Features
Constitutional Reforms to ABOLISH the executive presidency NOW the urgent need

Neelan – GL 2020 draft the best we might have had
BY Prof. Savitri Goonesekere
(Continued from last week)
When Chandrika Kumaranatunga took office she pledged to introduce a new Constitution that would repeal what she described in colourful Sinhala as Bahubootha Executive Presidential form of governance. This task was entrusted not to a Constituent Assembly of Parliament but to a group of individuals with a range of expertise, with leadership from, Prof GL Pieris, Minister of Constitutional Affairs and late Dr Neelan Tiruchelvam. Both were distinguished alumni of the Peradeniya and Colombo Law Faculty of that time. They had both competed for the prestigious Rhodes Scholarship. Late Lalith Athulathmudali said that the decision to award the scholarship to GL was based on a careful scrutiny of my husband’s letters of reference to each at some point in their careers. My husband was famous for attaching equal importance to opposing viewpoints and Lalith said they had a hard time figuring out from the references who was best!
Neelan and GL produced perhaps the best Constitution for Sri Lanka we might have had, in 2000. It had an excellent chapter on Fundamental Rights that reflected contemporary developments. It also had constructive proposals for power sharing and the independence of the judiciary and public service from political control. Most importantly, it replaced the Executive Presidency with the tried and tested method of an Executive branch with a Prime Minister and Cabinet responsible to Parliament.
Unfortunately a single provision that enabled President Kumaranatunga to become prime minister for the rest of her Presidential term, was used by the Opposition led by Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe to tear up into pieces the document on the 2000 Constitution on the floor of the House, when it was presented in Parliament, by Minister GL Pieris. The government fell, and this led to the first “cohabitation” in governance arrangement between President Kumaranatunga of the SLFP, and Prime Minister Wickremesinghe of the UNP. The 2000 Constitution has never entered the discussions on Constitutional reform that followed.
A short period of “cohabitation” was followed by a General Election and a further short second term for President Kumaranatunge. The 17th Amendment was passed by Parliament at this time with the leadership of the JVP and provided for the first time Independent Commissions to strengthen public administration, and a Constitutional Council empowered to make recommendations to the President on high post appointments to the judiciary and public service

Mr. Mahinda Rajapaksa was elected as Executive President in 2005. He was given a mandate to abolish the Executive Presidency. However, the focus of his administration was addressing the armed conflict in the North with his brother, who was appointed Secretary of Defence. Winning the war in 2009 was a catalyst for a sea change in the political life of an experienced and respected politician, who had also related to an agenda of human rights. My husband appeared for him as petitioner, and won a fundamental rights case for him, and also successfully argued the famous Janagosha case on the right to peaceful political protest.
From 2009 Mahinda Rajapaksa went on a different political path, surrounded by family and friends espousing a culture of political patronage that debilitated all institutions of governance. This was an inherent aspect of governance in this country even before that. However misuse of Presidential powers without any inhibitions, and family political patronage and empowerment and cronyism was carried to different and more significant levels. In a feudal culture the perception that the President was all powerful and could not be questioned created new levels of sycophancy or reluctance to express different points of view in the administrative services. This had a serious impact on all institutions and was replicated in the behaviour of Cabinet ministers and others who became notorious for abuse of power and corruption. The Proportional Representation system with the focus on a Party machinery choice of candidates also led to more and more incompetent persons being elected as members of Parliament.
The 18th Amendment to the Constitution that saw a removal of the limitation on terms of the Executive President, a core concept in the 1978 Constitution embedded in Presidential power during a term of office, was perhaps an inevitable outcome. A President who had been elected to office, promising to abolish the Executive Presidency was now quite comfortable with becoming a President for life. His cabinet and government was full of approval for this change. So also the Supreme Court in the judgment of Shirani Bandaranayaka CJ when the 18th Amendment was challenged in the Supreme Court. The environment of acceptance and passivity and self censorship in responding to this change was such that there was silence even in academia on this very controversial Supreme Court jurisprudence. It was the theme of my husband’s oration for the Bar Association, in memory of a former President, Desmond Fernando PC.
2015 to 2022
The protest against the worst excesses of Mahinda Rajapaksa led to its unexpected defeat and the election of President Maithripala Sirisena and what was described as a rainbow coalition of political parties led by Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe as Prime Minister. President Sirisena promised to abolish the Executive Presidency and was given this mandate by the majority of citizens who helped him get elected to office. This was also a personal commitment given to Maduluwawe Sobhita Thero who led the resistance to the previous Mahinda Rajapaksa government. However, in the first flush of victory he was persuaded to support a Constitutional Amendment that would REDUCE presidential powers and transfer them to his Prime Minister, Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe. The draft Constitution of 2000 which provided for the abolition of the Executive Presidency was unfortunately not considered in this constitutional reform process.
If anyone expected this change to facilitate cooperation between these two centres of power in one administration that was an impossible expectation. Perhaps it increased expectations on the part of the Prime Minister, and resistance on the part of the President to the anticipated happy cohabitation. Inevitably the “empowered” Prime Minister had to experience the full brunt of Presidential anger when they had conflicting view points on the Arjuna Mahendran, Ravi Karunanayake and Aloysius related bond scam. A hurriedly and sometimes poorly drafted proviso in the 19th Amendment facilitated the Constitutional crisis of 2018 and the replacement of the 19th Amendment “empowered” Prime Minister with (of all people ) Mahinda Rajapaksa whom President Sirisena said he was fleeing from in anticipation of grave violence as a candidate in the Presidential election.
When the Easter Sunday violence took place, Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe, the empowered 19th Amendment Prime Minister, told the nation in a BBC interview that he could not be held responsible for the appalling and reckless lapses in national security because he had been excluded by the President from the National Security Council and “was not in the loop”.
It is the 19th Amendment of the Sirisena/Wickremesinghe government which is the basis of the 21A (MoJ). The Gotabaya and Wickremesinghe government are telling us that this will be the best response in strengthening governance and satisfying the demand for systemic and institutional change. And every one they address including the media and political parties (most recently Maithipala Sirisena led SLFP) is applauding this initiative.
The Opposition’s counter arguments for the 21A (S) to abolish the Executive Presidency appears to be falling on deaf ears, due to ignorance, political expediency or a collective sense of amnesia. The only focus seems to be on a single issue – whether or not to support an amendment prohibiting dual citizens from holding office that may lead to another Rajapaksa sibling being compelled to forfeit his national list seat in Parliament. And that after facilitating another person occupying a national seat in Parliament to become the country’s Prime Minister.
A new Constitution for Sri Lanka as part of Incremental Constitutional Reform
When Minister Wijeyadasa Rajapakshe offers us the prospect of a new Constitution being drafted (after we have emerged from this crisis), he seems to have forgotten the much publicized efforts to do so during the Maithripala-Sirisena Ranil Wickremesinghe governments period in office. What emerged from the Constitution drafting Committee that Mr. Wickremesinghe himself chaired? Large and excellent reports by expert groups working on important areas of governance were produced. What happened to those reports? What also happened to the report submitted to government by the Lal Wijenayake Committee on Constitutional reform after islandwide consultations over a period of time? What happened to the report of the Manouri Muttetuwegama Committee on Transitional Justice mechanisms? And the Truth and Reconciliation Mechanism law that was drafted at the request of the government by a committee chaired by me with a dedicated team of persons who gave their time freely without fees?
Even more curious, what happened to the report of the Constitutional drafting Committee appointed by President Gotabaya Rajapaksa? This committee was chaired by Romesh de Silva PC with, it is said, the leadership of Minister GL Pieris. Where is this draft Constitution and what is its approach to the Executive Presidency and “systemic and institutional change?”
The Way Forward
Faced with a crisis of proportions and impact that has devastated the country it is incredible that we are now engaged in another round of political play acting on constitutional reform. Let us at least on this occasion take serious stock of the very real breakdown in governance that has led to this “man made and voluntary economic disaster” in a country renowned for its human development indicators in South Asia. In doing so let us recognize that we must abolish the Executive Presidency NOW and not later. This requires heeding the voice of the Aragalaya, and supporting the 21A (S) that will abolish the Executive Presidency and will also bring with it the institutional and systemic change in our governance that has been promised for decades by successive governments but never realized due to narrow and selfish political agendas. Saying Yes to the 21A (S) and No to the 21A (MoJ) which is a token gesture of Constitutional reform may be a last chance to save our country from further destabilization and “man made” disasters created through corrupt, inefficient and reckless governance.
Heeding the Voice of the People, Constitutional Reform and the Referendum Concept
The Rajapaksa governments 2005-2014 and 2019-2022 gave scant respect to the “Voice of the People”. Governments in which Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe had a leadership role, like the Yahapalanaya government, 2015-2019, appointed many “Consultative” and Advisory” Committees, on a range of important subjects of public concern, including Constitutional Reform. Yet the government consistently discarded their reports. Research on the functioning of these “Committees” demonstrates that the Yahapalanaya period had more consultative Committees than any other government. The record of law making and policy formulation in this period however demonstrates clearly government inaction rather than action for change.
So “consultation and listening to the voice of the People and experts” can mean nothing more than political rhetoric. This can also lead to unexpected consequences. The failure to improve and achieve intra-party democracy, in the UNP, the party led by Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe, despite the many Reports commissioned and Committees appointed, eventually led to a significant group breaking away, and forming a new party as Samagi Jana Balavegaya.
These experiences hardly inspire confidence in the Prime Minister’s address to the nation, saying he will appoint 12 or 15 “Committees” for effective public administration and financial management. A large Expert Advisory Committee of eminent economists, has also been appointed to the Central Bank. A promise has been made by the Prime Minister to provide opportunities for youth participation, including from the Aragalaya, in some of these Committees. The latter initiative is said to help youth to understand the difference between protest and participatory democracy!
It is time that our politicians understand what participatory democracy means, and that the people can see the difference between this concept, and the “Committee Consultation” fetish that is a diversionary political maneuver to resist or avoid change. The Constitutional requirement of having a Referendum and hearing the voice of the People, to initiate major Constitutional reform, must also not be permitted to prevent efforts to abolish the Executive Presidency through Constitutional reform. This is also a demand of the Aragalaya and street protests, which include a large and diverse youth population.
Article 3 of our Constitution articulates the concept of the Sovereignty of the People as including the “powers of governance”. Article 4 clarifies the MANNER in which the PEOPLE’S POWER OF GOVERNANCE can be EXERCISED AND ENJOYED. It is on the basis of this concept that it can be argued that the President in exercising the Executive power of the People with a Prime Minister and Cabinet, collectively responsible for the government of the country under Article 43, has a LEGAL and not just an ethical obligation to fullfil his responsibilities of good governance, preventing the type of economic and political crisis confronting the nation today.
International law is considered “law” that creates legal obligations, despite the limitations on enforcement. Consequently, incapacity for enforcement no longer indicates that there is no legal obligation. A President and Cabinet Ministers who fail in their legal obligations in governance, can be called upon by the People to resign. It is the lack of a procedure for enforcing that legal obligation of resignation, except by impeachment of the President, that has contributed to the urgent need for Constitutional reform to ABOLISH the Presidency in the executive branch of government.
The 19th Amendment made the President liable for a violation of rights and for the Supreme Court to provide “just and equitable relief” for such a violation. This provision was retained in the 20th Amendment. The possibility of a petition for violation of citizen rights, and a call for just and equitable relief in the form of a court order on resignation, in light of the serious responsibilities in governance under the Constitution, may seem theoretical and only aspirational at this time.
The Attorney General has advised that the Presidential status in the executive branch cannot be removed without a two thirds Majority support in Parliament, and a Referendum. The Referendum issue, and its impact on 21 A (S) is therefore an additional concern. This seems an obstacle in effecting a critically important Constitutional change, in responding to our political and economic crisis.
The Constitution has a clear provision in Article 83 which indicates that a two third majority and a Referendum are required for the amendment or repeal of Article 3. Therefore Article 4 on the status of the President in the Executive branch of governance is NOT covered by the Referendum clause. The requirement for a Referendum is thus an interpretive perspective, based on jurisprudence in the Supreme Court linking Articles 3 and 4. That jurisprudence is also not consistent.
In the 20th Amendment case counsel cited earlier cases linking Articles three and four and argued that since the concept of Presidential power had been significantly modified by the 19th Amendment, a Referendum was also necessary to go back to the earlier concept of near absolute Presidential executive power. The court in its opinion rejected this interpretation, and did not follow the jurisprudence linking Articles three and four on the meaning of executive power. It is this interpretation that is being cited in arguing that 21 A (MoJ) seeking to only reduce Presidential powers that can be passed without a Referendum.
There is nothing to prevent the other argument being canvassed again in litigation on the current Constitutional Bills. Besides the Referendum issue can also be resolved if the Supreme Court follows the approach it took in the Port City Bill litigation, where the Court decided that it was not necessary to consult the Provincial Councils on a matter that required their consent, when it was impossible to do so as these bodies were not functioning at the time. The current situation and an argument that it is not possible to have a Referendum, in the current context, is supported by that case.
The lack of clarity on the issue of the need for a Referendum does not mean that this should be used to prevent support for the 21A(S) that seeks to abolish the Executive Presidency. Besides holding such a Referendum is not as complicated and expensive as a General Election, that we cannot afford at this time. All that a citizen is required to do is to say “yes or no” to a single question, of the abolition of the Executive Presidency. They will be happy to provide the piece of paper for this task to the Election Commissioner’s officials, if the State cannot afford to provide this, rather in the manner they are collecting the one rupee coins, after the Minister said the State subsidizes the cost of a rupee for a litre of fuel!
If the Referendum issue is too complicated to resolve in initiating Constitutional reform to abolish the Executive Presidency the time may be ripe for demanding that the President exercises his powers under Article 86 of the Constitution to “submit to the People at a Referendum any matter which in his view is of national importance”. He claims that he has a mandate from 6.9 million people to complete his term. That is now an issue of public concern for him as well as the People. He can hear the Peoples’ voice, on this matter through a Referendum, helping to also solve the differences in viewpoint between him and the Peoples’ Movement of Aragalaya.
Many of the persons involved in this movement for systemic and institutional change are the youth of a next generation, who have come together from diverse communities that link across class, caste and race, calling for a different approach to accountable governance, realizing how poor and reckless government impacts the lives of the People and their future. Mr. Ranil Wickremesinghe has cited a literary source, the German playwright Bertol Brecht’s Caucasian Chalk Circle to explain the manner in which he will perform as the Prime Minister of the country.
Perhaps he as well as citizens, especially the youth, engaged in the Aragalaya should peruse the poem of WS Senior, an Englishman who was a poet and educationist in colonial Sri Lanka. His ashes are interred in Haputale with an epitaph from a poem he wrote on leaving this country: “oh my soul it will break with longing, it can never be good bye”. His poem “The Call of Lanka” has these lines:
I climbed o’er the crags of Lanka
And gazed on her golden sea
And out from her ancient places
Her soul came forth to me
“Give me a Bard said Lanka
A Bard of the things to be
A Bard for my joys and pains
But most shall he sing of Lanka
In the brave new days that come
When the races all have blended
And the voice of strife is dumb
Hark Bard of the fateful future
Hark Bard of the bright To-Be
A voice on the verdant mountains
A voice on the golden sea,
Rise Child of Lanka, and answer
Thy mother has called to Thee.
Features
A wage for housework? India’s sweeping experiment in paying women

In a village in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, a woman receives a small but steady sum each month – not wages, for she has no formal job, but an unconditional cash transfer from the government.
Premila Bhalavi says the money covers medicines, vegetables and her son’s school fees. The sum, 1,500 rupees ($16: £12), may be small, but its effect – predictable income, a sense of control and a taste of independence – is anything but.
Her story is increasingly common. Across India, 118 million adult women in 12 states now receive unconditional cash transfers from their governments, making India the site of one of the world’s largest and least-studied social-policy experiments.
Long accustomed to subsidising grain, fuel and rural jobs, India has stumbled into something more radical: paying adult women simply because they keep households running, bear the burden of unpaid care and form an electorate too large to ignore.
Eligibility filters vary – age thresholds, income caps and exclusions for families with government employees, taxpayers or owners of cars or large plots of land.
“The unconditional cash transfers signal a significant expansion of Indian states’ welfare regimes in favour of women,” Prabha Kotiswaran, a professor of law and social justice at King’s College London, told the BBC.
The transfers range from 1,000-2,500 rupees ($12-$30) a month – meagre sums, worth roughly 5-12% of household income, but regular. With 300 million women now holding bank accounts, transfers have become administratively simple.
Women typically spend the money on household and family needs – children’s education, groceries, cooking gas, medical and emergency expenses, retiring small debts and occasional personal items like gold or small comforts.
What sets India apart from Mexico, Brazil or Indonesia – countries with large conditional cash-transfer schemes – is the absence of conditions: the money arrives whether or not a child attends school or a household falls below the poverty line.

Goa was the first state to launch an unconditional cash transfer scheme to women in 2013. The phenomenon picked up just before the pandemic in 2020, when north-eastern Assam rolled out a scheme for vulnerable women. Since then these transfers have turned into a political juggernaut.
The recent wave of unconditional cash transfers targets adult women, with some states acknowledging their unpaid domestic and care work. Tamil Nadu frames its payments as a “rights grant” while West Bengal’s scheme similarly recognises women’s unpaid contributions.
In other states, the recognition is implicit: policymakers expect women to use the transfers for household and family welfare, say experts.
This focus on women’s economic role has also shaped politics: in 2021, Tamil actor-turned-politician Kamal Haasan promised “salaries for housewives”. (His fledgling party lost.) By 2024, pledges of women-focused cash transfers helped deliver victories to political parties in Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Odisha, Haryana and Andhra Pradesh.
In the recent elections in Bihar, the political power of cash transfers was on stark display. In the weeks before polling in the country’s poorest state, the government transferred 10,000 rupees ($112; £85) to 7.5 million female bank accounts under a livelihood-generation scheme. Women voted in larger numbers than men, decisively shaping the outcome.
Critics called it blatant vote-buying, but the result was clear: women helped the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)-led coalition secure a landslide victory. Many believe this cash infusion was a reminder of how financial support can be used as political leverage.
Yet Bihar is only one piece of a much larger picture. Across India, unconditional cash transfers are reaching tens of millions of women on a regular basis.
Maharashtra alone promises benefits for 25 million women; Odisha’s scheme reaches 71% of its female voters.
In some policy circles, the schemes are derided as vote-buying freebies. They also put pressure on state finances: 12 states are set to spend around $18bn on such payouts this fiscal year. A report by think-tank PRS Legislative Research notes that half of these states face revenue deficits – this happens when a state borrows to pay regular expenses without creating assets.
But many argue they also reflect a slow recognition of something India’s feminists have argued for decades: the economic value of unpaid domestic and care work.
Women in India spent nearly five hours a day on such work in 2024 – more than three times the time spent by men, according to the latest Time Use Survey. This lopsided burden helps explain India’s stubbornly low female labour-force participation. The cash transfers, at least, acknowledge the imbalance, experts say.
Do they work?
Evidence is still thin but instructive. A 2025 study in Maharashtra found that 30% of eligible women did not register – sometimes because of documentation problems, sometimes out of a sense of self-sufficiency. But among those who did, nearly all controlled their own bank accounts.

A 2023 survey in West Bengal found that 90% operated their accounts themselves and 86% decided how to spend the money. Most used it for food, education and medical costs; hardly transformative, but the regularity offered security and a sense of agency.
More detailed work by Prof Kotiswaran and colleagues shows mixed outcomes.
In Assam, most women spent the money on essentials; many appreciated the dignity it afforded, but few linked it to recognition of unpaid work, and most would still prefer paid jobs.
In Tamil Nadu, women getting the money spoke of peace of mind, reduced marital conflict and newfound confidence – a rare social dividend. In Karnataka, beneficiaries reported eating better, gaining more say in household decisions and wanting higher payments.
Yet only a sliver understood the scheme as compensation for unpaid care work; messaging had not travelled. Even so, women said the money allowed them to question politicians and manage emergencies. Across studies, the majority of women had full control of the cash.
“The evidence shows that the cash transfers are tremendously useful for women to meet their own immediate needs and those of their households. They also restore dignity to women who are otherwise financially dependent on their husbands for every minor expense,” Prof Kotiswaran says.
Importantly, none of the surveys finds evidence that the money discourages women from seeking paid work or entrench gender roles – the two big feminist fears, according to a report by Prof Kotiswaran along with Gale Andrew and Madhusree Jana.
Nor have they reduced women’s unpaid workload, the researchers find. They do, however, strengthen financial autonomy and modestly strengthen bargaining power. They are neither panacea nor poison: they are useful but limited tools, operating in a patriarchal society where cash alone cannot undo structural inequities.

What next?
The emerging research offers clear hints.
Eligibility rules should be simplified, especially for women doing heavy unpaid care work. Transfers should remain unconditional and independent of marital status.
But messaging should emphasise women’s rights and the value of unpaid work, and financial-literacy efforts must deepen, researchers say. And cash transfers cannot substitute for employment opportunities; many women say what they really want is work that pays and respect that endures.
“If the transfers are coupled with messaging on the recognition of women’s unpaid work, they could potentially disrupt the gendered division of labour when paid employment opportunities become available,” says Prof Kotiswaran.
India’s quiet cash transfers revolution is still in its early chapters. But it already shows that small, regular sums – paid directly to women – can shift power in subtle, significant ways.
Whether this becomes a path to empowerment or merely a new form of political patronage will depend on what India chooses to build around the money.
[BBC]
Features
People set example for politicians to follow

Some opposition political parties have striven hard to turn the disaster of Cyclone Ditwah to their advantage. A calamity of such unanticipated proportions ought to have enabled all political parties to come together to deal with this tragedy. Failure to do so would indicate both political and moral bankruptcy. The main issue they have forcefully brought up is the government’s failure to take early action on the Meteorological Department’s warnings. The Opposition even convened a meeting of their own with former President Ranil Wickremesinghe and other senior politicians who shared their experience of dealing with natural and man-made disasters of the past, and the present government’s failures to match them.
The difficulty to anticipate the havoc caused by the cyclone was compounded by the neglect of the disaster management system, which includes previous governments that failed to utilise the allocated funds in an open, transparent and corruption free manner. Land designated as “Red Zones” by the National Building Research Organisation (NBRO), a government research and development institute, were built upon by people and ignored by successive governments, civil society and the media alike. NBRO was established in 1984. According to NBRO records, the decision to launch a formal “Landslide Hazard Zonation Mapping Project (LHMP)” dates from 1986. The institutional process of identifying landslide-prone slopes, classifying zones (including what we today call “Red Zones”), and producing hazard maps, started roughly 35 to 40 years ago.
Indonesia, Thailand and the Philippines which were lashed by cyclones at around the same time as Sri Lanka experienced Cyclone Ditwah were also unprepared and also suffered enormously. The devastation caused by cyclones in the larger southeast Asian region is due to global climate change. During Cyclone Ditwah some parts of the central highlands received more than 500 mm of rainfall. Official climatological data cite the average annual rainfall for Sri Lanka as roughly 1850 mm though this varies widely by region: from around 900 mm in the dry zones up to 5,000 mm in wet zones. The torrential rains triggered by Ditwah were so heavy that for some communities they represented a rainfall surge comparable to a major part of their typical annual rainfall.
Inclusive Approach
Climate change now joins the pantheon of Sri Lanka’s challenges that are beyond the ability of a single political party or government to resolve. It is like the economic bankruptcy, ethnic conflict and corruption in governance that requires an inclusive approach in which the Opposition, civil society, religious society and the business community need to join rather than merely criticise the government. It will be in their self-interest to do so. A younger generation (Gen Z), with more energy and familiarity with digital technologies filled, the gaps that the government was unable to fill and, in a sense, made both the Opposition and traditional civil society redundant.
Within hours of news coming in that floods and landslides were causing havoc to hundreds of thousands of people, a people’s movement for relief measures was underway. There was no one organiser or leader. There were hundreds who catalysed volunteers to mobilise to collect resources and to cook meals for the victims in community kitchens they set up. These community kitchens sprang up in schools, temples, mosques, garages and even roadside stalls. Volunteers used social media to crowdsource supplies, match donors with delivery vehicles, and coordinate routes that had become impassable due to fallen trees or mudslides. It was a level of commitment and coordination rarely achieved by formal institutions.
The spontaneous outpouring of support was not only a youth phenomenon. The larger population, too, contributed to the relief effort. The Galle District Secretariat sent 23 tons of rice to the cyclone affected areas from donations brought by the people. The Matara District Secretariat made arrangements to send teams of volunteers to the worst affected areas. Just as in the Aragalaya protest movement of 2022, those who joined the relief effort were from all ethnic and religious communities. They gave their assistance to anyone in need, regardless of community. This showed that in times of crisis, Sri Lankans treat others without discrimination as human beings, not as members of specific communities.
Turning Point
The challenge to the government will be to ensure that the unity among the people that the cyclone disaster has brought will outlive the immediate relief phase and continue into the longer term task of national reconstruction. There will be a need to rethink the course of economic development to ensure human security. President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has spoken about the need to resettle all people who live above 5000 feet and to reforest those areas. This will require finding land for resettlement elsewhere. The resettlement of people in the hill country will require that the government address the issue of land rights for the Malaiyaha Tamils.
Since independence the Malaiyaha Tamils have been collectively denied ownership to land due first to citizenship issues and now due to poverty and unwillingness of plantation managements to deal with these issues in a just and humanitarian manner beneficial to the workers. Their resettlement raises complex social, economic and political questions. It demands careful planning to avoid repeating past mistakes where displaced communities were moved to areas lacking water, infrastructure or livelihoods. It also requires political consensus, as land is one of the most contentious issues in Sri Lanka, tied closely to identity, ethnicity and historical grievances. Any sustainable solution must go beyond temporary relocation and confront the historical exclusion of the Malaiyaha Tamil community, whose labour sustains the plantation economy but who remain among the poorest groups in the country.
Cyclone Ditwah has thus become a turning point. It has highlighted the need to strengthen governance and disaster preparedness, but it has also revealed a different possibility for Sri Lanka, one in which the people lead with humanity and aspire for the wellbeing of all, and the political leadership emulates their example. The people have shown through their collective response to Cyclone Ditwah that unity and compassion remain strong, which a sincere, moral and hardworking government can tap into. The challenge to the government will be to ensure that the unity among the people that the cyclone disaster has brought will outlive the immediate relief phase and continue into the longer term task of national reconstruction with political reconciliation.
by Jehan Perera
Features
An awakening: Revisiting education policy after Cyclone Ditwah

 In the short span of two or three days, Cyclone Ditwah, has caused a disaster of unprecedented proportions in our midst. Lashing away at almost the entirety of the country, it has broken through the ramparts of centuries old structures and eroded into areas, once considered safe and secure.
In the short span of two or three days, Cyclone Ditwah, has caused a disaster of unprecedented proportions in our midst. Lashing away at almost the entirety of the country, it has broken through the ramparts of centuries old structures and eroded into areas, once considered safe and secure.
The rains may have passed us by. The waters will recede, shops will reopen, water will be in our taps, and we can resume the daily grind of life. But it will not be the same anymore; it should not be. It should not be business as usual for any of us, nor for the government. Within the past few years, Sri Lankan communities have found themselves in the middle of a crisis after crisis, both natural and man-made, but always made acute by the myopic policies of successive governments, and fuelled by the deeply hierarchical, gendered and ethnicised divides that exist within our societies. The need of the hour for the government today is to reassess its policies and rethink the directions the country, as a whole, has been pushed into.
Neoliberal disaster
In the aftermath of the devastation caused by the natural disaster, fundamental questions have been raised about our existence. Our disaster is, in whole or in part, the result of a badly and cruelly managed environment of the planet. Questions have been raised about the nature of our economy. We need to rethink the way land is used. Livelihoods may have to be built anew, promoting people’s welfare, and by deveoloping a policy on climate change. Mega construction projects is a major culprit as commentators have noted. Landslides in the upcountry are not merely a result of Ditwah lashing at our shores and hills, but are far more structural and points to centuries of mismanagement of land. (https://island.lk/weather-disasters-sri-lanka-flooded-by-policy-blunders-weak-enforcement-and-environmental-crime-climate-expert/). It is also about the way people have been shunted into lands, voluntarily or involuntarily, that are precarious, in their pursuit of a viable livelihood, within the limited opportunities available to them.
Neo liberal policies that demand unfettered land appropriation and built on the premise of economic growth at any expense, leading to growing rural-urban divides, need to be scrutinised for their short and long term consequences. And it is not that any of these economic drives have brought any measure of relief and rejuvenation of the economy. We have been under the tyrannical hold of the IMF, camouflaged as aid and recovery, but sinking us deeper into the debt trap. In October 2025, Ahilan Kadirgamar writes, that the IMF programme by the end of 2027, “will set up Sri Lanka for the next crisis.” He also lambasts the Central Bank and the government’s fiscal policy for their punishing interest rates in the context of disinflation and rising poverty levels. We have had to devalue the rupee last month, and continue to rely on the workforce of domestic workers in West Asia as the major source of foreign exchange. The government’s negotiations with the IMF have focused largely on relief and infrastructure rebuilding, despite calls from civil society, demanding debt justice.
The government has unabashedly repledged its support for the big business class. The cruelest cut of them all is the appointment of a set of high level corporate personalities to the post-disaster recovery committee, with the grand name, “Rebuilding Sri Lanka.” The message is loud and clear, and is clearly a slap in the face of the working people of the country, whose needs run counter to the excessive greed of extractive corporate freeloaders. Economic growth has to be understood in terms that are radically different from what we have been forced to think of it as, till now. For instance, instead of investment for high profits, and the business of buy and sell in the market, rechannel investment and labour into overall welfare. Even catch phrases like sustainable development have missed their mark. We need to think of the economy more holistically and see it as the sustainability of life, livelihood and the wellbeing of the planet.
The disaster has brought on an urgency for rethinking our policies. One of the areas where this is critical is education. There are two fundamental challenges facing education: Budget allocation and priorities. In an address at a gathering of the Chamber of Commerce, on 02 December, speaking on rebuilding efforts, the Prime Minister and Minister of Education Dr. Harini Amarasuriya restated her commitment to the budget that has been passed, a budget that has a meagre 2.4% of the GDP allocated for education. This allocation for education comes in a year that educational reforms are being rolled out, when heavy expenses will likely be incurred. In the aftermath of the disaster, this has become more urgent than ever.
Reforms in Education
The Government has announced a set of amendments to educational policy and implementation, with little warning and almost no consultation with the public, found in the document, Transforming General Education in Sri Lanka 2025 published by the Ministry of Education. Though hailed as transformative by the Prime Minister (https://www.news.lk/current-affairs/in-the-prevailing-situation-it-is-necessary-to-act-strategically-while-creating-the-proper-investments-ensuring-that-actions-are-discharged-on-proper-policies-pm), the policy is no more than a regurgitation of what is already there, made worse. There are a few welcome moves, like the importance placed on vocational training. Here, I want to raise three points relating to vital areas of the curriculum that are of concern: 1) streamlining at an early age; relatedly 2) prioritising and privileging what is seen as STEM education; and 3) introducing a credit-based modular education.
1. A study of the policy document will demonstrate very clearly that streamlining begins with Junior Secondary Education via a career interest test, that encourages students to pursue a particular stream in higher studies. Further Learning Modules at both “Junior Secondary Education” and “Senior Secondary Education Phase I,” entrench this tendency. Psychometric testing, that furthers this goal, as already written about in our column (https://kuppicollective.lk/psychometrics-and-the-curriculum-for-general-education/) points to the bizarre.
2. The kernel of the curriculum of the qualifying examination of Senior Secondary Education Phase I, has five mandatory subjects, including First Language, Math, and Science. There is no mandatory social science or humanities related subject. One can choose two subjects from a set of electives that has history and geography as separate subjects, but a Humanities/Social Science subject is not in the list of mandatory subjects. .
3. A credit-based, modular education: Even in universities, at the level of an advanced study of a discipline, many of us are struggling with module-based education. The credit system promotes a fragmented learning process, where, depth is sacrificed for quick learning, evaluated numerically, in credit values.
Units of learning, assessed, piece meal, are emphasised over fundamentals and the detailing of fundamentals. Introducing a module based curriculum in secondary education can have an adverse impact on developing the capacity of a student to learn a subject in a sustained manner at deeper levels.
Education wise, and pedagogically, we need to be concerned about rigidly compartmentalising science oriented, including technological subjects, separately from Humanities and Social Studies. This cleavage is what has led to the idea of calling science related subjects, STEM, automatically devaluing humanities and social sciences. Ironically, universities, today, have attempted, in some instances, to mix both streams in their curriculums, but with little success; for the overall paradigm of education has been less about educational goals and pedagogical imperatives, than about technocratic priorities, namely, compartmentalisation, fragmentation, and piecemeal consumerism. A holistic response to development needs to rethink such priorities, categorisations and specialisations. A social and sociological approach has to be built into all our educational and development programmes.
National Disasters and Rebuilding Community
In the aftermath of the disaster, the role of education has to be rethought radically. We need a curriculum that is not trapped in the dichotomy of STEM and Humanities, and be overly streamlined and fragmented. The introduction of climate change as a discipline, or attention to environmental destruction cannot be a STEM subject, a Social Science/Humanities subject or even a blend of the two. It is about the vision of an economic-cum-educational policy that sees the environment and the economy as a function of the welfare of the people. Educational reforms must be built on those fundamentals and not on real or imagined short term goals, promoted at the economic end by neo liberal policies and the profiteering capitalist class.
As I write this, the sky brightens with its first streaks of light, after days of incessant rain and gloom, bringing hope into our hearts, and some cheer into the hearts of those hundreds of thousands of massively affected people, anxiously waiting for a change in the weather every second of their lives. The sense of hope that allows us to forge ahead is collective and social. The response by Lankan communities, to the disaster, has been tremendously heartwarming, infusing hope into what still is a situation without hope for many. This spirit of collective endeavour holds the promise for what should be the foundation for recovery. People’s demands and needs should shape the re-envisioning of policy, particularly in the vital areas of education and economy.
(Sivamohan Sumathy was formerly attached to the Department of English, University of Peradeniya)
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
By Sivamohan Sumathy
-
News6 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
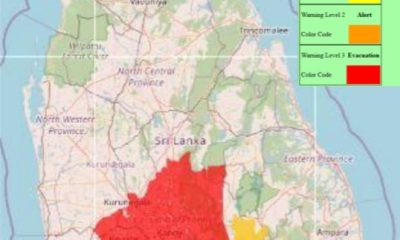
 News5 days ago
News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoHouse erupts over Met Chief’s 12 Nov unheeded warning about cyclone Ditwah













