Opinion
Safety issue of ‘traditional’ and ‘complementary’ medicines

By CHANDRE DHARMAWARDANA
Every country has a lore of “traditional medicine” in addition to the mainstream medical system, which today is based on a rigorous system of institutionalized medical education based on science. Even the WHO has recently recognized and attempted to give formal structure to such Traditional and Complementary (T&C) systems of medicine (see: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/312342;jsessionid=4ADD7EEB300760DC10D0C42745ABDC31).
Thus, the WHO defines “traditional medicine” as:
“The sum total of knowledge and practices, whether explicable or not, used in diagnosing, preventing or eliminating physical, mental and social diseases. This knowledge or practice may rely exclusively on past experience and observation handed down orally or in writing from generation to generation. These practices are native to the country in which they are practiced. The majority of indigenous traditional medicine has been practised at the primary healthcare level”.
Traditional medicine, and other so-called complementary systems of medicines, tend to be far less institutionalized, with the methods of treatment traditionally handed down from a teacher to a student, who becomes part of the teacher’s “family”. This is the “guru-kula” system, where the teaching is retained as a family secret and handed down. Nevertheless, as these systems progressed and received state patronage, institutionalization and open publication of medical practices began to appear. The Mahavansa alludes to hospitals even for animals in ancient Lanka. In India, too, Sanskrit texts like the Charaka Samhitha and the Sushrutha Samhitha of Ayurveda, record the level of surgery as well as methods of treatment available to the ancients.
Nevertheless, every physician was supposed to keep his/her “Guru-mushti” (what the teacher holds in his fist), i.e. secret knowledge that the teacher revealed to the pupil, only at his deathbed. They claim that such medical practices have been confirmed by use “down the ages”, and the epithets “prathyaksha” in Sanskrit, and “ath-dutu” in Sinhala are often used to indicate safe and “well tested” medications.
No record keeping of the treatment and their outcomes, adverse effects, etc., were practised until the rise of modern medicine. Hence the claim that these preparations are “ath-dutu”, or “prathyaksha” is unjustified. Case histories that can be scrutinized by independent investigators are lacking.
Even today, when individuals propose “new” treatments for Covid-19, they make claims that the treatment is based on “ath-dutu” ancient herbal lists ,etc., as if that is all there is to it. Others, e.g., the “Hela Suvaya” team, claim that their herbal prescriptions are guided by God Natha. When a person from Hettimulla, Kegalle claimed to have created a Covid-19 treatment, to be given “free”, it attracted massive crowds! Supporters even question the need for double-blind clinical tests or chemical analysis of the new product. Politicians rush to swallow the medicine in public, while the educated public can only groan in silence.
The traditional medicine that existed in Europe in medieval times, prior to the rise of modern scientific medicine, included traditional medicine from Indian, Greek and Arab sources, together with alchemy, which was the search for a means of transforming lead into gold. Many alchemists were also medical physicians who kept their medical as well as alchemical knowledge secret.
The rise of modern scientific medicine can be attributed to the recognition, during the renaissance, that secrecy must be replaced by openness and sharing of experience to ensure objectivity. It was recognized that one’s own observations or once own experiences can be highly unreliable. How one feels, or what one sees, depends on many factors besides the level of alcohol in the blood!
Learned societies like the Royal Society (November,1660) were created for open discussion and public proof. A claimant of a “new discovery” has to reveal all details in public, at a meeting of the learned society. The tradition of holding onto “secret knowledge” or “Guru-Mushti” was thrown out. Record keeping, use of quantitative data, and repeating the experiment or test in front of everybody were key features of the methods of empirical science put into practice by the Royal Society.
So, all claimants of “new” Ayurvedic or Traditional cures for Covid (or Dengue) must release carefully recorded case histories that the claimant can use to prove that there is a preliminary case for what is claimed. It is not enough to make claims of “paran-paraa-gatha vattoruvak” (herbal list handed down from generation to generation). The quality of the herbs used must be recorded, and weighed ingredients must be indicated in grams rather than in terms of some traditional ambiguous unit. A medical body should examine the case histories and decide if there is a case for undertaking further confirmatory studies. That is, bogus claims must be eliminated at the outset. In the scientific method, any claim has to be independently verified by repeating the process, using the same prescribed medications.
Purity and consumer protection are very important and unfortunately lacking in many T&C medications (See https://dh-web.org/place.names/bot2sinhala.html#herbal). Chemical analyses of commercial Ayurvedic preparations have revealed toxic ingredients like Lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), harmful alcohols like methanol, propanols, and other ingredients, as well as extreme variation in amounts of active ingredients. Some contain admixture of potent western drugs although this is illegal. So chemical analysis of proposed T&C drugs is necessary for consumer protection.
An attractive but dangerous feature of T&C medical systems is that they can become “personal health prescriptions” (PHP) that an individual may administer without going to a physician. Modern mega-Vitamin therapies are also PHPs from “complementary” or “alternative” medicine. They become “home remedies” that people swear on, although they may not have kept records of how the PHP worked for them. Patients lack the equipment and laboratory facilities to monitor their condition. In effect, a PHP is a herbal prescription, or the use of some exotic root, fruit or “Vitamin”, without a proper case record, evolved by oneself, or “given” by a “trusted Vaidya” or medical savant. The PHP may have been adopted from some old book or an “ola-leaf” record.
St. Jerome who lived to a very ripe age in the 4th century had his own PHP for good health.
“From his 31st to 35th year he had for food six ounces of barley bread, and vegetables slightly cooked without oil. But finding that his eyes were growing dim, and that his whole body was shriveled with an eruption and a sort of stony roughness he added oil to his former food, and up to the 63 rd year of his life followed this temperate course, tasting neither fruit nor pulse, nor anything whatsoever besides”.
Today, no one would recommend such a diet free of fruits and pulses, and yet, for many centuries, many Christian monks followed St Jerome’s diet claiming it to be a “proven” healthy diet.
In India, Vagabhatta and Nagarjuna were two great teachers who prescribed the use of “Rasaindur”, which turns out to be mercury sulfide. Although these authors prescribed many such metals in their “Rasha-shasthra”, today we recognize them to be toxic and dangerous to health if ingested even at a few parts per million. The Sanskrit text “Rasatarangani” prescribes preparations containing lead, mercury, gold, silver and many other metals which are cooked with lime and herbal juices (e..g, from Nuga, the banyan tree). Well known Ayurvedic texts like the Charaka Samhitha and the Sushrutha Samhitha recommend preparations containing substances now recognized to be toxic. So the “Rishis” failed to notice the toxic effects, probably because there was no recording of case histories and studying them objectively.
Unfortunately many T&C medications are taken over by individuals who transform them into personal health prescriptions (PHPs), without the knowledge to adequately control the quantities used. For instance, “polpala” (Aerva lanata) may be taken as a herbal tea but frequent use may have serious adverse effects on the urinary tract. Similarly, individuals may use “Thebu” (Costus igneus) to control blood sugar, but end up with hypoglycemia and other side effects.
In an earlier epoch, people used to relieve their bowls in their own backyards, near paddy fields (or on the beach!). Hook worm and other intestinal-parasite infections became common as people also walked barefoot in the same land area, or in the fields. Thus there was also a tradition of taking a purge, containing mainly Aralu (Terminalia chebula) at least every six months. This was “a good health practice” recommended by T&C medicine. However, as this was administered as a home remedy, the amount of “aralu” was never properly controlled, leading to dangerous purging in some cases, and no effect in other cases. Furthermore, the purge has little effect on hookworms and such parasites, but it dangerously disturbs the gut microbiome of the person taking the purge.
So, in conclusion, at least the following steps are needed to make T&C medicine safe:
1. Every new claim must be supported by well recorded certified case histories and clinical records that are needed to justify further trials.
2. The prescription must quantitatively specify the full formulation and be subject to a chemical analysis to ensure that no known toxins are contained in the product.
3. Marketing of the product must be done ensuring product-uniformity and product standards to ensure consumer protection.
4. T&C medications must NOT be adopted as home remedies as self-medication is always dangerous.
Opinion
A puppet show?
After jog for the camera, wearing shorts in Jaffna, thanks to the freedom gained by the country being liberated from the clutches of the Tigers by the valiant efforts led by Mahinda Rajapaksa, President Anura Kumara Dissanayaka, said: “Some come past Sri Maha Bodhi and other Buddhist temples all the way to Jaffna to observe Sil, not to spread compassion but hatred.” When the need of the hour is reconciliation what an outrageous statement that was, to be made by the head of state! Will he say that the people of the North and the East bypass many Kovils straddling the area and come to Kataragama to spread hate? Probably not! His claim has become a hot topic of conversation.
Having lost a majority of the votes garnered from the North at the presidential and parliamentary elections, to the Tamil nationalist parties at the local government elections, President Dissanayake’s claim may well have been a pitiful attempt to recover lost ground in the North. But at what cost?
It all started with AKD’s refusal to refer to those brave service personnel who saved the unity and the integrity of the country as Rana Viruwo. Interestingly, the most devastating rebuke for this came from a Tamil MP, who is an avowed admirer of Prabhakaran, stating in Parliament that a Sinhala Rana Viruwa saved his life when he was about to be washed off in the flood waters resulting from Cyclone Ditwah. He teased the government by asking in ‘raw’ Sinhala Ei umbalata lejjada unta Rana Viruwo kiyanna? (Are you shy to call them war heroes?)
In addition to slinging mud at MR and harassing service personnel, there is no doubt whatsoever that AKD’s government is trying to harass any Tamil politicians who helped eradicate the Tigers. This fact is borne out by the treatment meted out to Douglas Devananda. Shamindra Ferdinando has explained this in his article, “EPDP’s Devananda and missing weapons supplied by Army” (The Island, 7 January).
NPP ministers publicly insult Buddhist monks, but whenever they are in trouble, they rush to Kandy to meet the Maha Nayakas, the latest being Harini’s visit. Instead of admitting the mistake and trying to make amends, the government went on, until it realised the futility in trying to justify the ‘Buddy’ episode. Excuses given by Harini to the Maha Nayakas, to say the least, were laughable. She had the audacity to say that though the questionable web link was printed in the textbook there were no instructions to click on it! She may continue as Prime Minister but can anyone who does not know what to do with a link or who is trying to encourage ten-year-olds to have e-buddies when the rest of the world is heading towards banning 16-year-olds from social media, continue to be the Minister of Education?
Number of MOUs/pacts signed with India, including defence, have not yet been disclosed even to Parliament. The Cabinet Spokesman once stated that the contents of those MOUs/pacts could not be divulged without the consent of India. Interestingly, we have had very frequent visits from VVIP politicians and top government officials from India, some at very short notice. One of them referred to these as ‘usual’ ones! However, what is unusual is that a party that shed a lot of blood of Sri Lankans for even selling ‘Bombay’ onions, is now in government and seems under Indian command. Perhaps, its transformation occurred when India sponsored a visit by AKD in early 2024, which helped him secure the presidency. Among the NPP’s election pledges, the most touted one was to reveal the mastermind behind the Easter Sunday attacks. It has been alleged in some quarters that India was behind the attacks. The NPP government’s silence about this speaks volumes!
It has transpired recently that it was Indian High Commissioner Gopal Baglay who pressured Speaker Mahinda Yapa Abeywardena in July 2022 to take over the presidency after the elected President was toppled by protesters, but many believe that it was a joint effort by the Indian HC and the ‘Viceroy’ who just left, after an overstay! It is an illegal act as pointed out in the editorial “Conspiracy to subvert constitutional order” (The Island, 22 January) and may be investigated by a future government, if elections are not postponed forever!
We seem to be watching a puppet show where many puppeteers outside are pulling the strings! Are we paying the price for electing a bunch of inexperienced politicians?
By Dr Upul Wijayawardhana ✍️
Opinion
Remembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism

Salute to a brave father-son
Cedric Martenstyn was a very affluent man. He owned a house in Colombo 7, valuable properties throughout the country, vehicles / speed boats and ran the lucrative business of importing Johnson and Evinrude Outboard Motors (OBM) and sold them to local fishermen and businessmen.
Cedric was the local agent for the OBMs, which were known for reliability and after-sales service, and among his customers were humble fishermen. He was fondly known as Sudu Mahattaya “(white Gentleman) by humble fishermen and he would often travel in his double cab across the country to meet his customers and solve their problems.
He had a loving wife and children. He was an excellent scuba diver, member of Sri Lanka Navy Practical Pistol Firing team and his knowledge of wildlife and reptiles was amazing.
A member of the Dutch Burgher community of Sri Lanka, he was a true patriot, who volunteered to protect country and people from terrorists. An old boy of S. Thomas’ College, Mount Lavinia, he was an excellent sportsman.
The founding father of Sri Lanka Army Commando Unit, Colonel Sunil Peris, was his classmate at S.Thomas’.
I first met Cedric when I was a very junior officer at Pistol Firing Range at Naval Base, Welisara. I helped him catch a poisonous snake in the Range. I think he carried that snake home in a bottle! That was the type of person Cedric was!
We became very close friends as we both loved “guns and fishing rods”. His experience and tactics in angling helped me catch much bigger Paraw (Trevallies) in the Elephant Rock area at the Trincomalee harbour. He was a dangerous man to live with at Trincomalee Naval Base wardroom (officers’ mess), because he had various live snakes kept in bottles and fed them with little frogs!
Even though he was a keen angler, he was keen to conserve endangered species both on land and in water. He spent days in Horton Plains and the Knuckles Mountain Range streams to identify freshwater species in Sri Lanka. Did you know there is an endangered freshwater fish species he found in Horton Plains and Knuckles Mountain Range has been named after him?
Feeding of snakes was an amusement to all our stewards at the wardroom at that time! They all gathered and watched carefully what Cedric was doing, keeping a safe distance to run away if the snake escaped. Our Navy stewards dare to enter Cedric’s cabin (room) at Trincomalee wardroom (officers’ mess), even keeping his tea on a stool outside his cabin door. One day pandemonium broke in the officers’ mess when Cedric announced that one snake escaped! We never found that snake, and that was the end of his hobby as the Commander Eastern Naval Area, at that time, ordered him to ” get rid of all snakes! Sadly, Cedric released all snakes to Sober Island that afternoon.
Cedric was a volunteer Navy officer, but still joined me (he was 47 years old then) to help SBS trainees (first and second batch) on boat handling and OBM maintenance in 1993, when I raised SBS. It was exactly 31 years ago!
The Arrow Boat
Being an excellent speed boat race driver and boat designer, he prepared the blueprint of the first “18-foot Arrow Boat” and supervised building it at a private Boat Yard in 1993. This 18- foot Arrow Boat was especially designed to be used in the shallow waters of the Jaffna lagoon, fitted 115 HP OBMs, and with two weapons he recommended; 40mm Automatic Grenade Launcher (AGL) and 7.62×51 mm General Purpose Machine Guns (GPMGs). In no time, we had highly trained and highly motivated four SBS men on board each Arrow Boat at Jaffna lagoon, and they were very effective.
Same hull (deep V hull) developed during the tenure of Admiral of the Fleet Wasantha Karannagoda, as Commander of the Navy, by Naval architects, with knowledge-gained through captured LTTE Sea Tiger boats, designed 23- foot Arrow Boats and implemented the “Lanchester Theory” (theory of battle of attrition at sea in littoral sea battles) to completely nullify LTTE’s superiority which it had gained with small craft and deadly suicide boats.
Thank you, the Admiral of the Fleet for understanding the importance of Arrow Boat design and mass production at our own boatyard at Welisara. Karannagoda, under whom I was fortunate to serve as Director Naval Operations, Director Maritime Surveillance and Director Naval Special Forces during the last stages (2006/7) of the Humanitarian Operations, always used to tell us “You cannot buy a Navy- you have to build one”! Thank you, Sir!

Cedric craft display at Naval Museum, Trincomalee
The Hero he was
When I was selected for my Naval War Course (Staff Course) conducted by the Pakistan Navy Staff College at Karachi, Pakistan, (now known as Pakistan Navy War College relocated at Lahore), Cedric took over the command (even though he was a VNF officer) as Commanding Officer of SBS.
Being one of the co-founders of this elite unit, he was the most suitable person to take over as CO SBS. He was loved by SBS officers and sailors. They were extremely happy to see him at Kilali or Elephant Pass, where SBS was deployed during a very difficult time of our recent history – fighting against terrorists during the 1996-97 period.
Motivated by father’s patriotism, his younger son, Jayson, who was a pilot working in the UK at that time, came back to Sri Lanka and joined the SLAF as an volunteer pilot to fly transport aircraft to keep an uninterrupted air link between Palaly (Jaffna) and Ratmalana (Colombo). Sometimes Jayson flew his beloved father on board from Palaly to Ratmalana. Cedric was extremely happy and proud of his son.
Tragically, young Jayson was killed in action in a suspected LTTE Surface-to-Air missile attack on his aircraft. Cedric was sad, but more determined to continue the fight against LTTE terrorists. He would also lead the rescue and salvage operation to identify the aircraft wreckage his son flew in. The then Navy Commander advised him to demobilise from VNF and look after his grieving family or join Naval Operations Directorate and work from Colombo which he vehemently refused. When I called him from Pakistan to convey my deepest condolences, he said, he would look after the “SBS boys”, he had no intention of leaving them alone at that difficult hour of our nation. That was Cedric. He was such a hero—a hero very few knew about!
The young officers, and sailors in SBS were of his sons’ age, and Cedric would not leave them even when he was facing a personal tragedy. He was a dedicated and courageous person.

Scientific name: Systomus Martenstyni
English name : Martenstyn’s Barb
Local name: Dumbara Pethiya
Sadly, like many who served our nation and stood against terrorists, Cedric would go on to be considered Missing In Action (MIA) following a helicopter crash off the seas of Vettalikani with Lt. Palihena (another brave SBS officer- KDU intake). He was returning to Point Pedro after visiting the SBS boys at Elephant Pass, Jaffna.
Cedric and his son, Jayson, will go down in history as a brave father-son duo who paid the supreme sacrifice for the motherland. MAY THEY REST IN PEACE ! Salute!
Commander Martenstyn was considered missing in action (MIA) on 22 January 1996 in the sea off Vettalaikerni, while returning to Palaly Air Force Base in an SLAF helicopter when it was lost to enemy fire. He was returning from visiting an SBS detachment in Elephant Pass near the Jaffna Lagoon. Considering his contribution to the war effort, his gallentry and valour in fighting the enemy, and his steadfast service to the Sri Lanka Navy in manufacturing Arrow Boats, and training the SBS, all SLN Arrow Boats were renamed ‘Cedric’ on his 70th Birthday.
(The writer is former Chief of Defence Staff and Commander of The Navy, and former Chairman of the Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd.)
By Admiral Ravindra
C Wijegunaratne
(Retired from Sri Lanka Navy)
Former Chief of Defence Staff and Commander of the Sri Lanka Navy,
Former Sri Lanka High Commissioner to Pakistan
Opinion
History of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine Kandana
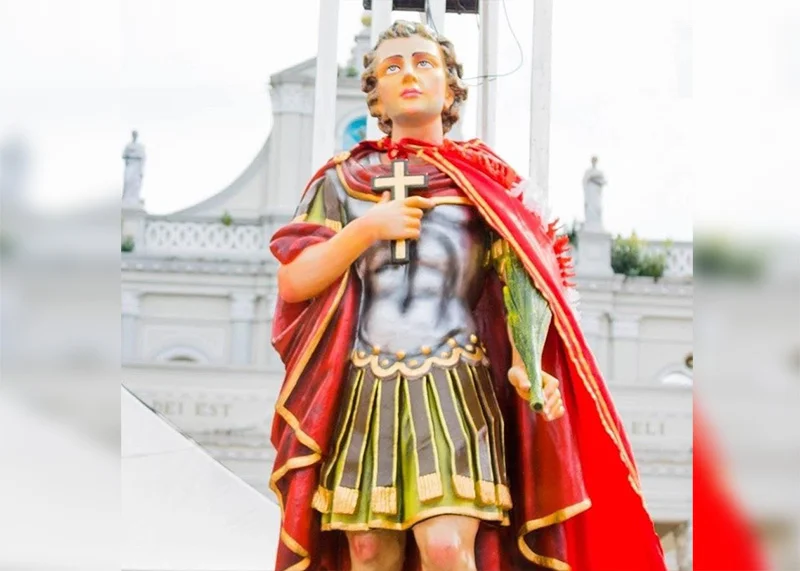

According to legend, St. Sebastian was born at Narbonne in Gaul. He became a soldier in Rome and encouraged Marcellian and Marcus, who were sentenced to death, to remain firm in their faith. St. Sebastian made several converts; among them were master of the rolls Nicostratus, who was in charge of prisoners, and his wife Zoe, a deaf mute whom he cured.
Sebastian was named captain in the Roman army by Emperor Diocletian, as by Emperor Maximian when Diocletian went to the east. Neither knew that Sebastian was a Christian. When it was discovered that Sebastian was indeed a Christian, he was ordered to be executed. He was shot with arrows and left to die but when the widow of St. Castulas went to recover his body, she found out that he was still alive and nursed him back to health. Soon after his recovery, St. Sebastian intercepted the Emperor; denounced him for his cruelty to Christians and was beaten to death on the Emperor’s order.
St. Sebastian was venerated in Milan as early as the time of St. Ambrose. St. Sebastian is the patron of archers, athletes, soldiers, the Saint of the youths and is appealed to protection against the plagues. St. Ambrose reveals that the parents that young Sebastian were living in Milan as a noble family. St. Ambrose further says that Sebastian, along with his three friends, Pankasi, Pulvius and Thorvinus, completed his education successfully with the blessing of his mother, Luciana. Rev. Fr. Dishnef guided him through his spiritual life. From his childhood Sebastian wanted to join the Roman army. With the help of King Karnus, young Sebastian became a soldier and within a short span of time he was appointed as the Commander of the army of King Karnus. The Emperor Diocletian declared Christians the enemy of the Roman Empire and instructed judges to punish Christians who have embraced the Catholic Church. Young Sebastian, as one of the servants of Christ, converted thousands of other believers into Christians. When Emperor Diocletian revealed that Sebastian had become a Catholic, the angry Emperor ordered for Sebastian to be shot to death with arrows. After being shot by arrows, one of Sebastian supporters, Irane, treated him and cured him. When Sebastian was cured he went to Emperor Diocletian and professed his faith for the second time disclosing that he is a servant of Christ. Astounded by the fact that Sebastian is a Christian, Emperor Diocletian ordered the Roman army to kill Sebastian with club blows.
In the liturgical calendar of the Church, the feast of the St. Sebastian is celebrated on the 20th of January. This day is indeed a mini Christmas to the people of Kandana, irrespective of their religion. The feast commenced with the hoisting of the flag staff on the 11th of January at 4 p.m. at the Kandana junction, along the Colombo-Negombo road. There is a long history attached to the flag staff. The first flag staff, which was an areca nut tree, 25 feet tall, was hoisted by the Aththidiya family of Kandana, and today their descendants continue hoisting of the flag staff as a tradition. This year’s flag staff, too, was hoisted by the Raymond Aththidiya family. Several processions, originating from different directions, carrying flags, meet at this flag staff junction. The pouring of milk on the flag staff has been a tradition in existence for a long time. The Nagasalan band was introduced by a well-known Jaffna businessman that had engaged in business in Kandana in the 1950s. The famous Kandaiyan Pille’s Nagasalan group takes the lead, even today, in the procession. Kiribath Dane in the Kandana town had been a tradition from time immemorial.
According to available history from the Catholic archives and volume III of the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka, the British period of vicariates of Colombo, written by Rev. Ft. Vito Perniola SJ, in 1806, states that the British government granted the freedom of conscious and religion to the Catholics in Ceylon and abolished all the anti-Catholic legislation enacted by the Dutch.
The proclamation was declared and issued on the 3rd of August 1796 by Colonel James Stuart, the officer commanding the British forces of Ceylon stated “freedom granted to Catholics” (Sri Lanka national archives 20/5).
Before the Europeans, the missioners were all Goans from South India. In the year 1834, on the 3rd of December, XVI Gregory the Pope, issued a document Ex Muwere pastoralis ministeric, after which the Ceylon Catholic Church was made under the South Indian Cochin diocese. Very Rev. Fr. Vincent Rosario, the Apostolic Vicar General, was appointed along with 18 Goan priests (The Oratorion Mission in Sri Lanka being a history of the Catholic Chruch 1796-1874 by Arthur C Dep Chapter 11 pg 12). Rev Fr. Joachim Alberto arrived in Sri Lanka as missionary on the 6th of March 1830 when he was 31 years old and he was appointed to look after the Catholics in Aluthkuru Korale, consisting Kandana, Mabole, Nagodaa and Ragama. There have been one Church built in 1810 in Wewala about three miles away from Kandana. The Wewala Chruch was situated bordering Muthurajawela which rose to fame for its granary. History reveals that the entire area was under paddy cultivation and most of them were either farmers or toddy tappers. History further reveals that there has been an old canal built by King Weera Parakrama Bahu. Later it was built to flow through the Kelani River, and Muthurajawela, up to Negombo, which was named as the Dutch Canal (RL Brohier historian). During the British time this canal was named as Hamilton Canal and was used to transport toddy, spices, paddy and tree planks of which tree planks were stored in Kandana. Therefore, the name Kandana derives from “Kandan Aana”.
Rev. Fr. Joachim Alberto purchased a small piece of land, called Haamuduruwange watte, at Nadurupititya, in Kandana, and put up a small cadjan chapel and placed a picture of St. Sebastian for the benefit of his small congregation. In 1837, with the help of the devotees, he dug a small well where the water was used for drinking and bathing and today this well is still operative. He bought several acres of land, including the present cemetery premises. Moreover, he had put up the Church at Kalaeliya in honour of his patron St. Joachim where his body has been laid to rest according to his wish of the Last Will attested by Weerasinghe Arachchige Brasianu Thilakaratne. Notary Public, dated 19th July 1855. The present Church was built on the property bought on the 13th of August 1875 on deed no. 146 attested by Graciano Fernando. Notary Public of the land Gorakagahawatta Aluthkuru Korale Ragam Pattu in Kandana within the extend ¼ acre from and out of the 16 acres. According to the old plan number 374 made by P.A. H. Philipia, Licensed surveyor on the 31st of January 195, 9 acres and 25 perches belonged to St. Sebastian Church. However, today only 3 acres, 3 roods and 16.5 perches are left according to plan number 397 surveyed by the same surveyor, while the rest had been sold to the villagers. According to the survey conducted by Orithorian priest on the 12th of February 1844 there were only 18 school-going Catholic students in AluthKuru Korale and only one Antonio was the teacher for all classes. In 1844 there was no school at Kandana (APF SCG India Volume 9829).
According to Sri Lanka National Archives (The Ceylon Almanac page 185) in the year 1852 there were 982 Catholics Male 265, female 290, children 365, with a total of 922. According to the census reports in 2014, prepared by Rev. Ft. Sumeda Dissanayake TOR, the Director Franciscan Preaching group, Kadirana Negombo a survey revealed that there are 13,498 Catholics in Kandana.
According to the appointment of the Missionaries in the year 1866-1867 by Bishop Hillarien Sillani, Rev. Fr. Clement Pagnani OSB was sent to look after the missions in Negoda, Ragama, Batagama, Thudella, Kandana, Kala Eliya and Mabole. On the 18th of April 1866, the building of the new Church commenced with a written agreement by and between Rec. Fr. Clement Pagnani and the then leaders of Kandana Catholic Village Committee. This committee consisted of Kanugalawattage Savial Perera Samarasinghe Welwidane, Amarathunga Arachchige Issak Perera Appuhamy, Jayasuriya Arachchige Don Isthewan Appuhamy, Jayasuriya Appuhamylage Elaris Perera Muhuppu, Padukkage Andiris Perera Opisara, Kanugalawattage Peduru Perera Annavi and Mallawa Arachchige Don Peduru Appujamy. The said agreement stated that they will give written undertaking that their labour and money will be utilised to build the new Church of St. Sebastian and if they failed to do so they were ready to bear any punishment which will be imposed by the Catholic Church.

Rev. Fr. Bede Bercatta’s book “A History of the Vicariate of Colombo page 359” says that Rev. Fr. Stanislaus Tabarani had problems of finding rock stones to lay the foundation. He was greatly worried over this and placed his due trust in divine providence. He prayed for days to St. Sebastian for his intercession. One morning after mass, he was informed by some people that they had seen a small patch of granite at a place in Rilaulla, close to the Church premises, although such stones were never seen there earlier, and requested him to inspect the place. The parish priest visited the location and was greatly delighted as his prayers has been answered. This small granite rock amount provided enough granite
blocks for the full foundation of the present church. This place still known as “Rilaulla galwala”. The work on the building proceeded under successive parish priests but Rev. Fr. Stouter was responsible for much of it. The façade of the Church was built so high that it crashed on the 2nd of April of 1893. The present façade was then built and completed in the year 1905. The statue of St. Sebastian, which is behind the altar, had been carved off a “Madan tree”. It was done by a Paravara man, named Costa Mama, who was staying with a resident named Miguel Baas a Ridualle, Kandana. This statue was made at the request of Pavistina Perera Amaratunge, mother of former Member of Parliament gatemuadliyer D. Panthi Jayasuirya. The Church was completed during the time of Rev. Fr. Keegar and was blessed by then Archbishop of Colombo Dr. Anthony Courdert OMI on the 20th of January 1912. In 1926, Rev. Fr. Romauld Fernando was appointed as the parish priest to the Kandana Church. He was an educationalist and a social worker. Without any hesitation he can be called as the father of education to Kandana. He was the pioneer to build three schools in Kandana: Kandana St. Sebastian Boys School, Kandana St. Sebastian English Girls School and, the Mazenod College Kandana. Later he was appointed as the Principal of the St. Sebastian Boys English School. He bought a property at Kandana, close to Ganemulla Road, and started De Mazenod College. Later, it was given officially to the Christian Brothers of Sri Lanka, by then Archbishop of Colombo, Peter Mark. In 1931, there were 300 students (history of De Lasalle brothers by Rev. Fr. Bro Michael Robert). Today, there are over 3,500 students and is one of the leading Catholic schools in Sri Lanka. In 1924, one Karolis Jayasuriya Widanage donated two acres to build De Mazenod College for its extension.
The frist priest from Kandana to be ordained was Rev. Fr. William Perera in 1904. With the help of Rev. Fr. Marcelline Jayakody, he composed the famous hymn “the Vikshopa Geethaya”, the hymn of our Lady of Sorrow.
The Life story of St. Sebastian was portrayed through a stage play called “Wasappauwa” and the world famous German passion play Obar Amargavewchi whichwas a sensation was initiated by Rev. Fr. Nicholas Perera. Legend reveals that in the year 1845 a South Indian Catholic, on his way to meet his relatives in Colombo, had brought down a wooden statue of St. Sebastian, one and half feet tail, to be sold in Sri Lanka. When he reached Kalpitiya he had unexpectedly contracted malaria. He had made a vow at St. Anne’s Church, Thalawila, expecting a full recovery. En route to Colombo, he had come to know about the Church in Kandana and dedicated to St. Sebastian. In the absence of the then parish Priest Rev. Fr. Joachim Alberto, the Muhuppu of the Church, with the help of the others, had agreed to by the statue for 75 pathagas (one pahtaga was 75 cent). Even though the seller had left the money in the hands of the “Muhuppu” to be collected later, he never returned.
On the 19th of January 2006, Archbishop Oswald Gomis declared St. Sebastian Church as “St. Sebastian Shrine” by way of a special notification and handed over the declaration to Rev. Fr. Susith Perera, the Parish Priest of Kandana.
On the 12th of January 2014, Catholics in Sri Lanka celebrated the reception of a reliquary containing a fragment of the arm of St. Sebastian. The reliquary was gifted from the administrator of the Basilica of St. Anthony of Padua and was brought to Sri Lanka by Monsignor Neville Perera. His Eminence Malcolm Cardinal Ranjit, Archbishop of Colombo, accompanied by priests and a large gathering, received the relic at the Katunayake International Airport, and brought it to Kandana, led by a procession, and was enthroned at the St. Sebastian Shrine.
Rev. Fr. Srinath Manoj Perera, the present administrator of the shrine, and assistant Priest Rev. Fr. Asela Mario, have finalised all arrangements to conduct the feast of St. Sebastian in a grand scale.
The latest book, written by Senior Lawyer Godfrey Cooray, named “Santha Sebastian Puranaya Saha Kandana” (The history of St. Sebastian and Kandana), was launched at De La Salle Auditorium, De Mazenod College, Kandana.
The Archbishop of Colombo His Eminence Most rev. Dr. Malcolm Cardinal Ranjith was the Chief Guests at the event.
The book discusses about the buried history of Muthurajawela and Aluth Kuru Korale civilisation, the history of Kandana and St. Sebastian. The author discusses the historical and archaeological values and culture.
158th Annual Feast of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine, Kandana, will be held on 20th of January 2026. On the 19th of January, Monday, Solemn Vespers were presided by His Lordship most Rev. Dr. Maxwell Silva Auxiliary Bishop of Colombo.
Festive High Mass will be presided by His Lordship Most Rev. Dr. J. D. Anthony, The Auxiliary Bishop of Colombo, on the 20th of January at 8pm.
By Godfrey Cooray
Senior Attorney -at -Law,
Former Ambassador to Norway and Finland
President, National Catholic Writers’ Association
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoIllusory rule of law
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoDaydreams on a winter’s day
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoSurprise move of both the Minister and myself from Agriculture to Education
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoExtended mind thesis:A Buddhist perspective
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe Story of Furniture in Sri Lanka
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoAmerican rulers’ hatred for Venezuela and its leaders
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoWriting a Sunday Column for the Island in the Sun
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL