedicated his soul to it.”
The museum will put the painting on public view from Wednesday.
Its value is not known, but the world record auction price for a Rembrandt painting is £20m, set in 2009.
Other Rembrandt paintings to be sold in recent years include one for £8.6m in 2019, a self-portrait for £12.6m in 2020, and another once-lost Rembrandt work for £11m in 2023.
In 2015, a Rembrandt painting was given a price tag of £35m by the UK government after being sold privately.
Last month, a drawing of a lion by the artist sold for $18m (£13m).

[BBC]
Rembrandt was 27 when he created the painting, which depicts the Biblical scene when priest Zacharias is told by the Archangel Gabriel that despite their age, he and his wife will have a son, John the Baptist.
The museum said Rembrandt had given the Biblical story an innovative twist. Instead of depicting the Archangel Gabriel visibly, he only suggested his presence. In doing so, he departed from established visual traditions and introduced a new way of representing this subject.
Rembrandt deliberately chose the decisive moment, just before Gabriel reveals his true identity.
It is one of the few history paintings Rembrandt created during this period. At the time, he was primarily producing portraits, which were highly lucrative.
[BBC]
Foreign News
War photographer Paul Conroy dies as tributes paid
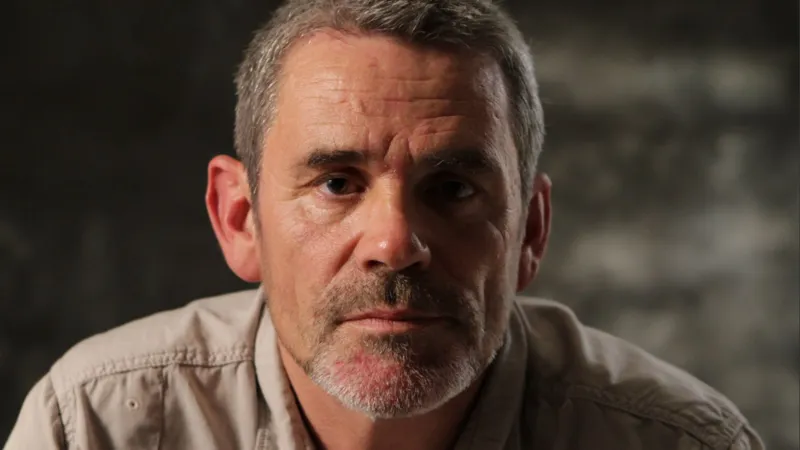

Tributes have been paid to the war photographer Paul Conroy who has died at the age of 61.
He covered conflicts around the world and was wounded in the Syrian army’s bombardment of Homs, which killed his Sunday Times colleague Marie Colvin in 2012.
Their fateful assignment was depicted in the 2018 movie A Private War, with the actor Jamie Dornan playing Conroy.
The Liverpool-born photographer died from a heart attack on Saturday in Devon, where he had lived, his brother Alan told the BBC.
“He did all his life what he wanted to do to make a difference – he found great pleasure in exposing wrongs,” Alan added.
BBC newsreader Clive Myrie posted that he was “utterly devastated” by the news, describing Conroy as “a wonderful photojournalist and a wonderful human being”.
“I counted him as a friend and a decent, principled and kind man. My brutha you will be sorely missed. RIP”
Lindsey Hilsum, international editor at Channel 4, added: “All of us who knew and loved him are devastated.”

Conroy also spent seven years with the Royal Artillery as a soldier before becoming a professional photographer and was a trustee of the Frontline Club for media professionals, diplomats and aid workers.
Its founder Vaughan Smith, who was also in the Army, said: “He was one of the characters – those people who stand out because everybody adores them and they make you feel better.”
The 2018 documentary Under the Wire was made about Conroy’s escape from the 2012 bombardment of a makeshift media centre in Homs, where his colleagues Marie Colvin and Remi Ochlik were killed.
Referring to the Syrians who were killed in the area, he said: “These beautiful people who were being slaughtered, I wanted to tell their story.”
He only realised how badly injured he was when he returned to the UK.
“Obviously I knew I had a huge hole in the back of my leg,” he said.
“But in London I found out I also had a great big piece of shrapnel wedged under my kidneys. I had 23 operations on my leg and others on my abdomen and back. I was in hospital for five months.”
Conroy worked in Libya and Ukraine and had recently returned from an assignment in Cuba.
He also took photos for the British singer Joss Stone and wrote music with her.
She said she was “so grateful to have known him and honoured to call him my friend”.
“I wouldn’t be the person I am today without Paul. Paul Conroy was a legend. A wonderful person through and through. Always standing up for what was right. Always there for those in need.”
He leaves behind a wife, three sons and grandchildren.
[BBC]
Foreign News
Iran begins 40-day mourning after Khamenei killed in US-Israeli attack
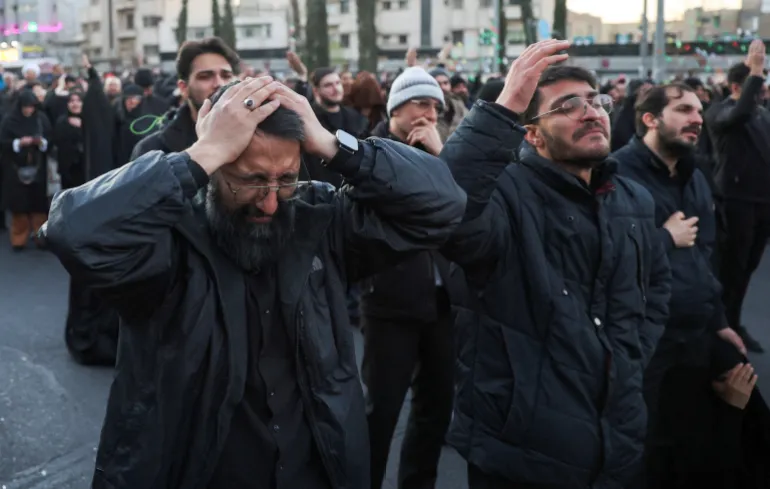

Iran has begun 40 days of mourning after Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei was killed in ongoing attacks by the United States and Israel, according to Iranian state media.
Top security officials were also killed in Saturday’s strikes, along with Khamenei’s daughter, son-in-law and grandson. The killings mark one of the most significant blows to Iran’s leadership since the 1979 Islamic revolution.
President Masoud Pezeshkian condemned the killing as “a great crime”, according to a statement from his office. He also declared seven days of public holidays in addition to the 40-day mourning period.
Reporting from Tehran, Al Jazeera’s Tohid Asadi said people were pouring into the streets of the capital following the news of Khamenei’s killing.
“There will be expected ceremonies,” he said, noting they would likely take place amid continuing bombardment across the country.
Protests denouncing Khamenei’s killing were also reported elsewhere, including Shiraz, Yasuj and Lorestan.
Footage aired by Iranian state media showed supporters mourning at the shrine of Imam Reza in Mashhad, with several people seen crying and collapsing in grief.
The killing also led to protests in neighbouring Iraq, which declared three days of public mourning. In Baghdad, protesters confronted security forces in the heavily fortified Green Zone, which houses Iraqi government buildings and foreign embassies.
Videos verified by Al Jazeera showed demonstrators waving flags and shouting slogans, with witnesses saying some were attempting to mobilise towards the US Embassy. Footage also showed protesters blocking vehicles at a roundabout near one of the entrances to the area.

There was also a protest in the Pakistani city of Karachi, where footage, verified by Al Jazeera, showed people setting fire to and smashing the windows of the US consulate.
However, there have also been reports of celebrations in Iran, with the Reuters news agency quoting witnesses as saying some people had taken to the streets in Tehran, the nearby city of Karaj and the central city of Isfahan.
Meanwhile, the official IRNA news agency reported that a three-person council, consisting of the country’s president, the chief of the judiciary, and one of the jurists of the Guardian Council, will temporarily assume all leadership duties in the country. The body will temporarily oversee the country until a new supreme leader is elected.
Khamenei assumed leadership of Iran in 1989 following the death of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, who had led the Islamic revolution a decade earlier.
While Khomeini was regarded as the ideological force behind the revolution that ended the Pahlavi monarchy, Khamenei went on to shape Iran’s military and paramilitary apparatus, strengthening both its domestic control and its regional influence.
Meanwhile, the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) pledged revenge and said it had launched strikes on 27 bases hosting US troops in the region, as well as Israeli military facilities in Tel Aviv.
[Aljazeera]
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-
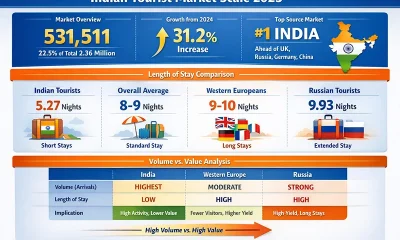
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans













