Features
Sustainable solution to decline in tea production, export revenue and livelihood issues

by Jayampathy Molligoda
Chairman, Sri Lanka Tea Board
(1) Introduction:
The word “sustainability” is often distorted without being used in ecological context to get its proper meaning. In simple terms, we have the responsibility to protect the right of future generations to live in a safe environment. Similarly, Climate change can be understood as a set of alterations in the average weather caused by global warming due to the emission of greenhouse gases. Climate change phenomenon is serious, which is worse than the COVID-19 pandemic. it is the one challenge that potentially has the most severe impacts globally and on Sri Lanka. The very reason for this is that climate change affects virtually every aspect of our ‘every day today’ life, economic, social and environmental. It is a multidimensional challenge, with its impacts ranging from issues like human health, supply of safe water and food, biodiversity, economic development, etc.
(2) Systems view of life:
Modern Science has come to realize that all scientific theories are approximations to the true nature of reality. Science doesn’t have answers to natural phenomena. Mechanistic view looks at a closed view of a specific area which is a tiny part of a large system. They have dominated our culture for the past three hundred years and is now about to change. Before 1500 AD the dominant world view was that people lived in small communities and experienced nature by the interdependence of spiritual and material phenomena.
The Systems view looks at the world in terms of relationships and integration, inter-dependence of all phenomena i.e.: physical, biological, social, and cultural. Instead of concentrating on basic building blocks, the systems approach emphasizes basic principles of organization.
According to Prof. Fritjof Capra, an Austrian-born American physicist, the architect of “systems view of life” to find lasting solutions, there are solutions to the major problems of our time. They require a radical shift in our perceptions, our thinking, and our values. An “Eco system” is a living system of communities of plants and animals, microbes sharing an environment with non- living plants such as air, water, climate, soil. In my view, the above is the best illustration to understand the importance of adhering to the “system view of life” to find lasting solutions. Capra’s view is that our traditional politicians and business leaders have been unable to provide long term solutions to these problems and he welcomed the creation of social movements founded on the premises to change the current traditional sociological paradigm and to build sustainable communities.
From the systemic point of view, the only viable solutions are those that are “sustainable” Therefore, the challenge of our time is to create sustainable communities, that is, social and cultural environments in which we can satisfy our needs and aspirations without diminishing the chances of future generations. The sustainable communities need to be designed in such a way its social structures do not interfere with natures inherent ability to sustain life but support and corporate with natures inherent ability to sustain life.
(3) Structures, Processes and patterns:
The following ten points are useful in order to understand as to how the eco- system works.
1. Eco system is a living system of communities of plants and animals, microbes sharing an environment with non- living plants such as air, water, climate, soil
2. The theory of living system tries to understand this and the ecological literature deals with the basic principles of ecology (and live accordingly)
3. Nature, every organism, plant, micro-organism, cells, tissues all are in a living system.
4. All living systems need energy and food.
5. All living systems produce waste, but there is no net waste
6. Capra expresses the life of any living organism as made up of pattern, process and structure.
7. If we apply these ideas to ourselves or our organizations, we can see that in the patterns we find our identity.
8. In the processes we develop our relationships, our beliefs, our principles and behaviours becoming more conscious.
9. In the structures we become more fluid, more focused on the present moment; we become alive.
10. The building of sustainable communities is deeply connected to our search for a new sociological paradigm.
This gave rise to the concept of Complex Adaptive Systems, as a multidisciplinary concept- are considered complex because they are made-up of diverse elements which are interconnected with each other and are adaptive in that they have the capacity to change and learn from experience.
(4) Decline in tea production, market share, revenue, despite chemical application:
In this connection, we wish to state that Sri Lankan tea production has been drastically declining over a period of time, despite supplying large quantities of imported artificial fertilizer. For an example, in 2010 the total tea production was 330 million kilos, covering 222,000 hectares, wherein some 160, 000 metric tons of fertilizer per year had been used on an average basis up to date on a regular basis, however, we have ended up with only 289 million kilos of tea production in 2020, covering 253,000 hectares. The compound annual average growth rate (CAGR) was negative 1.5% and the Sri Lankan tea industry cannot sustain anymore as both quality, quantity as well as the competitiveness have drastically eroded. As a result, our market share has come down and the foreign exchange revenue which was around US $ 1.6 Billion eight years back has now come down to US $ 1,24 million/year only. As you are aware, during the period 2017 to end 2019, a large number of tea factories had to close down and many smallholders were badly affected and the new/re planting extents were less than 1%, where as it should have been at least @2% of the cultivated extent.
As a result of excessive usage of agro-chemicals, there has been a number of rejections of our Ceylon tea consignments reported from the major important markets such as Japan, EU, UK, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan etc. This situation has arisen due to detection of pesticide residues in the Ceylon Teas exported, which are over and the above the permitted maximum residue levels (MRLs). Tea Exporters Association (TEA) has brought to the notice of SLTB notice on number of occasions the serious non- compliances which includes detection of excessive pesticide and other chemical residues over and above MRLs. In addition, the presence of foreign/extraneous matters and high moisture levels which lead to microbial contamination & fungus formation may end up in development of micro toxin fungus – these will become health hazard.
(5) Tea plantation system as a complex adaptive system:
My own view is that the long- term goal of Sri Lankan tea industry would be to build “sustainable communities” for the tea plantations and, achieving higher foreign exchange earnings from tea exports may be only one of the unit objectives.
A sustainable community is one that is economically, environmentally, and socially healthy and resilient. It meets challenges through integrated solutions rather than through fragmented approaches that meet one of those goals at the expense of the others. And it takes a long-term perspective—one that’s focused on both the present and future.
Scientists began to observe certain properties in biological systems. The adaptation of the individual independent components within the system to the environment was one such property. The experts observed this phenomenon was visible in systems such as eco-systems, global economics systems, and social systems.
(6) Strategies implemented by the new administration:
With the new administration, the government together with the private sector stakeholders have been able to reverse the negative trends experienced previously and the higher fob prices and increased tea auction sale averages are now getting tricked down to growers, thus addressing the livelihood income issues systematically.
The Sri Lanka tea industry witnessed a recovery amidst the COVID pandemic, with a substantial increase in production and the export volume during the first quarter of 2021 compared to the corresponding period as well as the year 2020 compared to 2019.
During the Q 1- January to march ’21, the tea export revenue was Rs. 65 Billion, up by Rs. 16 billion YoY, from Rs 49 Billion during the 1Q, 2020.
Q 1- January to march ’21 cumulative production totaled 74 million kgs, up by 20 Mn. kg.
FOB price was Rs. 939/= per kilo during the Q1, which is an increase of 13%, from Rs. 827/= during the corresponding period 2020.
FOB price in US $ during the Q1 was US$ 4.77 as against US$ 4.47 during Q1 -20.
March fob in US $ was ($ 4.87) the highest ever.
FOB price during the year 2020 was Rs 867/=per kilo, when compared to Rs 823/= per kilo during the year 2019.
Consequent to this cabinet decision under the caption “Towards a green socio-economic pattern with sustainable solutions to climate change” actions have been taken by SLTB to request stakeholders to encourage them to produce, supply and use organic manure to be set up on each agro- climatic region in large quantities. It was suggested in the SLTB circular that immediate action be taken by TRI to formulate and prepare specifications of organic manure applications covering different applications such as Nursery stage, immature, mature VP and Seedling and recommendations for small holdings etc. The development of the organic fertilizer business needs high tech inputs based on R&D, the required raw material availability and market acceptance based on different crops. The regulatory issues that prohibit or delay arranging import of trial quantities of organic materials (without micro- organism) for R&D evaluation need to be addressed. The necessary guidelines from the regulatory authorities should support development of organic fertilizer at large scale.
(7) Implementation of tea industry strategic plan:
As a solution, we have recommended the stakeholders to follow strategies which includes ‘Integrated weed management system’ and migrate in to offering high quality ‘Ceylon Tea’ with near Zero pesticide & other chemicals to the global market in accordance with our ‘Tea industry strategic plan 20-25’ and CTTA tea strategy-road map.
One of the most striking features of the current operations of the stakeholders is the increased awareness and adherence of the social & environmental considerations at estate level. Ceylon tea is at an advantageous position in the global market viz; other competitors for reasons such as “Zero tolerance” policy on child labour, adherence to environmental considerations on a sustainable basis and of course the quality of Ceylon tea as perceived by the buyers. As a result, Ceylon tea continues to fetch a higher price at the Colombo auction compared to teas from other producing countries, although the cost structures and productivity levels of our estates are totally disproportionate to make the industry commercially viable in short to medium term scenario.
Tea plantations have to therefore pursue environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices & methods in all their agricultural field operations (i) tea manufacturing processes(ii) and managing its employees (iii)to ensure that all-natural resources and eco-systems will be managed in a sustainable manner. The companies will have to make every endeavor to conserve the usage of all resources by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste through practicing cleaner production principles. They will strive to be self-sufficient in green energy to operate all our tea factories through harnessing the hydropower potential within all the lands belonging to the company.
There are many strategies recommended by TRI and others such as development of Agro- forestry farming systems using all unutilised estate land to have ‘nitrogen fixation’ as suggested by Chairman TRI. This will improve the soil porosity, provided we issue guidelines instructing them to follow TRI guidelines on Integrated soil fertility management strategies as mandatory good agricultural practices (GAP)towards minimizing soil acidity, top soil erosion and wastage of inputs etc.
(8) Conclusion:
As stated, it is a fact that there has been no increase in productivity, but a gradual decline in tea productivity measured in terms of the yield per hectare in Sri Lankan tea estates, partly due to continuous application of chemical fertilizer and due to difficulties in adopting mitigating strategies to arrest negative impact of climate change. This depleted soil condition and land degradation issues need to be corrected as a matter of priority. This proposed strategy will enable the growers at least to correct the high acidity levels in the soil and improve soil porosity and tea product quality.
In sustainability circles much is written about “three pillars of sustainability” or in other words, “triple bottom line” of environment, society, and economy. My own view is this is to confuse ends with means. The Environmental sustainability and Human well-being are two desirable points. Economic wellbeing in the long run is driven by those two. In other words, the necessary precondition for long term economic sustainability and profitability of the tea estates is environmental and social well-being from the long- term perspective.
As for marketing of tea in the global markets, the discerning customers have high expectations of the standards and practices applied by the supply chain including tea estates. For example, Tea” is made according to the principles of “sustainable food” thus providing values to discerning customers, employees and all other stake holders. SLTB global promotion campaign aims to popularize tea drinking around the world in order to expand demand and increase per capita consumption, using three USPs; authenticity means demonstrating sustainability credentials, wellness factor and the premium quality of Ceylon Tea.
If the estate management does not look at long term view, it is unlikely they make profits on a continuous basis. Eventually, the long- term value creation for the shareholders depends on the sustainable development of the estates and the community in which they operate. That is why I consider tea plantation sector as one of the truly complex adaptive systems.
Are we leaving the tea plantations to future generations in a better condition than the one we inherited?
Features
Challenges to addressing allegations during Sri Lanka’s armed conflict

A political commentator has attributed the UK sanctions against four individuals, three of whom were top ranking Army and Navy Officers associated with Sri Lanka’s armed conflict, to the failure of successive governments to address human rights allegations, which he describes as a self-inflicted crisis. The reason for such international action is the consistent failure of governments to conduct independent and credible inquiries into allegations of war crimes; no ‘effective investigative mechanism’ has been established to examine the conduct of either the Sri Lankan military or the LTTE.
He has not elaborated on what constitutes an “effective investigative mechanism. He has an obligation and responsibility to present the framework of such a mechanism. The hard reality however is that no country, not even South Africa, has crafted an effective investigative mechanism to address post conflict issues.
INVESTIGATIVE MECHANISMS
The hallmark of a credible investigative mechanism should be unravelling the TRUTH. No country has ventured to propose how such a Mechanism should be structured and what its mandate should be. Furthermore, despite the fact that no country has succeeded in setting up a credible truth-seeking mechanism, the incumbent government continues to be committed to explore “the contours of a strong truth and reconciliation framework” undaunted by the failed experiences of others, the most prominent being South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission.
South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission is often cited as the gold standard for post conflict Mechanisms. Consequently, most titles incorporate the word “Truth” notwithstanding the fact that establishing the “Truth” was a failure not only in South Africa but also in most countries that attempted such exercises.
Citing the South African experience, Prof. G. L. Peiris states: “pride of place was given to sincere truth-telling which would overcome hatred and the primordial instinct for revenge. The vehicle for this was amnesty…… Despite the personal intervention of Mandela, former State President P. W. Botha was adamant in his refusal to appear before the Commission, which he deemed as ‘a fierce unforgiving assault’ on Afrikaaners” (The Island, 01 April, 2025). In the case of Sri Lanka too, disclosures to find the “Truth” would be all about the other party to the conflict, thus making Truth seeking an accusatory process, instead of a commitment to finding the Truth. The reluctance to engage in frank disclosure is compounded by the fear of recrimination by those affected by the Truth.
Continuing Prof. Peiris cites experiences in other countries. “Argentina, the power to grant amnesty was withheld from the Commission. In Columbia, disclosure resulted not in total exoneration, but in mitigating sentences. In Chile, prosecutions were feasible only after a prolonged interval since the dismantling of Augusta Pinochet’s dictatorship ….” (Ibid).
The mechanisms adopted by the countries cited above reflect their own social and cultural values. Therefore, Sri Lanka too has to craft mechanisms in keeping with its own civilisational values of restorative and not retributive justice for true reconciliation, as declared by President J. R, Jayewardene in San Francisco as to what the global attitude should be towards Japan at the conclusion of World War II. Since the several Presidential Commissions appointed under governments already embody records of alleged violations committed, the information in these commission reports should be the foundation of the archival records on which the edifice of reconciliation should be built.
ESTABLISHING DUE CONTEXT
The suggestion that an independent and credible inquiry be conducted into allegations of war crimes reflects a skewed understanding of the actual context in which the armed conflict in Sri Lanka occurred. Even the UNHRC has acknowledged that the provisions of “Article 3 common to the four Geneva Conventions relating to conflicts not of an international character is applicable to the situation in Sri Lanka, as stated in para. 182 of the OISL Report by the UNHRC Office. Therefore, the correct context is International Humanitarian Law with appropriate derogations of Human Rights law during an officially declared Emergency as per the ICCPR.; a fact acknowledged in the OISL report.
Consequently, the armed conflict has to conform to provisions of Additional Protocol II of 1977, because “This Protocol, which develops and supplements Article 3 common to the Geneva Conventions is the due context. There is no provision for “alleged war crimes” in the Additional Protocol. Although Sri Lanka has not formally ratified Additional Protocol II, the Protocol is today accepted by the Community of Nations as Customary Law. On the other hand, “war crimes” are listed in the Rome Statute; a Statute that Sri Lanka has NOT ratified and not recognized as part of Customary Law.
Therefore, any “investigative mechanism” has to be conducted within the context cited above, which is Additional Protocol II of 1977.
SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE
On the other hand, why would there be a need for Sri Lanka to engage in an independent and credible inquiry into allegations, considering the following comment in Paragraph 9.4 and other Paragraphs of the Lessons Learnt and Reconciliation Commission (LLRC)?
“In evaluating the Sri Lankan experience in the context of allegations of violations of IHL (International Humanitarian Law), the Commission is satisfied that the military strategy that was adopted to secure the LTTE held areas was one that was carefully conceived in which the protection of the civilian population was given the highest priority”
9.7 “Having reached the above conclusion, it is also incumbent on the Commission to consider the question, while there is no deliberate targeting of civilians by the Security Forces, whether the action of the Security Forces of returning fire into the NFZs was excessive in the context of the Principle of Proportionality…” (Ibid)
The single most significant factor that contributed to violations was the taking of Civilians in the N Fire Zone hostage (NFZ) by the LTTE. This deliberate act where distinction between civilian and combatant was deliberately abandoned, exposed and compromised the security of the Civilians. The consequences of this single act prevent addressing whether military responses were proportionate or excessive, or whether the impact of firing at make-shift hospitals were deliberate or not, and whether limiting humanitarian aid was intentional or not. These issues are recorded and addressed in the Presidential Commission Reports such as LLRC and Paranagama. This material should be treated as archival material on which to build an effective framework to foster reconciliation.
UK SANCTIONS
Sanctions imposed by the UK government as part of an election pledge for Human Rights violations during the armed conflict is a direct act of intervention according to Article 3 of the Additional Protocol of 1977 that is the acknowledged context in which actions should be judged.
Article 3 Non-intervention states:
1 “Nothing in the Protocol shall be invoked for the purpose of affecting the sovereignty of a State or the responsibility of the government by all legislative means, to maintain or re-establish law and order in the State or to defend the national unity and territorial integrity of the State”.
2 “Nothing in the Protocol shall be invoked as a justification for intervening directly or indirectly, for any reason whatsoever, in the armed conflict or in the internal or external affairs of the High Contracting Party in the territory on which the conflict occurs”.
Targeting specific individuals associated with the armed conflict in Sri Lanka is a direct assault of intervention in the internal affairs of Sri Lanka. The UK government should be ashamed for resorting to violating International Law for the sake of fulfilling an election pledge. If Sri Lanka had issued strictures on the UK government for not taking action against any military officers responsible for the Bloody Sunday massacre where 26 unarmed civilians participating in a protest march were shot in broad daylight, Sri Lanka would, in fact be intervening in UK’s internal affairs.
CONCLUSION
The UK’s action reflects the common practice of making election pledges to garner targeted votes of ethnic diasporas. The influence of ethnic diasporas affecting the conduct of mainstream politics is becoming increasingly visible, the most recent being the Tamil Genocide Education Week Act of Ontario that was dismissed by the Supreme Court of Canada on grounds the Provincial Legislations have no jurisdiction over Federal and International Laws.
However, what should not be overlooked is that the armed conflict occurred under provisions of common Article 3 of the Geneva Conventions. This Article is developed and supplemented by Additional Protocol II of 1977. Therefore, since all Geneva Conventions are recognised as Customary Law, so should the Additional Protocol II be, because it is a development of common Article 3.
Imposing sanctions under provisions of Additional Protocol II amounts to Intervention in internal affairs of a State as stated in Article 3 of the Protocol; II cited above. Such interventions are prohibited under provisions of international law.
The need to revive independent and credible inquiries after the lapse of 16 years is unrealistic because those who were perpetrators and victims alike cannot be identified and/or located. Furthermore, the cost of disclosure because of the possibility of retribution would compromise their security. A realistic approach is to use the material recorded in the Presidential Commission Reports and treat them as archival records and use the lessons learnt from them to forge a workable framework that would foster unity and reconciliation with the survivors in all communities This is not to live in the past but to live in the here and now – the present, which incidentally, is the bedrock of Sri Lanka’s civilisational values.
by Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
The Silent Invasion: Unchecked spread of oil palm in Sri Lanka

Sri Lanka’s agricultural landscape is witnessing a silent yet profound transformation with the rapid expansion of oil palm plantations. Once introduced as a commercial crop, the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) is now at the center of a heated debate, with environmentalists and scientists warning of its devastating ecological consequences.
Speaking to The Island research scientist Rajika Gamage, said: “The spread of oil palm in Sri Lanka is not just a concern for biodiversity, but also for water resources, soil stability, and even local economies that rely on traditional crops.”
A Brief History of Oil Palm Cultivation
Oil palm, originally from West and Central Africa, was first cultivated for commercial purposes in Java in 1948 by Dutch colonists. It reached Malaysia and Indonesia by 1910, where its lucrative potential drove large-scale plantations.
According to Gamage, in Sri Lanka, the first significant oil palm plantation was established in 1968 at Nakiyadeniya Estate by European planters, initially covering a mere 0.5 hectares. Today, oil palm cultivation is predominantly concentrated in Galle, Matara, and Kalutara districts, with smaller plantations in Colombo, Rathnapura, and Kegalle.
Over the decades, he says the commercial viability of oil palm has prompted its expansion, often at the cost of native forests and traditional agricultural lands. Government incentives and private investments have further accelerated the spread of plantations, despite growing concerns over their environmental and social impacts.
Economic Boon or Environmental Curse?
Supporters of oil palm industry argue that it is the most efficient crop for vegetable oil production, yielding more oil per hectare than any other alternative. Sri Lanka currently imports a significant amount of palm oil, and expanding local production is seen as a way to reduce dependence on imports and boost local industries. However, Gamage highlights the hidden costs: “Oil palm plantations deplete water sources, contribute to soil erosion, and threaten native flora and fauna. These are long-term damages that far outweigh the short-term economic benefits.”
One of the primary environmental concerns is the aggressive water consumption of oil palm, which leads to the depletion of underground aquifers. This is particularly evident in areas such as Kalu River and Kelani River wetlands, where native ecosystems are being severely affected. Additionally, soil degradation caused by extensive monoculture farming results in loss of fertility and increased vulnerability to landslides in hilly regions.
Furthermore, studies show that oil palm plantations disrupt the natural habitats of endemic species. “Unlike rubber and coconut, oil palm does not support Sri Lanka’s rich biodiversity. It alters the soil composition and prevents the regeneration of native plant species,” Gamage explains. The loss of forest cover also exacerbates human-wildlife conflicts, as displaced animals venture into human settlements in search of food and shelter.
A Threat to Indigenous Agriculture and Culture
Beyond environmental concerns, oil palm is also threatening traditional crops like kitul (Caryota urens) and palmyrah (Borassus flabellifer), both of which hold economic and cultural significance. “These native palms have sustained rural livelihoods for centuries,” says Gamage. “Their gradual replacement by oil palm could lead to economic instability for small-scale farmers.”
Kitul tapping, an age-old tradition in Sri Lanka, provides a source of income for thousands of families, particularly in rural areas. The syrup extracted from kitul is used in local cuisine and traditional medicine. Similarly, palmyrah has deep roots in Sri Lankan culture, particularly in the Northern and Eastern provinces, where its products contribute to food security and local industries.
The rise of oil palm plantations has led to the clearing of lands that once supported the traditional crops. With large-scale commercial investments driving oil palm expansion, small-scale farmers are finding it increasingly difficult to sustain their livelihoods. Gamage warns, “If we allow oil palm to replace our native palms, we risk losing not just biodiversity, but also a vital part of our cultural heritage.”
The Global Perspective: Lessons from Other Nations
Sri Lanka is not the first country to grapple with the consequences of oil palm expansion. Malaysia and Indonesia, the world’s leading producers of palm oil, have faced severe deforestation, biodiversity loss, and socio-economic conflicts due to unchecked plantation growth.
In Indonesia, for example, vast tracts of rainforest have been cleared for palm oil production, leading to habitat destruction for endangered species such as orangutans and Sumatran tigers. Additionally, indigenous communities have been displaced, sparking legal battles over land rights.
Malaysia has attempted to address some of these issues by introducing sustainability certifications, such as the Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil (MSPO) standard. However, implementation challenges remain, and deforestation continues at an alarming rate.
Sri Lanka can learn valuable lessons from these experiences. Implementing strict land-use policies, promoting agroforestry practices, and ensuring transparency in plantation expansion are crucial steps in mitigating environmental damage while supporting economic development.
The Urgent Need for Action
Despite these concerns, Sri Lanka has yet to enforce strict regulations on oil palm expansion. Gamage urges authorities to intervene: “It is imperative that we implement policies to control its spread before it is too late. The unchecked expansion of oil palm will lead to irreversible environmental damage.”
To address this issue, experts suggest a multi-pronged approach:
Stronger Land-Use Policies
– The government must enforce restrictions on oil palm cultivation in ecologically sensitive areas, such as wetlands and forest reserves.
Reforestation and Rehabilitation
– Efforts should be made to restore degraded lands by reintroducing native tree species and promoting sustainable agroforestry.
Supporting Traditional Agriculture
– Incentives should be provided to farmers growing traditional crops like kitul and palmyrah, ensuring that these industries remain viable.
Public Awareness and Education
– Raising awareness among local communities about the environmental and social impacts of oil palm can empower them to make informed decisions about land use.
Sustainable Alternatives
– Encouraging research into alternative vegetable oil sources, such as coconut oil, which has long been a staple in Sri Lankan agriculture, could reduce reliance on palm oil.
As Sri Lanka stands at a crossroads, the decisions made today will determine the country’s ecological and agricultural future. While the economic benefits of oil palm are undeniable, its long-term environmental and social costs cannot be ignored. The challenge now is to strike a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability before the damage becomes irreversible.
In conclusion Gamage said, “We must act now. If we allow oil palm to spread unchecked, future generations will bear the cost of our inaction.”
Sri Lanka has the opportunity to take a different path—one that prioritises biodiversity conservation, sustainable agriculture, and the well-being of local communities. The time for decisive action is now.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
A plea for establishing a transboundary Blue-Green Biosphere Reserve in Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay
Blue-green land and waterscapes act as ecological corridors across land and water in creating an ecological continuity in order to protect and restore the habitats of native and naturalised species.
In addition, these ecological corridors also help to conserve and improve the habitats of migratory species, as well. One of the main objectives of establishing blue-green land-waterscapes is to reconcile increasing local/regional development and human livelihood challenges in a sustainable manner while, at the same time, safeguard biodiversity and their habitats/ecosystems, as far as possible.
While green landscapes are natural and semi-natural terrestrial vegetation types like natural forests and grasslands, blue waterscapes are aquatic or semi-aquatic vegetation types such as seagrass meadows, mangroves and coastal and other wetlands. These vegetated coastal ecosystems known as ‘blue carbon’ ecosystems are some of the most productive on Earth and located at the interfaces among terrestrial, freshwater and marine environments. They provide us with essential ecosystem services, such as serving as a buffer in coastal protection from storms and erosion, spawning grounds for fish, filtering pollutants and contaminants from coastal waters thus improving coastal water quality and contributing to all important food security.
In addition, they capture and store “blue” carbon from the atmosphere and oceans at significantly higher rates per unit area than tropical forests (Figure 1) and hence act as effective carbon sinks. By storing carbon, these ecosystems help to reduce the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, thus contributing significantly to mitigate the effects of climate change.

Figure 1: Carbon storage in different vegetation types (Source – What Is Blue Carbon and Why Does It Matter? – Sustainable Travel International)
.Blue-green Carbon Markets
The recognition of blue carbon (BC) ecosystems (primarily mangroves, seagrasses and tidal marshes) as an effective natural climate solution paved the way for their inclusion within carbon markets. Blue carbon is the marine analog of green carbon, which refers to carbon captured by terrestrial (i.e., land-based) plants. The blue-green carbon market involves buying and selling carbon credits from projects that protect and restore coastal and marine ecosystems (blue carbon) and terrestrial ecosystems (green carbon). Since Blue Carbon ecosystems have higher carbon sequestration (capture and store) potential compared to their terrestrial counterparts, blue Carbon credits are worth over two times more than green carbon credits. They offer opportunities for commercial enterprises to offset carbon emissions and in turn support climate action.
Blue Carbon projects are expected to grow twofold in the near future. With the recent surge in international partnerships and funding, there is immense growth potential for the blue carbon market. However, it is critically important to look beyond the value of the carbon sequestered to ensure the rights and needs of local communities that are central to any attempt to mitigate climate change using a blue and green carbon project.
Blue Carbon projects can serve as grassroot hubs for sustainable development by developing nature-based solutions in these ecosystems thus contributing to both climate change mitigation and adaptation. Globally, numerous policies, coastal management strategies, and tools designed for conserving and restoring coastal ecosystems have been developed and implemented. Policies and finance mechanisms being developed for climate change mitigation may offer an additional route for effective coastal management. The International Blue Carbon Initiative, for example, is a coordinated, global program focused on conserving and restoring coastal ecosystems for the climate, biodiversity and human wellbeing.
Until recently, most of these opportunities focus on carbon found in the above ground vegetative biomass and do not account for the carbon in the soil. On the other hand, blue carbon, in particular has the potential for immense growth in carbon capture economics in the near future and can provide significant socioeconomic and environmental benefits. Consequently, blue -green carbon habitats in the Gulf of Mannar – Palk Bay region represent invaluable assets in climate change mitigation and coastal ecosystem conservation and sustainable development.
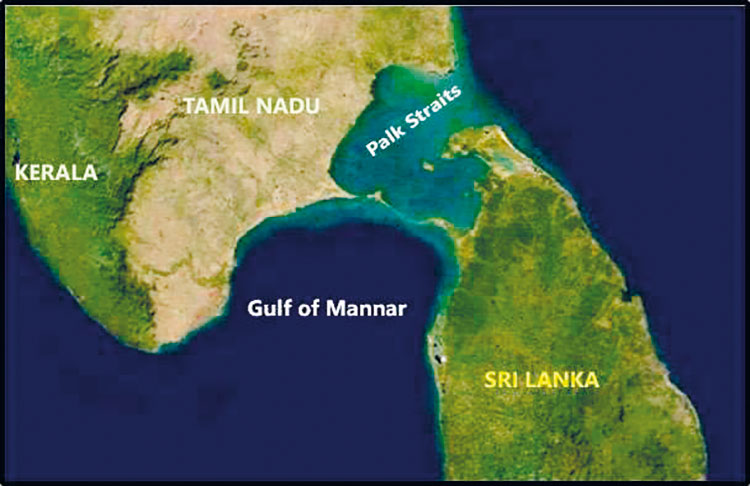
Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay Trans-boundary Region
The Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay region form a transboundary area within the waters of southeastern India and northwestern Sri Lanka. This region supports dense seagrass meadows having a high level of marine biodiversity including marine mammals such as dugong. Sea turtles are frequent visitors to the gulf while sharks, dolphins, sperm and baleen whales too, have been reported from this area. The Mannar region is recognized as an Important Marine Mammal Area (IMMA) of the world by IUCN (Figure 2) and also an Important Bird Area by Birdlife International. This region as a whole is a store house of unique biological wealth of global significance and as such is considered as one of the world’s richest regions from a marine biodiversity perspective.
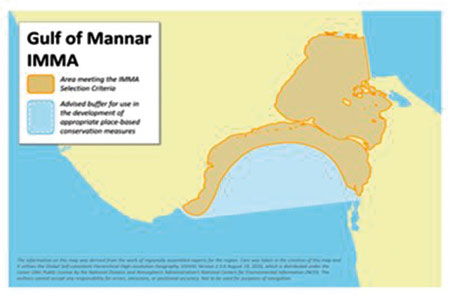
Figure 2. Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay IMMA (Source – IUCN Joint SSC/WCPA Marine Mammal Protected Areas Task Force, 2022 IUCN-MMPATF (2022)
Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve – India
India has already declared a part of this region as the UNESCO Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve covering an area of 10,500 km2 of ocean with 21 islands and the adjoining coastline. The islets and coastal buffer zone include beaches, estuaries, and tropical dry broadleaf forests, while the surrounding seascape of the Marine National Park (established in 1986) and a 10 km strip of the coastal landscape that include seaweed communities, seagrass communities, coral reefs, salt marshes and mangrove forests form the coastal and marine component of the biosphere reserve on the Indian side of the Gulf of Mannar.
Sri Lankan ‘Proposed’ Biosphere Reserve
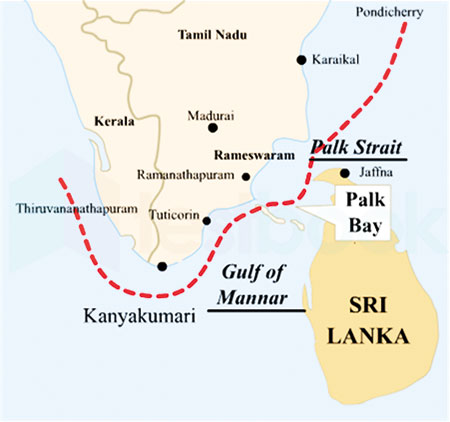
On the Sri Lankan side of the Palk Bay there is a semi-enclosed shallow water body between the southeast coast of India and Sri Lanka, with a water depth maximum of 13 m. To the south, a chain of low islands and reefs known as Adam’s Bridge or Rama Setu (Rama’s Bridge), separates Palk Bay from the Gulf of Mannar. The Palk Bay leads to Palk Strait (Figure 3). Palk Bay is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar. Sediments discharged by rivers and transported by the surf currents as littoral drift settle in this sink.
On the Sri Lankan side of the Palk Bay, studies are being conducted by the Dugong and Seagrass Conservation Project to establish an additional 10,000 hectares of Marine Protected Area to support the conservation of dugongs and their seagrass habitat in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay. This project will involve the preparation of a multiple-community-based management plan in conjunction with government, fishing communities and the tourism industry.
With this valuable information emerging from projects of this nature, Sri Lanka has real opportunities to create a large marine protected area in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay region and eventually merging them together with the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve of India to form a trans-boundary biosphere Reserve.
Terrestrial cum Marine Spatial Plan for the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay Region
Therefore, an excellent opportunity awaits both the Governments of Sri Lanka and India to collaborate in preparing of a terrestrial and marine spatial plan for this region, a prerequisite before going further on designing and implementing large scale development plans in establishing wind energy farms, mineral sand extraction, fishing industry, oil exploration and tourism development.
Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning (CMSP) is an integrated, place-based approach for allocating coastal and marine resources and space, while protecting the ecosystems that provide these vital resources.
On the Indian side, the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere reserve is well established and functional. On the Sri Lankan side, already there are three DWLC managed protected areas i) Adam’s Bridge Marine National Park (# 29 in the map – 18,990 ha declared in 2015), ii) Vedithalathiv Nature Reserve (# 35 -29,180 ha declared in 2016) and iii) Vankalai Sanctuary ( # 97 -4839 ha declared in 2008) (Figure 4) which can serve as the core zone of the Sri Lankan counterpart of a trans-boundary biosphere reserve. Due to the integrated nature of shallow wetland and terrestrial coastal habitats, Vankalai Sanctuary, in particular is highly productive, supporting high ecosystem and species diversity.
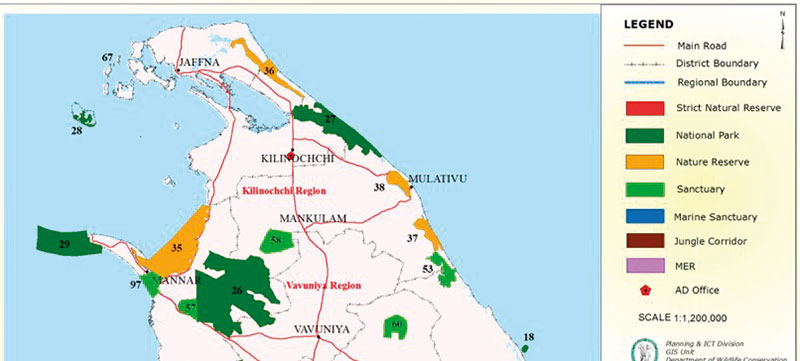
Figure 4: Protected Areas in Norther Sri Lanka Managed by the Department of Wildlife Conservation Source: DWLC
This site provides excellent feeding and living habitats for a large number of water bird species, including annual migrants, which also use this area on arrival and during their exit from Sri Lanka.
Having several coastal and marine protected areas already within the Sri Lankan territory provide an excellent opportunity to establish the Gulf of Mannar – Palk Bay blue-green Biosphere Reserve (Sri Lanka) initially and eventually to join up seamlessly with the already established Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve on the Indian side to create a trans-boundary blue-green biosphere reserve.
This makes perfect sense because unlike sedentary plant species, mobile animal and plant groups (phytoplankton, in particular) do not respect human demarcated territorial boundaries. The provision of a common and unhindered protected coastal and marine passage for their customary movement for food and raising young is therefore of crucial importance in conservation management. Scientific evidence-based selection of additional areas, if necessary and their respective boundaries are best be determined in consultation with expert groups on marine mammals and reptiles, birds, fish, coastal vegetation conservation, sociology and industrial development from both sides of the divide.
Proper spatial planning needs to be done before large-scale development plans are designed and implemented in order to avoid conflicts of interest leading to inordinate delays and teething problems in project initiation. As a priority, the protected blue-green core and buffer regions need to be demarcated for their conservation. This could best be done in this narrow passage of land and water between Sri Lanka and India
( Palk Strait & Gulf of Mannar) by preparing a marine and terrestrial spatial plan along the UNESCO Man and Biosphere conceptual guidelines differentiating core, buffer and transition zones. While the protected areas in the core and buffer zone provide all important ecosystem services that would also serve as breeding ground for fish, crustaceans, marine reptiles, birds and mammals thereby provisioning sustainable industries to be developed in the surrounding transition areas demarcated in the joint spatial plan.
In addition, the Satoyama Global Initiative established by the Japanese at UNESCO as a global effort in 2009 to realise ‘societies in harmony with nature’ in which – Satoumi – specifically referring to the management of socio-ecological production landscapes in marine and coastal regions, is also a good model to be considered for conservation of biodiversity and co-existence between humans and nature.
Final Plea
In order to take this proposal forward from the Sri Lankan side, a number of useful baseline reports are already available including, but not limited to, the following: i. Biodiversity Profile of the Mannar District (CEJ & USAID 2022), ii. The Gulf of Mannar and its surroundings (IUCN 2012), iii) Atlas of Mangroves, Salt Marshes and Sand Dunes of the Coastal Area from Malwathu Oya to Pooneryn in the Northwestern Coastal Region, Sri Lanka (Ecological Association of Sri Lanka, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 2020). iv. Integrated Strategic Environment Assessment of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka (CEA 2014).
If this proposal to establish a Trans-boundary Blue-Green Biosphere Reserve in the Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay is acceptable in principle to the Governments of Sri Lanka and India, it would be ideal if the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program UNESCO which is an intergovernmental scientific program whose mission is to establish a scientific basis for enhancing the relationship between people and their environments to partner with the relevant Government and non-governmental agencies in both countries in making it a reality. This proposed concept has all the necessary elements for developing a unique sustainable conservation cum industrial development strategy via nature-based solutions while at the same time contributing to both climate change mitigation and adaptation.
by Emeritus Professor Nimal Gunatilleke,
University of Peradeniya
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoStrengthening SDG integration into provincial planning and development process
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoBid to include genocide allegation against Sri Lanka in Canada’s school curriculum thwarted
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoSri Lanka’s eternal search for the elusive all-rounder
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoTo play or not to play is Richmond’s decision
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoComBank crowned Global Finance Best SME Bank in Sri Lanka for 3rd successive year
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoSanctions by The Unpunished
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoMore parliamentary giants I was privileged to know
-
 Business7 hours ago
Business7 hours agoNew SL Sovereign Bonds win foreign investor confidence