Features
I’ve witnessed a coup attempt before — and history bodes poorly for America’s future

by Alfred Mccoy, Tom Dispatch
As an eyewitness, I can recall the events of January 6th in Washington as if they were yesterday. The crowds of angry loyalists storming the building while overwhelmed security guards gave way. The slavishly loyal vice-president who would, the president hoped, restore him to power. The crush of media that seemed confused, almost overwhelmed, by the crowd’s fury. The waiter who announced that the bar had run out of drinks and would soon be closing…
Hold it! My old memory’s playing tricks on me again. That wasn’t the U.S. Capitol in January 2021. That was the Manila Hotel in the Philippines in July 1986. Still, the two events had enough similarities that perhaps I could be forgiven for mixing them up.
I’ve studied quite a number of coups in my day, yet the one I actually witnessed at the Manila Hotel remains my favorite, not just because the drinks kept coming, but for all it taught me about the damage a coup d’état, particularly a political coup, can do to any democracy. In February 1986, a million Filipinos thronged the streets of Manila to force dictator Ferdinand Marcos into exile. After long years of his corruption and callous indifference to the nation’s suffering, the crowds cheered their approval when Marcos finally flew off to Hawaii and his opponent in the recent presidential election restored democracy.
But Marcos had his hard-core loyalists. One Sunday afternoon, four months after his flight, they massed in a Manila park to call for the restoration of their beloved president. After speakers had whipped the crowd of 5,000 into a frenzy with — and yes, this should indeed sound familiar in 2021 — claims about a stolen election, thousands of ordinary Filipinos pushed past security guards and stormed into the nearby Manila Hotel, a storied symbol of their country’s history. Tipped off by one of the Filipino colonels plotting that coup, I was standing in the hotel’s entryway at 5:00 p.m. as the mob, fury written on their faces, surged past me.
For the next 24 hours, that hotel’s marbled lobby became the stage for an instructive political drama. From my table at the adjoining bar, I watched as armed warlords, ousted Marcos cronies, and several hundred disgruntled soldiers paraded through the lobby on their way to the luxury suites where the coup commanders had checked themselves in. Following in their wake were spies from every nation — Australian secret intelligence, American defense intelligence, and their Asian and European counterparts — themselves huddled in groups, whispering mysteriously, trying (just like me) to make sense of the bizarre spectacle unfolding around them.
 Later that same evening, Marcos’s former vice-president, the ever-loyal Arturo Tolentino, appeared at the head of the stairs flanked by a security detail to announce the formation of a “legitimate” new government authorized by Marcos who had reportedly called long-distance from Honolulu. As the vice president proclaimed himself acting president and read off the names of those to be in his cabinet, Filipino journalists huddling nearby scribbled notes. They were furiously trying to figure out whether there was a real coalition forming that could topple the country’s democracy. It was, however, just the usual suspects — Marcos cronies, leaders largely without followers.
Later that same evening, Marcos’s former vice-president, the ever-loyal Arturo Tolentino, appeared at the head of the stairs flanked by a security detail to announce the formation of a “legitimate” new government authorized by Marcos who had reportedly called long-distance from Honolulu. As the vice president proclaimed himself acting president and read off the names of those to be in his cabinet, Filipino journalists huddling nearby scribbled notes. They were furiously trying to figure out whether there was a real coalition forming that could topple the country’s democracy. It was, however, just the usual suspects — Marcos cronies, leaders largely without followers.
By midnight, the party was pretty much over. Our waiter, after struggling for hours to maintain that famed hotel’s standard of five-star service, apologized to our table of foreign correspondents because the bar had been drunk dry and was closing. Sometime before dawn, the hotel turned off the air conditioning, transforming those executive suites into saunas and, in the process, flushing out the coup plotters, their hangers-on, and most of the soldiers.
All day long, on the city’s brassy talk-radio stations and in the coffee shops where insiders gathered to swap scuttlebutt, Marcos’s loyalists were roasted, even mocked. The troops that had rallied to his side were sentenced to 30 push-ups on the parade ground — a source of more mirth. For spies and correspondents alike, the whole thing seemed like a one-day wonder, barely worth writing home about.
But it wasn’t. Not by a long shot. A coterie of colonels deep inside the Defense Ministry, my source among them, had observed that comedic coup attempt all too carefully and concluded that it had actually been a near-miss.
A year later, I found myself standing in the middle of an eight-lane highway outside the city’s main military cantonment, Camp Aguinaldo, ducking bullets from rebel soldiers who had seized the base and watching as government Marines and dive bombers attacked. This time, however, those colonels had launched a genuine coup attempt. No drinks. No waiters. No wisecracks. Just a day of bombs and bullets that crushed the plotters, leaving the country’s military headquarters a smoking ruin.
Two years later, the same coup colonels were back again for another attempt, leading 3,000 rebel troops in a multipronged attack on a capital that trembled on the brink of surrender. As a cavalcade of rebel armor drove relentlessly toward the presidential palace with nothing in their way, American President George H.W. Bush took a call aboard Air Force One over the Atlantic about a desperate request from his Philippine counterpart and ordered a pair of U.S. Air Force jet fighters to make a low pass over the rebel tanks and trucks. They got the message: turn back or be bombed into extinction. And so Philippine democracy was allowed to survive for another 30 years.
Message from the Manila Hotel
The message for democracy offered from the Manila Hotel was clear — so clear, in fact, that it helps explain the meaning of tangled events in Washington more than 30 years later. Whether it’s a poor country like the Philippines or a superpower like the United States, democracy is a surprisingly fragile construct. Its worst enemy is often an ousted ex-president, angry over his humiliation and perfectly willing to destroy the constitutional order to regain power.
No matter how angry such an ex-president might be, however, his urge for a political coup can’t succeed without the help of raw force, whether from a mob, a disgruntled military, or some combination of the two. The Manila Hotel coup teaches us one other fundamental thing: that coups need not be carefully planned. Most start with a handful of conspirators plotting some symbolic attack meant to shake the constitutional order, while hoping to somehow stall the security services for a few critical hours — just long enough for events to cascade spontaneously into a desired government collapse.
Whether in Manila or Washington, coup plotting usually starts right at the top. Just after the news networks announced that he had lost the election last November, Donald Trump launched a media blitz with spurious claims of “fraud on the American public,” firing off 300 tweets in the next two weeks loaded with false charges of irregularities and sparking loud, long protests by his loyalists at vote-counting centers in Michigan and Arizona.
When that response got little traction and Biden’s majority kept climbing, Trump began exploring three alternate routes, any of which might have led to a constitutional coup — manipulating the Justice Department to delegitimize the election, rigging the ratification of electoral votes in Congress, and the paramilitary (or military) option. At a White House meeting on December 18th, Michael Flynn, Trump’s former national security advisor, urged the president to “invoke martial law as part of his efforts to overturn the election” and accused his staff of “abandoning the president,” sparking “screaming matches” in the Oval Office.
By January 3, rumors and reports of Trump’s military option were circulating so credibly around Washington that all 10 living former defense secretaries — Dick Cheney, Donald Rumsfeld, and Mark Esper, among them — published a joint appeal to the armed forces to remain neutral in the ongoing dispute over the election’s integrity. Reminding the troops that “peaceful transfers of power… are hallmarks of our democracy,” they added that “efforts to involve the U.S. armed forces in resolving election disputes” would be “dangerous, unlawful, and unconstitutional.” They warned the troops that any “military officials who direct or carry out such measures would be… potentially facing criminal penalties.” In conclusion, they suggested to Trump’s secretary of defense and senior staff “in the strongest terms” that “they must…refrain from any political actions that undermine the results of the election.”
To legitimate his claims of fraud, according to the New York Times, the president also tried — on nine separate occasions in December and January — to force the Justice Department to take actions that would “undermine an election result.” In response, a mid-ranking Trump loyalist at Justice, a nonentity named Jeffrey Clark, began pressuring his boss, the attorney-general, to write Georgia officials claiming they had found “significant concerns that may have impacted the outcome of the election.” But at a three-hour White House meeting on January 3rd, Acting Attorney General Jeffrey Rosen balked at this evidence-free accusation. Trump promptly suggested that he could be replaced by that mid-ranking loyalist who could then send the fraud letter to Georgia. The president’s own top appointees at Justice, along with the White House counsel, immediately threatened to resign en masse, forcing Trump to give up on such an intervention at the state level.
Next, he shifted his constitutional maneuvering to Congress where, on January 6th, his doggedly loyal vice president, Mike Pence, would be presiding over the ratification of results from the Electoral College. In this dubious gambit, Trump was inspired by a bizarre constitutional theory advanced by former Chapman University law professor John Eastman — that the “Constitution assigns the power to the Vice President as the ultimate arbiter.”
In this scenario, Pence would unilaterally set aside electoral votes from seven states with “ongoing disputes” and announce that Trump had won a majority of the remaining electors — making him once again president. But the maneuver had no basis in law, so Pence, after scrambling desperately and unsuccessfully for a legal justification of some sort, eventually refused to play along.
A Political Coup
With the constitutional option closed, Trump opted for a political coup, rolling the dice with raw physical force, much as Marcos had done at the Manila Hotel. The first step was to form a crowd with some paramilitary muscle to stiffen the assault to come. On December 19th, Trump called on his hard-core followers to assemble in Washington, ready for violence, tweeting: “Big protest in D.C. on January 6th. Be there, will be wild!”
Almost immediately, the Internet’s right-wing chat boards lit up and indeed their paramilitaries, the Proud Boys and Three Percenters militia, turned up in Washington on the appointed day, ready to rumble. After President Trump roused the crowd at a rally near the White House with rhetoric about a stolen election, a mob of some 10,000 marched on the Capitol Building.
Starting at about 1:00 p.m., the sheer size of the crowd and strategic moves by the paramilitaries in their ranks broke through the undermanned lines of the Capitol Police, breaching the building’s first-floor windows at about 2:10 p.m. and allowing protesters to start pouring in. Once the rioters had accomplished the unimaginable and seized the Capitol, they were fresh out of plans, reduced to marching through the corridors hunting legislators and trashing offices.
At 2:24 p.m., President Trump tweeted: “Mike Pence didn’t have the courage to do what should have been done to protect our Country.” On the far-right social media site Parler, his supporters began messaging the crowd to get the vice president and force him to stop the election results. The mob rampaged through the marbled halls shouting “Hang Mike Pence.” Hunkered down inside the Capitol, Representative Adam Kinzinger (R-Illinois) tweeted: “This is a coup attempt.”
At 2:52 p.m., Representative Abigail Spanberger (D-Virginia), a former CIA agent, tweeted from inside the barricaded House chamber: “This is what we see in failing countries. This is what leads to the death of democracy.”
At 3:30 p.m., a small squad of military police arrived at the Capitol, woefully inadequate reinforcements for the overwhelmed Capitol Police. Ten minutes later, the D.C. Council announced that the Defense Department had denied the mayor’s request to mobilize the local National Guard. While the crowd fumbled and fulminated, some serious people were evidently slowing the military’s response for just the few critical hours needed for events to cascade into something, anything, that could shake the constitutional order and slow the ratification of Joe Biden’s election.
In nearby Maryland, Republican Governor Larry Hogan had immediately mobilized his state’s National Guard for the short drive to the Capitol while frantically phoning Acting Secretary of Defense Christopher Miller, who repeatedly refused him permission to send in the troops. Inside the Pentagon, Lieutenant General Charles Flynn, the brother of the same Michael Flynn who had been pushing Trump to declare martial law, was participating in what CNN called those “key January 6th phone calls” that refused permission for the Guard’s mobilization.
Following a phone call from the mayor of Washington and its police chief pleading for help, Secretary of the Army Ryan McCarthy “ran down the hall” of the Pentagon to get authorization for the Guard’s mobilization. After a crucial delay of 90 minutes, he finally called the Maryland governor, outside the regular chain of command, to authorize the Maryland Guard’s dispatch. Those would indeed be the first troops to arrive at the Capitol and would play a critical role in restoring order.
At about 4:30 p.m., Trump finally tweeted: “These are the things and events that happen when a sacred landslide election victory is so unceremoniously and viciously stripped away from great patriots who have been badly & unfairly treated for so long. Go home in love & peace.”
Ten minutes later, at 4:40 p.m., hundreds of riot personnel from the D.C. police, the FBI, and the Department of Homeland Security arrived, along with the Maryland Guard, to reinforce the Capitol Police. Within an hour, the protesters had been pushed out of the building and the Capitol was declared secure.
Just five days later, Dr. Fiona Hill, a senior Russia expert on the National Security Council under Trump, reviewed these events and concluded that President Trump had staged a coup “in slow motion… to keep himself in power.”
History’s Lessons
Beyond all the critical details of who did what and when, there were deeper historical forces at play, suggesting that Donald Trump’s urge for a political coup that would return him to power may be far from over. For the past 100 years, empires in decline have been roiled by coup attempts that sometimes have overturned constitutional orders. As their military reverses accumulate, their privileged economic position erodes, and social tensions mount, a succession of societies in the grip of a traumatic loss of global power have suffered coups, successful or not, including Great Britain, France, Portugal, Spain, the Soviet Union, and now the United States.
Britain’s plot was a bit fantastical. Amid the painful, protracted dissolution of their empire, Conservative leaders plotted with top generals in 1968 to oust leftist Labour Prime Minister Harold Wilson by capturing Heathrow airport, seizing the BBC and Buckingham Palace, and putting Lord Mountbatten in power as acting prime minister. Britain’s parliamentary tradition simply proved too strong, however, and key principals in the plot quickly backed out.
In April 1974, while Portugal was fighting and losing three bitter anticolonial wars in Africa, a Lisbon radio station played the country’s entry in that year’s Eurovision Song Contest (“After the Farewell”) just minutes before midnight on an evening that had been agreed upon. It was the signal to the military and their supporters to overthrow the entrenched conservative government of that moment, a success which became known as the “Carnation Revolution.”
However, the parallels between January 6th and the fall of France’s Fourth Republic in the late 1950s are perhaps the most telling. After liberating Paris from Nazi occupation in August 1944, General Charles de Gaulle headed an interim government for 18 months. He then quit in a dispute with the left, launching him into a decade of political intrigue against the new Fourth Republic, whose liberal constitution he despised.
By the mid-1950s, France was reeling from its recent defeat in Indochina, while the struggle against Muslim revolutionaries in its Algerian colony in North Africa turned ever more brutal, marked as it was by scandals over the widespread French use of torture. Amid that crisis of empire, an anti-elite, anti-intellectual, antisemitic politician named Pierre Poujade launched a populist movement that sent 56 members to parliament in 1956, including Jean-Marie Le Pen, later founder of the far-right National Front.
Meanwhile, a cabal of politicians and military commanders plotted a coup to return General de Gaulle to power, thinking he alone could save Algeria for France. After an army junta seized control of Algiers, the capital of that colony, in May 1958, paratroopers stationed there were sent to capture the French island of Corsica and to prepare to seize Paris should the legislature fail to install de Gaulle as prime minister.
As the country trembled on the brink of a coup, de Gaulle made his dramatic entry into Paris where he accepted the National Assembly’s offer to form a government, conditional upon the approval of a presidential-style constitution for a Fifth Republic. But when de Gaulle subsequently accepted the inevitability of Algeria’s independence, four top generals launched an abortive coup against him and then formed what they called the Secret Army Organization, or OAS. It would carry out terror attacks over the next four years, with 12,000 victims, while staging three unsuccessful assassination attempts against de Gaulle before its militants were killed or captured.
The Coup of 2024?
Just as the Filipino colonels spent five years launching a succession of escalating coups and those French generals spent four years trying to overthrow their government, so Trump’s Republicans are working with ferocious determination in the run-up to the 2022 and 2024 elections to ensure that their next constitutional coup succeeds. Indeed, if you look back on events over the past year through the prism of such historical precedents, you can see all the components for a future political coup falling into place.
No matter how improbable, discredited, or bizarre those election fraud claims are, Republican loyalists persist in endless ballot audits in Arizona, Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Georgia, and Texas. Their purpose is not really to find more votes for Trump in the 2020 election, but to maintain at least the present level of rage among the one-third of all Americans and more than half of all Republicans who believe that Joe Biden’s presidency is fraudulent.
Since the 2020 election coincided with the new census, Republicans have been working, reports Vox news, to “gerrymander themselves into control of the House of Representatives.” Simultaneously, Republican legislators in 19 states have passed 33 laws making it more difficult for certain of their residents to vote. Driven by the white nationalist “replacement theory” that immigrants and people of color are diluting the pool of “real American” voters, Trump and his Republican loyalists are fighting for “ballot integrity” on the principle that all non-white votes are inherently illegitimate. As Trump put it on the stump in 2016:
“I think this will be the last election that the Republicans have a chance of winning because you’re going to have people flowing across the border, you’re going to have illegal immigrants coming in… and they’re going to be able to vote and once that all happens you can forget it. You’re not going to have one Republican vote.”
In case all that electoral manipulation fails and Trump needs more muscle for a future political coup, right-wing fighters like the Proud Boys are still rumbling away at rallies in Oregon, California, and elsewhere across America. Just as the Philippine government made military rebels do a risible 30 push-ups for the capital crime of armed rebellion, so federal courts have generally been handing out the most modest of penalties to rioters who attempted nothing less than the overthrow of U.S. constitutional democracy last January 6th.
Among the 600 rioters arrested as of August, dozens have been allowed to plead guilty to misdemeanors and only three had been sentenced to jail time, leaving most cases languishing in pretrial motions. Already Republicans like Senator Ted Cruz have rallied to their defense, writing the U.S. attorney general to complain about an “unequal administration of justice” with “harsher treatment” for Capitol defendants than those arrested in Black Lives Matter protests.
So, in 2024, as the continuing erosion of America’s global power creates a crisis of confidence among ordinary Americans, expect Donald Trump to be back, not as the slightly outrageous candidate of 2016 or even as the former president eager to occupy the White House again, but as a militant demagogue with thundering racialist rhetoric, backed by a revanchist Republican Party ready, with absolute moral certainty, to bar voters from the polls, toss ballots out, and litigate any loss until hell freezes over.
And if all that fails, the muscle will be ready for another violent march on Washington. Be prepared, the America we know is worsening by the month.
Features
More state support needed for marginalised communities

Message from Malaiyaha Tamil community to govt:
Insights from SSA Cyclone Ditwah Survey
When climate disasters strike, they don’t affect everyone equally. Marginalised communities typically face worse outcomes, and Cyclone Ditwah is no exception. Especially in a context where normalcy is far from “normal”, the idea of returning to normalcy or restoring a life of normalcy makes very little sense.
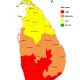
The island-wide survey (https://ssalanka.org/reports/) conducted by the Social Scientists’ Association (SSA), between early to mid-January on Cyclone Ditwah shows stark regional disparities in how satisfied or dissatisfied people were with the government’s response. While national satisfaction levels were relatively high in most provinces, the Central Province tells a different story.
Only 35.2% of Central Province residents reported that they were satisfied with early warning and evacuation measures, compared to 52.2% nationally. The gap continues across every measure: just 52.9% were satisfied with immediate rescue and emergency response, compared with the national figure of 74.6%. Satisfaction with relief distribution in the Central Province is 51.9% while the national figure stands at 73.1%. The figures for restoration of water, electricity, and roads are at a low 45.9% in the central province compared to the 70.9% in national figures. Similarly, the satisfaction level for recovery and rebuilding support is 48.7% in the Central Province, while the national figure is 67.0%.
A deeper analysis of the SSA data on public perceptions reveals something important: these lower satisfaction rates came primarily from the Malaiyaha Tamil population. Their experience differed not just from other provinces, but also from other ethnic groups living in the Central Province itself.
The Malaiyaha Tamil community’s vulnerability didn’t start with the cyclone. Their vulnerability is a historically and structurally pre-determined process of exclusion and marginalisation. Brought to Sri Lanka during British rule to work for the empire’s plantation economies, they have faced long-term economic exploitation and have repeatedly been denied access to state support and social welfare systems. Most estate residents still live in ‘line rooms’ and have no rights to the land they cultivate and live on. The community continues to be governed by an outdated estate management system that acts as a barrier to accessing public and municipal services such as road repair, water, electricity and other basic infrastructures available to other citizens.
As far as access to improved water sources is concerned, the Sri Lanka Demographic Health Survey (2016) shows that 57% of estate sector households don’t have access to improved water sources, while more than 90% of households in urban and rural areas do. With regard to the level of poverty, as the Department of Census and Statistics (2019) data reveals, the estate sector where most Malaiyaha Tamils live had a poverty headcount index of 33.8%; more than double the national rate of 14.3%. These statistics highlight key indicators of the systemic discrimination faced by the Malaiyaha Tamil community.
Some crucial observations from the SSA data collectors who enumerated responses from estate residents in the survey reveal the specific challenges faced by the Malaiyaha Tamils, particularly in their efforts to seek state support for compensation and reconstruction.
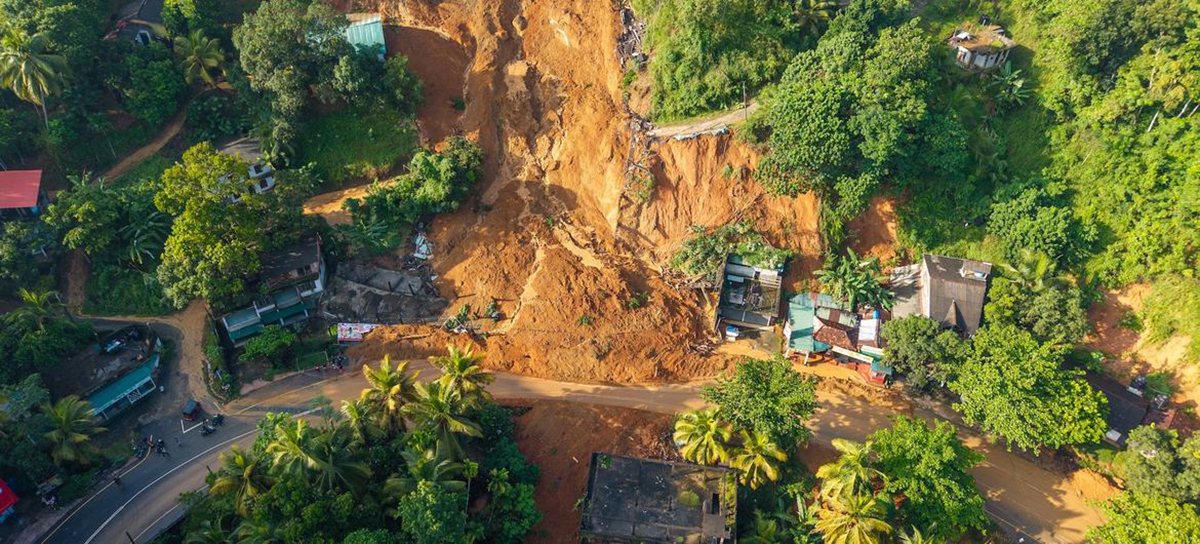
First, the Central Province experienced not just flooding but also the highest number of landslides in the island. As a result, some residents in the region lost entire homes, access roadways, and other basic infrastructures. The loss of lives, livelihoods and land was at a higher intensity compared to the provinces not located in the hills. Most importantly, the Malaiyaha Tamil community’s pre-existing grievances made them even more vulnerable and the government’s job of reparation and restitution more complex.
Early warnings hadn’t reached many areas. Some data collectors said they themselves never heard any warnings in estate areas, while others mentioned that early warnings were issued but didn’t reach some segments of the community. According to the resident data collectors, the police announcements reached only as far as the sections where they were able to drive their vehicles to, and there were many estate roads that were not motorable. When warnings did filter through to remote locations, they often came by word of mouth and information was distorted along the way. Once the disaster hit, things got worse: roads were blocked, electricity went out, mobile networks failed and people were cut off completely.
Emergency response was slow. Blocked roads meant people could not get to hospitals when they needed urgent care, including pregnant mothers. The difficult terrain and poor road conditions meant rescue teams took much longer to reach affected areas than in other regions.
Relief supplies didn’t reach everyone. The Grama Niladhari divisions in these areas are huge and hard to navigate, making it difficult for Grama Niladharis to reach all places as urgently as needed. Relief workers distributed supplies where vehicles could go, which meant accessible areas got help while remote communities were left out.
Some people didn’t even try to go to safety centres or evacuation shelters set up in local schools because the facilities there were already so poor. The perceptions of people who did go to safety centres, as shown in the provincial data, reveal that satisfaction was low compared to other affected regions of the country. Less than half were satisfied with space and facilities (42.1%) or security and protection (45.0%). Satisfaction was even lower for assistance with lost or damaged documentation (17.9%) and information and support for compensation applications (28.2%). Only 22.5% were satisfied with medical care and health services below most other affected regions.
Restoring services proved nearly impossible in some areas. Road access was the biggest problem. The condition of the roads was already poor even before the cyclone, and some still haven’t been cleared. Recovery is especially difficult because there’s no decent baseline infrastructure to restore, hence you can’t bring roads and other public facilities back to a “good” condition when they were never good, even before the disaster.
Water systems faced their own complications. Many households get water from natural sources or small community projects, and not the centralised state system. These sources are often in the middle of the disaster zone and therefore got contaminated during the floods and landslides.
Long-term recovery remains stalled. Without basic infrastructure, areas that are still hard to reach keep struggling to get the support they need for rebuilding.
Taken together, what do these testaments mean? Disaster response can’t be the same for everyone. The Malaiyaha Tamil community has been double marginalised because they were already living with structural inequalities such as poor infrastructure, geographic isolation, and inadequate services which have been exacerbated by Cyclone Ditwah. An effective and fair disaster response needs to account for these underlying vulnerabilities. It requires interventions tailored to the historical, economic, and infrastructural realities that marginalized communities face every day. On top of that, it highlights the importance of dealing with climate disasters, given the fact that vulnerable communities could face more devastating impacts compared to others.
(Shashik Silva is a researcher with the Social Scientists’ Association of Sri Lanka)
by Shashik Silva ✍️
Features
Crucial test for religious and ethnic harmony in Bangladesh

 Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
The apprehensions are mainly on the part of religious and ethnic minorities. The parliamentary poll of February 12th is expected to bring into existence a government headed by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and the Islamist oriented Jamaat-e-Islami party and this is where the rub is. If these parties win, will it be a case of Bangladesh sliding in the direction of a theocracy or a state where majoritarian chauvinism thrives?
Chief of the Jamaat, Shafiqur Rahman, who was interviewed by sections of the international media recently said that there is no need for minority groups in Bangladesh to have the above fears. He assured, essentially, that the state that will come into being will be equable and inclusive. May it be so, is likely to be the wish of those who cherish a tension-free Bangladesh.
The party that could have posed a challenge to the above parties, the Awami League Party of former Prime Minister Hasina Wased, is out of the running on account of a suspension that was imposed on it by the authorities and the mentioned majoritarian-oriented parties are expected to have it easy at the polls.
A positive that has emerged against the backdrop of the poll is that most ordinary people in Bangladesh, be they Muslim or Hindu, are for communal and religious harmony and it is hoped that this sentiment will strongly prevail, going ahead. Interestingly, most of them were of the view, when interviewed, that it was the politicians who sowed the seeds of discord in the country and this viewpoint is widely shared by publics all over the region in respect of the politicians of their countries.
Some sections of the Jamaat party were of the view that matters with regard to the orientation of governance are best left to the incoming parliament to decide on but such opinions will be cold comfort for minority groups. If the parliamentary majority comes to consist of hard line Islamists, for instance, there is nothing to prevent the country from going in for theocratic governance. Consequently, minority group fears over their safety and protection cannot be prevented from spreading.
Therefore, we come back to the question of just and fair governance and whether Bangladesh’s future rulers could ensure these essential conditions of democratic rule. The latter, it is hoped, will be sufficiently perceptive to ascertain that a Bangladesh rife with religious and ethnic tensions, and therefore unstable, would not be in the interests of Bangladesh and those of the region’s countries.
Unfortunately, politicians region-wide fall for the lure of ethnic, religious and linguistic chauvinism. This happens even in the case of politicians who claim to be democratic in orientation. This fate even befell Bangladesh’s Awami League Party, which claims to be democratic and socialist in general outlook.
We have it on the authority of Taslima Nasrin in her ground-breaking novel, ‘Lajja’, that the Awami Party was not of any substantial help to Bangladesh’s Hindus, for example, when violence was unleashed on them by sections of the majority community. In fact some elements in the Awami Party were found to be siding with the Hindus’ murderous persecutors. Such are the temptations of hard line majoritarianism.
In Sri Lanka’s past numerous have been the occasions when even self-professed Leftists and their parties have conveniently fallen in line with Southern nationalist groups with self-interest in mind. The present NPP government in Sri Lanka has been waxing lyrical about fostering national reconciliation and harmony but it is yet to prove its worthiness on this score in practice. The NPP government remains untested material.
As a first step towards national reconciliation it is hoped that Sri Lanka’s present rulers would learn the Tamil language and address the people of the North and East of the country in Tamil and not Sinhala, which most Tamil-speaking people do not understand. We earnestly await official language reforms which afford to Tamil the dignity it deserves.
An acid test awaits Bangladesh as well on the nation-building front. Not only must all forms of chauvinism be shunned by the incoming rulers but a secular, truly democratic Bangladesh awaits being licked into shape. All identity barriers among people need to be abolished and it is this process that is referred to as nation-building.
On the foreign policy frontier, a task of foremost importance for Bangladesh is the need to build bridges of amity with India. If pragmatism is to rule the roost in foreign policy formulation, Bangladesh would place priority to the overcoming of this challenge. The repatriation to Bangladesh of ex-Prime Minister Hasina could emerge as a steep hurdle to bilateral accord but sagacious diplomacy must be used by Bangladesh to get over the problem.
A reply to N.A. de S. Amaratunga
A response has been penned by N.A. de S. Amaratunga (please see p5 of ‘The Island’ of February 6th) to a previous column by me on ‘ India shaping-up as a Swing State’, published in this newspaper on January 29th , but I remain firmly convinced that India remains a foremost democracy and a Swing State in the making.
If the countries of South Asia are to effectively manage ‘murderous terrorism’, particularly of the separatist kind, then they would do well to adopt to the best of their ability a system of government that provides for power decentralization from the centre to the provinces or periphery, as the case may be. This system has stood India in good stead and ought to prove effective in all other states that have fears of disintegration.
Moreover, power decentralization ensures that all communities within a country enjoy some self-governing rights within an overall unitary governance framework. Such power-sharing is a hallmark of democratic governance.
Features
Celebrating Valentine’s Day …

 Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Merlina Fernando (Singer)
Yes, it’s a special day for lovers all over the world and it’s even more special to me because 14th February is the birthday of my husband Suresh, who’s the lead guitarist of my band Mission.
We have planned to celebrate Valentine’s Day and his Birthday together and it will be a wonderful night as always.
We will be having our fans and close friends, on that night, with their loved ones at Highso – City Max hotel Dubai, from 9.00 pm onwards.
Lorensz Francke (Elvis Tribute Artiste)
On Valentine’s Day I will be performing a live concert at a Wealthy Senior Home for Men and Women, and their families will be attending, as well.
I will be performing live with romantic, iconic love songs and my song list would include ‘Can’t Help falling in Love’, ‘Love Me Tender’, ‘Burning Love’, ‘Are You Lonesome Tonight’, ‘The Wonder of You’ and ‘’It’s Now or Never’ to name a few.
To make Valentine’s Day extra special I will give the Home folks red satin scarfs.
Emma Shanaya (Singer)
I plan on spending the day of love with my girls, especially my best friend. I don’t have a romantic Valentine this year but I am thrilled to spend it with the girl that loves me through and through. I’ll be in Colombo and look forward to go to a cute cafe and spend some quality time with my childhood best friend Zulha.
JAYASRI
Emma-and-Maneeka
This Valentine’s Day the band JAYASRI we will be really busy; in the morning we will be landing in Sri Lanka, after our Oman Tour; then in the afternoon we are invited as Chief Guests at our Maris Stella College Sports Meet, Negombo, and late night we will be with LineOne band live in Karandeniya Open Air Down South. Everywhere we will be sharing LOVE with the mass crowds.
Kay Jay (Singer)
I will stay at home and cook a lovely meal for lunch, watch some movies, together with Sanjaya, and, maybe we go out for dinner and have a lovely time. Come to think of it, every day is Valentine’s Day for me with Sanjaya Alles.
Maneka Liyanage (Beauty Tips)
On this special day, I celebrate love by spending meaningful time with the people I cherish. I prepare food with love and share meals together, because food made with love brings hearts closer. I enjoy my leisure time with them — talking, laughing, sharing stories, understanding each other, and creating beautiful memories. My wish for this Valentine’s Day is a world without fighting — a world where we love one another like our own beloved, where we do not hurt others, even through a single word or action. Let us choose kindness, patience, and understanding in everything we do.
Janaka Palapathwala (Singer)

Janaka
Valentine’s Day should not be the only day we speak about love.
From the moment we are born into this world, we seek love, first through the very drop of our mother’s milk, then through the boundless care of our Mother and Father, and the embrace of family.
Love is everywhere. All living beings, even plants, respond in affection when they are loved.
As we grow, we learn to love, and to be loved. One day, that love inspires us to build a new family of our own.
Love has no beginning and no end. It flows through every stage of life, timeless, endless, and eternal.
Natasha Rathnayake (Singer)
We don’t have any special plans for Valentine’s Day. When you’ve been in love with the same person for over 25 years, you realise that love isn’t a performance reserved for one calendar date. My husband and I have never been big on public displays, or grand gestures, on 14th February. Our love is expressed quietly and consistently, in ordinary, uncelebrated moments.
With time, you learn that love isn’t about proving anything to the world or buying into a commercialised idea of romance—flowers that wilt, sweets that spike blood sugar, and gifts that impress briefly but add little real value. In today’s society, marketing often pushes the idea that love is proven by how much money you spend, and that buying things is treated as a sign of commitment.
Real love doesn’t need reminders or price tags. It lives in showing up every day, choosing each other on unromantic days, and nurturing the relationship intentionally and without an audience.
This isn’t a judgment on those who enjoy celebrating Valentine’s Day. It’s simply a personal choice.
Melloney Dassanayake (Miss Universe Sri Lanka 2024)
 I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I’m incredibly blessed because, for me, every day feels like Valentine’s Day. My special person makes sure of that through the smallest gestures, the quiet moments, and the simple reminders that love lives in the details. He shows me that it’s the little things that count, and that love doesn’t need grand stages to feel extraordinary. This Valentine’s Day, perfection would be something intimate and meaningful: a cozy picnic in our home garden, surrounded by nature, laughter, and warmth, followed by an abstract drawing session where we let our creativity flow freely. To me, that’s what love is – simple, soulful, expressive, and deeply personal. When love is real, every ordinary moment becomes magical.
Noshin De Silva (Actress)
Valentine’s Day is one of my favourite holidays! I love the décor, the hearts everywhere, the pinks and reds, heart-shaped chocolates, and roses all around. But honestly, I believe every day can be Valentine’s Day.
It doesn’t have to be just about romantic love. It’s a chance to celebrate love in all its forms with friends, family, or even by taking a little time for yourself.
Whether you’re spending the day with someone special or enjoying your own company, it’s a reminder to appreciate meaningful connections, show kindness, and lead with love every day.
And yes, I’m fully on theme this year with heart nail art and heart mehendi design!
Wishing everyone a very happy Valentine’s Day, but, remember, love yourself first, and don’t forget to treat yourself.
Sending my love to all of you.
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Midweek Review4 days ago
Midweek Review4 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Midweek Review4 days ago
Midweek Review4 days agoTheatre and Anthropocentrism in the age of Climate Emergency