Features
Worker remittance inflows lose steam

Why they are important and how to revive them
By Charith Gamage
In a period of decreasing reserves and foreign exchange shortages, migrant worker remittances had once been a welcome stream of income for Sri Lanka in fulfilling its foreign exchange shortfalls. With the recent sharp fall in remittances, the ongoing situation is causing chaos in the island nation’s mission to increase foreign exchange revenues. The following is an examination of how remittances aided Sri Lanka in the past, the causes of the sudden drop, and most importantly, how to keep remittances flowing as before.
“That’s a nice set of coloured pencils; where did you buy it?” This is not an uncommon question a Sri Lankan student would ask their classmate after noticing that they have a school accessory not commonly available in Sri Lanka. The friend explains that it wasn’t bought from a local shop but that it has instead been sent by a parent working abroad. Although it is a trivial conversation at school, it reveals a unique segment in the Sri Lankan economy.
Nearly 1.5 million of the country’s labour force, ranging from unskilled to skilled and professional, migrate for employment purposes. These workers frequently contact their families and send home part of their earnings and occasional goods. These remittances, that trickle down to the larger economy, have been a vibrant component that balances out the island nation’s foreign exchange position in respect to the rest of the world.
At a time when the external sector is confronted with daunting challenges such as depleting foreign exchange reserves and a stumbling dollar-rupee exchange rate, there has recently been a sharp drop in remittances, making the efforts to get on top of the country’s forex crunch an uphill battle. As of October 2021, Sri Lanka’s remittances receipts have dropped 14 percent compared with the respective period of 2020. This divergence has become increasingly acute in recent months, with inward remittances in September and October 2021 falling sharply to USD 353 and 317 million, respectively, the lowest levels for both months since 2010 and 2009. (Data sources: CBSL historical data and the provisional figures mentioned in the institution’s weekly reports; the November and December 2021 figures were not known at the time of writing this article)
Why are remittances important?
Before explaining the reasons behind the recent shortfall, a simple current account analysis, which summarises what countries spend and take in from abroad, provides a more comprehensive picture of the importance of this vital economic undercurrent.
The current account (CA) of countries like Sri Lanka can be written as CA = (X-M) + NI + NT. Where (X-M) is the trade deficit or the gap between the country’s exports and imports (of goods and services), NI denotes net income, and NT indicates net transfers, of which remittances are a part. Remittances have been a lifesaver for decades, to fill the country’s persistent trade deficit and negative net income due to interest payments on foreign loans. Without this support, the country has to find other means, such as additional foreign borrowings, to fill the gap.
Figure 1, excluding 2021 data, shows that the flow of remittances has reached a tipping point in the mid-2000s and peaked around 2014, growing slowly since the 1990s. After this, it contributed roughly USD 7 billion per year from 2015 to 2020.
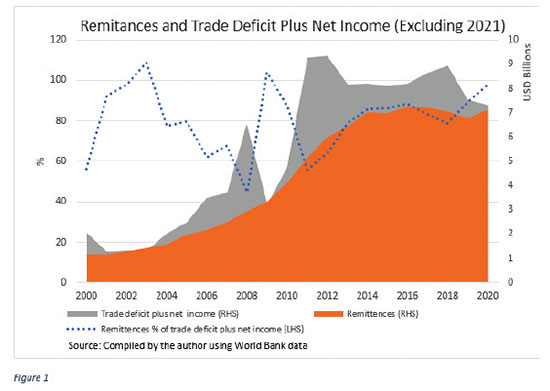
Figure 1
The figure also shows (X-M) plus NI and remittances as a percentage of (X-M) plus NI as separate series over the past two decades. One of the notable facts is that with the improved remittances flow, the widening trade deficit plus negative net income has been steadily supported by around 80 percent since 2014. Therefore, the recent remittances drop is a massive blow for the island nation, primarily in balancing its higher imports over exports (financing the deficit in the trade account).
What happened in 2021?
The South Asian region is a good proxy for analysing Sri Lanka’s remittances dynamics in 2021 to determine if this is a regional issue. First and foremost, is the remittances drop a common issue in the region? The answer is not quite so. The World Bank expects the region’s remittances to grow by eight percent in 2021 compared with the previous year, with key players India, Bangladesh and Pakistan earning more than they did in 2020 (https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2021/11/17/remittance-flows-register-robust-7-3-percent-growth-in-2021).
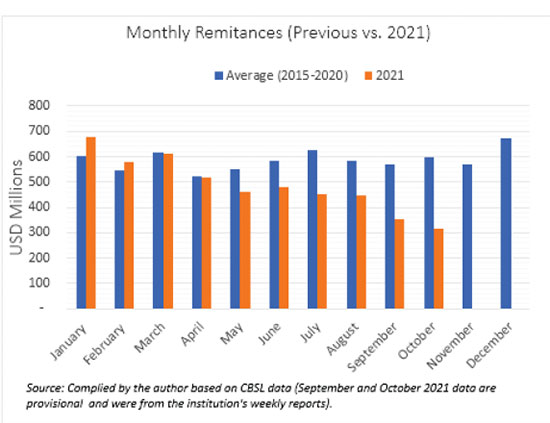
Figure 2
By comparison, Sri Lanka’s most recent remittances dynamics seem quite different from this regional theme. As Figure 2 shows, since May 2021, there has been an apparent divergence from its remittances flows compared with the corresponding periods of the previous years, indicating that remittances have entered a rocky road. Some explanations suggest that the overvalued formal dollar-rupee exchange rate provides remittances with a lower value than the informal channels; hence, remitters use informal channels such as the ‘Hawala’ or ‘Undiyal’ system, which offers them higher rates. (U. Jayasinghe. Reuters. December 6, 2021. https://www.reuters.com/markets/currencies/why-does-sri-lanka-want-migrant-workers-remit-funds-via-banking-channels-2021-12-06/). Those systems operate so that when workers hand over dollars to a middleman in their host country, the recipient in their home country can withdraw an equal amount of rupees through another agent. Consequently, this causes those remittances to bypass the formal banking system and be unaccounted for, and perhaps may not even be received in Sri Lanka.
Although this might be one of the reasons, the amount lost through the official channels appears to be greater than what studies reveal; for example, some studies show a three percent decrease from formal channels for a 10 percent rise in black market premium. Suggesting that there could be other reasons, such as official channel users restricting transfers in the belief that the rate differential in parallel markets is an implicit tax on them.
Consequently, it seems there are two tasks to fulfil in order to rectify the remittances flow:
(i) shifting informal channel users back to a formal banking channel
(ii) encouraging those who might have used formal channels and limited remittances to remit more.
The country’s ongoing actions, such as offering greater (premium) exchange rates to remitters and cracking down on illegitimate channels, seem to target shifting informal channel users back to a formal banking channel. However, it is important to remember that whenever there is a higher price for dollars outside the formal system, senders are likely to hunt for loopholes, reducing the effectiveness of the efforts.
As a result, these initiatives should be better paired with strategies that motivate workers themselves to use official channels and send more, rather than making them feel they should accept a lower price for their hard-earned money. To better design these policies, it is imperative to find out what motivates them to send money.
Other factors affecting remittances
Although an altruistic motive could be one reason migrant workers remit money, studies show (for example an Indian study by P. Jijin, et al. Macroeconomic determinants of remittances to India. Econ Change Restruct. [2021]) that it is an investment motive that motivates senders to remit money (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10644-021-09347-3). Investment motive could be more pronounced among seasoned workers willing to shift their savings in bulk for investments or start businesses for the family. These flows are due to their overall confidence in the home country economy and its ease of doing business, including fewer restrictions and regulations imposed on their goals.
Over the past decade, Sri Lanka’s highest percentage increases in remittances, 24 percent and 25 percent occurred respectively in 2010 and 2011, following the boost in confidence in the economy after the end of the country’s 30 year-long civil war in 2009. This shows how these flows are intertwined with better economic outlooks.
This idea is supported by Abbas, Masood, and Sakhawat (2017) in a Pakistani research study spanning from 1972 to 2012, who show that financial and political determinants and variables such as stable macroeconomic conditions influence increased remittance flows (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0161893817300248).
How to best manage remittances flow
Restoring remittances to previous levels is a critical challenge for Sri Lanka since it provides a lifeline to the economy in contrast to high-cost international borrowings. Studies show that, in most countries, the black market and the share of remittances flowing through it tend to feed each other; therefore, policies that bring remittances back to the formal channels would automatically shrink the black market as well.
Rather than predetermining the premium, authorities can identify the sender’s switching point between the informal and formal channels. From this, they can identify the level of relaxation on the exchange rate and the exact premium for remitters for a shorter period, for effective absorption of the parallel markets.
Given the disadvantages of the black market, such as lack of or no legal protection, lack of transparency, and the possibility of scams, there is no need to offer a stark contrast between the two markets to entice people to switch back. But, sufficient incentives need to be offered so that they do not feel they are penalised for using the formal channels.
In addition, since remittances are linked to investment intent, another front should encourage them to send more money home and through formal channels. It is important to build a network and boost their confidence by relaxing restrictions on them, providing investment opportunities and business guides for entrepreneurship, including credit and facilities to import machinery at concessional rates. Providing a robust safety net for their loved ones to help them out during the turbulent times of global economies is also essential. Overall, to help the country smooth out these flows, more diplomacy and a win-win situation for workers abroad seem to be key in harnessing effective outcomes.
Finally, given the procyclicality (tendency to move alongside the economy’s cyclical condition) of remittances, the issue should not be isolated from the rest of the economy. Higher remittances are tied to better home-country economic conditions, so they are linked with policies that promote higher investment and export-led growth with subdued inflation that does not erode home-country investments. In particular, one important requirement is allowing the formal rate to reflect the real situation in the external sector by improving the overall macroeconomic situation with a business-friendly environment and consistent policies. That is the key to perfecting this mission.
(The writer is a PhD candidate attached to Monash University, Australia. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the writer, and he could be reached at charith.gamage@monash.edu)
Features
When Batting Was Poetry: Remembering David Gower

For many Sri Lankans growing up in the late nineteen fifties and early sixties, our cricketing heroes were Englishmen. I am not entirely sure why that was. Perhaps it was a colonial hangover, or perhaps it reflected the way cricket was taught locally, with an emphasis on technical correctness, a high left elbow, and the bat close to the pad. English cricket, with its traditions and orthodoxy, became the benchmark.
I, on the other hand, could not see beyond Sir Garfield Sobers and the West Indian team. Sir Garfield remains my all-time hero, although only by a whisker ahead of Muttiah Muralitharan. For me, Caribbean flair and attacking cricket were infinitely superior to the Englishmen’s conservatism and defensive approach.
That said, England has produced many outstanding cricketers, with David Gower and Ian Botham being my favourites. Players such as Colin Cowdrey, Tom Graveney, Mike Denness, Tony Lewis, Mike Brealey, Alan Knott, Derek Underwood, Tony Greig, and David Gower were great ambassadors for England, particularly when touring the South Asian subcontinent, which posed certain challenges for touring sides until about three decades ago. Their calm and dignified conduct when touring is a contrast to the behaviour of the current lot.
I am no longer an avid cricket viewer, largely because my blood pressure tends to rise when I watch our Sri Lankan players. Therefore, I was pleasantly surprised recently when I was flipping through the TV channels to hear David Gower’s familiar voice commentating. It brought back fond memories of watching him bat during my time in the UK. I used to look forward to the summer for two reasons. To feel the sun on my back and watch David Gower bat!
A debut that announced a star
One of my most vivid cricketing memories is watching, in 1978, a young English batsman pull the very first ball he faced in Test cricket to the boundary. Most debutants play cautiously, trying to avoid the dreaded zero, but Gower nonchalantly swivelled and pulled a short ball from Pakistan’s Liaquat Ali for four. It was immediately apparent that a special talent had arrived.
To place that moment in perspective, Marvan Atapattu—an excellent Sri Lankan batsman—took three Tests and four innings to score his first run, yet later compiled 16 Test centuries.
Gower went on to score 56 in his first innings and captivated spectators with his full repertoire of strokes, particularly his exquisite cover drive. It is often said that a left-hander’s cover drive is one of the most pleasurable sights in cricket, and watching Sobers, Gower, or Brian Lara execute the cover drive made the entrance ticket worthwhile.
A young talent in a time of change
Gower made his Test debut at just 21, rare for an English player of that era. World cricket was in turmoil due to the Kerry Packer revolution, and England had lost senior players such as Tony Greig, Alan Knott, and Derek Underwood. Selectors were searching for young talent, and Gower’s inclusion injected fresh impetus.
Gower scored his first Test century in only his fourth match, just a month after his debut, against New Zealand, and a few months later scored his maiden Ashes century at Perth.
He finished with 18 Test centuries from 117 matches. His finest test innings, in my view, was the magnificent 154 not out at Kingston in 1981 against Holding, Marshall, Croft, and Garner. Batting for nearly eight hours and facing 403 balls, he set aside flair for determination to save the Test.
He and Ian Botham also benefited from playing their initial years under Mike Brealey, an average batsman but an outstanding leader. Rodney Hogg, the Australian fast bowler, famously said Brealey had a ‘degree in people’, and both young stars flourished under his guidance.
Captaincy and criticism and overall record
Few English batsmen delighted and frustrated spectators and analysts as much as Gower. The languid cover drive, so elegant and so pleasurable to the spectators, also resulted in a fair number of dismissals that, at times, gave the impression of carelessness to both spectators and journalists.
Despite his approach, which at times appeared casual, he was appointed as captain of the English team in 1983 and served for three years before being removed in 1986. He was again appointed captain in 1989 for the Ashes series. He led England in 1985 to a famous Ashes series win as well as a series win in India in1984-85.
In the eyes of some, the captaincy might not have been the best suited to his style of play. However, he scored 732 runs whilst captaining the team during the 1985 Ashes series, proving that he was able handle the pressure.
Under Gower, England lost two consecutive series to the great West Indian teams 5-0, which led to the coining of the phrase “Blackwashed”! He was somewhat unlucky that he captained the English team when the West Indies were at the peak, possessing a fearsome array of fast bowlers.
David Gower scored 3,269 test runs against Australia in 42 test matches. He scored nine centuries and 12 fifties, averaging nearly 45 runs per inning. His record against Australia as an English batsman is only second to Sir Jack Hobbs. Scoring runs against Australia has been a yardstick in determining how good a batsman is. Therefore, his record against Australia can easily rebut the critics who said that he was too casual. He scored 8,231 runs in 117 test matches and 3,170 runs in 114 One Day Internationals.
A gentleman of the game free of controversies
Unlike the other great English cricketer at the time, Ian Botham, David was not involved in any controversies during his illustrious career. The only incident that generated negative press was a low-level flight he undertook in a vintage Tiger Moth biplane in Queensland during the 1990-91 Ashes tour of Australia. The team management and the English press, as usual, made a mountain out of a molehill. David retired from international cricket in 1992.
In 1984, during the tour of India, due to the uncertain security situation after the assassination of the then Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, the English team travelled to Sri Lanka for a couple of matches. I was fortunate enough to get David to sign his book “With Time to Spare”. This was soon after he returned to the pavilion after being dismissed. There was no refusal or rudeness when I requested his signature.
He was polite and obliged despite still being in pads. Although I did not know David Gower, his willingness that day to oblige a spectator exemplified the man’s true character. A gentleman who played the game as it should be, and a great ambassador of England and world cricket. He was inducted into the ICC Cricket Hall of Fame in 2009 and appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire (OBE) in 1992 for his services to sport.
By Sanjeewa Jayaweera
Features
Sri Lanka Through Loving Eyes:A Call to Fix What Truly Matters

Love of country, pride, and the responsibility to be honest
I am a Sri Lankan who has lived in Australia for the past 38 years. Australia has been very good to my family and me, yet Sri Lanka has never stopped being home. That connection endures, which is why we return every second year—sometimes even annually—not out of nostalgia, but out of love and pride in our country.
My recent visit reaffirmed much of what makes Sri Lanka exceptional: its people, culture, landscapes, and hospitality remain truly world-class. Yet loving one’s country also demands honesty, particularly when shortcomings risk undermining our future as a serious global tourism destination.
When Sacred and Iconic Sites Fall Short
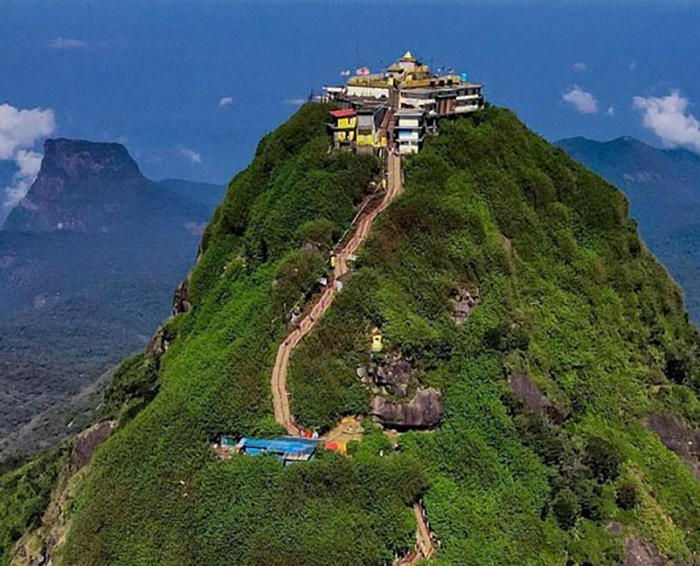
One of the most confronting experiences occurred during our visit to Sri Pada (Adam’s Peak). This sacred site, revered across multiple faiths, attracts pilgrims and tourists from around the world. Sadly, the severe lack of basic amenities—especially clean, accessible toilets—was deeply disappointing. At moments of real need, facilities were either unavailable or unhygienic.
This is not a luxury issue. It is a matter of dignity.
For a site of such immense religious and cultural significance, the absence of adequate sanitation is unacceptable. If Sri Lanka is to meet its ambitious tourism targets, essential infrastructure, such as public toilets, must be prioritized immediately at Sri Pada and at all major tourist and pilgrimage sites.
Infrastructure strain is also evident in Ella, particularly around the iconic Nine Arches Bridge. While the attraction itself is breathtaking, access to the site is poorly suited to the sheer volume of visitors. We were required to walk up a steep, uneven slope to reach the railway lines—manageable for some, but certainly not ideal or safe for elderly visitors, families, or those with mobility challenges. With tourist numbers continuing to surge, access paths, safety measures, and crowd management urgently needs to be upgraded.
Missed opportunities and first impressions
Our visit to Yala National Park, particularly Block 5, was another missed opportunity. While the natural environment remains extraordinary, the overall experience did not meet expectations. Notably, our guide—experienced and deeply knowledgeable—offered several practical suggestions for improving visitor experience and conservation outcomes. Unfortunately, he also noted that such feedback often “falls on deaf ears.” Ignoring insights from those on the ground is a loss Sri Lanka can ill afford.
First impressions also matter, and this is where Bandaranaike International Airport still falls short. While recent renovations have improved the physical space, customs and immigration processes lack coherence during peak hours. Poorly formed queues, inconsistent enforcement, and inefficient passenger flow create unnecessary delays and frustration—often the very first experience visitors have of Sri Lanka.
Excellence exists—and the fundamentals must follow
That said, there is much to celebrate.
Our stays at several hotels, especially The Kingsbury, were outstanding. The service, hospitality, and quality of food were exceptional—on par with the best anywhere in the world. These experiences demonstrate that Sri Lanka already possesses the talent and capability to deliver excellence when systems and leadership align.
This contrast is precisely why the existing gaps are so frustrating: they are solvable.
Sri Lankans living overseas will always defend our country against unfair criticism and negative global narratives. But defending Sri Lanka does not mean remaining silent when basic standards are not met. True patriotism lies in constructive honesty.
If Sri Lanka is serious about welcoming the world, it must urgently address fundamentals: sanitation at sacred sites, safe access to major attractions, well-managed national parks, and efficient airport processes. These are not optional extras—they are the foundation of sustainable tourism.
This is not written in criticism, but in love. Sri Lanka deserves better, and so do the millions of visitors who come each year, eager to experience the beauty, spirituality, and warmth that our country offers so effortlessly.
The writer can be reached at Jerome.adparagraphams@gmail.com
By Jerome Adams
Features
Seething Global Discontents and Sri Lanka’s Tea Cup Storms

Global temperatures in January have been polar opposite – plus 50 Celsius down under in Australia, and minus 45 Celsius up here in North America (I live in Canada). Between extremes of many kinds, not just thermal, the world order stands ruptured. That was the succinct message in what was perhaps the most widely circulated and listened to speeches of this century, delivered by Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney at Davos, in January. But all is not lost. Who seems to be getting lost in the mayhem of his own making is Donald Trump himself, the President of the United States and the world’s disruptor in chief.
After a year of issuing executive orders of all kinds, President Trump is being forced to retreat in Minneapolis, Minnesota, by the public reaction to the knee-jerk shooting and killing of two protesters in three weeks by federal immigration control and border patrol agents. The latter have been sent by the Administration to implement Trump’s orders for the arbitrary apprehension of anyone looking like an immigrant to be followed by equally arbitrary deportation.
The Proper Way
Many Americans are not opposed to deporting illegal and criminal immigrants, but all Americans like their government to do things the proper way. It is not the proper way in the US to send federal border and immigration agents to swarm urban neighbourhood streets and arrest neighbours among neighbours, children among other school children, and the employed among other employees – merely because they look different, they speak with an accent, or they are not carrying their papers on their person.
Americans generally swear by the Second Amendment and its questionably interpretive right allowing them to carry guns. But they have no tolerance when they see government forces turn their guns on fellow citizens. Trump and his administration cronies went too far and now the chickens are coming home to roost. Barely a month has passed in 2026, but Trump’s second term has already run into multiple storms.
There’s more to come between now and midterm elections in November. In the highly entrenched American system of checks and balances it is virtually impossible to throw a government out of office – lock, stock and barrel. Trump will complete his term, but more likely as a lame duck than an ordering executive. At the same time, the wounds that he has created will linger long even after he is gone.
Equally on the external front, it may not be possible to immediately reverse the disruptions caused by Trump after his term is over, but other countries and leaders are beginning to get tired of him and are looking for alternatives bypassing Trump, and by the same token bypassing the US. His attempt to do a Venezuela over Greenland has been spectacularly pushed back by a belatedly awakening Europe and America’s other western allies such as Australia, Canada and New Zealand. The wags have been quick to remind us that he is mostly a TACO (Trump always chickens out) Trump.
Grandiose Scheme or Failure
His grandiose scheme to establish a global Board of Peace with himself as lifetime Chair is all but becoming a starter. No country or leader of significant consequence has accepted the invitation. The motley collection of acceptors includes five East European countries, three Central Asian countries, eight Middle Eastern countries, two from South America, and four from Asia – Cambodia, Vietnam, Indonesia and Pakistan. The latter’s rush to join the club will foreclose any chance of India joining the Board. Countries are allowed a term of three years, but if you cough up $1 billion, could be member for life. Trump has declared himself to be lifetime chair of the Board, but he is not likely to contribute a dime. He might claim expenses, though. The Board of Peace was meant to be set up for the restoration of Gaza, but Trump has turned it into a retirement project for himself.
There is also the ridiculous absurdity of Trump continuing as chair even after his term ends and there is a different president in Washington. How will that arrangement work? If the next president turns out to be a Democrat, Trump may deny the US a seat on the board, cash or no cash. That may prove to be good for the UN and its long overdue restructuring. Although Trump’s Board has raised alarms about the threat it poses to the UN, the UN may end up being the inadvertent beneficiary of Trump’s mercurial madness.
The world is also beginning to push back on Trump’s tariffs. Rather, Trump’s tariffs are spurring other countries to forge new trade alliances and strike new trade deals. On Tuesday, India and EU struck the ‘mother of all’ trade deals between them, leaving America the poorer for it. Almost the next day , British Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer and Chinese leader Xi Jinping announced in Beijing that they had struck a string of deals on travel, trade and investments. “Not a Big Bang Free Trade Deal” yet, but that seems to be the goal. The Canadian Prime Minister has been globe-trotting to strike trade deals and create investment opportunities. He struck a good reciprocal deal with China, is looking to India, and has turned to South Korea and a consortium from Germany and Norway to submit bids for a massive submarine supply contract supplemented by investments in manufacturing and mineral industries. The informal first-right-of-refusal privilege that US had in Canada for defense contracts is now gone, thanks to Trump.
The disruptions that Trump has created in the world order may not be permanent or wholly irreversible, as Prime Minister Carney warned at Davos. But even the short term effects of Trump’s disruptions will be significant to all of US trading partners, especially smaller countries like Sri Lanka. Regardless of what they think of Trump, leaders of governments have a responsibility to protect their citizens from the negative effects of Trump’s tariffs. That will be in addition to everything else that governments have to do even if they do not have Trump’s disruptions to deal with.
Bland or Boisterous
Against the backdrop of Trump-induced global convulsions, politics in Sri Lanka is in a very stable mode. This is not to diminish the difficulties and challenges that the vast majority of Sri Lankans are facing – in meeting their daily needs, educating their children, finding employment for the youth, accessing timely health care and securing affordable care for the elderly. The challenges are especially severe for those devastated by cyclone Ditwah.
Politically, however, the government is not being tested by the opposition. And the once boisterous JVP/NPP has suddenly become ‘bland’ in government. “Bland works,” is a Canadian political quote coined by Bill Davis a nationally prominent premier of the Province of Ontario. Davis was responding to reporters looking for dramatic politics instead of boring blandness. He was Premier of Ontario for 14 years (1971-1985) and won four consecutive elections before retiring.
No one knows for how long the NPP government will be in power in Sri Lanka or how many more elections it is going to win, but there is no question that the government is singularly focused on winning the next parliamentary election, or both the presidential and parliamentary elections – depending on what happens to the system of directly electing the executive president.
The government is trying to grow comfortable in being on cruise control to see through the next parliamentary election. Its critics on the other hand, are picking on anything that happens on any day to blame or lampoon the government. The government for all its tight control of its members and messaging is not being able to put out quickly the fires that have been erupting. There are the now recurrent matters of the two AGs (non-appointment of the Auditor General and alleged attacks on the Attorney General) and the two ERs (Educational Reform and Electricity Reform), the timing of the PC elections, and the status of constitutional changes to end the system of directly electing the president.
There are also criticisms of high profile resignations due to government interference and questionable interdictions. Two recent resignations have drawn public attention and criticism, viz., the resignation of former Air Chief Marshal Harsha Abeywickrama from his position as the Chairman of Airport & Aviation Services, and the earlier resignation of Attorney-at-Law Ramani Jayasundara from her position as Chair of the National Women’s Commission. Both have been attributed to political interferences. In addition, the interdiction of the Deputy Secretary General of Parliament has also raised eyebrows and criticisms. The interdiction in parliament could not have come at a worse time for the government – just before the passing away of Nihal Seniviratne, who had served Sri Lanka’s parliament for 33 years and the last 13 of them as its distinguished Secretary General.
In a more political sense, echoes of the old JVP boisterousness periodically emanate in the statements of the JVP veteran and current Cabinet Minister K.D. Lal Kantha. Newspaper columnists love to pounce on his provocative pronouncements and make all manner of prognostications. Mr. Lal Kantha’s latest reported musing was that: “It is true our government is in power, but we still don’t have state power. We will bring about a revolution soon and seize state power as well.”
This was after he had reportedly taken exception to filmmaker Asoka Handagama’s one liner: “governing isn’t as easy as it looks when you are in the opposition,” and allegedly threatened to answer such jibes no matter who stood in the way and what they were wearing “black robes, national suits or the saffron.” Ironically, it was the ‘saffron part’ that allegedly led to the resignation of Harsha Abeywickrama from the Airport & Aviation Services. And President AKD himself has come under fire for his Thaipongal Day statement in Jaffna about Sinhala Buddhist pilgrims travelling all the way from the south to observe sil at the Tiisa Vihare in Thayiddy, Jaffna.
The Vihare has been the subject of controversy as it was allegedly built under military auspices on the property of local people who evacuated during the war. Being a master of the spoken word, the President could have pleaded with the pilgrims to show some sensitivity and empathy to the displaced Tamil people rather than blaming them (pilgrims) of ‘hatred.’ The real villains are those who sequestered property and constructed the building, and the government should direct its ire on them and not the pilgrims.
In the scheme of global things, Sri Lanka’s political skirmishes are still teacup storms. Yet it is never nice to spill your tea in public. Public embarrassments can be politically hurtful. As for Minister Lal Kantha’s distinction between governmental mandate and state power – this is a false dichotomy in a fundamentally practical sense. He may or may not be aware of it, but this distinction quite pre-occupied the ideologues of the 1970-75 United Front government. Their answer of appointing Permanent Secretaries from outside the civil service was hardly an answer, and in some instances the cure turned out to be worse than the disease.
As well, what used to be a leftist pre-occupation is now a right wing insistence especially in America with Trump’s identification of the so called ‘deep state’ as the enemy of the people. I don’t think the NPP government wants to go there. Rather, it should show creative originality in making the state, whether deep or shallow, to be of service to the people. There is a general recognition that the government has been doing just that in providing redress to the people impacted by the cyclone. A sign of that recognition is the number of people contributing to the disaster relief fund and in substantial amounts. The government should not betray this trust but build on it for the benefit of all. And better do it blandly than boisterously.
by Rajan Philips
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoComBank, UnionPay launch SplendorPlus Card for travelers to China
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoClimate risks, poverty, and recovery financing in focus at CEPA policy panel
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoSri Lanka, the Stars,and statesmen
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoLuck knocks at your door every day
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Editorial2 days ago
Editorial2 days agoGovt. provoking TUs













