Latest News
IMF Executive Board Concludes 2024 Article IV Consultation with Sri Lanka and Completes the Second Review Under the Extended Fund Facility

The Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) completed the second review under the 48-month Extended Fund Facility (EFF) Arrangement, allowing the authorities to draw SDR 254 million (about US$336 million). This brings the total IMF financial support disbursed so far to SDR 762 million (about US$1 billion). The Executive Board also concluded the 2024 Article IV Consultation with Sri Lanka.
The EFF arrangement for Sri Lanka was approved by the Executive Board on March 20, 2023 (see Press Release No. 23/79) in an amount of SDR 2.286 billion (395 percent of quota or about US$3 billion. The first review of the EFF was completed by the Executive Board on December 12, 2023 with disbursements of SDR 254 million (about US$337 million; see Press Release No. 23/439).
The EFF-supported program aims to restore Sri Lanka’s macroeconomic stability and debt sustainability, mitigate the economic impact on the poor and vulnerable, rebuild external buffers, safeguard financial sector stability, and strengthen governance and growth potential.
Signs of economic recovery are emerging. Real GDP expanded by 3 percent (y-o-y) in the second half of 2023. May 2024 inflation was 0.9 percent and gross international reserves increased to US$5.5 billion by end-April 2024. The primary balance improved to a surplus with tax revenue increasing to 9.8 percent of GDP in 2023. Despite improvements in non‑performing loans, pockets of vulnerabilities remain in the banking sector.
The recovery remains gradual, and the medium-term growth potential hinges on appropriate policy settings. Growth is projected to recover moderately in 2024-25 given constrained bank credit and fiscal consolidation, while facing uncertainties around the debt restructuring and policy direction following the elections. Inflation is expected to temporarily increase due to one-off factors. The current account is expected to remain positive in 2024, driven by improved tourist arrivals and remittances. Domestic risks could arise from waning reform momentum, especially on revenue mobilization. External risks are associated with intensified regional conflicts, commodity price volatility, and a global slowdown. Slow progress in debt restructuring could widen financing gaps.
Following the Executive Board’s discussion, Kenji Okamura, Deputy Managing Director and Acting Chair, issued the following statement:
“Sri Lanka’s performance under its Fund-supported program remains strong. All quantitative targets were met, except for the marginal shortfall of indicative target on social spending. Most structural benchmarks were either met or implemented with delay. Reforms and policy adjustment are bearing fruit. The economy is starting to recover, inflation remains low, revenue collection is improving, and reserves continue to accumulate. Despite these positive developments, the economy is still vulnerable and the path to debt sustainability remains knife-edged. Important vulnerabilities associated with the ongoing debt restructuring, revenue mobilization, reserve accumulation, and banks’ ability to support the recovery continue to cloud the outlook. Strong reform efforts, adequate safeguards, and contingency planning help mitigate these risks.
“To restore fiscal sustainability, sustained revenue mobilization efforts, promptly finalizing the debt restructuring in line with program targets, and protecting social and capital spending remain critical. Advancing public financial management will help enhance fiscal discipline, and strengthening the debt management framework is also needed.
“Monetary policy should continue prioritizing price stability, supported by a sustained commitment to refrain from monetary financing and safeguard central bank independence. Continued exchange rate flexibility and gradually phasing out the balance of payments measures remain critical to rebuild external buffers and facilitate external rebalancing.
“Restoring bank capital adequacy and strengthening governance and oversight of state-owned banks are top priorities to revive credit growth and support economic recovery.
“The authorities need to press ahead with their efforts to address structural challenges to unlock long-term potential. Key priorities include steadfast implementation of the governance reforms; further trade liberalization to promote exports and foreign direct investment; labor reforms to upgrade skills and increase female labor force participation; and state-owned enterprise reforms to improve efficiency and fiscal transparency, contain fiscal risks, and promote a level playing field for the private sector.
Executive Board Assessment
Executive Directors commended the authorities’ strong performance under the Fund‑supported program, noting that reforms are bearing fruit. The economy has started to recover, inflation remains low, revenue collection is improving, and reserves continue to accumulate. Directors underscored, however, that important vulnerabilities and uncertainties remain, including with respect to the ongoing debt restructuring and the upcoming elections. Against this backdrop, they called on the authorities to continue strengthening macroeconomic policies to restore economic stability and debt sustainability and to sustain the reform momentum to promote long‑term inclusive growth.
Directors underscored that restoring fiscal sustainability requires additional revenue measures underpinning the 2025 Budget, further tax administration reforms, as well as limiting tax exemptions and making them more transparent. They called for protecting growth‑enhancing and social spending, and for improving the social safety net. Directors welcomed the submission of the new Public Financial Management bill to Parliament, which would strengthen fiscal discipline and establish a solid fiscal framework. They noted that further efforts to strengthen the debt management framework are also needed. Directors welcomed the progress on achieving cost‑recovery in energy pricing, noting its criticality for containing risks from state‑owned enterprises (SOEs).
Directors welcomed the progress made to advance debt restructuring to restore Sri Lanka’s debt sustainability. They called for a swift finalization of the Memorandum of Understanding with the Official Creditor Committee and final agreements with the Export‑Import Bank of China. Directors stressed the importance of seeking comparable, transparent, and timely completion of restructurings with external private creditors consistent with program targets.
Directors emphasized that maintaining price stability remains the top priority for monetary policy, which requires anchoring inflation expectations, continuing to refrain from monetary financing, and the gradual unwinding of government security holdings as markets allow. They also stressed the importance of strengthening central bank independence. Directors underscored the need to continue building external buffers, while maintaining exchange rate flexibility to facilitate external rebalancing and preserve the credibility of the inflation targeting regime. They called for gradually phasing out the balance of payments measures.
Directors underscored the need to strengthen financial sector resilience to support the recovery. They called for swift completion of the restructuring of remaining domestic law, foreign currency loans and for adequate recapitalization of commercial and state‑owned banks. Directors welcomed the enactment of the Banking Act amendments and emphasized the importance of their effective implementation to enhance supervision and the governance of state‑owned banks. They also called for further efforts to strengthen the anti‑money laundering and counter‑terrorism financing framework.
Directors stressed that pressing ahead with governance and structural reforms, supported by development partners and IMF capacity development, is crucial to unlock growth potential. They welcomed the publication of the authorities’ action plan on the key governance reforms recommended in the Governance Diagnostic Report and called for its steadfast implementation. Directors also recommended prioritizing reforms to further liberalize trade, improve the investment climate and SOE efficiency, reduce gender gaps in the labor market, and mitigate climate vulnerabilities.
| Sri Lanka: Selected Economic Indicators 2021–2029
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Business
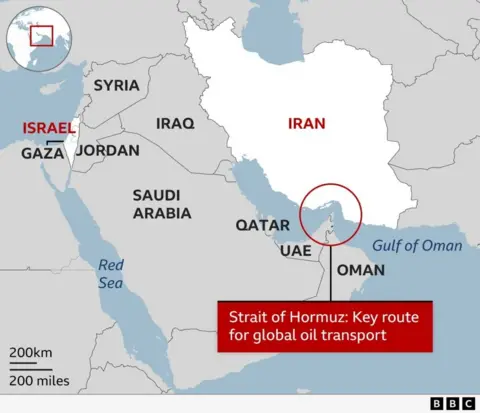
Oil prices rise after ships attacked near Strait of Hormuz

Global oil prices have risen after at least three ships were attacked near the Strait of Hormuz, as Iran continues to launch strikes across the Middle East in response to ongoing attacks by the US and Israel.
Two vessels have been struck, and an “unknown projectile” was reported to have “exploded in very close proximity” to a third, the UK Maritime Trade Operations Centre (UKMTO) said.
Iran has warned ships not to pass through the strait, which carries about 20% of the world’s oil and gas.
International shipping has almost come to a standstill at the strait’s entrance, with analysts warning that a prolonged conflict could push energy prices even higher.
In early trade in Asia on Monday, global oil prices jumped by more than 10% before those gains eased during the morning.
At 02:00 GMT, Brent crude was more than 4% higher at $76.16 (£56.53) a barrel, while US-traded oil was also up by around 4% at $69.67.
“The market isn’t panicking”, Saul Kavonic, head of energy research at MST Research told the BBC.
“There is more clarity that so far, oil transport and production infrastructure hasn’t been a primary target by any side,” he added.
“The market will be watching for signs that traffic through the Strait of Hormuz returns, which would see oil prices subside again.”
But some analysts have warned it could go over $100 in the event of a prolonged conflict.
On Sunday, the Opec+ group of oil producing nations – which includes Saudi Arabia and Russia – agreed to increase their output by 206,000 barrels a day to help cushion any price rises, but some experts doubt this would help much.
Edmund King, president of the AA, warned the disruption could drive up petrol prices around the world.
“The turmoil and bombing across the Middle East will surely be a catalyst to disrupt oil distribution globally, which will inevitably lead to price hikes,” he said.
“The magnitude and duration of pump price increases depends on how long the conflict goes on.”
Latest News
Allies of US in the Gulf bear brunt of Iran attacks

In the clear blue skies above Abu Dhabi, white contrails streak high above the sand-coloured villas and well-watered gardens.
These are no incoming Dreamliners or Airbuses bringing in the next manifest of tourists and guest workers. They are incoming ballistic missiles, launched by the Emirates’ giant neighbour just across the Gulf: Iran.
As of Sunday afternoon, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) defence ministry said it had so far “dealt with” 165 incoming ballistic missiles, two cruise missiles and 541 Iranian drones.
In Bahrain, a friend alerted me on Sunday morning that the airport was under attack after having a sleepless night.
“Woken by huge bangs and wailing siren,” he texted. “I think maybe around 20 booms and bangs. At least two hits”.
These are not familiar scenes in this region, but since this conflict began on Saturday morning, Iran appears to have expanded its target set from just hitting military targets, like the US Navy’s 5th Fleet headquarters in Bahrain, to airports and other civilian sites.
Now luxury hotels and shopping malls, high-rise apartment blocks, state-of-the-art airport departure terminals are getting sporadically hit as gaps appear in the Arab states’ air defences in the Gulf.
These places were never built with the prospect in mind that they would one day come under attack from drones and ballistic missiles.
Iran’s Foreign Minister, Abbas Aragchi, has denied targeting his country’s neighbours, telling Al Jazeera: “We are not attacking our neighbours in the Persian Gulf countries, we are targeting the presence of the US in these countries. Neighbours should direct their grievances to the decision-makers of this war”.
Some of the damage to civilian infrastructure in the Gulf states is accidental – resulting from debris falling from intercepted missiles.
But not all.
The number of attacks on airports in Bahrain and the UAE point to more than coincidence.
Iran always made it clear in advance that, if it was attacked, it would retaliate at any country it considered to be complicit in that attack.
The Gulf states went to some lengths to show Iran they were not part, in their eyes, of this US-Israeli attack.
Yet essentially they have been punished for being long-term military partners of Washington’s.
Before the Islamic Revolution, in the days of the shah, Iran was known as “the policeman of the Gulf”.
Since the revolution, it has always tried to convince its neighbours that it should resume that role, “taking charge of security” in what it calls Khaleej-e-Fars, the Persian Gulf (Arabs call it the Arabian Gulf).
Iranian leaders have tried, unsuccessfully, to persuade the Arab states in the Gulf to expel the US Navy and adopt them as their guardians instead.
But for rulers of the Gulf states – conservative, dynastic monarchies for whom the revolutionary zeal of the Islamic Republic is anathema – a line has been crossed here.
It is hard to see how they can ever have anything approaching normal relations again with the current Iranian leadership, that is, if it survives this war.
Saudi Arabia and Oman, two countries that have long hosted US and Western military forces, have both escaped a lot more lightly than the other four Gulf Arab states.
Oman, which remains on good terms with the Islamic Republic and was mediating the nuclear talks between the US and Iran, suffered a drone strike on its commercial port of Duqm, down on the Arabian Sea coast.
The Saudi capital Riyadh appears to have been targeted on Saturday, prompting an angry statement from its government.
“The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia expresses its rejection and condemnation in the strongest terms of the blatant and cowardly Iranian attacks that targeted the Riyadh Region and the Eastern Province, which were successfully intercepted. These attacks cannot be justified under any pretext,” the statement said.
This is not the first time Iran has attacked its Arab neighbours in the Gulf, either directly or indirectly, but never quite on this scale.
In 2019, an Iranian-backed militia in Iraq launched a volley of drones at Saudi Aramco’s petrochemical facilities at Abqaiq and Khurais, temporarily knocking out half of its daily export capacity.
Last June, Iran fired ballistic missiles at the al-Udaid airbase in Qatar but this was seen as a performative response to America’s Operation Midnight Hammer air raid that destroyed Iran’s nuclear sites at Isfahan, Natanz and Fordo, and Tehran quietly gave advance warning.
Bahrain, which has a large, sometimes restive Shia population, has long accused Iran of funding, training and arming insurgents in its country.
All of this, though, pales compared to the situation the Arab states of the Gulf are now experiencing.
For President Trump, for Israel, for many governments in the Middle East, and of course for many Iranians themselves the best result now would be a swift end to the regime of the Islamic Republic followed by a smooth transition to democracy and a world where Iran can enjoy normal relations with the rest of the world.
That, though, is far from certain.
A race is currently under way by the US and Israel to try to destroy Iran’s ability to keep launching these missiles and drones before they can fire them.
For Iran’s Revolutionary Guards Corps, the IRGC, the dilemma is whether to surge an attack on a major target like a US warship in the hopes of overcoming its defences, or hold back much of its concealed arsenal in the hopes of outlasting President Trump’s patience.
Iran also knows that while it has a finite number of missiles and drones, so, too, are its adversaries constrained by their number of remaining air defences.
If or when those run out before Iran runs out of missiles, drones or launchers then life for those on the ground in the Gulf could be about to get even more alarming.

The balance of power is heavily in favour of the US and Israel. These are two of the world’s most powerful and technologically advanced militaries in the world.
There are two US carrier strike groups in the region with over 200 warplanes while Iran, under sweeping sanctions for years, has no air force to speak of.
Both Israel and the US enjoy complete air superiority.
But Tehran still has some things on its side.
The regime, although weakened and unpopular with much of its population, only has to survive to proclaim itself the long-term winner in this conflict.
The Islamic Republic, with its cult of martyrdom, can take a lot more pain than the US can and the longer this conflict goes on the keener President Trump will be to find an off-ramp.
Will the US and Iran return to talks?
If the Iranian regime collapses, that will not be necessary.
But if the regime survives, and it may well, then Washington’s triple demands of Tehran will come back into focus, namely: a curb on Iran’s suspect nuclear programme, including a return to inspections; an end to Iran’s ballistic missile programme; and an end to Iran’s support for proxy militias around the region, such as the Hezbullah, Hamas, and the Houthis.
Oman says real progress was being made in talks in Geneva last month on the nuclear file.
But Iran ruled out discussing the other two issues – leading Donald Trump to say he was “not happy with the way the talks are going”.
It is possible that back channel contacts could well produce a ceasefire, followed by a return to talks.
But if the two sides’ bargaining positions have not moved then military action could well resume.
So this conflict has yet to run its course.
[BBC]
Latest News
Samson special leads India into the semi-finals
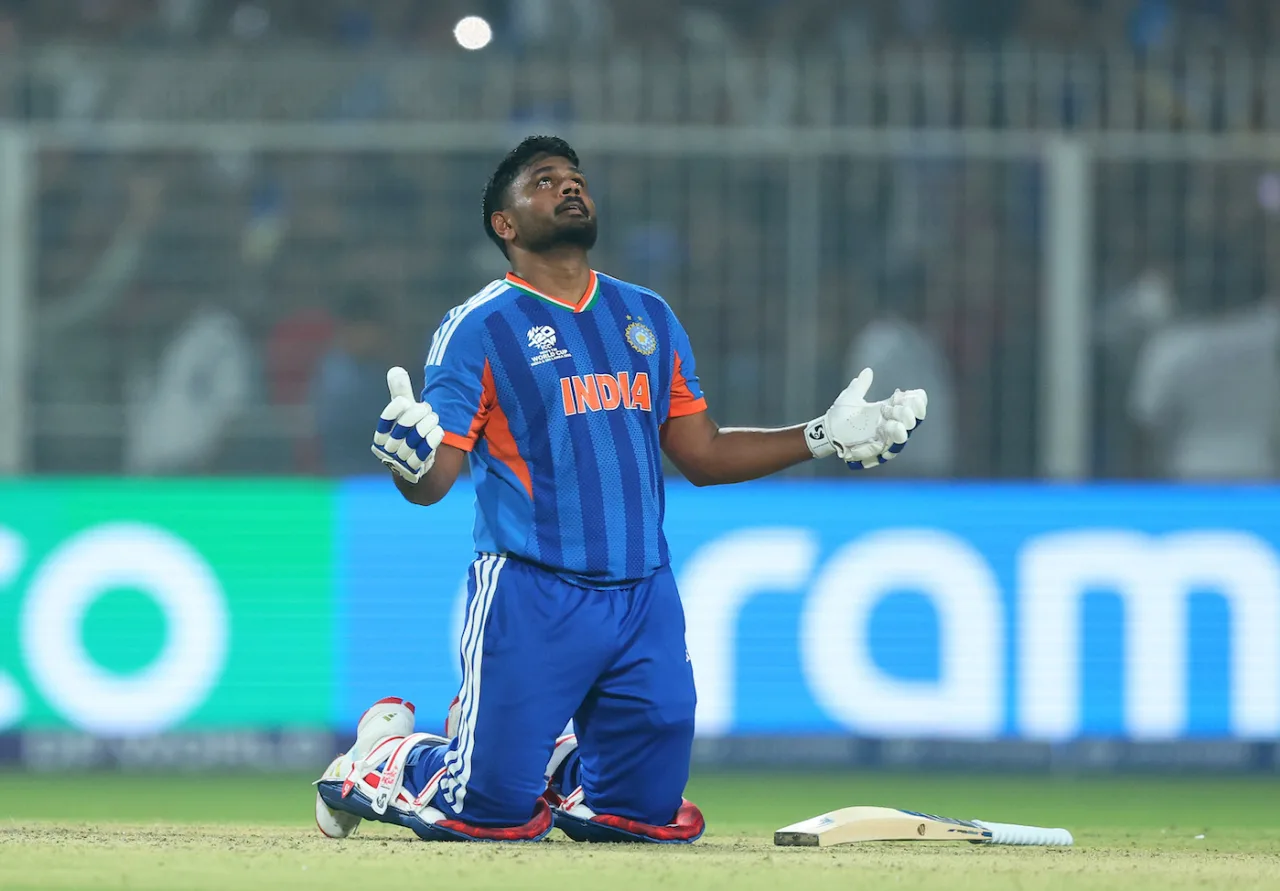

Sanju Samson was not India’s first-choice opener in the lead-up to the tournament. India changed that opening combination at the last moment, but Samson still wasn’t their first-choice opener for the first five matches of this World Cup. Brought in as an unlikely Plan B as India faced four must-win matches, Samson powered India’s highest successful chase at the T20 World Cups in the second of those.
It was good defensive bowling from India that restricted West Indies to 195 in this virtual quarter-final, a neat callback to the 2016 semi-final between these two sides when West Indies restricted India to 193. Like India were that night, West Indies were left ruing their opener’s slow innings, a 33-ball 32 from their captain Shai Hope. Outside that, the six-hitting pack scored 163 in 14.3 overs, more than the par for the conditions than their powerplay of 45 for 0.
Lacking extreme pace or mystery in their bowling, West Indies desperately needed asking-rate pressure or errors from batters who haven’t been in too many ICC must-win games. Those mistakes did come from Abhishek Dharma and Ishan Kishan, but Samson batted regally for his 97 not out off 50, taking few low-percentage options, reaching his first fifty in 13 innings in just 26 balls. This was the first time in the IPL and T20Is that Samson opened and stayed unbeaten in a successful chase, at the end of which he collapsed to his knees, looked at the heavens and crossed his heart.
West Indies brought in a new opener themselves, giving Roston Chase the job for the first time in international cricket so that they could have an offspinner for India’s left-hand batters. Chase surprisingly seemed much more at home, punishing errors in length from Arshdeep Singh, scooping Jasprit Bumrah, and sweeping Axar Patel, who completely handcuffed Hope.
Smartly, India kept bowling Axar, backloading Bumrah and Varun Chakravarthy for bigger hitters. Hope scored only 15 runs off 13 balls from Axar. He made only ten boundary attempts in his 33-ball stay. By the time Varun bowled him to make it 20 matches with at least one wicket, West Indies had dawdled to 68 for 1 in 8.5 overs, and were looking at six overs from Bumrah and Varun in the last 11.
Curiously, at this point, India didn’t go straight to Bumrah, but took the defensive option of bowling another Hardik Pandya over. Hetmyer wasted little time in regaining the record for most sixes in a single World Cup, hitting two in the first six balls to go past Sahibzada Farhan’s 19.
Having overplayed their hand, India brought Bumrah back for the 12th over, and he dismissed both the set batters for 27 off 16 and 40 off 25. When two of your three batters have such returns, you should really be doing much better than West Indies’ 103 for 3 in 12 overs.
It is a testament to the six-hitting prowess in that West Indies middle order that they still ended up with a competitive score. It started with the last ball of the 15th over when Jason Holder walked at Pandya and hit him for a straight six. Arshdeep had his figures rearranged when Powell bludgeoned him for a 98-metre six and then flicked him for one that just cleared the rope in the 16th over. Varun’s last over was taken down by Holder; his 1 for 40 meant that seven out of his ten costliest analyses in T20Is have come in the last two and a half months.
Arshdeep came back to finish off well with no boundaries in the 19th over, but Holder and Powell managed to take 26 from overs 18 and 20, bowled by Bumrah.
Abhishek practically played the entirety of the first two overs of the chase, taking India to 12 for 0. There was a bit of unease around with West Indies expecting a desperate shot. Samson didn’t need any of those. He backed away to create his first four off Akeal Hosein, and then swept and pulled him for sixes.
While Samson was caressing boundaries, Abhishek and Kishan offered catches to Hetmyer at deep square leg. Hetmyer took both of them to make it 41 for 2 in 4.3 overs.
For some reason, India, so big on right-left combinations in the lead-up to the World Cup, have been inflexible about Suryalumar Yadav batting at No. 4. He hit a trademark six over backward of square leg, but two right-hand batters in the middle allowed West Indies to bowl their left-arm spinners. Suryakumar’s contribution to the 58-run third-wicket stand was 18 off 16.
Samson stayed imperious at the other end, finding boundaries whenever the asking rate reached threatening proportions.
Against Tilak Varma, Chase created pressure, bowling three dots in his first over, the 12th of the innings. Shamar Joseph, who had taken Suryakumar’s wicket, started the 13th over with India in the most trouble they ever were in the chase, needing 92 off the last eight and a match-up against offspin in front of them.
Samson hit the first four, followed by a hat-trick of fours from Tilak to remove any alarm from the chase. As a final piece of the cherry on top, Tilak ended Chase’s second over with a straight six. He fell to a sharp catch from Hetmyer at mid-off, but Tilak did a big job with his 27 off 15.
Fittingly, Samson ended the chase with two languid hits for a six and a four to cap off “one of the greatest days of my life”.
Brief scores:
India 199 for 5 in 19.2 overs (Abhishek Sharma 10, Sanju Samson 97*, Ishan Kishan 10, Suryakumar Yadav 18, Tilak Varma 27, Hardik Pandya 17; Akeal Hosein 1-22, Jason Holder 2-38, Shamar Joseph 2-42) beat West Indies 195 for 4 in 20 overs (Shai Hope 32, Roston Chase 40, Shimron Hetmyer 27, Sherfane Rutherford 14, Rovman Powell 34*, Jason Holder 37*; Hardik Pandya 1-40, Jasprit Bumrah 2-36, Varun Chakravarthy 1-40) by five wickets
[Cricinfo]
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoPrime Minister Attends the 40th Anniversary of the Sri Lanka Nippon Educational and Cultural Centre
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoDottin out obstructing the field as Sri Lanka clinch series
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-
 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka

























