Opinion
Sri Lanka’s economy measured in endless queues

World’s first all-organic farming nation faces worst-ever crisis
By Faraz Shauketaly
There are queues for petrol, diesel, gas, kerosene, etc. Husbands, wives and children wait in separate queues. Sri Lankans have no time for work. About 62% Sri Lankan workers are daily wage earners. Properties of some members of Parliament have been destroyed by mobs. Frustration has reached unprecedented heights – not even the dark days of a 33-year-long civil war produced so much frustration among Sri Lankans, who are at the end of their tether. People are calling upon President Gotabaya Rajapaksa to go home.Tourism – a US$ 4.5 Billion industry pre-Covid-19 – has been badly hit. Says the owner of a niche-boutique hotel in Negombo, a well-known tourist resort area close to the Bandaranaike International Airport: ‘Sri Lanka is full of bad luck. Our industry was doing well and the euphoria of a government elected to curb corruption and increase transparency in 2015 saw our occupancy levels go through the roof. Things were looking up. Banks were happy to fund expansion and we were happy. Now we face ruin. No help at all from the government, except a moratorium on loan repayments. Two years later the banks are asking us to start repaying. We have had the Easter bombings, then as we were emerging from that, CV-19 struck. Coping with that, the government went all organic on cultivation. Our industry was barely able to produce US$ 100 million this year and government income plummeted. Today my hotel is near-empty, bank interest rates are rising, the rupee has depreciated over 100%. It is chaos’.
On the campaign trail in 2019, Gotabaya Rajapaksa, a military man turned bureaucrat, largely credited for steering the armed forces to a crushing victory over the much-dreaded LTTE, in 2009, promised to take Sri Lanka in a different direction. After his victory at the 2019 presidential polls, with a whopping 6.9 million votes, he proclaimed an immediate ban on the imports of agrochemicals.Farmers were aghast knowing that a shift to organic farming would require their lands to remain uncultivated for at least three years. They took to the streets across the country, thus fuelling protests in urban areas, including Colombo.
It is argued, in some quarters, that President Gotabaya was told that the financial position in terms of foreign currency reserves made it impossible to spend as much as USD 400 million, on chemical fertilisers. The government put into action an audacious plan to mislead the public on the real financial position in the hope that funds could be raised subsequently for the purchase of fertiliser later, and crop decreases during the Maha and Yala seasons would be manageable. This misadventure saw the Sri Lankan economy nosediving. Diminishing foreign reserves were used to settle a sovereign bond payment to the tune of USD 500 million despite calls from Opposition members to go for a rescheduling of debt before the country had to default.
Little surprise the people are now calling for a government without the members of the Rajapaksa family. The entire Cabinet, save the Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapaksa, had to resign en masse. Protesters were not happy with that response. They wanted President Gotabaya also to resign.One of President Rajapaksa’s confidants, Ali Sabry, was appointed as Finance Minister but his visits to the IMF did not yield forex needed for the purchase of petrol, diesel, kerosene, cooking gas and heavy fuel for power generation.India stepped in with immediate relief, Indonesia sent medicines. Immediate neighbours including Bangladesh answered Sri Lanka’s plea for assistance.
Thanks to the callous treatment meted out to the Muslim community in the past, oil-rich West Asian nations did not offer any help. Other nations were willing to send humanitarian assistance but remain concerned about Sri Lanka’s failure to address allegations of war crimes, accountability, return of lands and reparations despite repeated almost annual assurances to the contrary, the international perception and that of the Tamil community being that ‘nothing’ has been achieved.The appointment of a Prime Minister who has served no less than five times previously has been made out to be an interim measure to defuse tensions. However, the people are protesting opposite his residence as well. A well-read man, with a reputation for political survival, Ranil Wickremesinghe was immediately perceived as a man wheeled in by the principal puppeteer Basil Rajapaksa to create a ‘safe exit strategy’. It was interesting that there was no reference to an ‘honourable’ exit.
The attempt to portray Wickremesinghe, who lost his own seat at the last general election but entered parliament with via the National List thanks to Sri Lanka’s quirky electoral laws – as a national-consensus appointee to forge a broad alliance of all political parties, fell by the wayside when the Leader of the Opposition – another dynastic politician – Sajith Premadasa refused to be part of any government unless a timeframe was set for President Rajapaksa’s resignation.Sri Lanka’s economy is in grave danger with government debt amounting to approximately US$ 32 billion (private sector debt being approximately USD 18 billion) and foreign exchange inflow becoming scarce.
The IMF is still perusing Sri Lanka’s proposals, and so is its former colonial master, the UK, before deciding on some assistance. The Rajapaksas’ leaning towards China has been frowned on by the West, and there is little doubt that there is international pressure – covert perhaps – for President Rajapaksa to resign.The future appears uncertain not only for the Rajapaksa dynasty but also for the people, who are worried about a looming food crisis come August 2022 whoever will be in power – the Rajapaksas, Wickremesinghe or anyone else.
Opinion
Chlorophyll –The Life-giver is in peril
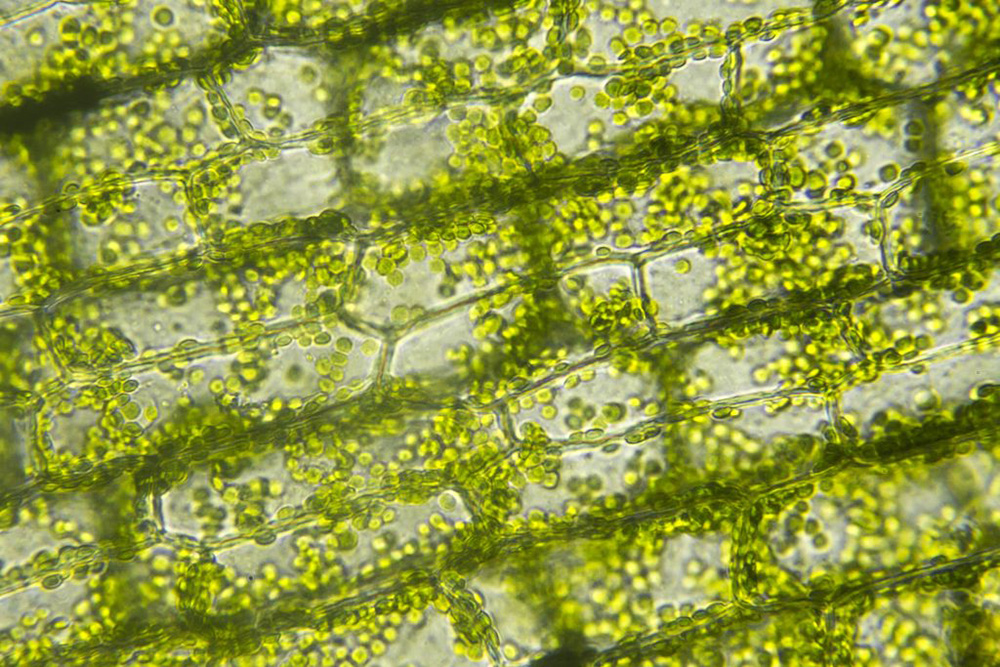
Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. It is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy to sustain life on Earth. As it is green it reflects Green of the sunlight spectrum and absorbs its Red and Blue ranges. The energy in these rays are used to produce carbohydrates utilising water and carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen in the process. Thus, it performs, in this reaction, three functions essential for life on earth; it produces food and oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to maintain equilibrium in our environment. It is one of the wonders of nature that are in peril today. It is essential for life on earth, at least for the present, as there are no suitable alternatives. While chlorophyll can be produced in a lab, it cannot be produced using simple, everyday chemicals in a straightforward process. The total synthesis of chlorophyll is an extremely complex multi-step organic chemistry process that requires specialized knowledge, advanced laboratory equipment, and numerous complex intermediary compounds and catalysts.
Chlorophyll probably evolved inside bacteria in water and migrated to land with plants that preceded animals who also evolved in water. Plants had to come on land first to oxygenate the atmosphere and make it possible for animals to follow. There was very little oxygen in the ocean or on the surface before chlorophyll carrying bacteria and algae started photosynthesis. Now 70% of our atmospheric oxygen is produced by sea phytoplankton and algae, hence the importance of the sea as a source of oxygen.
Chemically, chlorophyll is a porphyrin compound with a central magnesium (Mg²⁺) ion. Factors that affect its production and function are light intensity, availability of nutrients, especially nitrogen and magnesium, water supply and temperature. Availability of nutrients and temperature could be adversely affected due to sea pollution and global warming respectively.
Temperature range for optimum chlorophyll function is 25 – 35 C depending on the types of plants. Plants in temperate climates are adopted to function at lower temperatures and those in tropical regions prefer higher temperatures. Chlorophyll in most plants work most efficiently at 30 C. At lower temperatures it could slow down and become dormant. At temperatures above 40 C chlorophyll enzymes begin to denature and protein complexes can be damaged. Photosynthesis would decline sharply at these high temperatures.
Global warming therefore could affect chlorophyll function and threaten its very existence. Already there is a qualitative as well as quantitative decline of chlorophyll particularly in the sea. The last decade has been the hottest ten years and 2024 the hottest year since recording had started. The ocean absorbs 90% of the excess heat that reaches the Earth due to the greenhouse effect. Global warming has caused sea surface temperatures to rise significantly, leading to record-breaking temperatures in recent years (like 2023-2024), a faster warming rate (four times faster than 40 years ago), and more frequent, intense marine heatwaves, disrupting marine life and weather patterns. The ocean’s surface is heating up much faster, about four times quicker than in the late 1980s, with the last decade being the warmest on record. 2023 and 2024 saw unprecedented high sea surface temperatures, with some periods exceeding previous records by large margins, potentially becoming the new normal.
Half of the global sea surface has gradually changed in colour indicating chlorophyll decline (Frankie Adkins, 2024, Z Hong, 2025). Sea is blue in colour due to the absorption of Red of the sunlight spectrum by water and reflecting Blue. When the green chlorophyll of the phytoplankton is decreased the sea becomes bluer. Researchers from MIT and Georgia Tech found these color changes are global, affecting over half the ocean’s surface in the last two decades, and are consistent with climate model predictions. Sea phytoplankton and algae produce more than 70% of the atmospheric oxygen, replenishing what is consumed by animals. Danger to the life of these animals including humans due to decline of sea chlorophyll is obvious. Unless this trend is reversed there would be irreparable damage and irreversible changes in the ecosystems that involve chlorophyll function as a vital component.
The balance 30% of oxygen is supplied mainly by terrestrial plants which are lost due mainly to human action, either by felling and clearing or due to global warming. Since 2000, approximately 100 million hectares of forest area was lost globally by 2018 due to permanent deforestation. More recent estimates from the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicate that an estimated 420 million hectares of forest have been lost through deforestation since 1990, with a net loss of approximately 4.7 million hectares per year between 2010 and 2020 (accounting for forest gains by reforestation). From 2001 to 2024, there had been a total of 520 million hectares of tree cover loss globally. This figure includes both temporary loss (e.g., due to fires or logging where forests regrow) and permanent deforestation. Roughly 37% of tree cover loss since 2000 was likely permanent deforestation, resulting in conversion to non-forest land uses such as agriculture, mining, or urban development. Tropical forests account for the vast majority (nearly 94%) of permanent deforestation, largely driven by agricultural expansion. Limiting warming to 1.5°C significantly reduces risks, but without strong action, widespread plant loss and biodiversity decline are projected, making climate change a dominant threat to nature, notes the World Economic Forum. Tropical trees are Earth’s climate regulators—they cool the planet, store massive amounts of carbon, control rainfall, and stabilize global climate systems. Losing them would make climate change faster, hotter, and harder to reverse.
Another vital function of chlorophyll is carbon fixing. Carbon fixation by plants is crucial because it converts atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic compounds, forming the base of the food web, providing energy/building blocks for life, regulating Earth’s climate by removing greenhouse gases, and driving the global carbon cycle, making life as we know it possible. Plants use carbon fixation (photosynthesis) to create their own food (sugars), providing energy and organic matter that sustains all other life forms. By absorbing vast amounts of CO2 (a greenhouse gas) from the atmosphere, plants help control its concentration, mitigating global warming. Chlorophyll drives the Carbon Cycle, it’s the primary natural mechanism for moving inorganic carbon into the biosphere, making it available for all living organisms.
In essence, carbon fixation turns the air we breathe out (carbon dioxide) into the food we eat and the air we breathe in (oxygen), sustaining ecosystems and regulating our planet’s climate.
While land plants store much more total carbon in their biomass, marine plants (like phytoplankton) and algae fix nearly the same amount of carbon annually as all terrestrial plants combined, making the ocean a massive and highly efficient carbon sink, especially coastal ecosystems that sequester carbon far faster than forests. Coastal marine plants (mangroves, salt marshes, seagrasses) are extremely efficient carbon sequesters, absorbing carbon at rates up to 50 times faster than terrestrial forests.
If Chlorophyll decline, which is mainly due to human action driven by uncontrolled greed, is not arrested as soon as possible life on Earth would not be possible.
(Some information was obtained from Wikipedia)
by N. A. de S. Amaratunga ✍️
Opinion
Nihal Seneviratne – God’s good man

Nihal Seneviratne’s funeral on Wednesday was one of the best attended in recent times. He passed away on Tuesday after a short spell in hospital and no wonder a great many people came to bid him a final goodbye. He was not only a truly accomplished public servant with a 33-year long career in the legislature but was also God’s good man – humble, pleasant and ever ready to go out of his way to help anybody.
Like his predecessor as Secretary General of Parliament, Sam Wijesinha, Nihal passed the 91+ years landmark in his lifetime. These two top officials who headed the administration of the legislature for many long years were very different from each other. Sam made the office of Clerk to the House of Representatives he took over from retiring Ralph Deraniyagala, a very visible institution while Nihal, recruited as Assistant to the then Clerk Assistant in 1965 during Deraniyagala’s time, preferred to do his job away from the limelight.
He was affectionately nicknamed Galba from his days at the Royal Primary School in the 1940s – a teacher had asked him “Seneviratne, what’s in your lunchbox?” and he had replied “Gulbunis, Sir” – acquiring a nickname that withstood the ravages of time. Coincidentally, he married into the famous Perera and Sons bakery family and even his wife, Srima, often referred to him as “Galba.”.
His choice of career was somewhat accidental. Having taken an Ll.B. degree from Peradeniya in 1959 he had undergone the mandatory two years at the Law College to be enrolled as an advocate. He had won a scholarship to the US when an advertisement for the parliament vacancy was published. His close friend, Rajah Kuruppu (“Crumbs” to him) had typed out an application, got him to sign it and sent it off.
He was interviewed and selected. Therein lies an interesting story. The interview board comprised the Speaker (Pelpola), Leader of the House (CP de Silva), Leader of the Opposition (Dudley Senanayake) and the Clerk (Deraniyagala). When he said he was a Royalist, both Dudley and CP who were Thomians said “wrong school!”
Nihal asked Deraniyagala whether he could complete his American scholarship and take up the appointment on his return. This was refused but but he was told he’d be sent to the House of Commons for training. Nihal accepted these terms and a long career ending at the pinnacle ensued.
Srima used to joke that when she was engaged to Nihal, she would tell her friends that she was marrying an assistant clerk!
As an All Island JP, Nihal was of immense service to friends and acquaintances attesting various documents. Hundreds of these have been signed on his dining table. He would often offer to visit friends’ homes when attestations were required without making them come to him.
Nihal Seneviratne appropriately wore a Royal College tie when he was laid out after passing away. He had always been passionate about his old school, serving as Secretary of the Royal College Union and being its Vice President Emeritus when he died. The school was well represented st his funeral.
He also did much to keep the alive the memory of his late brother, Professor KN (Bull) Seneviratne, well known professor of pathology and founder of the Post Graduate Institute of Medicine, who passed away prematurely many years ago, organizing an annual oration in his memory. Despite challenges of age, he flew to Australia to visit his sister living there as often as he could.
Nihal published two books of memoirs with ringside stories of momentous events in the legislature of his time that included the JVP bomb lobbed into a committee room of parliament killing one MP and seriously injuring Lalith Athulaththmudali. JRJ miraculously escaped while then PM Premadasa was also hurt. The grenade bounced off the table at which the president, prime minister and chief government whip sat and exploded under Athulathmudali’s chair. Seneviratne had to cope with the mayhem that followed.
He was on the hot seat when the attempt to impeach President Premadasa was “entertained” by Speaker MH Mohamed who thereafter abandoned it. Therein lies a story that Nihal has written about. He was never consulted by the speaker and the original motion has vanished into thin air and is not in the parliament archives.
Not only Srima, his wife, children Satyajith and Shanika, and his three granddaughters who spoke warmly of their seeya when his last book was launched, but also a host of family, friends, subordinates, colleagues and many more will miss this remarkable human being who non-ostentatiously wore an important title during a long career in the national legislature.
Manik de Silva
Opinion
The minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II

(Continued from January 02, 2026)
From my perspective, it is obvious that Sri Lanka as a country/nation is still left in the lurch politically, economically and morally. The biggest problem is that there is no inspiring leadership. Strong moral leadership is a key component of good governance. ‘Raja bhavatu dhammiko’ (May the ruler be righteous) is the perennial chant of the bhikkhus we hear every morning. A country’s moral leadership is interwoven with its ethical foundation, which, in Sri Lanka’s case, is built on Buddhist moral values, which resonate with the best found in other faiths.
The two dynamic social activist monks, mentioned towards the end of Part I of this article, are being targeted for severe public denunciation as rabid racists in the media in Sri Lanka and abroad due to three main reasons, in my view: First, they are victims of politically motivated misrepresentation; second, when these two monks try to articulate the problems that they want responsible government servants such as police and civil functionaries to address in accordance with the law, they, due to some personality defect, fail to maintain the calm sedateness and composure normally expected of and traditionally associated with Buddhist monks; third, (perhaps the most important reason in this context), these genuine fighters for justice get wrongly identified, in public perception, with other less principled politician monks affiliated to different political parties. Unlike these two socially dedicated monks, monks engaged in partisan politics are a definite disadvantage to the parties they support, especially when they appear on propaganda platforms. The minstrel monk mentioned later in this writeup is one of them.
The occasional rowdy behaviour of Madakalapuwa Hamuduruwo is provoked by the deliberate non-responsiveness of certain unscrupulous government servants of the Eastern Province (who are under the sway of certain racist minority politicians) to his just demands for basic facilities (such as permits for plots of land and water for cultivation) for traditional Sinhalese dwellers in some isolated villages in the area ravaged by war. That is something that the government must take responsibility for. The well-known Galagoda-aththe Thera had long been warning about the Jihadist threat that finally led to the Easter Sunday attacks, but he was in jail when it actually happened. The Yahapalana government didn’t pay any attention to his evidence-based warnings. Instead they shot the messenger. Had the authorities heeded his urgent calls for alarm, the 275 men, women and children dead, and the 500 or so injured, some grievously, would have been safe.
The Mahanayakes should have taken a leaf out of Cardinal Malcolm Ranjith’s book. The Cardinal knows that his responsibility is to look after his flock as a single unanimously approved/accepted leader of the Catholic Church. He fulfills that responsibility well. But, the Mahanayakes couldn’t have resorted to the Cardinal’s strategies which he chooses in accordance with his Catholic/Christian conscience (ultimately fashioned by Christian moral values). The Mahanayakes however, like the Cardinal, could have brought pressure on any one or all of the Presidents and the Prime Ministers elected/appointed since the end of the separatist conflict in 2009 to implement Article 9 of the existing Constitution in its letter and spirit and the powerful earlier Antiquities Ordinance of 1940 fully (I hope it is not in abeyance now) to protect the extensive Buddhist archaeological heritage sites spread throughout the North and East, which have been encroached on and vandalised for decades now, and to look after the poverty-stricken Sinhalese peasants who have somehow managed to survive in the isolated villages in the the Batticaloa District.
A few errant monks, in my opinion, owe their existence primarily to the failure of two groups of people, opportunistic politicians and the indifferent Sangha leadership, to put it plainly. Politicians use monks for securing the Buddhist vote to come to power, and the Mahanayake theras fail to take a united stand against them. As a rule, politicians forget about monks after getting elected to power, apparently, in the hope of not alienating non-Buddhist voters, who naturally favour candidates of their own at elections. Their leaders acquire the influence they need to survive in politics by rubbing those in power the right way. But those non-Buddhist voters are as innocent and peace-loving as the traditionally hoodwinked Buddhist voters.
In this context, I remember having watched a YouTube video uploaded over four months ago featuring MP Namal Rajapaksa. The video (2025-08-30) contained a news clip taken from a mainstream TV channel that showed the young MP being snubbed by a certain Anunayake Thera in Kandy. This was when the MP, during his audience with the high priest, mentioned to him how a retired senior naval officer who had done so much selfless service in ridding the country of Tamil separatist terrorism had been arrested and remanded unjustly (as it appeared) under the present government which is being accused of succumbing unnecessarily to global Tamil diaspora pressure. The monk’s dismissive and insensitive comment in response to MP Namal Rajapaksa’s complaint revealed the senior monk’s blissful ignorance and careless attitude: “We can’t say who is right, who is wrong.” Are we any longer to believe that the Maha Sangha that this monk is supposed to represent are the guardians of the nation?
Please remember that the country has been plunged into the current predicament mainly due to the opportunistic politicians’ policy of politics for politics’ sake and the Mahanaykes’ inexplicable “can’t-be-bothered” attitude. It is not that they are not doing anything to save the country, the people, and the inclusive, nonintrusive Buddhist culture
A young political leadership must emerge free from the potentially negative influence of these factors. SLPP national organiser MP Namal Rajapaksa, among a few other young politicians like him of both sexes, is demonstrating the qualities of a person who could make a successful bid for such a leadership position. In a feature article published in The Island in September 2010 (well over fifteen years ago) entitled ‘Old fossils, out! Welcome, new blood!’ I welcomed young Namal Rajapaksa’s entry into politics on his own merits as a Sri Lankan citizen, while criticising the dynastic ambitions of his father, former president Mahinda Rajapaksa. Namal was already a Cabinet minister then, I think. I have made complimentary observations on his performance as a maturing politician on several occasions in my subsequent writings, most recently in connection with the Joint Opposition ‘Maha Jana Handa’ rally at Nugegoda that he organised on November 21, 2025 on behalf of the SLPP (The Island December 9 and 16). A novel feature he had introduced into his programme was having no monk speakers. I, for one, as a patriotic senior Sri Lankan, wholeheartedly approve of that change from the past. Let monks talk about politics, if they must, from a national platform, not from party political stages. That is, they should provide a disciplined, independent ethical voice on broad societal issues. Ulapane Sumangala Thera is approximating that in his current outspoken criticism of PM Harini Amarasuriya’s controversial education reforms. But I am not sure whether he will continue with non-partisan politics and also infuse some discipline and decency into his speech.
Namal should avoid the trodden path in a plausible manner and get rid of the minstrel monk who insists on accompanying him wherever he goes and tries to entertain your naturally growing audiences with his impromptu recitations”.
This monk reminds me of Rafiki the old mandrill in the 1994 The Lion King animation movie. But there is a world of difference between the monk and the mandrill. The story of The Lion King is an instructive allegory that embodies a lesson for a budding leader. One bright morning, while the royal parents are proudly watching behind him, and, as the sun is rising, Rafiki, the old wise shaman, presents lion king Mufasa’s new born cub, Simba, from the top of Pride Rock to the animals of the Pride Lands assembled below. Rafiki, though a bit of an eccentric old shaman, is a wise spiritual healer, devoted to his royal master, the great king Mufasa, Simba’s father. The film depicts how Simba grows from a carefree cub to a mature king through a life of troubles and tribulations after the death of his father, challenged by his cruel younger brother Scar, Simba’s uncle. Simba learns that ‘true leadership is rooted in wisdom and respect for the natural order, a realisation that contrasts Mufasa’s benevolent rule with Scar’s tyranny’.
Years later, another dawn, animals gather below the Pride Rock, from where Rafiki picks up the wiggling little first born cub of King Simba and Queen Nala and raises him above his head. All the animals cheer and stamp their feet.
The film closes with Simba standing at the top of Pride Rock watching the sunset beyond the western hills.
“Everything is all right, Dad”, Simba said softly. “You see, I remember …. He gazed upward. One by one each star took its place in the cold night sky.
The film describes the Circle of Life, the interconnectedness and interdependence of all living things, and the cycle of birth, death, and renewal. For me, this is a cheerful negation of T.S. Eliot’s pessimistic philosophical reflection on life: “Eating and drinking, dung and death”.
Namal has already developed his inherited political leadership skills, which he will be capable of enhancing further with growing experience. Let’s hope there are other promising, potential young leaders of both sexes as well, to offer him healthy competition eventually, so that, in the future, the country will be ruled by the best leaders. Concluded
by Rohana R. Wasala ✍️
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoInterception of SL fishing craft by Seychelles: Trawler owners demand international investigation
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoBroad support emerges for Faiszer’s sweeping proposals on long- delayed divorce and personal law reforms
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM













