Features
Reminiscing of Pengiriwatta, hundred hours later!
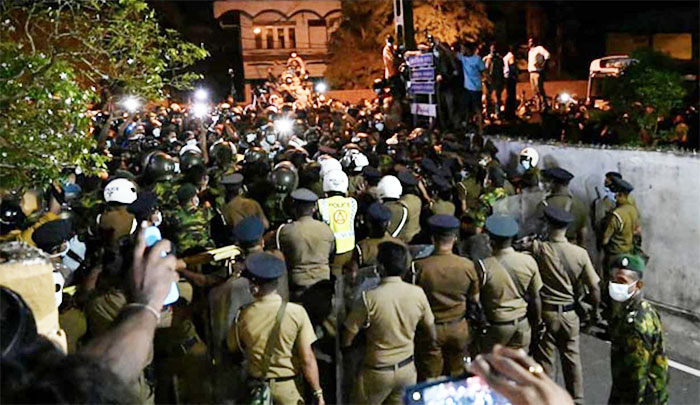
By Austin Fernando
The 31 March afternoon protest at the Jubilee Post against the high cost of living, various shortages, etc., initially caused by a dollar shortage, gathered momentum by the evening. By late evening it grabbed the headlines both nationally and internationally; the protesters’ slogans changed from a demand for redress to their grievances to a strident call for President Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s resignation. By the following morning—on April Fool’s Day—the Presidential Media Unit (PMU) sought to make the protest out to be an uprising engineered by ‘extremists’. It was no April Fool’s joke; the PMU was dead serious although their claim was laughable.
The intelligence services would have got wind of the 31 March event beforehand. This fact was borne out by special security arrangements at the Pengiriwatte Road that night. However, the man who lectured the police personnel and urged them to be tolerant of protestors, according to later reports, was found at the Kalubowila Hospital the following morning.
I have seen a video showing a person burning an Army bus when hundreds of military, police, and Special Task Force personnel were at the site. This man is a courageous ‘extremist’ for what he did in full view of the armed police and military personnel. I hope he is in custody and has been indicted for destroying public property.
Otherwise, immediate action should be taken against the security personnel who were on duty at the time for two reasons. The destruction of public property is illegal, and the offence was apparently committed with the connivance of the security personnel, as suggested by social media, which alleged that the arson attack had been aimed at facilitating the imposition of a curfew and the declaration of Emergency. However, the people defied the curfew and emergency regulations and protests continued.
Managerial weaknesses
Most commentators gave either a political or economic twist or a combination of both to the incident. I consider it essentially a managerial issue concerning the President, and his government. Let me look at these issues from a different perspective.
Everyone, except the President and the ruling party, says that the dollar crisis is due to the government’s financial mismanagement. The blame game continues with those in power holding their predecessors responsible for the economic crisis, and vice versa. As former Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe said, at the rate the buck was being passed, the blame would have to be laid at the feet of Prince Vijaya.
If the crisis has developed under successive governments why didn’t people during the Yahapalana or Suba Anagathyak, or Ranil- Sirisena Alliance, Chandrika Kumaratunga, JR Jayewardene, and R Premadasa regimes storm Ward Place, Gunasinghepura, Horagolla, Temple Trees, or Paget Road? Even during Prime Minister Sirimavo Bandaranaike’s tenure (1970-77), the people experienced hardships, albeit not to the same extent as today, but they did not besiege Tintagel, at 65 Rosmead Place, shouting, “Sirima go home!” The lady that she was, Mrs. B might have chucked up if such a thing ever happened!
The reaction of the government exhibits a lack of moral courage to accept guilt, accountability, and responsibility for its inefficiency and ineffectiveness in keeping with good governance. If it had demonstrated such courage, the people would have appreciated the President’s strength of character. They expected that of the President, who claimed to be apolitical in the run-up to the 2019 presidential election.
Negative constitutional responses
Firstly, the government’s disregard for legislative control over public finance caused the breakdown of financial management. The President, his government, and even the Speaker of the House have shown a callous disregard for Article 148, which gives Parliament the authority over public finance. In a way, why hold All-Party Meetings (APMs) when all parties in the Parliament could discuss all issues in the House?
There may have been a reason why the President did not want to expose the Minister of Finance to Parliament, but the half-witted responses from the State Minister of Finance Semasinghe only made an already bad situation worse.
The constitutional authority has a much larger implication too. The 20th Amendment enables the President to override other stakeholders including Ministers, State Ministers, any public officials, or even the Prime Minister. The fear of the President or his powers has taken a heavy toll on the other state institutions and their performance. The government is beset with demands for a referendum and elections.
It is imperative that the 20th Amendment be abolished and the 19th Amendment reintroduced with necessary improvements. Former President Maithripala Sirisena and Leader of the Opposition Sajith Premasada demanded this on 05 April 2022, in Parliament.
Respect for the rule of law is a cornerstone of good governance. The laws have not been passed by Parliament to promote the interests of the governments in power. Successive governments have disregarded the rule of law, but that does not mean it should continue.
The Opposition has been calling for a discussion of financial status, and agreements reached with foreign powers. But the government has not respected parliamentary traditions, and the Opposition’s request has not been granted. If securing the cooperation of other political stakeholders was uppermost in the minds of the government leaders, they should have cooperated by respecting parliamentary traditions and practices.
Management style
Secondly, the President’s military style of management – ‘Comply and complain’, which gives administrative leeway in decision-making, does not fit the public administration systems, especially in a troubled situation when large numbers are affected, and consultation and consensus-making pay better. “Treat verbal orders as circulars” (Hindu 26-9-2020) is not the accepted norm in public administration. Probably this difference in approach must be creating irritation and anxiety in the President when action is not taken on his verbal directives. This has led to a hierarchic system failure, evolving from Weberian times.
Preparedness
Thirdly, what we are facing is a national crisis, there should have been solutions proposed by the ‘greats’ in Viyathmaga, consisting of intellectuals who claim to be capable of ushering in prosperity. Unfortunately, this outfit has failed to live up to the people’s expectations. Those self-proclaimed experts should have had the courage to own up to their non-performance. For example, on the carbonic agriculture issue, serious studies were treated with disdain. Litro Gas managed by a top Viyathmaga member failed miserably.
They should also have called for support from other stakeholders. It is a managerial collaboration. The President and the government were elected by the people and all political parties should have done their best to solve the crisis because it is the people who suffer. I find this commitment lacking also in the Opposition. Both the government and the Opposition have put power politics before the interests of the people.
Political consensus
Fourthly, the crisis has existed for nearly twenty months, and an All-Party Meeting (APM) was held only a fortnight ago. Some in the Opposition boycotted it, probably suspecting the intentions of the government. At that event too, the approach of the Governor of the Central Bank Ajith Nivard Cabraal was antagonistic, and the President had to apologise to former Premier Ranil Wickremesinghe. It only showed the Governor’s attitude towards coping with a national crisis, which requires a concerted effort by both the government and the Opposition.
I do not blame the President personally for such weaknesses because as publicly acknowledged by him, he lacks political experience and comparatively expediency, and probably PM Mahinda Rajapaksa and others in the government are au fait with APMs. However, what is demonstrated is a lack of focus, positive attitudes, and preparedness as a team.
Failed communication
Fifthly, the Pengiriwatta protest was a response to the cumulative effect of several decisions of the government—the unplanned production and use of carbonic fertilizer, controversial tax concessions given in 2019, the mishandling of international sovereign bonds, the wrong prioritisation of development projects, alleged disposal of public assets to foreigners, etc. Some of these were resisted even by former President Maithripala Sirisena, Opposition parliamentarians, economists, academics, and business tycoons. But their concerns were pooh-poohed by the President, government spokespersons, and by the then Governor of CBSL. Therefore, it amounted to a failure in communication with stakeholders, reducing managerial cooperation.
The current wave of mass civil disobedience and public protests show what could happen when communication and the cause of natural justice (the right to be heard, a respected managerial/ legal principle) is ignored. This will be a lesson for everyone, inclusive of the protesters who aim to bring to power a new set of ‘undeclared leaders’.
Failed bureaucracy and advisors
Sixthly, senior bureaucrats and advisors have also failed. I remember how Presidents J. R. Jayewardene, R Premadasa et al respected their advisors and senior bureaucrats. I had the personal experience with President Maithripala Sirisena heeding even very critical decisions made by me along with the then-Attorney General. This was the case even with President Jayewardene as well. There were instances where we failed to convince ministers and the President, but we must continue to make representations. Overall, there was no retaliation as such, so much so that I was appointed a Secretary a short time after I had refused to carry out an irregular request made to me by President Jayewardene. There were also exceptions. Under Pohottuwa the best example of contradiction was how Secretaries of Agriculture were replaced, for reasons best known to them. We will hear about what the public officials are undergoing at present when they write their memoirs.
If views and proposals are not taken on board, it either shows their inability to convince the political authorities, or politicians’ unwillingness to heed wise counsel. Two cases in point are how financial experts advised the President and others on the need to restructure International Sovereign Bonds worth 500 million dollars and green agriculture experiments. Both were disregarded. Experts, researchers et al were removed from the planning and management system, and a medical trade unionist and a politically-affiliated priest replaced them in deciding on the fertilizer issue.
Weak coordination
Seventhly, a coordinated approach to management is lacking. The best example is how solutions are adopted in an ad hoc manner. Conflicting views end with Ministers resigning due to weakened policy implementation. The Ministry of Finance and the Governor of the Central Bank, who has now resigned, used to make contradictory statements.
Although it appears that the government wishes to go to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and letters are probably being exchanged through our Mission in Washington, it is not publicly supported by relevant stakeholders. It is unknown whether groundwork has been done to suit the operation such as the appointment of an advisory experts’ committee in Sri Lanka, the hiring of international consultants, lawyers, approaching the Paris Club and the London Club (both informal groups of creditor nations who engage in finding workable solutions to payment problems faced by debtor nations), meeting a group of helpful countries for short-term bridging finance, and other relevant institutions that matter. Preparing a roadmap is of the essence.
The IMF operation will require tough fiscal management and foreign exchange rate management, undertaking serious reforms for which the government will have to find a consensus with the Opposition and negotiations should commence thereon.
Conclusion
It is easy for me to make these observations. These weaknesses are not easy to rectify. Besides commitment, the task requires other things such as managerial skills, serious study, etc.
Using accepted systems of planning, organising, directing, staffing, coordinating, and reviewing, adjusting budgets to suit the best financial management must be adopted. Programmes such as the ‘distribution’ of nearly Rs. 220 billion to party-men a month after the passage of the national budget must be scrapped. However, hard decisions should be made, especially if a new IMF agenda is to commence. These issues are not easy to tackle.
They may include revenue generation, expenditure rationalisation, reviewing the operation of loss-making state-owned enterprises, reviewing, and restructuring the public service, addressing the subsidies for the affected poor, coordinating with many institutions here and abroad, structural changes, and focusing on new inclusive financing avenues, etc. Hard times are projected and a united effort is required.
The public demand for recovering stolen public assets may need new legal interventions under principles of recovery, for which assistance from the UN could be obtained.
The government must consider the importance of its obligation to its electors. The Opposition must also realise it will be its turn to face the guillotine will also come if the country continues battling.
The problem is gargantuan and we should find ways and means of overcoming the daunting challenges. Essentially, we must depend on ourselves as efficient and effective operatives. Dhammapada – Stanza 160, provides us with a guide:
Atta hi attano nathoko hi natho paro siyaattana hi sudantenanatham labhati dullabham.
(One indeed is one’s refuge; how can others be a refuge to one? With oneself thoroughly tamed, one can attain refuge, which is so difficult to attain.)
In the wake of Pengiriwatte, let the government be urged to work on its managerial weaknesses. It is our responsibility- the Government and the Opposition, to work together as a nation. Others cannot be a refuge; they could only be a prop. However, whether public protests continue or fizzle out, the government and other stakeholders must act fast to avoid disaster.
Features
Lasting solutions require consensus

Problems and solutions in plural societies like Sri Lanka’s which have deep rooted ethnic, religious and linguistic cleavages require a consciously inclusive approach. A major challenge for any government in Sri Lanka is to correctly identify the problems faced by different groups with strong identities and find solutions to them. The durability of democratic systems in divided societies depends less on electoral victories than on institutionalised inclusion, consultation, and negotiated compromise. When problems are defined only through the lens of a single political formation, even one that enjoys a large electoral mandate, such as obtained by the NPP government, the policy prescriptions derived from that diagnosis will likely overlook the experiences of communities that may remain outside the ruling party. The result could end up being resistance to those policies, uneven implementation and eventual political backlash.
A recent survey done by the National Peace Council (NPC), in Jaffna, in the North, at a focus group discussion for young people on citizen perception in the electoral process, revealed interesting developments. The results of the NPC micro survey support the findings of the national survey by Verite Research that found that government approval rating stood at 65 percent in early February 2026. A majority of the respondents in Jaffna affirm that they feel safer and more fairly treated than in the past. There is a clear improving trend to be seen in some areas, but not in all. This survey of predominantly young and educated respondents shows 78 percent saying livelihood has improved and an equal percentage feeling safe in daily life. 75 percent express satisfaction with the new government and 64 percent believe the state treats their language and culture fairly. These are not insignificant gains in a region that bore the brunt of three decades of war.
Yet the same survey reveals deep reservations that temper this optimism. Only 25 percent are satisfied with the handling of past issues. An equal percentage see no change in land and military related concerns. Most strikingly, almost 90 percent are worried about land being taken without consent for religious purposes. A significant number are uncertain whether the future will be better. These negative sentiments cannot be brushed aside as marginal. They point to unresolved structural questions relating to land rights, demilitarisation, accountability and the locus of political power. If these issues are not addressed sooner rather than later, the current stability may prove fragile. This suggests the need to build consensus with other parties to ensure long-term stability and legitimacy, and the need for partnership to address national issues.
NPP Absence
National or local level problems solving is unlikely to be successful in the longer term if it only proceeds from the thinking of one group of people even if they are the most enlightened. Problem solving requires the engagement of those from different ethno-religious, caste and political backgrounds to get a diversity of ideas and possible solutions. It does not mean getting corrupted or having to give up the good for the worse. It means testing ideas in the public sphere. Legitimacy flows not merely from winning elections but from the quality of public reasoning that precedes decision-making. The experience of successful post-conflict societies shows that long term peace and development are built through dialogue platforms where civil society organisations, political actors, business communities, and local representatives jointly define problems before negotiating policy responses.
As a civil society organisation, the National Peace Council engages in a variety of public activities that focus on awareness and relationship building across communities. Participants in those activities include community leaders, religious clergy, local level government officials and grassroots political party representatives. However, along with other civil society organisations, NPC has been finding it difficult to get the participation of members of the NPP at those events. The excuse given for the absence of ruling party members is that they are too busy as they are involved in a plenitude of activities. The question is whether the ruling party members have too much on their plate or whether it is due to a reluctance to work with others.
The general belief is that those from the ruling party need to get special permission from the party hierarchy for activities organised by groups not under their control. The reluctance of the ruling party to permit its members to join the activities of other organisations may be the concern that they will get ideas that are different from those held by the party leadership. The concern may be that these different ideas will either corrupt the ruling party members or cause dissent within the ranks of the ruling party. But lasting reform in a plural society requires precisely this exposure. If 90 percent of surveyed youth in Jaffna are worried about land issues, then engaging them, rather than shielding party representatives from uncomfortable conversations, is essential for accurate problem identification.
North Star
The Leader of the Lanka Sama Samaja Party (LSSP), Prof Tissa Vitarana, who passed away last week, gave the example for national level problem solving. As a government minister he took on the challenge the protracted ethnic conflict that led to three decades of war. He set his mind on the solution and engaged with all but never veered from his conviction about what the solution would be. This was the North Star to him, said his son to me at his funeral, the direction to which the Compass (Malimawa) pointed at all times. Prof Vitarana held the view that in a diverse and plural society there was a need to devolve power and share power in a structured way between the majority community and minority communities. His example illustrates that engagement does not require ideological capitulation. It requires clarity of purpose combined with openness to dialogue.
The ethnic and religious peace that prevails today owes much to the efforts of people like Prof Vitarana and other like-minded persons and groups which, for many years, engaged as underdogs with those who were more powerful. The commitment to equality of citizenship, non-racism, non-extremism and non-discrimination, upheld by the present government, comes from this foundation. But the NPC survey suggests that symbolic recognition and improved daily safety are not enough. Respondents prioritise personal safety, truth regarding missing persons, return of land, language use and reduction of military involvement. They are also asking for jobs after graduation, local economic opportunity, protection of property rights, and tangible improvements that allow them to remain in Jaffna rather than migrate.
If solutions are to be lasting they cannot be unilaterally imposed by one party on the others. Lasting solutions cannot be unilateral solutions. They must emerge from a shared diagnosis of the country’s deepest problems and from a willingness to address the negative sentiments that persist beneath the surface of cautious optimism. Only then can progress be secured against reversal and anchored in the consent of the wider polity. Engaging with the opposition can help mitigate the hyper-confrontational and divisive political culture of the past. This means that the ruling party needs to consider not only how to protect its existing members by cloistering them from those who think differently but also expand its vision and membership by convincing others to join them in problem solving at multiple levels. This requires engagement and not avoidance or withdrawal.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Unpacking public responses to educational reforms

 As the debate on educational reforms rages, I find it useful to pay as much attention to the reactions they have excited as we do to the content of the reforms. Such reactions are a reflection of how education is understood in our society, and this understanding – along with the priorities it gives rise to – must necessarily be taken into account in education policy, including and especially reform. My aim in this piece, however, is to couple this public engagement with critical reflection on the historical-structural realities that structure our possibilities in the global market, and briefly discuss the role of academics in this endeavour.
As the debate on educational reforms rages, I find it useful to pay as much attention to the reactions they have excited as we do to the content of the reforms. Such reactions are a reflection of how education is understood in our society, and this understanding – along with the priorities it gives rise to – must necessarily be taken into account in education policy, including and especially reform. My aim in this piece, however, is to couple this public engagement with critical reflection on the historical-structural realities that structure our possibilities in the global market, and briefly discuss the role of academics in this endeavour.
Two broad reactions
The reactions to the proposed reforms can be broadly categorised into ‘pro’ and ‘anti’. I will discuss the latter first. Most of the backlash against the reforms seems to be directed at the issue of a gay dating site, accidentally being linked to the Grade 6 English module. While the importance of rigour cannot be overstated in such a process, the sheer volume of the energies concentrated on this is also indicative of how hopelessly homophobic our society is, especially its educators, including those in trade unions. These dispositions are a crucial part of the reason why educational reforms are needed in the first place. If only there was a fraction of the interest in ‘keeping up with the rest of the world’ in terms of IT, skills, and so on, in this area as well!
Then there is the opposition mounted by teachers’ trade unions and others about the process of the reforms not being very democratic, which I (and many others in higher education, as evidenced by a recent statement, available at https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/ ) fully agree with. But I earnestly hope the conversation is not usurped by those wanting to promote heteronormativity, further entrenching bigotry only education itself can save us from. With this important qualification, I, too, believe the government should open up the reform process to the public, rather than just ‘informing’ them of it.
It is unclear both as to why the process had to be behind closed doors, as well as why the government seems to be in a hurry to push the reforms through. Considering other recent developments, like the continued extension of emergency rule, tabling of the Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PSTA), and proposing a new Authority for the protection of the Central Highlands (as is famously known, Authorities directly come under the Executive, and, therefore, further strengthen the Presidency; a reasonable question would be as to why the existing apparatus cannot be strengthened for this purpose), this appears especially suspect.
Further, according to the Secretary to the MOE Nalaka Kaluwewa: “The full framework for the [education] reforms was already in place [when the Dissanayake government took office]” (https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2025/08/12/wxua-a12.html, citing The Morning, July 29). Given the ideological inclinations of the former Wickremesinghe government and the IMF negotiations taking place at the time, the continuation of education reforms, initiated in such a context with very little modification, leaves little doubt as to their intent: to facilitate the churning out of cheap labour for the global market (with very little cushioning from external shocks and reproducing global inequalities), while raising enough revenue in the process to service debt.
This process privileges STEM subjects, which are “considered to contribute to higher levels of ‘employability’ among their graduates … With their emphasis on transferable skills and demonstrable competency levels, STEM subjects provide tools that are well suited for the abstraction of labour required by capitalism, particularly at the global level where comparability across a wide array of labour markets matters more than ever before” (my own previous piece in this column on 29 October 2024). Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) subjects are deprioritised as a result. However, the wisdom of an education policy that is solely focused on responding to the global market has been questioned in this column and elsewhere, both because the global market has no reason to prioritise our needs as well as because such an orientation comes at the cost of a strategy for improving the conditions within Sri Lanka, in all sectors. This is why we need a more emancipatory vision for education geared towards building a fairer society domestically where the fruits of prosperity are enjoyed by all.
The second broad reaction to the reforms is to earnestly embrace them. The reasons behind this need to be taken seriously, although it echoes the mantra of the global market. According to one parent participating in a protest against the halting of the reform process: “The world is moving forward with new inventions and technology, but here in Sri Lanka, our children are still burdened with outdated methods. Opposition politicians send their children to international schools or abroad, while ours depend on free education. Stopping these reforms is the lowest act I’ve seen as a mother” (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/17/pro-educational-reforms-protests-spread-across-sri-lanka). While it is worth mentioning that it is not only the opposition, nor in fact only politicians, who send their children to international schools and abroad, the point holds. Updating the curriculum to reflect the changing needs of a society will invariably strengthen the case for free education. However, as mentioned before, if not combined with a vision for harnessing education’s emancipatory potential for the country, such a move would simply translate into one of integrating Sri Lanka to the world market to produce cheap labour for the colonial and neocolonial masters.
According to another parent in a similar protest: “Our children were excited about lighter schoolbags and a better future. Now they are left in despair” (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/17/pro-educational-reforms-protests-spread-across-sri-lanka). Again, a valid concern, but one that seems to be completely buying into the rhetoric of the government. As many pieces in this column have already shown, even though the structure of assessments will shift from exam-heavy to more interim forms of assessment (which is very welcome), the number of modules/subjects will actually increase, pushing a greater, not lesser, workload on students.

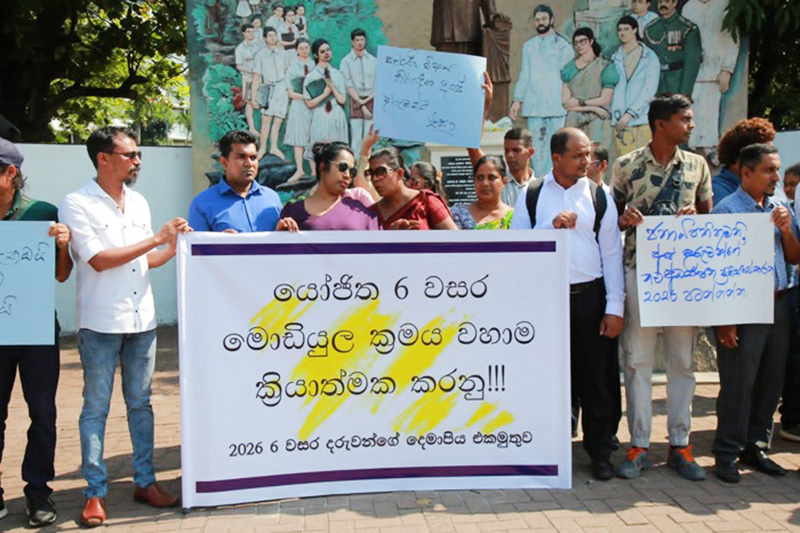
A file photo of a satyagraha against education reforms
What kind of education?
The ‘pro’ reactions outlined above stem from valid concerns, and, therefore, need to be taken seriously. Relatedly, we have to keep in mind that opening the process up to public engagement will not necessarily result in some of the outcomes, those particularly in the HSS academic community, would like to see, such as increasing the HSS component in the syllabus, changing weightages assigned to such subjects, reintroducing them to the basket of mandatory subjects, etc., because of the increasing traction of STEM subjects as a surer way to lock in a good future income.
Academics do have a role to play here, though: 1) actively engage with various groups of people to understand their rationales behind supporting or opposing the reforms; 2) reflect on how such preferences are constituted, and what they in turn contribute towards constituting (including the global and local patterns of accumulation and structures of oppression they perpetuate); 3) bring these reflections back into further conversations, enabling a mutually conditioning exchange; 4) collectively work out a plan for reforming education based on the above, preferably in an arrangement that directly informs policy. A reform process informed by such a dialectical exchange, and a system of education based on the results of these reflections, will have greater substantive value while also responding to the changing times.
Two important prerequisites for this kind of endeavour to succeed are that first, academics participate, irrespective of whether they publicly endorsed this government or not, and second, that the government responds with humility and accountability, without denial and shifting the blame on to individuals. While we cannot help the second, we can start with the first.
Conclusion
For a government that came into power riding the wave of ‘system change’, it is perhaps more important than for any other government that these reforms are done for the right reasons, not to mention following the right methods (of consultation and deliberation). For instance, developing soft skills or incorporating vocational education to the curriculum could be done either in a way that reproduces Sri Lanka’s marginality in the global economic order (which is ‘system preservation’), or lays the groundwork to develop a workforce first and foremost for the country, limited as this approach may be. An inextricable concern is what is denoted by ‘the country’ here: a few affluent groups, a majority ethno-religious category, or everyone living here? How we define ‘the country’ will centrally influence how education policy (among others) will be formulated, just as much as the quality of education influences how we – students, teachers, parents, policymakers, bureaucrats, ‘experts’ – think about such categories. That is precisely why more thought should go to education policymaking than perhaps any other sector.
(Hasini Lecamwasam is attached to the Department of Political Science, University of Peradeniya).
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
Features
Chef’s daughter cooking up a storm…
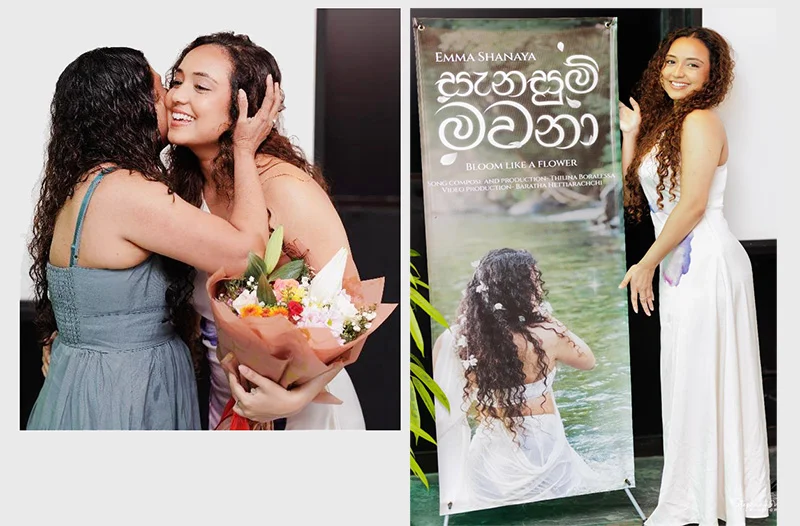
 Don Sherman was quite a popular figure in the entertainment scene but now he is better known as the Singing Chef and that’s because he turns out some yummy dishes at his restaurant, in Rajagiriya.
Don Sherman was quite a popular figure in the entertainment scene but now he is better known as the Singing Chef and that’s because he turns out some yummy dishes at his restaurant, in Rajagiriya.
However, now the spotlight is gradually focusing on his daughter Emma Shanaya who has turned out to be a very talented singer.
In fact, we have spotlighted her in The Island a couple of times and she is in the limelight, once gain.
When Emma released her debut music video, titled ‘You Made Me Feel,’ the feedback was very encouraging and at that point in time she said “I only want to keep doing bigger and greater things and ‘You Made Me Feel’ is the very first step to a long journey.”
Emma, who resides in Melbourne, Australia, is in Sri Lanka, at the moment, and has released her very first Sinhala single.
“I’m back in Sri Lanka with a brand new single and this time it’s a Sinhalese song … yes, my debut Sinhala song ‘Sanasum Mawana’ (Bloom like a Flower).
“This song is very special to me as I wrote the lyrics in English and then got it translated and re-written by my mother, and my amazing and very talented producer Thilina Boralessa. Thilina also composed the music, and mix and master of the track.”
Emma went on to say that instead of a love song, or a young romance, she wanted to give the Sri Lankan audience a debut song with some meaning and substance that will portray her, not only as an artiste, but as the person she is.
Says Emma: “‘Sanasum Mawana’ is about life, love and the essence of a woman. This song is for the special woman in your life, whether it be your mother, sister, friend, daughter or partner. I personally dedicate this song to my mother. I wouldn’t be where I am right now if it weren’t for her.”
On Friday, 30th January, ‘Sanasum Mawana’ went live on YouTube and all streaming platforms, and just before it went live, she went on to say, they had a wonderful and intimate launch event at her father’s institute/ restaurant, the ‘Don Sherman Institute’ in Rajagiriya.
It was an evening of celebration, good food and great vibes and the event was also an introduction to Emma Shanaya the person and artiste.
Emma also mentioned that she is Sri Lanka for an extended period – a “work holiday”.
“I would like to expand my creativity in Sri Lanka and see the opportunities the island has in store for me. I look forward to singing, modelling, and acting opportunities, and to work with some wonderful people.
“Thank you to everyone that is by my side, supporting me on this new and exciting journey. I can’t wait to bring you more and continue to bloom like a flower.”
-

 Life style2 days ago
Life style2 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:



















