Business
‘PUCSL electricity tariff revision is discriminatory’

Electricity tariff design must meet two main objectives: firstly, raising the money needed to pay for the costs of provision, and secondly, sending the right economic signals to each customer to favour the optimal socio-economic use of electricity.
To achieve the above objectives the principles that must be followed when designing tariffs are;
Economic sustainability or revenue sufficiency,
Equity or non-discrimination among users,
Economic efficiency in resource allocation, and
Transparency, simplicity, and stability of the methodology.
A well-defined and appropriate tariff structure must balance the financial sustainability of the sector on the one hand and the well-being of various segments of society on the other. The CEB’s tariff revisions seem to be mainly focused on the aspect of revenue sufficiency, ignoring the other aspects. As electricity is a commodity, there should be no difference in the prices charged to different users, except when reflecting any differences in the cost of providing services to different classes of users.
A differential tariff implies that some categories are subsidised leading to the question of who pays these subsidies. The current structure is such that households consuming an excess of 60 Kwh, and general purpose bulk supply users subsidise the industrial, hotel and charitable sectors.
Households that consume over 90 Kwh and general purpose bulk customers are charged a tariff that is double that of industries and hotels. With regards to hotels, in effect, domestic consumers subsidise foreign tourists. However, the differential tariff between general bulk supply and industrial/hotel users is meaningless. For example, a hall that hosts weddings and celebrations would be treated as a general bulk customer and be charged double the tariff that a hotel would be charged, even though both host similar events. A restaurant in a shopping mall would be charged as a general customer, but the same restaurant located within a hotel would enjoy a tariff half of that which a hotel incurs. While this differential existed under the previous tariff, it is made worse under the new structure; hotels faced a 10% increase in tariff while general users faced a 20% increase.
If the idea behind a lower tariff for hotels is to make the sector more competitive, then the solution is to address the causes of uncompetitiveness directly. One area is construction costs which raises the level of investment and the cost of maintenance. Protectionism for the domestic construction materials industry raises the costs of steel bars and rods, sanitary ware, aluminium extrusions, granite, electrical fittings, and carpets resulting in high overall construction cost. The effective protection granted on these items can exceed 200%; the savings in finance cost from a lower capital outlay would probably exceed the savings from a lower electricity tariff.
Economic value creation can take place in many different ways in an economy and the service sector is no less important than other sectors. The cross subsidisation between customers violates the equity or non-discrimination principle of a good tariff and discourages use by the overcharged and promotes overconsumption by the subsidised.
For example, the higher domestic tariff may serve as a disincentive for remote work. Remote or flexible work arrangements can reduce transport costs, congestion, energy use and for some, enable a better work/life balance. The government should be facilitating flexible work but the higher rates applicable to some domestic consumers may be a disincentive.
Economic activity is increasingly complex and a value chain can involve many different sectors. For example, the tea industry involves agriculture, processing in factories, transport, warehousing, blending, financing, marketing and exports. Moreover, products are now more knowledge intensive, so a greater part of the value addition arises in non-production-oriented components of the value chain. With differential tariffs, parts of the same value chain may pay different prices for use of the same commodity.
Further, a lower tariff to “industry” penalises new economy enterprises while promoting highly energy intensive users. This distorts resource allocation by encouraging excessive energy consumption, artificially promoting capital-intensive industries where the country may not have a clear comparative advantage. A subsidised tariff also blunts the incentive to economise.
The cost of supplying electricity fluctuates throughout the day, depending on the power generation mix, cost of fuels used, transmission costs and energy losses but as electricity storage is not economically viable, it has to be consumed whenever it is produced. Households with rooftop solar thus enjoy a subsidy. Domestic solar generation takes place in day time where the cost of generation is low but the import of electricity to the house takes place at night when the cost of generation is high. Offsetting units generated against units imported results in a subsidy because of the difference in costs between the two. Time of use metres should be mandated for all domestic users on net metering with the import/export being accounted for on the respective time of use tariff. Indeed all users who consume above 60 Kwh should move to the time of use tariff.
Should the government decide to subsidise the capital or operating costs to serve certain customer classes, it should do so directly from the budget and while a lifeline tariff for the poor is justified the high domestic users pay a tariff 7.4x that of the lowest. Not all households are the same size and an extended family living in a single house may face a much higher tariff although their income level may not differ greatly from the average.
The PUCSL should review tariffs to prevent the distortions highlighted above. Instead of cross-subsidies, the regulator should be working to reduce overall cost of the provision of electricity through better procurement and greater efficiency.
Treating all costs as a pass-through in computing the tariff is a mistake. The PUCSL needs to set efficiency targets in order to set fair and reasonable tariffs. The CEB should be incentivised to control its costs by specifying and enforcing performance requirements. Benchmarking CEB performance against regional and international peers to assess relative efficiency is necessary, as is consulting stakeholders on achievable efficiency targets.
Advocata is an independent policy think tank based in Colombo, Sri Lanka. We conduct research, provide commentary and hold events to promote sound policy ideas compatible with a free society in Sri Lanka. Visit advocata.org for more information.
Advocata spokespersons are available for live and pre-recorded broadcast interviews via 0774858401
CONTACT:
Subashini Kaneshwaren,
Senior Communications Executive, Advocata Institute
Email: subashini@advocata.org
Business
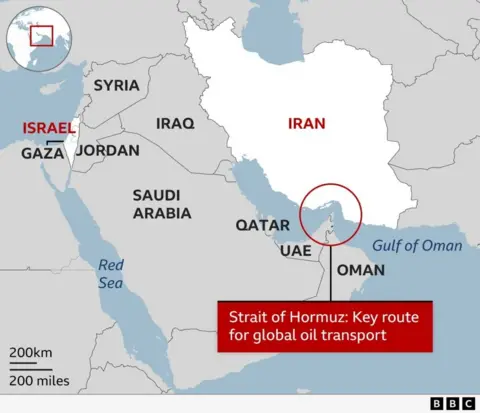
Oil prices rise after ships attacked near Strait of Hormuz

Global oil prices have risen after at least three ships were attacked near the Strait of Hormuz, as Iran continues to launch strikes across the Middle East in response to ongoing attacks by the US and Israel.
Two vessels have been struck, and an “unknown projectile” was reported to have “exploded in very close proximity” to a third, the UK Maritime Trade Operations Centre (UKMTO) said.
Iran has warned ships not to pass through the strait, which carries about 20% of the world’s oil and gas.
International shipping has almost come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with analysts warning that a prolonged conflict could push energy prices even higher.
In early trade in Asia on Monday, global oil prices jumped by more than 10% before those gains eased during the morning.
At 02:00 GMT, Brent crude was more than 4% higher at $76.16 (£56.53) a barrel, while US-traded oil was also up by around 4% at $69.67.
“The market isn’t panicking”, Saul Kavonic, head of energy research at MST Research told the BBC.
“There is more clarity that so far, oil transport and production infrastructure hasn’t been a primary target by any side,” he added.
“The market will be watching for signs that traffic through the Strait of Hormuz returns, which would see oil prices subside again.”
But some analysts have warned it could go over $100 in the event of a prolonged conflict.
On Sunday, the Opec+ group of oil producing nations – which includes Saudi Arabia and Russia – agreed to increase their output by 206,000 barrels a day to help cushion any price rises, but some experts doubt this would help much.
Edmund King, president of the AA, warned the disruption could drive up petrol prices around the world.
“The turmoil and bombing across the Middle East will surely be a catalyst to disrupt oil distribution globally, which will inevitably lead to price hikes,” he said.
“The magnitude and duration of pump price increases depends on how long the conflict goes on.”
Business
Iran strikes could add external pressure on Sri Lanka’s fragile recovery: Analyst

The U.S. and Israeli strikes on Iran have reignited geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, stoking fears of a broader conflict that could disrupt critical energy supply routes – particularly the Strait of Hormuz, through which roughly one-fifth of the world’s oil supply flows. Brent crude has already edged higher, and global oil markets warn prices could climb toward, or even exceed, US$80–100 a barrel if hostilities escalate.
Against this backdrop, an independent economic analyst told The Island that for Sri Lanka – a small, fuel-importing economy with limited domestic energy resources – the implications could be significant.
“Sri Lanka imports over 90% of its petroleum requirements, and any sustained rise in global crude prices would expand the annual import bill, placing renewed pressure on already tight foreign exchange reserves,” he said.
Even moderate spikes in oil prices, he noted, tend to filter quickly through the domestic economy. “Higher fuel costs translate into increased transport and production expenses, which feed into inflation and erode household purchasing power. Freight charges for essential goods – from food items to industrial inputs – would also rise.”
“The Middle East remains a key source of remittances and export demand,” the analyst explained. “A large share of Sri Lankan migrant workers are employed in Gulf economies, while regional markets absorb tea and other exports. Heightened instability could weaken remittance inflows and soften demand, further straining the balance of payments.”
When asked whether the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) might be compelled to shift policy in response, the analyst said the monetary authority faces a delicate balancing act.
“Rising import inflation stemming from higher global energy prices could push the Central Bank to maintain – or even tighten – its monetary policy stance in order to safeguard price stability and support the rupee. A firmer stance may be deemed necessary to anchor inflation expectations and preserve market confidence. The Central Bank is therefore likely to monitor inflation data closely in the coming weeks to assess whether energy-driven price pressures prove temporary or more entrenched,” he said.
Meanwhile, Ceylon Petroleum Corporation (CPC) Chairman S. Rajakaruna said that Sri Lanka’s fuel imports – sourced primarily from Singapore and India – reduce immediate exposure to supply disruptions directly linked to Middle Eastern routes. He also sought to allay public concerns, noting that the country currently maintains sufficient fuel stocks for approximately one month and that there need not be any queueing up by the public to hoard supplies.
However, the analyst cautioned that while physical supply may remain stable, global price pass-through effects are an unavoidable risk.
Meanwhile, Opposition politician Wimal Weerawansa said that official assurances of “one month’s stock” tend to unsettle the public, arguing that such statements evoke memories of past shortages and public distress.
By Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
Ministry of Education recognises LOLC Divi Saviya for restoring 200 schools

The Ministry of Education officially recognised LOLC Holdings PLC for its flagship humanitarian initiative, Divi Saviya, at a special ceremony held on 27th February 2026 in Battaramulla. The event marked the second time the Ministry has acknowledged the programme’s contribution to the nation’s education sector.
Group Managing Director/CEO Kapila Jayawardena presented a project update to Prime Minister and Education Minister Dr. Harini Amarasuriya, highlighting the rapid restoration of 200 schools under Phase 02 of ‘Obai, Mamai, Ape Ratai’. The schools were repaired and handed over within just 45 days, enabling students displaced by Cyclone Ditwah to safely resume learning.
Phase 02 follows a needs assessment that identified 200 damaged schools and 4,000 displaced families. Implemented with Divisional Secretariats and Disaster Management Centres, the Rs. 500 million programme has delivered Family Super Packs and school renovations across six districts.
Kapila Jayawardena stated, “It was a privilege to share these outcomes with the Prime Minister. This recognition reflects how private sector collaboration can complement government efforts during national challenges.” Plans are underway to fully rebuild select schools destroyed by the cyclone.
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoPrime Minister Attends the 40th Anniversary of the Sri Lanka Nippon Educational and Cultural Centre
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoDottin out obstructing the field as Sri Lanka clinch series
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-
 Features5 days ago
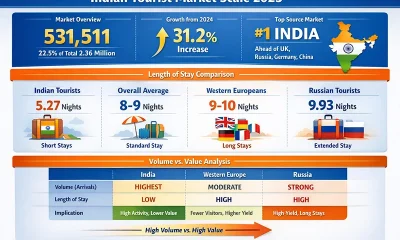
Features5 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka

















