Features
Teaching physiotherapy in Colombo, a workshop in Indonesia & contact with WHO

Excerpted from Memories that Linger: My journey in the word of disability
by Padmani Mendis
Knowing how to teach using the scientific method gave me confidence in my work. It was during my time at Guys that participatory and learner-centred teaching came to be used in pedagogy. Helen, our tutor, had made sure we knew these well. I now had the chance to use them with responsibility to benefit my students.
They responded well. With the first course that I started using these approaches, all the students passed the final examination, not a usual occurrence at the school. Examiners, included as well as physiotherapy tutors, medical consultants specialised in certain areas. With this batch of students, I had helped Mrs. Thera Fernando, Senior Tutor, to introduce a Community Field Training Module into the curriculum in the second year. The University of Colombo, Department of Community Medicine, our neighbour, gave us permission to use their field training area for our students.
This was the Ethul Kotte Medical Officer of Health or MOH area. On Friday mornings for twelve consecutive weeks our students in pairs visited ten homes within a specified area. On visits, they studied the health of members relating that to their socio-economic situation. Included was a focus on finding those who had mobility problems.
After a break for lunch, in the early afternoon session back at the school, we had a discussion of their findings and what they may do about it. We focused on the advice they would give the family. A record of all this they kept and were assessed on it. This was the first occasion that student therapists and even I, for that matter, had exposure to what community living for this, the poorer segment of our urban society, was like.
Embarking on an International Career
Now at last I really enjoyed working as a physiotherapist in Sri Lanka. Perhaps because I was teaching it. But this would not be for long. I would soon have the opportunity to use this knowledge and experience and journey on to something even more rewarding.
The memories of these new opportunities I would have I will start sharing with you in the next section called “Three Pioneers in Geneva”. In this section I have recalled how my work for the World Health Organization or WHO came about. And how I helped WHO to develop a new strategy for rehabilitation which came to be called Community-Based Rehabilitation, well-known as CBR.
CBR was more successful than one could have imagined. The demand for it grew and I was called upon to visit an ever-increasing number of countries for follow-up, monitoring, evaluation, planning, teaching, and expansion of this strategy. I was required to spend more time in these several roles continuing my journey in disability over the next few decades to promote the global development of CBR for disabled people.
To do this and to balance it with my home life with Nalin, I gave up teaching at the school in 1981. I would miss my students and my colleagues.
How My Work for WHO Came to Be
The year was 1978. I was teaching at the School of Physiotherapy of the Ministry of Health in Colombo. My colleague and boss Thera Fernando had just been nominated by the Department of Health to attend a meeting on Disability and Rehabilitation organised by the World Health Organisation or WHO to be held in Solo, Indonesia in December of that year.
Since she had attended the previous meeting on the same subject in Indonesia, she suggested to the department that I be nominated instead. Very unusual in those days when competition was rife to grab any and every trip abroad. But she was an unusually unselfish person.
Named first was a medical specialist in rheumatology and I was the second nominee. We were to travel together to Indonesia. As pre-workshop preparation, WHO called for two documents which would then be presented at the workshop. One was a Situational Analysis of Disability and Rehabilitation in Sri Lanka and the second was a Plan of Action to introduce what was then called Disability Oriented Rehabilitation to improve the lives of disabled people. Being the junior nominee in a hierarchical health sector the task of preparing these two documents fell on me.
And did I not carry out the task with joyful enthusiasm! As I shared with you, I had returned from the UK and Denmark a few months earlier having followed a two-year diploma course on the teaching of physiotherapy in London and having obtained some practical experience of it in London and Denmark. Well-versed in objectives, strategies, activities, plans of action, monitoring, evaluation and anything and everything else that goes with that, I was up to the task.
The Situation Analysis and the Plan of Action were prepared. So were presentations that were to be made in Solo. This was through the use of transparencies and overhead projectors, long before the advent of computers and multimedia equipment.
I started sharing my memories with you in my belief that I was, since my birth, blessed with good fortune. Some 40 years later, I believe it was that same good fortune that brought me face-to-face with Dr. Einar Helander at this meeting in Indonesia. Dr. Einar Helander had come from WHO, Geneva to facilitate the workshop. He was in charge of the Disability Prevention and Rehabilitation Programme at headquarters. This meeting led to my participating as a co-pioneer of Community-Based Rehabilitation or CBR for the World Health Organisation.
Interruption – Why Disabled People?
Before going further, you may wonder at my use of the description “disabled people”. There is a demand from many Disability Groups and Movements that they be referred to as “persons with disabilities”. It is mandatory now in the UN system that they be called so. There are however scattered groups and individuals, including disabled people, who see this differently and I am one of those.
People who have disabilities are, first and foremost human beings like you and me. They are that part of humanity that have been made disabled by society. Society does so primarily by considering them to be some other kind of human being, essentially different from us who are “normal”.
Society stigmatises them; by seeing only what they cannot do and not what they can do or have the capacities and potential to do; by not providing within our societies facilities that would enable them to do what they can do as human beings. That which would enable them to enjoy their rights as human beings. That which would enable them to carry out their role as citizens – such as adapting education systems with relevant legislation to meet the needs of all children and youth which will then include those who have disabilities participating alongside their peers; adapting transport and public spaces so that all people can use them, be they young or old or have disabilities, and so on.
By not doing these things it is we who disable them. It is not the fault of those that are born with or acquire disability at some point in their life. It is Society that creates disability.
Changing this first and foremost requires an acceptance that this is the fact, that this is the truth. Then only can we bring about change in our beliefs and attitudes so that we accept them as one of us; so that we make a change in our systems and services to enable them to access their right to share in the benefits of being a member of our families, of our communities and of global society; so that they could play their part and take responsibility within these as we do.
This is a Vision. But until we are well on the path to reaching that vision, Society will continue to be responsible for their situation. Society will continue to create disability. They will remain disabled people.
Back to Solo, Indonesia
The first day of the workshop in Solo was a novel experience. Thirty or so participants from the South-East Asian Region of WHO were present. Proceedings began with the customary round of introductions. I was floored when I realised that all bar one were medical specialists. Most in orthopaedic surgery, a few in rheumatology which was a relatively new speciality at the time. And yours truly was the only physiotherapist.
But I had youth on my side together with confidence because I had prepared for the workshop. Sri Lanka’s presentation was to be in the afternoon. I had handed over to my senior partner all the documents for presentation and briefed her on them. The time came for presentation, Sri Lanka was announced.
And lo and behold my senior partner got cold feet. She pushed the papers towards me with the words, “You present.” I tried to persuade her but her feet stayed cold. So I carried out my duty. That I had done so successfully was clear by the barrage of questions that I was asked at the end of the presentation.
And the challenge issued to me by the most senior orthopaedic surgeon of them all and the most eminent of the eminent. And what is more, from India – from the most prestigious rehabilitation institute in Bombay. This was, “We will see how Sri Lanka is going to do that.” Well I am happy to say that over the next few decades Sri Lanka did do a lot of that. Some of which I hope to share with you later in my memories.
Over the next few days we had many small group exercises, problem solving and plenary discussions. On the third day Dr. Helander called me aside and asked me whether I would have dinner with him. That evening we took two “Cyclos” which you may know as cycle rickshaws. I had been carried in a rickshaw to school when I was quite young. I was then staying with my cousins and the “rickshaw coolie” was sent for when their car which usually took us was not available. We had now progressed from man power to pedal power.
We went to a pleasant Indonesian restaurant. Einar, as he insisted on being called now, asked about me and my life back home. I asked about him and his family. And then he sprang a surprise on me. He asked me seemingly as a matter of course whether I would “do some work” for him. I thought perhaps that he would ask me to do some writing for him while sitting at home. Of course I agreed. There was no more talk about the subject for the rest of the week. I returned to Colombo content that I had made my contribution.
But many years later, when we were friends and colleagues working on a common agenda, I asked him about that workshop in Solo. I questioned him as to why he asked what he did and selected me without knowing me, for the pioneering work that he, Gunnel and I did together. He said it was because, “Every time I came round to your group you were challenging those eminent medical men.” Further, he said that I was, “doing it so very politely in a way that made them accept you.”
He did not refer to respect. But respectful I was, taking heed of their age and experience. If I had not done so, they would without doubt have crushed me to a pulp.
An Unexpected Invitation
Time passed. It was now a day in February 1979. I had just recently celebrated my 40th birthday with my family. The postman came as usual in the morning. Unusually though there was a letter indicating on the envelope that it was from WHO Geneva. I wondered, “What is this about?”
Soon to find out that it was from Einar, inviting me to come to Geneva for three months and undertake a short-term consultancy. I would be required to carry out a task preparing a Manual for implementing “Community-Oriented Rehabilitation”. My co-consultant would be Ms. Gunnel Nelson from Gothenburg, Sweden. He would work with us as well. I was expected in Geneva on May 15.
What excitement! With an increasing heart beat I ran next door to where my parents-in-law lived. Reading the letter, they shared my excitement and were oh so happy for me. In that excitement I remember saying foolish things to them – things like, “What on earth is community-oriented rehabilitation?” and “But I don’t know how to write a manual”, “What is a manual?” And I could hardly wait until Nalin came home from work to show him this marvellous letter.
That workshop in Solo marked a turning point in my life. It took me to an invitation to WHO Headquarters in Geneva to be a Consultant on the Disability and Rehabilitation Programme.
Features
Australia’s social media ban: A sledgehammer approach to a scalpel problem

 When governments panic, they legislate. When they legislate in panic, they create monsters. Australia’s world-first ban on social media for under-16s, which came into force on 10 December, 2025, is precisely such a monster, a clumsy, authoritarian response to a legitimate problem that threatens to do more harm than good.
When governments panic, they legislate. When they legislate in panic, they create monsters. Australia’s world-first ban on social media for under-16s, which came into force on 10 December, 2025, is precisely such a monster, a clumsy, authoritarian response to a legitimate problem that threatens to do more harm than good.
Prime Minister Anthony Albanese hailed it as a “proud day” for Australian families. One wonders what there is to be proud about when a liberal democracy resorts to blanket censorship, violates children’s fundamental rights, and outsources enforcement to the very tech giants it claims to be taming. This is not protection; it is political theatre masquerading as policy.
The Seduction of Simplicity
The ban’s appeal is obvious. Social media platforms have become toxic playgrounds where children are subjected to cyberbullying, addictive algorithms, and content that can genuinely harm their mental health. The statistics are damning: 40% of Australian teens have experienced cyberbullying, youth self-harm hospital admissions rose 47% between 2012 and 2022, and depression rates have skyrocketed in tandem with smartphone adoption. These are real problems demanding real solutions.
But here’s where Australia has gone catastrophically wrong: it has conflated correlation with causation and chosen punishment over education, restriction over reform, and authoritarian control over empowerment. The ban assumes that removing children from social media will magically solve mental health crises, as if these platforms emerged in a vacuum rather than as symptoms of deeper societal failures, inadequate mental health services, overworked parents, underfunded schools, and a culture that has outsourced child-rearing to screens.
Dr. Naomi Lott of the University of Reading hit the nail on the head when she argued that the ban unfairly burdens youth for tech firms’ failures in content moderation and algorithm design. Why should children pay the price for corporate malfeasance? This is akin to banning teenagers from roads because car manufacturers built unsafe vehicles, rather than holding those manufacturers accountable.
The Enforcement Farce
The practical implementation of this ban reads like dystopian satire. Platforms must take “reasonable steps” to prevent access, a phrase so vague it could mean anything or nothing. The age verification methods being deployed include AI-driven facial recognition, behavioural analysis, government ID scans, and something called “AgeKeys.” Each comes with its own Pandora’s box of problems.
Facial recognition technology has well-documented biases against ethnic minorities. Behavioural analysis can be easily gamed by tech-savvy teenagers. ID scans create massive privacy risks in a country that has suffered repeated data breaches. And zero-knowledge proof, while theoretically elegant, require a level of technical sophistication that makes them impractical for mass adoption.
Already, teenagers are bragging online about circumventing the restrictions, prompting Albanese’s impotent rebuke. What did he expect? That Australian youth would simply accept digital exile? The history of prohibition, from alcohol to file-sharing, teaches us that determined users will always find workarounds. The ban doesn’t eliminate risk; it merely drives it underground where it becomes harder to monitor and address.
Even more absurdly, platforms like YouTube have expressed doubts about enforcement, and Opposition Leader Sussan Ley has declared she has “no confidence” in the ban’s efficacy. When your own political opposition and the companies tasked with implementing your policy both say it won’t work, perhaps that’s a sign you should reconsider.

The Rights We’re Trading Away
The legal challenges now percolating through Australia’s High Court get to the heart of what’s really at stake here. The Digital Freedom Project, led by teenagers Noah Jones and Macy Neyland, argues that the ban violates the implied constitutional freedom of political communication. They’re right. Social media platforms, for all their flaws, have become essential venues for democratic discourse. By age 16, many young Australians are politically aware, engaged in climate activism, and participating in public debates. This ban silences them.
The government’s response, that child welfare trumps absolute freedom, sounds reasonable until you examine it closely. Child welfare is being invoked as a rhetorical trump card to justify what is essentially state paternalism. The government isn’t protecting children from objective harm; it’s making a value judgment about what information they should be allowed to access and what communities they should be permitted to join. That’s thought control, not child protection.
Moreover, the ban creates a two-tiered system of rights. Those over 16 can access platforms; those under cannot, regardless of maturity, need, or circumstance. A 15-year-old seeking LGBTQ+ support groups, mental health resources, or information about escaping domestic abuse is now cut off from potentially life-saving communities. A 15-year-old living in rural Australia, isolated from peers, loses a vital social lifeline. The ban is blunt force trauma applied to a problem requiring surgical precision.
The Privacy Nightmare
Let’s talk about the elephant in the digital room: data security. Australia’s track record here is abysmal. The country has experienced multiple high-profile data breaches, and now it’s mandating that platforms collect biometric data, government IDs, and behavioural information from millions of users, including adults who will need to verify their age to distinguish themselves from banned minors.
The legislation claims to mandate “data minimisation” and promises that information collected solely for age verification will be destroyed post-verification. These promises are worth less than the pixels they’re displayed on. Once data is collected, it exists. It can be hacked. It can be subpoenaed. It can be repurposed. The fine for violations, up to AUD 9.5 million, sounds impressive until you realise that’s pocket change for tech giants making billions annually.
We’re creating a massive honeypot of sensitive information about children and families, and we’re trusting companies with questionable data stewardship records to protect it. What could possibly go wrong?
The Global Domino Delusion
Proponents like US Senator Josh Hawley and author Jonathan Haidt praise Australia’s ban as a “bold precedent” that will trigger global reform. This is wishful thinking bordering on delusion. What Australia has actually created is a case study in how not to regulate technology.
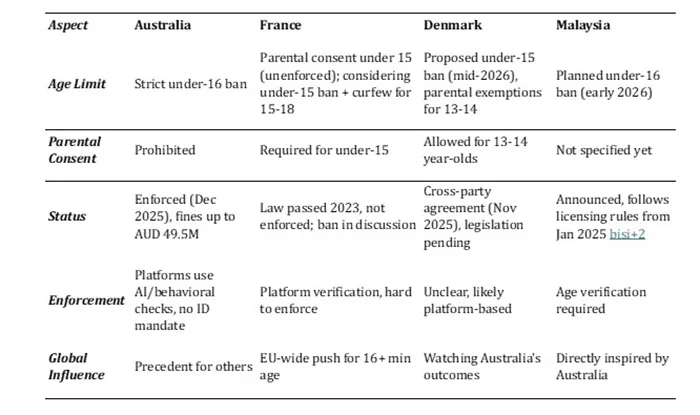
France, Denmark, and Malaysia are watching, but with notable differences. France’s model includes parental consent options. Denmark proposes exemptions for 13-14-year-olds with parental approval. These approaches recognise what Australia refuses to acknowledge: that blanket prohibitions fail to account for individual circumstances and family autonomy.
The comparison table in the document reveals the stark rigidity of Australia’s approach. It’s the only country attempting outright prohibition without parental consent. This isn’t leadership; it’s extremism. Other nations may cherry-pick elements of Australia’s approach while avoiding its most draconian features. (See Table)
The Real Solutions We’re Ignoring
Here’s what actual child protection would look like: holding platforms legally accountable for algorithmic harm, mandating transparent content moderation, requiring platforms to offer chronological feeds instead of engagement-maximising algorithms, funding digital literacy programmes in schools, properly resourcing mental health services for young people, and empowering parents with better tools to guide their children’s online experiences.
Instead, Australia has chosen the path of least intellectual effort: ban it and hope for the best. This is governance by bumper sticker, policy by panic.
Mia Bannister, whose son’s suicide has been invoked repeatedly to justify the ban, called parental enforcement “short-term pain, long-term gain” and urged families to remove devices entirely. But her tragedy, however heart-wrenching, doesn’t justify bad policy. Individual cases, no matter how emotionally compelling, are poor foundations for sweeping legislation affecting millions.
Conclusion: The Tyranny of Good Intentions
Australia’s social media ban is built on good intentions, genuine concerns about child welfare, and understandable frustration with unaccountable tech giants. But good intentions pave a very particular road, and this road leads to a place where governments dictate what information citizens can access based on age, where privacy becomes a quaint relic, and where young people are infantilised rather than educated.
The ban will fail on its own terms, teenagers will circumvent it, platforms will struggle with enforcement, and the mental health crisis will continue because it was never primarily about social media. But it will succeed in normalising digital authoritarianism, expanding surveillance infrastructure, and teaching young Australians that their rights are negotiable commodities.
When this ban inevitably fails, when the promised mental health improvements don’t materialize, when data breaches expose the verification systems, and when teenagers continue to access prohibited platforms through VPNs and workarounds, Australia will face a choice: double down on enforcement, creating an even more invasive surveillance state, or admit that the entire exercise was a costly mistake.
Smart money says they’ll choose the former. After all, once governments acquire new powers, they rarely relinquish them willingly. And that’s the real danger here, not that Australia will fail to protect children from social media, but that it will succeed in building the infrastructure for a far more intrusive state. The platforms may be the proximate target, but the ultimate casualties will be freedom, privacy, and trust.
Australia didn’t need a world-first ban. It needed world-class thinking. Instead, it settled for a world of trouble.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT, Malabe. The views and opinions expressed in this article are personal.)
Features
Sustaining good governance requires good systems

A prominent feature of the first year of the NPP government is that it has not engaged in the institutional reforms which was expected of it. This observation comes in the context of the extraordinary mandate with which the government was elected and the high expectations that accompanied its rise to power. When in opposition and in its election manifesto, the JVP and NPP took a prominent role in advocating good governance systems for the country. They insisted on constitutional reform that included the abolition of the executive presidency and the concentration of power it epitomises, the strengthening of independent institutions that overlook key state institutions such as the judiciary, public service and police, and the reform or repeal of repressive laws such as the PTA and the Online Safety Act.
The transformation of a political party that averaged between three to five percent of the popular vote into one that currently forms the government with a two thirds majority in parliament is a testament to the faith that the general population placed in the JVP/ NPP combine. This faith was the outcome of more than three decades of disciplined conduct in the aftermath of the bitter experience of the 1988 to 1990 period of JVP insurrection. The manner in which the handful of JVP parliamentarians engaged in debate with well researched critiques of government policy and actions, and their service in times of disaster such as the tsunami of 2004 won them the trust of the people. This faith was bolstered by the Aragalaya movement which galvanized the citizens against the ruling elites of the past.
In this context, the long delay to repeal the Prevention of Terrorism Act which has earned notoriety for its abuse especially against ethnic and religious minorities, has been a disappointment to those who value human rights. So has been the delay in appointing an Auditor General, so important in ensuring accountability for the money expended by the state. The PTA has a long history of being used without restraint against those deemed to be anti-state which, ironically enough, included the JVP in the period 1988 to 1990. The draft Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PSTA), published in December 2025, is the latest attempt to repeal and replace the PTA. Unfortunately, the PSTA largely replicates the structure, logic and dangers of previous failed counter terrorism bills, including the Counter Terrorism Act of 2018 and the Anti Terrorism Act proposed in 2023.
Misguided Assumption
Despite its stated commitment to rule of law and fundamental rights, the draft PTSA reproduces many of the core defects of the PTA. In a preliminary statement, the Centre for Policy Alternatives has observed among other things that “if there is a Detention Order made against the person, then in combination, the period of remand and detention can extend up to two years. This means that a person can languish in detention for up to two years without being charged with a crime. Such a long period again raises questions of the power of the State to target individuals, exacerbated by Sri Lanka’s history of long periods of remand and detention, which has contributed to abuse and violence.” Human Rights lawyer Ermiza Tegal has warned against the broad definition of terrorism under the proposed law: “The definition empowers state officials to term acts of dissent and civil disobedience as ‘terrorism’ and will lawfully permit disproportionate and excessive responses.” The legitimate and peaceful protests against abuse of power by the authorities cannot be classified as acts of terror.
The willingness to retain such powers reflects the surmise that the government feels that keeping in place the structures that come from the past is to their benefit, as they can utilise those powers in a crisis. Due to the strict discipline that exists within the JVP/NPP at this time there may be an assumption that those the party appoints will not abuse their trust. However, the country’s experience with draconian laws designed for exceptional circumstances demonstrates that they tend to become tools of routine governance. On the plus side, the government has given two months for public comment which will become meaningful if the inputs from civil society actors are taken into consideration.
Worldwide experience has repeatedly demonstrated that integrity at the level of individual leaders, while necessary, is not sufficient to guarantee good governance over time. This is where the absence of institutional reform becomes significant. The aftermath of Cyclone Ditwah in particular has necessitated massive procurements of emergency relief which have to be disbursed at maximum speed. There are also significant amounts of foreign aid flowing into the country to help it deal with the relief and recovery phase. There are protocols in place that need to be followed and monitored so that a fiasco like the disappearance of tsunami aid in 2004 does not recur. To the government’s credit there are no such allegations at the present time. But precautions need to be in place, and those precautions depend less on trust in individuals than on the strength and independence of oversight institutions.
Inappropriate Appointments
It is in this context that the government’s efforts to appoint its own preferred nominees to the Auditor General’s Department has also come as a disappointment to civil society groups. The unsuitability of the latest presidential nominee has given rise to the surmise that this nomination was a time buying exercise to make an acting appointment. For the fourth time, the Constitutional Council refused to accept the president’s nominee. The term of the three independent civil society members of the Constitutional Council ends in January which would give the government the opportunity to appoint three new members of its choice and get its way in the future.
The failure to appoint a permanent Auditor General has created an institutional vacuum at a critical moment. The Auditor General acts as a watchdog, ensuring effective service delivery promoting integrity in public administration and providing an independent review of the performance and accountability. Transparency International has observed “The sequence of events following the retirement of the previous Auditor General points to a broader political inertia and a governance failure. Despite the clear constitutional importance of the role, the appointment process has remained protracted and opaque, raising serious questions about political will and commitment to accountability.”
It would appear that the government leadership takes the position they have been given the mandate to govern the country which requires implementation by those they have confidence in. This may explain their approach to the appointment (or non-appointment) at this time of the Auditor General. Yet this approach carries risks. Institutions are designed to function beyond the lifespan of any one government and to protect the public interest even when those in power are tempted to act otherwise. The challenge and opportunity for the NPP government is to safeguard independent institutions and enact just laws, so that the promise of system change endures beyond personalities and political cycles.
by Jehan Perera
Features
General education reforms: What about language and ethnicity?

 A new batch arrived at our Faculty again. Students representing almost all districts of the country remind me once again of the wonderful opportunity we have for promoting social and ethnic cohesion at our universities. Sadly, however, many students do not interact with each other during the first few semesters, not only because they do not speak each other’s language(s), but also because of the fear and distrust that still prevails among communities in our society.
A new batch arrived at our Faculty again. Students representing almost all districts of the country remind me once again of the wonderful opportunity we have for promoting social and ethnic cohesion at our universities. Sadly, however, many students do not interact with each other during the first few semesters, not only because they do not speak each other’s language(s), but also because of the fear and distrust that still prevails among communities in our society.
General education reform presents an opportunity to explore ways to promote social and ethnic cohesion. A school curriculum could foster shared values, empathy, and critical thinking, through social studies and civics education, implement inclusive language policies, and raise critical awareness about our collective histories. Yet, the government’s new policy document, Transforming General Education in Sri Lanka 2025, leaves us little to look forward to in this regard.
The policy document points to several “salient” features within it, including: 1) a school credit system to quantify learning; 2) module-based formative and summative assessments to replace end-of-term tests; 3) skills assessment in Grade 9 consisting of a ‘literacy and numeracy test’ and a ‘career interest test’; 4) a comprehensive GPA-based reporting system spanning the various phases of education; 5) blended learning that combines online with classroom teaching; 6) learning units to guide students to select their preferred career pathways; 7) technology modules; 8) innovation labs; and 9) Early Childhood Education (ECE). Notably, social and ethnic cohesion does not appear in this list. Here, I explore how the proposed curriculum reforms align (or do not align) with the NPP’s pledge to inculcate “[s]afety, mutual understanding, trust and rights of all ethnicities and religious groups” (p.127), in their 2024 Election Manifesto.
Language/ethnicity in the present curriculum
The civil war ended over 15 years ago, but our general education system has done little to bring ethnic communities together. In fact, most students still cannot speak in the “second national language” (SNL) and textbooks continue to reinforce negative stereotyping of ethnic minorities, while leaving out crucial elements of our post-independence history.
Although SNL has been a compulsory subject since the 1990s, the hours dedicated to SNL are few, curricula poorly developed, and trained teachers few (Perera, 2025). Perhaps due to unconscious bias and for ideological reasons, SNL is not valued by parents and school communities more broadly. Most students, who enter our Faculty, only have basic reading/writing skills in SNL, apart from the few Muslim and Tamil students who schooled outside the North and the East; they pick up SNL by virtue of their environment, not the school curriculum.
Regardless of ethnic background, most undergraduates seem to be ignorant about crucial aspects of our country’s history of ethnic conflict. The Grade 11 history textbook, which contains the only chapter on the post-independence period, does not mention the civil war or the events that led up to it. While the textbook valourises ‘Sinhala Only’ as an anti-colonial policy (p.11), the material covering the period thereafter fails to mention the anti-Tamil riots, rise of rebel groups, escalation of civil war, and JVP insurrections. The words “Tamil” and “Muslim” appear most frequently in the chapter, ‘National Renaissance,’ which cursorily mentions “Sinhalese-Muslim riots” vis-à-vis the Temperance Movement (p.57). The disenfranchisement of the Malaiyaha Tamils and their history are completely left out.
Given the horrifying experiences of war and exclusion experienced by many of our peoples since independence, and because most students still learn in mono-ethnic schools having little interaction with the ‘Other’, it is not surprising that our undergraduates find it difficult to mix across language and ethnic communities. This environment also creates fertile ground for polarizing discourses that further divide and segregate students once they enter university.
More of the same?
How does Transforming General Education seek to address these problems? The introduction begins on a positive note: “The proposed reforms will create citizens with a critical consciousness who will respect and appreciate the diversity they see around them, along the lines of ethnicity, religion, gender, disability, and other areas of difference” (p.1). Although National Education Goal no. 8 somewhat problematically aims to “Develop a patriotic Sri Lankan citizen fostering national cohesion, national integrity, and national unity while respecting cultural diversity (p. 2), the curriculum reforms aim to embed values of “equity, inclusivity, and social justice” (p. 9) through education. Such buzzwords appear through the introduction, but are not reflected in the reforms.
Learning SNL is promoted under Language and Literacy (Learning Area no. 1) as “a critical means of reconciliation and co-existence”, but the number of hours assigned to SNL are minimal. For instance, at primary level (Grades 1 to 5), only 0.3 to 1 hour is allocated to SNL per week. Meanwhile, at junior secondary level (Grades 6 to 9), out of 35 credits (30 credits across 15 essential subjects that include SNL, history and civics; 3 credits of further learning modules; and 2 credits of transversal skills modules (p. 13, pp.18-19), SNL receives 1 credit (10 hours) per term. Like other essential subjects, SNL is to be assessed through formative and summative assessments within modules. As details of the Grade 9 skills assessment are not provided in the document, it is unclear whether SNL assessments will be included in the ‘Literacy and numeracy test’. At senior secondary level – phase 1 (Grades 10-11 – O/L equivalent), SNL is listed as an elective.
Refreshingly, the policy document does acknowledge the detrimental effects of funding cuts in the humanities and social sciences, and highlights their importance for creating knowledge that could help to “eradicate socioeconomic divisions and inequalities” (p.5-6). It goes on to point to the salience of the Humanities and Social Sciences Education under Learning Area no. 6 (p.12):
“Humanities and Social Sciences education is vital for students to develop as well as critique various forms of identities so that they have an awareness of their role in their immediate communities and nation. Such awareness will allow them to contribute towards the strengthening of democracy and intercommunal dialogue, which is necessary for peace and reconciliation. Furthermore, a strong grounding in the Humanities and Social Sciences will lead to equity and social justice concerning caste, disability, gender, and other features of social stratification.”
Sadly, the seemingly progressive philosophy guiding has not moulded the new curriculum. Subjects that could potentially address social/ethnic cohesion, such as environmental studies, history and civics, are not listed as learning areas at the primary level. History is allocated 20 hours (2 credits) across four years at junior secondary level (Grades 6 to 9), while only 10 hours (1 credit) are allocated to civics. Meanwhile, at the O/L, students will learn 5 compulsory subjects (Mother Tongue, English, Mathematics, Science, and Religion and Value Education), and 2 electives—SNL, history and civics are bunched together with the likes of entrepreneurship here. Unlike the compulsory subjects, which are allocated 140 hours (14 credits or 70 hours each) across two years, those who opt for history or civics as electives would only have 20 hours (2 credits) of learning in each. A further 14 credits per term are for further learning modules, which will allow students to explore their interests before committing to a A/L stream or career path.
With the distribution of credits across a large number of subjects, and the few credits available for SNL, history and civics, social/ethnic cohesion will likely remain on the back burner. It appears to be neglected at primary level, is dealt sparingly at junior secondary level, and relegated to electives in senior years. This means that students will be able to progress through their entire school years, like we did, with very basic competencies in SNL and little understanding of history.
Going forward
Whether the students who experience this curriculum will be able to “resist and respond to hegemonic, divisive forces that pose a threat to social harmony and multicultural coexistence” (p.9) as anticipated in the policy, is questionable. Education policymakers and others must call for more attention to social and ethnic cohesion in the curriculum. However, changes to the curriculum would only be meaningful if accompanied by constitutional reform, abolition of policies, such as the Prevention of Terrorism Act (and its proxies), and other political changes.
For now, our school system remains divided by ethnicity and religion. Research from conflict-ridden societies suggests that lack of intercultural exposure in mono-ethnic schools leads to ignorance, prejudice, and polarized positions on politics and national identity. While such problems must be addressed in broader education reform efforts that also safeguard minority identities, the new curriculum revision presents an opportune moment to move this agenda forward.
(Ramya Kumar is attached to the Department of Community and Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jaffna).
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
by Ramya Kumar
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoMembers of Lankan Community in Washington D.C. donates to ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka’ Flood Relief Fund
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPope fires broadside: ‘The Holy See won’t be a silent bystander to the grave disparities, injustices, and fundamental human rights violations’
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPakistan hands over 200 tonnes of humanitarian aid to Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoUnlocking Sri Lanka’s hidden wealth: A $2 billion mineral opportunity awaits
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoArmy engineers set up new Nayaru emergency bridge
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoOfficials of NMRA, SPC, and Health Minister under pressure to resign as drug safety concerns mount
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoExpert: Lanka destroying its own food security by depending on imported seeds, chemical-intensive agriculture
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoFlawed drug regulation endangers lives

























