Features
HOMES ON THURSTAN ROAD/ CAMBRIDGE PLACE 75 YEARS AGO

by Hugh Karunanayake
Seventy five years ago, the Thurstan Road/ Cambridge Place thoroughfare was one of the most picturesque in Colombo. It was lined on either side by gigantic specimens of flamboyant, or flame of the forest tree (poinciana regia), the saman tree (samanea saman) and the kaha mal or cassia fistula. The tree lined avenues provided a restful and shady canopy over the road. During the months of April and May when the avenues were in full bloom this stretch of road was most colourful and attractive, and indeed a magnificent spectacle – a remarkable living legacy from the spacious days of the city in the past.
Those were the days when Colombo was renowned the world over as the “garden city of the East.” The trees were planted around 1920, following a report by Professor Patrick Geddes, an Urban Planner, who was commissioned by the Government of the day, to recommend a Master Plan for the development of Colombo. He had a vision for Colombo in which trees, greenery, and open spaces played a significant role.Sometime in the nineteen forties, members of the Orchid Circle of Ceylon took the initiative of adding further colour and character to the tree lined environment, by planting varieties of epiphytic orchids on the branches of the larger trees. Specimens of cymbidium bicolor, vanda tesselata, and dendrobium superbiens could be seen albeit sporadically among the trees that survive along this once beautiful avenue.
The Thurstan Road/ Cambridge Place precinct was originally part of the Bagatelle Estate known later as Alfred House Estate, arguably the most expensive piece of real estate ever sub divided in the country. The folk who lived in the area were the crème-de la crème of Colombo’s society in th early 20th century. Thurstan Road (since renamed Munidasa Cumaranatunge Mawata, after the well known Sinhalese author and poet) commences at its intersection with Reid Avenue, and ends at the roundabout connecting Flower Road. Cambridge Place continues northwards from this point, and ends at its intersection with Edinburgh Crescent, now known as Sir Marcus Fernando Mawata. Thurstan Road was once the eastern boundary of the estate originally known as Bagatelle, and renamed later as Alfred House.The Fergusons Directory of 1871 lists Bagatelle as a cinnamon cum coconut estate of 125 acres. As the history of Alfred House has a significant bearing on the stately homes that exist on Thurstan Road to this day, a brief examination of its past would seem appropriate.
The property was first advertised for sale in the Ceylon Government Gazette of March 9, 1822 as “a thatched cottage with a tent roof, about two miles and half from the Fort of Colombo, to be disposed of by private contract.” The owner at the time was believed to be a prominent businessman in the Fort with the quaint name Daddy Parsee. Charles Edward Layard, the third son of the Dean of Bristol, arrived in Ceylon in 1803. He joined the Ceylon Civil Service in 1804 and served until 1839. It is not clear whether he owned Bagatelle Estate, but it is evident that he resided there, the thatched cottage having been replaced by a substantial two-storied bungalow at the time of his occupation.
Many of Layard’s children were born in Bagatelle House, and it is on record that the youngest of Layard’s 26 children, named Barbara, was born in Bagatelle in 1834.The Ceylon Almanacs of the 1840s lists Bagatelle Estate as a property owned by Arbuthnot and Co, who were agents for the Government of Ceylon in India, and who were the sole exporters of cinnamon from Ceylon, which was a government monopoly at the time. A plantation owner became the owner of Bagatelle Estate, which was thereafter called Bagatelle Walauwwa. His nephew Charles Henry de Soysa to whom the property passed on, demolished the old homestead and built a magnificent home comprising of around 100 rooms. This was the location of a historic dinner that was accorded by the De Soysas to the Duke of Edinburgh when he visited Ceylon in 1870.The house was named Alfred House with the permission of Prince Alfred, the Duke. C.H. de Soysa died in 1890, and his wife in 1914, leaving a large family of 14 sons and daughters to inherit an enormous estate which in addition to Alfred House included several thousand acres of coconut, tea and rubber lands spread around the island.
Over the years, the 125 acre Alfred House Estate underwent several sub divisions, some major changes being precipitated by the master plan for Colombo which foresaw many new roads across the estate. The earlier sub divisions were however made by the De Soysa family itself, which constructed several stately mansions within the property.
The ornate Lakshmigiri which was built in 1910 by A.J.R. de Soysa, the second son of C.H. de Soysa, is a classic example of extravagant building design of the time. This house with its extensive gardens and massive cast iron gates is at the southern end of Thurstan Road bordering Queens Road. It bears assessment No.102 Thurstan Road and is much the same fifty years ago, as it was when constructed almost half a century earlier. A few years after it was built, the house was mortgaged, and later foreclosed. It was then bought by the Adamjee Lukmanjee family and has remained in their ownership to date under the name Saifee Villa.
Seventy years ago there were no buildings between Saifee Villa and Queens Road. Adjoining Queens Road is the house originally named Regina Walauwwa by its owner T. H.A. de Soysa, the fourth son of C.H. de Soysa. It was named after his wife Regina, and was built in 1912. An imposing building with multiple roofs, turrets, and towers it was a palatial residence facing Thurstan Road. The owner was a keen turfite owning many horses, and with a penchant for heavy wagers. The story goes that whenever he won over Rs. 100, 000 at the races, he would hoist the family flag on the large flagstaff in front of the house to indicate to all and sundry that he had made a killing at the races. This ritual was locally referred to as “Lakseta kodiya” meaning “win a lakh of rupees and the flag goes up”. Fortunes do however fluctuate, and by 1920 he was in financial difficulties and the house sold to the newly emerging University College. It was then renamed College House. The flagstaff or ‘kodigaha’ remains on the property to this day.
On the opposite side of Thurstan Road was the University of Ceylon buildings constructed in 1913 as the home of Royal College. The school occupied the premises till 1923 when it was acquired by the Ceylon University College. Royal College later moved to the new premises on Racecourse Avenue, where it functions to this day.
Next to College House is a property extending to over three acres, purchased from the Dc Soysa family in 1926 by the Imperial Bank of India. It was earlier used as the dairy for Alfred House.
The Bank commissioned Walker and Sons to construct an impressive residence for its manager, and the house was named “Carlowrie”. In the mid 1950s it was acquired by the Government of India as the official residence for its High Commissioner, and has since been called “India House”. Many distinguished visitors have been entertained here, including Prime Minister Nehru, and later his daughter Indira Gandhi who have planted trees in commemoration of their visits, in its spacious gardens.
Adjoining India House were two bungalows belonging to Brooke Bonds Ceylon Ltd, the tea company. Hammerfaest was at No 80 Thurstan Road and was the residence of its Managing Director H. Broome.In the adjoining home lived his Deputy Roy Collins, and later S. E. Satarasinghe. At No. 76 was Chitrakala one time residence of Sepala Gunasena of M.D. Gunasena and Co. whose mortgage on the property was foreclosed by the bank.
Next to the University property was Thurstan College established in 1949 in the premises earlier used by the Government Training College, prior to its shift to Maharagama. Adjoining Thurstan College was Royal Primary School, whose Headmaster Major A.F. de Saa Bandaranayake resided in the official bungalow at No 13. Mr. J.C.A. Corea the Principal of Royal College occupied the adjoining bungalow. The buildings and grounds of Royal Primary School stood next.
Around 50 years ago the school was under the Headmastership of Mr.H.D. Sugathapala and Mr.H.P. Jayewardene under whose leadership the well facilitated school hall known as “Navarangahala” was built. It acquired a permanent place in the history of the island, when the constituent assembly convened to draft the 1972 Constitution, was held there. It was also the occasion for the change of name from Ceylon to Sri Lanka.
On the opposite side of Thurstan Road facing Thurstan College were the ends of Bagatelle Road and Alfred Place conjoining at the intersection with Thurstan Road. At this point along Thurstan Road were a few commercial buildings including a small restaurant known as “Villas” a haunt of generations of Royal College students who dropped in after school for a ‘cuppa’ often combined surreptitiously with a cigarette. Many were the abortive raids conducted by the college prefects in attempts to rein in the offending delinquents.
Next door was Thurstan Café run by Noel Perera. Further on towards Flower Road, near Pedris Road was the home of K.H.M. Fernando, who owned a successful motor spares shop in the Pettah.
Adjoining Pedris Road was the home of Mrs. A. Wijewardene. Her son, the entrepreneur Upali Wijewardene who disappeared tragically in his Learjet in 1982, built his house designed by Geoffrey Bawa in part of the land in the 1970s. Her sons-in-law Dr. Attygalle and Prof Stanley Wijesundera the latter killed during the JVP insurgency of 1989 also lived in houses within the same property. Adjoining was the entrance to 5th Lane, which was neighbouring the dental clinic of Dr. Ian de Silva.
Next-door was the home of the General Manager of the Shell Co, P.D. Finn. The house there was built on a property, which was earlier known as “the Monastery” The roundabout here links Thurstan Road on the south, Cambridge Place on the north, Racecourse Avenue on the East, and Flower Road on the west.
Racecourse Avenue in its entirety on one side provided boundaries to Royal College and Royal Primary School. At its western end was the Orient Club founded in 1894, and at one time an exclusive social club for the elites of Colombo. Its tennis courts border the southern end of Cambridge Place, near the roundabout. On the opposite side of Cambridge Place at No. 32 was the home of Sherman de Silva, the proprietor of a well-known produce company of the time.
Adjoining was the large home earlier called Cambridge House and later renamed Florence House when Sir Wilfred de Soysa, the sixth son of C.H. de Soysa, occupied it. Sir Wifred’s sons, Bishop Harold, Terrence, Cecil, Ryle, Anura, and Lalith, all grew up in this home, and were later to acquit themselves with great credit in adult life, whether it be business, sports, or in the “service of the Lord”. Ryle was for many years the opening batsman for the Ceylon Cricket team then known as “The All Ceylon Cricket Team”. As a schoolboy at Royal College he was a member of the unbeaten Royal team that toured Australia in 1938. Florence House stood on a large extent of land. It was demolished in the 1950s to give way to a cluster of large bungalows and a new roadway named Cambridge Terrace.

Adjoining Florence House was Mackinnon House the official home of the Managing Director of Mackinnon Mackenzie and Co. the well known shipping agents. H.W. Tatham lived in this house situated in a large garden enclosed by a high wall. In the late 1/950s Mr George Chitty the very successful criminal lawyer purchased this house and named it Goodwood. A humanist and a lover of people and company, he was a man of varied interests, and was an expert on cameras and photography, music, art, forensic medicine, woodwork, and motorcars. He led the successful prosecution in the Bandaranaike Assassination Case, at the invitation of the Crown.
As in all neighbourhoods, romance is always in the air, and it was no different in Thurstan Road. His son Ajit married Rapti, the daughter of Y.D. Gundevia the Indian High Commissioner who lived in India House on Thurstan Road, thus linking the two roads Thurstan and Cambridge by marriage! Two doors next to Goodwood was “St Catherine” the home of C.H.Z. Fernando whose father C.M. Fernando was a son in law of C.H. de Soysa of Alfred House. D.J. Wimalasurendra who pioneered hydroelectric schemes in Ceylon earlier owned St Catherine’s.
At the end of Cambridge Place fronting Edinburgh Crescent was “Lynwood” the home of Francis Amarasuriya a popular race horse owner of the time. His elder son Rukman ended his life tragically, at an early age, committing suicide in 1957 in Nuwara Eliya. Facing the Museum on the opposite side in Cambridge Place, in a house called “Brentham” lived Leslie de Saram the head of the legal firm F.J. and G de Saram. He sold the house to the Australian Government, which purchased it for its high commission. Leslie de Saram was a remarkable man known for his generosity and many acts of philanthropy.
He was educated at Royal College, and Clifton College in England, but gifted Gurutalawa Farm of 35 acres of cultivated land, and buildings, to S. Thomas’ College, which established a branch school there. He also gifted his unique collection of rare antiques to the University of Ceylon, when it established at Peradeniya, and was described as “the greatest benefactor and friend the Ceylon University ever had.”. After his retirement he settled all his affairs in Ceylon and migrated first to England and later to Australia where he lived in Canberra. Next to Brentham was “Oakleigh” the home of another legal luminary F.C. Rowan the senior Partner of Julius and Creasy. Rowan was the advisor and confidante to almost every leading mercantile firm in Colombo in the 1950s.
Further down Cambridge Place at “The Eyds” lived Stanley de Saram the brother of Leslie, and no less remarkable. He was also a partner of the family firm of de Saram’s but in 1946 relinquished it to take up a position as a Director of Leechman and Co, an Agency House, the first Ceylonese to be invited to the position. He later became the first Ceylonese Chairman of the firm. Stanley and his wife were well known personalities in the mercantile world of that era, and were renowned for their legendary hospitality. Stanley and his wife hosted Lady Churchill on a visit to Ceylon in 1953. Later, Sir Winston and Lady Churchill played host to the De Sarams when they were asked to dinner at their home in Chartwell. After Stanley’s death in the 1970s, “The Eyds’ was demolished and several new homes have come up on its grounds. Somewhere between “The Eyds” and Oakholme stood a house called Gresham, which has since been altered structurally.
At around this area in Cambridge Place, was the intersection with Edinburgh Crescent.Further on, adjoining the Orient Club was the Women’s International Club. The Thurstan Road /Cambridge Place belt still remains a salubrious area of Colombo, but its quiet and leafy environment may not be the same as it was 50 years ago,. The student population in the educational triangle, which it adjoins, has expanded dramatically, making the area a traffic controller’s nightmare during school hours. Mercifully, the commercial sprawl that is evident in most areas of Colombo has spared its blight here, and Thurstan Road and Cambridge Place together with its immediate environs, are still an absolutely charming area within Colombo.
Features
When floods strike: How nations keep food on the table

Insights from global adaptation strategies
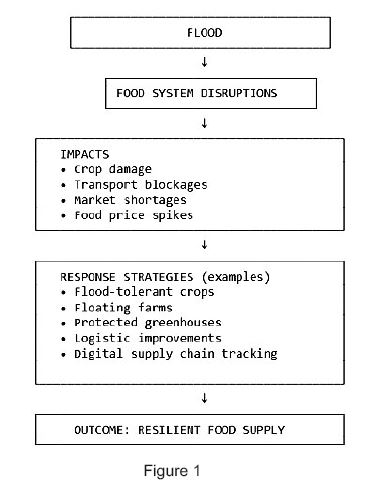
Sri Lanka has been heavily affected by floods, and extreme flooding is rapidly becoming one of the most disruptive climate hazards worldwide. The consequences extend far beyond damaged infrastructure and displaced communities. The food systems and supply networks are among the hardest hit. Floods disrupt food systems through multiple pathways. Croplands are submerged, livestock are lost, and soils become degraded due to erosion or sediment deposition. Infrastructural facilities like roads, bridges, retail shops, storage warehouses, and sales centres are damaged or rendered inaccessible. Without functioning food supply networks, even unaffected food-producing regions struggle to continue daily lives in such disasters. Poor households, particularly those dependent on farming or informal rural economies, face sharp food price increases and income loss, increasing vulnerability and food insecurity.
Many countries now recognie that traditional emergency responses alone are no longer enough. Instead, they are adopting a combination of short-term stabilisation measures and long-term strategies to strengthen food supply chains against recurrent floods. The most common immediate response is the provision of emergency food and cash assistance. Governments, the World Food Programme, and other humanitarian organisations often deliver food, ready-to-eat rations, livestock feed, and livelihood support to affected communities.
Alongside these immediate measures, some nations are implementing long-term strategic actions. These include technology- and data-driven approaches to improve flood preparedness. Early warning systems, using satellite data, hydrological models, and advanced weather forecasting, allow farmers and supply chain operators to prepare for potential disruptions. Digital platforms provide market intelligence, logistics updates, and risk notifications to producers, wholesalers, and transporters. This article highlights examples of such strategies from countries that experience frequent flooding.
China: Grain Reserves and Strategic Preparedness
China maintains a large strategic grain reserve system for rice, wheat, and maize; managed by NFSRA-National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration and Sinograin (China Grain Reserves Corporation (Sinograin Group), funded by the Chinese government, that underpins national food security and enables macro-control of markets during supply shocks. Moreover, improvements in supply chain digitization and hydrological monitoring, the country has strengthened its ability to maintain stable food availability during extreme weather events.
Bangladesh: Turning Vulnerability into Resilience
In recent years, Bangladesh has stood out as one of the world’s most flood-exposed countries, yet it has successfully turned vulnerability into adaptive resilience. Floating agriculture, flood-tolerant rice varieties, and community-run grain reserves now help stabilise food supplies when farmland is submerged. Investments in early-warning systems and river-basin management have further reduced crop losses and protected rural livelihoods.
Netherlands, Japan: High-Tech Models of Flood Resilience
The Netherlands offers a highly technical model. After catastrophic flooding in 1953, the country completely redesigned its water governance approach. Farmland is protected behind sea barriers, rivers are carefully controlled, and land-use zoning is adaptive. Vertical farming and climate-controlled greenhouses ensure year-round food production, even during extreme events. Japan provides another example of diversified flood resilience. Following repeated typhoon-induced floods, the country shifted toward protected agriculture, insurance-backed farming, and automated logistics systems. Cold storage networks and digital supply tracking ensure that food continues to reach consumers, even when roads are cut off. While these strategies require significant capital and investment, their gradual implementation provides substantial long-term benefits.
Pakistan, Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam: Reform in Response to Recurrent Floods
In contrast, Pakistan and Thailand illustrate both the consequences of climate vulnerability and the benefits of proactive reform. The 2022 floods in Pakistan submerged about one-third of the country, destroying crops and disrupting trade networks. In response, the country has placed greater emphasis on climate-resilient farming, water governance reforms, and satellite-based crop monitoring. Pakistan as well as India is promoting crop diversification and adjusting planting schedules to help farmers avoid the peak monsoon flood periods.
Thailand has invested in flood zoning and improved farm infrastructure that keep markets supplied even during severe flooding. Meanwhile, Indonesia and Vietnam are actively advancing flood-adapted land-use planning and climate-resilient agriculture. For instance, In Vietnam’s Mekong Delta, pilot projects integrate flood-risk mapping, adaptive cropping strategies, and ecosystem-based approaches to reduce vulnerability in agricultural and distribution areas. In Indonesia, government-supported initiatives and regional projects are strengthening flood-risk-informed spatial planning, adaptive farming practices, and community-based water management to improve resilience in flood-prone regions. (See Figure 1)
 The Global Lesson: Resilience Requires Early Investment
The Global Lesson: Resilience Requires Early Investment
The global evidence is clear: countries that invest early in climate-adaptive agriculture and resilient logistics are better able to feed their populations, even during extreme floods. Building a resilient future depends not only on how we grow food but also on how we protect, store, and transport it. Strengthening infrastructure is therefore central to stabilising food supply chains while maintaining food quality, even during prolonged disruptions. Resilient storage systems, regional grain reserves, efficient cold chains, improved farming infrastructure, and digital supply mapping help reduce panic buying, food waste, and price shocks after floods, while ensuring that production capacity remains secure.
Persistent Challenges
However, despite these advances, many flood-exposed countries still face significant challenges. Resources are often insufficient to upgrade infrastructure or support vulnerable rural populations. Institutional coordination across the agriculture, disaster management, transport, and environmental sectors remains weak. Moreover, the frequency and scale of climate-driven floods are exceeding the design limits of older disaster-planning frameworks. As a result, the gap between exposure and resilience continues to widen. These challenges are highly relevant to Sri Lanka as well and require deliberate, gradual efforts to phase them out.
The Role of International Trade and global markets
When domestic production falls in such situations, international trade serves as an important buffer. When domestic production is temporarily reduced, imports and regional trade flows can help stabilise food availability. Such examples are available from other countries. For instance, In October 2024, floods in Bangladesh reportedly destroyed about 1.1 million tonnes of rice. In response, the government moved to import large volumes of rice and allowed accelerated or private-sector imports of rice to stabilize supply and curb food price inflation. This demonstrates how, when domestic production fails, international trade/livestock/food imports (from trade partners) acted as a crucial buffer to ensure availability of staple food for the population. However, this approach relies on well-functioning global markets, strong diplomatic relationships, and adequate foreign exchange, making it less reliable for economically fragile nations. For example, importing frozen vegetables to Sri Lanka from other countries can help address supply shortages, but considerations such as affordability, proper storage and selling mechanisms, cooking guidance, and nutritional benefits are essential, especially when these foods are not widely familiar to local populations.
Marketing and Distribution Strategies during Floods
Ensuring that food reaches consumers during floods requires innovative marketing and distribution strategies that address both supply- and demand-side challenges. Short-term interventions often include direct cash or food transfers, mobile markets, and temporary distribution centres in areas where conventional marketplaces become inaccessible. Price stabilisation measures, such as temporary caps or subsidies on staple foods, help prevent sharp inflation and protect vulnerable households. Awareness campaigns also play a role by educating consumers on safe storage, cooking methods, and the nutritional value of unfamiliar imported items, helping sustain effective demand.
Some countries have integrated technology to support these efforts; in this regard, adaptive supply chain strategies are increasingly used. Digital platforms provide farmers, wholesalers, and retailers with real-time market information, logistics updates, and flood-risk alerts, enabling them to reroute deliveries or adjust production schedules. Diversified delivery routes, using alternative roads, river transport, drones, or mobile cold-storage units, have proven essential for maintaining the flow of perishable goods such as vegetables, dairy, and frozen products. A notable example is Japan, where automated logistics systems and advanced cold-storage networks help keep supermarkets stocked even during severe typhoon-induced flooding.
The Importance of Research, Coordination, and Long-Term Commitment
Global experience also shows that research and development, strong institutional coordination, and sustained national commitment are fundamental pillars of flood-resilient food systems. Countries that have successfully reduced the impacts of recurrent floods consistently invest in agricultural innovation, cross-sector collaboration, and long-term planning.
Awareness Leads to Preparedness
As the summary, global evidence shows that countries that act early, plan strategically, and invest in resilience can protect both people and food systems. As Sri Lanka considers long-term strategies for food security under climate change, learning from flood-affected nations can help guide policy, planning, and public understanding. Awareness is the first step which preparedness must follow. These international experiences offer valuable lessons on how to protect food systems through proactive planning and integrated actions.
(Premaratne (BSc, MPhil, LLB) isSenior Lecturer in Agricultural Economics Department of Agricultural Systems, Faculty of Agriculture, Rajarata University. Views are personal.)
Key References·
Cabinet Secretariat, Government of Japan, 2021. Fundamental Plan for National Resilience – Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries / Logistics & Food Supply Chains. Tokyo: Cabinet Secretariat.
· Delta Programme Commissioner, 2022. Delta Programme 2023 (English – Print Version). The Hague: Netherlands Delta Programme.
· Hasanuddin University, 2025. ‘Sustainable resilience in flood-prone rice farming: adaptive strategies and risk-sharing around Tempe Lake, Indonesia’, Sustainability. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/17/6/2456 [Accessed 3 December 2025].
· Mekong Urban Flood Resilience and Drainage Programme (TUEWAS), 2019–2021. Integrated urban flood and drainage planning for Mekong cities. TUEWAS / MRC initiative.
· Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, People’s Republic of China, 2025. ‘China’s summer grain procurement surpasses 50 mln tonnes’, English Ministry website, 4 July.
· National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration (China) 2024, ‘China purchases over 400 mln tonnes of grain in 2023’, GOV.cn, 9 January. Available at: https://english.www.gov.cn/archive/statistics/202401/09/content_WS659d1020c6d0868f4e8e2e46.html
· Pakistan: 2022 Floods Response Plan, 2022. United Nations / Government of Pakistan, UN Digital Library.
· Shigemitsu, M. & Gray, E., 2021. ‘Building the resilience of Japan’s agricultural sector to typhoons and heavy rain’, OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Papers, No. 159. Paris: OECD Publishing.
· UNDP & GCF, 2023. Enhancing Climate Resilience in Thailand through Effective Water Management and Sustainable Agriculture (E WMSA): Project Factsheet. UNDP, Bangkok.
· United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), 2025. ‘Rice Bank revives hope in flood hit hill tracts, Bangladesh’, UNDP, 19 June.
· World Bank, 2022. ‘Bangladesh: World Bank supports food security and higher incomes of farmers vulnerable to climate change’, World Bank press release, 15 March.
Features
Can we forecast weather precisely?

Weather forecasts are useful. People attentively listen to them but complain that they go wrong or are not taken seriously. Forecasts today are more probabilistically reliable than decades ago. The advancement of atmospheric science, satellite imaging, radar maps and instantly updated databases has improved the art of predicting weather.
Yet can we predict weather patterns precisely? A branch of mathematics known as chaos theory says that weather can never be foretold with certainty.
The classical mechanics of Issac Newton governing the motion of all forms of matter, solid, liquid or gaseous, is a deterministic theory. If the initial conditions are known, the behaviour of the system at later instants of time can be precisely predicted. Based on this theory, occurrences of solar eclipses a century later have been predicted to an accuracy of minutes and seconds.
The thinking that the mechanical behaviour of systems in nature could always be accurately predicted based on their state at a previous instant of time was shaken by the work of the genius French Mathematician Henri Poincare (1864- 1902).
Eclipses are predicted with pinpoint accuracy based on analysis of a two-body system (Earth- Moon) governed by Newton’s laws. Poincare found that the equivalent problem of three astronomical bodies cannot be solved exactly – sometimes even the slightest variation of an initial condition yields a drastically different solution.
A profound conclusion was that the behaviour of physical systems governed by deterministic laws does not always allow practically meaningful predictions because even a minute unaccountable change of parameters leads to completely different results.
Until recent times, physicists overlooked Poincare’s work and continued to believe that the determinism of the laws of classical physics would allow them to analyse complex problems and derive future happenings, provided necessary computations are facilitated. When computers became available, the meteorologists conducted simulations aiming for accurate weather forecasting. The American mathematician Edward Lorenz, who turned into a reputed meteorologist, carried out such studies in the early 1960s, arrived at an unexpected result. His equations describing atmospheric dynamics demonstrated a strange behaviour. He found that even a minute change (even one part in a million) in initial parameters leads to a completely different weather pattern in the atmosphere. Lorenz announced his finding saying, A flap of a butterfly wing in one corner of the world could cause a cyclone in a far distant location weeks later! Lorenz’s work opened the way for the development branch of mathematics referred to as chaos theory – an expansion of the idea first disclosed by Henri Poincare.
We understand the dynamics of a cyclone as a giant whirlpool in the atmosphere, how it evolves and the conditions favourable for their origination. They are created as unpredictable thermodynamically favourable relaxation of instabilities in the atmosphere. The fundamental limitations dictated by chaos theory forbid accurate forecasting of the time and point of its appearance and the intensity. Once a cyclone forms, it can be tracked and the path of movement can be grossly ascertained by frequent observations. However, absolutely certain predictions are impossible.
A peculiarity of weather is that the chaotic nature of atmospheric dynamics does not permit ‘long – term’ forecasting with a high degree of certainty. The ‘long-term’ in this context, depending on situation, could be hours, days or weeks. Nonetheless, weather forecasts are invaluable for preparedness and avoiding unlikely, unfortunate events that might befall. A massive reaction to every unlikely event envisaged is also not warranted. Such an attitude leads to social chaos. The society far more complex than weather is heavily susceptible to chaotic phenomena.
by Prof. Kirthi Tennakone (ktenna@yahoo.co.uk)
Features
When the Waters Rise: Floods, Fear and the ancient survivors of Sri Lanka
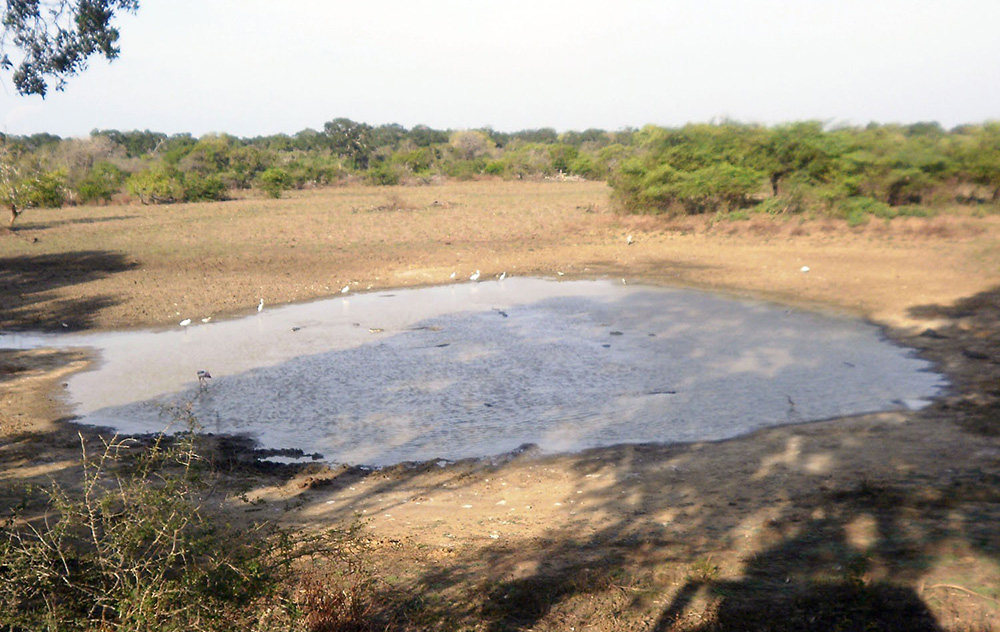

The water came quietly at first, a steady rise along the riverbanks, familiar to communities who have lived beside Sri Lanka’s great waterways for generations. But within hours, these same rivers had swollen into raging, unpredictable forces. The Kelani Ganga overflowed. The Nilwala broke its margins. The Bentara, Kalu, and Mahaweli formed churning, chocolate-brown channels cutting through thousands of homes.
When the floods finally began to recede, villagers emerged to assess the damage, only to be confronted by another challenge: crocodiles. From Panadura’s back lanes to the suburbs of Colombo, and from the lagoons around Kalutara to the paddy fields of the dry zone, reports poured in of crocodiles resting on bunds, climbing over fences, or drifting silently into garden wells.
For many, these encounters were terrifying. But to Sri Lanka’s top herpetologists, the message was clear: this is what happens when climate extremes collide with shrinking habitats.
“Crocodiles are not invading us … we are invading floodplains”
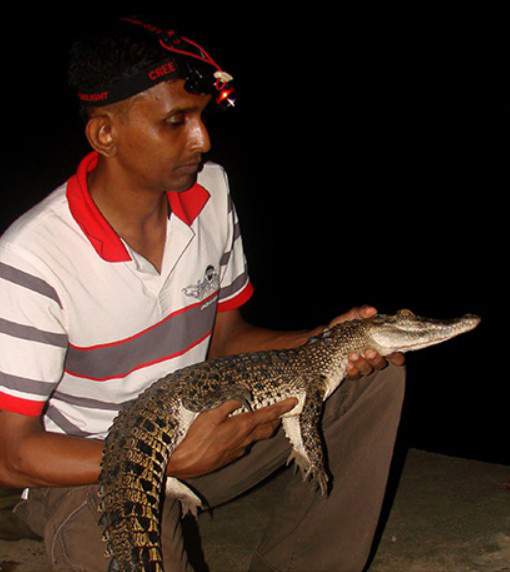
Sri Lanka’s foremost crocodile expert, Dr. Anslem de Silva, Regional Chairman for South Asia and Iran of the IUCN/SSC Crocodile Specialist Group, has been studying crocodiles for over half a century. His warning is blunt.
“When rivers turn into violent torrents, crocodiles simply seek safety,” he says. “They avoid fast-moving water the same way humans do. During floods, they climb onto land or move into calm backwaters. People must understand this behaviour is natural, not aggressive.”
In the past week alone, Saltwater crocodiles have been sighted entering the Wellawatte Canal, drifting into the Panadura estuary, and appearing unexpectedly along Bolgoda Lake.
“Saltwater crocodiles often get washed out to sea during big floods,” Dr. de Silva explains. “Once the current weakens, they re-enter through the nearest lagoon or canal system. With rapid urbanisation along these waterways, these interactions are now far more visible.”
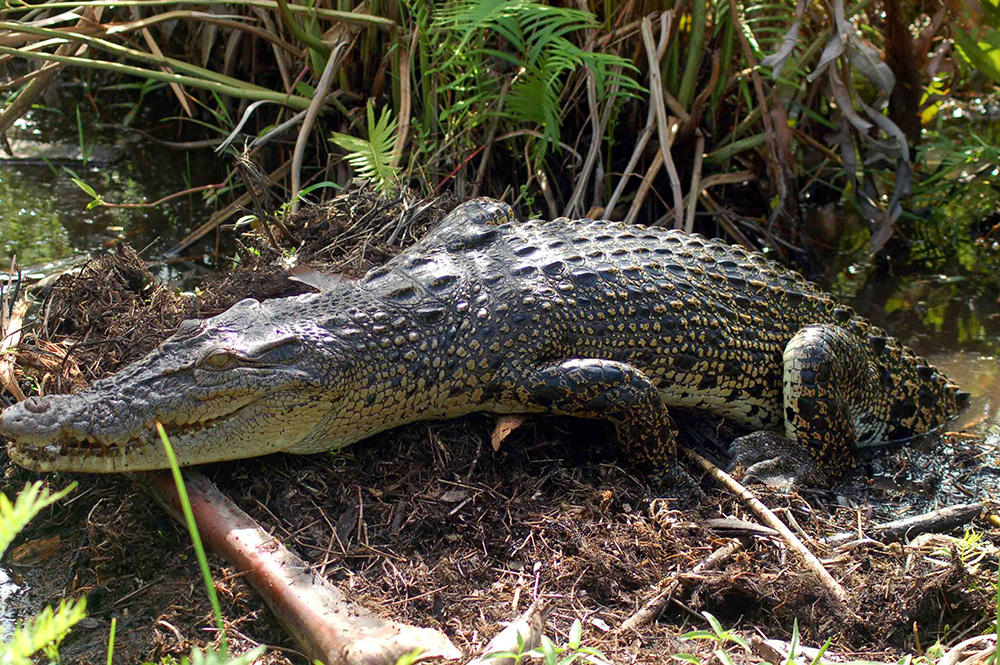
- An adult Salt Water Crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) (Photo -Madura de Silva)
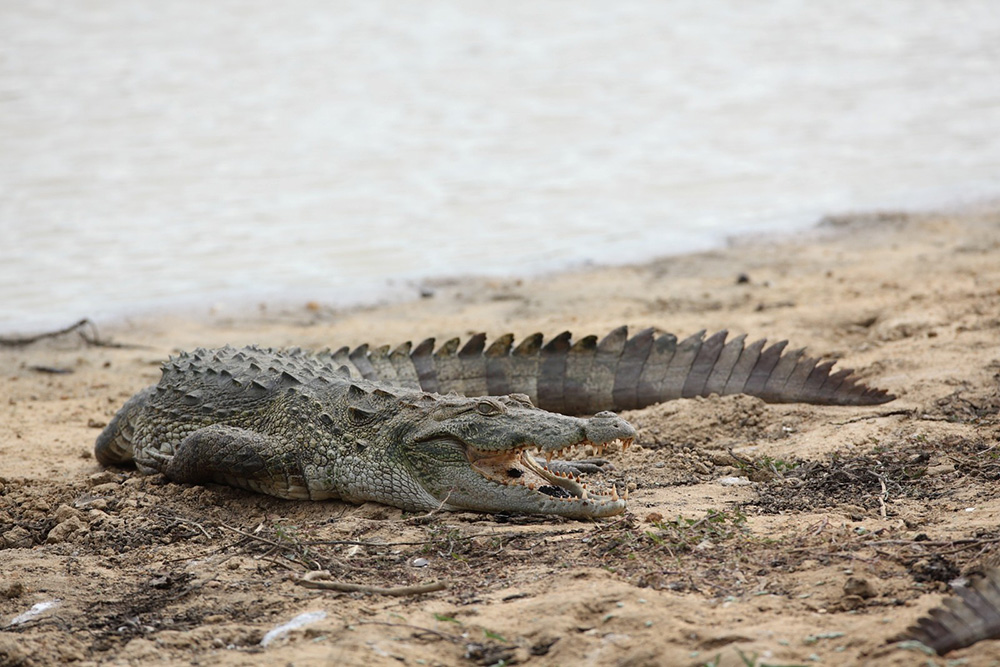
- Adult Mugger (Crocodylus plaustris) Photo -Laxhman Nadaraja
- A Warning sign board
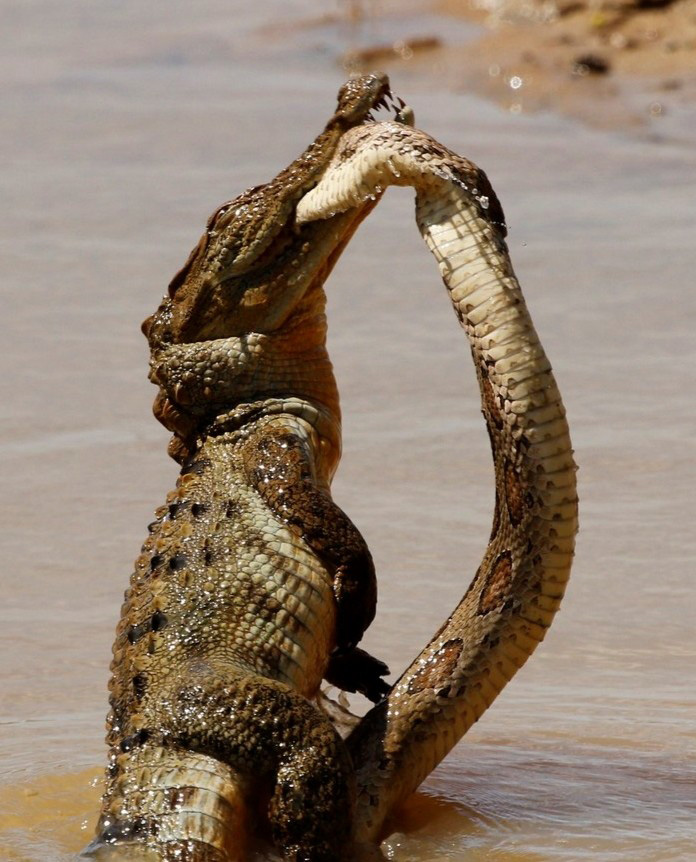
- A Mugger holding a a large Russell ’s viper (Photo- R. M. Gunasinghe)
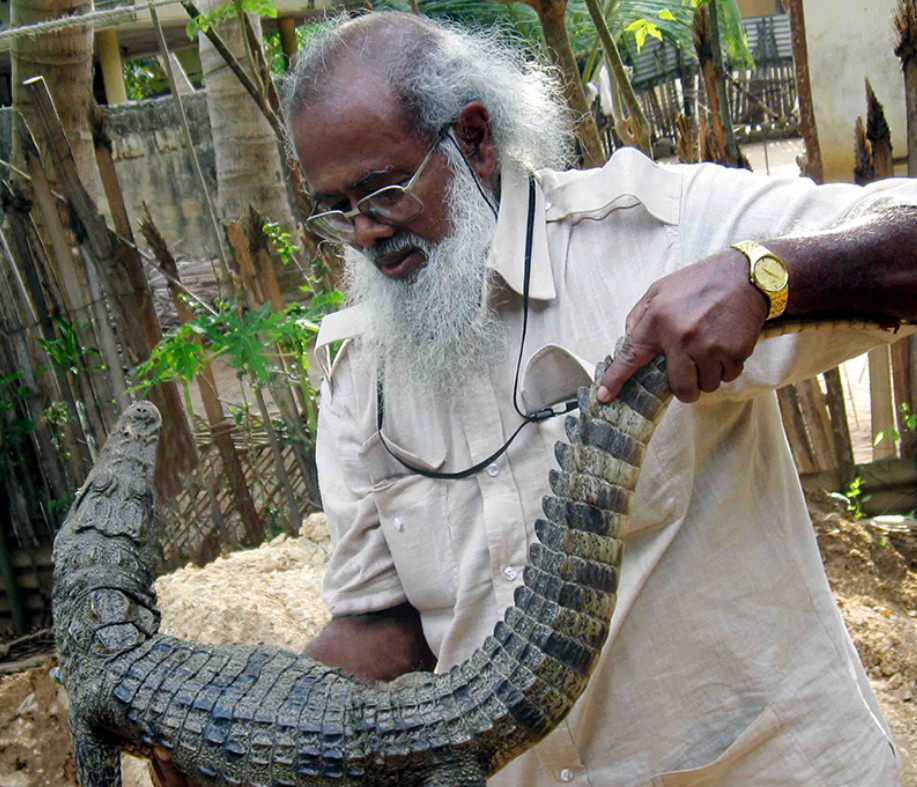
- Anslem de Silva
- Suranjan Karunarathna
This clash between wildlife instinct and human expansion forms the backdrop of a crisis now unfolding across the island.
A conflict centuries old—now reshaped by climate change
Sri Lanka’s relationship with crocodiles is older than most of its kingdoms. The Cūḷavaṃsa describes armies halted by “flesh-eating crocodiles.” Ancient medical texts explain crocodile bite treatments. Fishermen and farmers around the Nilwala, Walawe, Maduganga, Batticaloa Lagoon, and Kalu Ganga have long accepted kimbula as part of their environment.
But the modern conflict has intensified dramatically.
A comprehensive countrywide survey by Dr. de Silva recorded 150 human–crocodile attacks, with 50 fatal, between 2008 and 2010. Over 52 percent occurred when people were bathing, and 83 percent of victims were men engaged in routine activities—washing, fishing, or walking along shallow margins.
Researchers consistently emphasise: most attacks happen not because crocodiles are unpredictable, but because humans underestimate them.
Yet this year’s flooding has magnified risks in new ways.
“Floods change everything” — Dr. Nimal D. Rathnayake
Herpetologist Dr. Nimal Rathnayake says the recent deluge cannot be understood in isolation.
“Floodwaters temporarily expand the crocodile’s world,” he says. “Areas people consider safe—paddy boundaries, footpaths, canal edges, abandoned land—suddenly become waterways.”
Once the water retreats, displaced crocodiles may end up in surprising places.
“We’ve documented crocodiles stranded in garden wells, drainage channels, unused culverts and even construction pits. These are not animals trying to attack. They are animals trying to survive.”
According to him, the real crisis is not the crocodile—it is the loss of wetlands, the destruction of natural river buffers, and the pollution of river systems.
“When you fill a marsh, block a canal, or replace vegetation with concrete, you force wildlife into narrower corridors. During floods, these become conflict hotspots.”
Past research by the Crocodile Specialist Group shows that more than 300 crocodiles have been killed in retaliation or for meat over the past decade. Such killings spike after major floods, when fear and misunderstanding are highest.
“Not monsters—ecosystem engineers” — Suranjan Karunaratne
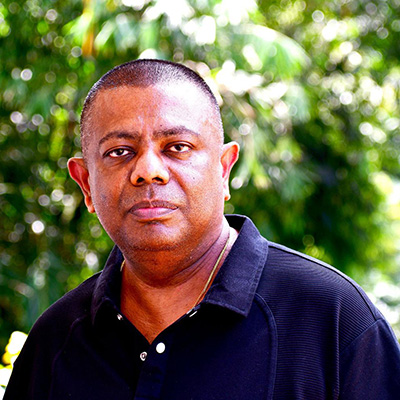
On social media, flood-displaced crocodiles often go viral as “rogue beasts.” But conservationist Suranjan Karunaratne, also of the IUCN/SSC Crocodile Specialist Group, says such narratives are misleading.
“Crocodiles are apex predators shaped by millions of years of evolution,” he says. “They are shy, intelligent animals. The problem is predictable human behaviour.”
In countless attack investigations, Karunaratne and colleagues found a repeated pattern: the Three Sames—the same place, the same time, the same activity.
“People use the same bathing spot every single day. Crocodiles watch, learn, and plan. They hunt with extraordinary patience. When an attack occurs, it’s rarely random. It is the culmination of observation.”
He stresses that crocodiles are indispensable to healthy wetlands. They: control destructive catfish populations, recycle nutrients, clean carcasses and diseased fish, maintain biodiversity, create drought refuges through burrows used by amphibians and reptiles.
“Removing crocodiles destroys an entire chain of ecological services. They are not expendable.”
Karunaratne notes that after the civil conflict, Mugger populations in the north rebounded—proof that crocodiles recover when given space, solitude, and habitat.
Floods expose a neglected truth: CEEs save lives—if maintained In high-risk communities, Crocodile Exclusion Enclosures (CEEs) are often the only physical barrier between people and crocodiles. Built along riverbanks or tanks, these enclosures allow families to bathe, wash, and collect water safely.
Yet Dr. de Silva recounts a tragic incident along the Nilwala River where a girl was killed inside a poorly maintained enclosure. A rusted iron panel had created a hole just large enough for a crocodile to enter.
“CEEs are a life-saving intervention,” he says. “But they must be maintained. A neglected enclosure is worse than none at all.”
Despite their proven effectiveness, many CEEs remain abandoned, broken or unused.
Climate change is reshaping crocodile behaviour—and ours
Sri Lanka’s floods are no longer “cycles” as described in folklore. They are increasingly intense, unpredictable and climate-driven. The warming atmosphere delivers heavier rainfall in short bursts. Deforested hillsides and filled wetlands cannot absorb it.
Rivers swell rapidly and empty violently.
Crocodiles respond as they have always done: by moving to calmer water, by climbing onto land, by using drainage channels, by shifting between lagoons and canals, by following the shape of the water.
But human expansion has filled, blocked, or polluted these escape routes.
What once were crocodile flood refuges—marshes, mangroves, oxbow wetlands and abandoned river channels—are now housing schemes, fisheries, roads, and dumpsites.
Garbage, sand mining and invasive species worsen the crisis
The research contained in the uploaded reports paints a grim but accurate picture. Crocodiles are increasingly seen around garbage dumps, where invasive plants and waste accumulate. Polluted water attracts fish, which in turn draw crocodiles.
Excessive sand mining in river mouths and salinity intrusion expose crocodile nesting habitats. In some areas, agricultural chemicals contaminate wetlands beyond their natural capacity to recover.
In Borupana Ela, a short study found 29 Saltwater crocodiles killed in fishing gear within just 37 days.
Such numbers suggest a structural crisis—not a series of accidents.
Unplanned translocations: a dangerous human mistake
For years, local authorities attempted to reduce conflict by capturing crocodiles and releasing them elsewhere. Experts say this was misguided.
“Most Saltwater crocodiles have homing instincts,” explains Karunaratne. “Australian studies show many return to their original site—even if released dozens of kilometres away.”
Over the past decade, at least 26 Saltwater crocodiles have been released into inland freshwater bodies—home to the Mugger crocodile. This disrupts natural distribution, increases competition, and creates new conflict zones.
Living with crocodiles: a national strategy long overdue
All three experts—Dr. de Silva, Dr. Rathnayake and Karunaratne—agree that Sri Lanka urgently needs a coordinated, national-level mitigation plan.
* Protect natural buffers
Replant mangroves, restore riverine forests, enforce river margin laws.
* Maintain CEEs
They must be inspected, repaired and used regularly.
* Public education
Villagers should learn crocodile behaviour just as they learn about monsoons and tides.
* End harmful translocations
Let crocodiles remain in their natural ranges.
* Improve waste management
Dumps attract crocodiles and invasive species.
* Incentivise community monitoring
Trained local volunteers can track sightings and alert authorities early.
* Integrate crocodile safety into disaster management
Flood briefings should include alerts on reptile movement.
“The floods will come again. Our response must change.”
As the island cleans up and rebuilds, the deeper lesson lies beneath the brown floodwaters. Crocodiles are not new to Sri Lanka—but the conditions we are creating are.
Rivers once buffered by mangroves now rush through concrete channels. Tanks once supporting Mugger populations are choked with invasive plants. Wetlands once absorbing floodwaters are now levelled for construction.
Crocodiles move because the water moves. And the water moves differently today.
Dr. Rathnayake puts it simply:”We cannot treat every flooded crocodile as a threat to be eliminated. These animals are displaced, stressed, and trying to survive.”
Dr. de Silva adds:”Saving humans and saving crocodiles are not competing goals. Both depend on understanding behaviour—ours and theirs.”
And in a closing reflection, Suranjan Karunaratne says:”Crocodiles have survived 250 million years, outliving dinosaurs. Whether they survive the next 50 years in Sri Lanka depends entirely on us.”
For now, as the waters recede and the scars of the floods remain, Sri Lanka faces a choice: coexist with the ancient guardians of its waterways, or push them into extinction through fear, misunderstanding and neglect.
By Ifham Nizam
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWeather disasters: Sri Lanka flooded by policy blunders, weak enforcement and environmental crime – Climate Expert
-
 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoLevel I landslide RED warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Colombo, Gampaha, Kalutara, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurnegala, Natale, Monaragala, Nuwara Eliya and Ratnapura
-
News3 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoINS VIKRANT deploys helicopters for disaster relief operations
-
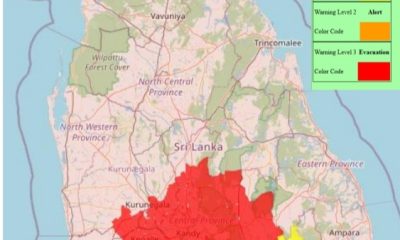
 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-
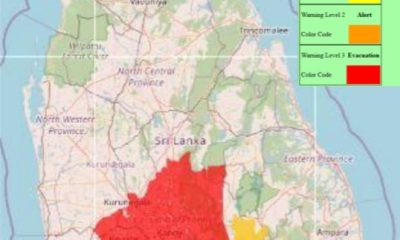
 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoUpdated Payment Instructions for Disaster Relief Contributions