Opinion
Increasing productivity of crop research institutes

by Dr. C .S. Weeraratna
(csweera@sltnet.lk)
Former Professor at Ruhuna and Rajarata Universities
Former Chairman, Sugarcane Research Institute
It has been reported that there is a dearth of trained scientists at the plantation crop research institutes. According to published data, there are 16 vacancies for research officers at the Tea Research Institute (TRI). The corresponding numbers for the Rubber Research Institute (RRI) and the Coconut Research Institute (CRI) are 42 and 18 respectively. The traditional plantation crop sector, which comprises Tea, Rubber, Coconut, and Sugarcane, play a key role in the Sri Lankan economy. The contribution to foreign exchange earnings, by these export crops, is the second-highest with a 21.5% share in the total export income, thus increasing the inflow of foreign exchange, substantially. It also provides employment opportunities to around 500,000.
The crop research institutes play a very important role in the development of the plantation sector. The output of these research institutions tend to be at a low level, in the absence of qualified and experience research personnel, for they carry out research in many important areas, such as breeding, control of pests and diseases, maintenance of soil fertility, economics, extension, etc., which are extremely important for the development of the plantation sector.
According to the Central Bank annual reports, the trade deficit, in Sri Lanka, has increased from Rs. 1141 billion, in 2015, to Rs 1673 billion, in 2018, and has decreased to Rs. 1430 billion, in 2019. Persistent trade deficits are detrimental to the country’s economy. If we are to reduce the trade deficit, it is essential that exports are increased and imports reduced. In this regard, plantation crops are important in increasing our export income, and crop research institutions (CIs) play an important role by developing appropriate technology.
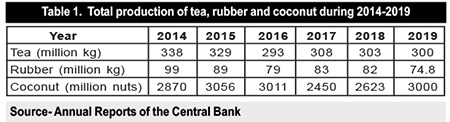
Around 800,000 ha are cultivated with plantation crops and as indicated in Table 1, production of the three major export crops, viz tea, rubber and coconut, do not show any substantial increase during the last six years. Tea production has been fluctuating around 300 million kg per year during this period. The annual total rubber production has decreased from 99 million kg in 2014 to 75 million kg in 2019. Coconut production, too, has fluctuated between 2800 and 3000 million nuts during 2015-2019. If the productivity of this sector is raised, it would be possible to increase foreign exchange earnings, thereby reducing the trade deficit. We spend nearly Rs. 50 billion annually to import sugar. Hence, it is important to increase our local sugar production, so that expenditure on imports can be reduced, thereby reducing trade deficit.
In any attempts to reduce the trade deficit by increasing production of exports crops/reducing imports of sugar, the four research institutions have an extremely important role to play. They need to conduct research to develop better clones/planting material, methods to control pests and diseases, effective management practices, better processing and value addition technologies, effective extension etc. In fact, among the many proposals in National Policy Framework “Vistas of Prosperity and Splendor” was promotion of research related to plantation crops
Hence, the Ministry of Plantation Industries need to take appropriate action to have an adequate qualified research staff at the four crop research institutions. The depletion of the research staff is likely to have contributed to the drop in crop production levels, as shown in Table 1.
 There is a significant requirement for both undergraduates and postgraduates trained in subject areas related to plantation crops. Hence, there is a need to have an institution/s to impart relevant knowledge and skills related to cultivation and processing of plantation crops. Currently, except the National Institute of Plantation Management (NIPM) which offers an external three-year degree programme jointly with the Wayamba University and a few diploma courses of short duration, there is no organization providing detail knowledge and skills required for those who need training at undergraduate and postgraduate level in plantation crops.
There is a significant requirement for both undergraduates and postgraduates trained in subject areas related to plantation crops. Hence, there is a need to have an institution/s to impart relevant knowledge and skills related to cultivation and processing of plantation crops. Currently, except the National Institute of Plantation Management (NIPM) which offers an external three-year degree programme jointly with the Wayamba University and a few diploma courses of short duration, there is no organization providing detail knowledge and skills required for those who need training at undergraduate and postgraduate level in plantation crops.
An organization, such as a university of plantation crops in collaboration with the four research institutes, would provide such knowledge and skills. In fact, during the sector budget discussions in Parliament, a few days ago, the State Minister of Company Estate Reforms Tea and Rubber Estate Related Crops, indicated that establishing a vocational university for plantation crops to operate, under the purview of Ministry of Plantation industries, would be desirable. Such a move would enhance the research capacity of the four research institutions. It will also enable to save a substantial amount of public funds, human resources, time and also pave the way to produce a team of skilled scientists for the industry and retain senior and experienced researchers. The modalities of this proposed mechanism need to be discussed by the relevant authorities to achieve the higher possible economic benefits to the country.
Increasing the number of research staff alone will not contribute to increase production or the productivity of the plantation crops. Scientists, with adequate industrial experiences, only can contribute to the needs of the industry. Hence, an attempt should be taken to employ those with appropriate experience. They need to be provided with essential equipment, chemicals and man power, etc. It is also important that the institutions conduct relevant research. Research priorities need to be based on the needs and problems in the sector. Conducting joint research and sharing equipment would reduce expenditure.
Opinion
Sri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans

Having watched Sri Lanka play in multiple World Cups (both formats) in six countries over the past 15 years, I regret that the worst facilities for fans are in the ongoing edition in Sri Lanka. I’m in my mid 60s and over many decades have watched our team play in every international cricket venue in Sri Lanka and several abroad. Even in developing countries such as in the Caribbean and Bangladesh, where I saw us triumph in 2014, there seems to be more concern for ordinary spectators and their basic expectations.
On this occasion, I travelled from the other side of the world and had to plan ahead. In the past editions, I recall tickets going on sale well ahead, but on this occasion, only a couple of months for some games and a couple of weeks for others. Even then, only low priced categories were released initially and I snapped them up, only to find better seats released a few days later. When I tried to buy those, I was told by the system that the maximum ticket quota is exceeded. I had to ask a friend to buy the tickets for me and transfer, hence paying multiple times for the same game. Why can’t all tickets be made available transparently to all fans at one time and sold to the 1st comers? Is there some racket in sending tickets “underground” initially to be resold at higher prices or given away free to cronies? I am tempted to believe this as in smaller grounds like P Sara and Galle, I have found in past bilateral tours such as vs England, where tickets are in high demand, the better tickets are never offered for public sale. But at the venue, I find many empty good seats. I understand that hundreds of tickets are given away as compliments to past cricketers families and friends and families of SLC big wigs, who routinely never turn up, depriving the opportunity to fans who are ready to pay for those same seats.
The most agonising part is entering and leaving the grounds which at both Premadasa and Pallekele this year was an absolute nightmare, with high possibilities of stampedes causing serious injuries or worse. Is the ICC not concerned – at least for the sake of avoiding legal liabilities? In past decades I remember long metal barricaded pathways set up a little away from the gates to force fans to queue up for body search, etc. This ensures more orderly entry as Sri Lankans are notorious for queue-jumping. Instead this time round it was a free-for-all for. The next shock is upon entry; there are clearly more people in each stand than the available seats. If you don’t arrive early and grab a seat, you end up standing in the aisles or stairs with an obstructed view and crushed on all sides. I saw some elderly foreign fans walk off half way in disgust. There was a time when in most stands at the R. Premadasa Stadium, a ticket guaranteed a seat. Now, it is not so even in the highest priced Grandstand. Seat numbers have been obliterated. With all the financial stability of the SLC that they claim in media, can’t they afford to repaint the seat numbers and set up some physical queuing pathways? Or is it that they are simply unconcerned about the suffering of ordinary fans? Or do they prefer free seating so that it’s easier to admit favoured individuals free of charge? At a world cup in New Zealand, I observed they had engaged many volunteers, young and old to act as guides/ ushers in and around the stadium. This is a common practice even in Olympics. Apart from trips for multiple board members, their families and other companions, can’t SLC spend a little to send some operational level staff to study and apply the best practices of other member countries to improve things at our local facilities? Moving onto toilets, without exaggeration, Pallekelle had 3 inches of filthy water (maybe urine) on the men’s toilet floor to wade through. In Sri Lanka, it is essential to have the constant presence of several janitors to ensure clean toilets. There wasn’t even one in sight. At the previous edition of this tournament in St. Lucia, West Indies, a small island where Sri Lanka played, I found impeccably clean toilets at the Gros Islet grounds.
Food and beverages is the next bone of contention. Quality and range offered was pathetic compared to the past in Sri Lanka and certainly compared to world cup venues elsewhere. Only plain instant noodle, hot dogs and some Chinese Rolls were generally available and some of the vendor stalls were unbranded, causing doubt in the minds of about the origin and quality of the offerings. Beer was the next scam, at Premadasa only Corona R. 2000 per cup and Budweiser Rs, 1500 were on offer, both unknown brands to most Sri Lankans. Budweiser also ran out early in the match, leaving a Hobson’s choice for fans. Apparently, this was a global sponsorship deal, but strangely at Pallekele, there was a small, unbranded shed in a corner selling Beer (presumably local) at Rs. 500. Was this something underhand? SLC Office bearers boast of their good relationships and having influence at the top levels within ICC. They also sit on their Boards and committees. Can’t they influence better deals on offerings and prices appropriate to local crowds? Finally, at the end of many hours of suffering, we come to the chaotic exit with everybody pouring out into narrow highly populated streets around the Premadasa stadium. With all the millions they are reportedly raking in, can’t SLC attempt to collaborate with the local authorities and acquire some of the surrounding lands, offering the residents attractive deals. Sri Lanka already has a very high number of stadia per capita. Building more and more may be lucrative for some, but investing in improving say three select existing venues to international standards in different parts of the country is the need of the hour. Once I took a flight via Mattala to watch Sri Lanka play at the Sooriyawewa stadium. Built in the middle of nowhere, with no surrounding infrastructure, it fell into total neglect just a few years after it was opened. When thousands of spectators attempt to find their way home at once, it can be anticipated that all modes of public transport including Uber and Pickme get overwhelmed. I had to walk about three kilometres and try repeatedly for almost one hour to secure a ride. After watching Sri Lanka play a world cup match at Sydney Cricket Ground, (capacity 50,000) we were able to calmly walk about 15 minutes to a long line of parked busses which took us painlessly to different points of the city. At the Oval, London, three underground tube stations are within 15 m walking distance and extra trains are deployed to handle the load after matches. Are SLC officers too busy to engage in some discussion with Public and Private sector transportation providers to make some special arrangement for the weary cricket fans?
I bought tickets to watch Sri Lanka play Pakistan in their final game in this tournament, but decided that the hardship and risks of bodily injury to be endured to support our team was not worthwhile at my age. Since that triumphant day in Dhaka in 2014, not only the standard of our Cricket but the facilities and basic comforts expected by ordinary fans have sadly declined drastically.
Sujiva Dewaraja
sujiva.dewaraja@gmail.com
Opinion
Jamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?

Political commentators have long been divided over the role of U.S. President Donald Trump, particularly following what critics describe as the first-ever sudden military aggression against a sovereign state by a legitimate military force involving direct attacks on security and civilian targets and the kidnapping a country’s legitimate ruler. This act stands in sharp contrast to conventional invasions that were previously justified through various false pretenses. Accordingly, there is little debate that the invasion of Venezuela and the kidnapping of President Nicolás Maduro represents a fundamentally different situation—a new beginning—when compared with the conventional invasion of Iraq and the capture of President Saddam Hussein, or the invasion of Libya and the killing of President Muammar Gaddafi.
It is also evident that this incident marks a clear departure from the long-standing strategies employed against Cuba for more than sixty years and against Venezuela for over a decade, which relied on sanctions, covert operations, and political pressure to subjugate governments and societies or engineer regime change. Although this new model constitutes a serious violation of the United Nations Charter, the UN has failed to take any meaningful action, thereby severely undermining its role and credibility. In the past, when sanctions were imposed on Cuba, leaders from a majority of countries mobilised to submit resolutions to the UN General Assembly and exert pressure on the United States. Under the present circumstances, however, there has been no significant intervention by member states to demand that the UN condemn the kidnapping of President Nicolás Maduro and secure his immediate release.
Such silence, particularly at a time when global public opinion increasingly portrays Donald Trump as operating like a leader of a underworld network, sets a deeply troubling precedent. Consequently, the public has begun to question whether Trump’s new approach has succeeded in imposing psychological barriers on other world leaders who openly challenge American imperialism. Beyond violating the UN Charter by acting as the head of what critics describe as a “terrorist state,” Trump has also imposed psychological pressure on the UN’s own bureaucratic structure by deliberately weakening its institutional foundations.
This strategy is further confirmed by Trump’s announcement that the United States would withdraw from thirty-one United Nations bodies and thirty-five other international conventions and organisations, while also terminating financial contributions. These decisions effectively signal that U.S. solidarity with the international community on climate change, world peace, and democratic governance is no longer a priority.
Earlier funding cuts to the World Health Organization have already forced it to rely heavily on corporate financing. Given the WHO’s significant authority over global food and pharmaceutical markets—and its power to shape the world economy during pandemics—this dependency has created conditions in which global health governance can be heavily influenced by the commercial interests of multinational corporations and billionaires. Research presented by Dr. David Bell indicates that global health regulations during the COVID-19 pandemic contributed to the closure of approximately 200,000 small businesses worldwide while simultaneously creating 40 new billionaires. There is little doubt that the United Nations will face a similar fate under sustained financial pressure.
This trajectory suggests that the United Nations, too, may be compelled to operate increasingly in accordance with the interests of global billionaires. The Public–Private Partnership Agreement signed between the UN and the World Economic Forum in 2019 further reinforces this concern. Following this agreement, the World Economic Forum, meeting in Davos in 2020, advanced the concept of the “Great Reset,” arguing that the world must be re-established through global multilateral institutional systems.
Implicit in this vision is the notion that before the world can be “reset,” it must first be disrupted, Jammed or effectively dismantled.
The World Economic Forum has also promoted the idea of establishing a new form of global governance system through such disruption. Critics argue that the ultimate objective of this strategy is the creation of a “Global Government” controlled by the world’s billionaires. This structure is widely viewed as an extension of the existing global level decision-making system often referred to as the “Deep State,” which operates above sovereign governments. This so-called parastate is understood to consist of entrenched senior officials, intelligence agencies, military leadership, and some corporate actors functioning beyond the authority of democratically elected leaders.
As such a strong global perception has emerged that this parastate is dominated by a small group of roughly one hundred billionaires and reinforced by a network of global media institutions under their influence. At times, President Trump has strategically accused certain U.S. officials of representing this parastate in an effort to distance himself from similar accusations. However, the electoral process that brought him to power, along with the major policy decisions he implemented thereafter, have revealed a close alignment between his administration and the interests of this new global power structure. Increasingly, independent critics argue that Trump himself has functioned as the shadow executive of this global parastate. His rise to power is seen as a critical precondition for advancing the final phase of a broader global roadmap aimed at dismantling and reconstructing the world order. In this interpretation, Trump’s role was to elevate the operational capacity of this system—previously managed more discreetly by other U.S. presidents—to an unprecedented level of intensity.
This transformation of American imperialism was vividly reflected in Trump’s military actions against Venezuela. Initially, familiar tactics were deployed, including economic sanctions, drug-trafficking accusations, naval provocations and arrest of vessels by Coast Guard and unilateral legal actions against President Maduro under the pretext of internal security. Such measures are consistent with long-standing U.S. practices toward states perceived as geopolitical or economic challengers.
However, in the cases of Venezuela and Cuba, political defiance, and close relations with China and Russia have also played decisive roles. The anti-imperialist political identity of leaders in these countries has inspired resistance movements worldwide, which is also explaining the deep hostility directed toward them by U.S. policymakers. Through the kidnapping of President Maduro, Trump sent a stark warning to other anti-imperialist leaders—an unmistakable act of psychological warfare carried out with unprecedented openness.
However, for the parastate to dismantle and rebuild the world as envisioned, a crucial condition must be met which is the restoration of a unipolar world order similar to that which emerged after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1992. This requires weakening or geopolitically constraining the economic and military power of China and Russia. To achieve this, pro-Chinese and pro-Russian states—particularly those rich in natural resources or located in strategic regions—must be destabilised, subjected to crises, and subjected to regime change. The culmination of this process would involve widespread military tension and a severe global economic crisis, making destruction a prerequisite for reconstruction.
When viewed within this broader framework, Trump’s global strategy becomes more coherent. Russia has been drawn into a prolonged conflict in Ukraine, while China faces escalating military pressure around Taiwan and the South China Sea created through U.S. alliances with Japan and the Philippines.
Simultaneously, renewed efforts are underway to reassert U.S. dominance over Latin America and the Caribbean by disrupting their economic and military relations with China, Russia, and even the European Union—reviving a modernised version of the Monroe Doctrine. At present in those counties US is having highest foreign investment, but China is the largest trading Partners. However, Trump’s use of tariffs as political weapons, often in violation of World Trade Organization principles, further exaggerates this situation.
Trumps interest in acquiring Greenland must also be understood within this strategic context. Greenland’s geographic position between the U.S. and Russia, its growing importance in Arctic shipping routes, and its vast natural resources make it a key geopolitical asset. The expansion of Russian military infrastructure in the Arctic and increased Chinese economic engagement have further heightened strategic value of Greenland. Under the 1951 U.S.–Greenland defense agreement, American military installations and missile- monitoring systems already operate on the island. Beyond military considerations, Greenland’s estimated US$4 trillion worth of oil, gas, and rare-earth resources are critical in light of China’s restrictions on rare- earth exports when have intensified U.S. interest, particularly following the escalation of the trade war in May 2025.
Meanwhile, Trump’s proposal to financially incentivise Greenland’s population to sever ties with Denmark to be annexed to US underscores how sovereign states may be divided and annexed under future strategies driven by global economic elites. Such actions also threaten the stability of NATO, an alliance in which the U.S. bears approximately 70% of defence costs, placing Europe at significant risk of severe conflicts between member countries. Ultimately, these developments highlight the growing role of parastate actors in dismantling existing political, economic, and security systems in to the world to facilitate a billionaire- controlled global order. In that process through funding cuts, public–private partnerships, political manipulation, intelligence operations, and engineered crises, sovereign states are weakened and destabilised. Examples from geopolitically sensitive regions, including Sri Lanka, illustrate how economic collapse and political fragmentation can be externally induced.
The invasion of Venezuela and the kidnapping of its legitimate leader signal a dangerous escalation in this process. Ongoing destabilisation efforts in Iran, coupled with rising tensions in the Middle East and volatility in global energy markets, further increase the risk of worldwide economic and military catastrophe which could be the ultimate precondition for the so called Great-Reset of the world. In this context, sovereign states and the global community must align in the Pretext of Preventing a third world war and recognising the urgent need for an alternative, genuinely independent multilateral institutional system to undermine the ultimate grand strategy of the deep state. In that process the bottom line must be to reverse the unprecedented approach of the President Donald Trump by condemning military aggression in Venezuela and demanding the release of the President Nicolas Maduro immediately.
by Dr. K. M. Wasantha Bandara
Secretary
Patriotic National Movement
Opinion
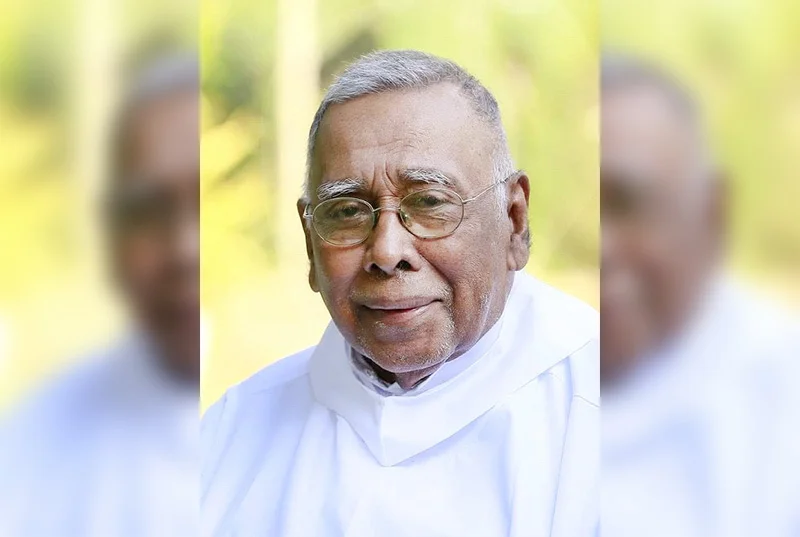
A beloved principal has departed!

“When the principal sneezes, the whole school catches a cold. This is neither good nor bad; it is just the truth. The principal’s impact is significant; his focus becomes the school’s focus.” These are Whitaker’s words and they illustrate the predominant role that a principal has to execute in a school. The Wallace Foundation has identified the following as the five key responsibilities of a school principal.
- Establishing a school wide vision of commitment to high standards and success of all students.
- Ensuring that learning is at the centre of all activities.
- Cultivating leadership in others
- Improving achievement by focusing on the quality of instruction.
- Managing people and resources at hand.
Rev. Fr. Stephen Abraham is one such principal who fulfilled these commitments at the highest level possible at St. Anthony’s College, Katugastota, for a period of 15 years from 1979 to 1994. He was born on the 15th of February 1933 and ordained a Priest in the Benedictine Order of the Catholic Church on 17 December 1964. His demise was on 21st February 2026, on the fourth day of the period of lent in the catholic calendar. As such he has been in the service of God as a priest for 62 years of his life of 93 years. This article contains extracts from a piece that I wrote when he celebrated the Golden Jubilee of his priesthood in December 2014.
St. Anthony’s College went through a burdensome period after the handing over of the school to the government as the teachers, support staff and parents were baffled about the direction of the school. It is at this stage that Fr. Stephen was appointed as the Principal. In his own inimitable manner he took control with authority and raised the confidence of the staff and the community. This was needed as the confidence was at its lowest ebb and he had the vision to realise that boosting the level of confidence had to be the priority. As the famous quote says “A good leader inspires others with confidence in him; a great leader inspires them with confidence in themselves”. He could not have done this without self-confidence which he had in abundance. Alongside, he laid his emphasis on maintaining a strict code of discipline as it had degraded due to the unfortunate incidents paving way for the handing over of the school.
A quality that any good principal should possess is to be a great communicator. Fr. Stephen had a natural ability to be dexterous with people. He made connections with each person showing them that he cares about their own situations. Through these connections he set high expectations for each individual letting them know that they cannot get away with mediocrity. The articulation and eloquence of his expression convinced people of his opinions and decisions. He is blessed with a sound sense of humour and it helped to ease tensions and resolve conflicting situations. More importantly, he was passionate about his responsibilities as the head of the school and he spent all his time and energy with the sole objective of creating a proper environment for the students to be responsible learners striving for personal excellence. Fr. Stephen was everywhere in the school and knew everything that was happening within the premises and he made himself visible at all times. He fits well with the description of a leader in Harold Seymour’s quotation “Leaders are the ones who keep faith with the past, keep step with the present, and keep the promise to posterity”. No wonder therefore, that he is considered as an outstanding principal.
In 1979 when the school celebrated its 125th anniversary, Fr. Stephen invited His Excellency the President J. R. Jayewardene as the chief guest of the Prize Giving ceremony. His emphasis on discipline is highlighted through this excerpt from his speech at this function. “The progress of any society depends mainly on discipline and discipline is not come by so easily unless the members of the society work towards it. No nation can be great unless its students aspire to greatness. But all this calls for training which is impossible without quality in teaching. Teachers should command the greatest respect in the land. Teaching is not a mere avocation, it is indeed a vocation and a very noble one at that.”
When it comes to educating the youth, Fr. Stephen believed in developing the whole person. This is reflected in the emphasis that he laid not only in the academic arena but also the field of extra-curricular activities. He believed that inculcating, promoting and enhancing values such as compassion, integrity, courage, appreciation, determination, gratitude, loyalty and patience are crucial for the proper upbringing of the younger generation. In 1980, he invited the Prime Minister Hon. R. Premadasa for that year’s prize giving ceremony and in the principal’s address he said “When our young charges leave this emotionally safe and secure world of school with all its disciplines, they must be able to adjust to the wider world in which they must live and work. It is our responsibility to see that they leave the College mentally, spiritually and physically whole, so that they in turn may assume the roles they will be called upon to fulfill in the future”, demonstrating his belief in the advocacy of values.
He identified sports activities as a healthy medium to instill discipline and an acceptable value system and did his utmost in promoting, encouraging and popularising all types of sports in the school. With his foresight and guidance, the school gained new heights in almost all spheres of sports activity. Just to name three great sportsmen who had their grounding in that era are Muttiah Muralidharan – record breaking cricket bowler, Priyantha Ekanayake – a respected past rugby captain of Sri Lanka and president of SLRFU and Udaya Weerakoon – a former national and world inter airline badminton champion.
He did not neglect the expansion of the infra-structure in the school in keeping with the needs of the time. Some of the projects completed during his time were the building of a two-story block of classrooms with the assistance of funds released by the Prime Minister, completion of the indoor sports complex and later a pavilion named after the famous Antonian cricketer Jack Anderson, with the help of the old boys association.
The inspiration that Fr. Stephen Abraham had as Principal within the school community of St. Anthony’s College can be aptly described by John Quincy Adam’s quotation ” May God grant him the eternal reward!
R.N.A. de Silva
The author had his secondary education at St. Anthony’s College, Katugastota, and later served as a member of its staff
rnades@gmail.com
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoPrime Minister Attends the 40th Anniversary of the Sri Lanka Nippon Educational and Cultural Centre
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoDottin out obstructing the field as Sri Lanka clinch series
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-
 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository













