Business
New IPS publication, ‘Palm Oil Industry in Sri Lanka: An Economic Analysis’
Q&A Explainer with Author
Featuring:Dr Erandathie Pathiraja
Research Fellow – Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka
- The palm oil industry in Sri Lanka saves USD 17 million annually in foreign exchange and contributes to the economy through employment and capital investments.
- Oil palm cultivation was allowed initially to reduce reliance on imported palm oil, but concerns over environmental and health impacts led to a decision to phase out cultivation within ten years.
- Environmental concerns associated with oil palm cultivation involve deforestation and water degradation and health risks from edible oil consumption include concerns on cardiovascular diseases.
- While the evidence remains inconclusive, there is clearly a need for robust and unbiased technical analysis on this hotly disputed issue.
Dr Erandathie Pathiraja, Research Fellow at the Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka (IPS), provides valuable insights into the recently published IPS study, ‘Palm Oil Industry in Sri Lanka: An Economic Analysis’. The study authored by Dr. Erandathie Pathiraja, Ruwan Samaraweera, Hiruni Fernando, and Jaan Bogodage, offers a comprehensive analysis of the economic and environmental impacts of the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka.
In the following Q&A session, Dr Pathiraja shares her perspectives on the reasons behind the ban on oil palm cultivation, the potential impact on the economy and environment, the industry’s economic contributions, environmental concerns and their mitigation, health issues related to edible oil consumption, and alternative solutions to meet the local edible oil demand.
Q: In light of the recent ban on oil palm cultivation in Sri Lanka, there has been much debate surrounding the decision. Could you share your insights on the reasons behind the ban and its potential impact on the economy and environment?
The palm oil industry in Sri Lanka has been an import substitution policy initiative aimed at reducing palm oil imports and boosting the economy. The 2021 ban on oil palm cultivation in Sri Lanka was primarily driven by concerns over its long-term environmental impact, owing to “soil erosion, drying of springs thus, affecting biodiversity and life of the community”. The policy further directs systematically removing the existing plantations and nurseries at an annual rate of 10% and replacing these with rubber or any other cultivation favourable for water resources.
The ban aims to shift the country towards more sustainable agricultural practices and protect Sri Lanka’s natural resources. In addition, by diversifying agricultural production, Sri Lanka aims to reduce its dependence on palm oil imports and strengthen domestic industries.
The ban on oil palm cultivation has generated mixed opinions and sparked debates. Some argue it could negatively affect the economy, as palm oil contributes to Sri Lanka’s edible oil requirements. The ban may increase reliance on imports, potentially impacting the country’s trade balance and food security. Furthermore, the ban has raised concerns among the Regional Plantation Companies (PRCs), who have already invested in cultivation and processing. Against such a backdrop, our study aims to revisit the reasons for the ban on oil palm cultivation and arguments against the ban focusing on economic, environmental, health and social factors.
Q: The study reveals that the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka contributes significantly to the economy. Could you shed some light on the economic aspects highlighted in the study and the potential benefits to the country?
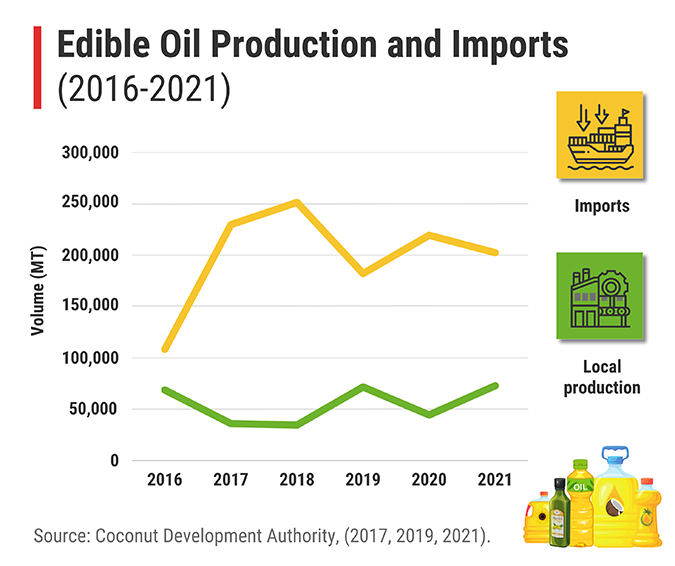
Certainly, the study demonstrates that the palm oil industry in Sri Lanka currently saves approximately USD 17 million annually in foreign exchange outflows and meets around 6% of the domestic edible oil demand. Moreover, it generates employment for over 33,000 individuals and attracts a capital investment of LKR 23 billion. These numbers illustrate the industry’s positive economic impact, but we must also consider the long-term sustainability and environmental impacts.
Q: Environmental concerns surrounding oil palm cultivation have been a major point of contention. What are some of the specific environmental issues associated with the industry, and how can they be addressed?
Oil Palm cultivation has faced criticism globally due to its environmental impacts primarily linked to deforestation. Some of the specific criticisms include groundwater depletion, water quality degradation, regeneration, siltation, floods, landslides, and palm oil mill effluent handling. These issues directly affect the surrounding communities and ecosystems.
In Sri Lanka, RPCs were allowed to cultivate oil palms in marginal rubber lands. Therefore, deforestation is not relevant unless rubber is considered a forest tree. Environmental issues are common to any agricultural land use and are observed in oil palm cultivation. However, the degree of impact varies depending on factors such as high input consumption (due to high oil productivity), vertical and horizontal root systems, and management practices. Global literature on these studies remains inconclusive due to their context-specific nature and lobby group research. Therefore, conducting further investigations and closely monitoring these issues within the local context is crucial to make informed decisions.
Implementing sustainable management practices, periodic monitoring, and potentially financing the environmental costs through mechanisms like import Cess or domestic levy can mitigate the negative externalities. However, monitoring smallholder cultivations would be challenging in the absence of policy provisions. Balancing economic benefits with environmental sustainability is key to a responsible palm oil industry.
Q: The study also mentions health concerns related to edible oil consumption. Could you elaborate on these concerns and propose possible solutions to address them effectively?
The study highlights that local edible oil consumption in Sri Lanka poses serious health risks due to improper processing, storage, and potential adulteration with repeatedly used oils. Therefore, addressing these issues at the forefront is crucial to overcome these hazards. This can be achieved by enforcing proper quality checks during importation and local edible oil production, ensuring adherence to processing and storage regulations, and avoiding repeatedly used oils. Additionally, it is equally important to raise public awareness about these aspects. By prioritising these measures, we can mitigate the health hazards associated with edible oil consumption and ensure public safety.
Q: Given the ban on oil palm cultivation, what alternatives exist to meet the local edible oil demand in Sri Lanka?
Meeting the local edible oil demand in Sri Lanka is indeed a challenge without imports. Nearly 74% of the demand is met through imports. Local palm oil supplies 6% and the rest is through local coconut oil, which varies with annual coconut production. While coconut oil is often considered a substitute, the current coconut production capacity is inadequate and does not remain a perfect substitute for industrial needs owing to different properties and prices. Given the limited land availability for expanding commercial cultivations in Sri Lanka for coconut and oil palm, productivity improvements would support partially bridging the gap. This can be facilitated by lowering the import tariff on edible oils, easing the burden on consumers. Adopting modern and safe oil production technologies such as virgin coconut oil and promoting high value-added products such as lauric acid for the export market are crucial to mitigate the impact on the coconut oil industry. Considering the economic crisis and foreign exchange deficit, a comprehensive evaluation of feasible alternatives is necessary.
Erandathie Pathiraja is a Research Economist at the Institute of Policy Studies of Sri Lanka (IPS) with research interests in the analysis of industries and markets, competitiveness and SMEs. She holds a BSc in Agriculture from the University of Peradeniya, an MPhil in Agricultural Economics from the Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture, and a PhD in Agricultural Economics from The University of Melbourne, Australia. (Talk with Erandathie – erandathie@ips.lk)
Business
ADB pledges over $1 billion annually to Sri Lanka in post-cyclone recovery push

Asian Development Bank (ADB) President Masato Kanda met with Sri Lanka Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya at ADB’s Manila headquarters recently. The meeting reaffirmed the strong development partnership between ADB and Sri Lanka, with both leaders underscoring their commitment to post-cyclone recovery, inclusive growth, and advancing women’s equality.
“Sri Lanka’s resilience in the face of crises has been remarkable,” said Kanda. “We are committed to helping Sri Lanka rebuild after Cyclone Ditwah, while also investing in the country’s future by empowering women entrepreneurs and strengthening education and essential skills.”
Looking ahead, ADB is ready to provide more than $1 billion annually to Sri Lanka from 2026 to 2029. This financing will target macroeconomic stability, private sector-led growth, education and skills development, and resilient infrastructure. Key initiatives include a major digital transformation program to help unlock Sri Lanka’s digital economy, alongside support for its accession to the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership to deepen its integration into regional trade and investment networks.
During their discussion, Kanda emphasized ADB’s response to the devastation caused by Cyclone Ditwah. Building on emergency financing already mobilized, ADB is fast-tracking an emergency assistance loan to restore damaged infrastructure and support affected livelihoods.
With Dr. Amarasuriya serving as the keynote speaker for ADB’s International Women’s Day event, the leaders highlighted women’s equality as a cornerstone of inclusive development. Kanda noted ADB’s long-standing work as an implementing partner of the Women Entrepreneurs Finance Initiative, which expands access to finance, business skills training, and policy reform for women-owned enterprises. This partnership has helped drive lasting change, with Sri Lanka becoming one of the first countries to adopt the Women Entrepreneurs Finance Code at the national level in March 2025.
Dr. Amarasuriya also engaged in dialogue facilitated by ADB to advance Sri Lanka’s skills agenda, including discussions on referencing skills and qualifications with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations and on mutual areas of interest with the Philippines related to technical and vocational education and training.
Business
New Board appointed to lead Unit Trust Association of Sri Lanka

The Unit Trust Association of Sri Lanka (UTASL) announced its new Board of Directors, appointing Jeevan Sukumaran of SENFIN Asset Management as President. The Board assumes leadership at a time of significant growth and resilience in Sri Lanka’s Unit Trust industry. Over the past five years, the number of unit holders has more than doubled, while assets under management have grown substantially, reflecting a clear shift in investor behaviour amid evolving economic conditions.
The 2026–2027 Board includes Vice President Kavin Karunamoorthy (First Capital Wealth Management), Secretary Asanka Herath (Lynear Wealth Management), Assistant Secretary Gayan De Silva (Capital Alliance), and Treasurer Wishan Perera (Softlogic Invest).
President Jeevan Sukumaran highlighted the importance of expanding the industry’s reach and increasing retail participation nationwide. “Whilst the Unit Trust industry has grown significantly in recent years, the next phase must focus on broadening retail investor participation across Sri Lanka’s different geographic/demographic sectors, with the key priority being strengthening investor education and awareness, particularly outside major urban centres. Improving financial literacy and expanding access to professionally managed investment solutions are essential to building long-term confidence and encouraging more Sri Lankans to invest in unit trusts.”
The new Board intends to build on the industry’s recent momentum by prioritising investor education, digital accessibility, and product innovation. Over the coming years, enhanced digital platforms are expected to make Unit Trust products more accessible, enabling investors across the country to participate in capital markets in a convenient and transparent manner.
Business
Indiya at Cinnamon Life enters a flavourful new chapter
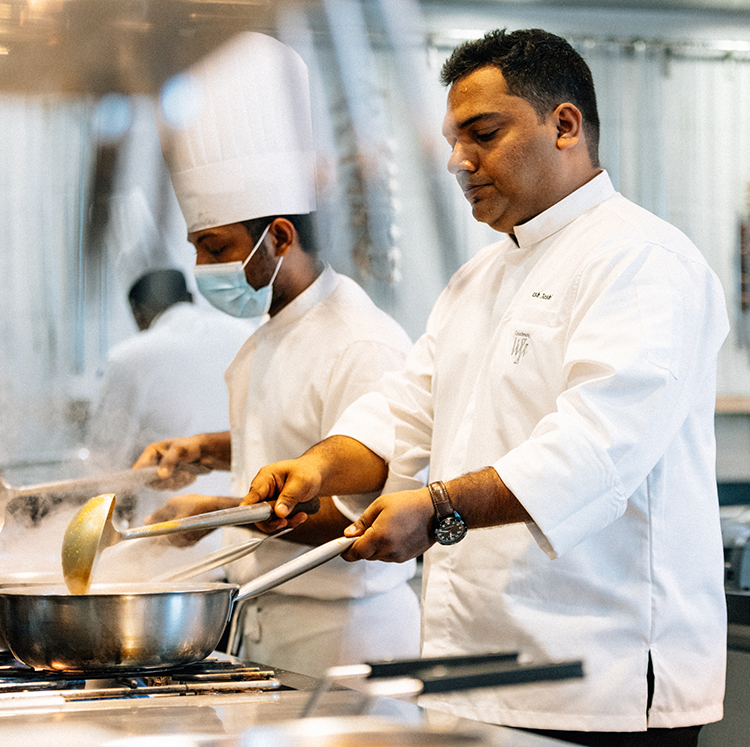

Colombo’s vibrant dining landscape has received a fresh infusion of flavour with the renewed culinary direction of Indiya, the signature Indian restaurant perched high above the city at Cinnamon Life at City of Dreams. With celebrated Indian chef Mukesh Joshi now steering the kitchen, the restaurant is presenting a menu that celebrates the depth, diversity and soul of Indian cuisine while subtly weaving in Sri Lankan influences.
Located on the spectacular Level 23 of the sprawling Cinnamon Life complex, Indiya’s setting itself feels like a prelude to the culinary journey that unfolds at the table.
The restaurant’s sweeping views of Colombo’s skyline provide a dramatic backdrop to a menu designed to take diners across India’s many culinary regions — from the fragrant biryani traditions of Awadh to the bold spice profiles of coastal kitchens.
At the heart of this new chapter is Chef Mukesh Joshi, a culinary craftsman whose career spans some of India’s most renowned hospitality institutions as well as prominent dining establishments in the Middle East.
Having honed his skills at luxury hotels such as The Westin and St. Regis Mumbai before leading kitchens in Dubai’s thriving Indian dining scene, Joshi is known for his ability to balance traditional flavours with contemporary finesse.
At Indiya, his philosophy is simple yet compelling: celebrate the authenticity of Indian cooking while creating dishes that encourage sharing and conversation.
The experience begins with a vibrant array of small plates that capture the playful spirit of India’s street food traditions. The crisp Sev Papdi Chaat offers bursts of sweet, tangy and spicy notes, while a generous Pakora Platter brings together an assortment of golden-fried fritters that evoke the comforting flavours of roadside tea stalls across the subcontinent.
From there, the menu moves naturally into the world of the tandoor — the clay oven that lies at the heart of many Indian kitchens. Among the highlights is the Hariyali Tandoori Gobi, where cauliflower is marinated in a fragrant blend of herbs before being charred to smoky perfection. Equally intriguing is the Rajma Galouti, a vegetarian reinterpretation of the famed Lucknowi kebab, delivering a melt-in-the-mouth texture that surprises and delights.
Seafood lovers will find much to savour as well. Jhinga Koliwada, a coastal delicacy of spiced prawns fried to a crisp exterior, offers a lively contrast to the delicately seasoned Rawa Fried Surmai. These dishes reflect Chef Mukesh’s confident handling of spice and texture — two essential pillars of Indian cooking.
No Indian dining experience would be complete without the ritual of sharing freshly baked breads, and Indiya’s basket arrives warm and inviting. Chilli Cheese Naan brings a playful modern twist to a classic favourite, while flaky parathas and stuffed Aloo Kulcha provide comforting companions to the restaurant’s richly spiced curries.
By Ifham Nizam
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoWinds of Change:Geopolitics at the crossroads of South and Southeast Asia
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoProf. Dunusinghe warns Lanka at serious risk due to ME war
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoHeat Index at ‘Caution Level’ in the Sabaragamuwa province and, Colombo, Gampaha, Kurunegala, Anuradhapura, Vavuniya, Hambanthota and Monaragala districts
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoRoyal start favourites in historic Battle of the Blues
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe final voyage of the Iranian warship sunk by the US