Business
Sampath Bank Posts Steady Results for the First Quarter of 2024

Sampath Bank posted a profit before tax (PBT) of Rs 6.2 billion and a profit after tax (PAT) of Rs 3.4 billion for the three months ended 31st March 2024, notwithstanding an exchange loss of Rs 4.3 billion due to the appreciation of the LKR against the USD by Rs 23.70. These figures signify growth rates of 39.1% and 27.8% respectively, in comparison to the financial results reported in the first quarter of 2023. The Sampath Group also reported PBT and PAT figures of Rs 6.9 billion and Rs 3.8 billion respectively, reflecting growth rates of 38.0% and 26.0%.
Key Highlights for the Period Ended 31st March 2024:
A significant increase of 27.8% in the Bank’s PAT, reaching Rs 3.4 billion.
12.7% growth in Net Interest Income (NII).
17.1% decrease in net fee and commission income due to decreased trade-related operations.
An exchange loss of Rs 4.3 billion due to the appreciation of LKR against USD by Rs 23.70.
36.8% decline in impairment charges.
Robust LKR deposit growth of Rs 68 billion.
Tier 1 and Total Capital Adequacy Ratios stood at 15.18% and 18.22% respectively, as of 31st March 2024, comfortably above regulatory minimum requirements.
During the period, Net Interest Income (NII) reached Rs 20.5 billion, marking a growth of 12.7% compared to Rs 18.1 billion recorded in the corresponding period of the previous year. This increase in NII primarily stemmed from a reduction in interest expenses which outpaced the decrease in interest income. The Bank’s prudent asset and liability management strategies played a pivotal role in driving the notable growth of NII, especially amid declining interest rates. Additionally, the Net Interest Margin (NIM) witnessed an increase, rising from 5.16% as of 31st December 2023, to 5.24% as of the reporting date.
In 1Q 2024, the Bank experienced a significant 75.3% decrease in its total non-fund-based income, declining from Rs 2.8 billion reported in the corresponding period of last year to Rs 0.7 billion in the current period. Net fee and commission income recorded a 17.1% decrease compared to 1Q 2023, primarily due to reduced income from trade-related activities. The decline was driven by several factors including lower commission rates for import-related transactions, decreased trade volumes, and the appreciation of LKR against the USD. However, fees generated from credit, electronic channels, cards, and remittance-related activities showed growth compared to the same period last year.
The Bank reported a net trading loss of Rs 4.5 billion in 1Q 2024 whereas there was a gain of Rs 1.7 billion recognised in the previous period. This was primarily due to revaluation losses incurred on forward exchange contracts. The Bank managed to mitigate the impact of this loss through realised exchange gains reported under net other operating income as opposed to the loss of Rs 4.5 billion recorded in 1Q 2023. Consequently, the Bank’s net exchange loss from foreign exchange operations for the period under review amounted to Rs 4.3 billion, compared to the Rs 2.9 billion loss reported in the corresponding period of the previous year.
In the first quarter of 2024, the Bank reported a total impairment charge of Rs 4.4 billion, a 36.8% decrease compared to the charge for the comparative period in the previous year. Of this total, Rs 2.4 billion was attributed to loans and advances (1Q 2023: Rs 6.2 billion), while Rs 0.9 billion related to other financial instruments (1Q 2023: Rs 0.4 billion). In addition, an impairment charge of Rs 1.1 billion was recorded for commitments and contingencies (1Q 2023: Rs 0.4 billion).
Business
HNB Assurance delivers industry leading 42% revenue (GWP) growth and 28% rise in profits (PAT)

HNB Assurance PLC reported an outstanding financial performance for the year ended 31st December 2025, delivering a 42% year-on-year growth in Life Insurance Gross Written Premium (GWP), this along with the growth rate in Renewals are the highest in the industry.
Life GWP reached Rs. 19.49 Bn compared to Rs. 13.71 Bn in 2024, reflecting strong New Business generation and Renewal Collection. Net Written Premium grew even faster at 43% to Rs. 18.44 Bn, highlighting the quality and sustainability of the Company’s topline expansion.
Commenting on the results, Chairman Stuart Chapman stated, “The year under review was marked by gradual macroeconomic stabilisation, improved investor sentiment and a more predictable policy environment. Although the economy continues to recover from prior volatility, we are beginning to see renewed financial confidence among individuals and businesses. Against this backdrop, HNB Assurance has delivered strong growth in both revenue and profits, while maintaining robust capital adequacy and prudent risk management. Our improvement in top line, profitability and balance sheet strength demonstrates the resilience of our business model and our ability to navigate changing economic conditions which are reflected in an ROE which increased to 18.5% from 16.9% a year earlier.”
Profit Before Tax increased by 28% to Rs. 3.03 Bn from Rs. 2.36 Bn in the previous year, while Profit After Tax (including Life Surplus Transfer) rose by 28% to Rs. 2.12 Bn compared to Rs. 1.66 Bn in 2024. Earnings Per Share improved by 28% to Rs. 14.15 from Rs. 11.04, reinforcing the Company’s ability to consistently translate business growth into enhanced shareholder value. In line with this strong performance, the Board of Directors has proposed a first and final dividend of Rs. 5.00 per share for 2025, representing a 28% increase over the Rs. 3.90 per share declared in the previous year.
Executive Director and Chief Executive Officer Lasitha Wimalaratne highlighted the consistency of the Company’s upward trajectory. “Our 2025 performance reflects a sustained pattern of high growth and disciplined execution over the past four years. During this period, we have consistently strengthened our distribution reach, enhanced advisor productivity, invested in digital enablement and sharpened our customer centric value proposition. Each year we have built on the previous year’s gains, and the 42% growth in Life GWP in 2025 is the strongest affirmation yet of that strategy. Importantly, we have achieved this while maintaining underwriting discipline, expanding our Life Fund and delivering a 28% increase in PAT.”
The strength of the Company’s balance sheet continued to improve during the year. Total Assets grew by 28% to Rs. 68.44 Bn from Rs. 53.40 Bn, while financial investments increased by 29% to Rs. 62.49 Bn from Rs. 48.49 Bn in 2024, reflecting disciplined asset accumulation and prudent investment management. Total Equity rose to Rs. 12.19 Bn from Rs. 10.81 Bn, supported by Retained Earnings which grew by 18% to Rs. 10.23 Bn.
The Life Insurance Fund recorded a significant expansion of 27%, increasing to Rs. 48.87 Bn from Rs. 38.34 Bn in the previous year. During the year, the Company paid Rs. 4.40 Bn in Net Insurance Benefits and Claims, honouring its commitments to policyholders and their families while further strengthening long term reserves. Investment Income remained a key contributor to performance, with interest and dividend income rising by 10% to Rs. 7.49 Bn.
The Market Capitalisation as at the end of the year stood at Rs. 17.21 Bn up 43% from a year ago when it was Rs. 12.02 Bn, while trading for year ended at Rs. 114.75 per share increasing by 43% from Rs. 81.10 a year ago.
Business
Phoenix Ogilvy Dominates Sri Lanka’s Creative Rankings

Standout year with international award show wins at LIA, One Asia, Clio, AdFest, Spikes Asia & The Work
Phoenix Ogilvy has been named 2025 Sri Lanka Agency of the Year after topping The Campaign Brief Asia’s Creative Rankings as the most internationally awarded agency in the country, an agency news release said..
The agency’s ranking also marks Sri Lanka’s return to the list in 2025, following the country’s absence from it the previous year.
The Campaign Brief Asia Creative Rankings annually evaluate the top 100 most awarded creative agencies in Asia, based on their achievements across leading international award shows.
The rankings are widely regarded as one of Asia’s most credible measures of creative excellence. Agencies accumulate points purely from award wins across major international creative shows, making it one of the longest-running and most respected benchmarks of creative performance in the region.
Phoenix Ogilvy secured the top spot in the national table, amassing an impressive 295 Creative Ranking points after standout wins across six major international creative award shows, including London International Awards (LIA), One Asia Awards, Clio Awards, AdFest, Spikes Asia, and Campaign Brief’s The Work.
Being ranked at the top not only signals national creative leadership for Phoenix Ogilvy but also exhibits the agency’s talent strength. In a testament to this creative calibre, the agency’s talent dominated the Campaign Brief Asia’s Individual Creative Rankings in Sri Lanka.
Leading this list is Nadeera Warawita with 250 Creative Ranking points, followed by Sakuna Ranasinghe at No. 2 with 220 points, and Samitha Kaushalya at No. 3 with 150 points. Meanwhile ranked jointly at No. 4, are Dilshi Aberaja, Dilshard Ahamed, Harsha Kumara, Kasun Wadumestri, Keshan Silva, and Suresh Kumar. At no. 10 is Dilshi Thathsarani.
Speaking on these achievements, Irvin Weerackody, Chairman of the Ogilvy Group Sri Lanka, said, “Creativity has always been our lifeblood, and it is encouraging to see that commitment recognised on the world stage. The real test of an agency is not the trophies, but the courage to create with integrity, especially today. These achievements not only reflect the capability of our talent, but importantly their discipline, their cultural instinct and their refusal to take the easy way out. I am proud of our teams, who continue to push themselves year after year to raise the bar and uphold the standards we believe in.”
For five decades, Phoenix Ogilvy has been a defining pillar of the country’s marketing landscape and an influential creative powerhouse. From its earliest days, the agency has challenged convention and advocated brave thinking, producing work that commands attention, both locally and internationally.
Renowned as a formidable training ground for Sri Lankan advertising talent, the agency has also played a pivotal role in shaping generations of trailblazing creatives, strategic thinkers, and industry leaders who continue to leave their mark across the region and beyond.
Strengthened by the global Ogilvy network, the agency enjoys a rare blend of global creative rigour and deep local intelligence. Over the years, it has diversified across multiple disciplines and today stands as a talent hub for 290 industry specialists spanning creative, strategy, digital, media, public relations and integrated communications in Sri Lanka.
At its core, the agency remains true to the principles it was built on: that great ideas come from disciplined minds, uncompromising craft, and the refusal to settle for the ordinary.
Business
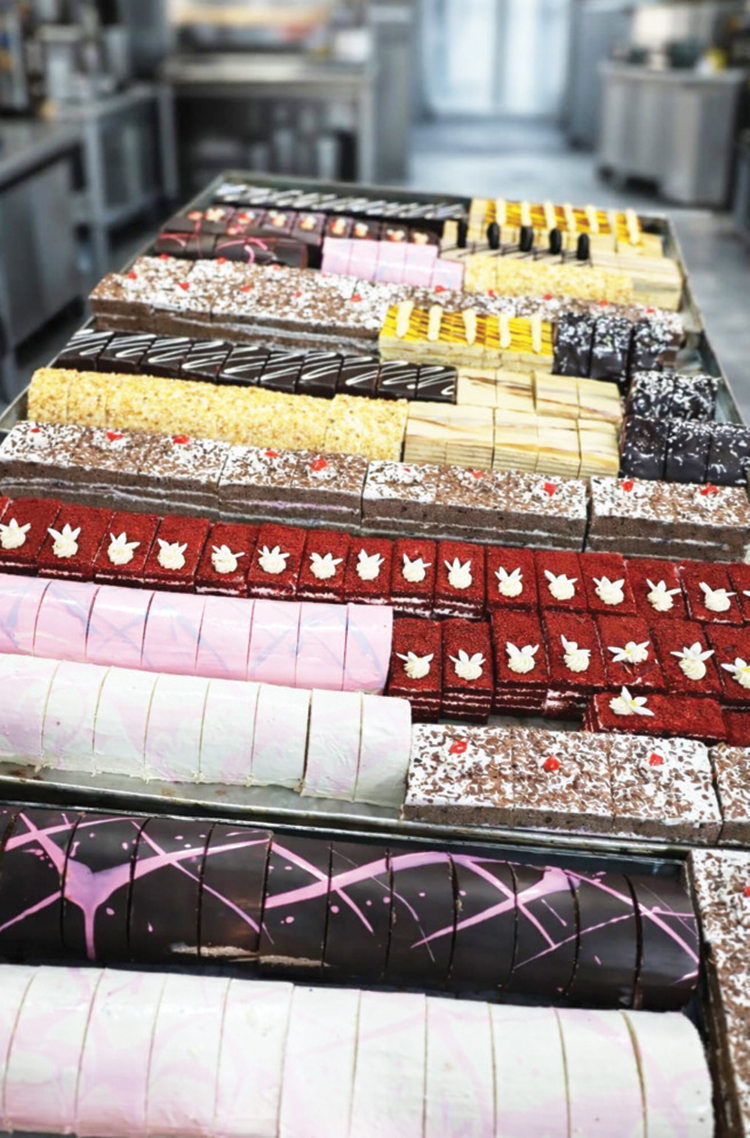
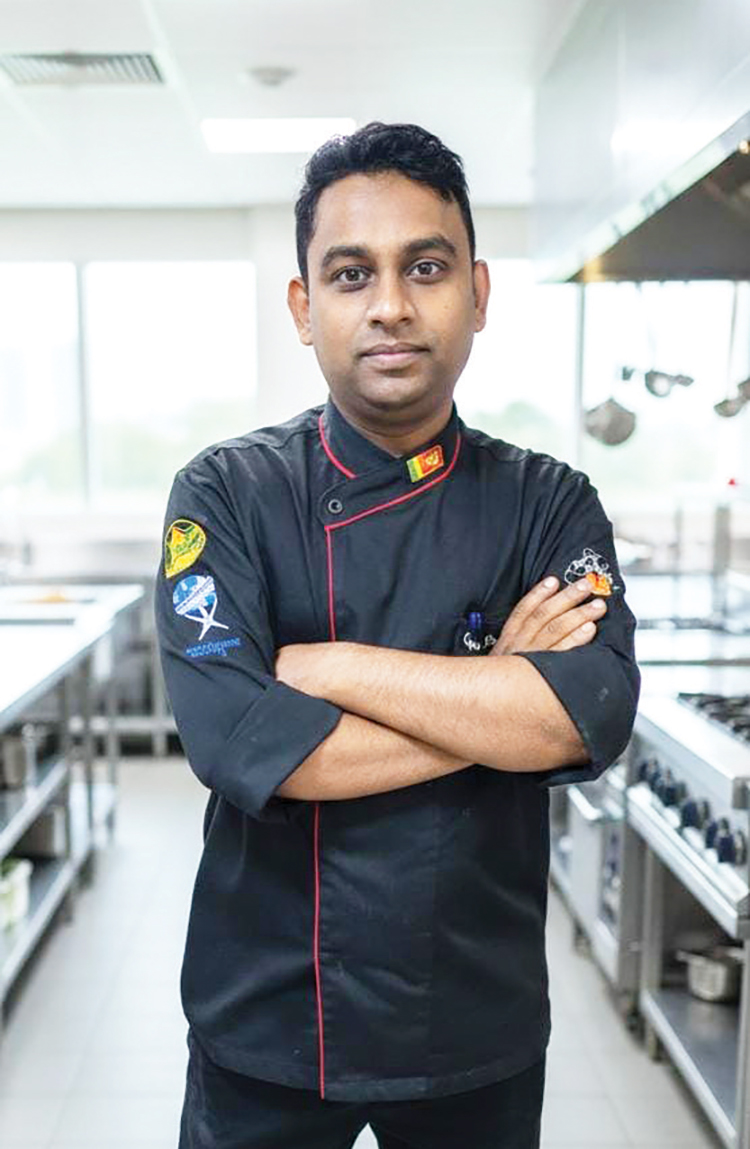
Oak Ray Chef Marks a Culinary Milestone with 118 Unique Creations
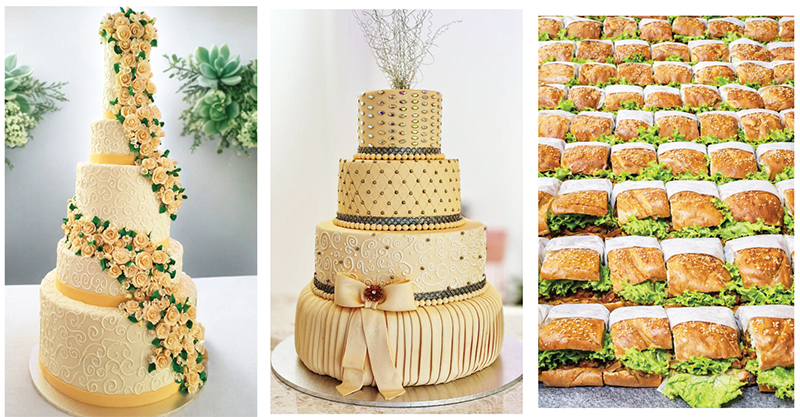

In the intricate world of pastry and bakery arts, R.S. Weerakoon has emerged as a visionary creator, known for his extraordinary ability to transform any concept into a stunning cake masterpiece. Currently serving as the Head Chef (Pastry & Bakery) at the Oak Ray Group in Kandy, Weerakoon’s journey is a blend of local talent and international expertise.
An alumnus of Udispattuwa Maha Vidyalaya, Weerakoon holds an NVQ Level 04 qualification from NAITA and is a distinguished member of the Chefs’ Guild of Sri Lanka. With over 14 years of experience in the industry, including valuable tenures in Kuwait and Oman, he has successfully integrated Middle Eastern culinary trends with local flavors.
One of his most significant contributions to the industry is the introduction of 118 unique products to the Oak Ray Group. Remarkably, all these creations are made without the use of any artificial food colorings, prioritizing the health and well-being of consumers.
Speaking about this talented professional, the Chairman of the Oak Ray Group, Mr. Sujeewa Palliyaguruge, stated that his vision is to provide a creative platform for such skilled young individuals.
“Our goal is to allow talented creators like Weerakoon the freedom to innovate and bring their unique visions to life, which ultimately benefits the entire culinary industry in Sri Lanka,” he said.
Weerakoon’s dedication to natural ingredients and his mastery of cake architecture continue to set new benchmarks for the next generation of chefs in the hill capital.
- R.S. Weerakoon
By S.K. Samaranayake
Pix by Razik Jabbar
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoBathiya & Santhush make a strategic bet on Colombo
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoSeeing is believing – the silent scale behind SriLankan’s ground operation
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoProtection of Occupants Bill: Good, Bad and Ugly
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPrime Minister Attends the 40th Anniversary of the Sri Lanka Nippon Educational and Cultural Centre
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCoal ash surge at N’cholai power plant raises fresh environmental concerns
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHuawei unveils Top 10 Smart PV & ESS Trends for 2026
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?