Business
Overcoming Obstacles: The economic case for a Sri Lanka-Thailand FTA

By Asanka Wijesinghe and Nilupulee Rathnayake
In 2019, only 6 % of tea imported by Thailand was from Sri Lanka. This low percentage can be attributed to the difference in preferences and Thailand’s high tariffs of 90 % on imported tea, which act as barriers to Sri Lanka’s tea exports. Additionally, Thailand imposes up to 30 % tariffs on nearly 120 product lines of wearing apparel.
These high tariffs for products with a comparative advantage are not exclusive to Sri Lanka. Thailand also faces higher tariffs for vehicles, rubber, and light-electronics exports which Thailand exports competitively. This tariff structure hampers the bilateral trade of products with a higher comparative advantage for both countries.
Despite these challenges, Sri Lanka and Thailand have expedited the process of signing a free trade agreement (FTA) to boost bilateral trade by threefold to USD 1.5 billion. This article discusses the trade effect of an FTA and a way forward to maximise the gains from an FTA.
Existing Trade is Skewed
towards Thailand
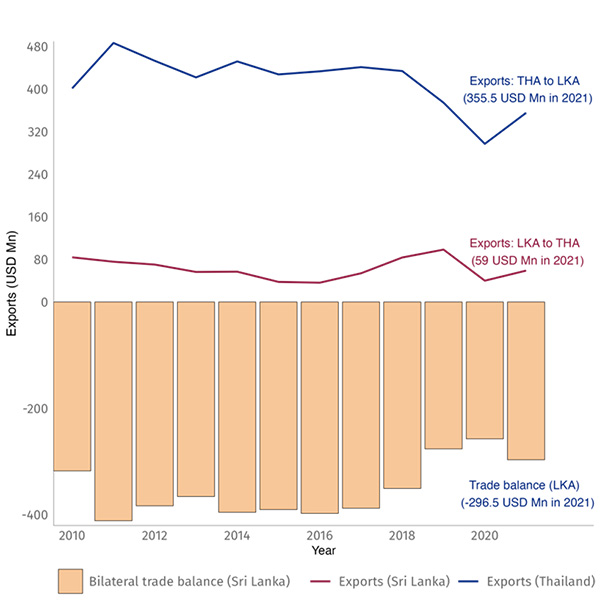 In the pre-pandemic period, Sri Lanka-Thailand bilateral trade was nearly USD 500 million. The three-year-2017, 2018 and 2019- average exports from Sri Lanka to Thailand were USD 62.9 million, while the exports from Thailand to Sri Lanka were USD 416.8 million. In 2019, Thailand was the 9th largest import source for Sri Lanka, but Sri Lanka is only the 73rd largest import source for Thailand. The mismatch resulted in a bilateral trade deficit of USD 353.9 million.
In the pre-pandemic period, Sri Lanka-Thailand bilateral trade was nearly USD 500 million. The three-year-2017, 2018 and 2019- average exports from Sri Lanka to Thailand were USD 62.9 million, while the exports from Thailand to Sri Lanka were USD 416.8 million. In 2019, Thailand was the 9th largest import source for Sri Lanka, but Sri Lanka is only the 73rd largest import source for Thailand. The mismatch resulted in a bilateral trade deficit of USD 353.9 million.
The existing exports from Sri Lanka to Thailand do not represent Sri Lanka’s typical export basket. The contribution of traditional exports like ready-made garments, tea, rubber, and coconuts is relatively low, and gems, electrical equipment, wheat flour, and activated carbon contribute to a greater extent. Technically specified natural rubber and latex are the top exports from Thailand which are essential raw materials in the value-added rubber industry of Sri Lanka.
Effect of Lowering Tariffs on Bilateral Trade to Zero
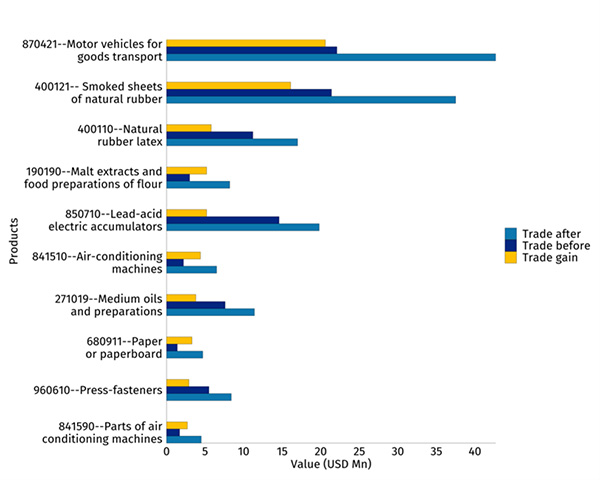
 As estimated from partial equilibrium analysis, Sri Lanka will realise a 38 % increase in exports to Thailand if tariffs are reduced to zero (Figure 2). The wearing apparel sector would be the biggest beneficiary, with exports projected to increase by 251 % from USD 6.4 million to USD 22.5 million. Figure 3A provides the top ten exports by Sri Lanka benefitting from a tariff removal by Thailand. The export effect for Thailand will be 27.8 % and Thailand’s rubber and plastic products will be increased by 71.9 % or USD 35.4 million. Products such as smoked sheets of rubber and natural latexwould benefit the most from tariff elimination, as shown in Figure 3B.
As estimated from partial equilibrium analysis, Sri Lanka will realise a 38 % increase in exports to Thailand if tariffs are reduced to zero (Figure 2). The wearing apparel sector would be the biggest beneficiary, with exports projected to increase by 251 % from USD 6.4 million to USD 22.5 million. Figure 3A provides the top ten exports by Sri Lanka benefitting from a tariff removal by Thailand. The export effect for Thailand will be 27.8 % and Thailand’s rubber and plastic products will be increased by 71.9 % or USD 35.4 million. Products such as smoked sheets of rubber and natural latexwould benefit the most from tariff elimination, as shown in Figure 3B.
Assuming an immediate phasing-out of the existing tariffs, an FTA would increase bilateral trade to USD 619.6 million by 29.1 %. This increase falls short of the ambitious goal of a threefold increase in bilateral trade, at least in the short run.
However, partial equilibrium analysis does not estimate the trade gains from new product innovations due to FDI movements. The estimates also do not account for trade effects through input-output linkages and magnification of tariff effects along the value chains. However, tariff phasing out takes time, and FTA coverages are less than 100 %.
Notes: Simulations were done for Global Trade Analysis Project (GTAP) 47-sectors using sector-specific Armington Elasticities. The base years were 2021, and 2017 for Thailand and Sri Lanka, respectively.
Maximising Trade Gains
through Offensive Lists
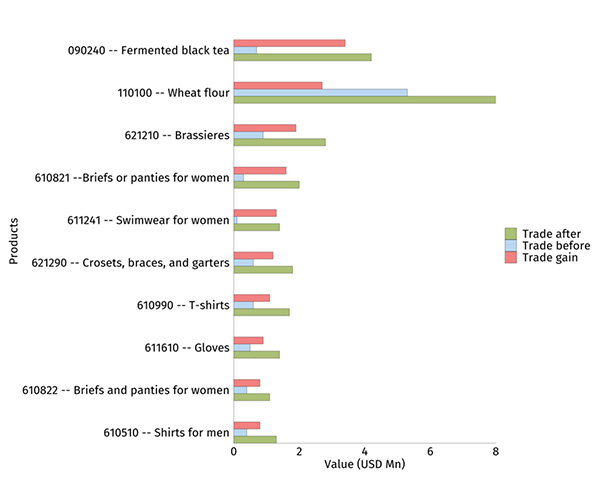 An offensive list contains products for which a country has a comparative advantage, capacity for expansion, and a favourable tariff from the importing country. There are 154 such products for Sri Lanka. Notably, 81 % of the USD 27.6 million export gain from an FTA comes from these 154 product lines. Similarly, 69 % of Thailand’s export gains to Sri Lanka in an FTA comes from 147 products identified for the offensive list.
An offensive list contains products for which a country has a comparative advantage, capacity for expansion, and a favourable tariff from the importing country. There are 154 such products for Sri Lanka. Notably, 81 % of the USD 27.6 million export gain from an FTA comes from these 154 product lines. Similarly, 69 % of Thailand’s export gains to Sri Lanka in an FTA comes from 147 products identified for the offensive list.
Once ordered by the estimated export gains, nine out of the top ten products of Sri Lanka’s offensive list are from the wearing apparel sector. For Thailand, vital offensive products are rubber, electric equipment like air-conditioners and refrigerators, and motor vehicles for goods transportation.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
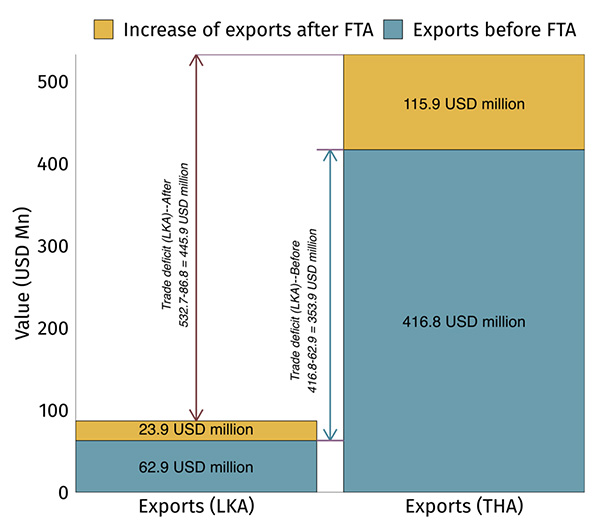
 Applying tariff cuts for all the products in the offensive lists is a challenge. Thailand’s high tariffs for tea and ready-made exports indicate its protectionist intent. Likewise, Sri Lanka might prefer to keep tariffs on rubber products. Significant political manoeuvring and delicate negotiations will be required to bring the coverage of the FTA to a satisfactory level. Secondly, an FTA will widen Sri Lanka’s trade deficit with Thailand by 26 % (Figure 4). Although a trade deficit is not necessarily detrimental, it does present a short-term challenge due to increased dollar outflow.
Applying tariff cuts for all the products in the offensive lists is a challenge. Thailand’s high tariffs for tea and ready-made exports indicate its protectionist intent. Likewise, Sri Lanka might prefer to keep tariffs on rubber products. Significant political manoeuvring and delicate negotiations will be required to bring the coverage of the FTA to a satisfactory level. Secondly, an FTA will widen Sri Lanka’s trade deficit with Thailand by 26 % (Figure 4). Although a trade deficit is not necessarily detrimental, it does present a short-term challenge due to increased dollar outflow.
A possible solution is tariff elimination for the products in bilateral value chains. Sri Lanka uses Thailand’s rubber and textile products to produce finished goods. If Thailand removes tariffs for these finished products, increased exports will demand more raw materials. Sri Lanka can reciprocate by eliminating tariffs on raw materials. Phasing-in of the FTA, accounting for required adjustments, will also increase the political feasibility.
Strengthening bilateral trade ties with Thailand offers additional benefits to Sri Lanka. An FTA provides an opportunity to join electric equipment manufacturing value chains and a gateway to ASEAN economies. Thus, Sri Lanka should negotiate a comprehensive trade agreement with investment promotion, trade facilitation, and competition laws. Thailand can leverage Sri Lanka’s position as a distributional hub for regional exports.
Link to Talking Economics blog: https://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2023/05/11/overcoming-obstacles-the-economic-case-for-a-sri-lanka-thailand-fta/
Asanka Wijesinghe is a Research Fellow at IPS with research interests in macroeconomic policy, international trade, labour and health economics. He holds a BSc in Agricultural Technology and Management from the University of Peradeniya, an MS in Agribusiness and Applied Economics from North Dakota State University, and an MS and PhD in Agricultural, Environmental and Development Economics from The Ohio State University. (Talk with Asanka – asanka@ips.lk)
Nilupulee Rathnayake is a Research Assistant working on Macro, Trade and Competitiveness research at IPS. She holds an MSc in Development Economics from the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom, and a BA in Economics from the University of Colombo, Sri Lanka. (Talk with Nilupulee – nilupulee@ips.lk)
Business
Dialog delivers strong growth, stronger national contribution in FY 2025

Dialog Axiata PLC announced, Friday 6th February 2026, its consolidated financial results (Reviewed) for the year ended 31st December 2025. Financial results included those of Dialog Axiata PLC (the “Company”) and of the Dialog Axiata Group (the “Group”).
Group Performance
The Group delivered a strong performance across Mobile, Fixed Line and Digital Pay Television businesses recording a positive Core Revenue growth of 16% Year to Date (“YTD”). Group Headline Revenue reached Rs179.6Bn, up 5% YTD, despite the continued strategic scaling down of low-margin international wholesale business. In Q4 2025, Revenue was recorded at Rs46.5Bn up 2% Quarter-on-Quarter (“QoQ”) and 2% Year-on-Year (“YoY”).
The Group Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation and Amortisation (“EBITDA”) reached Rs86.0Bn up 30% YTD supported by Core Revenue performance and Cost Rescaling Initiatives. On a QoQ basis Group EBITDA demonstrated a modest growth to record at Rs23.0Bn up 2% QoQ with an EBITDA margin of 49.5% in line with the Revenue performance. Group EBITDA margin reached 47.9% for FY 2025, up 9.2pp.
Group Net Profit After Tax (“NPAT”) reached Rs20.8Bn for FY 2025, up 67% YTD mainly resulting from robust EBITDA growth, despite higher tax and net finance costs. Normalized for forex impact, NPAT growth was recorded at +>100% YTD to reach Rs22.1Bn. On a QoQ basis NPAT grew 3% to reach Rs5.9Bn resulting from strong EBITDA performance.
On the back of strong operational performance, the Group recorded Operating Free Cash Flow (“OFCF”)
of Rs49.3Bn for FY 2025 up >100% YTD.
Dividend Payment to Shareholders
In line with the dividend policy and financial performance of the Group and taking into account the forward investment requirements to serve the nation’s demand for Broadband and Digital services, the Board of Directors of Dialog Axiata PLC at its meeting held on 6th February 2026, resolved to propose for consideration by the Shareholders of the Company, a dividend to ordinary shareholders amounting to Rs1.50 per share. The said dividend, if approved by shareholders, would translate to a Dividend Yield of 5.0% based on share closing price for FY 2025. The dividend so proposed will be considered for approval by the shareholders at the Annual General Meeting (AGM) of the Company, the date pertaining to which would be notified in due course.
Company and Subsidiary Performance
At an entity level, Dialog Axiata PLC (the “Company”) continued to be the primary contributor to Group Revenue (76%) and Group EBITDA (74%). Aided by sustained growth in the Data segment and cost-rescaling initiatives, Company revenue was recorded at Rs135.8Bn for FY 2025, up 18% YTD, EBITDA rose 32% YTD to reach Rs63.6Bn. On a QoQ basis, Q4 2025 Revenue was recorded at Rs34.8Bn, down 1% QoQ due to a reclassification of Hubbing Revenue, while EBITDA decline 1% QoQ to record Rs17.0Bn, largely attributable to network restoration costs and donations made in relation to the Cyclone Ditwah relief efforts. Furthermore, NPAT was recorded at Rs15.6Bn for FY 2025, up 41% YTD. Normalised for forex impacts, the company NPAT was up +>100% YTD to reach Rs17.0Bn. On a QoQ basis, Company NPAT was recorded at Rs4.5Bn, down 6% QoQ.
Business
Ceylinco Life’s Pranama Scholarships reach 25-year milestone

Ceylinco Life has announced the launch of the 25th consecutive edition of its flagship Pranama Scholarships programme, marking a significant milestone in the company’s long-standing commitment to recognising and rewarding excellence among the children of its policyholders.
Under the 2026 programme, the life insurance market leader will present scholarships with a total cumulative value of Rs. 22.7 million, continuing a rewards initiative that has now been conducted without interruption for a quarter of a century. Since its inception, the Ceylinco Life Pranama Scholarships programme has benefitted 3,466 students across the country, representing a total investment of Rs. 240 million in nurturing academic achievement and outstanding performance in sports, arts and other extracurricular pursuits.
Business
Sri Lankans’ artistic genius glowingly manifests at Kala Pola ‘26

The artistic genius of Sri Lankans was amply manifest all over again at ‘Kala Pola ‘26’ which was held on February 8th at Ananda Coomaraswamy Mawatha Colombo 7; the usual, teeming and colourful venue for this annual grand exhibition and celebration of the work of local visual artists.
If there is one thing that has flourished memorably and resplendently in Sri Lanka over the centuries it is the artistic capability or genius of its people. It is something that all Sri Lankans could feel a sense of elation over because from the viewpoint of the arts, Sri Lanka is second to no other nation. With regard to the visual arts a veritable dazzling radiance of this inborn and persisting capability is seen at the annual open air ‘Kala Pola’.
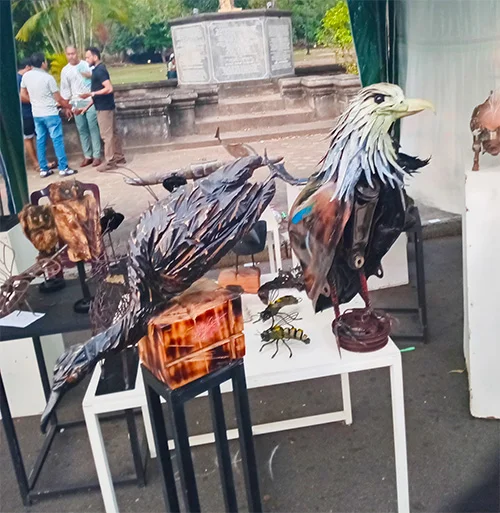

A bird of Sri Lanka created from scraps of iron waste.
All capable visual artists, wherever they hail from in Sri Lanka, enjoy the opportunity of exhibiting their work at the ‘Kala Pola’ and this is a distinctive ‘positive’ of this annual event that draws numberless artists and viewers. There was an abundance of paintings, sketches and sculptures, for instance, and one work was as good as the other. Ample and equal space was afforded each artist. Its widely participatory and open nature enables one to describe the exhibition as exuding a profoundly democratic ethos.
Accordingly, this time around at ‘Kala Pola ‘26’ too Sri Lankans’ creative efforts were there to be viewed, studied and enjoyed in the customary carnival atmosphere where connoisseurs, local and foreign, met in a sprit of camaraderie and good cheer. Many thanks are owed once again to the George Keyt Foundation for the presentation of the event in association with the John Keells Group and the John Keells Foundation, not forgetting the Nations Trust Bank, which was the event’s Official Banking Partner. The exhibition was officially declared open by Chief Guest Marc-Andre Franche, UN Resident Coordinator in Sri Lanka.
By Lynn Ockersz
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?












