Features
Right Thought (Samma Sankappa ) in Buddhism

by Dr. Justice Chandradasa Nanayakkara
Buddhism rests on the pivot of suffering. Lord Buddha declared ‘the world is established on suffering, it is founded on suffering’ (Duke loko patititthhito).
All problems in life bring about suffering (Dukka or unsatisfactoriness) and as we attempt to put an end to them, they give rise to another. Solution of one problem leads to another problem, in many other diverse ways. We are constantly confronted with fresh problems, in our daily life, and problems go on incessantly and interminably. Such is the nature of suffering, and it is the universal characteristic of sentient existence. Suffering can be either physical or psychological. Dukka is inescapable and ubiquitous and it constitutes the first of the four Noble Truths in Buddhism. The Four Noble Truths, which the Buddha himself discovered, and revealed to the world, are the chief characteristics and unshakable foundations of Buddhism.
In the first Noble truth, the Buddha defines the truth of dukka, thus. “What monks, is the Noble Truth of Dukka? Birth is dukka, decay is dukka, death is dukka, sorrow, lamentation, pain, displeasure and despair are dukka; union with the unpleasant dukka, separation from the pleasant dukka, not what one wants is dukka; in brief, the five aggregates of clinging are dukka. These monks, is the Noble Truth of Dukka”.
The solution for the aforesaid problems of dukka (unsatisfactoriness) of life is the Noble Eightfold Path, propounded by Lord Buddha more than 2600 years ago. This is the only way to the cessation of suffering and also a vital step in emancipating ourselves from an interminable cycle of rebirths.
It is said that the Noble Eightfold Path leads to the cessation of dukka. This path consists of a set of eight interconnected factors, or conditions, that when developed together, leads to the cessation of dukka.
The eight factors of the paths are 1. Right Understanding (sammaditthi) 2. Right Thought (sammasankappa) 3. Right Speech (sammavacca). 4. Right Action (sammakammanta) 5. Right Livelihood (sammaajiva) 6. Right Effort, (sammavayama). 7. Right Mindfulness (samma sati) 8. Right concentration (samma samadhi).
These eight factors aim at promoting and perfecting the three essentials of Buddhist training and discipline. For the purpose for coherent and better understanding of, the eight divisions of the path have been grouped according to the under-mentioned three headings.
The first two are classified as Wisdom (panna), the second three as Morality (sila) and the last three as Concentration (samadhi). These three stages in the Eightfold Path are encapsulated in a Buddhist stanza (sabba papassa akaranan – kusalassa upa sammapada – sacitta priyo dapanan – etan buddhanu sasanan). To cease from all evil to cultivate good, in order to purify one’s mind, that is the advice of all Buddhas.
The eight steps of the path are not expected to be realised in sequence, one after the other. Rather, they are considered a unity and an organic whole. They are interdependent and interrelated. All eight factors are preceded by the word “Right” classified as Right, which means perfect. It is a mode of transcendence that leads to sotapanna sakadagami, anâgâmi and arahant. No doubt, it is a difficult feat to be achieved. The Noble Eightfold path is in effect the path to Nibbana. It is a path which avoids the extreme of self-mortification that weakens the intellect and the extreme of self-indulgence that retards moral progress. Although it is generally spoken as a path to be treaded, in actual fact the eight steps signify mental factors to be practised. All eight factors should converge simultaneously, each supporting the other in order to reach a sufficient level of development to experience of sotapanna, sakadagame, anâgâmi or arahant. It is said that the path proceeds from a lower state of purity to higher state and factors of the path should coalesce at a certain level of perfection. Path is not meant to be practiced a little each day.
The Buddha taught the eightfold path in virtually all his discourses, and his directions are clear and practical to his followers, today, as they were when he first disclosed them.
According to Walpola Rahula, the divisions of the Noble Eightfold Path should be developed more or less simultaneously, as far as possible, according to the capacity of each individual. They are linked together and each helps the cultivation of the others.
The second factor of the noble Eight-fold Path, with which this article deals, is called in Pali; samma sankappa, (Right Thought) which is sometimes identified as “Right Intention” in Buddhist literature. In this instance, the word specifically refers to the purposive or conative aspect of mental activity, as the first factor in the Noble Eightfold path (samma ditthi or right understanding) encompasses cognitive aspect of the mental activity. Nevertheless, no clear demarcation can be made between these two divisions because, from the Buddhist perspective, the cognitive and purposive sides of the mind intertwine and interact in close correlation, inducing them into activity. Right Thought is important because it is one’s thoughts which either defile or purify a person. It is one’s thoughts and nature that control one’s destiny. Evil thoughts tend to debase one just as good thought tends to elevate one. Sometimes a single thought can either destroy or save a world. Right Thought serves the dual purpose of eliminating evil thoughts and developing pure thoughts.
Our thoughts are as important to us as our actions because they make up who we are, thus it becomes imperative that we keep thoughts pure.
Buddha, emphasising the value of Right Thought, declared “Your worst enemy cannot harm you as much as your own thoughts, unguarded. But once mastered, no one can help you as much, not even your father or your mother”.
Right Thought (right intention) is threefold. It is comprised of 1. Nekkamma: Renunciation of worldly pleasures, which is opposed to attachment, selfishness and self-possessiveness. 2. Avyapada: Loving Kindness, goodwill, or benevolence which is opposed to hatred, ill will or aversion and 3. Avihimsa: Harmlessness or compassion which is opposed to cruelty and callousness. In a moment of insight, the Buddha, at the time of his enlightment, saw that everything contains all these opposites. He saw the duality in nature and realised that everything can be replaced by the opposite. For instance, each kind of Right Thought counters the corresponding kind of wrong thought or intention, the thought of renunciation (Nekkama) counters the intention of desire, the thought of goodwill counters the intention of ill will and the thought of harmlessness counters the intention of harmfulness.
Buddha declared if one acts and speaks with a pure thought, happiness follows him like a shadow that never leaves him and if he acts or speaks with an impure mind then suffering follows as the hoof of the ox. Right thought means avoiding desire and ill will. The importance of wisdom is evident from this, as the cause of suffering is described in terms of desire, ill will and ignorance. Right understanding removes ignorance and Right thought removes desire and ill will.
Renunciation (Nekkama) is often a difficult task. Grappling with the power of desire and attachment may require a great deal of personal struggle, as the mind does not want to relinquish its hold on the objects to which it has become attached. But that struggle yields many benefits, as putting an end to dukkha depends on eliminating craving thereby directing the mind to renunciation. We develop the inner strength to overcome temptation and compulsion. Attachment coupled with ignorance are the chief causes of all evil prevalent in this deluded world. One can either be attached to desirable objects or is repulsed with aversion if the objects are found to be undesirable. The word “Nekkamma” generally conjures up the idea of leaving your household life for the monastic life by discarding all sensual pleasures completely. But it is not so, as renunciation can apply to lay practice as well. Real renunciation does not require you to give all things inwardly cherished but changing our perspective on them so that they no longer bind us. It is letting go of whatever that binds us to ignorance and suffering. It is only an abandonment of overly material comforts for spiritual enlightment. The degree to which a person renounces depends on his disposition and situation.
It is the attachment or desire that put us on an endless cycle of grasping and keeps us unsatisfied. Therefore, it is important that we maintain an attitude of detachment from worldly pleasures and realise the ephemeral nature of our possessions and to not be selfishly attached to them.
The Buddha says unfulfilled desire is the root cause of unhappiness and dissatisfaction, and the way to overcome such unhappiness is to eliminate the craving or desire by eradicating the root of unwholesome desire through renunciation. The Mind is in the habit of grasping. We have to break this habit and strive to let go of grasping.
When we look realistically at the desire and unhappiness that eventually follows in its wake, it is constantly shadowed by dukkha (unsatisfactoriness). When desire is not fulfilled there is always frustration, disappointment, sometimes despair. Even if the desire is fulfilled it does not a guarantee of happiness and it might not last long and sometimes we lose the object of desire. This is called grasping. When we hang on too hard this becomes a cause of unhappiness. It is important to realize the fulfillment of desire is impermanent, nothing lasts whether it be height of sensual delight, or the achievement of wealth or fame or power. The pursuit of such pleasures brings the pain of separation from the object of desire, which increases in intensity in proportion to the degree of attachment.
Our mental states such as happiness or sadness and consequent actions are determined by our thoughts. The cause for endless suffering, conflict, discontent and injustice does not lie outside the mind. They are all just manifestations of intentions, outcroppings of thoughts propelled by greed, driven by hatred and delusion.
Right thoughts can mean different things and it is essentially directed towards shunning away from the vicious cycle of craving and desire by committing to a life style of self improvement and ethical conduct. The Buddha identified two types of thought: wandering thought(vicara) and logical or directed thought. Normally our mind is filled with scattered, random and wandering thoughts. For instance, when we are asked to perform a task our thoughts are directed towards in a particular direction. Once that task is over our thoughts are directed towards another direction and begin their erratic wandering again. The Buddha making an important observation in this connection and declared “Whatever one thinks about and ponders on often the mind gets a leaning in that way” (M.I)
The Buddha broadly defines Right Thoughts as thoughts of detachment, of love and of helpfulness. Therefore, an important aspect of Buddhist training is to cultivate Right Thought, not to let negative thoughts persist in our mind and to encourage positive thoughts.
Right Thought basically refers to wholesome thoughts, which is closely linked to Right Understanding because it results eventually through the practice and attainment of wisdom.
The first two verses of the first chapter of the Dhammapada by the Buddha would also be relevant in this connection. “All we are is the result of what we have thought. It is founded on our thoughts, it is made up of our thoughts. If a man speaks or acts with a pure thought, happiness follows him like a shadow that never leaves him”.
Avyapada as the second constituent of Right thought literally means non-enmity and corresponds to the most important virtue of Metta. In Sanskrit Maittri is loving kindness or goodwill towards all without any distinction or discrimination. The Pali word Metta also connotes loving kindness, goodwill, benevolence friendliness. A person whose mind is full of loving kindness can harbor no hatred towards anybody just like a mother who makes no difference between herself and her only child and protects it even at the risk of her own life. Metta is the strong wish for the welfare and happiness of others and devoid of self interest. It is indeed a universal, unselfish and all-embracing love. Metta is opposed to hatred, ill will or aversion. A person who radiates metta refuses to be offensive and renounces bitterness, resentment and animosity of every kind. It is a love that has no ulterior motive. Metta does not make a distinction among beings. It embraces all and no one falls outside of its domain. Ill will is countered by Metta. The kind of love implied by Metta should be distinguished from sensual love and also from the love involved in personal affection.
The third and the last of the three constituents of Right Thought is Avihimsa or Karuna. It is guided by compassion (Karuna) which is opposed to cruelty, aggressiveness and violent thoughts. Like Buddhist Mettta, Karuna too is limitless and boundless. Karuna (compassion) is a virtue which makes the tender hearts of the noble quiver at the sufferings of others. The characteristics of Karuna are comparable to that of loving mother whose thoughts, words and deeds always tend to relieve the distress of her ailing son. (Narada). Karuna complements loving kindness (Metta). While loving kindness has the quality of wishing for the happiness and the wellbeing others, Karuna (compassion) has the quality of wishing that others be free from suffering. Bhikkhu Bodhi describing the thought of harmlessness (avihimsa) in the context of Right Thought states “The intention of harmlessness is thought guided by compassion (Karuna) aroused in opposition to cruel, aggressive, and violent Thoughts. Compassion supplies the complement to loving kindness. Whereas loving loving kindness as the characteristic of wishing for happiness and welfare of others, compassion has the characteristic of wishing that others be free from suffering, a wish to be extended without limits to all living beings. Like Metta, compassion arises by entering into the subjectivity of others, by sharing their interioty in a deep and total way. It springs up by considering that all beings, like ourselves, wish to be free from suffering, yet despite their wishes continue to be harassed by pain, fear sorrow and other forms dukkha.
Features
Putin in Modi’s India

That was no ordinary greeting; on the frosty evening of last Thursday, Indian Prime Minister Modi embraced Russian President Vladimir Putin in a bear hug at Delhi airport and, within moments, presented him with a copy of the Bhagavad Gita in Russian. The choice of gift was laden with symbolism—echoes of Robert Oppenheimer, who drew profound philosophical reckoning from the same text, declaring, “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds,” after witnessing the first atomic explosion. Was Modi signaling the weight of nuclear-age responsibility to Putin, or was this a deliberate affirmation of India’s comfort in maintaining ties with a pariah state under global sanctions?
The streets of Delhi, festooned with Russian and Indian flags and dominated by colossal billboards of Modi and Putin, suggested more than ceremonial protocol—it was pageantry of influence, an audacious statement of India’s strategic independence. In that gesture, New Delhi appeared to assert that moral judgment from the West would no longer dictate its choices, and that the Indo-Russian relationship, forged during the Cold War and hardened by decades of defence dependence, remains a pivot capable of unsettling the established order in South Asia and beyond.
Putin’s first visit to India in four years, coinciding with talks in Washington over a possible Ukraine peace framework, came at a time when New Delhi is walking an increasingly delicate tightrope between Moscow and Washington. The optics of the visit—from ceremonial receptions at Rashtrapati Bhavan to summit talks at Hyderabad House—reflected not merely diplomacy but an overt projection of influence. Modi’s presentation of the Bhagavad Gita in Russian was emblematic: a centuries-old text of dharma and duty, layered with the moral weight of choice, now inserted into the theatre of high-stakes realpolitik.
Putin himself, in an interview with India Today, described India as a “major global player, not a British colony,” praising Modi as a “reliable person” who does not succumb to pressure. These words, spoken against the backdrop of US sanctions, EU manoeuvres to leverage frozen Russian assets for Ukraine, and growing Chinese assertiveness, highlight India’s determination to claim agency in a multipolar world where Washington and Brussels no longer set the rules unilaterally.
Historically, the Indo-Russian relationship has oscillated between strategic necessity and opportunism. Declassified CIA documents from the 1980s reveal the delicate dance India played with the USSR during the Cold War. Indira Gandhi’s approach, as the CIA observed, was staunchly nationalist and fiercely protective of India’s regional supremacy. The United States feared that India’s policies towards its neighbours, coupled with its Soviet alignment, could destabilize South Asia while simultaneously granting Moscow a strategic foothold. Today, the echoes of that era reverberate: New Delhi remains Moscow’s top arms buyer, leases nuclear-powered submarines, and maintains energy ties that have drawn ire from Washington, while ensuring that its engagement with Russia does not fully alienate the United States or Western partners.
What is important to see here is the economic metrics. India-Russia trade in 2025 is estimated at roughly $18 billion, heavily skewed in Moscow’s favour due to energy imports, while India continues to negotiate with the United States to mitigate punitive tariffs, including a 25 percent secondary tariff imposed over India’s purchases of Russian oil. Both nations aim to expand bilateral trade to a target of $100 billion by 2030, a goal that falls just two years after the next general elections, when Prime Minister Modi is widely expected to contest again despite the symbolic 75-year age limit for party leadership—a restriction that has largely been treated as political theatre and quickly forgotten. It is worth noting that India’s trade deficit with the US has ballooned to approximately $42 billion in the last fiscal year, reflecting both structural imbalances and the impact of these punitive measures. Remittances provide a partial counterweight: Indians working in the US send home over $90 billion annually, dwarfing Russian remittances, which are negligible in comparison. This indicates that while India faces challenges in trade metrics, its diaspora injects substantial financial resilience into the economy.
The summit also highlighted defence collaboration in stark terms. India’s $2 billion lease of a Russian nuclear-powered attack submarine, with delivery scheduled for 2028, signals an unprecedented deepening of underwater capabilities. The vessel, unable to enter combat under lease terms, is intended to train crews and refine India’s nuclear submarine operations—a critical step for strategic deterrence in the Indian Ocean amid rising Chinese and US naval competition. Russia, despite sanctions and Western pressure, continues to sustain a military-industrial complex capable of producing tanks, missiles, and drones at accelerating rates. As reports from Ukraine’s Center for Analytical Studies and Countering Hybrid Threats indicate, nearly half of Russian defence enterprises remain unsanctioned, exposing the limitations of Western punitive measures. In this context, India’s engagement with Russian defence capabilities is both a practical necessity and a symbolic assertion that strategic imperatives can outweigh Western orthodoxy.
Sanctions, however, remain a persistent backdrop. The European Union, under Ursula von der Leyen, has attempted to deploy emergency measures to convert frozen Russian assets into loans for Ukraine, challenging EU treaties and raising the prospect of legal confrontations with countries such as Hungary and Belgium. The United States, meanwhile, has explored using the same assets in US-led investment frameworks to facilitate reconstruction or political leverage. India, observing these efforts, has maintained a stance of strategic neutrality—resisting calls to condemn Russia while advocating for diplomacy, and emphasizing that selective sanctioning by Western powers is inconsistent and self-serving. Putin, speaking to India Today, noted that Washington and Moscow presented papers in parallel but reached no compromises, and highlighted that over 90 percent of Russia-India transactions are conducted in national currencies—a subtle yet potent challenge to dollar dominance.
The optics extend into nuclear and high-tech collaboration. India is developing nuclear-capable submarine-launched ballistic missiles, advancing its underwater fleet, and exploring high-tech partnerships with Russia, recalibrating the strategic environment in South Asia. Putin’s rhetoric that “Kiev is the mother of all Russian cities” and his framing of Russia’s role in eastern Ukraine resonate with historical narratives of great power assertion, yet they also serve as a conscious projection of strength aimed at partners like India. Modi’s reception was far from ceremonial; it underlined a shared understanding that global power is increasingly multipolar and that alliances must be flexible, resilient, and insulated from Western censure.
Even in the economic sphere, India challenges conventional assumptions. While the trade deficit with Russia persists due to energy imports, India’s broader engagement with global markets—including remittances from its diaspora and ongoing negotiations with the US—allows New Delhi to balance sovereignty with strategic interest. Putin’s discussions emphasizing bilateral trade growth, high-technology collaboration, and future energy projects further solidify this interdependence. The bottom line is clear: the India-Russia partnership, far from being a relic of Cold War calculations, has evolved into a sophisticated framework for navigating sanctions, economic competition, and regional security challenges, and it may yet redefine the balance of power in South Asia.
by Nilantha Ilangamuwa
in New Delhi
Features
Lalith Athulathmudali: an exceptional minister who managed time and got the best out of his team

His hallmark was efficiency, wit and much more
I would now like to devote some space to Minister Athulathmudali and how he ran his Ministry. His was a disciplined approach to work. Everyone knew that he was very happy in his previous portfolio of Trade and Shipping, where in addition to numerous achievements he had steered through Parliament path breaking legislation to modernize these sectors. The Port Authorities Act; the new Companies Act; the Intellectual Property Act; the Consumer Protection Act; and many others were evidence of significant productivity.
Therefore, many thought that he would be unhappy in his new portfolio. In fact some one asked him this question one day, in our presence. His reply was characteristic of his professional approach to work. He said that the Ministry he was given did not matter. Whatever Ministry, hie was given, it was his duty to comprehend the issues and productively address them. “Even if I was given the Buddha Sasana Ministry, I will still find plenty to do to improve matters,” he concluded. This spirit and this approach illuminated the work of the Ministry. I have yet to see anyone, apart from a Minister, who budgeted time so rigorously.
He desired to pack value to every passing minute. He was the only Minister, I knew in nearly 37 years of public service, who always fixed a starting as well as a finishing time for all his meetings. Perhaps the only meeting where he could not have a firm grip on time was the Cabinet meeting. There were no welcoming speeches or votes of thanks in his regime. He came to a meeting and got straight to the point. He despised visibly the sycophantic panegyrics which had become a part of the culture of welcoming speeches and votes of thanks.
He used to say publicly that we had become a society of humbugs and lick-spittles. He wanted none of it. With him performance was all. You either kept to his pace of work and requirement for relevancy in all matters, or you were quickly marginalized. To some of us, who had cultivated a life long habit of hard work, and of being up to date, it was both pleasurable and at times even exhilarating to work with him. The lazy or the unprepared had to encounter him with considerable dread as a companion. Not that he was ever harsh. He did not raise his voice, or even scold. He had the capacity to marginalize and dismiss you with wit and verve.
Mr. Athulathmudali just did not have time for pedlars in excuses or shirkers. Again, this did not mean that he expected us to be superhuman. He was a quick judge of the genuine and the credible. He was well aware that those who work hard and take scores of decisions a day would sometimes make mistakes. That was to be expected, provided however that they were not due to gross negligence or egregious blunder. Reasonable errors of judgment were a different matter provided of course they were not too frequent. With him all the officers knew what to expect.
I often wondered whether in Mr. Athulathmudali’s case, his intense preoccupation with time had something to do with the near death experience he suffered when he was seriously injured in a grenade explosion in Parliament. Those who rushed him to hospital on that day said that they could feel no pulse. He himself later said that he went beyond and then returned. My opportunity to work closely with him as Secretary was after he had undergone this experience. Everyone knew of course that he was a quick decision maker and an efficient Minister even before this incident. But I have no means of telling whether this obsession with time to this degree was a post incident reaction or not.
Linked together with this preoccupation with time was the intensity of his desire to be completely up to date both on matters relating to the subject areas of his Ministry as well as all aspects of current affairs. He regularly read the major current affairs magazines and journals. He read rapidly and was therefore able to pack in more into his reading time. He almost always read in the car, a habit which I shared with him. On one occasion, on a trip outside Colombo, he invited me to join him in his car for the journey back. After about half an hour’s conversation, both of us settled down to read, for I too always carried a stock of reading matter in the car. Some cannot read in a moving vehicle. They get nausea if they try. I have been fortunate that this does not happen to me, because I have finished whole books, whilst commuting to and fro.
The alternative would have been vacantly gazing on familiar sights. To round up this aspect of Mr. Athulathmudali’s character, one thing more needs to be said. He was the only person I knew who nearly always carried a World band radio in his brief case. He used to briefly interrupt meetings some times in order to catch the latest news bulletin from the BBC, Voice of America or some other station. Such was the importance he placed on being completely up to date. I hope all these do not convey an image of some grim automaton. That would be far from the truth.
His was a complex character. It was in fact fun to work with him. We got through discussing serious subjects with a considerable degree of wit, repartee and light banter. He encouraged criticism and dissent. But you had to have an arguable point and be prepared to sustain the argument with him. He also insisted on politeness in conversation and in argument. I myself as well as some of the senior pfficials of our team regularly argued with him. Both sides enjoyed this.
Mr. Athulathmudali created the conditions that made us feel comfortable arguing with him or dissenting. In this process, we were treated as equals. Mrs. Bandaranaike was another one of those persons who welcomed an argument with her officials, and did not try to stamp down dissent. She too, like Mr. Athulathmudali had high regard for such officials, a regard which she carried with her well past her own political vicissitudes.
Main areas of focus
Mr. Athulathmudali focused on two main areas. The first area related to the numerous operations of the Ministry. These Included a close and detailed pursuit of the progress of the two main paddy crops in the seasons of Maha and Yala; the review of the position from time to time of the situation in regard to the production of subsidiary food crops such as chillies, onions and potatoes, the review of issues relating to what were called minor export crops such as coffee, cocoa, cardamoms, cloves and cinnamon; the addressing of major issues relating to timely water distribution, pest control, etc; urgent issues of agricultural marketing and the roles of the Paddy Marketing Board, the Co-operatives and the private sector; problems in regard to food buffer stocking; issues relating to milk production, and so on.
These areas were covered in detail by the overall official team of Additional Secretaries, Directors, Heads of Department and myself. We had a system of regular meetings at various levels, culminating in a few large meetings chaired by me, at which issues that could not be addressed at lower levels were brought up for discussion and resolution. Meetings chaired by the Minister served two purposes. They kept film fully briefed and up to date. Also residual problems that could not be resolved at official level were taken up in these fora. Often, problems discussed with him by us had a political or important policy element. On all other matters we decided freely and without interference. The prevailing environment led to easy information flows and speedy decision making. The Minister would have countenanced nothing less.
His second area of concentration was on research, development and quality improvement. Here, unlike on operational matters we did not have several layers of meetings. These meetings were single overall meetings chaired by the Minister himself with all the relevant actors present. Whatever the subject area discussed at these meetings, the Minister wished to have his four State Ministers present. This was done for two reasons. In the first instance, he wanted his State Ministers exposed to all areas and aspects of the Ministry. They already had some exposure at Mini-Cabinet meetings. But these meetings were generally on operational and co-ordination issues and not on quality and research.
Secondly, the Minister followed a policy of recommending to the President that each one of his State Ministers act in turn for him, when he was out of the country, beginning with the most senior of them, and following subsequently the order of seniority. This was another reason why he wanted them to know everything that was going on in the Ministry. The Minister followed the same principle in regard to the State Secretaries, when I had to be out of the country.
What were some of the areas that the Minister took up for regular discussions at these special meetings? They consisted of issues such as the stagnation in rice yields over a considerable period of time; new varieties of rice being developed; issues such as Nitrogen fixation in plants and the reduction in the use of chemical fertilizers; the possibility of introducing better varieties of maize; issues relating to the fragmentation of cultivable land, especially paddy lands and its impact on production, productivity and long term sustainability; issues relating to the growing and the use of soya, and the question of Sri Lankan food habits in relation to its consumption; issues of post harvest losses and possible remedies; issues relating to growing for a market and the relationship that should be developed between the producer and the buyer; matters relating to quality control at all levels, and a number of other matters.
These meetings were extremely interesting. They were attended by senior scientists, researchers, agricultural economists and marketing experts. The Minister was greatly exercised with the central issues of high quality research, bringing the findings of such research to the field, and obtaining a detailed feedback from between research and growers back into the research process. This was a virtuous circle, he wished to encourage and to improve. But in this, all of us were to suffer bitter disappointment.
The link between research and the field and back to research were the army of agricultural instructors. They were an old and a tried and tested institution. They were a highly trained staff with a high degree of professional pride in their work. In fact, Sri Lanka had the reputation of having one of the best agricultural extension systems in the whole of Asia. But along with the President’s Janasaviya program of poverty alleviation arose the necessity for much larger numbers of Grama Sevakas or village level officers. The agricultural instructors were diverted for this purpose.
In spite of all the reasoning we could adduce, the President and his advisors thought that these officers could function in a dual capacity. The passage of time clearly revealed that as foreseen by us, they couldn’t. Thus was broken a tried, tested and an effective system. The Minister was more cynical than angry. He regarded the action as an act of irresponsibility and vandalism. So did everyone connected with agriculture.
(Excerpted from In Pursuit of Governance, autobiography of MDD Peiris) ✍️
Features
How climate change fuels extreme weather:
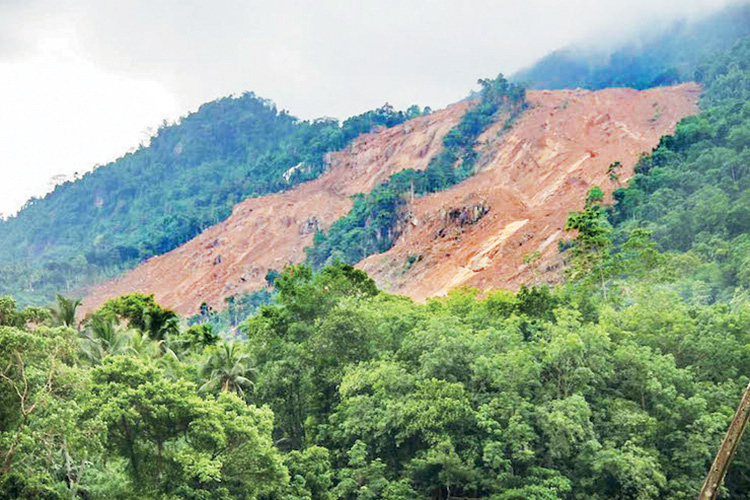

What Sri Lanka’s recent disasters tell us
Sri Lanka has always lived with the moods of the monsoon. For generations, people have grown used to seasonal rhythms of rain, wind and sunshine. Yet what the country has witnessed in recent months feels different. The storms have been stronger, the rainfall more intense, the destruction more widespread and the recovery more painful. The nation has been battered by floods, landslides and hurricane force winds that arrived with little warning and left thousands struggling to rebuild their lives. Scientists say this new pattern is not an accident of nature. It is a direct outcome of the world’s changing climate, which is heating the atmosphere and oceans and turning familiar weather cycles into something far more volatile.
To understand why Sri Lanka is experiencing such severe storms and flooding, it helps to begin with a simple idea. A warmer world holds more energy. When the atmosphere and ocean temperatures rise, they behave like an overheated engine. The monsoon winds strengthen. Rain clouds grow heavier. Sea levels climb. All these changes amplify the forces that produce extreme weather. What used to be occasional, manageable disasters are turning into regular and overwhelming events.
One of the clearest links between climate change and extreme weather is found in rising ocean temperatures. The Indian Ocean is warming faster than most other major bodies of water on the planet. This has serious consequences for Sri Lanka because the surrounding sea regulates the island’s climate. Warm oceans feed moisture into the atmosphere. This moisture then forms clouds that can trigger heavy downpours. When ocean temperatures climb beyond their normal range, the atmosphere becomes supercharged. Rain that once fell steadily over several days can now fall in a matter of hours. This explains why many parts of the country have witnessed sudden cloudbursts that turn roads into rivers and fields into lakes.
Warmer oceans also influence wind patterns. A heated sea surface disturbs air circulation, sometimes producing swirling systems that carry destructive winds and torrential rain. While full scale cyclones are less frequent in Sri Lanka than in parts of India or Bangladesh, the island is increasingly experiencing hybrid storms that bring cyclone like winds without being classified as named cyclones. These storms uproot trees, blow roofs off houses and knock down electricity lines, making post disaster life even harder for affected communities.
Another major factor behind Sri Lanka’s recent extreme weather is the shifting behaviour of the monsoon. For centuries, the island has relied on two monsoons that arrive at predictable times. Farmers, fishermen and traders built their lives around this rhythm. Climate change has disrupted this familiar pattern. The monsoons are becoming erratic. They may arrive later than usual or withdraw too early. In some years they bring too little rain, causing droughts. In other years they arrive with overwhelming intensity, bringing rain far beyond the land’s capacity to absorb. This unpredictability makes it difficult for people to prepare. It also increases the risk of disasters because infrastructure, agriculture and drainage systems were designed for a different climate.
In many regions of Sri Lanka, the land itself has become more vulnerable. Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall weaken soil structures. When long dry spells are followed by sudden downpours, the earth cannot hold together. Hillsides become unstable and landslides occur with devastating speed. Villages that once felt safe now face new threats as slopes collapse without warning. These disasters are not simply natural. They are intensified by human activities such as deforestation, poor land management and unplanned construction. Climate change acts as a catalyst, magnifying these risks and turning minor vulnerabilities into life threatening dangers.
The Sea level rise adds yet another layer of concern. The coasts of Sri Lanka are home to millions of people, as well as vital industries such as fishing, tourism and trade. Higher sea levels make coastal flooding far more common, especially when combined with storm surges. During recent storms, waves pushed much farther inland than usual, damaging homes, shops and fishing equipment. Saltwater intrusion also harms soil and freshwater supplies, threatening agriculture in coastal zones. With sea levels continuing to rise, these risks will only grow unless long term protective measures are put in place.
It is also important to recognise the human side of these disasters. Climate change is not only about shifting weather patterns. It is about the people who must confront the consequences. In the aftermath of the recent events, Sri Lankans have shown remarkable courage. Families have worked together to clear debris, rebuild houses, restore livelihoods and comfort those in distress. Yet the burden has not been evenly distributed. Low income households, informal settlements and rural communities often face the greatest hardships. Many of them live in areas more prone to flooding and landslides. They also have fewer resources to recover when disasters strike. Climate change therefore deepens existing inequalities, making vulnerable groups even more exposed.
Children are among the worst affected. Schools often close for days or weeks after floods, interrupting education and adding stress to families already struggling with upheaval. Health risks rise as stagnant water becomes a breeding ground for mosquito borne diseases. Malnutrition can worsen when livelihoods are disrupted and food prices increase. Elderly people face additional risks because they may have difficulty moving quickly during emergencies or accessing medical care after the disaster.
In cities, extreme weather strains essential services. Heavy rains overwhelm drainage systems, causing urban flooding that brings traffic to a halt and damages vehicles and businesses.
Hospitals face sudden influxes of patients. Water treatment plants struggle to maintain supply when rivers overflow or become contaminated. Power outages become common as strong winds damage transmission lines. These disruptions show how deeply interconnected human systems are with the natural environment. When the climate changes, every part of society feels the impact.
Despite the grim realities, there is reason for hope. Sri Lanka has a long history of resilience. Communities have rebuilt after countless storms, droughts and conflicts. Today the country has access to better technology, stronger scientific knowledge and more global support than ever before. What is needed is a clear commitment to prepare for the future rather than react only after disasters strike.
One of the most promising strategies is early warning systems. Accurate forecasts can save lives by giving people the time they need to move to safety. Sri Lanka has already improved its meteorological capabilities, but there is still room to strengthen local communication networks so that warnings reach everyone, including those in remote areas or without internet access. Community education is equally important. When people understand what climate change means for their region, they can make informed choices about housing, farming and water use.
Infrastructure must also evolve. Drainage systems in many towns need upgrading to handle more intense rainfall. Riverbanks require reinforcement to prevent flooding. New buildings, particularly in risk prone zones, must follow safety standards that take climate change into account rather than relying on outdated assumptions about weather patterns. At the same time, restoring natural ecosystems can offer powerful protection. Replanting mangroves, preserving wetlands and maintaining forest cover all help buffer the impact of floods, storms and landslides. Nature is one of the most effective defences against extreme weather when it is allowed to function properly.
On a broader level, Sri Lanka will benefit from global efforts to slow climate change. The island is a small emitter of greenhouse gases compared to many industrialised nations, yet it bears a heavy share of the consequences. International cooperation is essential to reduce harmful emissions, invest in renewable energy and support adaptation in vulnerable countries. Sri Lanka can also strengthen its energy security by expanding solar, wind and other sustainable sources, which reduce dependence on fossil fuels that contribute to climate change.
However, even as governments and scientists work on long term solutions, the experience of ordinary Sri Lankans during the recent storms offers an important lesson. Climate change is not a distant threat. It is happening now. It is felt in flooded living rooms, damaged paddy fields, broken bridges and displaced families. It reshapes the choices parents make for their children and the fears felt by those who live close to rivers or hillsides. It influences food prices, housing stability and health. It is a lived reality, not just an environmental problem.
At its heart, the story of Sri Lanka’s extreme weather is a story about people trying to protect their homes and loved ones. It shows how a global crisis can land with fierce intensity on a small island. But it also reveals the strength of human solidarity. Neighbours rescuing neighbours. Strangers offering food and shelter. Volunteers stepping into danger to help those trapped in rising waters. This spirit of care will be essential in the years ahead as the climate continues to warm and weather events become even more unpredictable.
There is no single solution that will shield Sri Lanka from every future storm. Yet there are many steps the country can take to reduce risk, strengthen communities and build resilience. These efforts will require resources, planning and political will. They will demand cooperation across regions, sectors and generations. Above all, they will require recognising that climate change is not someone else’s problem. It is a shared challenge that demands collective responsibility.
The recent disasters have served as a warning and a call to action. They have shown how quickly weather can turn violent and how deeply it can disrupt daily life. But they have also shown the urgency of preparing for a hotter and more unpredictable world. Sri Lanka has the knowledge and the capability to adapt. Its people have the determination. If these strengths are harnessed with foresight and compassion, the country can chart a safer path through the stormy decades ahead.
Climate change may be reshaping the monsoon, but it does not have to dictate Sri Lanka’s destiny. With the right choices, the island can remain not only a place of natural beauty but also a place of resilience, hope and human connection in the face of a changing planet.
(The writer is an environmentalist.)
by Vincent David ✍️
-
News5 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-
 News4 days ago
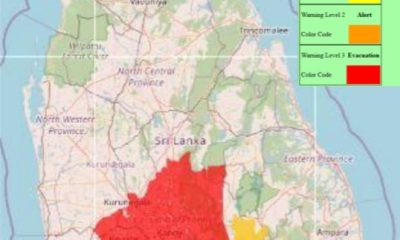
News4 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-
 Latest News6 days ago
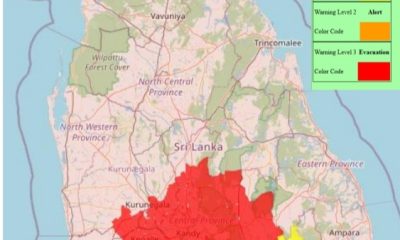
Latest News6 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoUpdated Payment Instructions for Disaster Relief Contributions
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth














