Features
No Christmas in Bethlehem, Breakthrough in Vatican, and Himalayan Declaration

by Rajan Philips
In Bethlehem where it all began, there is no Christmas this year. Bethlehem is located in Israeli occupied West Bank of Palestine. Palestinian churches have reportedly cancelled Christmas celebrations and some of them have set up nativity scenes showing the symbolic Baby Jesus lying in a manger of rubble destruction. Death and destruction now define life in Gaza less than 100 km to the west, but Palestinians on the West Bank are also subject to unchecked attacks by illegal Jewish settlers and retaliation by the Israeli army against Palestinian protests.
It is all Christmas in the US but in a climate of national political confusion in spite of a robustly performing economy. The confusion about the war in Israel, not to mention the one in Ukraine; the hysteria over antisemitism, with the US Congress declaring opposition to Zionism as antisemitism; the for and against moves centered on Donald Trump; and competing expectations and forebodings for the great election year of 2024.
There will be little Christmas time in Washington for the Biden Administration, which is literally on the horns of its own dilemma of simultaneously supporting and restraining the Israeli government’s devastation of Gaza.
At the last UN General Assembly vote on October 12 when 153 countries called for a ‘humanitarian ceasefire,’ 20 countries abstained, and the US voted against the resolution along with Israel and eight other minions. But the US encouraged its allies (e.g., Australia, Canada and New Zealand, three of the Five Eyes along with the US and the UK) to take up a united position and support the resolution.
At the time of writing (Thursday evening, New York / Friday morning, Colombo), the US is finally trying to give support to a UN Security Council resolution calling for “suspension of hostilities” and “scaled-up humanitarian aid access to Gaza.” Unlike the General Assembly resolutions, Security Council resolutions have legal teeth.
The Security Council vote has been delayed several times at the US’s asking to find acceptable wording to support it and not veto it. If the resolution passes, that would be the first in the current crisis. With Hamas insisting that there will be no more release of hostages until Israel completely stops its attacks on Gaza, the US and its Middle East allies are looking for alternative avenues to bring about a ceasefire, howsoever it might be called.
As Canadian academic and international relations expert Janice Stein observed after the UN General Assembly vote, the US has “significant influence over what comes next … Starting in 1956 the United States has frequently forced Israel both to stop the fighting, accept the ceasefire and at times to pull back.” So, this will not be the first time that the US might use its influence to bring about a ceasefire.
How soon the US will be able to do it this time is the question. Otherwise, there is no immediate end in sight to this conflict even well into the New Year. With Yemen’s Houthis emboldened to attack merchandise ships in the Red Sea, the whole conflict may take a different turn. The other conflict in Ukraine has entered a stalemate favourable to Russia, with fatigue setting in among Ukraine’s sponsors about continuing their material support of the war.
Breakthrough in Vatican
Lost in the din of war is what otherwise would have been an excellent Christmas gift and news. Last Monday, a week before Christmas, Pope Francis, the Jesuit Pope, issued a landmark authorization for priests to administer blessings on same-sex couples but outside the Church’s regular mass or formal rituals. This is a reversal of the Church’s 2021 declaration disallowing such blessings in keeping with the Catechism of the Catholic Church. The change is considered as providing a “simple blessing” and not the sacrament of (heterosexual) marriage. Yet, it is a huge step for the Vatican.
The change will have its supporters and decriers, and more so in the US than anywhere else. American Jesuit Father James Martin who works among LGBT communities, has welcomed the change as “a major step forward in the church’s ministry” to them. Many same sex-couples are delighted. The conservatives in the Church are obviously opposed to it. Ulrich L. Lehner, a US theology professor, reflecting his nation’s penchant for culture wars, has called it “an invitation to schism”.
The Vatican breakthrough comes two months after the conclusion of the historic synod that Pope Francis had convened to guide the future of the Catholic Church. For the first time in its history the Church convened an official gathering of 364 members that included non-clerical members of the Church including 54 women. The Pope called for the meeting in 2021 as part of his efforts to reform the church and to bring the superstructure of the Church into alignment with the base of its faithful followers. Preparations over two years included consultations among Catholics around the world. Women’s role in the Church emerged as a central question with almost universal call for opening up opportunities for women to take on decision-making roles in the Church.
After nearly a month of deliberations the Synod issued a Synthesis Report of 41 pages with each paragraph voted separately and receiving over two-thirds majority. The synod process and experience were based on listening and formulating positions rather than receiving top down resolutions. The report covered all the current challenges facing the Church including clerical sexual abuse, women’s roles in the church, outreach to poor and the concept of “synodality” itself.
The report noted that throughout the synod process, “many women expressed deep gratitude for the work of priests and bishops. They also spoke of a Church that wounds. Clericalism, a chauvinist mentality and inappropriate expressions of authority continue to scar the face of the Church and damage its communion.” “A profound spiritual conversion is needed as the foundation for any effective structural change,” it said. “Sexual abuse and the abuse of power and authority continue to cry out for justice, healing and reconciliation.” The same issues will be in focus again when the synod reconvenes in October 2024.
A Himalayan Declaration
Sri Lanka has its problems, a continuation of the economic crisis that began last year, and unprecedented in its own historical parallels. Yet it is fortunate enough to be where it is unlike many of the other world’s troubled spots. And all of a sudden the country received a shot in the arm, so to speak, aimed at addressing its most chronic problem involving the political relationship among its communities. The shot came literally entitled as the Himalayan Declaration, and it became public after it was formally presented by its authors to President Wickremesinghe. More presentations to other notables are reported to be in the offing. But what difference the declaration is going to make is too early to tell.
The grand sounding name Himalayan Declaration is apparently derived from the small town of Nagarkot in Nepal, where the signatories to the declaration gathered and reached their six-point agreement as the basis for yet another initiative to resolve Sri Lanka’s national question. After the experiences of Thimphu, Oslo, and numerous other gatherings and consultations in many parts of the world including many cities in India, one can only wish heavenly blessings for the latest initiative coming down from the Himalayas to finally succeed. Most of us can only wish and watch, but the success of the initiative will ultimately depend on who among Sri Lanka’s current political actors will take over the initiative and cross the finish line.
The signatories to the new initiative portray an interesting coalescence comprising all Buddhist Priests from among the Sinhalese, and all Tamil expatriates living in western countries seemingly acting on behalf of the Tamils.
One would think the involvement of the Buddhist Priests, all of whom appear to be at the higher echelons of the Sangha hierarchy is intended to maximize the declaration’s purchase among the Sinhalese. Conversely, if their presence in the declaration can dampen the usual rabble rousing against such initiatives, that in itself would be a significant contribution.
The expatriate Tamil signatories to the declaration and others who worked on it are not household political names in Sri Lanka or among the Sri Lankan diasporas. But they have been in the business of ethnic politics for all their adult lives, and their intervention at this stage deserves due commendation. Unlike the interlopers who used to pop up during the Rajapaksa and Sirisena years, the present group is obviously not looking for handouts from the government. But that is not going to save them from brickbats that will be flung at them from their far flung compatriots, which seem to have already started.
There is never going to be unanimity among the Tamils on any proposal(s) for reconciliation. That is not in their collective DNA. But if there is substantial support among the Sinhalese for a significant initiative that is also championed by the government in power, then the collective Tamil response will be equally positive. Otherwise, even if the Tamils are unanimous in their support for an initiative it will not go anywhere without sufficient purchase among the Sinhalese. One shortcoming of the initiative is the absence of Muslim and Indian Tamil participants and signatories. Obviously, it could not have been an intended omission, but in ethnic relationships inadvertent omissions can be as damaging as deliberate ones.
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
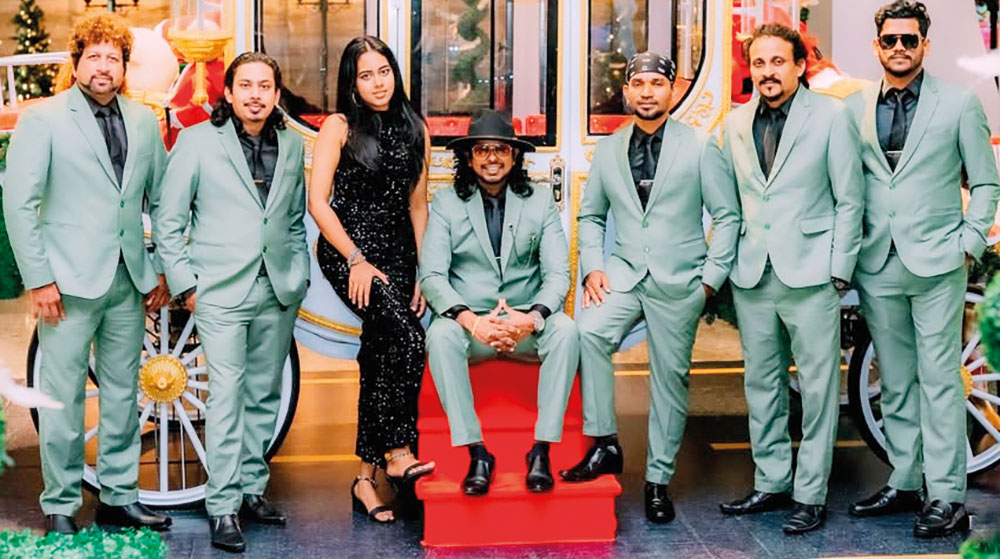
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Opinion1 day ago
Opinion1 day agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans




























