Features
Fiftieth anniversary of Martinair pilgrim flight crash near Maskeliya

by Capt Elmo Jayawardena
On December 4, 1974 a DC-8 aircraft belonging to Martinair crashed into the Anjimalai mountain range also known as the Seven Virgins. The accident happened around 10.15 PM and the location was in the vicinity of Maskeliya. This was the worst air disaster that had taken place in Sri Lanka. As many as 191 lives were lost with no survivors. That is how December 4 became a sad night to remember.
Corona curfews give us time to read and in my isolation at home at that timeI have been pulling out ‘bucket-listed’ stories to reflect on. Most articles I browsed through about the Martinair DC-8 crash had covered all aspects of this horrible disaster. Adequate details were available to re-construct the story and come to reasonable conclusions of what may have happened.
We all know the easy way out on most aeroplane crashes has been the first-choice of the hit-parade – PILOT ERROR. The captain is buried beneath the Seven Virgins hills in shamed silence. So is his First Officer and the Flight Engineer. The case is closed and forgotten. I have no defense to rub on behalf of the crew to give even a shallow coating of an excuse.
But and there is a ‘BUT’ I need to mention here. On one side we have technology inundated with fancy aviation jargon. Add to that a half-burnt Black Box and communication tapes between the pilot and the controller. Plus, all the details of the flying records of the crew and what they have done and what they have not done. Then comes a hundred titbits of aeronautical specifics that act as tinsel to an investigation.
All that is fine, valid to be used at round table conferences where aviation-related head umpires and leg umpires, third umpires plus match referees discuss and make decisions taking all the time in the world. It is not the same for the Captain and his crew. No doubt they are professionally competent aircrew. Yet, some decisions to be made in an aeroplane are instant. You win some and you lose some and the ones you lose may have devastating repercussions.
Worst is you may not even be living to tell your side of the story. A few seconds make the difference between life and death. In such calamitous situations we tend to forget that the most lethal ingredient in an aviation disaster is – The Human Factor.
The Captain is not an infallible demi-god who jumped from Mount Olympus and sat in the cockpit of his aeroplane. He is human and so are his crew. They are no different to the ordinary you and me. I have been a Captain for a considerable number of years. I have made many mistakes flying aeroplanes. I humbly say I was lucky I escaped without an accident. There is nothing courageous or brilliant about that, it is simply the way fate rolled the dice. Such would be the story of any Captain. Admitted or not, it is the truth, the absolute truth.
The scales of justice in an aviation accident investigation is handled by competent authorities. In the case of the Martinair DC-8 crash there were three Civil Aviation Departments associated with the inquiry. Sri Lanka, The Netherlands, and Indonesia. Plus, there would have been the McDonnell Douglas Company that built the aeroplane and insurance companies that were present to protect their dollar.
There had been whispers about the Doppler system in this aeroplane having errors which resulted in inaccuracies in the ‘distance to go’. It was also said that the crew were not informed of this. There is nothing to substantiate such statements and as such, it is best that I leave them out and keep them buried along with the aeroplane. I also read that the co-pilot had a traumatic childhood and that could have affected his behavior when approaching to land. I make no comment on such absurdities.
 Let me now take you to the story of the DC 8 that crashed into the Seven Virgins mountain range. The accident tragically killed 191 innocent people (182 passengers + 9 crew). It sure is a terrible night to remember.
Let me now take you to the story of the DC 8 that crashed into the Seven Virgins mountain range. The accident tragically killed 191 innocent people (182 passengers + 9 crew). It sure is a terrible night to remember.
The flight was from Surabaya, Java, to Jeddah via Colombo which was a re-fueling stop. This was Muslim pilgrimage time to Mecca for the Haj. Devotees came from all parts of the world. Some flew in on private jets but most travelled on chartered aeroplanes. The flight that took off from Surabaya was a DC-8 55CF aeroplane owned by Martinair of The Netherlands which had been leased by Garuda Indonesia to fly the Haj charters.
In command was Capt Hendrik Lamme, 58 years old, a very experienced pilot who had flown 27,000 plus flying hours of which 4,000 were on DC-8s. The First Officer Robert Blomsma had 2,480 hours and was new on the DC-8 type with 47 hours. The third crew member, the flight engineer was Johannes Wijnands who had flown 3,000 hours on DC-8 type aeroplanes. Back in the cabin there were six crew members, four were Dutch and two were from Indonesia. The aircraft had a Dutch registration of PH-MBH and was less than 10 years old. The flight plan filed call-sign for the flight was MP 138.
Here I must explain to the reader something about the navigational instruments that the aeroplane had. I want to make it as simple as possible for a non-aviator to understand.
The route from Surabaya to Sri Lanka is mostly oceanic. It starts with an airway called Red-61 and extends on a North-Westerly direction till it reaches the Sri Lankan Flight Information Region (FIR – 92 East longitude) and follows route Golf-462 to cross the coast at a way-point located over Yala. This reporting point unfortunately had no Radio Aid for the pilots to cross-check their navigation when flying overhead.
The primary navigation system that was in use by Martinair was called Doppler. This was operated worldwide by many airlines and during that era it was a primary navigational aid for jet aeroplanes flying long haul sectors. Doppler gave the pilots a digital reading of the distance to go to the way-point it was heading to. However, Doppler system was not overly accurate when flying over water for a long period and had to be updated over a radio beacon or a known geographical position (maybe a river or town) to maintain its accuracy.
Flight MP 138’s route initially had radio beacons to update the Doppler. But the final ocean crossing before coast of Sri Lanka had no radio beacon for the crew to update the Doppler position. That was a long leg, too long to fly without an update.
The last point the DC-8 could have done a navigational cross-check would have been at a way-point closer to Banda Archi airport which was about 135 miles right of their track. From there Capt. Lamme still had to fly close to two hours to reach the coast of Sri Lanka. He was navigating now purely by rudimentary ‘dead-reckoning’ and Doppler ‘distance to go’ readouts without any cross-check to update his position.
Flight MP138 crossed the FIR (Flight Information Region) at 8.27 pm local time – six minutes earlier than the estimate. Calculating its speed by distance between two way-points and time taken, the ground speed would be 478. That is at eight miles a minute. Six minutes would be almost 50 miles. The FIR was about 850 miles from the Sri Lankan coastal way-point. Maybe Capt. Lamme and his crew were getting a wrong ‘distance to go’ reading from their Doppler. It is difficult to fathom whether it was because of the reported fault in this particular aeroplane Doppler or it was because of a very long sea track flown without an update. It could even have been both.
Already there had been a six-minute (50 miles) correction made. Was it correct or was it a Doppler error? There was no way to cross check and update. If it was a Doppler fault that could have been the cause the Martinair DC-8 flew all the way to its death in Maskeliya.
Flight MP 138 first contacted Colombo Air Traffic Control located at Ratmalana at 9.52 PM and reported 130 miles out at 35,000ft. They were only going by the Doppler. The controller answered ‘MP-138 clear descend 10,000 when ready and call 50 miles from Katunayake.” When Capt. Lamme commenced his descent by what his Doppler reading displayed his actual position would have been 50 miles east of where he thought he was. Unfortunately, Katunayake Airport at that time did not have Approach Radar nor a Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) which would have digitally told the pilot exactly how far he was from the airfield.
Few minutes later the DC-8 called “50 miles” and was cleared to 6000 and handed over to Colombo Approach Control at Katunayake. The First Officer who was doing the radio called Colombo Approach at 10.08 PM and reported he was ‘one four” (14) miles from the Katunayake airport passing 7,000 for 6,000. Approach Control had no Radar to see him. The controller had to go purely by the MP 138’s estimate of 14 miles from the airfield. He cleared MP 138 to 2000 ft and told him to call “field in sight” or overhead the KAT radio beacon.
“Roger, cleared 2,000, to KAT or field in sight.” This was at 10.10 by the first Officer.
That sadly was the last communication.
On descent the DC-8 hit the fifth of the Seven Virgins mountains at a height of 4,354 feet. The impact place was about 65 miles from Katunayake. When F/O Blomsma reported 14 miles from the airport, he was most certainly giving the distance from the cockpit Doppler. He had no other instrument to read from other than a possible error-tainted Doppler. If you add 14 miles to the error of 50 miles on the Doppler the answer is 64. Give or take a few miles for the random calculation I am doing and then perhaps the 64 coincides with the distance from Katunayake to where the crash occurred in the Anjimalai (Seven Virgins) hills.
The only other explanation for Capt. Lamme to initiate an early descent could have been a wrongly interpreted weather radar sighting of the eastern coast. These were black and white radar displays and it is possible that a low cloud could have been mistaken for the coast maybe 50 miles before ALGET.
I, in no way can say what I have written is the gospel truth. I have no crystal-clear facts to ponder on. It is just my opinion I am stating. I do have some knowledge on Doppler matters as I have flown these routes in similar aeroplanes using Doppler navigation. Many opinions are expressed by journalists about this disaster. How true such inferences are, is another side of the coin. I was greatly assisted by Sri Lankan Air Traffic Controllers and communication officers, some who handled MP 138 arrival. I am deeply grateful for their first-hand information.
The possibility remains that Capt. Lamme may have commenced his descent approximately 50 miles before the planned point to leave 35,000.
The aeroplane crashed, there were many mitigating factors that left room and would have contributed to human error.
Capt. Hendrik Lamme was guilty of being a human being.
—- —–
Today people driving past Norton Bridge town see a strange sight. A structure displaying a large tyre. It is a wheel from the DC-8 that crashed in the Seven Virgins mountains. It could be all that is left of that magnificent aeroplane owned and flown by the Dutch. If one’s interest is kindled, on the road from Norton Bridge to Maskeliya there is a place where one should stop.
A plaque of remembrance is there, erected in memory of those who are buried around this place at the foot of this hill. The Martinair crew and the Indonesian pilgrims who died on the slopes of the mountain were buried in a common grave by the roadside. People say flowers do get placed off and on at the memorial. In remembrance of who we know but by whom is a question mark?
Up in the mountain is the main memorial, a stone pillar-like monument erected at the actual crash site. Wind-swept and rain-soaked it stands in its forgotten loneliness. Perhaps it whispers its sadness amidst the Seven Virgins mountain range. The column had been erected in remembrance of the 191 innocent people who died there on a sorrowful December night, a long time ago.
(Elmojay1@gmail.com)
Features
A 20-year reflection on housing struggles of Tsunami survivors

Revisiting field research in Ampara
by Prof. Amarasiri de Silva
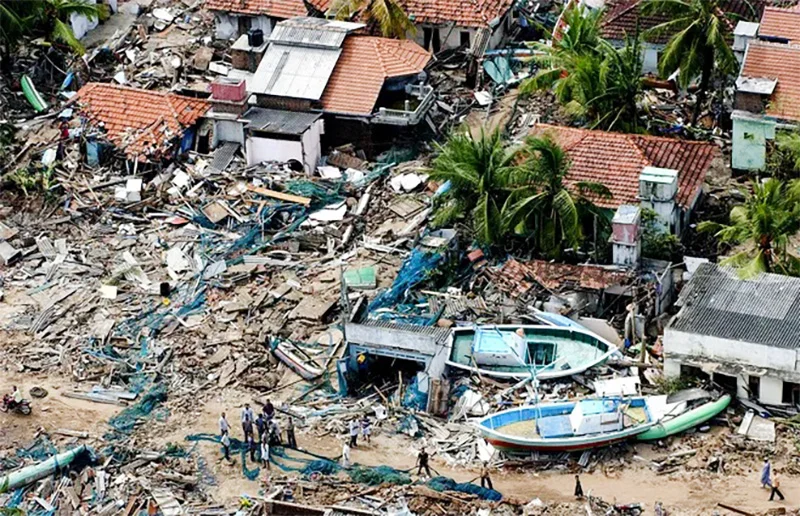
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, also known as the Boxing Day tsunami, triggered by a magnitude 9.1 earthquake off the coast of Sumatra on 26 Dec., 2004, had a catastrophic impact on Sri Lanka. It is estimated to have released energy equivalent to 23,000 Hiroshima-type atomic bombs, wiping out hundreds of communities in minutes. The tsunami struck Sri Lanka’s eastern and southern coasts approximately two hours after the earthquake. The eastern shores, facing the earthquake’s epicenter, bore the brunt of the waves, affecting settlements on the east coast. The tsunami displaced many families and devastated villages and communities in the affected districts of Sri Lanka. Although Boxing Day is associated with exchanging gifts after Christmas and was a time to give to the less fortunate, it brought havoc in Sri Lanka to many communities. It resulted in approximately 31,229 deaths and 4,093 people missing. In terms of the dead and missing numbers, Sri Lanka’s toll was second only to Indonesia (126,804, missing 93,458, displaced 474,619). Twenty-five beach hotels were severely damaged, and another 6 were completely washed away. More than 240 schools were destroyed or sustained severe damage. Several hospitals, telecommunication networks, coastal railway networks, etc., were also damaged. In addition, one and a half million people were displaced from their homes.
Ampara district was a hard-hit district, where more than 10,000 people died. A Galle bound train from Colombo, carrying about 1,700 passengers visiting their ancestral homes and villages, on the Sunday after the Christmas holidays, was struck by the tsunami near Telwatta; most of them were killed.
About 8,000 people were killed in the northeast region, which the LTTE controlled at the time. The Ampara district was a hard-hit district, with more than 10,000 people dying and many more displaced. In sympathy with the victims, the Saudi Arabian government established a grant to construct houses to assist 500 displaced families in Ampara in 2009. The Saudi Envoy in Colombo presented the house keys to President Mahinda Rajapaksa in 2011 for distribution to tsunami victims in the Ampara district. However, due to the protests by local majoritarian ethnic groups, the government intervened, and a court ruling halted the housing distribution to the victims, mandating that houses be allocated according to the country’s population ratio. The project includes residential units and amenities such as a school, a supermarket complex, a hospital, and a mosque, making it unique for Muslim people. Saudi government ambassador Khalid Hamoud Alkahtani engaged in discussions with the Sri Lankan government to sort out the issues and agreed to give the houses to the respective victims.
Immediate Recovery
The immediate relief work was initiated just after the disaster, and the government had financial and moral support from local people and countries worldwide. As most displaced people were children and women, restoring at least basic education facilities for affected children was a high priority. By mid-year, 85 percent of the children in tsunami-affected areas were back in school, which showed that the relief programme in school education was a success.
Relief efforts for households included the provision of finances to meet immediate needs. Compensation of Rs.15,000 (US$150) was offered for victims towards funeral expenses; livelihood support schemes included Payment of Rs.375 (US$3.75) in cash and rations for each member of a family unit per week, a payment of Rs. 2,500 (US$25) towards kitchen utensils per family. These initial measures were largely successful, though there were some problems with a lack of coordination, as witnessed. (See Map 1)
The most considerable financing needs were in the housing sector. The destruction of private assets was substantial (US$700 million), in addition to public infrastructure and other assets. Loss of current output in the fisheries and tourism sectors—which were severely affected—was estimated at US$200 million and US$130 million, respectively.
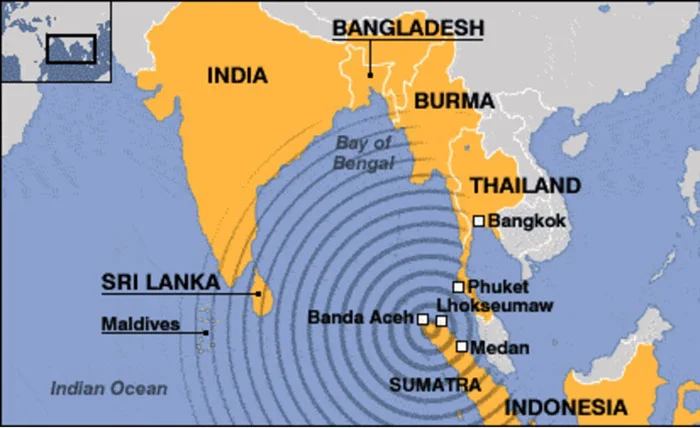
2004 tsunami-impacted zone. (Image courtesy Reliefweb)
Strands of Hope: Progress Made for Tsunami-Affected Communities of Sri Lanka
By mid-June 2005, the number of displaced people was down to 516,000 from approximately 800,000 immediately after the tsunami, as people went home—even if the homes in question were destroyed or damaged—and were taken off the books then. At first, an estimated 169,000 people living in schools and tents were mainly transferred to transitional shelters/camps—designed to serve as a stopgap between emergency housing and permanent homes. This transitional shelter was only supplied to affected households in the buffer zone.
By late August 2005, The Task Force for Rebuilding the Nation (TAFREN) estimated that 52,383 transitional shelters, accommodating an estimated 250,000 tsunami-affected people, had been completed since February 2005 at 492 sites. Those transitional housing programme shelters were expected to be completed with 55,000 by the end of September 2005. This goal seems more than achievable. I did not find evidence to show that it has been achieved.
I did my field research in Ampara district with support from UNDP Colombo, the Department for Research Cooperation, and the Swedish International Development Cooperation.
My research shows that the tsunami affected families in Muslim settlements along the East Coast had a severe housing problem for two reasons.
• First, the GoSL has declared that land within 65 meters of the sea is unsafe for living due to possible seismic effects, and people are thus prohibited from engaging in any construction in that beach area. This land strip is the traditional living area of the Muslims, particularly the fisher folk. Families living along the narrow beach strip have not been offered alternative land or adequate compensation to buy land outside the 65-metre zone.
• Second, the LTTE has prohibited Muslims from building houses on land purchased for them by outside agencies on the pretext that it belongs to the Tamils.
The GoSL established several institutions as a response strategy for post-tsunami recovery after the failure of P-TOMS. The Task Force for Rebuilding the Nation (TAFREN), the Task Force for Relief (TAFOR), and the Tsunami Housing Reconstruction Unit (THRU) were the lead agencies created through processes involving private and public sector participation. In November 2005, following the election of President Mahinda Rajapaksa, the Reconstruction and Development Agency (RADA)was set up. This became an authority with executive powers following the parliamentary ratification of the RADA Act in 2006. RADA’s mandate was to accelerate reconstruction and development activities in the affected areas, functionally replacing all the tsunami organizations and a significant part of the former RRR Ministry. According to RADA, the total number of houses built so far (as of May 2006) in Ampara is 629, while the total housing units pledged is 6,169. At the time of the research (March to June 2006), no housing projects were completed in a predominantly Muslim area.
Compensation for damaged houses was not based on a consistent scheme. As a result, some families received large sums, while others did not get any money. In some instances, those who collected compensation were not the affected families. The Auditor General, S.C. Mayadunne, noted that Payment of an excessive amount, even for minor damages, is due to the payments being made without assessing the cost of restoring the houses to normal condition. (For example, Rs. 100,000 had been paid for minor damages of Rs. 10,000) … Payments made without identifying the value of the damaged houses, thus resulting in heavy expenditure by the government (For example, a sum of Rs. 250,000 had been paid for the destruction of a temporary house valued at Rs. 10,000) (Mayadunne, 2005, p. 8). That compensation was not paid according to an acceptable scheme, which led to agitation among the affected people and provided an opportunity for political manipulation. The LTTE and the TRO requested direct aid for reconstruction work in LTTE-controlled areas. The poor response of the GoSL to this demand was interpreted as indifference on its part towards ethnic minorities in Ampara. Meanwhile, the GoSL provided direct support for tsunami-affected communities in southern Sri Lanka, where the majority were Sinhalese, strengthening this allegation.
Land scarcity in tsunami-affected Ampara and disputes over landownership in the area were the main reasons for not completing the housing programmes. The LTTE contended that the land identified for building houses by the GoSL or purchased by civil society organisations for constructing such houses belongs to the Tamils, an ideology based on a myth of their own, a Tamil hereditary Homeland—paarampariyamaana taayakam’ (Peebles, 1990, p. 41). Consequently, housing programmes could not be implemented at that time.
The land question in the Eastern Province has a history that dates back to 1951 when the Gal Oya Colonisation scheme was established. According to the minority version of this history, in a report submitted by Dr. Hasbullah and his colleagues, it shows that the colonists were selected overwhelmingly from among the Sinhalese rather than the Muslims and Tamils, who were a majority in Ampara at that time, and, as a result, the ethnic balance of Ampara District was disrupted. However, conversely, B.H. Farmer reported in 1957 that Tamils, especially Jaffna Tamils, were ‘chary’ and did not have a ‘tradition of migration,’ which was the apparent reason for less Tamil representation among the colonists of Gal Oya. According to Farmer, up to December 31, 1953, between five and 16 percent of the colonists were chosen from the Districts of Batticaloa, Jaffna and Trincomalee, predominantly Tamil. Contradictory evidence (with a political coloring following the recent rise of ethnicity in this discourse) reports by Dr. Hasbullah that 100,000 acres of agricultural land in the East have been ‘illegally transferred from Muslims to the Tamils’ since the 1990s. The Tamils, however, believe that the land in the Eastern Province is part and parcel of the Tamil Homeland. This new political ideology of landownership that emerged at that time in the ethnopolitical context of the Eastern Province has intensified land (re)claiming in Ampara by Muslims and Tamils.
According to Tamil discourse, the increase in the value of land in Ampara over the past two decades has led to rich Muslims purchasing land belonging to poor Tamils, resulting in ethnic homogenization in the coastal areas of the District in favor of the Muslims. ‘Violence against Tamils was also used in some areas to push out the numerically small Tamil service caste communities’ as Hasbullah says. In a situation with an ideological history of land disputes, finding new land for the construction of houses for Muslim communities affected by the tsunami posed a challenge at that time.
 In the face of this challenge, Muslims in Ampara sought assistance from Muslim politicians and organisations that willingly came forward to assist them. The efforts made by these politicians and civil society organisations to erect houses for tsunami-affected Muslim families were forcibly curtailed by the LTTE. Consequently, a proposed housing program for Muslims in Kinnayady Kiramam in Kaththankudi was abandoned in 2005. Development of the four acres of land bought by the Memon Sangam in Colombo for tsunami victims of Makbooliya in Marathamunai was prohibited in 2005. Similar occurrences have been reported in Marathamunai Medduvedday. Mrs. Ferial Ashraff, at that time Minister of Housing and Common Amenities, wanted to build houses in Marathamunai, Periyaneelavanai DS division (Addaippallam), the Pandirippu Muslim area, and in Oluvil–Palamunai, but the LTTE proscribed all such initiatives.
In the face of this challenge, Muslims in Ampara sought assistance from Muslim politicians and organisations that willingly came forward to assist them. The efforts made by these politicians and civil society organisations to erect houses for tsunami-affected Muslim families were forcibly curtailed by the LTTE. Consequently, a proposed housing program for Muslims in Kinnayady Kiramam in Kaththankudi was abandoned in 2005. Development of the four acres of land bought by the Memon Sangam in Colombo for tsunami victims of Makbooliya in Marathamunai was prohibited in 2005. Similar occurrences have been reported in Marathamunai Medduvedday. Mrs. Ferial Ashraff, at that time Minister of Housing and Common Amenities, wanted to build houses in Marathamunai, Periyaneelavanai DS division (Addaippallam), the Pandirippu Muslim area, and in Oluvil–Palamunai, but the LTTE proscribed all such initiatives.
The Islamabad housing scheme in Kalmunai Muslim DS division and the construction of houses by Muslim individuals in Karaithivu were banned, and threats were issued by the LTTE and a Tamil military organisation called Ellai Padai (Boundary Forces). Because the GoSL and the intervening agencies could not resolve the housing problem, the affected communities became disillusioned and lost confidence in the GoSL departments, aid agencies, and international NGOs. Much effort and resources were wasted in finding land and designing housing programmes that have not materialised. Some funds pledged by external agencies failed to materialise, causing harm to low-income families. Efforts to provide housing for tsunami-affected people in the Ampara District at that time highlighted their vulnerability to LTTE threats and the power politics of participating agencies. Regarding housing and land issues, the Muslim people of Ampara adopted two approaches to address their challenges. First, in some cases, they reached a compromise with the LTTE, agreeing that upon completion of a housing project, a portion of the houses would be allocated to the Tamil community under LTTE supervision.
For instance, this approach proved successful in the Islamabad housing programme, which was halfway complete as of the time of the research (March–June 2006). Similarly, a housing scheme in Ninthavur followed a comparable compromise with the LTTE. According to Mohamed Mansoor, the then President of the Centre for East Lanka Social Service, 22 of the 100 houses were to be allocated to the Tamil community upon completion. This allocation was deemed reasonable because Muslims owned 80 percent of the land in the area, while Tamils owned 20 percent. At the time of the author’s fieldwork, approximately 30 houses had been completed at this site. I don’t know what happened afterward.
The second approach adopted by the people was to build houses in the areas they had lived in before the tsunami, despite construction being prohibited within 65 meters of the sea. Muslims in Marathamunai knew they would not be allocated any land for housing and sought funds from organisations such as the Eastern Human Economic Development to construct homes on their original plots. The affected individuals have made efforts to urge their leaders to engage with the TRO and the LTTE to reclaim the funds borrowed by Muslim people and organisations to purchase land. The four-acre plot that the Memon Society had acquired for housing development was sold to a Tamil organisation for Rs. 1,000,000 (roughly USD 10,000) and was one such land in question.
The national political forces operating in Ampara have deprived the poor (Muslim) fisher folk of their right to land and build houses in their villages. These communities have resorted to non-violent strategies involving accepting the status quo without questioning it and fighting for their rights. The passivity among the poor affected families is a result of them not having representation in the civil society organisations in the area. These bodies are run by elites who do not wish to contest the GoSL rule of a 65-metre buffer zone or LTTE land claims. The tsunami not only washed away the houses and took the land of the poor communities that lived by the sea, but it also made them even poorer, more marginalised, and more ethnically segregated.
Here, 20 years later, it is time that justice was done to the Muslim families in the Ampara district who were severely hit by the tsunami. It is also a significant and timely commitment made by President Dissanayake to offer 500 houses to the Muslim tsunami victims. Such a promise is overdue and essential, as these marginalised communities have desperately needed a voice and action in their favour for over 20 years. Delivery of such homes to the victims would be an important step in restoring social harmony and the dignity and livelihoods of those affected by the tragic incident.
Features
Worthless corporations, boards and authorities

Prof. O. A. Ileperuma
The Cabinet has recently decided to review the state-owned, non-commercial institutions, many of which are redundant or are of no use. The government manages 86 departments, 25 District Secretariats, 339 Divisional Secretariats, 340 state-owned enterprises and 115 non-commercial state statutory institutions. The national budget allocates Rs. 140 billion to manage these institutions.
We have inherited a large number of redundant Corporations, Boards and Authorities causing a huge drain on our financial resources. These institutions were basically created by previous governments to give jobs to defeated candidates and friends of government politicians. For instance, we have the State Pharmaceutical corporation and the State Pharmaceutical Manufacturing corporation. They can be merged. Then, we have the Coconut Development authority and the Coconut Cultivation Board, which is redundant. Decades ago, coconut cultivation came under the coconut research institute (CRI). An extension section of the CRI can easily undertake the functions of these two institutions. Another example is the still existing Ceylon Cement corporation which earlier ran two cement mills at Puttalam and Kankesanthurai. Now, the Kankasenthurai factory does not exist and the Puttalam factory is under the private sector. Still this Ceylon Cement Corporation exists and the only activity they are doing is to lease the lands for mining which earlier belonged to them. There is a chairman appointed by the minister in charge based on political connections and a general manager and a skeleton staff of about ten workers. This corporation can be easily dissolved and the Ministry Secretary can take up any functions of this corporation.
In the field of sciences, the National Science Foundation was created in 1968 to promote science and technology and to provide funding for researchers. Then a former president created two other institutions, National Science and Technology Commission (NASTEC) and National research Council (NRC). While NASTEC is tasked with science policy and NRC provides research grants; both these tasks were earlier carried out by the National Science Foundation. In the field of education, curriculum revisions, etc., were carried out earlier by the Department of Education, and later the National Institute of Education was created, and for educational policy, the National Education Commission was created. The latter was created to provide a top position for an academic who supported the then government in power.
There is a Water Supply and Drainage Board and also a separate Water Resources Board, and they can easily be amalgamated. There is also the Cashew corporation serving no useful purpose and its duties can be taken over by an institution such as the Department of Minor Crops. There is also the State Development & Construction Corporation and the State Engineering Corporation of Sri Lanka which appear to be doing similar jobs.
We still have Paranthan Chemicals Ltd., which is the successor to the Paranthan Chemicals Corporation involved in manufacturing caustic soda and chlorine. Their factory was destroyed during the war nearly 20 years ago, but it exists and its only function is to import chlorine and sell it to the Water Board for the water purification process. Why can’t the Water Board import chlorine directly?
I am aware that my views on this subject are likely to draw criticism but such redundancies are a severe drain on the Treasury, which faces the difficult task of allocating funds.
Features
Head-turner in Egypt…

 Prathibha Liyanaarchchi, Miss Intercontinental Sri Lanka 2024, is back in town after participating in the 52nd edition of Miss Intercontinental held at the Sunrise Remal Resort, Sharm El-Sheik, in Egypt.
Prathibha Liyanaarchchi, Miss Intercontinental Sri Lanka 2024, is back in town after participating in the 52nd edition of Miss Intercontinental held at the Sunrise Remal Resort, Sharm El-Sheik, in Egypt.
There were nearly two weeks of activities, connected with this event, and Prathibha says she enjoyed every minute of it.
“It was wonderful being in the company of over 52 beautiful girls from around the world and we became great friends.
“My roommate was Miss Greece. She was simply awesome and I even taught her a few Sinhala words.
“Most of the contestants were familiar with Ceylon Tea but didn’t quite know much about Sri Lanka.”
However, having won a special award at Miss Intercontinental 2024 – Queen of Tourism – Prathibha says she is seriously thinking of working on a campaign to show the world that Sri Lanka is a paradise island and that tourists would love to experience our scene.
Although our queen was not in the final list, she made it into the Top 22 and was quite a drawcard wherever she went.
“I guess it was my tan complexion and my height 5 ft. 10 inches.”
She even impressed an international audience with her singing voice; the organisers were keen to have a contestant from the Asia Oceania group showcase her talent, as a singer, and Prathibha was selected.
She sang Madonna’s ‘La Isla Bonita’ and was roundly applauded.
Even in the traditional costume section, her Batik Osariya and the traditional seven-piece necklace impressed many.
With her new buddies…at the beauty pageant
The grand finale was held on 6th December with Miss Puerto Rico being crowned Miss Intercontinental 2024.
“I would like to say a big thank you to everyone who supported me throughout this journey. I’m honoured to have been named a Top 22 Finalist at Miss Intercontinental 2024 and awarded the Special title of Miss Tourism Queen. It was a challenging yet unforgettable experience competing in Egypt. Preparing, in just three weeks, and performing, was no easy feat, but I’m so proud of what I accomplished.”
For the record, Prathibha, who celebrated her birthday on Christmas Day (25), is a technical designer at MAS holdings, visiting lecturer, model, and a graduate from the University of Moratuwa.
Unlike most beauty queens who return after an international event and hardly think of getting involved in any community work, Prathibha says she plans to continue serving her community by expanding her brand – Hoop The Label – and using it as a platform to create a positive change for the underprivileged community.
“At the same time, I am committed to furthering my education in fashion design and technology, aiming to combine creativity with innovation to contribute to the evolving fashion industry. By blending these passions, I hope to make a lasting impact, both in my community, and in the world of fashion.”
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoSri Lanka to mend fences with veterans
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoPathirana set to sling his way into Kiwi hearts
-
 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoIs AKD following LKY?
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoOffice of CDS likely to be scrapped; top defence changes on the cards
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoSL issues USD 10.4 bn macro-linked bonds
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days ago‘A degree is not a title’ – a response
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoRanil’s advice
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoLest watchdogs should become lapdogs












