Business
Oil supply tightens in Europe over Red Sea disruptions

The structure of the global benchmark Brent crude futures market and some physical markets in Europe and Africa have been reflecting tighter supply partly over concerns about shipping delays as vessels avoid the Red Sea due to missile and drone attacks.
The disruptions – which have been the largest to global trade since the COVID-19 pandemic – have combined with other factors such as rising Chinese demand to increase competition for crude supply that does not have to transit the Suez Canal, and analysts say this is most evident in European markets.
In a sign of tighter supply, the market structure of Brent – which is used to price nearly 80 percent of the world’s traded oil – hit its most bullish in two months on Friday, as tankers diverted from the Red Sea following recent air strikes by the United States and United Kingdom on targets in Yemen.
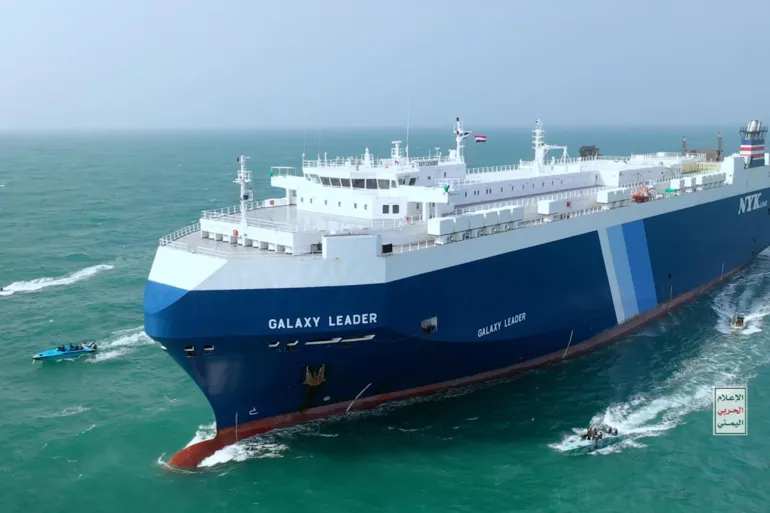
In response to Israel’s war on Gaza, rebels from the Iran-aligned group that controls northern Yemen and its western coastline have launched a wave of assaults on ships in the Red Sea.
By targeting vessels with perceived links to Israel, the Houthis are attempting to force Tel Aviv to stop the war and allow humanitarian aid into the Gaza Strip.
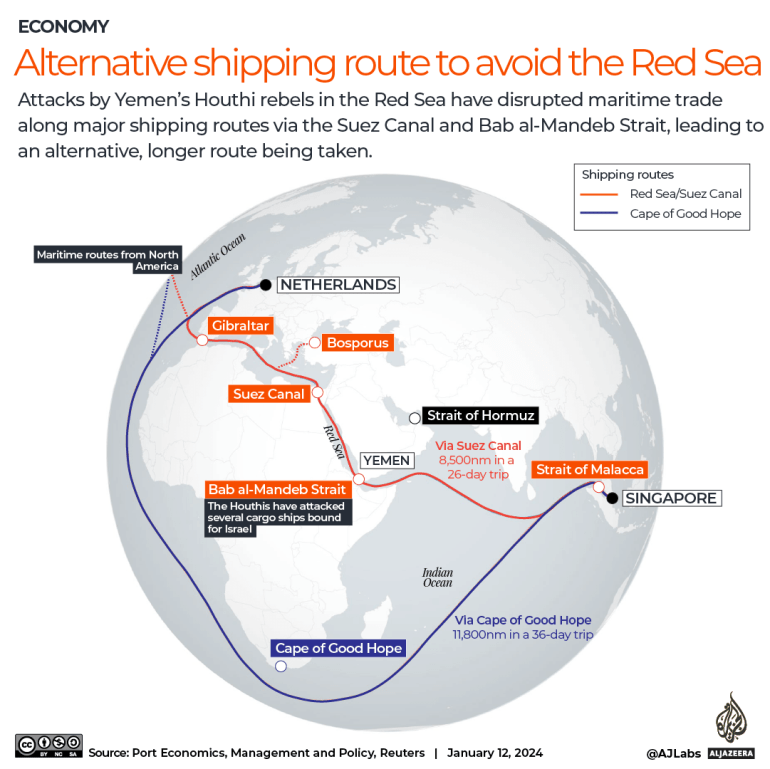
Houthi activity has so far been concentrated in the narrow strait of Bab al-Mandeb, which connects the Gulf of Aden to the Red Sea. Approximately 50 ships sail through the strait every day, heading to and from the Suez Canal – a central artery for global trade.
Some of the world’s largest shipping companies have suspended transit in the region, forcing vessels to sail around the Cape of Good Hope in Southern Africa. The lengthier route has raised freight rates due to higher fuel, crew and insurance costs.
“Brent is the most impacted futures contract when it comes to Red Sea/Suez Canal disruptions,” Viktor Katona, lead crude analyst at Kpler, told the Reuters news agency. “So who suffers the most on the physical front? Undoubtedly, it is European refiners.”
The premium of the first-month Brent contract to the six-month contract LCOc1-LCOc7 rose to as much as $2.15 a barrel on Friday, the highest since early November. This structure, called backwardation, indicates a perception of tighter supply for prompt delivery.
Less Middle Eastern crude is heading to Europe, with the volume nearly halved to about 570,000 barrels per day (bpd) in December from 1.07 million bpd in October, Kpler data showed.
Ships travelling through the Suez Canal have taken on greater strategic significance since the war in Ukraine, as sanctions against Russia have made Europe more dependent on oil from the Middle East, which supplies one-third of the world’s Brent crude.
But it’s challenging to measure the impact of Red Sea shipping separately, one crude trader told Reuters. “It’s a strong market everywhere, but people are very nervous.”
Other developments have also tightened the European crude market including a drop in Libyan supply due to protests, the first such disruption for months, and lower Nigerian exports.
Angolan crude, which also heads to Europe without having to pass through the Suez Canal, is seeing higher demand from China and India because of issues around Iranian and Russian crude, reducing the supply that could come to Europe.
China’s oil trade with Iran has stalled as Tehran withholds shipments and demands higher prices, while India’s imports of Russian crude have fallen due to currency challenges, although India attributed the drop to unattractive prices.
Meanwhile, Russia leapfrogged Saudi Arabia to become China’s top crude oil supplier in 2023, data showed on Saturday, as the world’s biggest crude importer defied Western sanctions over Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine to buy vast quantities of discounted oil for its processing plants.
Russia shipped a record 107.02 million metric tonnes of crude oil to China last year, equivalent to 2.14 million bpd, the Chinese customs data showed, far more than other major oil exporters such as Saudi Arabia and Iraq.
Imports from Saudi Arabia, previously China’s largest supplier, fell 1.8 percent to 85.96 million tonnes, as the Middle East oil giant lost market share to cheaper Russian crude.
(Aljazeera)
Business
CDS accounts on the increase, crosses one million accounts

Central Depository Systems (Pvt) Ltd (CDS), a subsidiary of the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE), has reached a milestone as total registered accounts surpassed the 1 million mark. This achievement coincides with the approach of the organization’s 35th anniversary in September 2026, marking three and a half decades of providing depository infrastructure for the Sri Lankan capital market.
Since its inception in 1991, the CDS has held the distinction of being the first depository in the South Asian region. In its core capacity as a depository, the institution is responsible for holding a wide array of securities including shares, debentures, corporate bonds, and units belonging to investors in electronic form.
The crossing of the one million account threshold also reflects the aggressive broad basing of the retail investor market over the past five years. This expansion is largely attributed to the comprehensive digitalization of the CSE, which has created accessibility for individuals across the country. Digital tools such as the CSE Mobile App and the “CDS e-Connect” portal have revolutionized how investors interact with the stock market, providing them with real time access to their holdings and a seamless interface for account management. The “CDS e-Connect”, originally launched in 2016 and revamped in 2021, has become a one stop shop for stakeholders, by offering services such as client profile management, real time balance and transaction viewing, eNomination facility, monthly statements and newly introduced dividend payment history viewing option. From 2016, by offering eStatements and SMS alert facilities CDS ensures transparency and security for the CDS accountholders. By decentralizing account openings and introducing online facilities in 2020, the CDS successfully brought the stock market to the fingertips of the general public, moving away from the traditional, paperwork heavy processes that once characterized the industry.
A critical pillar of this 35-year history was the 2011 launch of the full dematerialization drive. This initiative was designed to significantly reduce the movement of physical certificates, which were prone to loss, damage, and forgery. Today, the success of this drive is evident as the CDS holds 97 percent of listed equity and 100 percent of corporate debt in scripless form. This near total transition to electronic records has provided a secure and accessible service environment. The Central Control Unit plays a vital role, ensuring that all functions performed by the depository and its participants align with strict rules and regulatory guidelines. By identifying operational, financial, and market risks early, the CDS maintains the integrity of the ecosystem and fosters trust among both domestic and international investors.
Beyond its primary depository functions, the CDS has significantly expanded its influence through the Corporate Solutions Unit (CSU), established in 2017. The CSU was created to standardize and elevate the benchmarks for corporate action services in Sri Lanka and has since grown through the strategic acquisition of PW Corporate Registrar arm. This diversification allows the CDS to expand registrar services and manage corporate actions for both listed and unlisted companies, providing a holistic suite of services that includes the distribution of dividends, rights issues, and e-applications for Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). The digitization of issuer services has been a hallmark of the CSU’s work, introducing innovations such as eDividend payments, eWarrants, and eNotices. These advancements have streamlined the process for issuers while ensuring that shareholders receive their entitlements promptly and securely.
The strategic outlook for the CDS is now centred on the newly formed Research and Development Unit, which is essential to the organization’s vision for the future. This unit functions as a Project Management Office and is responsible for developing innovative services. By cultivating strategic alliances and international collaborations, the R&D unit ensures that the CDS remains a future forward institution capable of adapting to the evolving needs of the global financial sector.
As the CDS looks toward its 35th year of service, it remains focused on digital transformation, strategic partnerships that power progress, new service offerings and enhanced international relations. The integration of new technologies continues to ensure robust infrastructure for the next generation of market participants.
Head of CDS Nadeera Athukorale commenting on the vision of the CDS, remarked “By balancing its core depository duties with non-core registrar and consultancy services, the CDS has positioned itself for long term sustainability and industry leadership.”
The achievement of one million accounts serves as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the Sri Lankan capital market infrastructure, demonstrating CDS’ ability to facilitate a growing digitized market while continuing to serve as the backbone of the nation’s investment landscape. (CSE)
Business
TONIK set to become next Sri Lankan hospitality brand reaching the global stage

TONIK, a new hospitality venture under Sri Lanka’s Acorn Group, has unveiled its vision to place culture, storytelling and design at the heart of island exploration, positioning itself as the next Sri Lankan hospitality brand to achieve global recognition.
Built on the Acorn Group’s decades of expertise across aviation, travel, logistics and leisure in multiple Asian markets, TONIK aims to elevate Sri Lanka’s tourism by translating the “soul” of destinations into curated experiences. The brand’s philosophy, “Every Stay Is a Story”, treats villas and boutique hotels as “living narratives” shaped by architecture, memory, craft and community.
The venture addresses a key market gap: while Sri Lanka features exceptional independent villas, many struggle with visibility and global reach. TONIK seeks to resolve this by amplifying each property’s unique value proposition – transforming distinctiveness into revenue -generating potential for owners.
“TONIK’s philosophy aligns with the evolution of our industry- where authenticity and meaningful experiences are no longer optional but essential,” said Harith Perera, Partner at Acorn Group. “Sri Lanka’s narrative deserves platforms that elevate its voice globally.”
For property owners, TONIK offers access to Acorn’s intelligence networks across the Maldives, Middle East, Europe and Asia, including insight into High-Net-Worth travel patterns.
CEO Sundararajah Kokularajah said: “By nurturing properties as living narratives, we aim to shape a new chapter for tourism – authentic, future-ready and deeply Sri Lankan.”
By Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
SDB bank relocates Warakapola branch to enhance customer experience

SDB bank relocated its Warakapola Branch to a new location with a modern, fresh look and ample parking, further strengthening its commitment to delivering an enhanced, customer-centric banking experience. The newly refurbished branch, located at No. 221/E, Colombo Road, Warakapola, will officially open its doors to customers.
The relocation reflects SDB bank’s ongoing efforts to adapt its branch network to today’s banking requirements, ensuring clients enjoy a refreshed, welcoming, and efficient service. The upgraded branch features contemporary design and improved facilities, providing greater convenience and a seamless banking experience for individuals, entrepreneurs, and businesses in the Warakapola area.
As part of its continuous transformation journey, SDB bank has prioritised innovation and service excellence in reimagining the Warakapola Branch. The new premises have been thoughtfully designed to meet evolving customer needs while fostering stronger engagement with the local community and business sector.
Kapila Ariyaratne, Executive Director / Chief Executive Officer of SDB bank, stated, “The relocation of our Warakapola Branch reflects SDB bank’s dedication to providing our customers a modern and enhanced banking experience with convenience and personalised service. This modern space is designed to meet evolving needs while reinforcing our strong ties with the local community. We remain committed to delivering innovative and customer-focused financial solutions that support regional and national growth.”
The enhanced branch environment is expected to serve both existing customers and new clients in the region, reinforcing SDB bank’s growing island wide presence. Through this relocation, the Bank continues to demonstrate its commitment to sustainable growth, service excellence, and meaningful community engagement.
SDB bank invites its valued customers and the Warakapola community to visit the new branch and experience the enhanced facilities firsthand.
A future-ready bank, dedicated to offering customer-centric and comprehensive support tailored to each individual’s needs, SDB bank is a licensed specialized bank regulated by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, with a listing on the Main Board of the Colombo Stock Exchange and a Fitch Rating of BB +(lka).
Through the network of 94 branches island-wide, the bank provides a comprehensive range of financial services to its Retail, SME, Co-operative, and Business Banking clients across the country. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles are deeply ingrained in SDB bank’s ethos, with a steadfast focus on uplifting local communities and businesses through sustainable practices. The bank is particularly committed to promoting women’s empowerment, sustainable development of SMEs, and digital inclusion, aiming to propel Sri Lanka to new heights.
Ceremonial opening of SDB bank Warakapola Branch
From left to right,
Binesh Aravinda – Head of Branch Banking – SDB bank,.A.D.Walisinghe – Chairman Kegalle Sanasa District Union, Kapila Ariyaratne – Executive Director/ Cheif Executive Officer – SDB bank, Chitral De Silva – Cheif Business Officer – SDB bank
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoSri Lanka to Host First-Ever World Congress on Snakes in Landmark Scientific Milestone