Features
Is Catastrophic Collapse Imminent?

by Kumar David
An optimist would venture to say that an economic catastrophe is not imminent, using the adjective imminent literally. He would be emboldened to make this remark because a restructuring deal, maybe a tough one, seems likely to come out of the negotiations with the IMF. Since all other lenders take their cue from the IMF thanks to its expertise and experience, Sri Lanka is likely to clinch agreements of different forms with China, India and Japan; life will go on. The country seems important enough for international actors such as India, China, America, Britain, Japan and the QUAD to be concerned about; in the case of India strategic concern is natural. America threatened war if Cuba stationed Soviet nuclear missiles, and now Russia is apoplectic at the thought of NATO getting its fingers around its neck via Ukraine, Finland and Sweden. No great or regional power will allow foreign bases near its land borders or its littoral waters. India’s anxiety is no surprise but such concerns should not be a passage to America and Europe. Actually, Lanka has little relevance to the Quad strategy of encircling China and is irrelevant to NATO’s scheme to suffocate Russia. The so-called Indian Ocean strategic zone too is a myth.
Therefore, my view is that the ongoing flurry is not primarily strategic or about world-power relations; the spurt of foreign interest is political and psychological. The psychological facet is that though we know we are a bunch of s.o.bs, foreigners, poor suckers, have affection for this island, and believe it or not its undeserving people. Let’s not spoil this advantage; let’s keep the charm of genuine non-alignment alive. Competition for mating-rights gets us, petrol, cooking-gas, milk-powder, pharmaceuticals and dhal. It would have been helpful if we had slaughtered fewer Tamils and now refrain from harassing Muslims on trumped-up charges. Lanka is no dream democracy; it is the site of militant and state-terrorism and crass military-police human rights abuse at the instigation of the JR, Premadasa Snr. and Mahinda regimes. It has been a locale of brazen plunder by political leaders, and not only in the (Raja)Paksa era. Racism is widespread among the people, but then ethnic intolerance is a global pandemic.
This is all true but there is another crucial aspect. Lanka is one of few post-colonial outposts where constitutional governance, admittedly imperfect, survives. Our giant neighbour India is another. This is different from Burma, Pakistan, Cambodia, Thailand (never colonised) and 50+ countries across Africa, Central Asia and Latin America. Hence my thesis is: India and the West, though they will be tough on economic reforms (IMF, West) and political changes (India), will not allow Lanka to collapse into anarchy and chaos. The uncles and aunties crowding over our crib will throw a lifeline before we asphyxiate. Can you imagine India, the West or China standing by and doing nothing if Lanka sinks into bedlam? We do not deserve a reprieve, but international political and psychological concerns will play out to our profit to prevent catastrophic meltdown. This is my hypothesis; let’s see if events prove the hunch correct.
However, this hypothesis does not allow conclusions to be drawn about politics or the traumatic fuel crisis of this (late June) moment; fuel is the litmus test that will decide whether RW’s administration survives. So far it has been paralysed and it has failed to inspire confidence that it has a way out. It must stop deceiving the public about the state of the fuel supply-chain. It will have to find an immediate fuel fix if mounting violence outside petrol stations is to be contained. This is the moment’s do-or-die challenge.
Of course, our congenital problems will persist but sudden death will likely be averted for now, that this till the IMF negotiations are finalised and implemented. Three IMF teams visited the country, one examining fiscal balance and seeking to restore a measure of equality between government expenditure and revenue and a second looking broadly at public finances (money supply, debt, banking, financial stability, social welfare). The third team worked on debt restructuring and interacted with legal advisors cum consultants hired by the government, Lazard and Clifford Chance. Chance is a London based law firm; Lazard engages in asset management, financial services and is also an investment bank with offices in New York, Paris and London. Judged by conventional norms, we have a strong squad on our side.
The wisest stance for Parliament and the opposition (SJB, TNA and JVP-NPF) to adopt at this juncture is to allow these negotiations to proceed and do nothing to disrupt them. Walking out of parliament when critical negotiations about the country’s financial destiny are in full-swing and the 21st Amendment (maybe renamed 22?) is about to be tabled, is both imprudent and irresponsible. The protocols imposed by the IMF could, at worst, be a repletion of its old Structural Adjustment designs: laissez-faire (nearly unchecked free-markets as in JR, Premadasa Snr times), pro-business, privatisation and foreign capital oriented, inimical to state participation in the economy, hostile to state spending on welfare (health and education) and pushing for labour-market reform (easier firing, lowering real wages). To be fair however we have to wait and see, and some changes to Lanka’s economic structures are in any case justified. RW’s natural inclinations would be to go along with right-wing, market-oriented proposals.
21A (22A?) now finalised and about to be tabled in Parliament is defective; too much power retained by the president despite substantial pruning. Instead of debating and discussing these two urgent matters in the House and from there taking them to the public arena, for the Opposition to walk out of Parliament is an unbelievable act of stupidity. I am surprised Anura, Vijitha Herath and Harini fell for this senseless stunt. They must return forthwith and address the tasks that await them; that is, critically examining the protocols agreed with the IMF and proposing amendments to 21 (22) A.
The RW government should be given the space to work through this emergency (EX) period when the country is in intensive care (say a month or two), but this is not what RW seems to have in his mind. He speaks of remaining in office for much longer: “Once we have established a firm economic foundation you (the people) can hand over power to any political party you wish”. This could be one year, or maybe he has it in mind to hang on till the November 2024 (Presidential) and August 2025 (Parliamentary) elections. RW would then be governing without a mandate from the people (reasonable during an existential crisis such as now) for an extended period; this is unreasonable.
Another matter is that the emergency medications that Lanka will be forced to swallow, whether it likes it or not, to secure urgent foreign debt restructuring via IMF and space from foreign creditors, will not be much different whether Ranil Wickremesinghe or Vladimir Lenin is PM. We are in such a mess that we have to grab any rope that is thrown to us. That’s why I say, allow Ranil to steer during the emergency (EX) period – which madman wants to shoot the pilot in mid-air halfway through a flight?
RW has his known proclivities and policy preferences and some will dovetail with anticipated IMF protocols. We can criticise but may have no option but to accept some. But allowing RW to set the economic direction of the country in next medium-term (MT) say three-year period is another matter; his remit has no electoral mandate. He has a right to his preferences and proclivities but no right to impose them on the country without a mandate. I make a crucial distinction between the period of negotiations with the IMF (the emergency EX phase) and a three to five-year MT economic, financial and social programme that requires a mandate. This is the distinction between trauma-therapy urgently administered during EX and longer-term recuperation strategies to rebuild economy and society.
Will a government elected in say one year be any better? Will there be a smaller number of donkeys and crooks? Have people learnt their lesson? There is a convicted felon seated in Cabinet right now – Mr President and Mr Prime Minister please explain. A multi-billion-rupee tax-dodger has been made a Minister. The voters of Ratnapura returned a convicted murderer to parliament. But this is what we call democracy – the right of the people to choose which bunch of vampires will suck their blood next time. Unfortunately, there is no acceptable alternative to democracy; a one-party state will not survive without open revolt because of our post-Donoughmore past and also because our national ethos and psychology will not accept it. The other option, a military regime will be hell on earth, so no more mention of that.
Why has the Lankan economy collapsed? Depending on how far back you go and your preferred ideology the answers are many, and all true. The following are the most frequently adduced.
* National consumption far exceeded production for seventy years and we ate our way into debt.
* Excess consumption was financed in part by foreign borrowing which plunged the country into the black-hole of ‘dollar indebtedness’.
* Export earnings fell far short of import expenditure (chronic balance-of-payments deficit).
* Government finances were out of kilter, with revenue falling way short of expenditure and the indebtedness was paid for by reckless rupee printing (chronic fiscal-deficit).
* Stupid projects by Rajapaksa regimes (Mattala Airport, Hambantota Harbour, Lotus Tower, Hambantota Stadium, show pieces named after Mahinda Rajapaksa) bankrupted the country.
* These projects were financially wasteful and executed either as prestige ventures or to collect commissions from contractors. These are part of staggering corruption activities amounting to billions of dollars perpetrated by the Rajapaksa Clan, re-elected with a massive majority!
* Breakdown of the rule of law and judicial independence.
No country can withstand such an inferno of epidemics, pestilences and plagues. It is all of this that has come together in 2022 to sink the ship. If it survives for the few EX-months, then the next step is elections to empower a government for MT. My preference is social-democracy with a well thought out dirigisme (state directed) component in its economic policy package. If it is necessary to wait till next time round for the electorate to mature and elect this option, let’s wait till vox populi comes around. Most likely a centrist or centre-right alliance will be elected in an election right now (options, Sajith, Ranil-Sajith, Dulles-led SLPP). Their right or centre-right policy spaces will be defined by terms like, market-oriented, business-friendly, private-sector led development, privatisation, restructured labour-market, FDI oriented, and rather harsh on the grassroots regarding welfare and subsidies.
A social-democratic alternative will have to borrow some of this but the difference will be in implementation and orientation. Eran Wickramaratne in “A Just Tax System” Daily Mirror 27 June writes in a vein where social-democrats seeking to direct the economy (dirigisme) into just directions cannot ask for more (Was he ever a Party Member!). In recent decades, lines have blurred everywhere between avant-garde liberalism and 21st-Century social-democracy.
This brings me to a last thought. The LSSP’s Tissa is sharp and intelligent; what on earth is he doing with that spent force Vasu and two jackals Wimal and Udaya? Isn’t it as clear as daylight that the LSSP must move over and align itself with the new left (JVP, FSP etc)? Yes, yes there’s 1971 and 1989 and the five-lessons, and etc and etc. Who doesn’t know all this? I wrote the first left critique of the JVP (Ajith Samaranayake did a brilliant translation) which the Party published 50 years ago. But it’s not that same world any longer Comrade!
Features
Democracy faces tougher challenges as political Right beefs-up presence

 It is becoming increasingly evident that the democracy-authoritarianism division would be a major polarity in international politics going forward. It shouldn’t come as a surprise if quite a few major states of both East and West gain increasing inspiration from the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ under President Donald Trump from now on and flout the core principles of democratic governance with impunity.
It is becoming increasingly evident that the democracy-authoritarianism division would be a major polarity in international politics going forward. It shouldn’t come as a surprise if quite a few major states of both East and West gain increasing inspiration from the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ under President Donald Trump from now on and flout the core principles of democratic governance with impunity.
It is the political Right that would gain most might in this evolving new scheme of things. Whether it be the US itself, France, Israel or Turkey, to name just a few countries in the news, it is plain to see that the Right is unleashing its power with hardly a thought for the harm being done to key democratic institutions and norms.
In fact, Donald Trump and his Republican hard liners led from the front, so to speak, in this process of unleashing the power of the Right in contemporary times. It remains a very vital piece of history that the Right in the US savaged democracy’s most valued institutions on January 6, 2021, when it ran amok with the tacit backing of Trump in the US Capitol.
What was being challenged by the mob most was the ‘will of the people’ which was manifest in the latter’s choice of Joe Biden as US President at the time. To date Trump does not accept that popular verdict and insists that the election in question was a flawed one. He does so in the face of enlightened pronouncements to the contrary.
The US Right’s protégé state, Israel, is well on course to doing grave harm to its democratic institutions, with the country’s judiciary being undermined most. To cite two recent examples to support this viewpoint, the Israeli parliament passed a law to empower the country’s election officials to appoint judges, while Prime Minister Netanyahu has installed the new head of the country’s prime security agency, disregarding in the process a Supreme Court decision to retain the former head.
Such decisions were made by the Netanyahu regime in the face of mounting protests by the people. While nothing new may be said if one takes the view that Israel’s democratic credentials have always left much to be desired, the downgrading of a democratic country’s judiciary is something to be sorely regretted by democratic opinion worldwide. After all, in most states, it is the judiciary that ends up serving the best interests of the people.
Meanwhile in France, the indications are that far Right leader Marine Le Pen would not be backing down in the face of a judicial verdict that pronounces her guilty of corruption that may prevent her from running for President in 2027. She is the most popular politician in France currently and it should not come as a surprise if she rallies further popular support for herself in street protests. Among other things, this will be proof of the growing popular appeal of the political Right. Considering that France has been a foremost democracy, this is not good news for democratic opinion.
However, some heart could be taken from current developments in the Gaza and Turkey where the people are challenging their respective dominant governing forces in street protests largely peacefully. In the Gaza anti-Hamas protests have broken out demanding of the group to step down from power, while in Turkey, President Erdogan’s decades-long iron-fist rule is being challenged by pro-democracy popular forces over the incarceration of his foremost political rival.
Right now, the Turkish state is in the process of quashing this revolt through a show of brute force. Essentially, in both situations the popular demand is for democracy and accountable governance and such aims are generally anathema in the ears of the political Right whose forte is repressive, dictatorial rule.
The onus is on the thriving democracies of the world to ensure that the Right anywhere is prevented from coming to power in the name of the core principles and values of democracy. Right now, it is the European Union that could fit into this role best and democratic opinion is obliged to rally behind the organization. Needless to say, peaceful and democratic methods should be deployed in this historic undertaking.
Although the UN is yet to play an effective role in the current international situation, stepped up efforts by it to speed up democratic development everywhere could yield some dividends. Empowerment of people is the goal to be basically achieved.
Interestingly, the Trump administration could be seen as being in league with the Putin regime in Russia at present. This is on account of the glaringly Right wing direction that the US is taking under Trump. In fact, the global balance of political forces has taken an ironic shift with the hitherto number one democracy collaborating with the Putin regime in the latter’s foreign policy pursuits that possess the potential of plunging Europe into another regional war.
President Trump promised to bring peace to the Ukraine within a day of returning to power but he currently is at risk of cutting a sorry figure on the world stage because Putin is far from collaborating with his plans regarding Ukraine. Putin is promising the US nothing and Ukraine is unlikely to step down from the position it has always held that its sovereignty, which has been harmed by the Putin regime, is not negotiable.
In fact, the China-Russia alliance could witness a firming-up in the days ahead. Speculation is intense that the US is contemplating a military strike on Iran, but it would face strong opposition from China and Russia in the event of such an adventurist course of action. This is on account of the possibility of China and Russia continuing to be firm in their position that Western designs in the Gulf region should be defeated. On the other hand, Iran could be expected to hit back strongly in a military confrontation with the US.
Considering that organizations such as the EU could be expected to be at cross-purposes with the US on the Ukraine and connected questions, the current world situation could not be seen as a replication of the conventional East-West polarity. The East, that is mainly China and Russia, is remaining united but not so the West. The latter has broadly fragmented into a democratic states versus authoritarian states bipolarity which could render the international situation increasingly unstable and volatile.
Features
Chikungunya Fever in Children
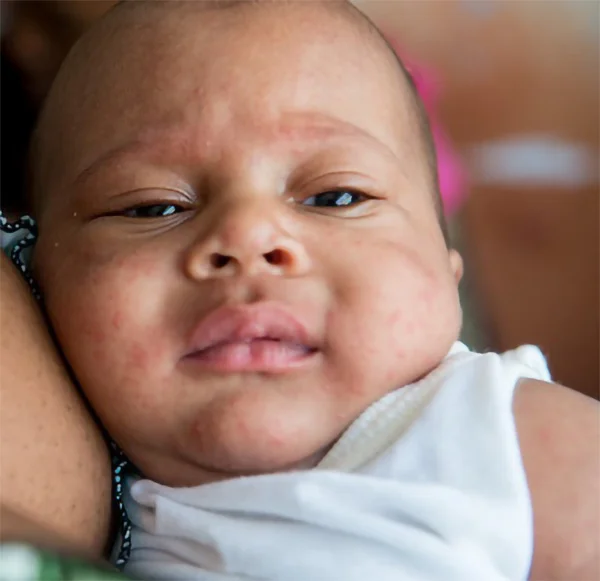
Chikungunya fever, a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, poses a significant health concern, particularly for children. It has been around in Sri Lanka sporadically, but there are reports of an increasing occurrence of it in more recent times. While often associated with debilitating joint pain in adults, its manifestations in children can present unique challenges. Understanding the nuances of this disease is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Chikungunya fever is caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), an alphavirus transmitted to humans through the bites of infected Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the same mosquitoes that transmit dengue and Zika viruses, highlighting the overlapping risks in many areas of the world. It is entirely possible for chikungunya and dengue to co-circulate in the same area, leading to co-infections in individuals.
When a mosquito bites a person infected with CHIKV, it ingests the virus. After a period of growth and multiplication of the virus within the mosquito, the virus can be transmitted to another person through subsequent bites. Therefore, the mosquito acts as a vector or an intermediate transmitting agent that spreads the disease, but not as a reservoir of the disease. The spread of chikungunya is influenced by environmental factors that support mosquito breeding, such as stagnant water and warm climates. Urbanization and poor sanitation can exacerbate the problem by creating breeding grounds for these mosquitoes.
The clinical presentation of chikungunya in children can vary, ranging from mild to severe. While some infected children may even be asymptomatic and be normal for all intents and purposes, others can experience a range of symptoms, including a sudden onset of high fever, a common initial symptom. Pain in the joints of the body, while being a hallmark of chikungunya in adults, may be less pronounced in children. However, they can still experience significant discomfort and this must be kept in mind during processes of diagnosis and treatment. It is also important to remember that joint pains can present in various forms, as well as in different locations of the body. There is no characteristic pattern or sites of involvement of joints. Muscle aches and pains can accompany the fever and joint pain as well. A headache, too, could occur at any stage of the disease. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue as well.
A reddish elevated rash, referred to in medical jargon as a maculopapular rash, is frequently observed in children, sometimes more so than in adults. While chikungunya is known to cause such a rash, there is a specific characteristic related to nasal discoloration that is worth noting. It is called the “Chik sign” or “Brownie nose” and refers to an increased darkening of the skin, particularly on the nose. This discolouration just appears and is not associated with pain or itching. It can occur during or after the fever, and it can be a helpful clinical sign, especially in areas with limited diagnostic resources. While a generalised rash is a common symptom of chikungunya, a distinctive darkening of the skin on the nose is a particular characteristic that has been observed.
In some rare instances, particularly in infants and very young children, chikungunya can lead to neurological complications, such as involvement of the brain, known as encephalitis. This is associated with a change in the level of alertness, drowsiness, convulsions and weakness of limbs. Equally rarely, some studies indicate that children can experience bleeding tendencies and haemorrhagic manifestations more often than adults.
Diagnosis is typically made through evaluating the patient’s symptoms and medical history, as well as by special blood tests that can detect the presence of CHIKV antibodies (IgM and IgG) or the virus itself through PCR testing.
There is no specific antiviral treatment for chikungunya. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and allowing the body to recover on its own. Adequate rest is essential for recovery, and maintaining hydration is crucial, especially in children with fever. Paracetamol in the correct dosage can be used to reduce fever and pain. It is important to avoid aspirin, as it can increase the risk of a further complication known as Reye’s syndrome in children. In severe cases, hospitalisation and supportive care may be necessary.
While most children recover from chikungunya without any major issues, some may experience long-term sequelae. Joint pain can persist for months or even years in some individuals, impacting their quality of life. In rare cases, chikungunya can lead to chronic arthritis. Children that have suffered from neurological complications can have long term effects.
The ultimate outcome or prognosis for chikungunya in children is generally favourable. Most children recover fully within a few days or a couple of weeks. However, the duration and severity of symptoms can vary quite significantly.
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of chikungunya. Mosquito control is of paramount importance. These include eliminating stagnant water sources where mosquitoes breed, using mosquito repellents, wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants, using mosquito nets, especially for young children and installing protective screens on windows and doors. While a chikungunya vaccine is available, its current use is mainly for adults, especially those traveling to at risk areas. More research is being conducted for child vaccinations.
Chikungunya outbreaks can strain healthcare systems and have significant economic consequences. Public health initiatives aimed at mosquito control and disease surveillance are crucial for preventing and managing outbreaks.
Key considerations for children are that some of them, especially infants and young children, are more vulnerable to severe chikungunya complications and early diagnosis and supportive care are essential for minimising the risk of long-term sequelae. Preventing mosquito bites is the most effective way to protect children from chikungunya. By understanding the causation, clinical features, treatment, and prevention of chikungunya, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to protect children from this illness that could sometimes be quite debilitating.
 Dr B. J. C. Perera
Dr B. J. C. Perera
MBBS(Cey), DCH(Cey), DCH(Eng), MD(Paed), MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin), FRCP(Lond), FRCPCH(UK), FSLCPaed, FCCP, Hony. FRCPCH(UK), Hony. FCGP(SL)
Specialist Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Fellow, Postgraduate Institute of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Joint Editor, Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health and Section Editor, Ceylon Medical Journal
Founder President, Sri Lanka College of Paediatricians – 1996-97)
Features
The Great and Little Traditions and Sri Lankan Historiography

Power, Culture, and Historical Memory:
(Continued from yesterday)
Newton Gunasinghe, a pioneering Sri Lankan sociologist and Marxist scholar, made significant contributions to the study of culture and class in Sri Lanka by incorporating the concepts of great and little traditions within an innovative Marxist framework. His theoretical synthesis offered historians a fresh perspective for evaluating the diversity of past narratives.
At the same time, Michel Foucault’s philosophical intervention significantly influenced the study of historical knowledge. In particular, two of his key concepts have had a profound impact on the discipline of history:
1. The relationship between knowledge and power – Knowledge is not merely an objective truth but a manifestation of the power structures of its time.
2. The necessity of considering the ‘other’ in any conceptual construction – Every idea or framework takes shape in relation to its opposite, highlighting the duality inherent in all intellectual constructs.
These concepts challenged historians to rethink their approaches, prompting them to explore the dynamic interplay between knowledge, power, and culture. The existence of Little Tradition prompted historians to pay attention to ‘other’ histories.
The resurgence of ethnic identities and conflicts has brought renewed attention to the dichotomy of culture, steering the discourse in a new direction. The ethnic resurgence raises three key issues. First, the way non-dominant cultures interpret the past often differs from the narratives produced by dominant cultures, prompting the question: What is historical truth? Second, it underscores the importance of studying the histories of cultural identities through their own perspectives. Finally, and most importantly, it invites reflection on the relationship between ‘Little Traditions’ and the ‘Great Tradition’—how do these ‘other’ histories connect to broader historical narratives?
When the heuristic construct of the cultural dichotomy is applied to historical inquiry, its analytical scope expands far beyond the boundaries of social anthropology. In turn, it broadens the horizons of historical research, producing three main effects:
1. It introduces a new dimension to historical inquiry by bringing marginalised histories to the forefront. In doing so, it directs the attention of professional historians to areas that have traditionally remained outside their scope.
2. It encourages historians to seek new categories of historical sources and adopt more innovative approaches to classifying historical evidence.
3. It compels historians to examine the margins in order to gain a deeper understanding of the center.
The rise of a new theoretical school known as Subaltern Studies in the 1980s provided a significant impetus to the study of history from the perspective of marginalised and oppressed groups—those who have traditionally been excluded from dominant historical narratives and are not linked to power and authority. This movement sought to challenge the Eurocentric and elitist frameworks that had long shaped the study of history, particularly in the context of colonial and postcolonial societies. The writings of historians such as Ranajit Guha and Eric Stokes played a pioneering role in opening up this intellectual path. Guha, in particular, critiqued the way history had been written from the perspective of elites—whether colonial rulers or indigenous upper classes—arguing that such narratives ignored the agency and voices of subaltern groups, such as peasants, laborers, and tribal communities.
Building upon this foundation, several postcolonial scholars further developed the critical examination of power, knowledge, and representation. In her seminal essay Can the Subaltern Speak?, Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak questioned whether marginalized voices—especially those of subaltern women—could truly be represented within dominant intellectual and cultural frameworks, or whether they were inevitably silenced by hegemonic. Another major theorist in this field, Homi Bhabha, also focused on the relationship between knowledge and social power relations. His analysis of identity formation under colonialism revealed the complexities of power dynamics and how they persist in postcolonial societies.
Together, these scholars significantly reshaped historical and cultural studies by emphasising the voices and experiences of those previously ignored in dominant narratives. Their work continues to influence contemporary debates on history, identity, and the politics of knowledge production.
The Sri Lankan historiography from very beginning consists of two distinct yet interrelated traditions: the Great Tradition and the Little Traditions. These traditions reflect different perspectives, sources, and modes of historical transmission that have influenced the way Sri Lanka’s past has been recorded and understood. The Great Tradition refers to the formal, written historiography primarily associated with elite, religious, and state-sponsored chronicles. The origins of the Great Tradition of historiography directly linked to the introduction of Buddhism to the island by a mission sent by Emperor Asoka of the Maurya dynasty of India in the third century B.C. The most significant sources in this tradition include the Mahāvaṃsa, Dīpavaṃsa, Cūḷavaṃsa, and other Buddhist chronicles that were written in Pali and Sanskrit. These works, often compiled by Buddhist monks, emphasise the island’s connection to Buddhism, the role of kingship, and the concept of Sri Lanka as a sacred land linked to the Buddha’s teachings. The Great Tradition was influenced by royal patronage and aimed to legitimise rulers by presenting them as protectors of Buddhism and the Sinhala people.
In contrast, the Little Tradition represents oral histories, folk narratives, and local accounts that were passed down through generations in vernacular languages such as Sinhala and Tamil. These traditions include village folklore, ballads, temple stories, and regional histories that were not necessarily written down but played a crucial role in shaping collective memory. While the Great Tradition often portrays a centralised, Sinhala-Buddhist perspective, the Little Tradition captures the diverse experiences of various communities, including Tamils, Muslims.
What about the history of those who are either unrepresented or only marginally represented in the Great Tradition? They, too, have their own interpretations of the past, independent of dominant narratives. Migration from the four corners of the world did not cease after the 3rd century BC—so what about the cultural traditions that emerged from these movements? Can we reduce these collective memories solely to the Sokari Nadagams?
The Great Traditions often celebrate the history of the ruling or majority ethnic group. However, Little Traditions play a crucial role in preserving the historical memory and distinct identities of marginalised communities, such as the Vedda and Rodiya peoples. Beyond caste history, Little Traditions also reflect the provincial histories and historical memories of peripheral communities. Examples include the Wanni Rajawaliya and the Kurunegala Visthraya. The historical narratives presented in these sources do not always align with those of the Great Tradition.
The growth of caste histories is a key example of Little Historical Traditions. Jana Wansaya remains an important source in this context. After the 12th century, many non-Goigama castes in Sri Lanka preserved their own oral historical traditions, which were later documented in written form. These caste-based histories are significant because they provide a localised, community-centered perspective on historical developments. Unlike the dominant narratives found in the Great Tradition, they capture the social, economic, and cultural transformations experienced by different caste groups. For instance, the Karava, Salagama, and Durava castes have distinct historical narratives that have been passed down through generations.
Ananda S. Kulasuriya traced this historical tradition back to the formal establishment of Buddhism, noting that it continued even after the decline of the Polonnaruwa Kingdom. He identified these records as “minor chronicles” and classified them into three categories: histories of the Sangha and Sasana, religious writings of historical interest, and secular historical works. According to him, the first category includes the Pujavaliya, the Katikavatas, the Nikaya Sangrahaya, and the Sangha Sarana. The second category comprises the Thupavamsa, Bodhi Vamsa, Anagatha Vamsa, Dalada Sirita, and Dhatu Vamsa, along with the two Sinhalese versions of the Pali Hatthavanagalla Vihara Vamsa, namely the Ehu Attanagalu Vamsa and the Saddharma Ratnakaraya. The third category consists of works that focus more on secular events than religious developments, primarily the Rajavaliya. Additionally, this category includes the Raja Ratnakaraya and several minor works such as the Sulu Rajavaliya, Vanni Rajavaliya, Alakesvara Yuddhaya, Sri Lanka Kadaim Pota, Kurunegala Vistaraya, Buddharajavaliya, Bamba Uppattiya, Sulu Pujavaliya, Matale Kadaim Pota, Kula Nitiya, and Janavamsaya (Kulasuriya, 1978:5). Except for a few mentioned in the third category, all other works are products of the Great Historical tradition.
Over the last few decades, Gananath Obeyesekera has traversed the four corners of Sri Lanka, recovering works of the Little Historical Traditions and making them accessible for historical inquiry, offering a new lens through which to reread Sri Lankan history. Obeyesekera’s efforts to recover the Little Historical Traditions remind us that history is never monolithic; rather, it is a contested space where power, culture, and memory continuously shape our understanding of the past. By bringing the Little Historical Traditions into the fold of Sri Lankan historiography, Obeyesekera challenges us to move beyond dominant narratives and embrace a more pluralistic understanding of the past. The recovery of these traditions is not just an act of historical inquiry but a reminder that power shapes what we remember—and what we forget. Sri Lankan history, like all histories, is a dialogue between great and little traditions and it is to engage both of them. His latest work, The Doomed King: A Requiem for Sri Vikrama Rajasinghe, is a true testament to his re-reading of Sri Lankan history.
BY GAMINI KEERAWELLA
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoSri Lanka’s eternal search for the elusive all-rounder
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoBid to include genocide allegation against Sri Lanka in Canada’s school curriculum thwarted
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoGnanasara Thera urged to reveal masterminds behind Easter Sunday terror attacks
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoAIA Higher Education Scholarships Programme celebrating 30-year journey
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoComBank crowned Global Finance Best SME Bank in Sri Lanka for 3rd successive year
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoSanctions by The Unpunished
-

 Sports12 hours ago
Sports12 hours agoTo play or not to play is Richmond’s decision
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMore parliamentary giants I was privileged to know











